Pollution and Potential Ecological Risk Evaluation Associated with Toxic Metals in an Impacted Mangrove Swamp in Niger Delta, Nigeria
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection
2.2.1. Blue Crabs (Callinectes amnicola)
2.2.2. Water Samples
2.2.3. Sediment Samples
2.3. Sample Preparation and Digestion
2.4. Quality Assurance
2.5. Sample Analysis
2.5.1. The Pollution Load Index (PLI)
2.5.2. Contamination Factor (CF)
2.5.3. Ecological Risk Factor (ERi)
2.5.4. Potential Ecological Risk Index (PERI)
2.5.5. Contamination Degree (CD)
2.5.6. Geo-Accumulation Index (Igeo)
2.5.7. Degree of Contamination (DC)
2.5.8. Enrichment Factor (EF)
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Concentrations of the Toxic Metals
3.2. Contamination Factor (CF)
3.3. Ecological Risk Assessment
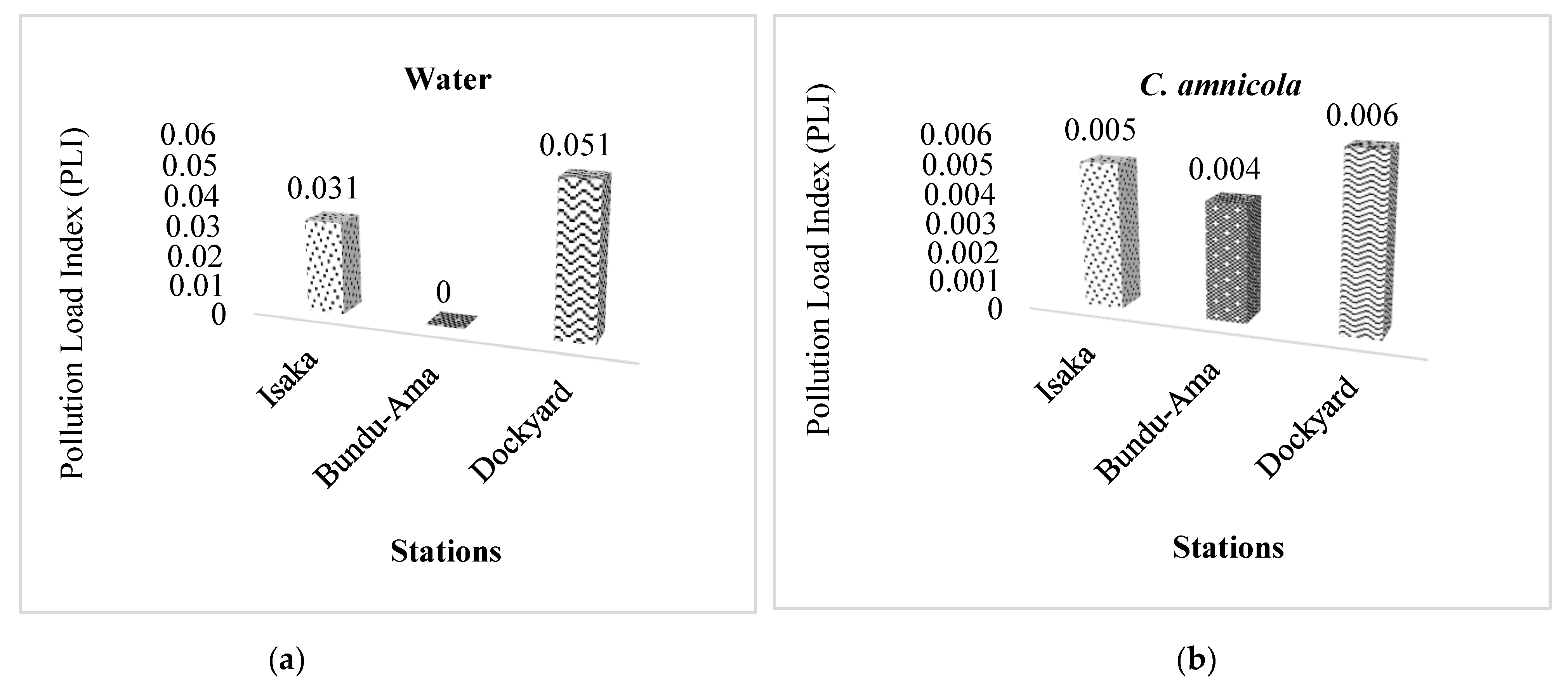
3.4. Pollution Load Index (PLI)
3.5. Geo-Accumulation Index (Igeo)
3.6. The Enrichment Factor
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nduka, J.K.; Okafor, V.N.; Odiba, I.O. Impact of Oil and Gas Activities on Acidity of Rain and Surface Water of Niger Delta, Nigeria: An Environmental and Public Health Review. J. Environ. Prot. 2016, 7, 566–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onojake, M.C.; Sikoki, F.D.; Omokheyeke, O.; Akpiri, R.U. Surface water characteristics and trace metals level of the Bonny/New Calabar River Estuary, Niger Delta, Nigeria. Appl. Water Sci. 2015, 7, 951–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, A.D.I.; Abowei, J.F.N. Physical and Chemical Parameters and Some Heavy Metal for Three Rainy Season Months in Water and Sediments of Upper New Calabar River, Niger Delta, Nigeria. OALib 2018, 5, e4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mungai, T.M.; Owino, A.A.; Makokha, V.A.; Gao, Y.; Yan, X.; Wang, J. Occurrences and toxicological risk assessment of eight heavy metals in agricultural soils from Kenya, Eastern Africa. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 18533–18541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adanwo, E.O.; Elechi, O. Risk assessment of heavy metals in crops and soil from a dumpsite in Rumuolumeni, Port Harcourt. J. Appl. Chem. Sci. Int. 2019, 10, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Edokpayi, J.N.; Odiyo, J.O.; Popoola, O.E.; Msagati, T.A.M. Assessment of Trace Metals Contamination of Surface Water and Sediment: A Case Study of Mvudi River, South Africa. Sustainability 2016, 8, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyi, A.A.; Babalola, B.A. Lead and Cadmium Levels in Residential Soils of Lagos and Ibadan, Nigeria. J. Health Pollut. 2017, 7, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoye, E.A.; Bocca, B.; Ruggieri, F.; Ezejiofor, A.N.; Nwaogazie, I.L.; Domingo, J.L.; Rovira, J.; Frazzoli, C.; Orisakwe, O.E. Metal pollution of soil, plants, feed and food in the Niger Delta, Nigeria: Health risk assessment through meat and fish consumption. Environ. Res. 2021, 198, 111273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kpee, F.; Edori, O.S.; Okotume, S.C. Geo-accumulation and Ecological Risks of Heavy Metals in Sediments of Andoni River, Rivers State, Niger Delta, Nigeria. Int. J. Res. Sci. Innov. 2019, 6, 197–202. [Google Scholar]
- Odekina, M.U.; Davies, I.C.; Akoko, S.; Vincent-Akpu, I.F. Bioaccumulation of Heavy Metals in Periophthalmus papillio, Sediment and Interstitial Water from Isaka-Bundu Water Front in Rivers State. Acad. J. Curr. Res. 2021, 8, 19–38. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, I.C.; Oghenetekevwe, E. Physico-chemical Parameters and Heavy Metals Distribution in Selected Shell Fishes along the Opuro-Ama Creek in the Rivers State of Nigeria. Asian J. Fish. Aquat. Res. 2022, 17, 15–26. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, I.C.; Nkeeh, D.K.; Akoko, S.; Ariri, I.P. Spatial Variation of Heavy Metals in Blue Crab Calinectes amnicola Harvested from The Water Front of Some Fishing Communities in River State, Nigeria. Int. Res. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2021, 7, 33–49. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, H.; Khan, E.; Ilahi, I. Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology of Hazardous Heavy Metals: Environmental Persistence, Toxicity, and Bioaccumulation. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 6730305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, S.; Muzammal, M.; Rehman, A.; Rustam, S.A.; Shehzadi, Z.; Mehmood, A.; Waqar, M. Water pollution on heavy metals and its effects on fishes. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2020, 8, 6–14. [Google Scholar]
- Mehana, E.-S.E.; Khafaga, A.F.; Elblehi, S.S.; El-Hack, M.E.A.; Naiel, M.A.; Bin-Jumah, M.; Othman, S.I.; Allam, A.A. Biomonitoring of Heavy Metal Pollution Using Acanthocephalans Parasite in Ecosystem: An Updated Overview. Animals 2020, 10, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, I.C.; Agarin, O.J.; Onoja, C.R. Study On Heavy Metals Levels and Some Physicochemical Parameters of a Polluted Creek Along the Tin Can Island in Lagos. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. Res. 2021, 9, 25–39. [Google Scholar]
- Javed, M.; Usmani, N. An Overview of the Adverse Effects of Heavy Metal Contamination on Fish Health. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India Sect. B Boil. Sci. 2017, 89, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.M.; Ali, M.L.; Proshad, R.; Islam, S.; Rahman, Z.; Tusher, T.R.; Kormoker, T.; Al, M.A. Heavy metal concentrations in commercially valuable fishes with health hazard inference from Karnaphuli river, Bangladesh. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2019, 26, 2646–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alengebawy, A.; Abdelkhalek, S.; Qureshi, S.; Wang, M.-Q. Heavy Metals and Pesticides Toxicity in Agricultural Soil and Plants: Ecological Risks and Human Health Implications. Toxics 2021, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahiduzzaman; Islam, M.; Sikder, A.H.F.; Parveen, Z. Bioaccumulation and Heavy Metal Contamination in Fish Species of the Dhaleswari River of Bangladesh and Related Human Health Implications. Biol. Trace Element Res. 2021, 200, 3854–3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Shi, J.; Wang, J.; Dai, Y.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, P. Interactions Between Microplastics and Heavy Metals in Aquatic Environments: A Review. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwankwoala; Ogunka, H.; Nwanosike, A.A.; Omoniyi, I.O.; Desmond, O.A.; Chibueze, U.C.; Daniel, K.B.; Ayodele, B.T.; Akudo, O.E.; Cheneboso, O.D. Health implications of selected heavy metals around hydrocarbon impacted sites in the Niger Delta: A preliminary investigation. GSC Adv. Res. Rev. 2022, 11, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Deng, R.; Wan, J.; Zeng, G.; Xue, W.; Wen, X.; Zhou, C.; Hu, L.; Liu, X.; Xu, P.; et al. Remediation of lead-contaminated sediment by biochar-supported nano-chlorapatite: Accompanied with the change of available phosphorus and organic matters. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 348, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bundschuh, J.; Schneider, J.; Alam, M.A.; Niazi, N.K.; Herath, I.; Parvez, F.; Tomaszewska, B.; Guilherme, L.R.G.; Maity, J.P.; López, D.L.; et al. Seven potential sources of arsenic pollution in Latin America and their environmental and health impacts. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 780, 146274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.T.; Prasad, S.M. Remediation of heavy metal contaminated ecosystem: An overview on technology advancement. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 12, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achary, M.S.; Satpathy, K.; Panigrahi, S.; Mohanty, A.; Padhi, R.; Biswas, S.; Prabhu, R.; Vijayalakshmi, S.; Panigrahy, R. Concentration of heavy metals in the food chain components of the nearshore coastal waters of Kalpakkam, southeast coast of India. Food Control. 