Disinfection through Advance Oxidation Processes: Optimization and Application on Real Wastewater Matrices
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strain Maintenance and Inoculum
2.2. Disinfection Assays
2.2.1. FP Disinfection Assays
2.2.2. FLP Disinfection Assays
2.3. Design of Experiments with Response Surface Methodology
2.4. Analytical Methods
2.4.1. Disinfection Efficiency
2.4.2. Total Organic Carbon and Chemical Oxygen Demand
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preliminary Assays
3.2. CCD Experiments
3.3. Response Surfaces FP
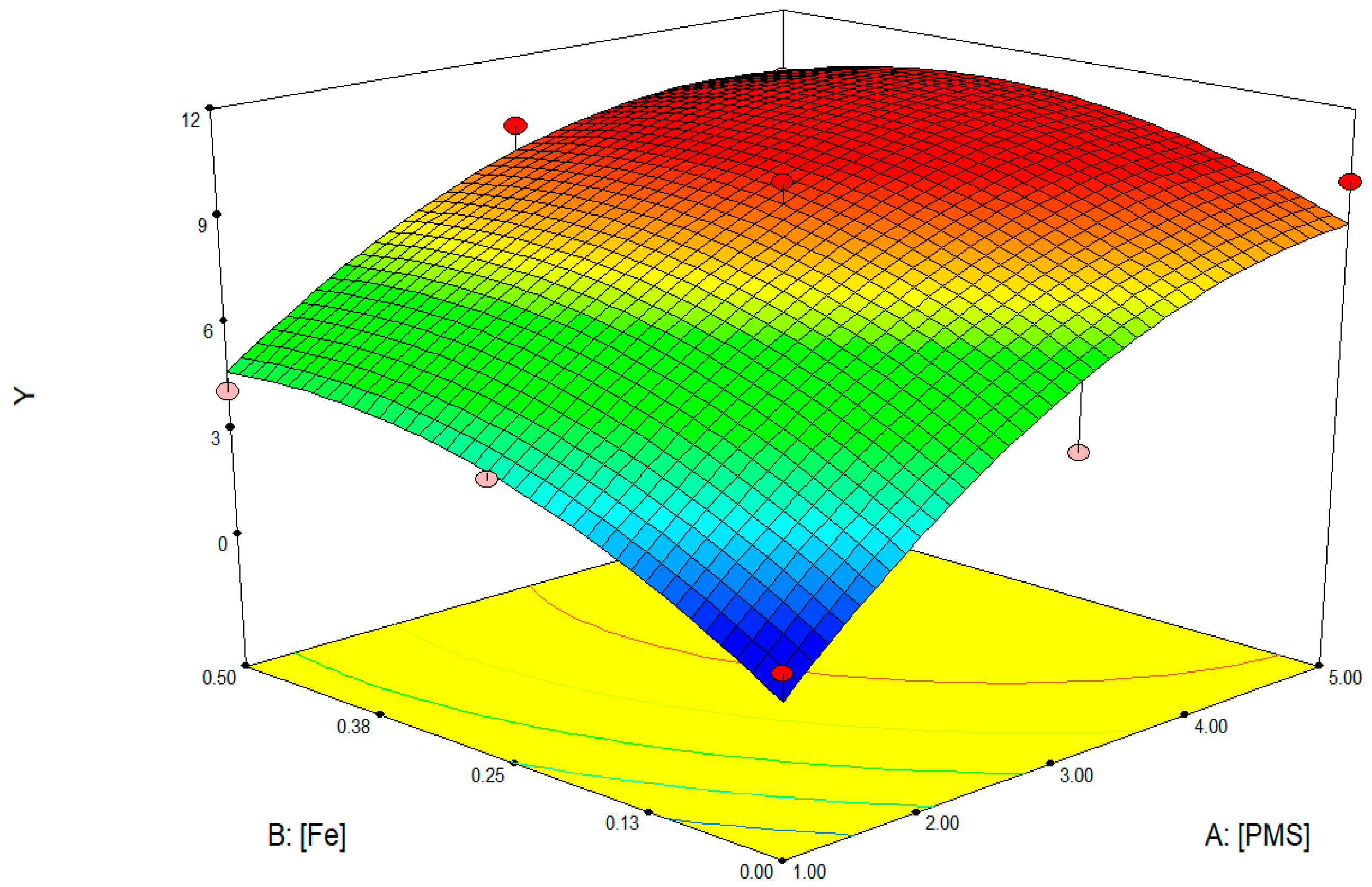
3.4. Response Surfaces FLP
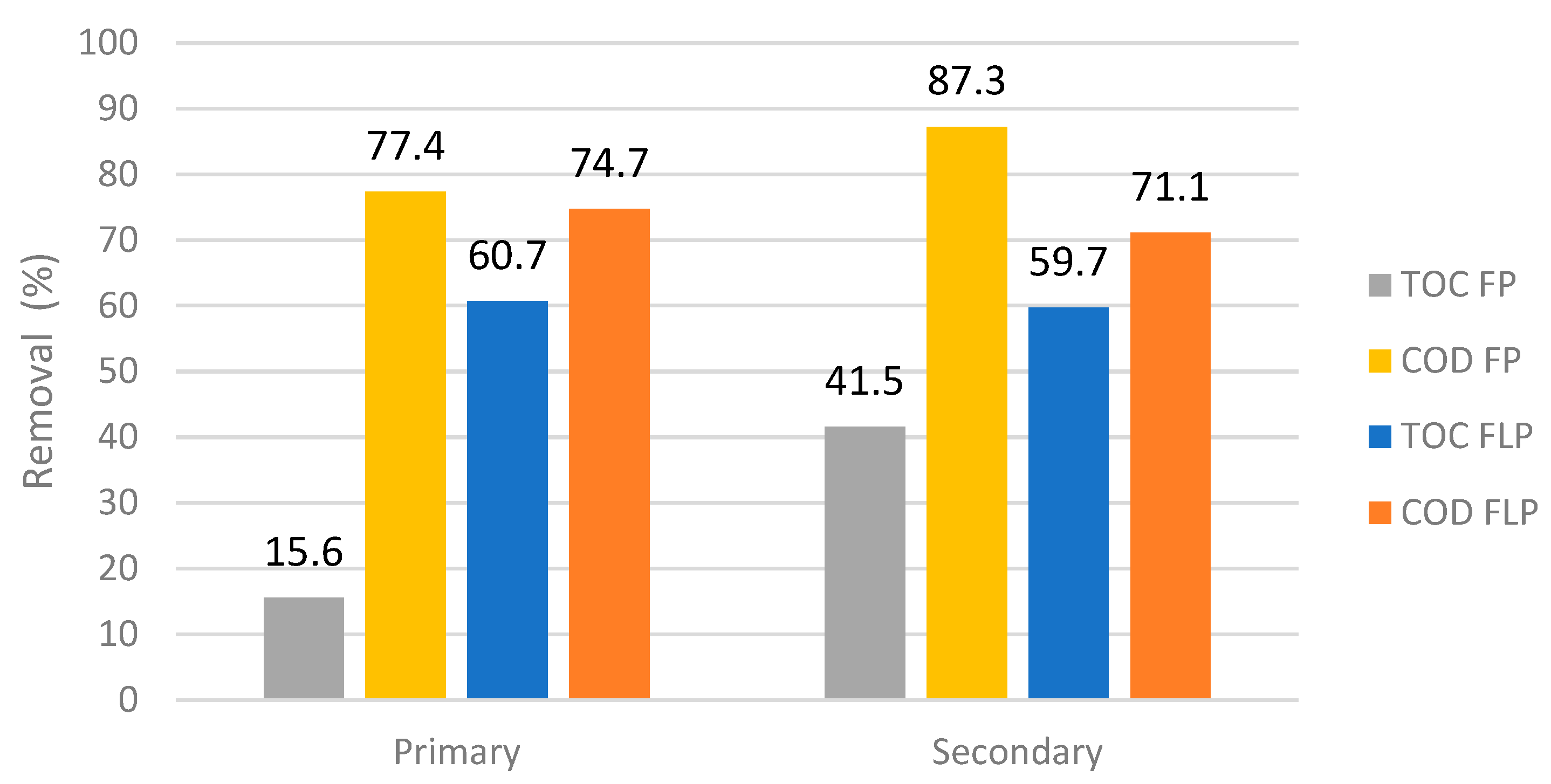
3.5. Optimization and Validation in Real Wastewater Plant Matrices
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, T.; Li, W.; Ma, Y.; Liu, J. Sewers Induce Changes in the Chemical Characteristics, Bacterial Communities, and Pathogen Distribution of Sewage and Greywater. Environ. Res. 2020, 187, 109628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, S.Y.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Y.W.; Liu, G.L.; Wang, D.L.; Wu, H.M.; Chen, D.; Liu, H. Fabrication of Polypyrrole Nanowire Arrays-Modified Electrode for Point-of-Use Water Disinfection via Low-Voltage Electroporation. Water Res. 2021, 207, 117825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentino, A.; Lofrano, G.; Cucciniello, R.; Carotenuto, M.; Motta, O.; Proto, A.; Rizzo, L. Disinfection of Roof Harvested Rainwater Inoculated with E. Coli and Enterococcus and Post-Treatment Bacterial Regrowth: Conventional vs Solar Driven Advanced Oxidation Processes. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 801, 149763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-D.; Duan, X.; Zhou, X.; Wang, R.; Wang, S.; Ren, N.-Q.; Ho, S.H. Advanced Oxidation Processes for Water Disinfection: Features, Mechanisms and Prospects. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 409, 128207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasani, M.; Chudyk, J.; Murray, K.; Lim, L.T.; Lubitz, D.; Warriner, K. Inactivation of Salmonella, Listeria Monocytogenes, Aspergillus and Penicillium on Lemons Using Advanced Oxidation Process Optimized through Response Surface Methodology. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2019, 54, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniakova, G.; Salmerón, I.; Polo-López, M.I.; Oller, I.; Rizzo, L.; Malato, S. Simultaneous Removal of Contaminants of Emerging Concern and Pathogens from Urban Wastewater by Homogeneous Solar Driven Advanced Oxidation Processes. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 766, 144320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oturan, M.A.; Brillas, E. Electrochemical Advanced Oxidation Processes (EAOPs) for Environmental Applications. Port. Electrochim. Acta 2007, 25, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira Ferraz, N.; Nogueira, A.E.; Candian, F.; Marcos, F.; Machado, V.A.; Rojas Rocca, R.; Assaf, M.; Jesus, Y.; Asencios, O. CeO2-Nb2O5 Photocatalysts for Degradation of Organic Pollutants in Water. Rare Met. 2020, 39, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Wang, W.; Pan, X.; Li, C. Improving the Fenton Catalytic Performance of FeOCl Using an Electron Mediator. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Vione, D.; Rivoira, L.; Carena, L.; Castiglioni, M.; Bruzzoniti, M.C. A Review on the Degradation of Pollutants by Fenton-like Systems Based on Zero-Valent Iron and Persulfate: Effects of Reduction Potentials, Ph, and Anions Occurring in Waste Waters. Molecules 2021, 26, 4584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Zeng, G.; Huang, D.; Lai, C.; Xu, P.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y. Hydroxyl Radicals Based Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) for Remediation of Soils Contaminated with Organic Compounds: A Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 284, 582–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhl, L.; Gerstel, A.; Chabalier, M.; Dukan, S. Hydrogen Peroxide Induced Cell Death: One or Two Modes of Action? Heliyon 2015, 1, E00049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diao, H.F.; Li, X.Y.; Gu, J.D.; Shi, H.C.; Xie, Z.M. Electron Microscopic Investigation of the Bactericidal Action of Electrochemical Disinfection in Comparison with Chlorination, Ozonation and Fenton Reaction. Process Biochem. 2004, 39, 1421–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Dong, C.; Deng, Y.; Ji, J.; Bao, S.; Chen, C.; Shen, B.; Zhang, J.; Xing, M. Molybdenum Sulfide Co-Catalytic Fenton Reaction for Rapid and Efficient Inactivation of Escherichia Coli. Water Res. 2018, 145, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Bai, L.; Shi, Y.; Wei, Z.; Spinney, R.; Göktaş, R.K.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Xiao, R. Simultaneous Disinfection of E. Faecalis and Degradation of Carbamazepine by Sulfate Radicals: An Experimental and Modelling Study. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakis, S.; Lin, K.Y.A.; Ghanbari, F. A Review of the Recent Advances on the Treatment of Industrial Wastewaters by Sulfate Radical-Based Advanced Oxidation Processes (SR-AOPs). Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 406, 127083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Li, R.; Li, C.; Wang, W. Piezo-Promoted Regeneration of Fe2+ Boosts Peroxydisulfate Activation by Bi2Fe4O9 Nanosheets. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2022, 310, 121330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Cheng, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Luo, K.; He, D.; Pan, X. Rapid Removal of Organic Micropollutants by Heterogeneous Peroxymonosulfate Catalysis over a Wide PH Range: Performance, Mechanism and Economic Analysis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 248, 117023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Liu, K.; Bai, L.; Minakata, D.; Seo, Y.; Kaya Göktaş, R.