Reduced Survival and Disruption of Female Reproductive Output in Two Copepod Species (Acartia clausi and A. tonsa) Exposed to the Model Endocrine Disruptor 17α-Ethinylestradiol
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. A. tonsa and A. clausi Collection and Maintenance
2.2. Preparation of 17ɑ-ethinylestradiol Stock and Working Solutions
2.3. Experiment Setup and Studied Endpoints
2.4. Integrated Biological Response (IBR)/n Index
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
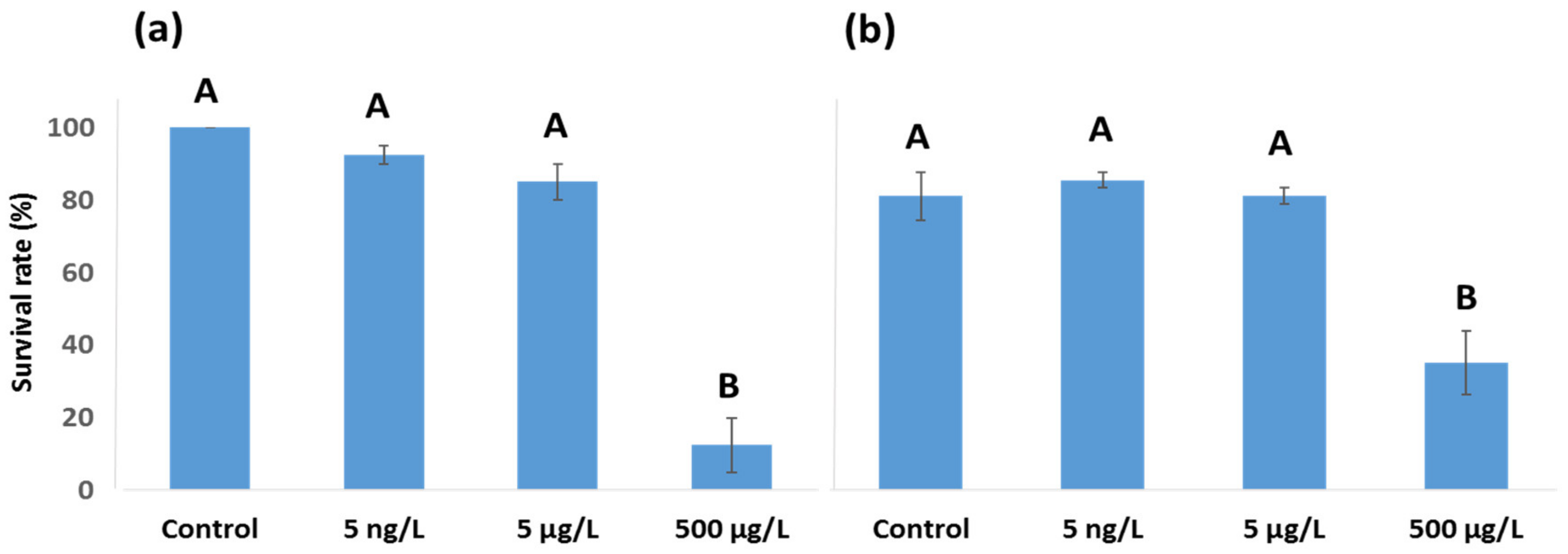
3.1. EE2 24 h Survival Rate and LC50 Values for Female A. tonsa and A. clausi
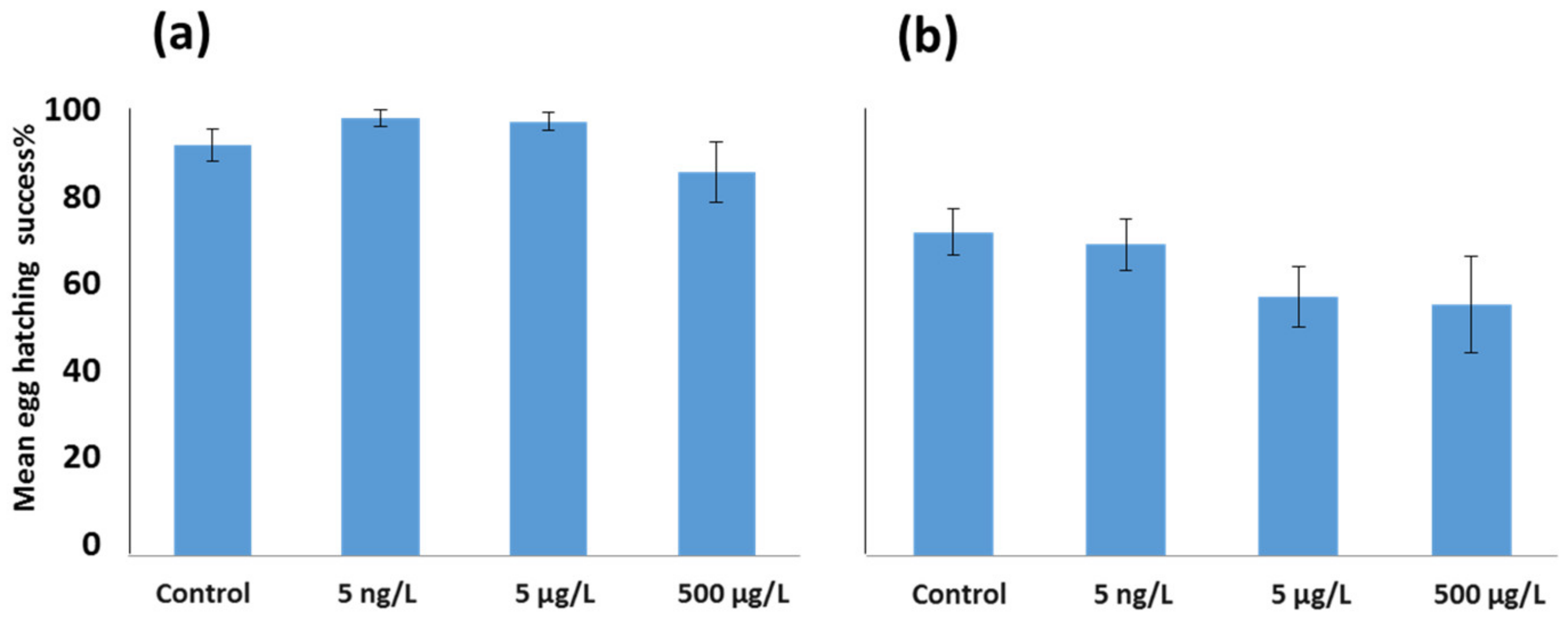
3.2. Effects of EE2 on Reproductive Output in A. tonsa and A. clausi Adult Females
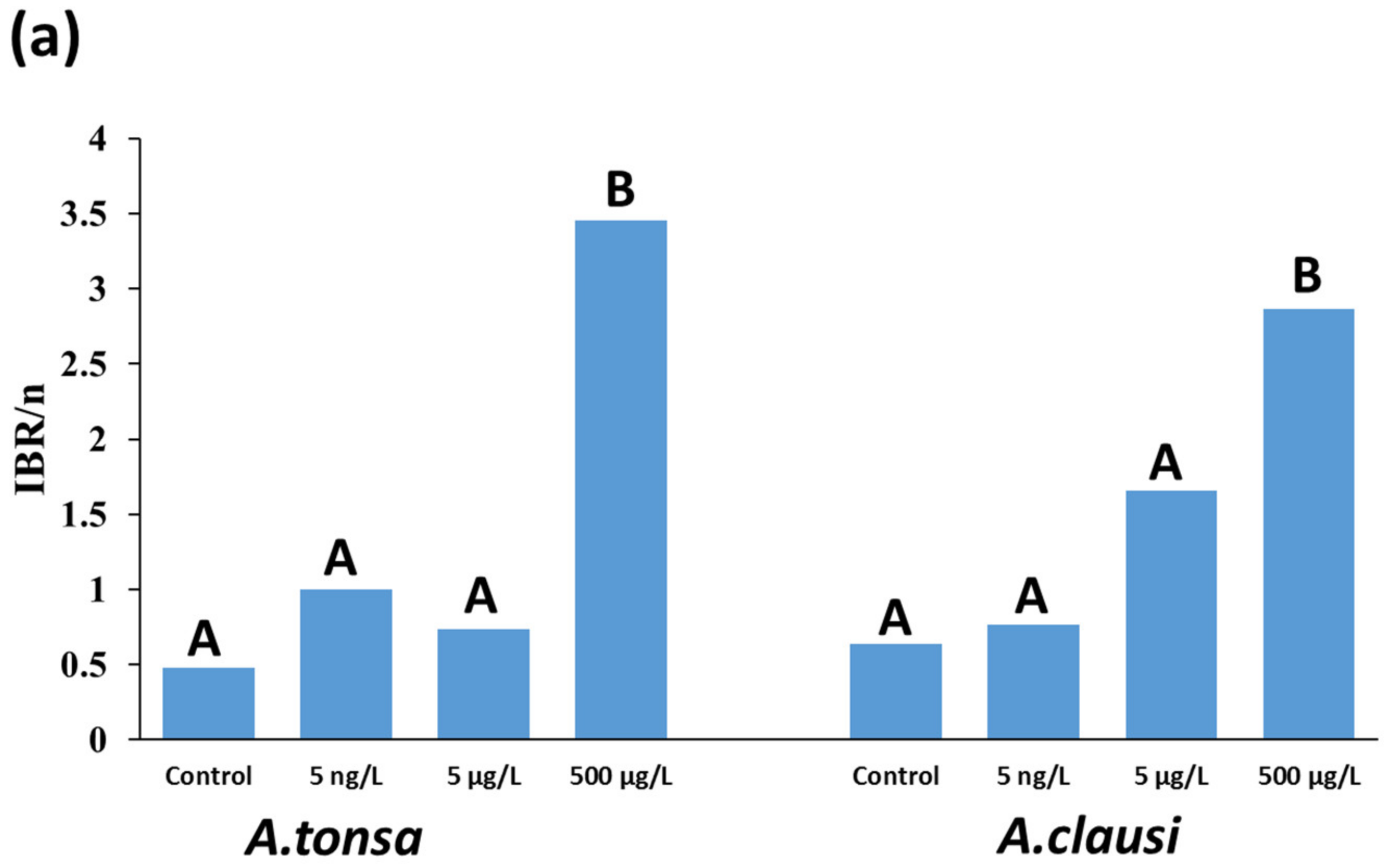
3.3. IBR/n Index
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kummu, M.; de Moel, H.; Ward, P.J.; Varis, O. How Close Do We Live to Water? A Global Analysis of Population Distance to Freshwater Bodies. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrman, V.; Tal, A.; Arnon, S. Why endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) challenge traditional risk assessment and how to respond. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 286, 589–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamanti-Kandarakis, E.; Bourguignon, J.P.; Giudice, L.C.; Hauser, R.; Prins, G.S.; Soto, A.M.; Zoeller, R.T.; Gore, A.C. Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals: An Endocrine Society Scientific Statement. Endocr. Rev. 2009, 30, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, G.; Sutton, E.L. Oral contraception. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 99, 479–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Combalbert, S.; Pype, M.L.; Bernet, N.; Hernandez-Raquet, G. Enhanced methods for conditioning, storage, and extraction of liquid and solid samples of manure for determination of steroid hormones by solid-phase extraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 398, 973–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.; Zhou, X.; Xu, D.; Xiang, Y.; Ling, W.; Chen, M. Contamination and Risk Assessment of Estrogens in Livestock Manure: A Case Study in Jiangsu Province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, E.M.; Allinson, M.; Allinson, G.; Swearer, S.E.; Hassell, K.L. Fluctuations in natural and synthetic estrogen concentrations in a tidal estuary in south-eastern Australia. Water Res. 2013, 47, 1604–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusceddu, F.H.; Sugauara, L.E.; de Marchi, M.R.; Choueri, R.B.; Castro, Í.B. Estrogen levels in surface sediments from a multi-impacted Brazilian estuarine system. