Life Cycle Exposure to Cyhalofop-Butyl Induced Reproductive Toxicity in Zebrafish
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Zebrafish Rearing and CyB Exposure
2.3. Gonadal Histological Examination
2.4. E2, T, 11-KT and VTG Concentrations Measurement
2.5. Gene Expression Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
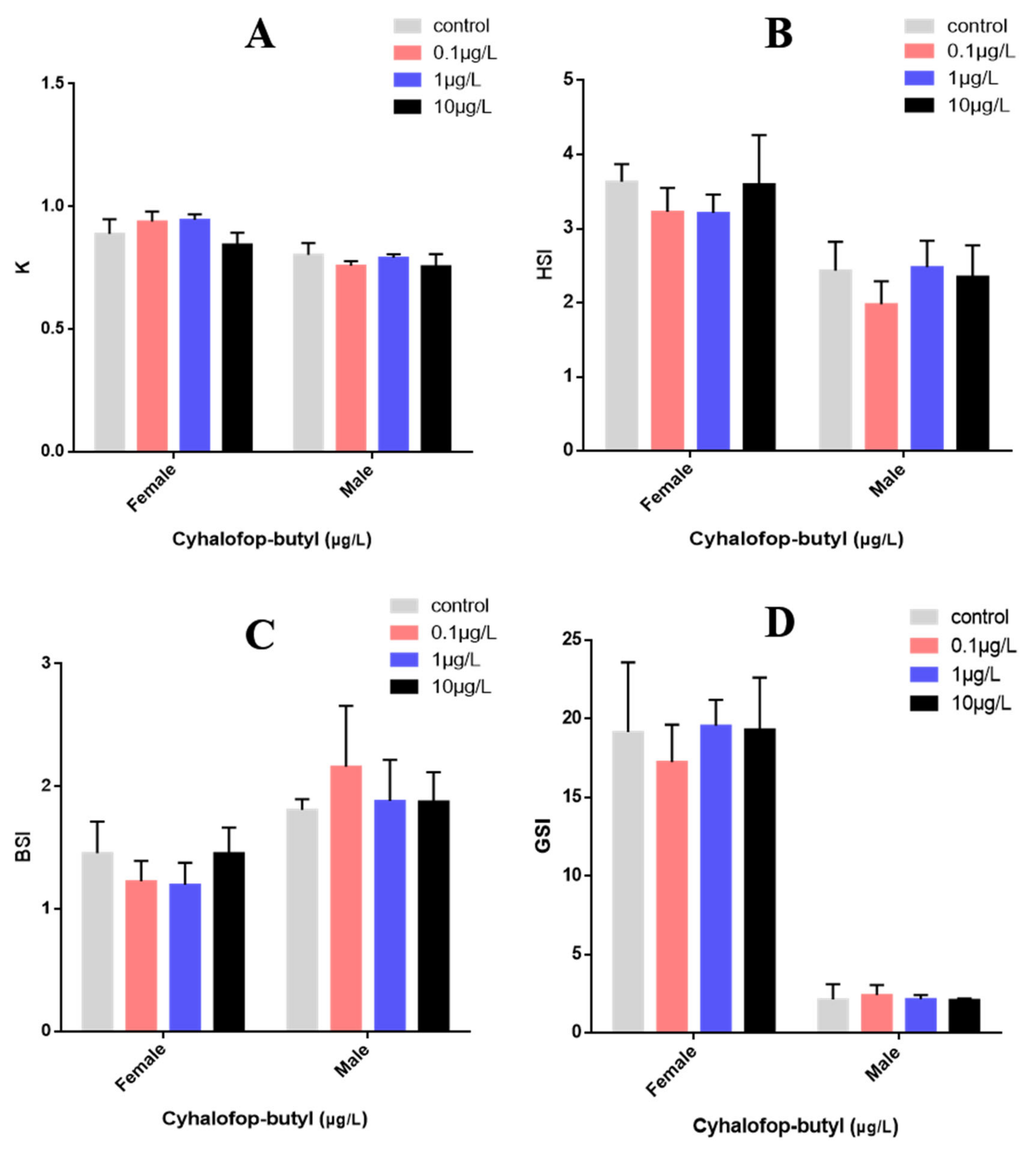
3.1. Development of Zebrafish
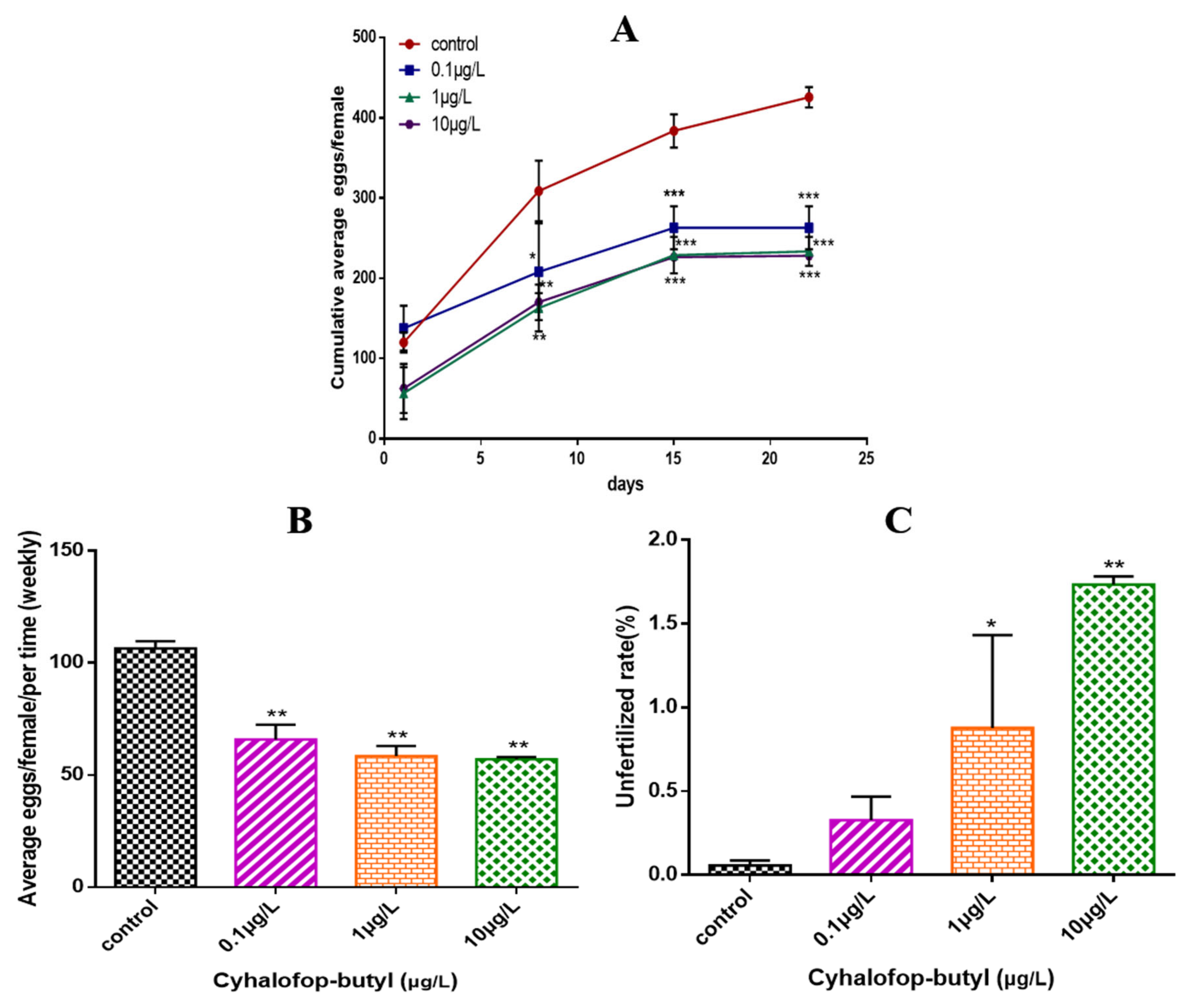
3.2. Measurement of Zebrafish Fertility
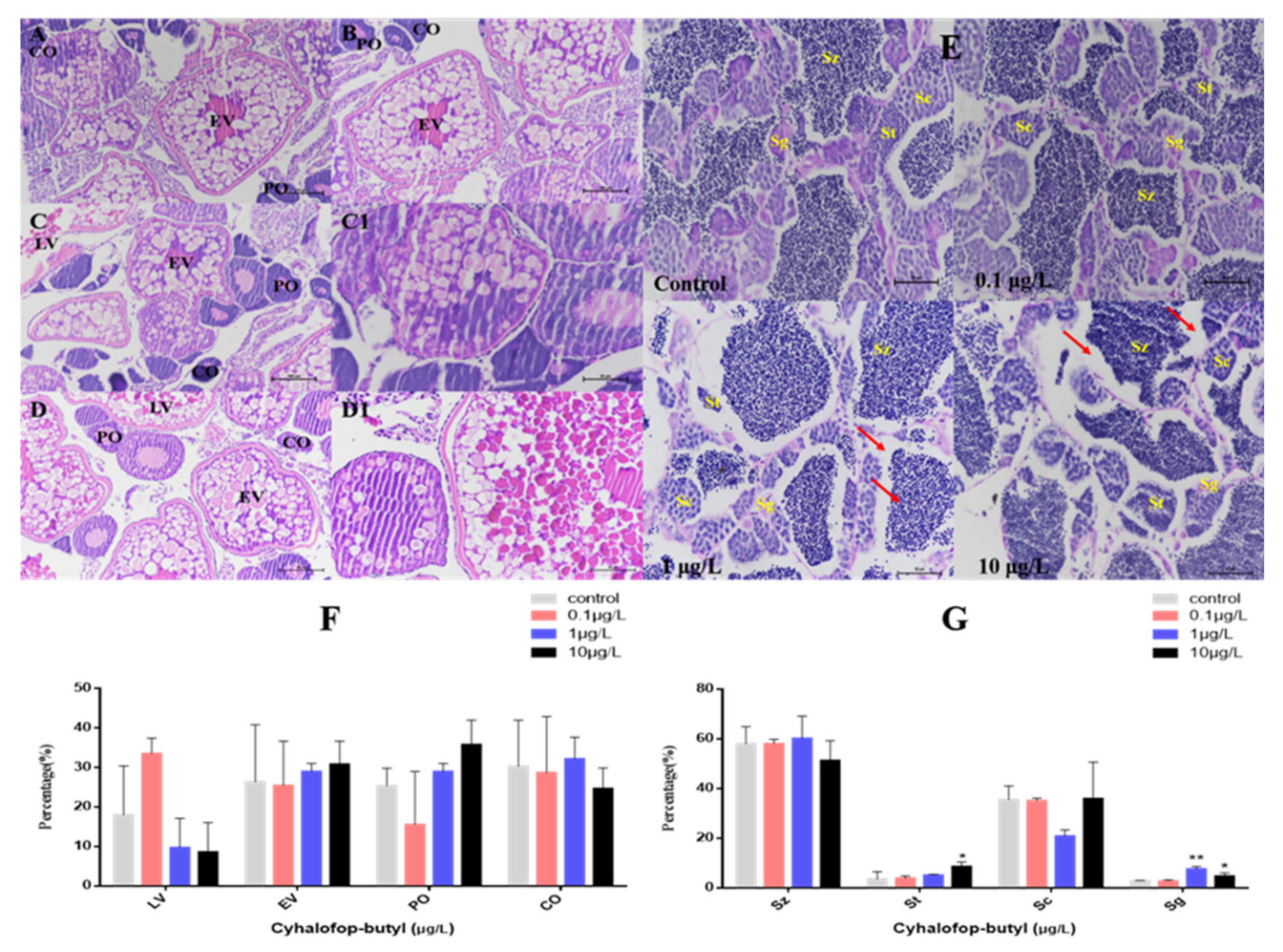
3.3. Gonadal Histological Examination
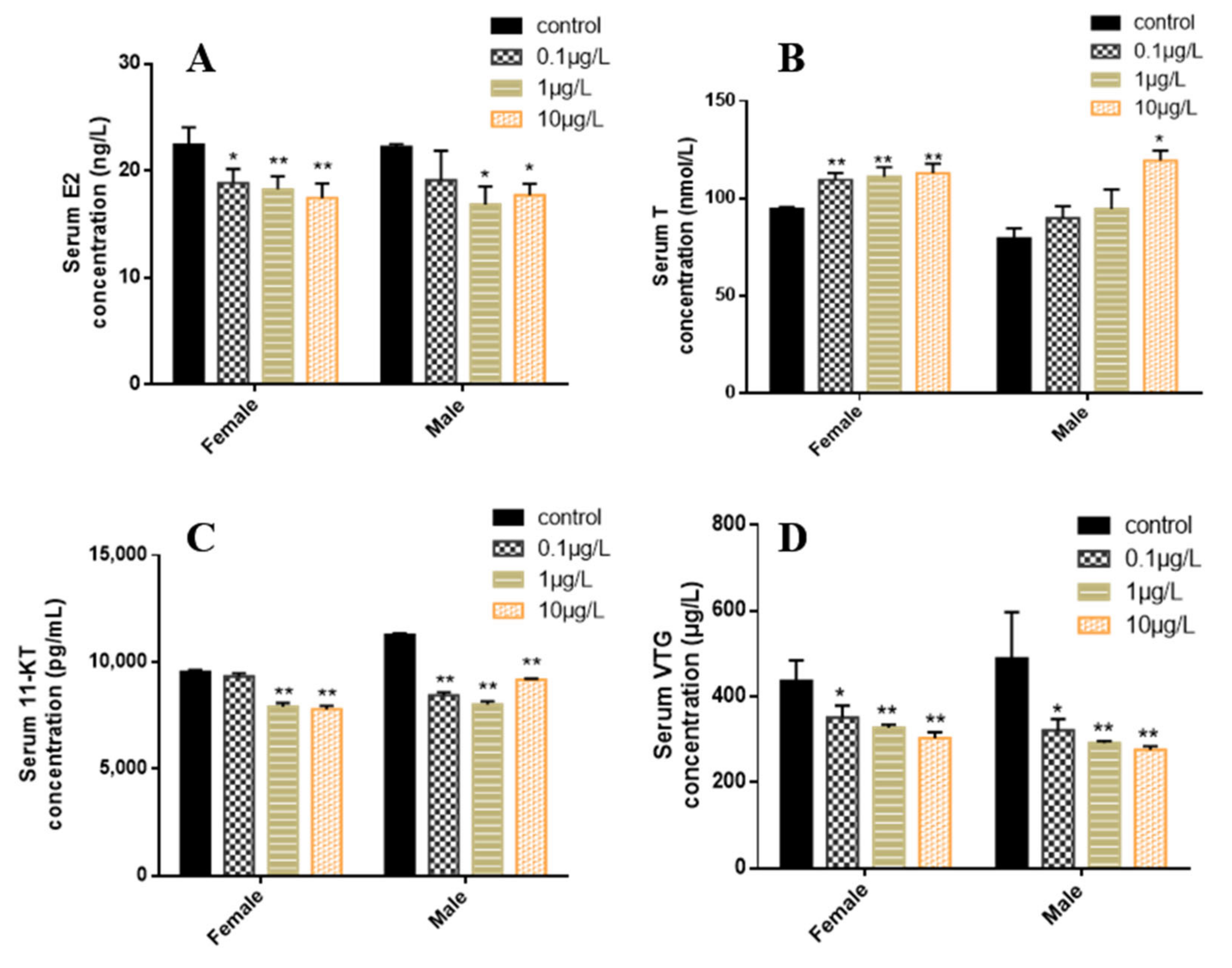
3.4. Contents of Sex Steroid Hormones and VTG
3.5. Gene Expression Alteration Related to the HPGL Axis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Zebrafish Rearing Methods during Exposure
Appendix B. The Method of Sex Steroid Hormone and VTG Concentrations Measurement
- (1)
- Add 10 μL of diluted serum supernatant and 40 μL of sample diluent into antibody-coated microtiter plates.
- (2)
- After a series of incubation, washing plates, enzyme catalysis, incubation, washing plates, color rendering and termination, the absorbance was measured at 450 nm using a microplate reader.
