Breeding, Biosorption Characteristics, and Mechanism of a Lead-Resistant Strain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Isolation and Screening of Lead-Resistant Strains
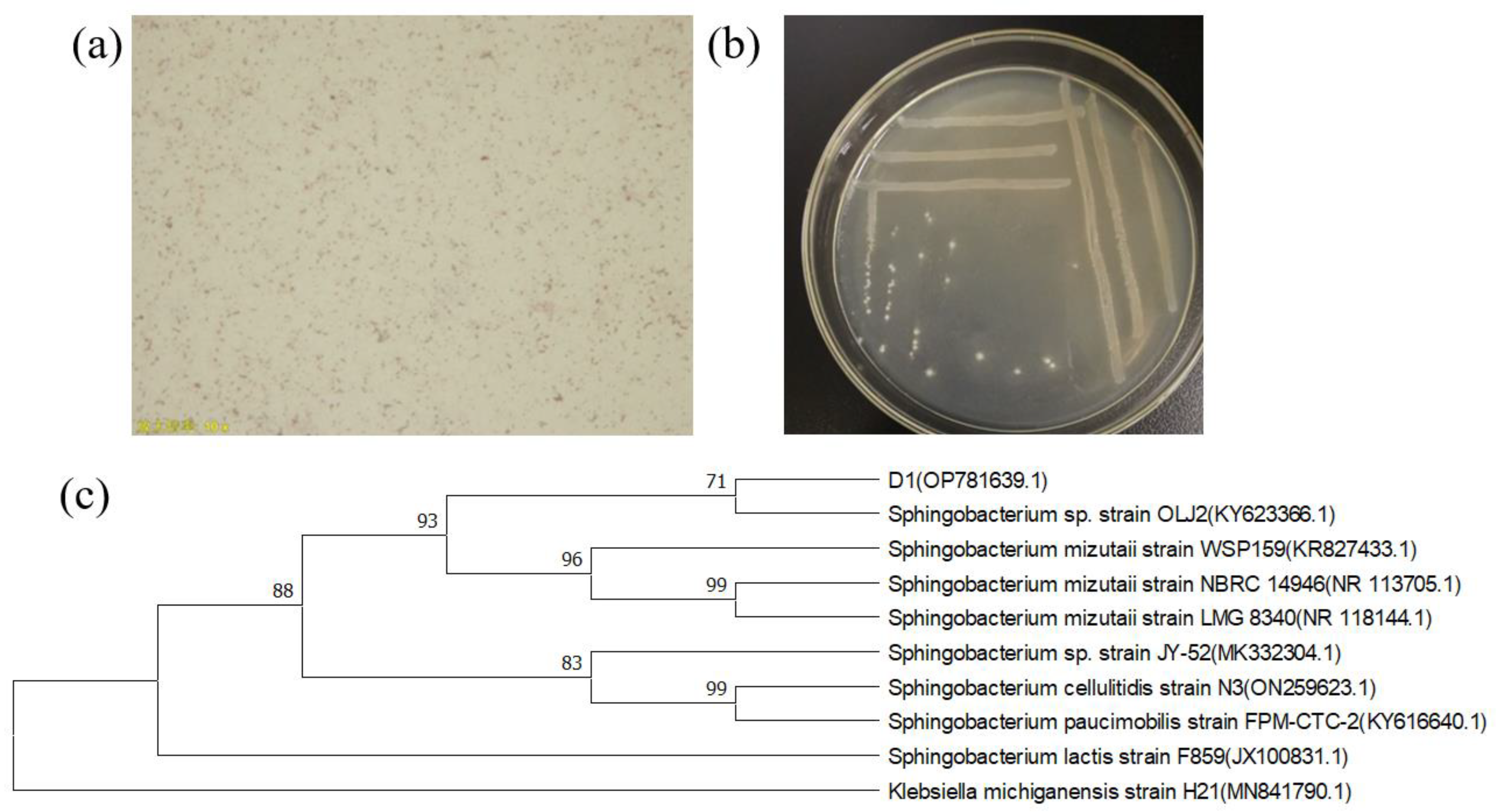
2.3. Identification of Screened Strains
2.4. Effects of Environmental Factors on the Growth of Screened Strains and Lead Removal Rate
2.4.1. Effect of Medium Types on Strain Growth and Lead Removal Rate
2.4.2. Effect of Temperature on Strain Growth and Lead Removal Rate
2.4.3. Effect of pH Value on Strain Growth and Lead Removal Rate
2.4.4. Effect of Inoculation Volume on Strain Growth and Lead Removal Rate
2.4.5. Effect of Rotational Speed on Strain Growth and Lead Removal Rate
2.4.6. Effect of Adsorption Time on Strain Growth and Lead Removal Rate
2.5. Orthogonal Test
2.6. SEM and EDS Analysis
2.7. FTIR Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Isolation, Screening, and Identification of Strains
3.2. Effect of Environmental Factors on the Growth and Lead Removal Rate of Strain D1
3.3. Analysis of Orthogonal Test
3.4. Mechanistic Study on the Removal of Lead by Strain D1
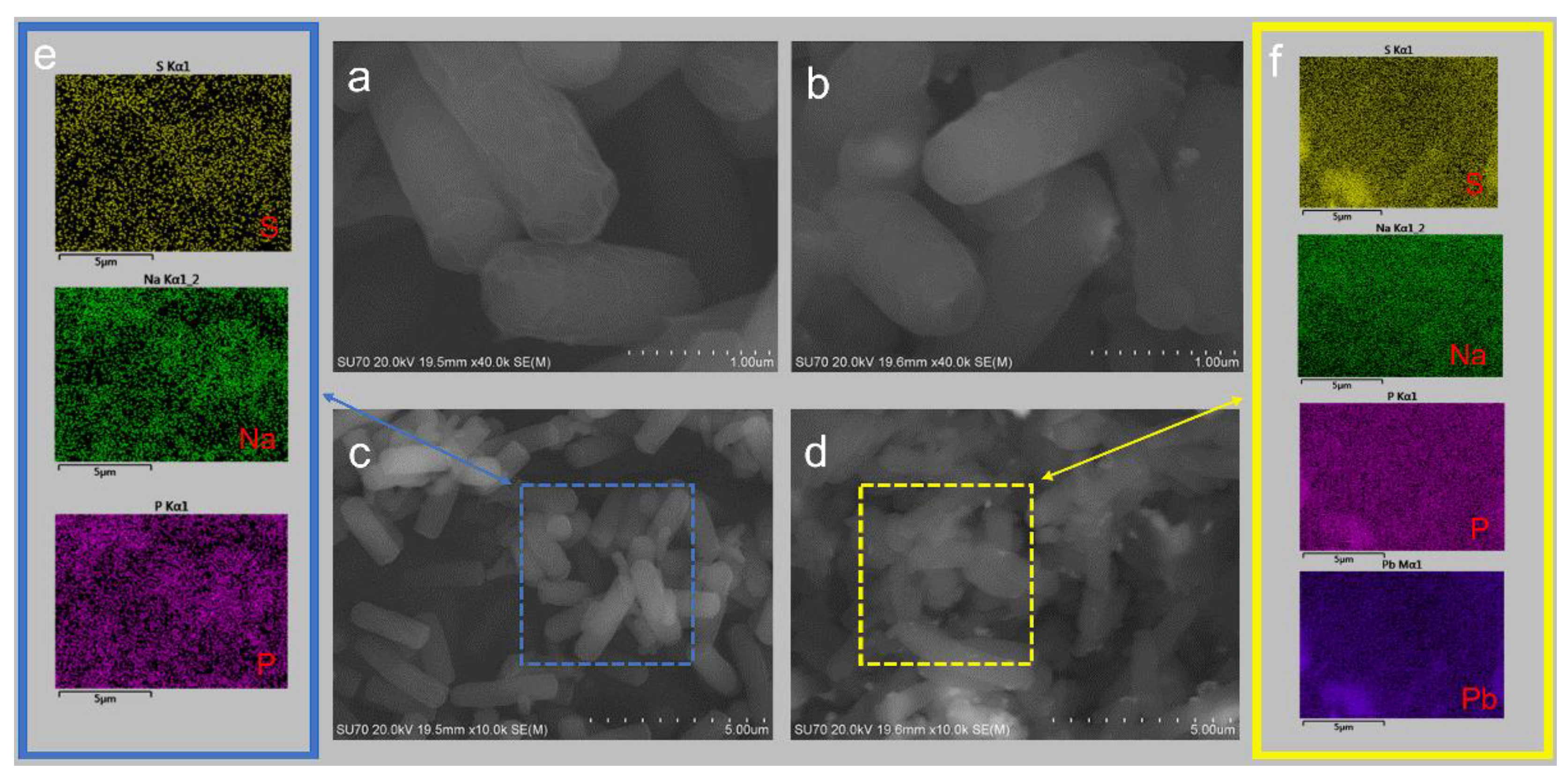
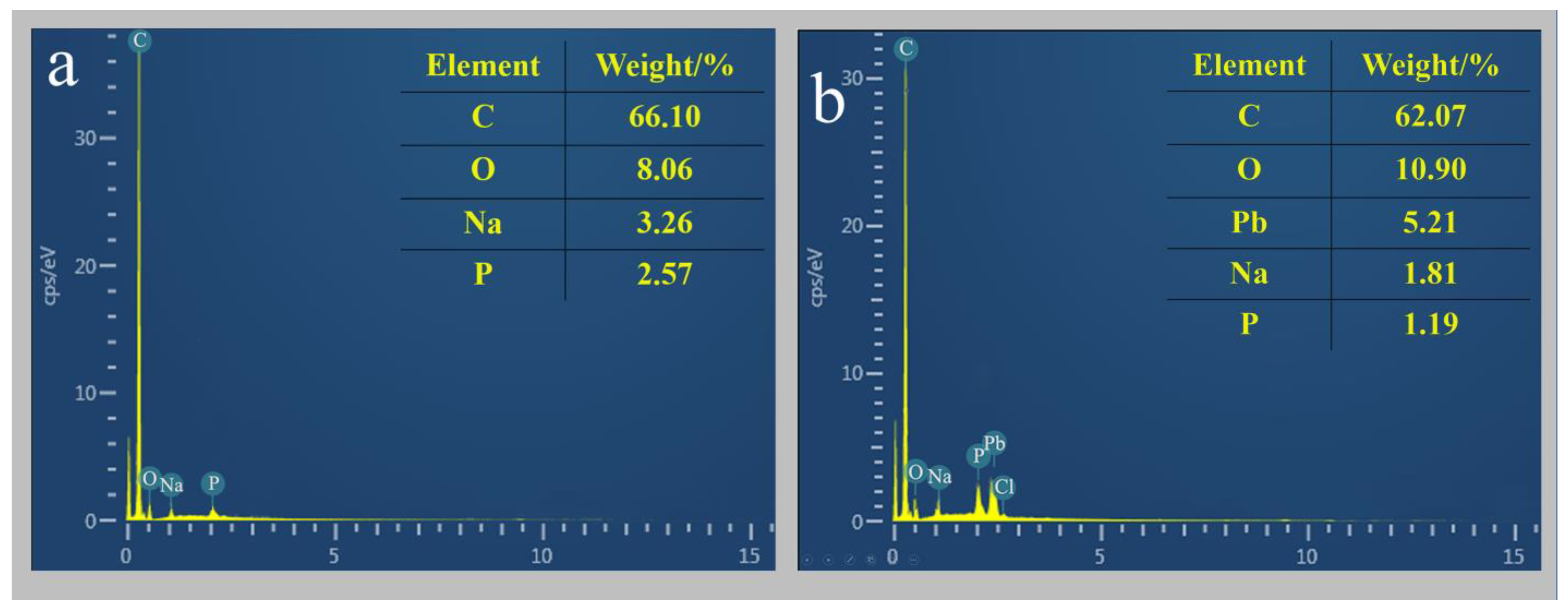
3.4.1. SEM-EDS Analysis of D1 Strains Grown in the Lead and Lead-Free Environments
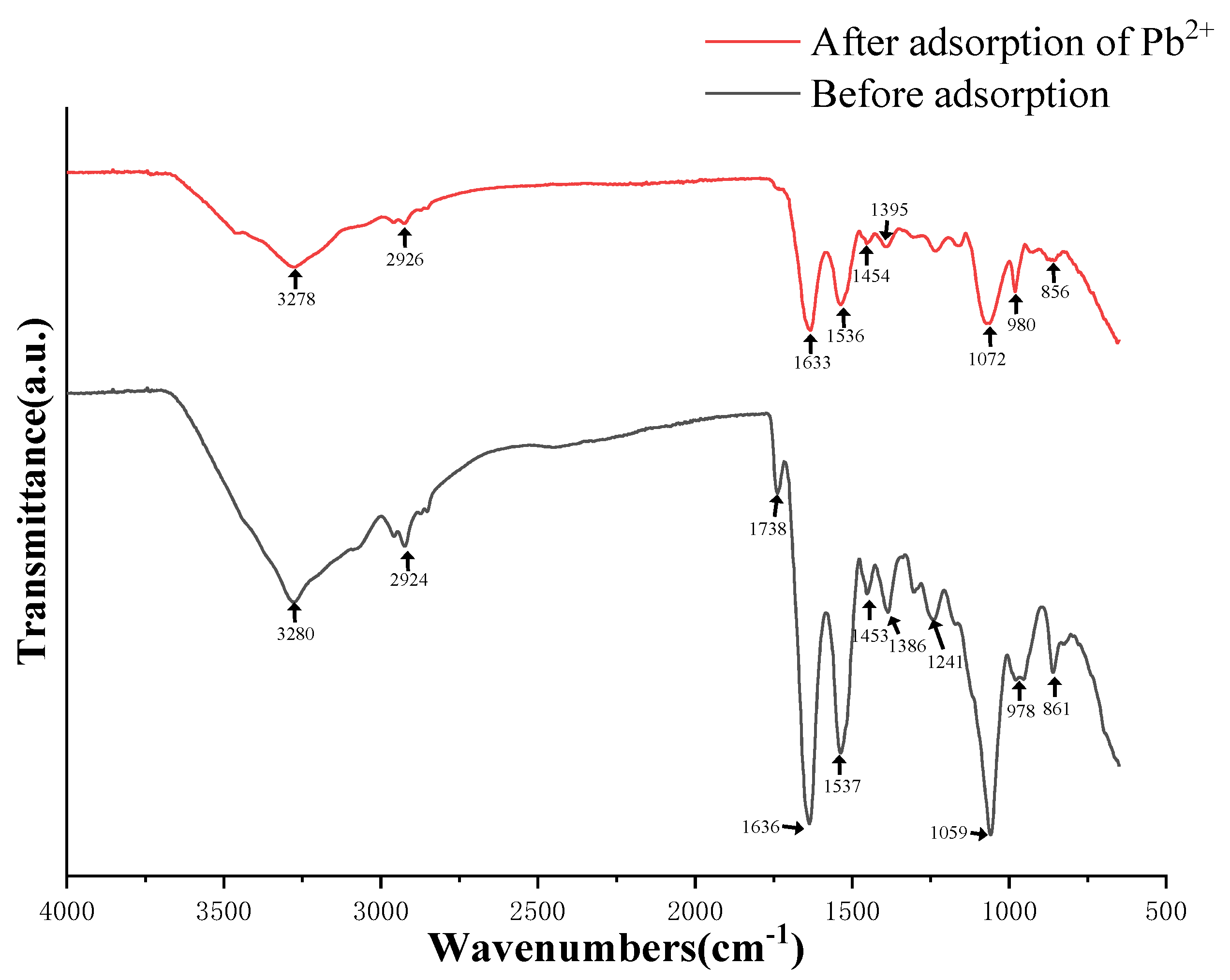
3.4.2. FTIR Spectra of the Screened Strains before and after Pb2+ Adsorption
3.5. Discussion
3.5.1. The Effect of Culture Conditions on the Growth and Pb2+ Adsorption Effect of the Strains
3.5.2. Study of Pb2+ Adsorption Mechanism by Strain D1
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yamada, D.; Hiwatari, M.; Narita, D.; Hangoma, P.; Chitah, B.; Nakata, H.; Nakayama Shouta, M.M.; Yabe, J.; Ito, M.; Igarashi, T.; et al. Social cost of mining-related lead (Pb) pollution in Kabwe, Zambia, and potential remediation measures. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 865, 161281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alissa Eman, M.; Ferns Gordon, A. Heavy metal poisoning and cardiovascular disease. J. Toxicol. 