2017, 72, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Lin, J.; Xie, D.; Yao, Y.; Wang, X.; Huang, Y.; Xin, M.; Yang, F.; Liu, K.; Li, Y. Soil properties and heavy metal concentrations affect the composition and diversity of the diazotrophs communities associated with different land use types in a mining area. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 155, 103669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Lin, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhang, C. Continental-scale spatial distribution, sources, and health risks of heavy metals in seafood: Challenge for the water-food-energy nexus sustainability in coastal regions? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 63815–63828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.-S.; Yan, J.; Guo, X.-P.; Xu, M.; Sun, Y.; Tou, F.-Y.; Yin, G.-Y.; Hou, L.-J.; Liu, M.; Yang, Y. Human activities can drive sulfate-reducing bacteria community in Chinese intertidal sediments by affecting metal distribution. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 786, 147490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, W.-L.; Dang, N.-L.; Kok, Y.-Y.; Yap, K.-S.I.; Phang, S.-M.; Convey, P. Heavy metal pollution in Antarctica and its potential impacts on algae. Polar Sci. 2019, 20, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lan, B.; Fei, H.; Wang, S.; Zhu, G. Heavy metal could drive co-selection of antibiotic resistance in terrestrial subsurface soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 411, 124848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, C.T.; Lin, C.; Shern, C.-C.; Yeh, G.; Le, V.G.; Tran, H.T. Contamination, ecological risk and source apportionment of heavy metals in sediments and water of a contaminated river in Taiwan. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 82, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, K.; Wu, Q.; Liu, P.; Hu, W.; Huang, B.; Shi, B.; Zhou, Y.; Kwon, B.-O.; Choi, K.; Ryu, J.; et al. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments and water from the coastal areas of the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea. Environ. Int. 2020, 136, 105512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, J.; Cui, X.; Feng, H.; Yan, S. Environmental Background Values and Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Watershed Sediments: A Comparison of Assessment Methods. Water 2021, 14, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.K.; Islam, S.; Rahman, S.; Haque, M.; Islam, M.M. Heavy metals in water, sediment and some fishes of Buriganga River, Bangladesh. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology, Bangkok, Thailand, 23–25 April 2010; Volume 6, pp. 384–388. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, S. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediment and human health risk assessment of heavy metals in fishes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River basin. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2575–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayotunde, E.O.; Offem, B.O.; Ada, F.B. Heavy metal profile of water, sediment and freshwater cat fish, Chrysichthys nigrodigitatus (Siluriformes: Bagridae), of Cross River, Nigeria. Rev. Biol. Trop. 2012, 60, 1289–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoro, H.K.; Fatoki, O.S. A Review of Sequential Extraction Procedures for Heavy Metals Speciation in Soil and Sediments. J. Environ. Anal. Toxicol. 2012, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.-W. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals both in wild and mariculture food chains in Daya Bay, South China. Estuarine Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 163, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mziray, P.; Kimirei, I.A. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in marine fishes (Siganus sutor, Lethrinus harak, and Rastrelliger kanagurta) from Dar es Salaam Tanzania. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2016, 7, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isangedighi, I.A.; David, G.S. Heavy metals contamination in fish: Effects on human health. J. Aquat. Sci. Mar. Biol. 2019, 2, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, M.; Gupta, N.; Ratn, A.; Awasthi, Y.; Prasad, R.; Trivedi, A.; Trivedi, S.P. Biomonitoring of Heavy Metals in River Ganga Water, Sediments, Plant, and Fishes of Different Trophic Levels. Biol. Trace Element Res. 2020, 193, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Förstner, U.; Wittmann, G.T. Metal Pollution in the Aquatic Environment; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Häder, D.-P.; Banaszak, A.; Villafañe, V.E.; Narvarte, M.A.; González, R.A.; Helbling, E.W. Anthropogenic pollution of aquatic ecosystems: Emerging problems with global implications. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 713, 136586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabu, E.; Felix, S.; Felix, N.; Ahilan, B.; Ruby, P. An overview on significance of fish nutrition in aquaculture industry. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2017, 5, 349–355. [Google Scholar]
- Saher, N.U.; Kanwal, N. Assessment of some heavy metal accumulation and nutritional quality of shellfish with reference to human health and cancer risk assessment: A seafood safety approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 5189–5201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hixson, S.M. Fish Nutrition and Current Issues in Aquaculture: The Balance in Providing Safe and Nutritious Seafood, in an Environmentally Sustainable Manner. J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2014, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopal, V.; Gopakumar, K. Shellfish: Nutritive Value, Health Benefits, and Consumer Safety. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 1219–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maulvault, A.L.; Anacleto, P.; Lourenço, H.M.; Carvalho, M.L.; Nunes, M.L.; Marques, A. Nutritional quality and safety of cooked edible crab (Cancer pagurus). Food Chem. 2012, 133, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, P.K.; Das, A.K.; Dandapat, P.; Dhar, P.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Dib, A.L.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Gagaoua, M. Nutritional aspects, flavour profile and health benefits of crab meat based novel food products and valorisation of processing waste to wealth: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 112, 252–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, M.M.M.; Morte, E.S.d.B.; Cardoso, L.G.; Nunes, D.V.; de Souza, C.O.; Druzian, J.I.; Cardoso, R.D.C.V. Nutritional contribution of shellfish from the biodiversity of Todos os Santos Bay, Brazil. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 102, 103999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawarazuka, N.; Béné, C. The potential role of small fish species in improving micronutrient deficiencies in developing countries: Building evidence. Public Health Nutr. 2011, 14, 1927–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeshu, M.A.; Lelisa, A.; Geleta, B. Complementary Feeding: Review of Recommendations, Feeding Practices, and Adequacy of Homemade Complementary Food Preparations in Developing Countries—Lessons from Ethiopia. Front. Nutr. 2016, 3, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omuvwie, U.; Atobatele, O.E. Growth pattern, condition factor, trace metal studies and ectoparasitic load of the blue crab, Callinectes amnicola from Lagos Lagoon, Badore, Ajah, Lagos, Nigeria. Cameroon J. Exp. Biol. 2013, 9, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osayande, O.; Zou, E. Lead Inhibits Postecdysial Exoskeletal Calcification in the Blue Crab ( Callinectes sapidus ). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 41, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yum, H.-W.; Na, H.-K.; Surh, Y.-J. Anti-inflammatory effects of docosahexaenoic acid: Implications for its cancer chemopreventive potential. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2016, 40, 141–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Sim, T.-B.; Lee, J.-E.; Na, H.-K. Chemopreventive and Chemotherapeutic Effects of Fish Oil derived Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on Colon Carcinogenesis. Clin. Nutr. Res. 2017, 6, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Frame for Metals Risk Assessment; Office of the Science AdvisorP: Washington, DC, USA, 2007; EPA 630/P-03/001F. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Liu, L.; Pan, R. Pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the surface sediments from a source water reservoir. Chem. Speciat. Bioavailab. 2016, 28, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, A.; Ennaji, W.; Krimissa, S.; Bouzaid, M. Heavy metal contamination and ecological-health risk evaluation in peri-urban wastewater-irrigated soils of Beni-Mellal city (Morocco). Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2020, 30, 372–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, D.L.; Wilson, J.G.; Harris, C.R.; Jeffrey, D.W. Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgoländer Meeresunters. 1980, 33, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Håkanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.M.; Ali, M.L.; Islam, S.; Rahman, Z. Preliminary assessment of heavy metals in water and sediment of Karnaphuli River, Bangladesh. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2016, 5, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutiani, R.; Kulkarni, D.B.; Khanna, D.R.; Gautam, A. Geochemical distribution and environmental risk assessment of heavy metals in groundwater of an industrial area and its surroundings, Haridwar, India. Energy Ecol. Environ. 2016, 2, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yisa, J.; Jacob, J.O.; Onoyima, C.C. Assessment of Toxic Levels of Some Heavy Metals in Road Deposited Sediments in Suleja, Nigeria. Am. J. Chem. 2016, 2, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Muller, G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geojournal 1969, 2, 10818. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, S.; Ahmed, K.; Raknuzzaman, M.; Al Mamun, H.; Masunaga, S. Metal Speciation in Sediment and Their Bioaccumulation in Fish Species of Three Urban Rivers in Bangladesh. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 68, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essien, J.P.; Inam, E.D.; Ikpe, D.I.; Udofia, G.E.; Benson, N.U. Ecotoxicological status and risk assessment of heavy metals in municipal solid wastes dumpsite impacted soil in Nigeria. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2019, 11, 100215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buat-Menard, P.; Chesselet, R. Variable influence of the atmospheric flux on the trace metal chemistry of oceanic suspended matter. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1979, 42, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manno, E.; Varrica, D.; Dongarrà, G. Metal distribution in road dust samples collected in an urban area close to a petrochemical plant at Gela, Sicily. Atmospheric Environ. 2006, 40, 5929–5941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoye, E.A.; Ezejiofor, A.N.; Nwaogazie, I.L.; Frazzoli, C.; Orisakwe, O.E. Heavy metals and arsenic in soil and vegetation of Niger Delta, Nigeria: Ecological risk assessment. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2022, 6, 100222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacatusu, R. Appraising levels of soil contamination and pollution with heavy metals. Eur. Soil Bureau. 2000, 4, 93–102. [Google Scholar]
