Responses of Mytilus galloprovincialis in a Multi-Stressor Scenario: Effects of an Invasive Seaweed Exudate and Microplastic Pollution under Ocean Warming
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Acclimation of Mytilus galloprovincialis
2.2. Sampling of Asparagopsis armata and Exudate Production
2.3. Microplastics Solution Preparation
2.4. Experimental Setup
2.5. Extraction and Quantification of Microplastics
2.6. Biochemical Analysis
2.6.1. Sample Preparation
2.6.2. Neurophysiological and Oxidative Stress Biomarkers
2.6.3. Biomarkers of Energy Metabolism
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Quantification of PE-MPs in M. galloprovincialis
3.2. Biomarkers
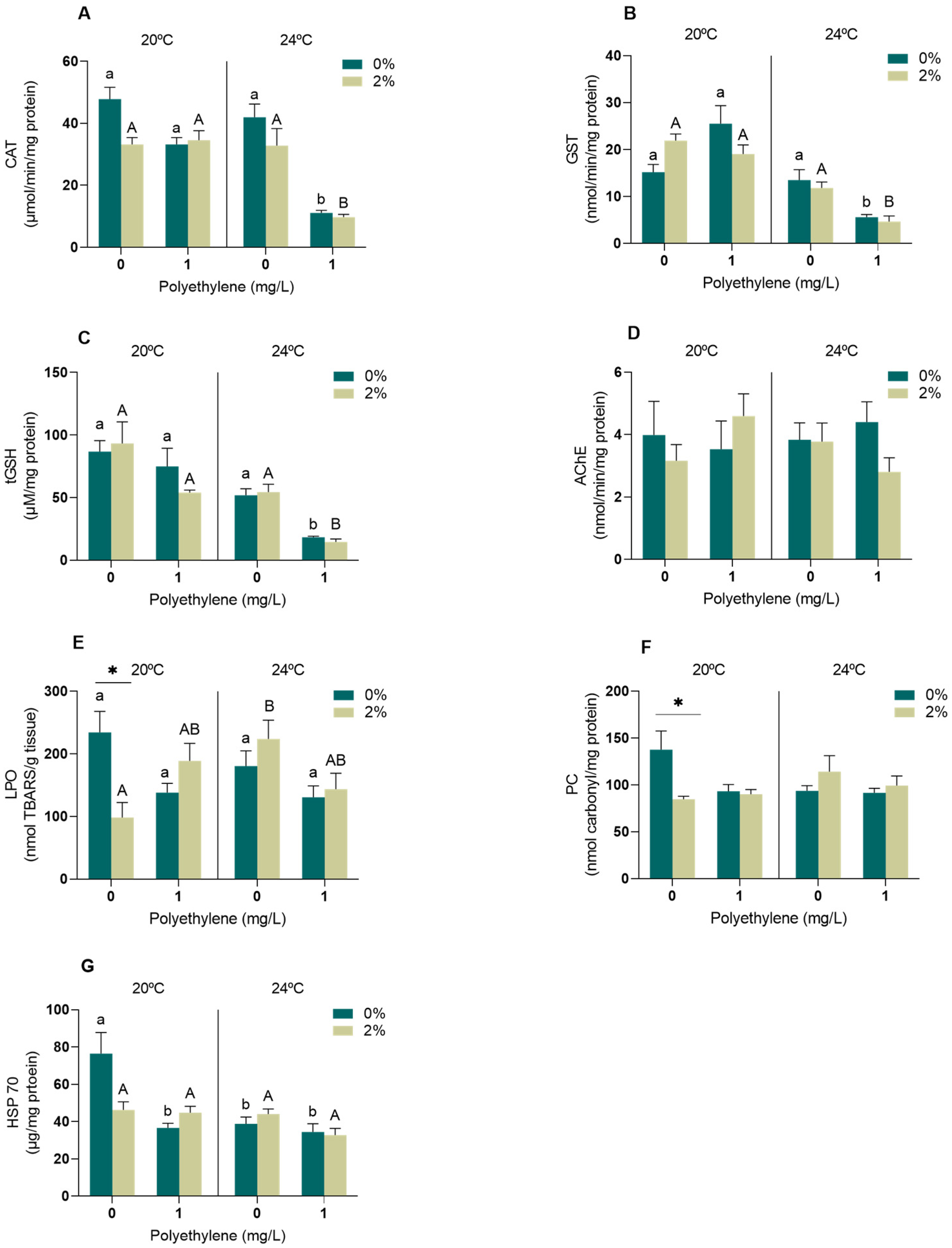
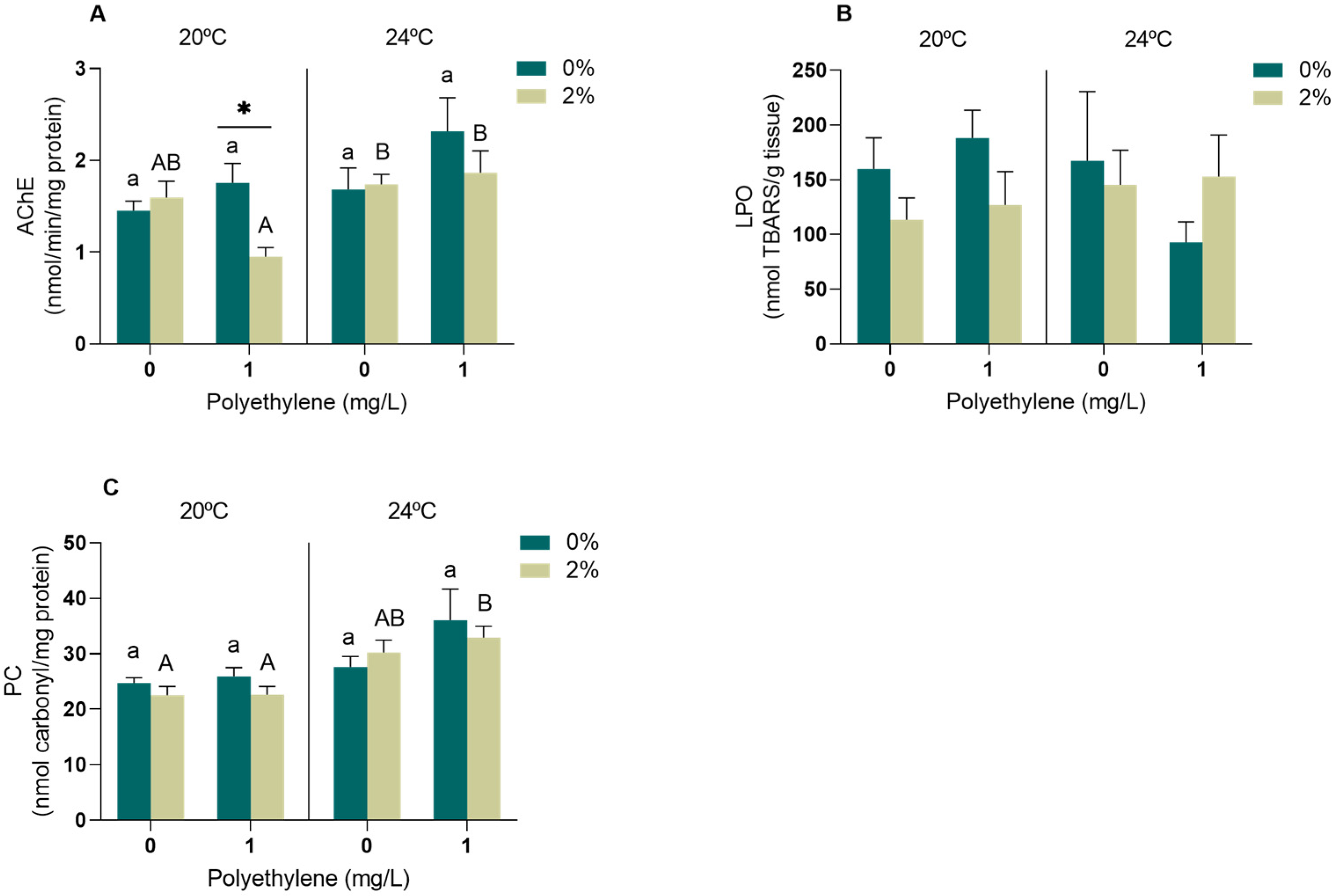
3.2.1. Neurophysiological and Oxidative Stress Biomarkers
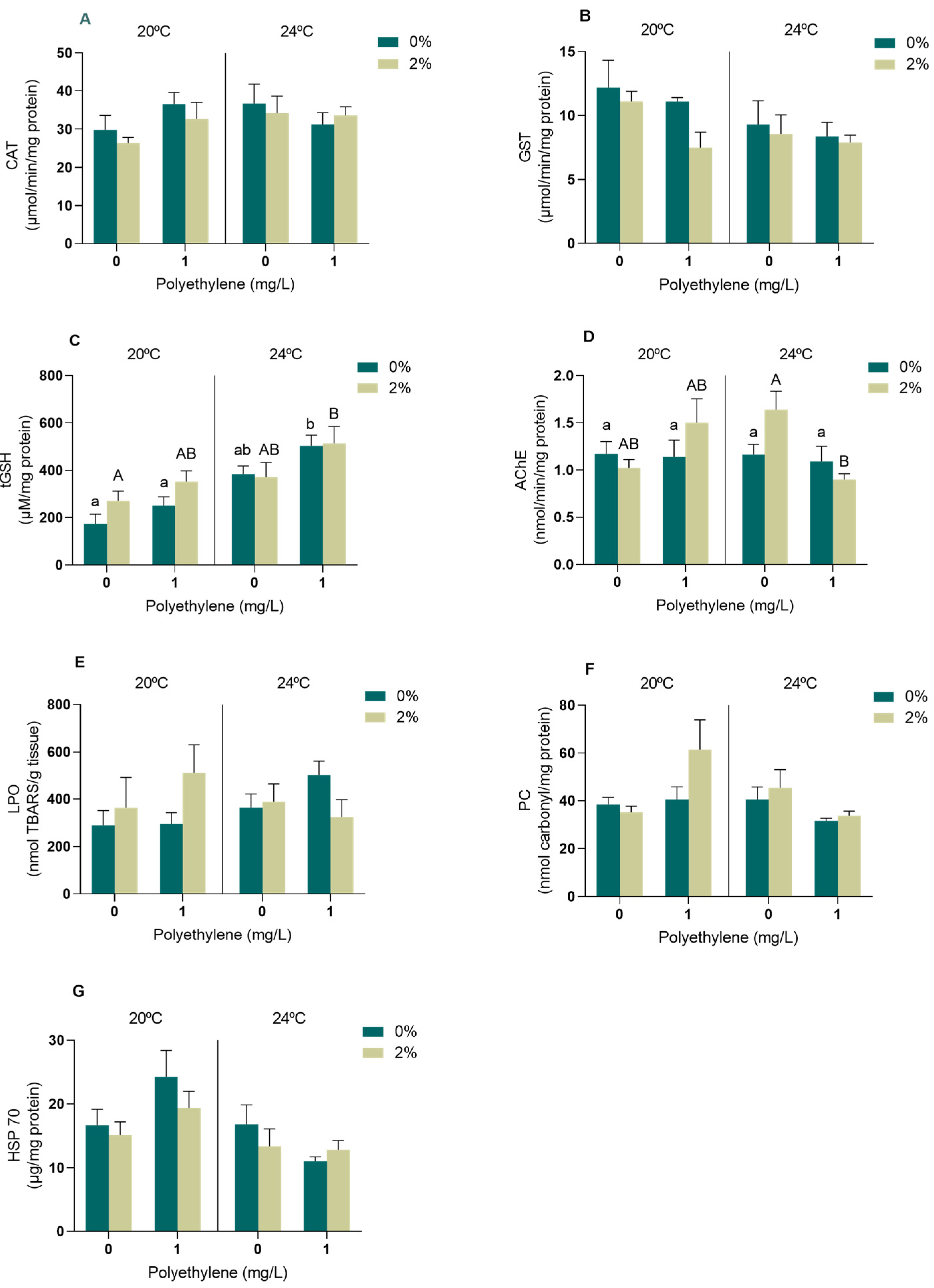
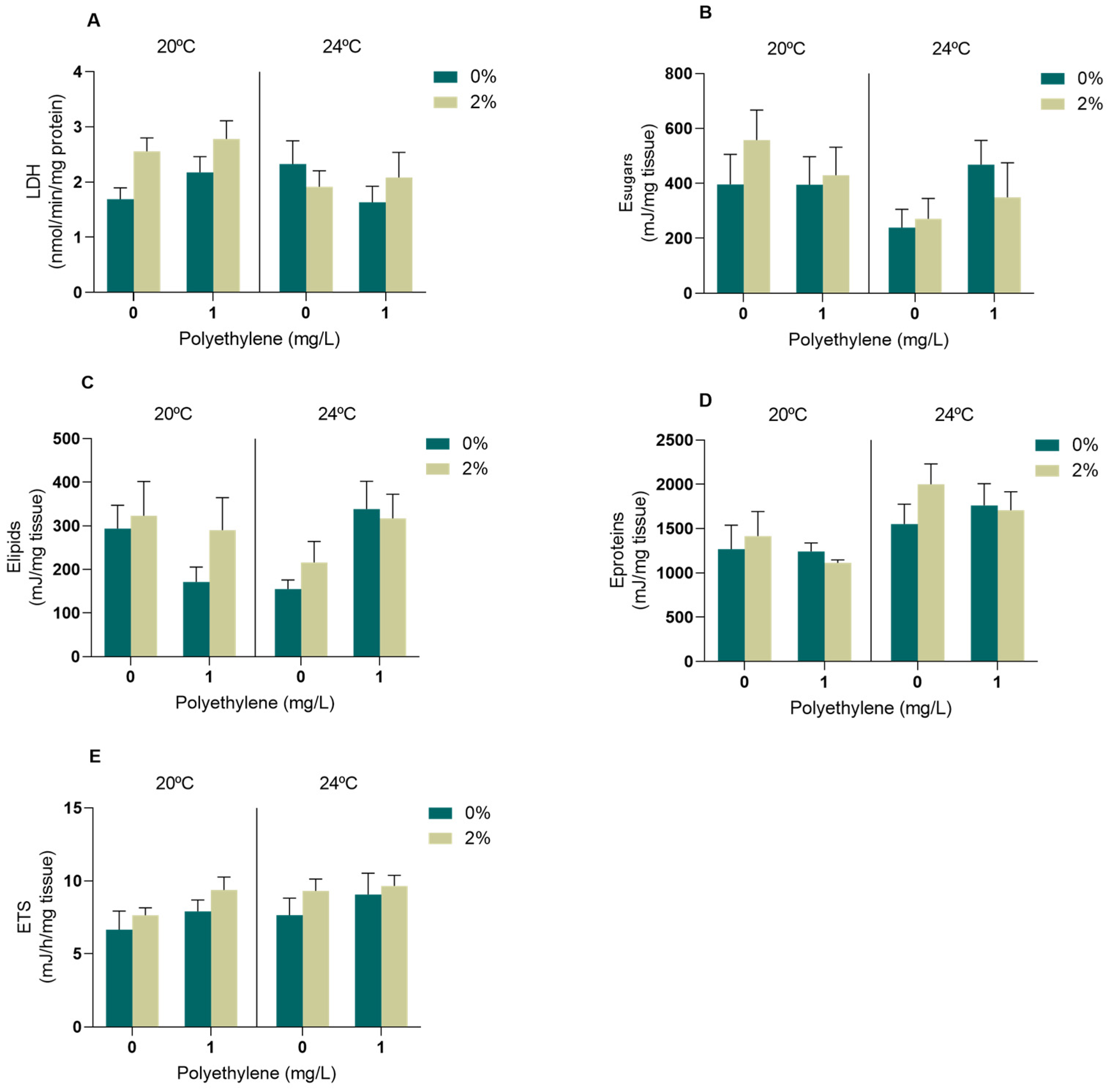
3.2.2. Biomarkers of Energy Metabolism
3.3. Byssal Thread Production in M. galloprovincialis
4. Discussion
4.1. PE-MPs in M. galloprovincialis Tissues and Biodeposits
4.2. Biomarkers
4.2.1. Neurophysiological and Oxidative Stress Biomarkers
4.2.2. Energy Metabolism Biomarkers
4.3. Byssal Thread Production
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, C.; Liu, G.; Yang, Q.; Luo, T.; He, P.; Paolo, P.; Virginia, G. Emergy-based evaluation of world coastal ecosystem services. Water Res. 2021, 204, 117656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, E.B. Marine ecosystem services. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 507–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuthbert, R.N.; Diagne, C.; Hudgins, E.J.; Turbelin, A.; Ahmed, D.A.; Albert, C.; Bodey, T.W.; Briski, E.; Essl, F.; Haubrock, P.J.; et al. Biological invasion costs reveal insufficient proactive management worldwide. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 819, 153404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, C.; Zhang, M.; Cao, X.; Chen, C.; Wang, C.; Xiu, C.; Du, D.; Cui, H.; et al. Multiple pollutants stress the coastal ecosystem with climate and anthropogenic drivers. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulme, P.E. Unwelcome Exchange: International trade as a direct and indirect driver of biological invasions worldwide. One Earth 2021, 4, 666–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentry, R.R.; Rassweiler, A.; Ruff, E.O.; Lester, S.E. Global pathways of innovation and spread of marine aquaculture species. One Earth 2023, 6, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinteus, S.; Lemos, M.F.L.; Alves, C.; Neugebauer, A.; Silva, J.; Thomas, O.P.; Botana, L.M.; Gaspar, H.; Pedrosa, R. Marine Invasive Macroalgae: Turning a real threat into a major opportunity-the biotechnological potential of Sargassum muticum and Asparagopsis armata. Algal Res. 2018, 34, 217–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, H.C.; Rodrigues, A.C.M.; Pires, S.F.S.; Oliveira, J.M.M.; Rocha, R.J.M.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Bordalo, M.D. Ocean warming may enhance biochemical alterations induced by an invasive seaweed exudate in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Toxics 2021, 9, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, A.D.; Campbell, M.L.; Hewitt, C.L.; Schaffelke, B. Assessing the impacts of nonindigenous marine macroalgae: An update of current knowledge. Bot. Mar. 2015, 58, 55–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decreto-Lei. No. 92/2019 de 10 de Julho; Diário da República: Lisbon, Portugal, 2019; pp. 3428–3441. [Google Scholar]
