Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal in Farmlands and Crops Near Pb–Zn Mine Tailing Ponds in Niujiaotang, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
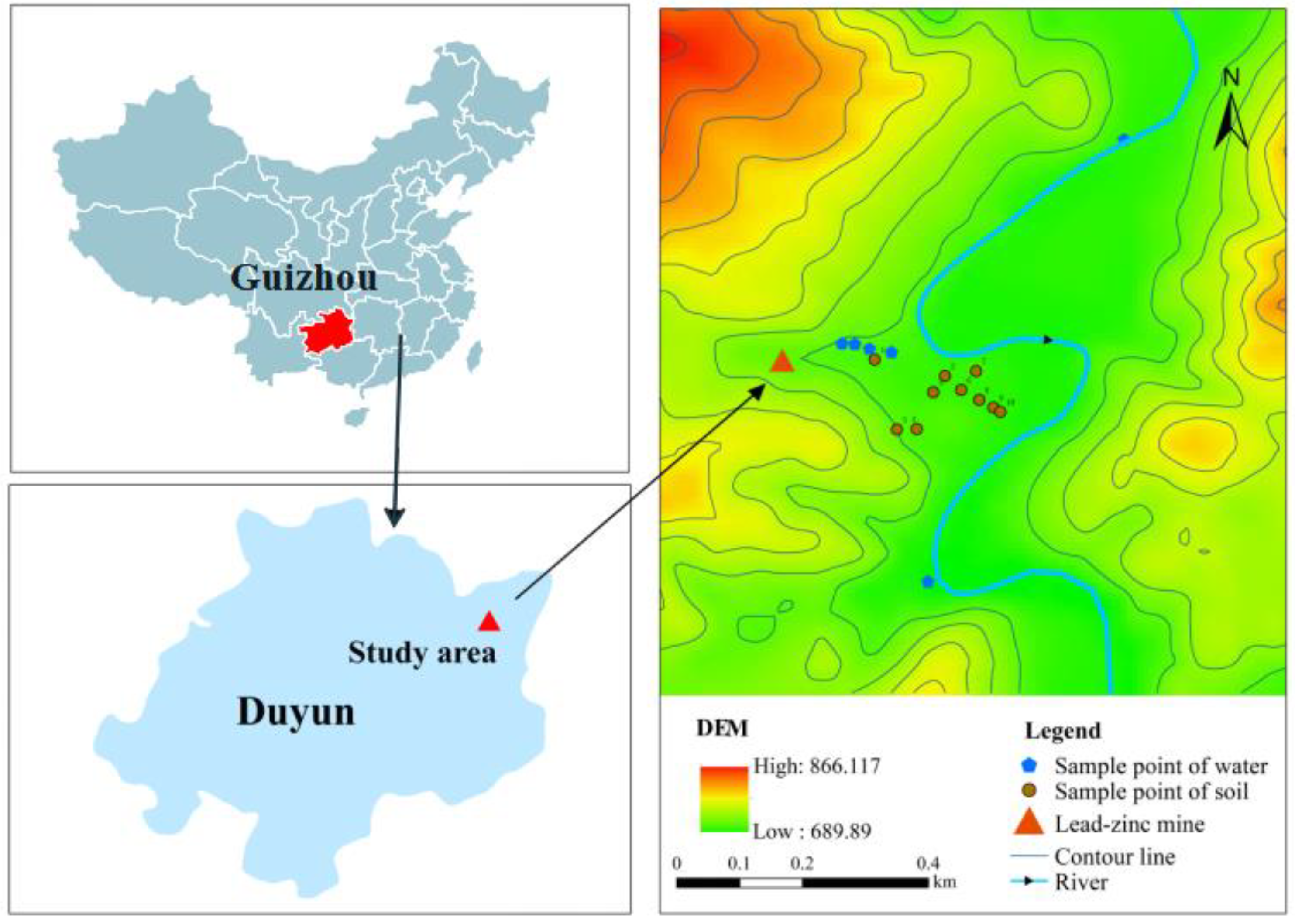
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Preprocessing
2.3. Sample Analysis
2.4. Pollution and Ecological Risk Assessment
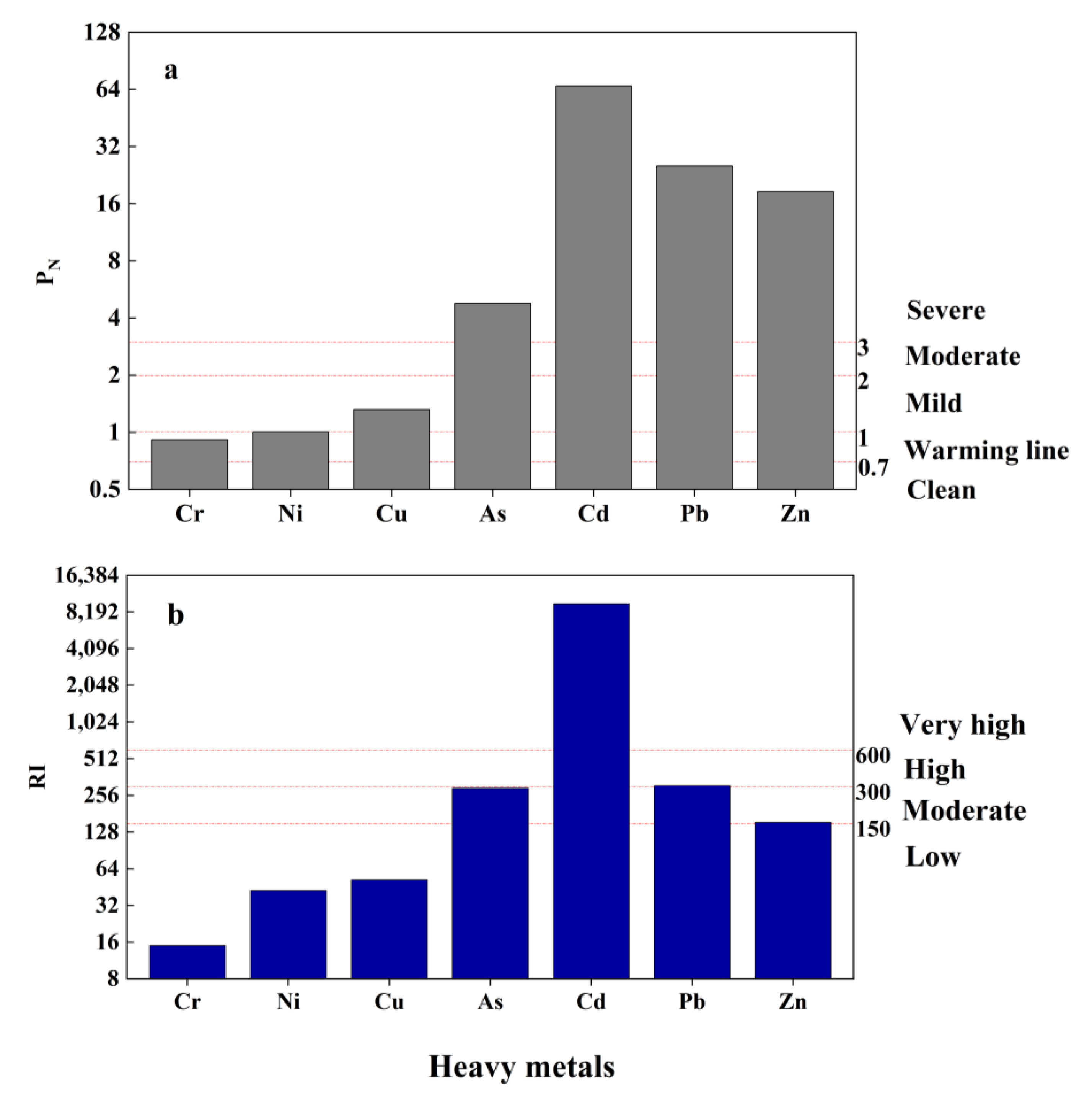
2.4.1. Potential Ecological Risk Index (RI) Method
2.4.2. Nemeiro Comprehensive Pollution Assessment
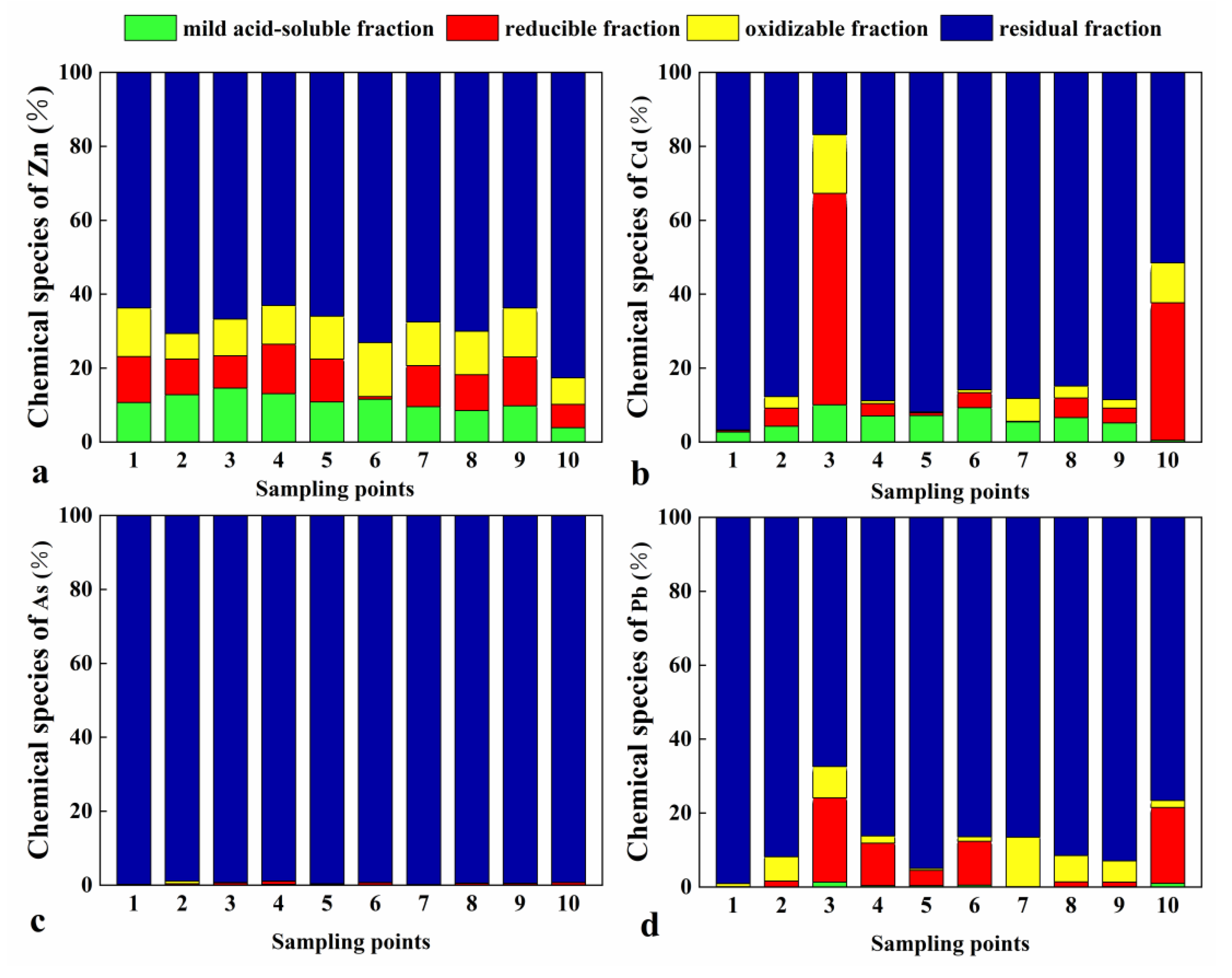
2.4.3. RAC Method (Risk Assessment Code)
2.4.4. RSP Method (Ratio of Secondary Phase to Primary Phase)
2.5. Human Health Risk Assessment
3. Results and Discussion
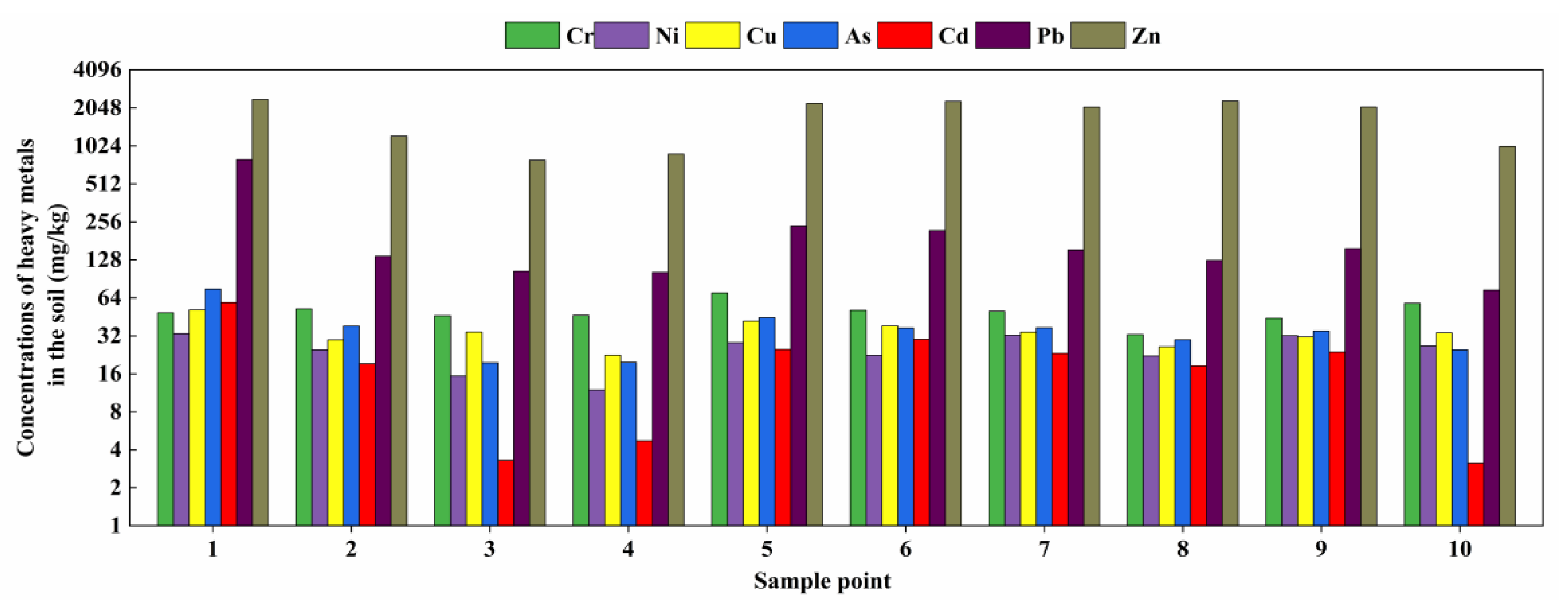
3.1. Heavy Metal Contents and Geochemical Characteristics of Agricultural Soils
3.2. Soil–Plant Heavy Metal Migration and Enrichment Characteristics
3.2.1. Morphological Distribution of Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soils
3.2.2. Heavy Metal Pollution of Crops
3.2.3. Enrichment and Transport of Heavy Metals
3.3. Ecological Environment and Human Health Risk Assessment
3.3.1. Ecological Risk Assessment
3.3.2. Health Risk Assessment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shen, W.; Xiong, K.; Gao, Y.; Quan, M.; Peng, H.; Yang, T.; He, L.; Bao, K. Distribution of Potential Harmful Trace Elements and Potential Ecological Risk in the Jiulongchi Wetland of Fanjing Mountain, Southwest China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Heal. 2020, 17, 1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, C.A.; Moore, B.; Vervoort, J.; Beutel, M. Tracking long-distance atmospheric deposition of trace metal emissions from smelters in the upper Columbia River valley using Pb isotope analysis of lake sediments. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 5501–5513. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, N.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, D. Health risk of Hg, Pb, Cd, Zn, and Cu to the inhabitants around Huludao Zinc Plant in China via consumption of vegetables. Sci. Total. Environ. 