Exposure Profile and Characteristics of Parabens and Alkylphenols in Plasma among Rural Adults in Central China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Chemicals Analysis
2.3. Quality Control and Quality Assurance
2.4. Estimated Daily Intake and Health Risk Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Characteristics
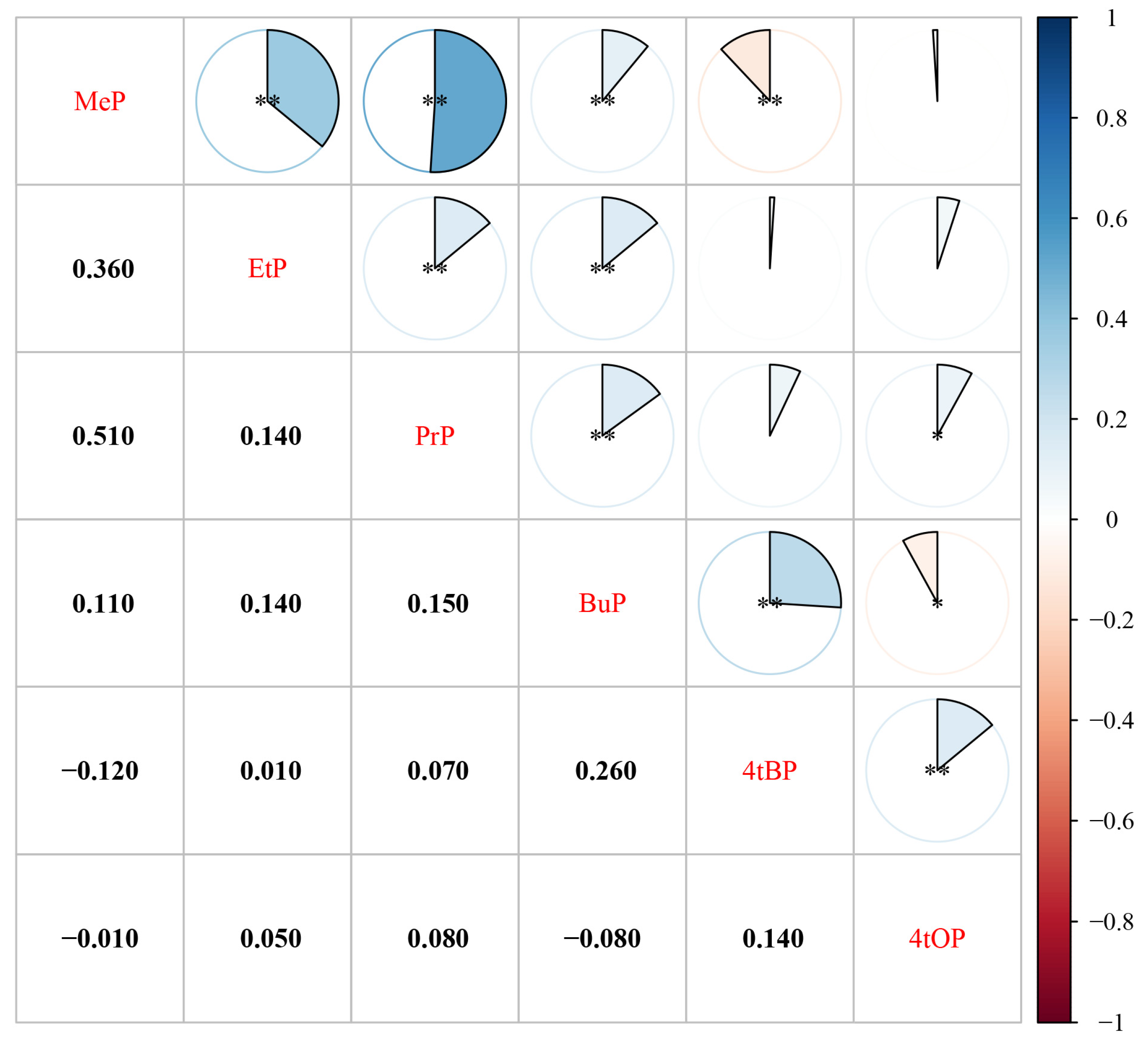
3.2. Plasma Concentrations, and Correlations of Parabens and Alkylphenols
3.3. Correlation between Demographic Characteristics and Pollutant Concentration
3.3.1. Total Population
3.3.2. Stratification by Gender
3.4. Health Risk Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, Y.; Li, W.; Lu, S.; Wu, S.; Wang, F.; Tse, L.A.; Kang, L.; Ma, S. Urinary parabens in adults from South China: Implications for human exposure and health risks. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 182, 109419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.R.; Park, S.J.; Jeong, M.J.; Choi, J.C.; Kim, M. Fast and simple determination and exposure assessment of bisphenol A, phenol, p-tert-butylphenol, and diphenylcarbonate transferred from polycarbonate food-contact materials to food simulants. Chemosphere 2018, 203, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janicki, T.; Długoński, A.; Felczak, A.; Długoński, J.; Krupiński, M. Ecotoxicological Estimation of 4-Cumylphenol, 4-t-Octylphenol, Nonylphenol, and Volatile Leachate Phenol Degradation by the Microscopic Fungus Umbelopsis isabellina Using a Battery of Biotests. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Tobino, T.; Nakajima, F. Determining the Relative Importance of Dietborne and Waterborne Toxicity of 4-tert-Butylphenol and 4-tert-Octylphenol to the Benthic Crustacean, Heterocypris incongruens. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 7939–7948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klancic, V.; Gobec, M.; Jakopin, Z. Environmental contamination status with common ingredients of household and personal care products exhibiting endocrine-disrupting potential. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 73648–73674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiraagni, I.A.; Mohd, M.A.; Rashid, R.A.; Haron, D.E.b.M. Trace Level Detection of Bisphenol A Analogues and Parabens by LC-MS/MS in Human Plasma from Malaysians. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 2581287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y.; Hwang, Y.T.; Chen, P.C.; Sung, F.C.; Su, T.C. Association of serum levels of 4-tertiary-octylphenol with cardiovascular risk factors and carotid intima-media thickness in adolescents and young adults. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Liang, J.; Zheng, L.; Lv, Q.; Wang, H. Application of dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for the preconcentration of eight parabens in real samples and their determination by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 4385–4393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lester, C.; Hewitt, N.J.; Müller-Vieira, U.; Mayer, M.; Ellison, C.; Duplan, H.; Genies, C.; Jacques-Jamin, C.; Fabian, E.; Sorrell, I.; et al. Metabolism and plasma protein binding of 16 straight- and branched-chain parabens in in vitro liver and skin models. Toxicol. In Vitro Int. J. Publ. Assoc. BIBRA 