- Coelho, S.D.; Vieira, H.C.; Oliveira, J.M.M.; Pires, S.F.S.; Rocha, R.J.M.; Rodrigues, A.C.M.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Bordalo, M.D. How does Mytilus galloprovincialis respond when exposed to the gametophyte phase of the invasive red macroalgae Asparagopsis armata exudate? Water 2021, 13, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.O.; Lemos, M.F.L.; Gaspar, R.; Gonçalves, C.; Neto, J.M. The effects of the invasive seaweed Asparagopsis armata on native rock pool communities: Evidences from experimental exclusion. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, N.A.; De Nys, R.; Steinberg, P.D. Chemical defence against bacteria in the red alga Asparagopsis armata: Linking structure with function. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2006, 306, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, N.A.; De Nys, R.; Steinberg, P.D. Seaweed-herbivore interactions at a small scale: Direct tests of feeding deterrence by filamentous algae. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2006, 323, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yuan, J.; Lu, X.; Su, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Cao, X.; Li, Q.; Su, J.; Ittekkot, V.; et al. Major threats of pollution and climate change to global coastal ecosystems and enhanced management for sustainability. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 239, 670–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazeau, F.; Alliouane, S.; Bock, C.; Bramanti, L.; Lópex Correa, M.; Gentile, M.; Hirse, T.; Pörtner, H.-O.; Patrizia, Z. Impact of ocean acidification and warming on the mediterranean mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis). Front. Mar. Sci. 2014, 1, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, M.A.; Scott, J.D.; Friedland, K.D.; Mills, K.E.; Nye, J.A.; Pershing, A.J.; Thomas, A.C. Projected sea surface temperatures over the 21 St century: Changes in the mean, variability and extremes for large marine ecosystem regions of Northern Oceans. Sci. Anthr. 2018, 6, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Pirone, G.; Coppola, F.; Pretti, C.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Freitas, R.; Solé, M. The effect of temperature on triclosan and lead exposed mussels. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 232, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourebrahimi, S.; Pirooz, M. Microplastic pollution in the marine environment: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2023, 10, 100327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provenza, F.; Rampih, D.; Pignattelli, S.; Pastorino, P.; Barceló, D.; Prearo, M.; Specchiulli, A.; Renzi, M. Mussel watch program for microplastics in the Mediterranean Sea: Identification of biomarkers of exposure using Mytilus galloprovincialis. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 142, 109212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Détrée, C.; Gallardo-Escárate, C. Single and repetitive microplastics exposures induce immune system modulation and homeostasis alteration in the edible mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 83, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Pu, S.; Liu, S.; Bai, Y.; Mandal, S.; Xing, B. Microplastics in aquatic environments: Toxicity to trigger ecological consequences. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 261, 114089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, F.G.; Vieira, H.; Campos, D.; Pires, S.F.; Rodrigues, A.C.M.; Silva, A.L.P.