Effect of Embryonic Alcohol Exposure on Craniofacial and Skin Melanocyte Development: Insights from Zebrafish (Danio rerio)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Zebrafish Strains and Maintenance
2.2. Alcohol Treatment and Embryo Fixation
2.3. Whole-Mount Double Staining
2.4. Tooth Measurements
2.5. Whole-Mount Cartilage Staining
2.6. Ethmoid Bone Measurements
2.7. Melanophore Density
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
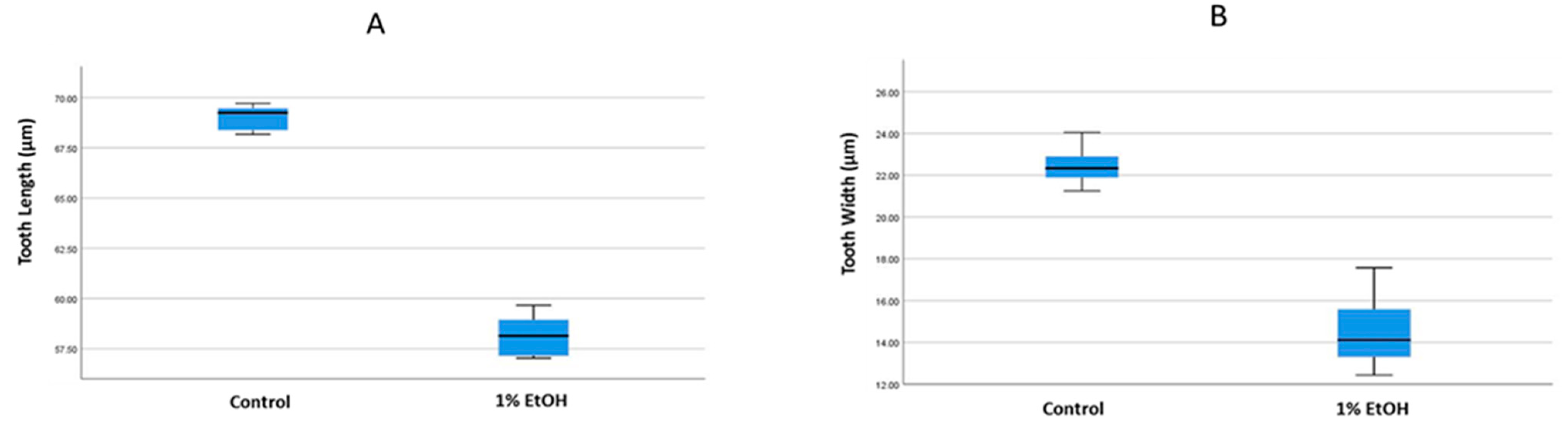
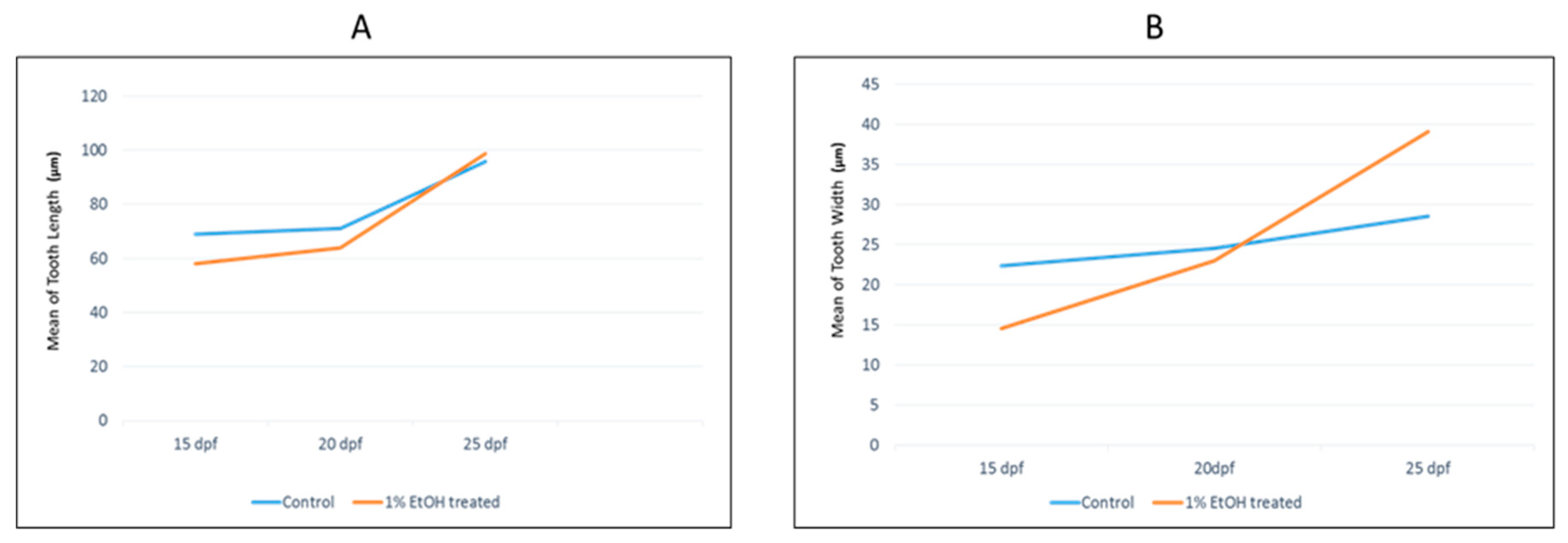
3.1. Analysis of Tooth Morphology
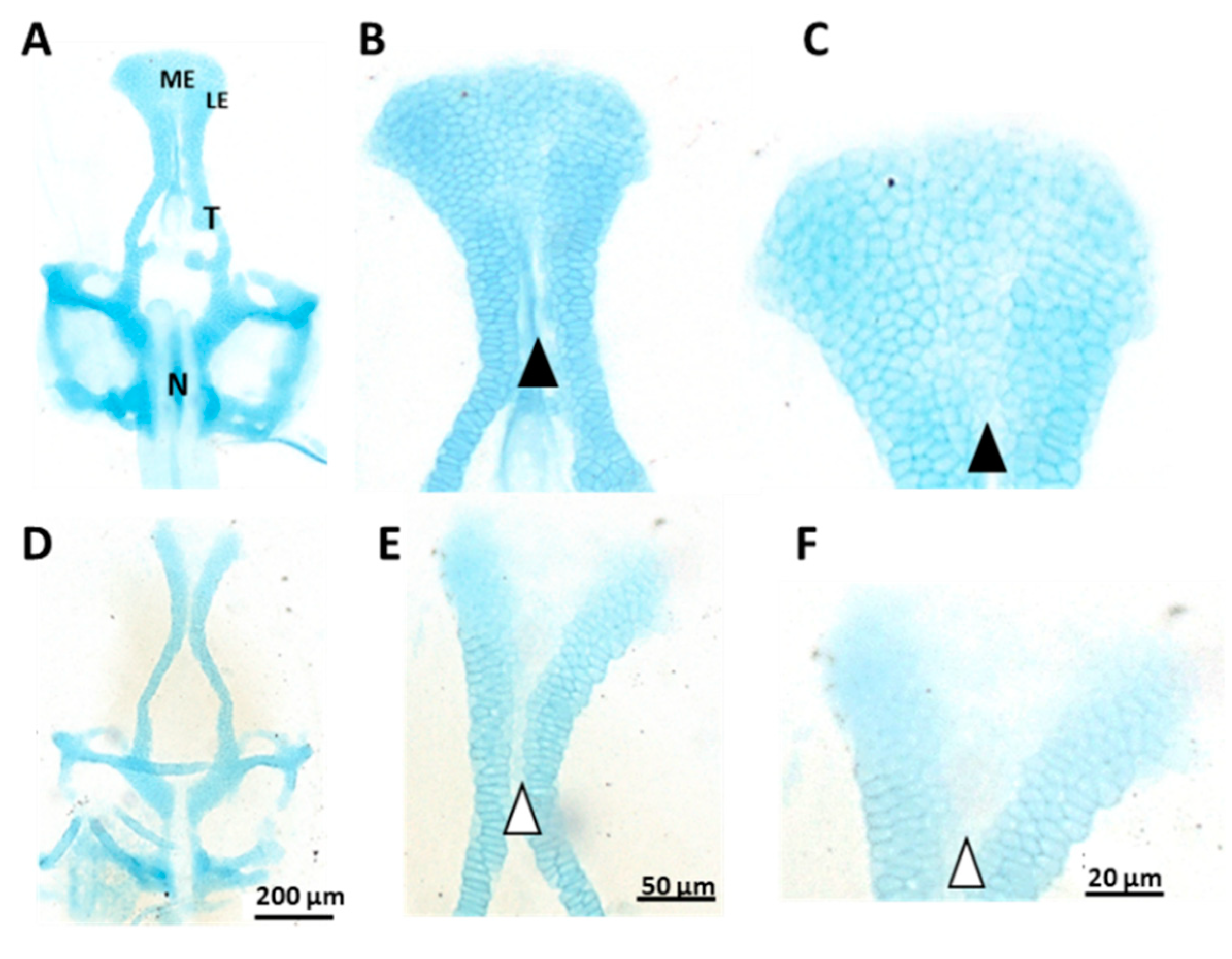
3.2. Ethmoid Cartilage
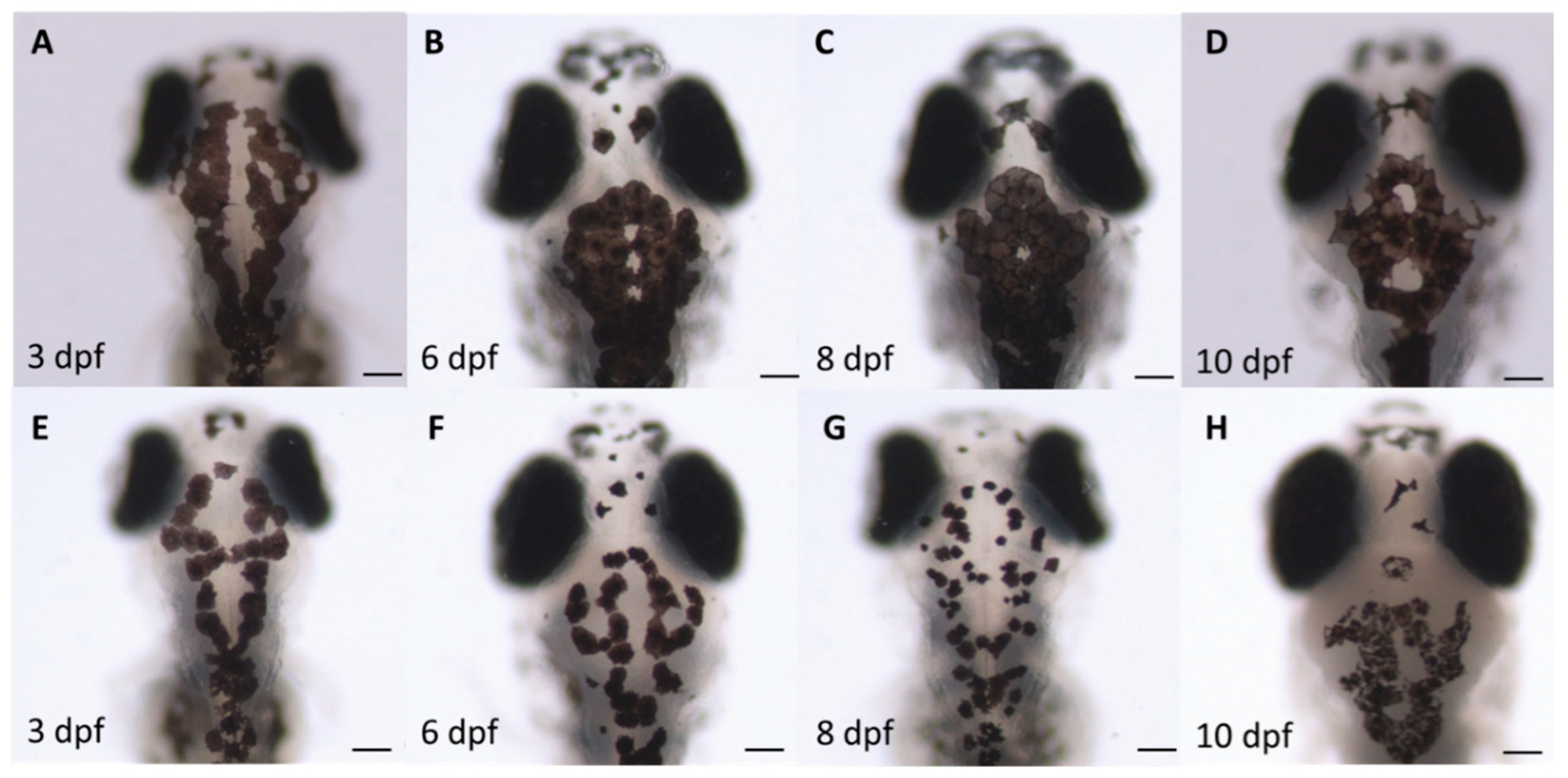
3.3. Assessment of Melanocyte Density
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- DeRoo, L.A.; Wilcox, A.J.; Lie, R.T.; Romitti, P.A.; Pedersen, D.A.; Munger, R.G.; Moreno Uribe, L.M.; Wehby, G.L. Maternal alcohol binge-drinking in the first trimester and the risk of orofacial clefts in offspring: A large population-based pooling study. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 31, 1021–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovely, C.B.; Fernandes, Y.; Eberhart, J.K. Fishing for Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders: Zebrafish as a Model for Ethanol Teratogenesis. Zebrafish 2016, 13, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, G.J.; Zhang, C.; Ojiaku, P.; Bell, V.; Devkota, S.; Mukhopadhyay, S. Effects of ethanol exposure on nervous system development in zebrafish. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2012, 299, 255–315. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Yin, X.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Pan, X.; Li, N.; Yu, Z. Retinoic acid remodels extracellular matrix (ECM) of cultured human fetal palate mesenchymal cells (hFPMCs) through down-regulation of TGF-beta/Smad signaling. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 225, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boschen, K.E.; Gong, H.; Murdaugh, L.B.; Parnell, S.E. Knockdown of Mns1 increases susceptibility to craniofacial defects following gastrulation-stage alcohol exposure in mice. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2018, 42, 2136–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munger, R.G.; Romitti, P.A.; Daack-Hirsch, S.; Burns, T.L.; Murray, J.C.; Hanson, J. Maternal alcohol use and risk of orofacial cleft birth defects. Teratology 1996, 54, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, S.; Probst, C.; Gmel, G.; Rehm, J.; Burd, L.; Popova, S. Global Prevalence of Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder Among Children and Youth: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Pediatr. 2017, 171, 948–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cudd, T.A. Animal model systems for the study of alcohol teratology. Exp. Biol. Med. 2005, 230, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, J.I.; Egana, A.L.; Sponholtz, T.R.; Adolph, A.R.; Dowling, J.E. Effects of ethanol on photoreceptors and visual function in developing zebrafish. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 4589–4597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arenzana, F.; Carvan III, M.J.; Aijon, J.; Sanchez-Gonzalez, R.; Arevalo, R.; Porteros, A. Teratogenic effects of ethanol exposure on zebrafish visual system development. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2006, 28, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilotta, J.; Barnett, J.A.; Hancock, L.; Saszik, S. Ethanol exposure alters zebrafish development: A novel model of fetal alcohol syndrome. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2004, 26, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dlugos, C.A.; Rabin, R.A. Ocular deficits associated with alcohol exposure during zebrafish development. J. Comp. Neurol. 2007, 502, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoyme, H.E.; May, P.A.; Kalberg, W.O.; Kodituwakku, P.; Gossage, J.P.; Trujillo, P.M.; Buckley, D.G.; Miller, J.H.; Aragon, A.S.; Khaole, N. A practical clinical approach to diagnosis of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders: Clarification of the 1996 institute of medicine criteria. Pediatrics 2005, 115, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouko, L.A.; Shantikumar, K.; Knezovich, J.; Haycock, P.; Schnugh, D.J.; Ramsay, M. Effect of alcohol consumption on CpG methylation in the differentially methylated regions of H19 and IG-DMR in male gametes—Implications for fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2009, 33, 1615–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, B.; Gangluff, D.; Mengel, M. Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders: Flying under the radar. J. Ark. Med. Soc. 2011, 107, 260–262. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reik, W.; Dean, W.; Walter, J. Epigenetic reprogramming in mammalian development. Science 2001, 293, 1089–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsay, M. Genetic and epigenetic insights into fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Genome Med. 2010, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deltour, L.; Ang, H.L.; Duester, G. Ethanol inhibition of retinoic acid synthesis as a potential mechanism for fetal alcohol syndrome. FASEB J. 1996, 10, 1050–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kot-Leibovich, H.; Fainsod, A. Ethanol induces embryonic malformations by competing for retinaldehyde dehydrogenase activity during vertebrate gastrulation. Dis. Models Mech. 2009, 2, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrs, J.A.; Clendenon, S.G.; Ratcliffe, D.R.; Fielding, S.M.; Liu, Q.; Bosron, W.F. Zebrafish fetal alcohol syndrome model: Effects of ethanol are rescued by retinoic acid supplement. Alcohol 2010, 44, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, R.J.; Godin, E.A.; O’leary-Moore, S.K.; Parnell, S.E.; Sulik, K.K. Genesis of teratogen-induced holoprosencephaly in mice. In American Journal of Medical Genetics Part C: Seminars in Medical Genetics; Wiley Subscription Services, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA; pp. 29–42.