- El-Amier, Y.A.; Bonanomi, G.; Al-Rowaily, S.L.; Abd-ElGawad, A.M. Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals along Three Main Drains in Nile Delta and Potential Phytoremediation by Macrophyte Plants. Plants 2020, 9, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, J.; Mazurek, R.; Gąsiorek, M.; Setlak, M.; Zaleski, T.; Waroszewski, J. Soil pollution indices conditioned by medieval metallurgical activity—A case study from Krakow (Poland). Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 1023–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.M.; Rahman, S.; Islam, S.; Rakib, R.J.; Hossen, S.; Rahman, Z.; Kormoker, T.; Idris, A.M.; Phoungthong, K. Distribution of heavy metals in water and sediment of an urban river in a developing country: A probabilistic risk assessment. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2022, 37, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banu, Z.; Alam Chowdhury, S.; Hossain, D.; Nakagami, K. Contamination and Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal in the Sediment of Turag River, Bangladesh: An Index Analysis Approach. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2013, 5, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahabadi, A.; Malvandi, H. Contamination and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals and metalloids in surface sediments of the Tajan River, Iran. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 133, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, N.U.; Anake, W.U.; Essien, J.P.; Enyong, P.; Olajire, A.A. Distribution and risk assessment of trace metals in Leptodius exarata, surface water and sediments from Douglas Creek in the Qua Iboe Estuary. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2017, 11, 434–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekere, N.; Yakubu, N.; Ihedioha, J. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments of rivers Niger and Benue confluence, Lokoja, Central Nigeria. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 18966–18978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enuneku, A.; Omoruyi, O.; Tongo, I.; Ogbomida, E.; Ogbeide, O.; Ezemonye, L. Evaluating the potential health risks of heavy metal pollution in sediment and selected benthic fauna of Benin River, Southern Nigeria. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirisu, C.E.; Biose, E.; Aighewi, I.T. Heavy metal contamination of Ewhare dumpsite environment in Nigeria’s Niger Delta. SCIREA J. Env. 2019, 3, 30–45. [Google Scholar]
- Ezewudo, B.I.; Mgbenka, B.O.; Islam, S.; Proshad, R.; Odo, G.E. Appraisal of metal contamination in sediments of lower reaches of Niger River, Nigeria, using contamination indices and sediment quality guidelines. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 101, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zuo, H.; Tian, M.; Zhang, L.; Meng, J.; Zhou, X.; Min, N.; Chang, X.; Liu, Y. Assessment of heavy metals contamination in sediments from three adjacent regions of the Yellow River using metal chemical fractions and multivariate analysis techniques. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decena, S.C.P.; Arguilles, M.S.; Robel, L.L. Assessing Heavy Metal Contamination in Surface Sediments in an Urban River in the Philippines. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2018, 27, 1983–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, N.U.; Adedapo, A.E.; Fred-Ahmadu, O.H.; Williams, A.B.; Udosen, E.D.; Ayejuyo, O.O.; Olajire, A.A. New ecological risk indices for evaluating heavy metals contamination in aquatic sediment: A case study of the Gulf of Guinea. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2018, 18, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Zhu, T.; Li, M.; He, J.; Huang, R. Heavy Metal Contamination in Soil and Brown Rice and Human Health Risk Assessment near Three Mining Areas in Central China. J. Health Eng. 2017, 2017, 4124302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Q.; Sun, Z.; Tian, L.; Li, J.; Sun, W.; Sun, W. Assessment of arsenic and heavy metal pollution and ecological risk in inshore sediments of the Yellow River estuary, China. Stoch. Hydrol. Hydraul. 2018, 32, 2889–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, P.O.; Rashid, A.; Nkinahamira, F.; Wang, H.; Sun, Q.; Gad, M.; Yu, C.-P.; Hu, A. Integrated assessment of major and trace elements in surface and core sediments from an urban lagoon, China: Potential ecological risks and influencing factors. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 170, 112651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, A.E.; de Vries, N.; Nyarko, K.B. Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution in the Sediments of the River Pra and Its Tributaries. Water Air, Soil Pollut. 2018, 229, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahaya, S.M.; Abubakar, F.; Abdu, N. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metal-contaminated soils of selected villages in Zamfara State, Nigeria. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, R.A. Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu, Hawaii. Environ. Geol. 2000, 39, 611–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.-T.; Lee, C.-W.; Ahn, B.-Y. Sedimentation pattern and sediments bioavailability in a wastewater discharging area by sequential metal analysis. Microchem. J. 2001, 68, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, I.; Abdu, N. Horizontal and Vertical Distribution of Lead, Cadmium, and Zinc in Farmlands Around a Lead-Contaminated Goldmine in Zamfara, Northern Nigeria. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2014, 66, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhou, X.; Lei, M.; Gao, D.; Qiao, P.; Du, G. Risk assessment of heavy metal contamination in farmland soil in Du’an Autonomous County of Guangxi Zhuang autonomous region, China. Huanjing Kexue 2015, 36, 2964–2971. [Google Scholar]
- Raji, B.; Jimba, W.B.; Alagbe, S.A. The distribution and geochemical assessment of trace elements from the semi-arid to sub-humid savanna of Nigeria. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 3555–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| S/n | Elements | APHA Method | Wavelength (nm) | Method Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cd | APHA 3111B | 326.11 | Direct Air–Acetylene Flame Method |
| 2. | Pb | APHA 3111B | 202.20 | Direct Air–Acetylene Flame Method |
| 3. | Zn | APHA 3111B | 213.86 | Direct Air–Acetylene Flame Method |
| 4. | Fe | APHA 3111B | 248.30 | Direct Air–Acetylene Flame Method |
| 5. | As | APHA 3111B | 197.20 | Direct Air–Argon Flame Method |
| 6. | Cu | APHA 3111B | 217.89 | Direct Air–Acetylene Flame Method |
| Source | Sampling Site | Station | Cd | Pb | Zn | Fe | As | Cu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crab (mg kg−1) | Isaka | 1 | 0.001 ± 0.000 | 0.004 ± 0.001 | 97.09 ± 0.001 | 10.73 ± 0.000 | 0.002 ± 0.001 | 0.69 ± 0.001 |
| Bundu-Ama | 2 | 0.001 ± 0.000 | 0.002 ± 0.001 | 100.01 ± 0.001 | 12.67 ± 0.000 | 0.002 ± 0.001 | 0.78 ± 0.001 | |
| Dockyard | 3 | 0.001 ± 0.000 | 0.005 ± 0.003 | 117.34 ± 0.001 | 12.52 ± 0.000 | 0.002 ± 0.001 | 0.67 ± 0.001 | |
| Water (mg/L) | Isaka | 1 | 0.05 ± 0.003 | 0.060 ± 0.003 | 8.29 ± 0.003 | 25.12 ± 0.003 | 0.001 ± 0.00 | 136.35 ± 0.01 |
| Bundu-Ama | 2 | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 0.074 ± 0.001 | 9.84 ± 0.01 | 46.41 ± 0.00 | 0.000 ± 0.00 | 147.35 ± 0.01 | |
| Dockyard | 3 | 0.05 ± 0.001 | 0.094 ± 0.001 | 14.50 ± 0.07 | 39.20 ± 0.07 | 0.001 ± 0.00 | 160.05 ± 0.01 | |
| Sediment (mg kg−1) | Isaka | 1 | 2.33 ± 0.001 | 6.160 ± 0.001 | 215.44 ± 0.00 | 1609 ± 0.67 | 0.012 ± 0.00 | 473.19 ± 0.0 |