2021, 72, 105051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Asimakopoulos, A.G.; Kannan, K. Accumulation of 19 environmental phenolic and xenobiotic heterocyclic aromatic compounds in human adipose tissue. Environ. Int. 2015, 78, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moos, R.K.; Apel, P.; Schröter-Kermani, C.; Kolossa-Gehring, M.; Brüning, T.; Koch, H.M. Daily intake and hazard index of parabens based upon 24 h urine samples of the German Environmental Specimen Bank from 1995 to 2012. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2016, 27, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Li, W.; Yang, C.; Chen, X.; Liu, X.; He, J.; Tong, C.; Peng, C.; Ding, Y.; Geng, Y.; et al. Exposure to ethylparaben and propylparaben interfere with embryo implantation by compromising endometrial decidualization in early pregnant mice. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2021, 41, 1732–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zhou, S.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Yan, W.; Guo, Q.; Xi, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, M.; et al. Prenatal exposure to propylparaben at human-relevant doses accelerates ovarian aging in adult mice. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 285, 117254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, F.; Susiarjo, M.; Bartolomei, M.S. Multigenerational and transgenerational effects of endocrine disrupting chemicals: A role for altered epigenetic regulation? Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 43, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrz, J.; Hosikova, B.; Svobodova, L.; Ocadlikova, D.; Kolarova, H.; Dvorakova, M.; Kejlova, K.; Malina, L.; Jirova, G.; Vlkova, A.; et al. Comparison of methods used for evaluation of mutagenicity/genotoxicity of model chemicals—Parabens. Physiol. Res. 2020, 69 (Suppl. S4), S661–S679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, K.; Ratajczak-Wrona, W.; Gorska, M.; Jablonska, E. Parabens and their effects on the endocrine system. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2018, 474, 238–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolatorova, L.; Vitku, J.; Hampl, R.; Adamcova, K.; Skodova, T.; Simkova, M.; Parizek, A.; Starka, L.; Duskova, M. Exposure to bisphenols and parabens during pregnancy and relations to steroid changes. Environ. Res. 2018, 163, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wu, C.; Lu, D.; Jiang, S.; Liang, W.; Chang, X.; Xu, H.; Wang, G.; Zhou, Z. Urinary paraben concentrations and their associations with anthropometric measures of children aged 3 years. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 222, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.H.; Franke, A.A.; Wilkens, L.R.; Tseng, C.; Conroy, S.M.; Li, Y.; Sangaramoorthy, M.; Polfus, L.M.; DeRouen, M.C.; Caberto, C.; et al. Risk of breast cancer and prediagnostic urinary excretion of bisphenol A, triclosan and parabens: The Multiethnic Cohort Study. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 149, 1426–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coiffier, O.; Nakiwala, D.; Rolland, M.; Malatesta, A.; Lyon-Caen, S.; Chovelon, B.; Faure, P.; Sophie Gauchez, A.; Guergour, D.; Sakhi, A.K.; et al. Exposure to a mixture of non-persistent environmental chemicals and neonatal thyroid function in a cohort with improved exposure assessment. Environ. Int. 2023, 173, 107840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Kim, K. Urinary Levels of 4-Nonylphenol and 4-t-Octylphenol in a Representative Sample of the Korean Adult Population. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Qin, T.; Chen, G.; Wang, G.; Hu, T. The toxicity of 4-tert-butylphenol in early development of zebrafish: Morphological abnormality, cardiotoxicity, and hypopigmentation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 45781–45795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Zhou, Q.; Yu, M.; Liu, Y.; Teng, X.; Gu, X. 4-tert-butylphenol triggers common carp hepatocytes ferroptosis via oxidative stress, iron overload, SLC7A11/GSH/GPX4 axis, and ATF4/HSPA5/GPX4 axis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 242, 113944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graca, B.; Rychter, A.; Staniszewska, M.; Smolarz, K.; Sokolowski, A.; Bodziach, K. Bioaccumulation of phenolic endocrine disruptors in the clam Rangia cuneata: Storage in shells and influence of size and sex. Environ. Res. 2021, 197, 111181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Chen, M.; Wu, W.; Xu, B.; Tang, R.; Chen, X.; Du, G.; Lu, C.; Meeker, J.D.; Zhou, Z.; et al. Interactions between urinary 4-tert-octylphenol levels and metabolism enzyme gene variants on idiopathic male infertility. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrijman, C.; Willemsen, K.J.; Tjin, E.P.M.; Kammeyer, A.; van den Boorn, J.G.; van der Veen, J.P.W.; Jungbauer, F.H.W.; Kardaun, S.H.; Luiten, R.M. T-cell responses against 4-tert-butylphenol-exposed pigmented cells in a patient with occupational vitiligo. Br. J. Dermatol. 2019, 181, 387–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Mortimer, M.; Cheng, H.; Sang, N.; Guo, L.H. Parabens as chemicals of emerging concern in the environment and humans: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, M.; Robinson, M.; Kannan, K. Parabens in human urine from several Asian countries, Greece, and the United States. Chemosphere 2018, 201, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, L.; Liu, W.; Liu, Y.; Yang, M.; Wang, B.; Zhu, H.; Zhu, L.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, H. Occurrence and profile characteristics of environmental phenols in human urine from a rural area in Northwestern China. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 315, 120405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wu, W.; Mao, Z.; Huo, W.; Tu, R.; Qian, X.; Zhang, X.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, J.; et al. Prevalence and influencing factors of overweight and obesity in a Chinese rural population: The Henan Rural Cohort Study. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Xia, W.; Yang, S.; Pan, X.; He, Z.; Kannan, K. Spatial distribution of bisphenol S in surface water and human serum from Yangtze River watershed, China: Implications for exposure through drinking water. Chemosphere 2018, 199, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L. Volume of Blood in a Human. The Physics Factbook. 1998. Available online: https://hypertextbook.com/facts/1998/LanNaLee.shtml (accessed on 11 April 2023).