- Li, Y.-X.; Yang, H.-T.; Zdanowicz, M.; Sicklick, J.K.; Qi, Y.; Camp, T.J.; Diehl, A.M. Fetal alcohol exposure impairs Hedgehog cholesterol modification and signaling. Lab. Investig. 2007, 87, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Monte, S.M.; Wands, J.R. Role of central nervous system insulin resistance in fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. J. Popul. Ther. Clin. Pharmacol. = J. De La Ther. Des Popul. Et De La Pharamcologie Clin. 2010, 17, e390. [Google Scholar]
- Haron, M.H.; Powe, D.; Khan, I.A.; Dasmahapatra, A.K. Feasibility of medaka (Oryzias latipes) as an animal model to study fetal alcohol spectrum disorder. In Advances in Molecular Toxicology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 6, pp. 77–128. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen-Kerem, R.; Koren, G. Antioxidants and fetal protection against ethanol teratogenicity: I. Review of the experimental data and implications to humans. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2003, 25, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemma, S.; Vichi, S.; Testai, E. Metabolic and genetic factors contributing to alcohol induced effects and fetal alcohol syndrome. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2007, 31, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisen, J.S.; Weston, J. Development of the neural crest in the zebrafish. Dev. Biol. 1993, 159, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, M.; Singh, N.; Ahsan, K.; Beiriger, A.; Prince, V.E. Neural crest development: Insights from the zebrafish. Dev. Dyn. 2020, 249, 88–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.M.; Garic, A.; Flentke, G.R.; Berres, M.E. Neural crest development in fetal alcohol syndrome. Birth Defects Res. Part C Embryo Today Rev. 2014, 102, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovasio, R.; Battiato, N. Role of early migratory neural crest cells in developmental anomalies induced by ethanol. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2002, 39, 421–422. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Bieberich, E. Prenatal alcohol exposure triggers ceramide-induced apoptosis in neural crest-derived tissues concurrent with defective cranial development. Cell Death Dis. 2010, 1, e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garic, A.; Flentke, G.R.; Amberger, E.; Hernandez, M.; Smith, S.M. CaMKII activation is a novel effector of alcohol’s neurotoxicity in neural crest stem/progenitor cells. J. Neurochem. 2011, 118, 646–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, W.; Crawford, L.; Cooper, O.; Farmer, G.; Thomas, D.; Freeman, B. Ethanol induces the generation of reactive free radicals by neural crest cells in vitro. J. Craniofacial Genet. Dev. Biol. 1990, 10, 277–293. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.y.; Sulik, K.K. Free radicals and ethanol-induced cytotoxicity in neural crest cells. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1996, 20, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, K.K.; Gupta, V.K.; Shirasaka, T. An Update on Fetal Alcohol Syndrome-Pathogenesis, Risks, and Treatment. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2016, 40, 1594–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czarnobaj, J.; Bagnall, K.M.; Bamforth, J.S.; Milos, N.C. The different effects on cranial and trunk neural crest cell behaviour following exposure to a low concentration of alcohol in vitro. Arch. Oral Biol. 2014, 59, 500–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huysseune, A.; Sire, J.-Y.; Van der Heyden, C. Initiation and development of cichlid and zebrafish first-generation teeth: An in vitro study. Biol. Jaarb. (Dodonaea) 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Huysseune, A.; Sire, J.-Y. The role of epithelial remodelling in tooth eruption in larval zebrafish. Cell Tissue Res. 2004, 315, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huysseune, A.; Thesleff, I. Continuous tooth replacement: The possible involvement of epithelial stem cells. Bioessays 2004, 26, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Xu, R.; He, H.; Duan, X. Grading and quantification of dental fluorosis in zebrafish larva. Arch. Oral Biol. 2016, 70, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mork, L.; Crump, G. Zebrafish Craniofacial Development: A Window into Early Patterning. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2015, 115, 235–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atukorala, A.D.S.; Ratnayake, R.K. Cellular and molecular mechanisms in the development of a cleft lip and/or cleft palate; insights from zebrafish (Danio rerio). Anat. Rec. 2020, 304, 1650–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, T.F.; Kimmel, C.B. Musculoskeletal patterning in the pharyngeal segments of the zebrafish embryo. Development 1997, 124, 2945–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, G.; Wellings, S. Electron microscopy of the skin of the teleost, Hippoglossoides elassodon. Z. Für Zellforsch. Und Mikrosk. Anat. 1970, 103, 149–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, R. Cytophysiology of fish chromatophores. In International Review of Cytology; Elsevier: San Diego, CA, USA, 1993; Volume 143, pp. 191–255. [Google Scholar]
- Aspengren, S.; Hedberg, D.; Wallin, M. Studies of pigment transfer between Xenopus laevis melanophores and fibroblasts in vitro and in vivo 1. Pigment Cell Res. 2006, 19, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thody, A.; Shuster, S. Melanophores, melanocytes and melanin: Endocrinology and pharmacology. In Pharmacology of the Skin I; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1989; pp. 257–269. [Google Scholar]
- Dlugos, C.A.; Rabin, R.A. Ethanol effects on three strains of zebrafish: Model system for genetic investigations. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2003, 74, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockwood, B.; Bjerke, S.; Kobayashi, K.; Guo, S. Acute effects of alcohol on larval zebrafish: A genetic system for large-scale screening. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2004, 77, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, M.; Kimmel, C. A two-color acid-free cartilage and bone stain for zebrafish larvae. Biotech. Histochem. 2007, 82, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliesfehani, T. Modified double skeletal staining protocols with Alizarinred and Alcian blue in laboratory animals. Ann. Mil. Health Sci. Res. • Vol 2015, 13, 76. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.C.; Fox, Z.D.; Crimp, J.L.; Littleford, H.E.; Jowdry, A.L.; Jackman, W.R. Hedgehog signaling regulates dental papilla formation and tooth size during zebrafish odontogenesis. Dev. Dyn. 2015, 244, 577–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javidan, Y.; Schilling, T.F. Development of cartilage and bone. Methods Cell Biol. 2004, 76, 415–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillot, R.; Muriach, B.; Rocha, A.; Rotllant, J.; Kelsh, R.N.; Cerdá-Reverter, J.M. Thyroid hormones regulate zebrafish melanogenesis in a gender-specific manner. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, B.K. The neural crest and neural crest cells: Discovery and significance for theories of embryonic organization. J. Biosci. 2008, 33, 781–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trainor, P.A.; Melton, K.R.; Manzanares, M. Origins and plasticity of neural crest cells and their roles in jaw and craniofacial evolution. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2003, 47, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sant’Anna, L.; Tosello, D. Fetal alcohol syndrome and developing craniofacial and dental structures—A review. Orthod. Craniofac. Res. 2006, 9, 172–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanck-Lubarsch, M.; Dirksen, D.; Feldmann, R.; Sauerland, C.; Hohoff, A. Tooth malformations, DMFT index, speech impairment and oral habits in patients with fetal alcohol syndrome. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sltuckey, E.; Blerry, C. The effects of high dose sporadic (binge) alcohol intake in mice. J. Pathol. 1984, 142, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloomquist, R.F. Chemical Manipulation of Dental Patterning in Malawi Cichlids. 2008. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/1853/21816 (accessed on 14 September 2022).