| Bundu-Ama | 2 | 3.84 ± 0.00 | 8.510 ± 0.00 | 209.02 ± 0.00 | 1634 ± 0.67 | 0.013 ± 0.00 | 531.03 ± 0.00 | |
| Dockyard | 3 | 2.59 ± 0.006 | 12.07 ± 0.003 | 246.41 ± 0.003 | 1846 ± 0.58 | 0.016 ± 0.003 | 596.73 ± 0.003 | |
| DPR * | Standard | 0.8 | 85 | 140 | 38,000 | 1.0 | 36 |
| Isaka | Bundu-Ama | Dockyard | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toxic Metals | Water | C. amnicola | Sediment | Water | C. amnicola | Sediment | Water | C. amnicola | Sediment |
| Cd | 5.4 × 101 | 1.0 × 102 | 23.3 | 5.1 × 101 | 1.0 × 102 | 38.42 | 5.4 × 101 | 1 × 102 | 25.88 |
| Pb | 2.9 × 10³ | 2.0 × 104 | 3.08 × 101 | 3.7 × 105 | 1.0 × 104 | 4.25 × 101 | 4.7 × 103 | 2.5 × 105 | 6.03 × 101 |
| Zn | 1.27 × 101 | 1.484 | 3.294159 | 1.504 × 101 | 1.529189 | 24.984 | 2.22 × 101 | 1.7942354 | 3.767798 |
| Fe | 6.5 × 103 | 2.78 × 103 | 4179 × 101 | 1.21 × 102 | 3.291 × 103 | 4.2 × 101 | 1.02 × 102 | 3.25 × 105 | 4.8 × 101 |
| As | 7.69 × 105 | 1.53 × 104 | 9.23 × 104 | 0.0 | 1.538 × 104 | 1.0 × 103 | 7.69 × 105 | 1.5384 × 104 | 1.23 × 103 |
| Cu | 1.947 | 9.885 × 104 | 6.759786 | 2.105 | 1.114 × 102 | 7.5859 | 2.286414 | 9.6285 × 104 | 8.524686 |
| DC | 169.868 | 108.52 | 2306.12 | 203.725 | 113.465 | 3811.37 | 213.902 | 130.543 | 2703.813 |
| Isaka | Bundu-Ama | Dockyard | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toxic Metals | Water | Sediment | Water | Sediment | Water | Sediment |
| Cd | 1.62 | 69.90 | 1.53 | 115.26 | 1.62 | 77.64 |
| Pb | 0.29 | 30.78 | 0.37 | 42.55 | 0.47 | 60.34 |
| Zn | 8.29 | 215.44 | 9.84 | 1634.00 | 14.50 | 246.41 |
| As | 0.01 | 0.12 | 0.00 | 0.13 | 0.01 | 0.16 |
| Cu | 681.73 | 2365.93 | 736.75 | 2655.07 | 800.25 | 2983.64 |
| PERI | 691.94 | 2682.16 | 748.49 | 4447.0 | 816.85 | 3368.19 |
| Isaka | Bundu-Ama | Dockyard | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toxic Metals | Water | C. amnicola | Sediment | Water | C. amnicola | Sediment | Water | C. amnicola | Sediment |
| Cd | 0.108 | 0.002 | 4.676 | 0.102 | 0.002 | 7.710 | 0.108 | 0.002 | 5.194 |
| Pb | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.062 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.085 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.121 |
| Zn | 0.025 | 0.298 | 0.661 | 0.030 | 0.307 | 5.014 | 0.044 | 0.360 | 0.756 |
| Fe | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.084 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.085 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.096 |
| As | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Cu | 0.391 | 0.002 | 1.357 | 0.422 | 0.002 | 1.522 | 0.459 | 0.002 | 1.711 |
| Isaka | Bundu-Ama | Dockyard | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Toxic Metals | Sediment | Sediment | Sediment |
| Cd | 52.89 | 87.22 | 58.75 |
| Pb | 0.70 | 0.97 | 1.37 |
| Zn | 7.48 | 56.72 | 8.55 |
| As | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Cu | 15.35 | 17.22 | 19.35 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chris, D.I.; Anyanwu, B.O. Pollution and Potential Ecological Risk Evaluation Associated with Toxic Metals in an Impacted Mangrove Swamp in Niger Delta, Nigeria. Toxics 2023, 11, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11010006
Chris DI, Anyanwu BO. Pollution and Potential Ecological Risk Evaluation Associated with Toxic Metals in an Impacted Mangrove Swamp in Niger Delta, Nigeria. Toxics. 2023; 11(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleChris, Davies Ibienebo, and Brilliance Onyinyechi Anyanwu. 2023. "Pollution and Potential Ecological Risk Evaluation Associated with Toxic Metals in an Impacted Mangrove Swamp in Niger Delta, Nigeria" Toxics 11, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11010006
APA StyleChris, D. I., & Anyanwu, B. O. (2023). Pollution and Potential Ecological Risk Evaluation Associated with Toxic Metals in an Impacted Mangrove Swamp in Niger Delta, Nigeria. Toxics, 11(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11010006