2007, 383, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.C.; Nejad, Z.D.; Jung, M.C. Arsenic and heavy metals in paddy soil and polished rice contaminated by mining activities in Korea. Catena 2017, 148, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; Fan, L.; Chen, T.; Bai, Y.; Yu, Q.; Liu, Y. Assessment of multiple exposure to chemical elements and health risks among residents near Huodehong lead-zinc mining area in Yunnan, Southwest China. Chemosphere 2017, 174, 613–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Cook, N.J.; Liu, T.; Ciobanu, C.L.; Gao, W.; Yang, Y. The Niujiaotang Cd-rich zinc deposit, Duyun, Guizhou province, southwest China: Ore genesis and mechanisms of cadmium concentration. Miner. Depos. 2012, 47, 683–700. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Wei, H.; Yang, R.; Gao, J.; Qu, Y. Study on Distribution Characteristics of Heavy Metals in Tailings from Niujiaotang Lead-zinc Mine Area, Duyun City, Guizhou Province. Nonferrous Met. Eng. 2018, 8, 122–127. [Google Scholar]
- Nassiri, O.; Rhoujjati, A.; EL Hachimi, M.L. Contamination, sources and environmental risk assessment of heavy metals in water, sediment and soil around an abandoned Pb mine site in North East Morocco. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candeias, C.; Ávila, P.F.; Da Silva, E.F.; Ferreira, A.; Durães, N.; Teixeira, J.P. Water–Rock Interaction and Geochemical Processes in Surface Waters Influenced by Tailings Impoundments: Impact and Threats to the Ecosystems and Human Health in Rural Communities (Panasqueira Mine, Central Portugal). Water Air Soil Pollut. 2015, 226, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.R.; Ye, L.; Yang, D.; Hu, Y.; Wei, C.; Dai, D.; Li, Z. A Discussion on the Pb-Zn Mineralization Regularity and Ore Prospecting Targets in the Kaili-Duyun Area, Guizhou Province, China. Acta Mineral. Sin. 2018, 38, 675–683. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.; Lu, H.; Cao, Z.; Xie, J. Morphological characteristics of homozygous wild rice phytoliths and their significance in the study of rice origins. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2021, 65, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.-F.; Song, Y.-H.; Yuan, P.; Cui, X.-Y.; Qiu, G.-L. The remediation of heavy metals contaminated sediment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Arocena, J.M.; Zhang, Q.; Thring, R.W.; Li, J. Heavy metals and nutrients (carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus) in sediments: Relationships to land uses, environmental risks, and management. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 7403–7412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.-J.; Feng, J.; Zhang, L.-M.; He, J.-Z.; Liu, Y.-R. Ecological drivers of methanotrophic communities in paddy soils around mercury mining areas. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 721, 137760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, H.E.; Yun, Z.J.; Shi, J.B.; Jiang, G.B. Research progress of heavy metal pollution in China: Sources, analytical methods, status, and toxicity. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 134–140. [Google Scholar]
- Weike, Z.; Liao, Y.; Zhou, S.; Zhou, B. Ecological remediation strategy for urban brownfield renewal in Sichuan Province, China: A health risk evaluation perspective. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4300. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, M.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Lei, K.; Li, Y.; Li, F.; Zheng, D.; Fang, X.; Cao, Y. Heavy metal contamination risk assessment and correlation analysis of heavy metal contents in soil and crops. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 278, 116911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordean, D.-M.; Pirvulescu, L.; Poiana, M.-A.; Alexa, E.; Cozma, A.; Raba, D.; Borozan, A.; Misca, C.; Morar, A.; Obistioiu, D.; et al. An Innovative Approach to Assess the Ecotoxicological Risks of Soil Exposed to Solid Waste. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salar, R.; Moghaddam, S.S.; Nouri, A.; Aqdam, K.K. Urbanization influences the distribution, enrichment, and ecological health risk of heavy metals in croplands. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3868. [Google Scholar]
- Sajid, R.; AliShah, I.; Tulcan, R.X.S.; Rashid, W.; Sillanpaa, M. Contamination, exposure, and health risk assessment of Hg in Pakistan: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 301, 118995. [Google Scholar]
- Mazumder, P.; Das, A.; Khwairakpam, M.; Kalamdhad, A.S. A comprehensive insight into ecological risk assessment and remediation of metal contaminated coal mine soil: Towards a cleaner and sustainable environment. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 324, 129185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asare, E.A.; Assim, Z.; Wahi, R.; Fianko, J.R. Eco-toxic risk assessment and source distribution of trace metals in surface sediments of the coastal and in four rivers estuary of Sarawak. Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2022, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panghal, V.; Singh, A.; Kumar, R.; Kumari, G.; Kumar, P.; Kumar, S. Soil heavy metals contamination and ecological risk assessment in Rohtak urban area, Haryana (India). Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xianfei, H.; Wu, X.; Tang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H. Distribution characteristics and risk of heavy metals and microbial community composition around the Wanshan mercury mine in Southwest China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 227, 112897. [Google Scholar]
- Sayma, S.; Khan, A.A.; Khan, M.R.; Ansari, S.A.; Khan, A. Assessment of Phytoremediation Potential of Seven Weed Plants Growing in Chromium- and Nickel-Contaminated Soil. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 209. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, B.; Hong, C.; Tong, W.; Xu, M.; Huang, C.; Yin, H.; Lin, Y.; Fu, Q. Health risk assessment of heavy metal pollution in a soil-rice system: A case study in the Jin-Qu Basin of China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wang, L. Ecological and human health risk assessments in the context of soil heavy metal pollution in a typical industrial area of Shanghai, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 27090–27105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deep, R.; Kumar, A.; Tripti; Risk, S.K.M.H. Assessment of Children Exposed to the Soil Containing Potentially Toxic Elements: A Case Study from Coal Mining Areas. Metals 2022, 12, 1795. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, S.; Tang, L.; Zheng, N.; Yang, Y.Y. Bioaccessibility and health risk assessment of heavy metals in vegetables of typical mining area. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2018, 38, 343–349. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.-W.; Xu, Y.; Liu, S.-J.; He, J.-F.; Long, F.-Y. Concentration and potential health risk of heavy metals in market vegetables in Chongqing, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2011, 74, 1664–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Response, E.P.A.O. Superfund Public Health Evaluation Manual; EPA: Washington, DC, USA.
