New-Onset and Exacerbation of Lung Diseases after Short-Term Exposures to Humidifier Disinfectant during Hospitalization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Disease Change during Hospitalization
2.3. Humidifier Disinfectant Exposure
2.4. Characteristics of Participants
2.5. Statistical Analysis
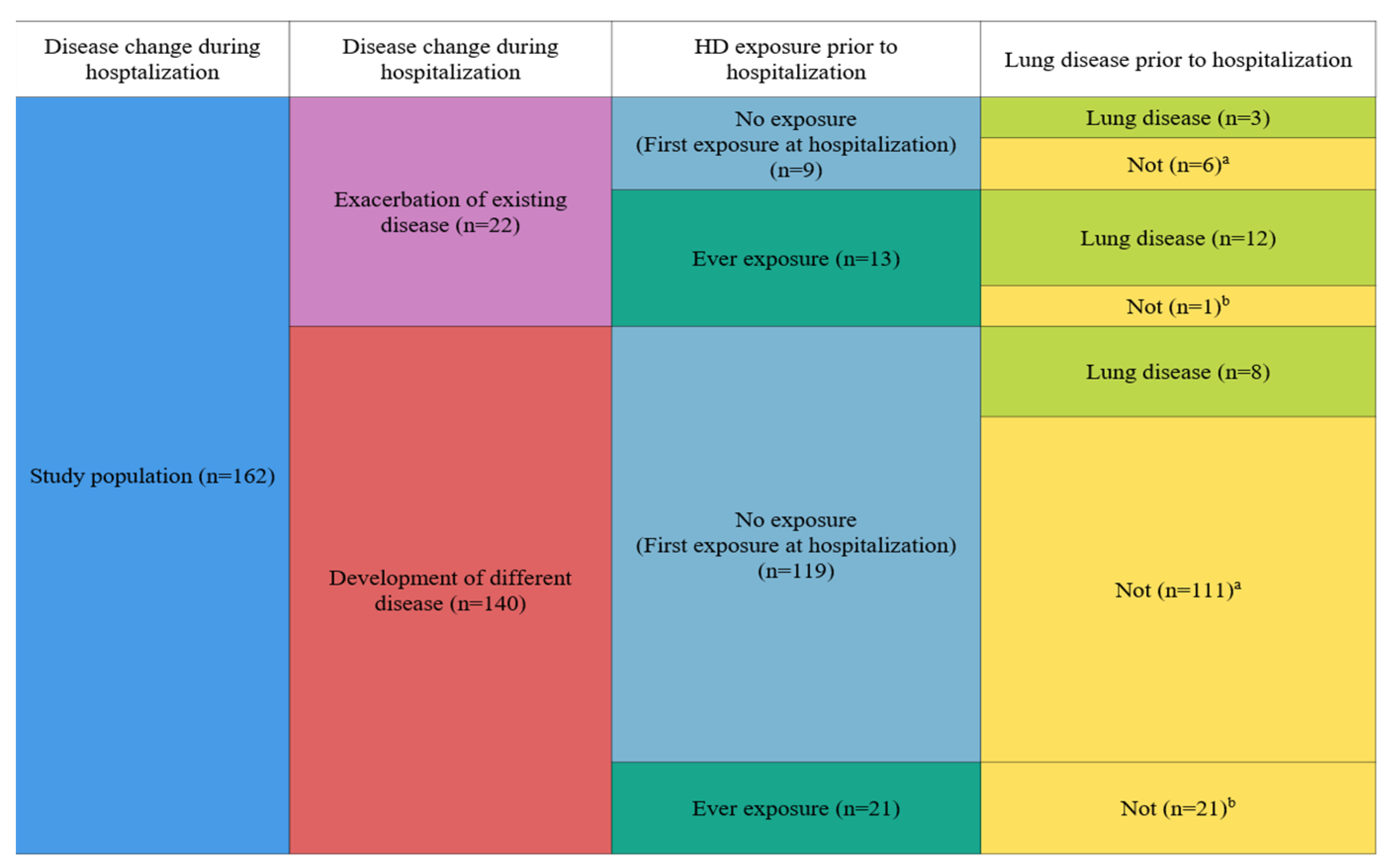
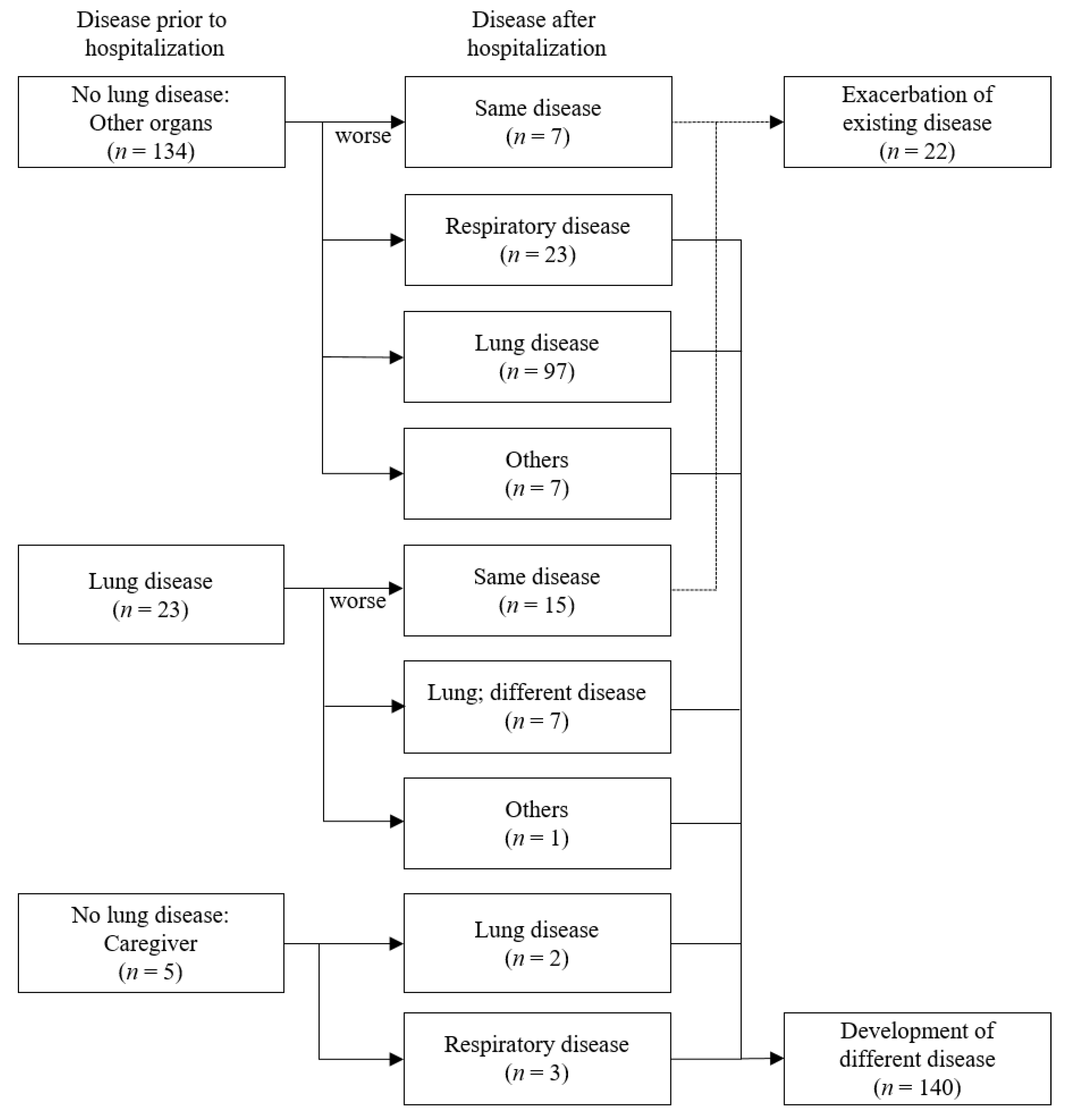
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- ACCEH. Report on Total Sales of Humidifier Disinfectant. Available online: http://eco-health.org/bbs/board.php?bo_table=sub02_04&wr_id=254&sca=2017%EB%85%84 (accessed on 12 January 2021). (In Korean).