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 142, 576–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberdörster, E.; Cheek, A.O. Gender benders at the beach: Endocrine disruption in marine and estuarine organisms. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2001, 20, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Üstün, F.; Bat, L. The egg production rate of Acartia (Acartiura) clausi Giesbrecht, 1889 (Copepoda) in Sinop Peninsula (southern Black Sea). Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2014, 14, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cailleaud, K.; Budzinski, H.; Lardy, S.; Augagneur, S.; Barka, S.; Souissi, S.; Forget-Leray, J. Uptake and elimination, and effect of estrogen-like contaminants in estuarine copepods: An experimental study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2011, 18, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, H.Y.; Huang, K.C.; Cheng, J.O.; Lo, W.T.; Meng, P.J.; Ko, F.C. Environmental effects on the bioaccumulation of PAHs in marine zooplankton in Gaoping coastal waters, Taiwan: Concentration, distribution, profile, and sources. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 144, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, D.; Valiela, I.; Tomasky, G. Estuarine calanoid copepod abundance in relation to season, salinity, and land-derived nitrogen loading, Waquoit Bay, MA. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2004, 61, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uriarte, I.; Villate, F. Spatial variations in size, weight and condition factor of the females of Acartia clausi (Copepoda: Calanoida) along a salinity gradient in two contrasting estuaries of the Basque coast (Bay of Biscay). Hydrobiologia 2006, 571, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehberger, K.; Wernicke von Siebenthal, E.; Bailey, C.; Bregy, P.; Fasel, M.; Herzog, E.L.; Neumann, S.; Schmidt-Posthaus, H.; Segner, H. Long-term exposure to low 17α-ethinylestradiol (EE2) concentrations disrupts both the reproductive and the immune system of juvenile rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Environ. Int. 2020, 142, 105836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, R.; Smith, M.D.; Spary, C.J.; Tyler, C.R.; Hill, E.M. Mixtures of estrogenic contaminants in bile of fish exposed to wastewater treatment works effluents. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 2461–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchinson, T.H. Reproductive and developmental effects of endocrine disrupters in invertebrates: In vitro and in vivo approaches. Toxicol. Lett. 2002, 131, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clubbs, R.L.; Brooks, B.W. Daphnia magna responses to a vertebrate estrogen receptor agonist and an antagonist: A multigenerational study. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2007, 67, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schramm, K.W.; Jaser, W.; Welzl, G.; Pfister, G.; Wöhler-Moorhoff, G.F.; Hense, B.A. Impact of 17α-ethinylestradiol on the plankton in freshwater microcosms—I: Response of zooplankton and abiotic variables. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2008, 69, 437–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, H.R.; Wollenberger, L.; Halling-Sørensen, B.; Kusk, K.O. Development of copepod nauplii to copepodites—A parameter for chronic toxicity including endocrine disruption. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2001, 20, 2821–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djebbi, E.; Yahia, M.N.D.; Farcy, E.; Pringault, O.; Bonnet, D. Acute and chronic toxicity assessments of 17β-estradiol (E2) and 17α-ethinylestradiol (EE2) on the calanoid copepod Acartia clausi: Effects on survival, development, sex-ratio and reproduction. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irabien, M.J.; Cearreta, A.; Serrano, H.; Villasante-Marcos, V. Environmental regeneration processes in the Anthropocene: The Bilbao estuary case (northern Spain). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 135, 977–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Iruretagoiena, A.; Elejoste, N.; Gredilla, A.; Fdez-Ortiz de Vallejuelo, S.; Arana, G.; Madariaga, J.M.; de Diego, A. Occurrence and geographical distribution of metals and metalloids in sediments of the Nerbioi-Ibaizabal estuary (Bilbao, Basque Country). Mar. Chem. 2016, 185, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolomé, L.; Etxebarria, N.; Martínez-Arkarazo, I.; Raposo, J.C.; Usobiaga, A.; Zuloaga, O.; Raingeard, D.; Cajaraville, M.P. Distribution of organic microcontaminants, butyltins, and metals in mussels from the estuary of Bilbao. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 59, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orbea, A.; Ortiz-Zarragoitia, M.; Solé, M.; Porte, C.; Cajaraville, M.P. Antioxidant enzymes and peroxisome proliferation in relation to contaminant body burdens of PAHs and PCBs in bivalve molluscs, crabs and fish from the Urdaibai and Plentzia estuaries (Bay of Biscay). Aquat. Toxicol. 