- Khezerlou, A.; Dehghan, P.; Moosavy, M.-H.; Kochakkhani, H. Assessment of Heavy Metal Contamination and the Probabilistic Risk via Salad Vegetable Consumption in Tabriz, Iran. Biol. Trace Element Res. 2020, 199, 2779–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IRIS, U.E.O.N. Zinc and Compounds (CASRN 7440-66-6); | IRIS | US EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Environmental Protection Agency. Supplemental Guidance for Developing Soil Screening Levels for Superfund Sites; US EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2002.
- Zhang, J.; Li, C.; Li, G.; He, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J. Effects of biochar on heavy metal bioavailability and uptake by tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) in two soils. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 317, 107453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Rajkumar, M.; Zhang, C.; Freitas, H. Inoculation of Brassica oxyrrhina with plant growth promoting bacteria for the improvement of heavy metal phytoremediation under drought conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 320, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.E.; Li, C.Y.; Liu, T.G.; Li, X.B.; Pi, D.H. The environmental impact of Cadmium-rich Pb-Zn deposit for the example of Niujiaotang Cd rich Znic deposit, Duyun, Guizhou, China. Adv. Earth Sci. 2004, 67, 456–460. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Z.P. The pollution characteristic of water during mining in Cadmium-rich Pb-Zn ore area as exemplifed by the NiujiaotangG Cd-rich znic deposit, Duyun, Guizhou Province. Acta Mineral. Sin. 2008, 28, 401–406. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, L.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y.; Tan, X.; Yang, Y. Spatial Distributions, Pollution Assessment, and Qualified Source Apportionment of Soil Heavy Metals in a Typical Mineral Mining City in China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhao, X.; Dong, J.; Zheng, B. Risk assessment of heavy metals in the surface sediment at the drinking water source of the Xiangjiang River in South China. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.; Han, Z.; Tan, Y.; Xiao, H.; Yang, M. Chemical characteristics and quality evaluation of shallow groundwater in a typical karst plateau basin of Guizhou province: A case study of Houzhai river in Puding county. Environ. Chem. 2017, 36, 858–866. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Ren, E. Chemical state analysis of lead and zinc in soil of xitieshan mining area in the northern margin of qaidam basin. IOP Conf. Series: Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 186, 012066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chlopecka, A.; Bacon, J.R.; Wilson, M.J.; Kay, J. Forms of Cadmium, Lead, and Zinc in Contaminated Soils from Southwest Poland. J. Environ. Qual. 1996, 25, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Han, Z.; Xiong, J.; He, Y.; Liao, J.; Wu, P. Heavy metal pollution and ecological risk assessment of tailings in the Qinglong Dachang antimony mine, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 33491–33504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haili, M.; Long, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, H.T. Speciation and Distribution Characteristics of Heavy Metals in Soil of Guizhou Niujiaotang Lead-Zinc Mining Area. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 37 (Suppl. S2), 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Kza, B.; Tappero, R.; Ruytinx, J.; Branco, S.; Liao, H.-L. Disentangling the role of ectomycorrhizal fungi in plant nutrient acquisition along a Zn gradient using in-situ X-ray imaging. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 801, 149481. [Google Scholar]
- Wahsha, M.; Fontana, S.; Nadimi-Goki, M.; Bini, C. Potentially toxic elements in foodcrops (Triticum aestivum L., Zea mays L.) grown on contaminated soils. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 147, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayat, U.; Khaliq, M.; Ullah, N.; Iqbal, A.; Fozia; Ullah, I. Health Risk Assessment and Multivariate Statistical Analysis of Heavy Metals in Vegetables of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Region, Pakistan. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 3023–3038. [Google Scholar]
- Mohsen, J.; Amir, M. Heavy metal contents, soil-to-plant transfer factors, and associated health risks in vegetables grown in western Iran. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 106, 104316. [Google Scholar]
- Mengxue, W.; Hu, W.; Wang, H.; Tian, K.; Huang, B. Comprehensive assessment of heavy metal risk in soil-crop systems along the Yangtze River in Nanjing, Southeast China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146567. [Google Scholar]
- Min, M.; Yang, L.; Wei, B.; Cao, Z.; Yu, J.; Liao, X. Plastic shed production systems: The migration of heavy metals from soil to vegetables and human health risk assessment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 215, 112106. [Google Scholar]
- Deep, R.; Kumar, M.S. Risk assessment of potentially toxic elements in soils and vegetables around coal-fired thermal power plant: A case study of Dhanbad, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 699. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, M.; Liang, Y.; Lakshmanan, P.; Guan, X.; Liu, D.; Chen, X. Magnesium application reduced heavy metal-associated health risks and improved nutritional quality of field-grown Chinese cabbage. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 289, 117881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.M.; Wang, L.; Xie, H.; Wang, H. Enrichment characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in vegetables in Sanshan District of Wuhu City of Anhui Province. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2010, 29, 1471–1476. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammad, M.S. Human health risk from Heavy metal via food crops consumption with wastewater irrigation practices in Pakistan. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 2230–2238. [Google Scholar]