- KCDC. White Paper on the Health Damage Disaster from Humidifier Disinfectants; MOHW: Sejong, Korea, 2014; pp. 26–28. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.-Y. Questions and answers about the humidifier disinfectant disaster as of february 2017. J. Environ. Health Sci. 2017, 43, 1–22. (In Korean) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Kwon, J.H. Fatal misuse of humidifier disinfectants in Korea: Importance of screening risk assessment and implications for management of chemicals in consumer products. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 2498–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Kang, H.-J.; Seol, H.-S.; Kim, C.-K.; Yoon, S.-K.; Gwack, J.; Kim, Y.-H.; Kwon, J.-H. Refined exposure assessment for three active ingredients of humidifier disinfectants. Environ. Eng. Res. 2013, 18, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, C.A. Humidifiers: The use of biocides and lung disease. Thorax 2014, 69, 692–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- KCDC. Interim Report of Epidemiologic Investigation of Lung Injury with Unknown Causes in Korea; KCDC: Cheongju, Korea, 2011; pp. 817–818. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Lee, H.; Jang, S.; Hong, S.-H.; Kim, W.J.; Ryu, S.M.; Park, S.-M.; Lee, K.-H.; Cho, S.-J.; Yang, S.-R. CMIT/MIT induce apoptosis and inflammation in alveolar epithelial cells through p38/JNK/ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 2019, 15, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.J.; Jeong, M.H.; Bang, I.J.; Kim, H.R.; Chung, K.H. Guanidine-based disinfectants, polyhexamethylene guanidine-phosphate (PHMG-P), polyhexamethylene biguanide (PHMB), and oligo(2-(2-ethoxy)ethoxyethyl guanidinium chloride (PGH) induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in A549 alveolar epithelial cells. Inhal. Toxicol. 2019, 31, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Jung, K.J.; Yang, M.J.; Han, S.C.; Lee, K. Assessment of acute and repeated pulmonary toxicities of oligo(2-(2-ethoxy)ethoxyethyl guanidium chloride in mice. Toxicol. Res. 2021, 37, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, M.; Lee, S.Y.; Hwang, S.S.; Park, H.; Sheen, S.; Cheong, H.K.; Choi, B.Y. Evaluation report on the causal association between humidifier disinfectants and lung injury. Epidemiol. Health 2016, 38, e2016037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Lee, M.S.; Hong, S.B.; Huh, J.W.; Do, K.H.; Jang, S.J.; Lim, C.M.; Chae, E.J.; Lee, H.; Jung, M.; et al. A cluster of lung injury cases associated with home humidifier use: An epidemiological investigation. Thorax 2014, 69, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamichhane, D.K.; Leem, J.H.; Lee, S.M.; Yang, H.J.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.H.; Ko, J.K.; Kim, H.C.; Park, D.U.; Cheong, H.K. Family-based case-control study of exposure to household humidifier disinfectants and risk of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KEITI. Statistical Data 2021. Available online: https://www.healthrelief.or.kr/home/content/stats01/view.do (accessed on 31 July 2021).
- Han, K.; Yoon, J.; Jo, E.-K.; Ryu, H.; Yang, W.; Choi, Y.-H. Case studies of exposures to humidifier disinfectant in hospitals: Focusing on the exposure assessment of the fourth round of applicants. J. Environ. Health Sci. 2019, 45, 358–369. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.-H.; Ryu, H.; Yoon, J.; Lee, S.; Kwak, J.H.; Han, B.-Y.; Chu, Y.-H.; Kim, P.-G.; Yang, W. Demographic characteristics and exposure assessment for applicants who have been injured by humidifier disinfectant-focusing on 4–1 and 4–2 applicants. J. Environ. Health Sci. 2018, 44, 301–314. [Google Scholar]
- Park, D.-U. A strategy for exposure assessment of humidifier disinfectant associated to health effects. Korean Soc. Environ. Health 2017, 44, 107–114. [Google Scholar]
- Paek, D.; Koh, Y.; Park, D.U.; Cheong, H.K.; Do, K.H.; Lim, C.M.; Hong, S.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Leem, J.H.; Chung, K.H.; et al. Nationwide study of humidifier disinfectant lung injury in South Korea, 1994–2011. Incidence and dose-response relationships. Ann. Am. Thorac Soc. 2015, 12, 1813–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.U.; Friesen, M.C.; Roh, H.S.; Choi, Y.Y.; Ahn, J.J.; Lim, H.K.; Kim, S.K.; Koh, D.H.; Jung, H.J.; Lee, J.H.; et al. Estimating retrospective exposure of household humidifier disinfectants. Indoor Air 2015, 25, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.-U.; Ryu, S.-H.; Lim, H.-K.; Kim, S.-K.; Roh, H.-S.; Cha, W.-S.; Park, D. Estimation of humidifier disinfectant amounts inhaled into the respiratory system. Korean Soc. Environ. Health 2016, 42, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ECHA. Biocides Human Health Exposure Methodology; ECHA: Helsinki, Finland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Weerdesteijn, M.C.H.; Bremmer, H.J.; Zeilmaker, M.J.; van Veen, M.P. Hygienic Cleaning Products Used in the Kitchen; Exposure and Risks; RIVM: Bilthoven, The Netherlands, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- MOWH. National Health Insurance act. Ed. 2016. KLRI. Available online: https://elaw.klri.re.kr/kor_service/lawView.do?hseq=59574&lang=ENG (accessed on 14 April 2022).