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Oliveira, J.M.M.; Bordalo, M.D. Co-exposure with an invasive seaweed exudate increases toxicity of polyamide microplastics in the marine mussel. Toxics 2022, 10, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curpan, A.; Impellitteri, F.; Plavan, G.; Ciobica, A.; Faggio, C. Review: Mytilus galloprovincialis: An essential, low-Cost model organism for the impact of xenobiotics on oxidative stress and public health. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C 2022, 256, 109302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shumway, S.E.; Davis, C.; Downey, R.; Karney, R.; Kraeuter, J.; Parsons, J.; Rheault, R.; Wikfors, G. Shellfish aquaculture—In praise of sustainable economies and environments. World Aquac. 2003, 34, 15–17. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, C.L.; Burnett, N.P.; Ramsey, M.J.; Wagner, K.; Zippay, M.L. Physiological responses to heat stress in an invasive mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis depend on tidal habitat: Habitat-specific stress responses in mussels. Mar. Environ. Res. 2020, 154, 104849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, F.; Almeida, Â.; Henriques, B.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Figueira, E.; Pereira, E.; Freitas, R. Biochemical responses and accumulation patterns of Mytilus galloprovincialis exposed to thermal stress and arsenic contamination. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 147, 954–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, F.; Almeida, Â.; Henriques, B.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Figueira, E.; Pereira, E.; Freitas, R. Biochemical impacts of Hg in Mytilus galloprovincialis under present and predicted warming scenarios. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 1129–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardi, A.; Mincarelli, L.F.; Benedetti, M.; Fattorini, D.; d’Errico, G.; Regoli, F. Indirect effects of climate changes on cadmium bioavailability and biological effects in the Mediterranean mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Chemosphere 2017, 169, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Seong, H.J.; Jang, Y. Environmental toxicity and decomposition of polyethylene. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 242, 113933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-hernández, J.R.; Fernández, B.; Santos-echeandia, J.; Garrido, S.; Morante, M.; Santos, P.; Albentosa, M. Biodynamics of mercury in mussel tissues as a function of exposure pathway: Natural vs microplastic routes. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 674, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindoff, N.L.; Cheung, W.W.L.; Kairo, J.G.; Aristegui, J.; Guinder, V.A.; Hallberg, R.; Hilmi, N.; Jiao, N.; Karim, M.S.; Levin, L.; et al. Changing ocean, marine ecosystems, and dependent communities. IPCC Spec. Rep. Ocean Cryosph. Chang. Clim. 2019, 447–588. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, D.; Rodrigues, A.C.M.; Rocha, R.J.M.; Martins, R.; Candeias-mendes, A.; Castanho, S.; Soares, F.; Ferreira-Pousão, P.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Gravato, C.; et al. Are microplastics impairing marine fish larviculture?