2011, 2011, 870125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Wang, Q.; Gao, S.; Poon, C.S.; Zhou, Y.; Li, J.S. Novel recycling of incinerated sewage sludge ash (ISSA) and waste bentonite as ceramsite for Pb-containing wastewater treatment: Performance and mechanism. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 288, 112382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.S.; Li, L.; Li, S.R.; Santosh, M.; Alam, M. Age and mineralization processes of decratonic lode gold deposits in the southern North China Craton: Constraints from trace elements, in-situ S-Pb isotopes and Rb-Sr geochronology of pyrite from the Chen’er gold deposit. Ore Geol. Rev. 2022, 145, 104888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhong, L.; Wang, Q.; Hu, J.; Tang, A. Effect of the occurrence state of magnesium in talc on the adsorption of Pb (II). J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 887, 161288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, S.V.; Grusson, Y.; Chimienti, M.; Claustres, A.; Jean, S.; Le Roux, G. Legacy Pb pollution in the contemporary environment and its potential bioavailability in three mountain catchments. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 671, 1227–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, D.T.; Petroni, M.; Larsen, D.A.; Bendinskas, K.; Heffernan, K.; Atallah-Yunes, N.; Parsons, P.J.; Palmer, C.D.; MacKenzie, J.A.; Collins, M.B.; et al. Linking metal (Pb, Hg, Cd) industrial air pollution risk to blood metal levels and cardiovascular functioning and structure among children in Syracuse, NY. Environ. Res. 2021, 193, 110557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Chardi, A. Biomonitoring potential of five sympatric Tillandsia species for evaluating urban metal pollution (Cd, Hg and Pb). Atmos. Environ. 2016, 131, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, M.; Wang, L.; Feng, Q.; Niu, L.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, P.; Song, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z. Thiol-functionalized nano-silica for in-situ remediation of Pb, Cd, Cu contaminated soils and improving soil environment. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 280, 116879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.K.; Lee, S.S.; Zhang, M.; Tsang, Y.F.; Kim, K.-H. Heavy metals in food crops: Health risks, fate, mechanisms, and management. Environ. Int. 2019, 125, 365–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xie, X.; Meng, X.; Li, Y.; Zhu, W. The critical role of oxidative debris in the adsorption and desorption of Pb (II) to graphene oxides under alkaline groundwater conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, A.; Bishnoi, N.R.; Gupta, A. Optimization study for Pb (II) and COD sequestration by consortium of sulphate-reducing bacteria. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 2309–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Chen, L.; Hu, P.; Wang, Y.; Deng, J.; Mi, B. Industrial alkali lignin-derived biochar as highly efficient and low-cost adsorption material for Pb (II) from aquatic environment. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 322, 124539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Li, P.; Zhang, M.; Wang, J.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, G.; Li, F. Designing three-dimensional half-embedded ES-PAN/AHCNs adsorption membrane for removal of Pb (II), Cu (II) and Cr (III). Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 627, 127177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, Z.; Song, Y.; You, Y.; Li, J.; Cheng, X. Synthesis of Mg (II) doped ferrihydrite-humic acid coprecipitation and its Pb (II)/Cd (II) ion sorption mechanism. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 3231–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yu, W.; Zeng, D.; Zhu, L.; Gao, C.; Hu, M.; Le, C.; Qiu, T. Volatilization of Zn and Pb and preparation of integrated micro-electrolysis filter from copper slag and its application for removing Cr (VI) from aqueous solution. Chemosphere 2022, 288, 132596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, A.K.; Gnanasekaran, L.; Dutta, K.; Rajendran, S.; Balakrishnan, D.; Soto-Moscoso, M. Biosorption of heavy metals by microorganisms: Evaluation of different underlying mechanisms. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesmana, S.O.; Febriana, N.; Soetaredjo, F.E.; Sunarso, J.; Ismadji, S. Studies on potential applications of biomass for the separation of heavy metals from water and wastewater. Biochem. Eng. J. 2009, 44, 19–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Peter, A.P.; Chew, K.W.; Munawaroh, H.S.H.; Show, P.L. Resource recovery from industrial effluents through the cultivation of microalgae: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 337, 125461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, R.K.; Parhi, P.K.; Pandey, S.; Bindhani, B.K.; Thatoi, H.; Panda, C.R. Active and passive biosorption of Pb (II) using live and dead biomass of marine bacterium Bacillus xiamenensis PbRPSD202: Kinetics and isotherm studies. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 247, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, V.; Volesky, B. Biosorption of La, Eu and Yb using sargassum biomass. Water Res. 2005, 39, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Jin, M.R.; Chung, C.H.; Yun, Y.S.; Jahng, K.Y.; Yu, K.Y. Biosorption of cationic basic dye and cadmium by the novel biosorbent Bacillus catenulatus JB-022 strain. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2015, 119, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aravindhan, R.; Madhan, B.; Rao, J.R.; Nair, B.U.; Ramasami, T. Bioaccumulation of chromium from tannery wastewater: An approach for chrome recovery and reuse. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Li, G.; Xue, P.; Wei, Q.; Li, Q. Competitive effect of Cu (II) and Zn (II) on the biosorption of lead (II) by Myriophyllum spicatum. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngabura, M.; Hussain, S.A.; Ghani, W.A.W.A.; Jami, M.S.; Tan, Y.P. Utilization of renewable durian peels for biosorption of zinc from wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 2528–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, D.; Li, X.; Xue, Y. Biomineralization of lead in wastewater: Bacterial reutilization and metal recovery. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, W.; Fuxing, K.; Jiahao, L. Nature and value of freely dissolved EPS ecosystem services: Insight into molecular coupling mechanisms for regulating metal toxicity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, Z.; Amin, M.; Khan, N.; Khan, M.N.; Sami, S.K.; Khan, S.B.; Hafeez, I.; Khan, S.A.; Bakhsh, E.M.; Cheng, C.K. Potential application of Allium Cepa seeds as a novel biosorbent for efficient biosorption of heavy metals ions from aqueous solution. Chemosphere 2021, 279, 130545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, S.W.; Vijayaraghavan, K.; Mao, J.; Kim, S.; Yun, Y.-S. Reinforcement of carboxyl groups in the surface of Corynebacterium glutamicum biomass for effective removal of basic dyes. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 6301–6306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çolak, F.; Atar, N.; Yazıcıoğlu, D.; Olgun, A. Biosorption of lead from aqueous solutions by Bacillus strains possessing heavy-metal resistance. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 173, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Ali, A.; Li, Y.; Su, J.; Zhang, S. The performance and mechanism of simultaneous removal of calcium and heavy metals by Ochrobactrum sp. GMC12 with the chia seed (Salvia hispanica) gum as a synergist. Chemosphere 2022, 297, 134061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Li, B.; Ou, J.; Xue, W.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Li, T.; Chen, S.; Deng, R.; Guo, X. Megamerger of biosorbents and catalytic technologies for the removal of heavy metals from wastewater: Preparation, final disposal, mechanism and influencing factors. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 261, 109879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanda, M.; Jaiswal, K.K.; Kumar, V.; Verma, M.; Vlaskin, M.S.; Gururani, P.; Kim, H.; Alajmi, M.F.; Hussain, A. Bio-remediation capacity for Cd (II) and Pb (II) from the aqueous medium by two novel strains of microalgae and their effect on lipidomics and metabolomics. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 44, 102404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevak, P.I.; Pushkar, B.K.; Kapadne, P.N. Lead pollution and bacterial bioremediation: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 4463–4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranthi Raj, K.; Sardar, U.R.; Bhargavi, E.; Devi, I.; Bhunia, B.; Tiwari, O.N. Advances in exopolysaccharides based bioremediation of heavy metals in soil and water: A critical review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 199, 353–364. [Google Scholar]
- Mathew, B.B.; Krishnamurthy, N.B. Screening and identification of bacteria isolated from industrial area groundwater to study lead sorption: Kinetics and statistical optimization of biosorption parameters. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2018, 7, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, M.M.; Khanolkar, D.; Dubey, S.K. Lead-resistant Providencia alcalifaciens strain 2EA bioprecipitates Pb+2 as lead phosphate. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 56, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratochvil, D.; Volesky, B. Advances in the biosorption of heavy metals. Trends Biotechnol. 1998, 16, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, L.; Xu, R.; Yang, Y.; Yin, H.; Jin, S.; Jiang, T. Potentiality of phosphorus− accumulating organisms biomasses in biosorption of Cd (II), Pb (II), Cu (II) and Zn (II) from aqueous solutions: Behaviors and mechanisms. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 135095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadivinia, E.; Sharafi, H.; Hadi, F.; Zahiri, H.S.; Modiri, S.; Tohidi, A.; Mousavi, A.; Salmanian, A.H.; Noghabi, K.A. Cadmium biosorption by a glyphosate-degrading bacterium, a novel biosorbent isolated from pesticide-contaminated agricultural soils. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 4304–4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Level | Factor | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | Inoculation Volume (%) | Temperature (°C) | Rotational Speed (r/min) | |