2002, 58, 75–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albaina, A.; Uriarte, I.; Aguirre, M.; Abad, D.; Iriarte, A.; Villate, F.; Estonba, A. Insights on the origin of invasive copepods colonizing Basque estuaries; A DNA barcoding approach. Mar. Biodivers Rec. 2016, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iriarte, A.; Villate, F.; Uriarte, I.; Bidegain, G.; Barroeta, Z. Shifts in neritic copepod communities off the Basque coast (southeastern Bay of Biscay) between 1998 and 2015. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2022, 79, 830–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroeta, Z.; Villate, F.; Uriarte, I.; Iriarte, A. Differences in the colonization success and impact of non-indigenous and other expanding copepod species on the zooplankton of two contrasting estuaries of the Bay of Biscay. Biol. Invasions 2020, 22, 3239–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleppel, G.S.; Burkart, C.A.; Houchin, L. Nutrition and the regulation of egg production in the calanoid copepod Acartia tonsa. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1998, 43, 1000–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broeg, K.; Lehtonen, K.K. Indices for the assessment of environmental pollution of the Baltic Sea coasts: Integrated assessment of a multi-biomarker approach. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2006, 53, 508–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beliaeff, B.; Burgeot, T. Integrated biomarker response: A useful tool for ecological risk assessment. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2002, 21, 1316–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devin, S.; Burgeot, T.; Giamb’erini, L.; Minguez, L.; Pain-Devin, S. The integrated biomarker response revisited: Optimization to avoid misuse. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 4, 2448–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marigómez, I.; Garmendia, L.; Soto, M.; Orbea, A.; Izagirre, U.; Cajaraville, M.P. Marine ecosystem health status assessment through integrative biomarker indices: A comparative study after the Prestige oil spill “mussel Watch”. Ecotoxicology 2013, 22, 486–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, K. Probit Analysis. 2008. Available online: http://userwww.sfsu.edu/efc/classes/biol710/probit/ProbitAnalysis.pdf (accessed on 19 November 2022).