- (3)
- Calculate the actual concentrations of E2, T, 11-KT and VTG of serum sample according to the standard curve.
References
- Bleau, H.; Daniel, C.; Chevalier, G.; Van Tra, H.; Hontela, A. Effects of acute exposure to mercury chloride and methylmercury on plasma cortisol, T3, T4, glucose and liver glycogen in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquat. Toxicol. 1996, 34, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.; Liu, X.; Wang, C.; Zheng, M.; Li, X.; Qiu, L. Acute and short-term developmental toxicity of cyhalofop-butyl to zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 10080–10089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondhia, S.; Khare, R.R. Soil adsorption studies of a rice herbicide, cyhalofop-butyl, in two texturally different soils of India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 5969–5976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H. Determination and study on dissipation and residue determination of cyhalofop-butyl and its metabolite using HPLC-MS/MS in a rice ecosystem. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 6959–6967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalsing, A.; Tronquini, S.M.; Mariot, C.H.P.; Rubin, R.D.S.; Bundt, A.D.C.; Fadin, D.A.; Marques, L.H. Susceptibility of Echinochloa populations to cyhalofop-butyl in Southern region of Brazil and impact of the weed phenology on its efficacy of control. Ciência Rural. 2017, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.-H.; Mei, H.-X.; Ru, Z.-J.; Li, L.-L. Analytical Study on Volatilization of Main Dosage Forms and Preparations of Cyhalofop-butyl by Thermogravimetric Analysis. Agro Chem. 2020, 59, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, T.; Shi, C.; Qin, Z.; Peng, M.; Jia, B.; Xia, X. Toxic effects of cyhalofop-butyl to Misgurnus anguillicaudatus. J. Henan Agric. Sci. 2019, 48, 162–167. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, S.; Di, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Cai, J.; Deng, W. Target-site resistance to cyhalofop-butyl in bearded sprangletop (Diplachne fusca) from China. Weed Sci. 2019, 67, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phong, T.K.; Yoshino, K.; Hiramatsu, K.; Harada, M.; Inoue, T. Pesticide discharge and water management in a paddy catchment in Japan. Paddy Water Environ. 2010, 8, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Huang, F.; Xu, Z. Residue dynamics of 10% fenoxaprop-p-ethyl + cyhalofop-butyl EC in rice. J. Ecol. Rural. Environ. 2008, 24, 51–54. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, B.; Zou, L.; Zhang, H.; Cao, Z.; Liao, X.; Shen, T.; Xiong, G.; Xiao, J.; Liu, H.; Lu, H. Effects of cyhalofop-butyl on the developmental toxicity and immunotoxicity in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Chemosphere 2021, 263, 127849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Mu, X.; Wang, K.; Chai, T.; Yang, Y.; Qiu, L.; Wang, C. Cyhalofop-butyl has the potential to induce developmental toxicity, oxidative stress and apoptosis in early life stage of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Pollut. 2015, 203, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.; Wang, P.; Wan, R.; Huo, W.; Chang, Z. Toxic effects of cyhalofop-butyl on embryos of the Yellow River carp (Cyprinus carpio var.): Alters embryos hatching, development failure, mortality of embryos, and apoptosis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 24305–24315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Zhao, X.; Wu, S.; Cheng, L.; Wang, Y.; Chang, T.; Yu, R.; Ping, L. Toxicity and risk of herbicide cyhalofop-butyl on Rana limnocharis. Acta Agric. Zhejiangensis 2011, 23, 771–775. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, R.H.; Nagahama, Y. Sex determination and sex differentiation in fish: An overview of genetic, physiological, and environmental influences. Aquaculture 2002, 208, 191–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, K.; Liu, X.; Lee, S.; Kang, S.; Kho, Y.; Giesy, J.P.; Choi, K. Effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on hormones and genes of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonad axis, and reproduction of zebrafish. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 254–255, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilscherova, K.; Jones, P.D.; Gracia, T.; Newsted, J.L.; Zhang, X.W.; Sanderson, J.T.; Yu, R.M.K.; Wu, R.S.S.; Giesy, J.P. Assessment of the effects of chemicals on the expression of ten steroidogenic genes in the H295R cell line using real-time PCR. Toxicol. Sci. 2004, 81, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plant, T.M. The hypothalamo-pituitary-gonadal axis. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 226, T41–T54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villeneuve, D.L.; Blake, L.S.; Brodin, J.D.; Cavallin, J.E.; Durhan, E.J.; Jensen, K.M.; Kahl, M.D.; Makynen, E.A.; Martinovic, D.; Mueller, N.D.; et al. Effects of a 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase inhibitor, trilostane, on the fathead minnow reproductive axis. Toxicol. Sci. 2008, 104, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Huang, W.; Zhong, C.R.; Luo, D.J.; Li, S.F.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Hu, W. Defining Global Gene Expression Changes of the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Gonadal Axis in Female sGnRH-Antisense Transgenic Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio). PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.F.; Ke, M.J.; Fan, X.J.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, Y.C.; Lu, T.; Sun, L.W.; Qian, H.F. Reproductive and endocrine-disrupting toxicity of Microcystis aeruginosa in female zebrafish. Chemosphere 2018, 192, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiser, U.B. The Pituitary, 3rd ed. In Gonadotropin Hormones; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011; pp. 205–260. [Google Scholar]
- Son, Y.L.; Ubuka, T.; Tsutsui, K. Regulation of stress response on the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis via gonadotropin-inhibitory hormone. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2022, 64, 100953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, D.; Schnell, S.; Porte, C. Can pharmaceuticals interfere with the synthesis of active androgens in male fish? An in vitro study. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 2250–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clelland, E.; Peng, C. Endocrine/paracrine control of zebrafish ovarian development. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2009, 312, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trant, J.M.; Gavasso, S.; Ackers, J.; Chung, B.C.; Place, A.R. Developmental expression of cytochrome P450 aromatase genes (CYP19a and CYP19b) in zebrafish fry (Danio rerio). J. Exp. Zool. 2001, 290, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busby, E.R.; Roch, G.J.; Sherwood, N.M. Endocrinology of zebrafish: A small fish with a large gene pool. Zebrafish 2010, 29, 173–247. [Google Scholar]
- Nagahama, Y.; Yamashita, M. Regulation of oocyte maturation in fish. Dev. Growth Differ. 2008, 50, S195–S219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofikitis, N.; Giotitsas, N.; Tsounapi, P.; Baltogiannis, D.; Giannakis, D.; Pardalidis, N. Hormonal regulation of spermatogenesis and spermiogenesis. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 109, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, M.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Qian, L.; Chen, X.; Zhao, F.; Zhao, W.; Zhong, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, C. Toxic effects of broflanilide exposure on development of zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos and its potential cardiotoxicity mechanism. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 286, 117481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Fish short-term toxicity test on embryo and sac-fry stages. In OECD Guideline for Testing of Chemicals; OECD: Paris, France, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Di Paola, D.; Natale, S.; Gugliandolo, E.; Cordaro, M.; Crupi, R.; Siracusa, R.; D’Amico, R.; Fusco, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Assessment of 2-Pentadecyl-2-oxazoline Role on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation on Early Stage Development of Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Life 2022, 12, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Qi, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Yuan, L.; Qian, L.; Li, T.; Huang, Y.; Wang, C.; Guo, Y.; et al. Environmental level of bisphenol F induced reproductive toxicity toward zebrafish. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 149992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, L.; Qi, S.; Zhang, J.; Duan, M.; Schlenk, D.; Jiang, J.; Wang, C. Exposure to Boscalid Induces Reproductive Toxicity of Zebrafish by Gender-Specific Alterations in Steroidogenesis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 14275–14287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcand-Hoy, L.D.; Benson, W.H. Fish reproduction: An ecologically relevant indicator of endocrine disruption. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1998, 17, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, M.Z.A.; Fahmy, M.A. Effects of some environmental factors on the population density and species diversity of phytoplankton in Bitter Lakes, Egypt. Rend. Lincei 2015, 27, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Verma, S.K. Impacts of herbicide pendimethalin on sex steroid level, plasma vitellogenin concentration and aromatase activity in teleost Clarias batrachus (Linnaeus). Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 75, 103324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soni, R.; Verma, S.K. Impact of herbicide pretilachlor on reproductive physiology of walking catfish, Clarias batrachus (Linnaeus). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 46, 2065–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uren Webster, T.M.; Laing, L.V.; Florance, H.; Santos, E.M. Effects of glyphosate and its formulation, roundup, on reproduction in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 1271–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyle, G.G.; Rajotte, J.W.; Couture, P. Effects of industrial metals on wild fish populations along a metal contamination gradient. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2005, 61, 287–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Belt, K.; Wester, P.W.; Van der Ven, L.T.M.; Verheyen, R.; Witters, H. Effects of ethynylestradiol on the reproductive physiology in zebrafish (Danio rerio): Time dependency and reversibility. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2002, 21, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.; Martyniuk, C.J.; Wu, P.; Zhao, F.; Pang, S.; Wang, C.; Qiu, L. Long-Term Exposure to Environmental Concentrations of Azoxystrobin Delays Sexual Development and Alters Reproduction in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 1672–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.; Zhu, L.; Li, H.; Yu, S.; Wang, C.; Qiu, L. Reproductive toxicity of azoxystrobin to adult zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 1109–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navas, J.M.; Segner, H. Vitellogenin synthesis in primary cultures of fish liver cells as endpoint for in vitro screening of the (anti)estrogenic activity of chemical substances. Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 80, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Chan, K.M. Regulation of vitellogenin (vtg1) and estrogen receptor (er) gene expression in zebrafish (Danio rerio) following the administration of Cd(2)(+) and 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD). Chemosphere 2016, 147, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flouriot, G.; Pakdel, F.; Valotaire, Y. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of rainbow trout estrogen receptor and vitellogenin gene expression. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1996, 124, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundararaj, B.I.; Goswami, S.V.; Lamba, V.J. Role of Testosterone, Estradiol-17-Beta, and Cortisol During Vitellogenin Synthesis in the Catfish, Heteropneustes-Fossilis (BLOCH). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 1982, 48, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phumyu, N.; Boonanuntanasarn, S.; Jangprai, A.; Yoshizaki, G.; Na-Nakorn, U. Pubertal effects of 17alpha-methyltestosterone on GH-IGF-related genes of the hypothalamic-pituitary-liver-gonadal axis and other biological parameters in male, female and sex-reversed Nile tilapia. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2012, 177, 278–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weltzien, F.A.; Andersson, E.; Andersen, O.; Shalchian-Tabrizi, K.; Norberg, B. The brain-pituitary-gonad axis in male teleosts, with special emphasis on flatfish (Pleuronectiformes). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2004, 137, 447–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, K.; Hong, S.; Kho, Y.; Choi, K. Effects of bisphenol s exposure on endocrine functions and reproduction of zebrafish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 8793–8800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, M.; Chen, X.; Wang, C.; Song, M.; Zhang, J.; Bi, S.; Wang, C. Life cycle exposure to propiconazole reduces fecundity by disrupting the steroidogenic pathway and altering DNA methylation in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Int. 2020, 135, 105384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauser, R. Small Animal Clinical Diagnosis by Laboratory Methods, 5th Edition. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2014, 55, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, R.W.; Vischer, H.F.; Cavaco, J.E.B.; Santos, E.M.; Tyler, C.R.; Goos, H.J.T.; Bogerd, J. Gonadotropins, their receptors, and the regulation of testicular functions in fish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B-Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2001, 129, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, H.F.; So, W.K.; Wang, Y.J.; Ge, W. Zebrafish gonadotropins and their receptors: 1. Cloning and characterization of zebrafish follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone receptors-evidence for their distinct functions in follicle development. Biol. Reprod. 2005, 72, 1370–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anway, M.D. Epigenetic transgenerational actions of endocrine disruptors and male fertility (June, pg 1466, 2005). Science 2010, 328, 690. [Google Scholar]