- Moos, R.K.; Koch, H.M.; Angerer, J.; Apel, P.; Schroter-Kermani, C.; Bruning, T.; Kolossa-Gehring, M. Parabens in 24 h urine samples of the German Environmental Specimen Bank from 1995 to 2012. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2015, 218, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukuroglu, A.A.; Battal, D.; Kocadal, K.; Sungur, M.A.; Cok, I.; Unlusayin, I. Biomonitoring of bisphenol A, 4-nonylphenol, and 4-t-octylphenol in Turkish population: Exposure and risk assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 26250–26262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, J.; Wang, Y.; Tang, W.; Aimuzi, R.; Luo, K.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J. Patterns of environmental exposure to phenols in couples who plan to become pregnant. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 821, 153520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Q.; Huang, H.; Zhang, X.; Ma, X.; Peng, J.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, C.; Lv, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zheng, J.; et al. Assessment of health risk and dose-effect of DNA oxidative damage for the thirty chemicals mixture of parabens, triclosan, benzophenones, and phthalate esters. Chemosphere 2022, 308 Pt 2, 136394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tefre de Renzy-Martin, K.; Frederiksen, H.; Christensen, J.S.; Boye Kyhl, H.; Andersson, A.M.; Husby, S.; Barington, T.; Main, K.M.; Jensen, T.K. Current exposure of 200 pregnant Danish women to phthalates, parabens and phenols. Reproduction 2014, 147, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Y.; Chen, P.P.; Zhang, M.; Cui, F.P.; Liu, C.; Deng, Y.L.; Zeng, J.Y.; Yin, W.J.; Zeng, Q. Within-day variability, predictors, and risk assessments of exposure to parabens among Chinese adult men. Environ. Res. 2023, 218, 115026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekhar, S.; Sood, S.; Showkat, S.; Lite, C.; Chandrasekhar, A.; Vairamani, M.; Barathi, S.; Santosh, W. Detection of phenolic endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) from maternal blood plasma and amniotic fluid in Indian population. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2017, 241, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, S.; Shin, C.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.; Lee, A.; Park, J.; Kho, Y.; Moos, R.K.; Koch, H.M.; et al. Urinary parabens and triclosan concentrations and associated exposure characteristics in a Korean population—A comparison between night-time and first-morning urine. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2018, 221, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Wu, C.; Lu, D.; Qi, X.; Xu, H.; Guo, J.; Liang, W.; Chang, X.; Wang, G.; Zhou, Z. Birth outcome measures and prenatal exposure to 4-tert-octylphenol. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 212, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Kannan, K. A survey of alkylphenols, bisphenols, and triclosan in personal care products from China and the United States. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2014, 67, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Gao, J.; Liao, C.; Jiang, G. Co-exposure and health risks of several typical endocrine disrupting chemicals in general population in eastern China. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 112366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.-S.; Kyung, M.-S.; Ko, A.; Park, J.-H.; Hwang, M.-S.; Kwon, J.-E.; Suh, J.-H.; Lee, H.-S.; Moon, G.I.; Hong, J.