- Hansen, B.H.; Altin, D.; Rørvik, S.F.; Øverjordet, I.B.; Olsen, A.J.; Nordtug, T. Comparative study on acute effects of water accommodated fractions of an artificially weathered crude oil on Calanus finmarchicus and Calanus glacialis (Crustacea: Copepoda). Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 704–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carotenuto, Y.; Vitiello, V.; Gallo, A.; Libralato, G.; Trifuoggi, M.; Toscanesi, M.; Lofrano, G.; Esposito, F.; Buttino, I. Assessment of the relative sensitivity of the copepods Acartia tonsa and Acartia clausi exposed to sediment-derived elutriates from the Bagnoli-Coroglio industrial area. Mar. Environ. Res. 2020, 155, 104878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jager, T.; Salaberria, I.; Hansen, B.H. Capturing the life history of the marine copepod Calanus sinicus into a generic bioenergetics framework. Ecol. Model. 2015, 299, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, B.H.; Jager, T.; Altin, D.; Øverjordet, I.B.; Olsen, A.J.; Salaberria, I.; Nordtug, T. Acute toxicity of dispersed crude oil on the cold-water copepod Calanus finmarchicus: Elusive implications of lipid content. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 2016, 79, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubareva, E.; Svetlichny, L.; Kideys, A.; Isinibilir, M. Fate of the Black Sea Acartia clausi and Acartia tonsa (Copepoda) penetrating into the Marmara Sea through the Bosphorus. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2008, 76, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizarro, C.; Ros, O.; Vallejo, A.; Prieto, A.; Etxebarria, N.; Cajaraville, M.P.; Ortiz-Zarragoitia, M. Intersex condition and molecular markers of endocrine disruption in relation with burdens of emerging pollutants in thicklip grey mullets (Chelon labrosus) from Basque estuaries (South-East Bay of Biscay). Mar. Environ. Res. 2014, 96, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Barcina, J.M.; González-Oreja, J.A.; De La Sota, A. Assessing the improvement of the Bilbao estuary water quality in response to pollution abatement measures. Water Res. 2006, 40, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cajaraville, M.P.; Orive, E.; Villate, F.; Laza-Martínez, A.; Uriarte, I.; Garmendia, L.; Ortiz-Zarragoitia, M.; Seoane, S.; Iriarte, A.; Marigómez, I. Health status of the Bilbao estuary: A review of data from a multidisciplinary approach. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 179, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, H.R.; Halling-Sørensen, B.; Kusk, K.O. A Parameter for Detecting Estrogenic Exposure in the Copepod Acartia tonsa. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1999, 44, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jukosky, J.A.; Watzin, M.C.; Leiter, J.C. Elevated concentrations of ethinylestradiol, 17β-estradiol, and medroxyprogesterone have little effect on reproduction and survival of Ceriodaphnia dubia. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2008, 81, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafez, T.; Bilbao, D.; Etxebarria, N.; Duran, R.; Ortiz-Zarragoitia, M. Application of a biological multilevel response approach in the copepod Acartia tonsa for toxicity testing of three oil Water Accommodated Fractions. Mar. Environ. Res. 2021, 169, 105378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkett, J.W.; John, N.L. Endocrine Disrupters in Wastewater and Sludge Treatment Processes; IWA Publishing: Washington, DC, USA, 2002; pp. 12–14. [Google Scholar]
- Luna, T.O.; Plautz, S.C.; Salice, C.J. Chronic Effects of 17α-Ethinylestradiol, Fluoxetine, and the Mixture on Individual and Population-Level End Points in Daphnia magna. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 68, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, S.; Silva, A.M.; Antunes, S.C. Assessment of 17α-ethinylestradiol effects in Daphnia magna: Life-history traits, biochemical and genotoxic parameters. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 23160–23173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sverdrup, L.E.; Fürst, C.S.; Weideborg, M.; Vik, E.A.; Stenersen, J. Relative sensitivity of one freshwater and two marine acute toxicity tests as determined by testing 30 offshore E & P chemicals. Chemosphere 2002, 46, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hafez, T.; Villate, F.; Ortiz-Zarragoitia, M. Reduced Survival and Disruption of Female Reproductive Output in Two Copepod Species (Acartia clausi and A. tonsa) Exposed to the Model Endocrine Disruptor 17α-Ethinylestradiol. Toxics 2023, 11, 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11050405
Hafez T, Villate F, Ortiz-Zarragoitia M. Reduced Survival and Disruption of Female Reproductive Output in Two Copepod Species (Acartia clausi and A. tonsa) Exposed to the Model Endocrine Disruptor 17α-Ethinylestradiol. Toxics. 2023; 11(5):405. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11050405
Chicago/Turabian StyleHafez, Tamer, Fernando Villate, and Maren Ortiz-Zarragoitia. 2023. "Reduced Survival and Disruption of Female Reproductive Output in Two Copepod Species (Acartia clausi and A. tonsa) Exposed to the Model Endocrine Disruptor 17α-Ethinylestradiol" Toxics 11, no. 5: 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11050405
APA StyleHafez, T., Villate, F., & Ortiz-Zarragoitia, M. (2023). Reduced Survival and Disruption of Female Reproductive Output in Two Copepod Species (Acartia clausi and A. tonsa) Exposed to the Model Endocrine Disruptor 17α-Ethinylestradiol. Toxics, 11(5), 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11050405