- Schulz, R.W.; de Franca, L.R.; Lareyre, J.J.; Le Gac, F.; Chiarini-Garcia, H.; Nobrega, R.H.; Miura, T. Spermatogenesis in fish. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2010, 165, 390–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eidem, J.K.; Kleivdal, H.; Kroll, K.; Denslow, N.; van Aerle, R.; Tyler, C.; Panter, G.; Hutchinson, T.; Goksoyr, A. Development and validation of a direct homologous quantitative sandwich ELISA for fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas) vitellogenin. Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 78, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mindnich, R.; Haller, F.; Halbach, F.; Moeller, G.; de Angelis, M.H.; Adamski, J. Androgen metabolism via 17 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 3 in mammalian and non-mammalian vertebrates: Comparison of the human and the zebrafish enzyme. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2005, 35, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheshenko, K.; Brion, F.; Le Page, Y.; Hinfray, N.; Pakdel, F.; Kah, O.; Segner, H.; Eggen, R.I.L. Expression of zebra fish aromatase cyp19a and cyp19b genes in response to the ligands of estrogen receptor and aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Toxicol. Sci. 2007, 96, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheshenko, K.; Pakdel, F.; Segner, H.; Kah, O.; Eggen, R.I.L. Interference of endocrine disrupting chemicals with aromatase CYP19 expression or activity, and consequences for reproduction of teleost fish. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2008, 155, 31–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.Y.; Sun, Q.Q.; Wu, Q.; Gui, W.J.; Zhu, G.N.; Schlenk, D. Endocrine disrupting effects of tebuconazole on different life stages of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 1049–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Zhang, Z.; Meng, S.L.; Pan, C.Y.; Yang, M.; Wu, X.Y.; Yang, L.Q.; Xu, H. Parental exposure to bisphenol A and its analogs influences zebrafish offspring immunity. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluru, N.; Leatherland, J.F.; Vijayan, M.M. Bisphenol A in Oocytes Leads to Growth Suppression and Altered Stress Performance in Juvenile Rainbow Trout. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.G.; Wang, X.F.; Zhang, X.H.; Lam, P.K.S.; Guo, Y.Y.; Lam, J.C.W.; Zhou, B.S. Transgenerational endocrine disruption and neurotoxicity in zebrafish larvae after parental exposure to binary mixtures of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) and lead. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 230, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galus, M.; Rangarajan, S.; Lai, A.; Shaya, L.; Balshine, S.; Wilson, J.Y. Effects of chronic, parental pharmaceutical exposure on zebrafish (Danio rerio) offspring. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 151, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurem, S.; Gomes, T.; Brede, D.A.; Hansen, E.L.; Mutoloki, S.; Fernandez, C.; Mothersill, C.; Salbu, B.; Kassaye, Y.A.; Olsen, A.K.; et al. Parental gamma irradiation induces reprotoxic effects accompanied by genomic instability in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. Environ. Res. 2017, 159, 564–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.J.; Qiao, Q.; Chen, Y.Y.; Wu, K.; Zhang, X.Z. Microcystin-LR exposure to adult zebrafish (Danio rerio) leads to growth inhibition and immune dysfunction in F1 offspring, a parental transmission effect of toxicity. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 155, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duan, M.; Guo, X.; Chen, X.; Guo, M.; Xu, H.; Hao, L.; Wang, C.; Yang, Y. Life Cycle Exposure to Cyhalofop-Butyl Induced Reproductive Toxicity in Zebrafish. Toxics 2022, 10, 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10090495
Duan M, Guo X, Chen X, Guo M, Xu H, Hao L, Wang C, Yang Y. Life Cycle Exposure to Cyhalofop-Butyl Induced Reproductive Toxicity in Zebrafish. Toxics. 2022; 10(9):495. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10090495
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuan, Manman, Xuanjun Guo, Xiangguang Chen, Mengyu Guo, Hao Xu, Lubo Hao, Chengju Wang, and Yang Yang. 2022. "Life Cycle Exposure to Cyhalofop-Butyl Induced Reproductive Toxicity in Zebrafish" Toxics 10, no. 9: 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10090495
APA StyleDuan, M., Guo, X., Chen, X., Guo, M., Xu, H., Hao, L., Wang, C., & Yang, Y. (2022). Life Cycle Exposure to Cyhalofop-Butyl Induced Reproductive Toxicity in Zebrafish. Toxics, 10(9), 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10090495