-H.; et al. Urinary concentrations of parabens and their association with demographic factors: A population-based cross-sectional study. Environ. Res. 2016, 146, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokumura, M.; Nitta, S.; Hayashi, T.; Yamaguchi, R.; Wang, Q.; Miyake, Y.; Amagai, T.; Makino, M. Probabilistic exposure assessment of aggregate rates of dermal exposure of Japanese women and children to parabens in personal care products. Chemosphere 2020, 239, 124704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, H.; Lee, I.; Jeong, Y.; Kim, S.; Choi, G.; Kim, S.; Park, J.; Moon, H.B.; Choi, K. Urinary paraben concentrations of adult women by fasting status: Comparison between Korea and the United States. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 849, 157761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.; Liu, R.; Liu, T.; Liang, J.; Wu, Y.; Feng, B.; Liu, S.; Li, H.; Pan, D.; Qiu, X.; et al. Relationship between exposure of alkylphenols in serum of pregnant women during early pregnancy and adverse birth outcomes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 52954–52963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.; Hong, Y.; Lee, D.; Pang, K.; Kim, Y. The association between some endocrine disruptors in human plasma and the occurrence of congenital hypothyroidism. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2013, 35, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics | Whole | Men | Women | p-Value a |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 804 | n = 286 | n = 518 | ||
| Age, years, median (IQR) | 61 (54,66) | 61 (54,66) | 61 (54,66) | 0.935 |
| 18~45 | 46 (5.72) | 13 (4.55) | 33 (6.37) | |
| 46~65 | 541 (67.29) | 197 (68.88) | 344 (66.41) | |
| >65 | 217 (26.99) | 76 (26.57) | 141 (27.22) | |
| Education level, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| never attended school | 211 (26.24) | 45 (15.73) | 166 (32.05) | |
| primary school | 247 (30.72) | 74 (25.87) | 173 (33.40) | |
| junior secondary and above | 346 (43.03) | 167 (58.39) | 179 (34.55) | |
| Average monthly income, n (%) | 0.553 | |||
| CNY <500 | 311 (38.68) | 104 (36.36) | 207 (39.96) | |
| CNY 500~ | 258 (32.09) | 93 (32.52) | 165 (31.85) | |
| CNY 1000~ | 235 (29.23) | 89 (31.12) | 146 (28.19) | |
| Marital status, n (%) | 0.920 | |||
| married/cohabiting | 710 (88.31) | 253 (88.46) | 457 (88.22) | |
| widowed/single/divorced | 94 (11.69) | 33 (11.54) | 61 (11.78) | |
| Smoking, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| current | 138 (17.16) | 135 (47.20) | 3 (0.58) | |
| never/past | 666 (82.84) | 151 (52.80) | 515(99.42) | |
| Alcohol status, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| current | 101 (12.56) | 89 (31.12) | 12(2.32) | |
| never/past | 703 (87.44) | 197 (68.88) | 506(97.68) | |
| Physical activity, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| low | 188 (23.38) | 92 (32.17) | 96 (18.53) | |
| moderate | 413 (51.37) | 108 (37.76) | 305 (58.88) | |
| high | 2043 (25.25) | 87 (30.07) | 117 (22.59) | |
| BMI, kg/m2, mean ± SD | 23.53 ± 3.30 | 23.14 ± 3.05 | 23.75 ± 3.41 | 0.014 |
| <18.5 | 45 (5.60) | 16 (5.59) | 29 (5.60) | |
| 18.5–23.9 | 412 (51.24) | 162 (56.64) | 250 (48.26) | |
| ≥24 | 347 (43.16) | 108 (37.76) | 239 (46.14) |
| Pollutants | Group | DF (%) | 25th | 50th | 75th | Max | LOD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MeP | whole | 92.91 | 0.185 | 0.444 | 1.008 | 28.842 | 0.0458 |
| men | 92.66 | 0.160 | 0.352 | 0.880 | 28.842 | ||
| women | 93.05 | 0.193 | 0.488 | 1.087 | 28.787 | ||
| EtP | whole | 78.98 | 0.018 | 0.067 | 0.125 | 9.136 | 0.0001 |