- Pukalchik, M.A.; Terekhova, V.A.; Karpukhin, M.M.; Vavilova, V.M. Comparison of Eluate and Direct Soil Bioassay Methods of Soil Assessment in the Case of Contamination with Heavy Metals. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2019, 52, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.-Q.; Xiao, K.; Wang, X.-D.; Lv, Z.-H.; Mao, M. Evaluating the distribution and potential ecological risks of heavy metal in coal gangue. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 28, 18604–18615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Huerta, E.A.; Armienta-Hernández, M.A.; Dubrovsky, J.G.; Gómez-Bernal, J.M. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals and As in maize (Zea mays L.) grown close to mine tailings strongly impacts plant development. Ecotoxicology 2022, 31, 447–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdi, M.; Kolahi, M.; Kazemi, E.M.; Barnaby, A.G. Study of the contamination rate and change in growth features of lettuce (Lactuca sativa Linn.) in response to cadmium and a survey of its phytochelatin synthase gene. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 180, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


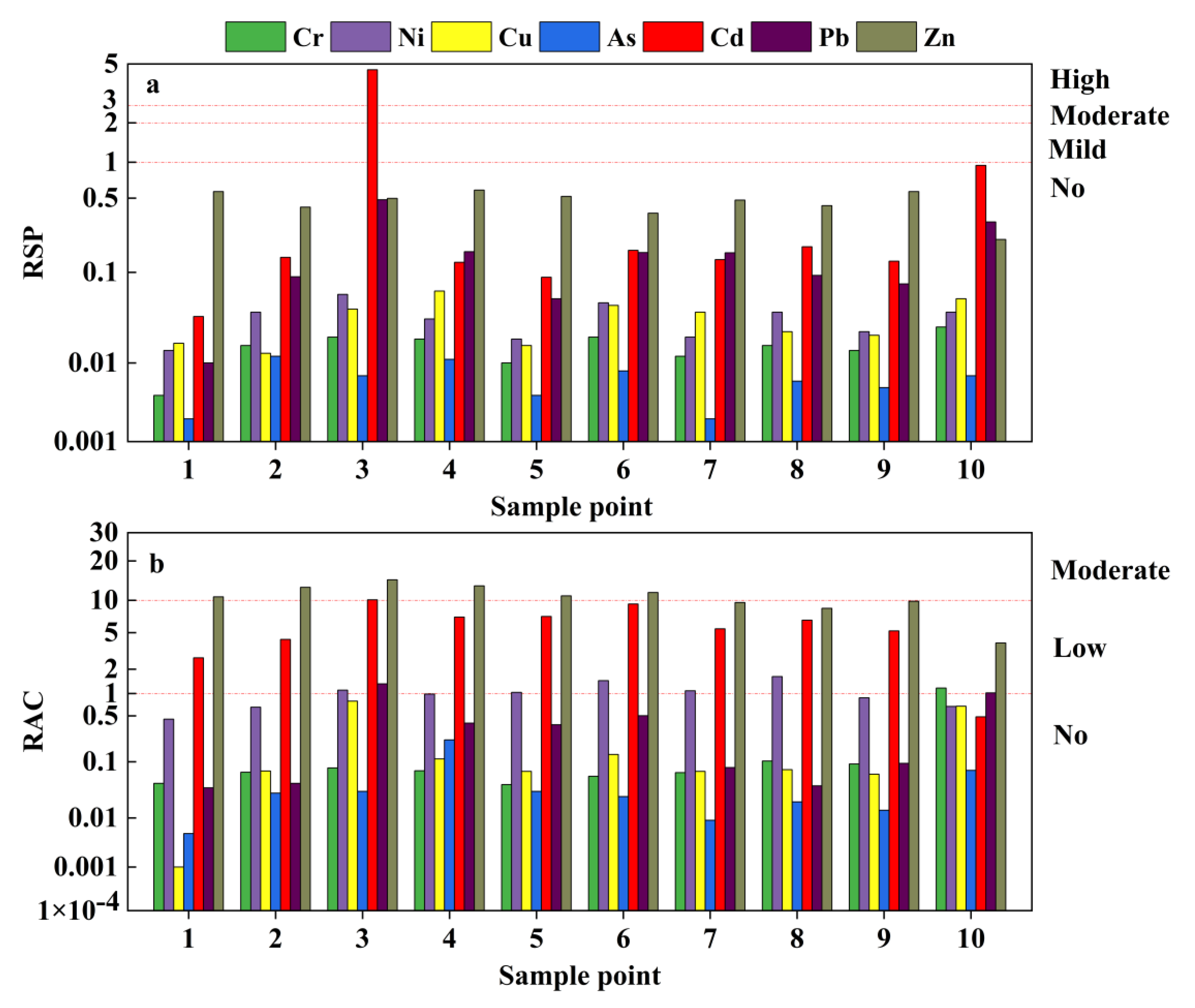
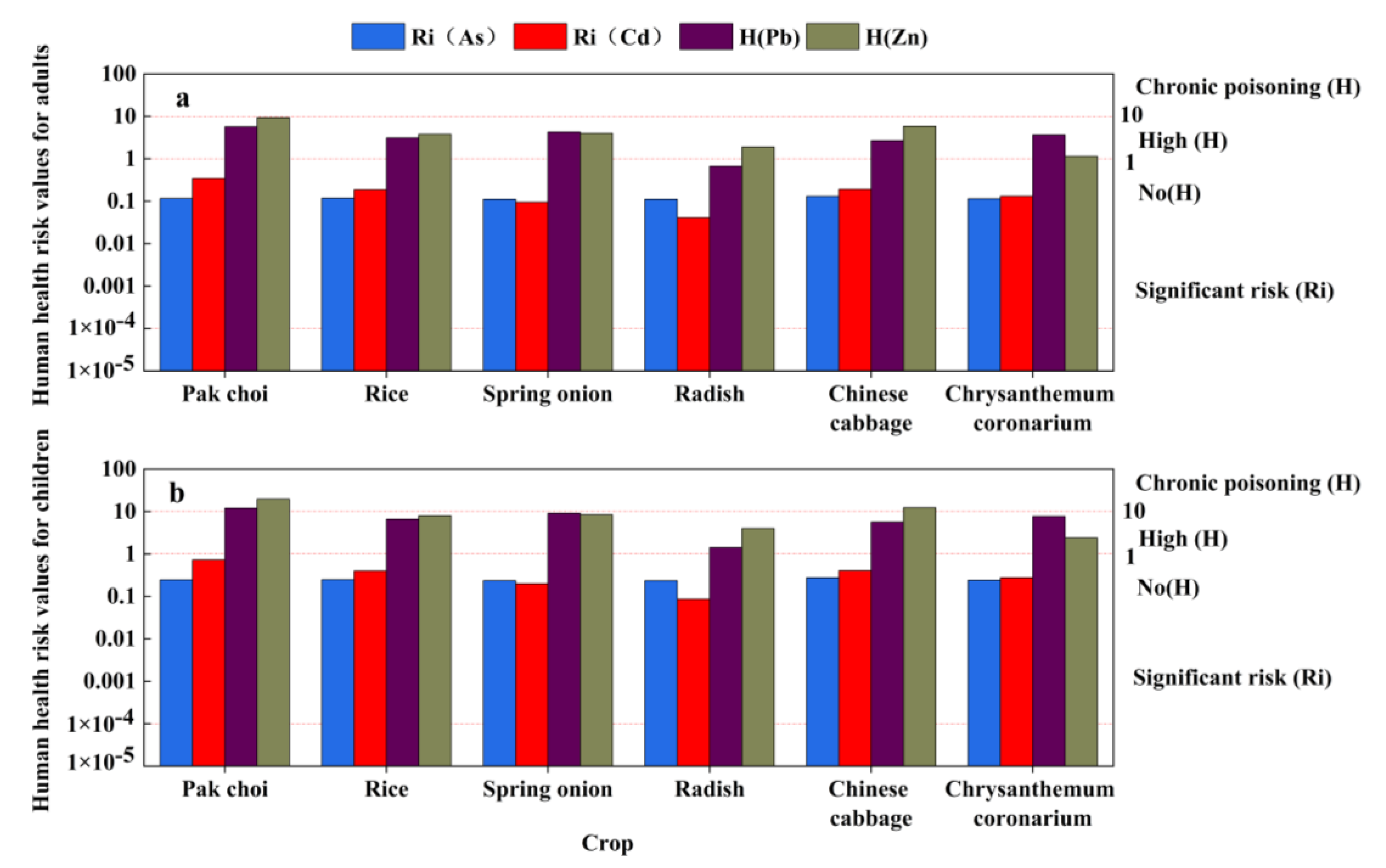
| Element | Cin (mg/kg) | Tir |
|---|---|---|
| As | 12.33 | 10 |
| Cd | 0.23 | 30 |
| Cr | 66.6 | 2 |
| Cu | 33.18 | 5 |
| Ni | 29.39 | 5 |
| Pb | 23.02 | 5 |
| Zn | 112.75 | 1 |
| Method | Risk Levels | Literature | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Potential ecological risk index (RI) method | RI < 150 | 150 ≤ RI < 300 | 300 ≤ RI < 600 | 600 ≤ RI | / | [23] |
| Low | Moderate | High | Very high | / | ||
| Nemeiro index method | PN ≤ 0.7 | 0.7 < PN ≤ 1 | 1 < PN ≤ 2 | 2 < PN ≤ 3 | PN > 3 | [26] |
| Clean | Warning Line | Mild | Moderate | Severe | ||
| Risk assessment code (RAC) | RAC < 1% | RAC < 10% | 10% ≤ RAC < 30% | 30% ≤ RAC < 50% | ≥50% | [22] |
| No | Low | Moderate | High | Very high | ||
| Ratio of secondary phase to primary phase (RSP) | RSP ≤ 1 | 1 < RSP ≤ 2 | 2 < RSP ≤ 3 | RSP > 3 | / | [27] |
| No | Mild | Moderate | High | / | ||
| Parameter | Adults | Children | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| IR | 0.355 | 0.233 | [29] |
| EF | 350 | 350 | [30] |
| ED | 24 | 6 | |
| BW | 61.8 | 19.2 | |
| AT | ED × 365 | ED × 365 | [31] |
| RfD | Pb = 0.0035 | [32] | |
| Zn = 0.3 | [33] | ||
| SF | As = 1.5; Cd = 6.1 | [34] | |
| Heavy Metals | Cr | Ni | Cu | Zn | As | Cd | Pb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| River 1 | 4.579 | 0.233 | 0.331 | 17.45 | 0.445 | N.D | 0.272 |
| River 2 | 3.659 | 0.026 | 1.198 | 6.834 | 0.372 | N.D | 0.298 |
| Leachate | 3.146 | 4.73 | 2.215 | 49.82 | 0.051 | N.D | 0.241 |
| Paddy water | 4.051 | 3.292 | 1.996 | 100.1 | 0.053 | 0.278 | 0.278 |