—Preliminary results with Argyrosomus regius. Water 2021, 13, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, S.H.; Williams, P.R.; Hall, B.D. Microplastics in the gastrointestinal tracts of fish and the water from an urban prairie creek. Facets 2017, 2, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.E.; Zhao, S.; Holohan, B.A.; Mladinich, K.M.; Griffin, T.W.; Wozniak, J.; Shumway, S.E. Selective ingestion and egestion of plastic particles by the blue mussel (Mytilus edulis) and eastern oyster (Crassostrea virginica): Implications for using bivalves as bioindicators of microplastic pollution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 8776–8784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.D.; Andres, V.; Featherstone, R.M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilhermino, L.; Lopes, M.C.; Carvalho, A.P.; Soared, A.M.V.M. Inhibition of acetylcholinesterase activity as effect criterion in acute tests with juvenile Daphnia magna. Chemosphere 1996, 32, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, I.; Gravato, C. Oxidative stress assessment in zebrafish larvae. In Teratogenicity Testing. Methods in Molecular Biology; Félix, L., Ed.; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 1797, pp. 477–486. ISBN 9781493978830. [Google Scholar]
- Clairborne, A. Catalase Activity. In CRC Handbook of Methods in Oxygen Radical Research; Greenwald, R.A., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1985; pp. 283–284. [Google Scholar]
- Habig, W.H.; Pabst, M.J.; Jakoby, W.B. Glutathione S-Transferases. The first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J. Biol. Chem. 1974, 249, 7130–7139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.A.; Cerniglia, G.J.; Zaman, A. Microtiter plate assay for the measurement of glutathione and glutathione disulfide in large numbers of biological samples. Anal. Biochem. 1990, 190, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tietze, F. Enzymic method for quantitative determination of nanogram amounts of total and oxidized glutathione: Applications to mammalian blood and other tissues. Anal. Biochem. 1969, 27, 502–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bird, R.P.; Draper, H.H. Comparative studies on different methods of malonaldehyde determination. Methods Enzymol. 1984, 105, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesquita, C.S.; Oliveira, R.; Bento, F.; Geraldo, D.; Rodrigues, J.V.; Marcos, J.C. Simplified 2, 4-dinitrophenylhydrazine spectrophotometric assay for quantification of carbonyls in oxidized proteins. Anal. Biochem. 2014, 458, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, H.C.; Bordalo, M.D.; Rodrigues, A.C.M.; Pires, S.F.S.; Rocha, R.J.M.; Abreu, S.N.; Morgado, F. Water temperature modulates mercury accumulation and oxidative stress status of common goby (Pomatoschistus microps). Environ. Res. 2021, 193, 110585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnaiger, E. Calculation of Energetic and Biochemical Equivalents of Respiratory Oxygen Consumption; Gnaiger, E., Forstner, H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1983; ISBN 978-3-642-81863-9. [Google Scholar]
- Vassault, A. Lactate dehydrogenase, UV-method with pyruvate and NADH. Methods Enzym. Anal. 1983, 3, 118. [Google Scholar]
- Rist, S.E.; Assidqi, K.; Zamani, N.P.; Appel, D.; Perschke, M.; Huhn, M.; Lenz, M. Suspended micro-sized PVC particles impair the performance and decrease survival in the Asian green mussel Perna viridis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 111, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avio, C.G.; Gorbi, S.; Milan, M.; Benedetti, M.; Fattorini, D.; DÉrrico, G.; Pauletto, M.; Bargelloni, L.; Regoli, F. Pollutants bioavailability and toxicological risk from microplastics to marine mussels. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 198, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, B.; Santos-Echeandía, J.; Rivera-Hernández, J.R.; Garrido, S.; Albentosa, M. Mercury interactions with algal and plastic microparticles: Comparative role as vectors of metals for the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 396, 122739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anestis, A.; Lazou, A.; Po, H.O.; Michaelidis, B. Behavioral, metabolic, and molecular stress responses of marine bivalve Mytilus galloprovincialis during long-term acclimation at increasing ambient temperature. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2007, 293, 911–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosling, E. Marine Bivalve Molluscs, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Morosetti, B.; Freitas, R.; Pereira, E.; Hamza, H.; Andrade, M.; Coppola, F.; Maggioni, D.; Torre, C. Della Will temperature rise change the biochemical alterations induced in Mytilus galloprovincialis by cerium oxide nanoparticles and mercury? Environ. Res. 2020, 188, 109778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lushchak, V.I. Glutathione homeostasis and functions: Potential targets for medical interventions. J. Amino Acids 2012, 2012, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, M.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Solé, M.; Pereira, E.; Freitas, R. Do climate change related factors modify the response of Mytilus galloprovincialis to lanthanum? The case of temperature rise. Chemosphere 2022, 307 Part 2, 135577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regoli, F.; Giuliani, M.E. Oxidative pathways of chemical toxicity and oxidative stress biomarkers in marine organisms. Mar. Environ. Res. 2014, 93, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feki, A.; Cherif, B.; Sellem, I.; Naifar, M.; Amar, I.B.; Azaza, Y.B.; Kallel, R.; Hariz, L.; Zeghal, S.; Ayadi, F.M.; et al. Biomedical applications of polysaccharide derived from tetrasporophyte tufts of Asparagopsis armata (Falkenbergia rufolanosa): Focus on antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-coagulant and hepato-protective activities. Algal Res. 2023, 69, 102958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, D.C.G.A.; Lesenfants, M.L.; Rosa, G.P.; Barreto, M.C.; Silva, A.M.S.; Seca, A.M.L. GC- and UHPLC-MS profiles as a tool to valorize the red alga Asparagopsis armata. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, J.; Raisuddin, S.; Lee, K.; Seo, J.S.; Ki, J.; Kim, I.; Park, H.G.; Lee, J. Heatshock protein (Hsp) gene responses of the intertidal copepod Tigriopus japonicus to environmental toxicants. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C 2009, 149, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Yang, J.; Qi, Z.; Wu, H.; Wang, B.; Zou, F.; Mei, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, W.; Liu, Q. Heat shock proteins: Biological functions, pathological roles, and therapeutic opportunities. Medcomm 2022, 3, e61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamer, B.; Hamer, D.P.; Müller, W.E.G.; Batel, R. Stress-70 proteins in marine mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis as biomarkers of environmental pollution: A field study. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidli, S.; Pinheiro, M.; Lahbib, Y.; Neuparth, T.; Santos, M.M.; Menif, N.T. EL Effects of environmentally relevant levels of polyethylene microplastic on Mytilus galloprovincialis (Mollusca: Bivalvia): Filtration rate and oxidative stress. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 26643–26652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attig, H.; Kamel, N.; Sforzini, S.; Dagnino, A.; Jamel, J.; Boussetta, H.; Viarengo, A.; Banni, M. Effects of thermal stress and nickel exposure on biomarkers responses in Mytilus galloprovincialis (Lam). Mar. Environ. Res. 2014, 94, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, J.; Monteiro, M.S.; Quintaneiro, C.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Loureiro, S. Characterization of cholinesterases in Chironomus riparius and the effects of three herbicides on chlorpyrifos toxicity. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 144–145, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tlili, S.; Jemai, D.; Brinis, S.; Regaya, I. Microplastics mixture exposure at environmentally relevant conditions induce oxidative stress and neurotoxicity in the wedge clam Donax trunculus. Chemosphere 2020, 258, 127344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.; Ribeiro, A.; Hylland, K.; Guilhermino, L. Single and combined effects of microplastics and pyrene on juveniles (0+ Group) of the common goby Pomatoschistus microps (Teleostei, Gobiidae). Ecol. Indic. 2013, 34, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, S.K.; Hur, Y.B. Temperature-mediated changes in stress responses, acetylcholinesterase, and immune responses of juvenile olive flounder Paralichthys olivaceus in a bio-floc environment. Aquaculture 2019, 506, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botté, E.S.; Smith-keune, C.; Jerry, D.R. Temperature: A prolonged confounding factor on cholinesterase activity in the tropical reef fish Acanthochromis polyacanthus. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 140–141, 337–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapple, J.P.; Smerdon, G.R.; Hawkins, A.J. Stress-70 protein induction in Mytilus edulis: Tissue-specific responses to elevated temperature reflect relative vulnerability and physiological function. J. Exp. Biol. Ecol. 1997, 217, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, C.; Dowling, V.; Tedengren, M.; Gardestro, J.; Hartl, M.G.J.; O’Brien, N.; van Pelt, F.N.A.M.; O’Halloran, J.; Sheehan, D. Variability of heat shock proteins and glutathione S-transferase in gill and digestive gland of blue mussel, Mytilus edulis. Mar. Environ. Res. 2003, 56, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Claros, J.D.; Checa, A.; Lucena, C.; Pearson, J.R.; Salas, C. Shell-adductor muscle attachment and Ca2+ transport in the bivalves Ostrea stentina and Anomia ephippium. Acta Biomater. 2021, 120, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobal, V.; Suárez, P.; Ruiz, Y.; García-martín, O.; Juan, F.S. Activity of antioxidant enzymes in Mytilus galloprovincialis ex-posed to tar: Integrated response of different organs as pollution biomarker in aquaculture areas. Aquaculture 2022, 548 Part 1, 737638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, P.; Gomes, A.Q.; Pacheco, T.R.; de Almeida, V.V.; Saldanha, C.; Calado, A. Cell-specific regulation of acetylcholinesterase expression under inflammatory conditions. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2012, 51, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.J.; Yang, L.; Zhao, Q.; Caen, J.P.; He, H.Y.; Jin, Q.H.; Guo, L.H.; Alemany, M.; Zhang, L.Y.; Shi, Y.F. Induction of acetylcholinesterase expression during apoptosis in various cell types. Cell Death Differ. 