| 1 | 6 | 4 | 25 | 130 |
| 2 | 7 | 6 | 30 | 150 |
| 3 | 8 | 8 | 35 | 170 |
| Processing Number | pH | Inoculation Volume (%) | Temperature (°C) | Rotational Speed (r/min) | OD660 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6 | 4 | 25 | 130 | 0.82 |
| 2 | 6 | 6 | 30 | 150 | 0.87 |
| 3 | 6 | 8 | 35 | 170 | 0.86 |
| 4 | 7 | 4 | 30 | 170 | 0.84 |
| 5 | 7 | 6 | 35 | 130 | 0.87 |
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 25 | 150 | 0.85 |
| 7 | 8 | 4 | 35 | 150 | 0.86 |
| 8 | 8 | 6 | 25 | 170 | 0.84 |
| 9 | 8 | 8 | 30 | 130 | 0.78 |
| K1 | 2.55 | 2.52 | 2.51 | 2.47 | |
| K2 | 2.56 | 2.58 | 2.49 | 2.58 | |
| K3 | 2.48 | 2.49 | 2.59 | 2.54 | |
| K1/3 | 0.850 | 0.840 | 0.837 | 0.823 | |
| K2/3 | 0.853 | 0.860 | 0.830 | 0.860 | |
| K3/3 | 0.827 | 0.830 | 0.863 | 0.847 | |
| R | 0.027 | 0.030 | 0.033 | 0.037 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bao, L.; Cui, Y.; Wu, H.; Xu, J.; Zhu, S. Breeding, Biosorption Characteristics, and Mechanism of a Lead-Resistant Strain. Toxics 2023, 11, 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11050412
Bao L, Cui Y, Wu H, Xu J, Zhu S. Breeding, Biosorption Characteristics, and Mechanism of a Lead-Resistant Strain. Toxics. 2023; 11(5):412. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11050412
Chicago/Turabian StyleBao, Lining, Yu Cui, Haiwei Wu, Jingwen Xu, and Shuguang Zhu. 2023. "Breeding, Biosorption Characteristics, and Mechanism of a Lead-Resistant Strain" Toxics 11, no. 5: 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11050412
APA StyleBao, L., Cui, Y., Wu, H., Xu, J., & Zhu, S. (2023). Breeding, Biosorption Characteristics, and Mechanism of a Lead-Resistant Strain. Toxics, 11(5), 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11050412