| men | 77.62 | 0.015 | 0.058 | 0.099 | 9.136 | ||
| women | 79.73 | 0.023 | 0.074 | 0.131 | 4.630 | ||
| PrP | whole | 89.18 | 0.057 | 0.078 | 0.107 | 3.112 | 0.0254 |
| men | 87.76 | 0.055 | 0.074 | 0.100 | 1.171 | ||
| women | 89,96 | 0.059 | 0.080 | 0.110 | 3.112 | ||
| BuP | whole | 79.48 | 0.026 | 0.053 | 0.074 | 1.269 | 0.0156 |
| men | 77.27 | 0.019 | 0.052 | 0.071 | 0.804 | ||
| women | 80.69 | 0.027 | 0.055 | 0.077 | 1.269 | ||
| BzP | whole | 2.99 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 0.0128 |
| men | 2.80 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | ||
| women | 3.09 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | ||
| 4-t-BP | whole | 97.39 | 4.863 | 8.810 | 15.068 | 99.436 | 0.0063 |
| men | 98.26 | 4.674 | 8.511 | 14.086 | 99.436 | ||
| women | 96.91 | 4.915 | 8.988 | 15.399 | 95.488 | ||
| 4-t-OP | whole | 100.00 | 2.914 | 6.401 | 8.664 | 134.368 | 0.1477 |
| men | 100.00 | 2.534 | 5.442 | 7.386 | 134.368 | ||
| women | 100.00 | 3.139 | 6.957 | 9.466 | 115.956 | ||
| ToTPA b | whole | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.008 | 0.240 | ||
| men | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.007 | 0.210 | |||
| women | 0.002 | 0.005 | 0.009 | 0.240 | |||
| ToTAPs b | whole | 0.061 | 0.091 | 0.154 | 0.800 | ||
| men | 0.057 | 0.089 | 0.140 | 0.800 | |||
| women | 0.062 | 0.095 | 0.161 | 0.730 |
| Pollutants | Whole | Men | Women | p-Value c | N (%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25th | 50th | 75th | Max | 25th | 50th | 75th | Max | 25th | 50th | 75th | Max | HQ > 1 | ||
| MeP | 6.092 | 14.816 | 32.788 | 1071.437 | 4.989 | 11.787 | 27.918 | 1071.437 | 6.929 | 16.988 | 36.316 | 946.829 | 0.001 | - |
| EtP | 0.645 | 2.166 | 4.005 | 332.527 | 0.417 | 1.844 | 3.347 | 332.527 | 0.783 | 2.559 | 4.578 | 152.288 | 0.000 | - |
| PrP | 1.805 | 2.643 | 3.792 | 102.357 | 1.592 | 2.291 | 3.316 | 42.618 | 1.972 | 2.828 | 4.024 | 102.357 | 0.000 | - |
| BuP | 0.862 | 1.761 | 2.539 | 41.739 | 0.585 | 1.602 | 2.327 | 29.278 | 0.956 | 1.885 | 2.658 | 41.739 | 0.000 | - |
| 4-t-BP | 163.121 | 295.366 | 512.503 | 3329.595 | 146.706 | 269.091 | 448.849 | 2773.016 | 178.007 | 311.857 | 544.479 | 3329.595 | 0.019 | 689 (85.70) |
| 4-t-OP | 42.973 | 138.775 | 299.862 | 4993.825 | 40.085 | 117.782 | 241.106 | 3924.032 | 46.111 | 151.107 | 350.961 | 4993.825 | 0.014 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Q.; Huan, C.; Song, Y.; Jia, Z.; Cao, Q.; Wang, C.; Mao, Z.; Huo, W. Exposure Profile and Characteristics of Parabens and Alkylphenols in Plasma among Rural Adults in Central China. Toxics 2023, 11, 926. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110926
Gao Q, Huan C, Song Y, Jia Z, Cao Q, Wang C, Mao Z, Huo W. Exposure Profile and Characteristics of Parabens and Alkylphenols in Plasma among Rural Adults in Central China. Toxics. 2023; 11(11):926. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110926
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Qian, Changsheng Huan, Yu Song, Zexin Jia, Qingqing Cao, Chongjian Wang, Zhenxing Mao, and Wenqian Huo. 2023. "Exposure Profile and Characteristics of Parabens and Alkylphenols in Plasma among Rural Adults in Central China" Toxics 11, no. 11: 926. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110926
APA StyleGao, Q., Huan, C., Song, Y., Jia, Z., Cao, Q., Wang, C., Mao, Z., & Huo, W. (2023). Exposure Profile and Characteristics of Parabens and Alkylphenols in Plasma among Rural Adults in Central China. Toxics, 11(11), 926. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110926