2002, 9, 790–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnell, O.; Fenical, W. Halogen chemistry of the red alga Asparagopsis. Phytochemistry 1977, 16, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolova, I.M.; Frederich, M.; Bagwe, R.; Lannig, G.; Sukhotin, A.A. Energy homeostasis as an integrative tool for assessing limits of environmental stress tolerance in aquatic invertebrates. Mar. Environ. Res. 2012, 79, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laudicella, V.A.; Beveridge, C.; Carboni, S.; Franco, S.C.; Doherty, M.K.; Long, N.; Mitchell, E.; Stanley, M.S.; Whitfield, P.; Hughes, A.D. Lipidomics analysis of juveniles blue mussels (Mytilus edulis L. 1758), a key economic and ecological species. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0223031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolders, R.; De Boeck, G.; Blust, R. Changes in Celular Energy budget as a measures of whole effluent toxicity in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2003, 22, 890–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paciello, S.; Russo, T.; De Marchi, L.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Meucci, V.; Pretti, C.; He, Y.; Della, C.; Freitas, R. Sub-lethal effects induced in Mytilus galloprovincialis after short-term exposure to sodium lauryl sulfate: Comparison of the biological responses given by mussels under two temperature scenarios. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C 2023, 270, 109644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamantino, T.C.; Almeida, E.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Guilhermino, L. Lactate dehydrogenase activity as an effect criterion in toxicity tests with Daphnia magna straus. Chemosphere 2001, 45, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queirós, V.; Azeiteiro, U.M.; Barata, C.; Santos, J.L.; Alonso, E.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Freitas, R. Effects of the antineoplastic drug cyclophosphamide on the biochemical responses of the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis under different temperatures ☆. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 288, 117735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, C.; Coppola, F.; Queirós, V.; Russo, T.; Polese, G.; Pretti, C.; Pereira, E.; Freitas, R. Can temperature influence the impacts induced in Mytilus galloprovincialis by neodymium? Comparison between exposure and recovery periods. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 97, 104029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrington, E.; Moeser, G.M.; Dimond, J.; Mello, J.J.; Boller, M.L. Seasonal disturbance to mussel beds: Field test of a mechanistic model predicting wave dislodgment. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 978–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, H.; Liu, C.; Sokolova, I.M.; Chen, Y.; Deng, F.; Xie, Z.; Li, L.; Liu, W.; Frang, J.K.-H.; et al. Dietary exposure to NTiO2 reduces byssus performance of mussels under ocean warming. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 881, 163499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, E.C.; Gosline, J.M. Mechanical design of mussel byssus: Material yield enhances attachment strength. J. Exp. Biol. 1996, 199, 1005–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Sun, C.; Wang, Y.; Cai, H.; Li, L.; Li, J.; Shi, H. Fusion of microplastics into the mussel byssus. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252 A, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, E.A.; Newcomb, L.A.; Mccartha, M.M.; Harrington, K.J.; Laframboise, S.A.; Carrington, E.; Sebens, K.P. Resource allocation to a structural biomaterial: Induced production of byssal threads decreases growth of a marine mussel. Funct. Ecol. 2021, 35, 1222–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garner, Y.L.; Litvaitis, M.K. Effects of wave exposure, temperature and epibiont fouling on byssal thread production and growth in the blue mussel, Mytilus edulis, in the Gulf of Maine. J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol. 2013, 446, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newcomb, L.A.; George, M.N.; Donnell, M.J.O.; Carrington, E. Only as strong as the weakest link: Structural analysis of the combined effects of elevated temperature and pCO2 on mussel attachment. Conserv. Physiol. 2019, 7, coz068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, W.; Liang, X.; Yang, J.-L. Near-future levels of ocean temperature weaken the byssus production and performance of the mussel Mytilus coruscus. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 139347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Gu, H.; Li, S.; Chang, X.; Sokolova, I.; Fang, J.K.H.; Wei, S.; Chen, X.; Hu, M.; Huang, W.; et al. Microplastics and food shortage impair the byssal attachment of thick-shelled mussel Mytilus coruscus. Mar. Environ. Res. 2021, 171, 105455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, D.S.; Colgan, T.J.; Thompson, R.C.; Carolan, J.C. Exposure to microplastics reduces attachment strength and alters the haemolymph proteome of blue mussels (Mytilus Edulis). Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, S.; Gaw, S.; Marsden, I.D.; McRae, N.K. Biomarker responses in new zealand green-lipped mussels Perna canaliculus exposed to microplastics and triclosan. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 201, 110871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Treatments | Number of Particles per Tissue Gram (Wet Weight) | Number of Particles | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digestive Gland | Gills | Biodeposits | |
| PE-MPs (20 °C) | 137.5 ± 34.9 | 30.0 ± 18.3 | 2605 ± 252.1 |
| PE-MPs + Exudate (20 °C) | 272.4 ± 115.7 | 3.8 ± 0.50 | 2948 ± 692.7 |
| PE-MPs (24 °C) | 50.6 ± 25.5 | 25.3 ± 11.6 | 1826 ± 285.9 |
| PE-MPs + Exudate (24 °C) | 117.7 ± 25.8 | 21.5 ± 6.4 | 1758 ± 304.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lopes, C.; Rodrigues, A.C.M.; Pires, S.F.S.; Campos, D.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Vieira, H.C.; Bordalo, M.D. Responses of Mytilus galloprovincialis in a Multi-Stressor Scenario: Effects of an Invasive Seaweed Exudate and Microplastic Pollution under Ocean Warming. Toxics 2023, 11, 939. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110939
Lopes C, Rodrigues ACM, Pires SFS, Campos D, Soares AMVM, Vieira HC, Bordalo MD. Responses of Mytilus galloprovincialis in a Multi-Stressor Scenario: Effects of an Invasive Seaweed Exudate and Microplastic Pollution under Ocean Warming. Toxics. 2023; 11(11):939. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110939
Chicago/Turabian StyleLopes, Cristiana, Andreia C. M. Rodrigues, Sílvia F. S. Pires, Diana Campos, Amadeu M. V. M. Soares, Hugo C. Vieira, and Maria D. Bordalo. 2023. "Responses of Mytilus galloprovincialis in a Multi-Stressor Scenario: Effects of an Invasive Seaweed Exudate and Microplastic Pollution under Ocean Warming" Toxics 11, no. 11: 939. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110939
APA StyleLopes, C., Rodrigues, A. C. M., Pires, S. F. S., Campos, D., Soares, A. M. V. M., Vieira, H. C., & Bordalo, M. D. (2023). Responses of Mytilus galloprovincialis in a Multi-Stressor Scenario: Effects of an Invasive Seaweed Exudate and Microplastic Pollution under Ocean Warming. Toxics, 11(11), 939. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110939