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Tang, C.J.; Wei, Z.; Spinney, R. Inactivation of Pathogenic Microorganisms by Sulfate Radical: Present and Future. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 371, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wordofa, D.N.; Walker, S.L.; Liu, H. Sulfate Radical-Induced Disinfection of Pathogenic Escherichia Coli O157:H7 via Iron-Activated Persulfate. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2017, 4, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Chueca, J.; Moreira, S.I.; Lucas, M.S.; Fernandes, J.R.; Tavares, P.B.; Sampaio, A.; Peres, J.A. Disinfection of Simulated and Real Winery Wastewater Using Sulphate Radicals: Peroxymonosulphate/Transition Metal/UV-A LED Oxidation. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 149, 805–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldrovandi, A.; Marsili, E.; Stante, L.; Paganin, P.; Tabacchioni, S.; Giordano, A. Sustainable Power Production in a Membrane-Less and Mediator-Less Synthetic Wastewater Microbial Fuel Cell. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 3252–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raffellini, S.; Schenk, M.; Guerrero, S.; Alzamora, S.M. Kinetics of Escherichia Coli Inactivation Employing Hydrogen Peroxide at Varying Temperatures, PH and Concentrations. Food Control 2011, 22, 920–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Fu, C.; Zhang, X.; Feng, J.; Xu, Z.; Song, Q. Degradation of Bisphenol A by Persulfate Coupled with Dithionite: Optimization Using Response Surface Methodology and Pathway. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 699, 134258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Li, J. Improved Disinfection Performance towards Human Adenoviruses Using an Efficient Metal-Free Heterojunction in a Vis-LED Photocatalytic Membrane Reactor: Operation Analysis and Optimization. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 392, 123687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dowd, K.; Pillai, S.C. Photo-Fenton Disinfection at near Neutral PH: Process, Parameter Optimization and Recent Advances. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorontsov, A.V. Advancing Fenton and Photo-Fenton Water Treatment through the Catalyst Design. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 372, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Von Gunten, U.; Kim, J.H. Persulfate-Based Advanced Oxidation: Critical Assessment of Opportunities and Roadblocks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 3064–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lado Ribeiro, A.R.; Moreira, N.F.F.; Li Puma, G.; Silva, A.M.T. Impact of Water Matrix on the Removal of Micropollutants by [anced Oxidation Technologies. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 363, 155–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, L. Sulfate-Radical Induced Removal of Organic Micro-Pollutants from Aqueous Solution Influence of Natural Water Constituents. Thesis, Université de Lyon, Lyon, France, 2017. NNT: 2017LYSE1171. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Sulfate-radical-Induced-Removal-of-Organic-from-of-Zhou/c8ac5545c99a6a0dc8300b9d47a7cfee587946ca (accessed on 24 August 2022).


| Factors | Variables | Levels | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (−1) | Central (0) | High (−1) | ||
| [H2O2] (mM) | X1 | 44.12 | 88.24 | 132.36 |
| [Fe+2] (mM) | X2 | 0.00 | 0.29 | 0.58 |
| pH | X3 | 3 | 5 | 7 |
| Factors | Symbols | Levels | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (−1) | Central (0) | High (−1) | ||
| [PMS] (mM) | X4 | 1.00 | 3.00 | 5.00 |
| [Fe+2] (mM) | X5 | 0.00 | 0.29 | 0.58 |
| Run | X1 | X2 | X3 | [H2O2] (mM) | [Fe+2] (mM) | pH | Y1 (5 min) | Y2 (15 min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | 44.12 | 0.00 | 3 | 0.246 | 1.125 |
| 2 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 132.36 | 0.00 | 3 | 0.846 | 4.358 |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | −1 | 88.24 | 0.29 | 3 | 3.023 | 4.406 |
| 4 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 44.12 | 0.58 | 3 | 3.342 | 4.437 |
| 5 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 132.36 | 0.58 | 3 | 4.694 | 6.016 |
| 6 | 0 | −1 | 0 | 88.24 | 0.00 | 5 | 1.203 | 2.295 |
| 7 | −1 | 0 | 0 | 44.12 | 0.29 | 5 | 1.523 | 2.422 |
| 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 88.24 | 0.29 | 5 | 3.257 | 4.448 |
| 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 88.24 | 0.29 | 5 | 3.257 | 4.448 |
| 10 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 132.36 | 0.29 | 5 | 4.348 | 5.470 |
| 11 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 88.24 | 0.58 | 5 | 4.125 | 4.602 |
| 12 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 44.12 | 0.00 | 7 | 0.083 | 0.152 |
| 13 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 132.36 | 0.00 | 7 | 0.873 | 3.861 |
| 14 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 88.24 | 0.29 | 7 | 0.883 | 1.561 |
| 15 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 44.12 | 0.58 | 7 | 2.750 | 2.638 |
| 16 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 132.36 | 0.58 | 7 | 2.809 | 4.254 |
| Run | X4 | X5 | [PMS] (mM) | [Fe+2] (mM) | Y1 (5 min) | Y2 (15 min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | −1 | 3 | 0.00 | 1.485 | 4.530 |
| 2 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 0.50 | 1.790 | 4.138 |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0.25 | 10.000 | 10.000 |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0.25 | 10.000 | 10.000 |
| 5 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 0.00 | 0.000 | 1.043 |