| Ditch 1 | 3.914 | 3.64 | 1.888 | 253.3 | 0.048 | 0.208 | 0.290 |
| Ditch 2 | 3.6 | 2.833 | 1.839 | 134.4 | N.D | 0.31 | 0.248 |
| Ditch 3 | 3.8 | 3.339 | 1.834 | 42.08 | 0.95 | N.D | 0.328 |
| Surface water standard (Class V) | 100 | 20 | 1000 | 200 | 100 | 10 | 100 |
| Type of Value | Cr | Ni | Cu | As | Cd | Pb | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum | 69.99 | 33.40 | 51.34 | 75.15 | 58.75 | 796.22 | 2382.21 |
| Minimum | 32.83 | 11.93 | 22.52 | 19.58 | 3.15 | 73.68 | 788.42 |
| Average | 50.00 | 24.97 | 34.40 | 36.10 | 20.98 | 210.50 | 1730.28 |
| Median | 49.47 | 25.71 | 34.06 | 35.95 | 21.24 | 144.91 | 2078.39 |
| Standard deviation values | 9.10 | 6.85 | 7.72 | 15.20 | 15.63 | 201.09 | 630.02 |
| Content in tailings | 1183.37 | 4328.82 | 346.03 | 30.64 | 69.25 | 200.93 | 5470.01 |
| Background in Niujiaotang | 66.60 | 29.39 | 33.18 | 12.33 | 0.23 | 23.02 | 112.75 |
| Background in Guizhou Province | 95.90 | 39.10 | 32.00 | 20.00 | 0.66 | 35.20 | 99.50 |
| Crop | Sampling Point | Cr | Ni | Cu | As | Cd | Pb | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pak choi | 1 | 2.974 | 2.614 | 4.068 | 13.609 | 9.277 | 0.663 | 323.529 |
| 3 | 2.052 | 1.911 | 4.864 | 13.002 | 5.184 | 1.714 | 779.324 | |
| 5 | 17.962 | 7.639 | 12.316 | 17.778 | 15.065 | 11.441 | 618.290 | |
| 6 | 62.525 | 16.899 | 13.106 | 11.958 | 11.262 | 0.599 | 305.666 | |
| Rice | 2 | 49.042 | 21.713 | 3.443 | 14.230 | 5.561 | 1.982 | 206.058 |
| Spring onion | 4 | 2.625 | 0.870 | 5.160 | 13.435 | 2.797 | 2.723 | 216.351 |
| Chinese cabbage | 8 | 2.997 | 2.663 | 4.691 | 15.736 | 5.672 | 1.700 | 317.910 |
| Chrysanthemum coronarium | 9 | 2.846 | 1.531 | 12.994 | 13.793 | 3.891 | 2.311 | 62.066 |
| Radish | 7 | 2.142 | 1.517 | 3.076 | 14.796 | 1.631 | 0.594 | 181.095 |
| 10 | 2.137 | 1.678 | 0.706 | 12.016 | 0.791 | 0.255 | 24.330 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Q.; Han, Z.; Tian, Y.; Xiao, H.; Yang, M. Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal in Farmlands and Crops Near Pb–Zn Mine Tailing Ponds in Niujiaotang, China. Toxics 2023, 11, 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11020106
Li Q, Han Z, Tian Y, Xiao H, Yang M. Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal in Farmlands and Crops Near Pb–Zn Mine Tailing Ponds in Niujiaotang, China. Toxics. 2023; 11(2):106. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11020106
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Qinyuan, Zhiwei Han, Yutong Tian, Han Xiao, and Miao Yang. 2023. "Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal in Farmlands and Crops Near Pb–Zn Mine Tailing Ponds in Niujiaotang, China" Toxics 11, no. 2: 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11020106
APA StyleLi, Q., Han, Z., Tian, Y., Xiao, H., & Yang, M. (2023). Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal in Farmlands and Crops Near Pb–Zn Mine Tailing Ponds in Niujiaotang, China. Toxics, 11(2), 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11020106