- Sant’Anna, L.B.; Tosello, D.O.; Pasetto, S. Effects of maternal ethanol intake on immunoexpression of epidermal growth factor in developing rat mandibular molar. Arch. Oral Biol. 2005, 50, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthiessen, M.; Rømert, P. Changes of secretory ameloblasts in mini-pig fetuses exposed to ethanol in vivo. J. Dent. Res. 1988, 67, 1402–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terry, D.E.; Chopra, R.K.; Ovenden, J.; Anastassiades, T.P. Differential use of Alcian blue and toluidine blue dyes for the quantification and isolation of anionic glycoconjugates from cell cultures: Application to proteoglycans and a high-molecular-weight glycoprotein synthesized by articular chondrocytes. Anal. Biochem. 2000, 285, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murawski, N.J.; Moore, E.M.; Thomas, J.D.; Riley, E.P. Advances in Diagnosis and Treatment of Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders: From Animal Models to Human Studies. Alcohol Res. 2015, 37, 97–108. [Google Scholar]
- Lovely, C.B. Animal models of gene–alcohol interactions. Birth Defects Res. 2020, 112, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, H.C.; Diaz-Granados, J.L.; Randall, C.L. Teratogenic actions of ethanol in the mouse: A minireview. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1996, 55, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raterman, S.T.; Metz, J.R.; Wagener, F.; Von den Hoff, J.W. Zebrafish Models of Craniofacial Malformations: Interactions of Environmental Factors. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 600926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fushimi, S.; Wada, N.; Nohno, T.; Tomita, M.; Saijoh, K.; Sunami, S.; Katsuyama, H. 17beta-Estradiol inhibits chondrogenesis in the skull development of zebrafish embryos. Aquat. Toxicol. 2009, 95, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.-J.; Brand, M.; Heisenberg, C.-P.; Beuchle, D.; Furutani-Seiki, M.; Kelsh, R.N.; Warga, R.M.; Granato, M.; Haffter, P.; Hammerschmidt, M. Mutations affecting neurogenesis and brain morphology in the zebrafish, Danio rerio. Development 1996, 123, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schilling, T.F.; Piotrowski, T.; Grandel, H.; Brand, M.; Heisenberg, C.-P.; Jiang, Y.-J.; Beuchle, D.; Hammerschmidt, M.; Kane, D.A.; Mullins, M.C. Jaw and branchial arch mutants in zebrafish I: Branchial arches. Development 1996, 123, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halpern, M.E.; Ho, R.K.; Walker, C.; Kimmel, C.B. Induction of muscle pioneers and floor plate is distinguished by the zebrafish no tail mutation. Cell 1993, 75, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odenthal, J.; Haffter, P.; Vogelsang, E.; Brand, M.; Van Eeden, F.; Furutani-Seiki, M.; Granato, M.; Hammerschmidt, M.; Heisenberg, C.-P.; Jiang, Y.-J. Mutations affecting the formation of the notochord in the zebrafish, Danio rerio. Development 1996, 123, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Azimian Zavareh, P.; Silva, P.; Gimhani, N.; Atukorallaya, D. Effect of Embryonic Alcohol Exposure on Craniofacial and Skin Melanocyte Development: Insights from Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Toxics 2022, 10, 544. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10090544
Azimian Zavareh P, Silva P, Gimhani N, Atukorallaya D. Effect of Embryonic Alcohol Exposure on Craniofacial and Skin Melanocyte Development: Insights from Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Toxics. 2022; 10(9):544. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10090544
Chicago/Turabian StyleAzimian Zavareh, Parnia, Praneeth Silva, Nuwanthika Gimhani, and Devi Atukorallaya. 2022. "Effect of Embryonic Alcohol Exposure on Craniofacial and Skin Melanocyte Development: Insights from Zebrafish (Danio rerio)" Toxics 10, no. 9: 544. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10090544
APA StyleAzimian Zavareh, P., Silva, P., Gimhani, N., & Atukorallaya, D. (2022). Effect of Embryonic Alcohol Exposure on Craniofacial and Skin Melanocyte Development: Insights from Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Toxics, 10(9), 544. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10090544