| 6 | 1 | −1 | 5 | 0.00 | 10.000 | 10.000 |
| 7 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 0.50 | 10.000 | 10.000 |
| 8 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 0.25 | 0.822 | 3.806 |
| 9 | 1 | 0 | 5 | 0.25 | 10.000 | 10.000 |
| 10 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 0.50 | 10.000 | 10.000 |
| Sum of | Mean | F | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source | Squares | df | Square | Value | Prob > F | |
| Model | 38.1519 | 9 | 4.2391 | 11.8137 | 0.0035 | significant |
| X1 | 17.3821 | 1 | 17.3821 | 48.4409 | 0.0004 | significant |
| X2 | 10.3153 | 1 | 10.3153 | 28.7469 | 0.0017 | significant |
| X3 | 6.2019 | 1 | 6.2019 | 17.2835 | 0.006 | significant |
| X1X2 | 1.7541 | 1 | 1.7541 | 4.8883 | 0.0691 | |
| X1X3 | 0.0329 | 1 | 0.0329 | 0.0917 | 0.7722 | |
| X2X3 | 0.5471 | 1 | 0.5471 | 1.5248 | 0.2631 | |
| X12 | 0.1966 | 1 | 0.1966 | 0.5480 | 0.4871 | |
| X22 | 0.1328 | 1 | 0.1328 | 0.3702 | 0.5652 | |
| X32 | 1.2527 | 1 | 1.2527 | 3.4911 | 0.1109 | |
| Residual | 2.1530 | 6 | 0.3588 | |||
| Pure Error | 0.0000 | 1 | 0 | |||
| R2 | 0.947 | R2ad | 0.866 | R2pred | 0.656 | Adeq precision 13.87 |
| Sum of | Mean | F | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source | Squares | df | Square | Value | Prob > F | ||
| Model | 104.5328 | 5 | 20.9066 | 10.1898 | 0.0215 | significant | |
| X4 | 73.5910 | 1 | 73.5910 | 35.8681 | 0.0039 | significant | |
| X5 | 12.2255 | 1 | 12.2255 | 5.9587 | 0.0711 | ||
| X4X5 | 2.3945 | 1 | 2.3945 | 1.1671 | 0.3408 | ||
| X42 | 8.2602 | 1 | 8.2602 | 4.0260 | 0.1153 | ||
| X52 | 5.3850 | 1 | 5.3850 | 2.6247 | 0.1805 | ||
| Residual | 8.2068 | 4 | 2.0517 | ||||
| Pure Error | 0.0000 | 1 | 0 | ||||
| R2 | 0.927 | R2ad | 0.836 | R2pred | 0.494 | Adeq precision | 9.666 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blanco-Canella, P.; Lama, G.; Sanromán, M.A.; Pazos, M. Disinfection through Advance Oxidation Processes: Optimization and Application on Real Wastewater Matrices. Toxics 2022, 10, 512. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10090512
Blanco-Canella P, Lama G, Sanromán MA, Pazos M. Disinfection through Advance Oxidation Processes: Optimization and Application on Real Wastewater Matrices. Toxics. 2022; 10(9):512. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10090512
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlanco-Canella, Pablo, Gabriela Lama, Mª Angeles Sanromán, and Marta Pazos. 2022. "Disinfection through Advance Oxidation Processes: Optimization and Application on Real Wastewater Matrices" Toxics 10, no. 9: 512. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10090512
APA StyleBlanco-Canella, P., Lama, G., Sanromán, M. A., & Pazos, M. (2022). Disinfection through Advance Oxidation Processes: Optimization and Application on Real Wastewater Matrices. Toxics, 10(9), 512. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10090512