- HIRA. National Health Insurance Statistical Yearbook 2020. Available online: https://www.hira.or.kr/bbsDummy.do?pgmid=HIRAA020045020000&brdScnBltNo=4&brdBltNo=2313&pageIndex=1 (accessed on 13 April 2022).
- Park, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kwon, G.Y.; Gwack, J.; Park, Y.J.; Youn, S.K.; Kwon, J.W.; Yang, B.G.; Lee, M.S.; Jung, M.; et al. Humidifier disinfectants are a cause of lung injury among adults in South Korea: A community-based case-control study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.R.; Lee, K.; Park, C.W.; Song, J.A.; Shin, D.Y.; Park, Y.J.; Chung, K.H. Polyhexamethylene guanidine phosphate aerosol particles induce pulmonary inflammatory and fibrotic responses. Arch. Toxicol. 2016, 90, 617–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.S.; Han, J.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Jeon, D.; Lee, K. Polyhexamethylene guanidine phosphate induces IL-6 and TNF-alpha expression through JNK-dependent pathway in human lung epithelial cells. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 43, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.R.; Shin, D.Y.; Chung, K.H. The role of NF-κB signaling pathway in polyhexamethylene guanidine phosphate induced inflammatory response in mouse macrophage RAW264.7 cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2015, 233, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristics | Value |
|---|---|
| Age (years) a | 53.40 ± 25.74 |
| ≤6 | 17 (8.6) |
| 7–19 | 8 (7.4) |
| 20–64 | 62 (37.0) |
| ≥65 | 70 (46.9) |
| Sex | |
| Male | 96 (59.3) |
| Female | 66 (40.7) |
| Survival status | |
| Survivor | 52 (32.1) |
| Death | 110 (67.9) |
| Cigarette smoking a | |
| Never smoker | 101 (62.7) |
| Former smoker | 56 (34.8) |
| Current smoker | 4 (2.5) |
| Education level a | |
| ≤Elementary school | 59 (38.6) |
| Middle school | 25 (16.3) |
| High school | 42 (27.5) |
| ≥College | 27 (17.6) |
| Exposure prior to hospitalization | |
| Ever | 34 (21.0) |
| Non (first exposure during hospitalization) | 128 (79.0) |
| Disease after hospitalization | |
| Lung disease development | 121 (74.7) |
| No development | 41 (25.3) |
| Disease status change | |
| Exacerbation of existing disease | 22 (13.6) |
| Development of different disease | 140 (86.4) |
| HD exposure characteristics a | |
| Exposure proximity | |
| <1 m | 132 (85.7) |
| ≥1 m | 22 (14.3) |
| Exposure direction | |
| Toward the face | 136 (87.2) |
| Toward the other sides | 20 (12.8) |
| Daily exposure time | |
| <24 h | 51 (35.9) |
| 24 h (whole day) | 91 (64.1) |
| Exposure duration (month) | 29.52 ± 32.99 |
| Cumulative exposure time (h) | 14,642.88 ± 19,871.96 |
| Indoor air concentration b (μg/m3) | 547.99 ± 662.20 |
| Characteristics | Exacerbation of Existing Disease (n = 22) | Development of Different Disease (n = 140) | p- Value a |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) b | 34.76 ± 26.30 | 56.28 ± 24.51 | <0.001 |
| ≤6 | 6 (28.6) | 11 (8.1) | <0.001 |
| 7–19 | 2 (9.5) | 6 (4.4) | |
| 20–64 | 11 (52.4) | 51 (37.5) | |
| ≥65 | 2 (9.5) | 68 (50.0) | |
| Sex | 0.986 | ||
| Male | 13 (59.1) | 83 (59.3) | |
| Female | 9 (40.9) | 57 (40.7) | |
| Survival status | 0.976 | ||
| Survivor | 7 (31.8) | 45 (32.1) | |
| Death | 15 (68.2) | 95 (67.9) | |
| Cigarette smoking b | 0.292 | ||
| Never smoker | 16 (72.7) | 85 (61.2) | |
| Former smoker | 5 (22.7) | 51 (36.7) | |
| Current smoker | 1 (4.5) | 3 (2.2) | |
| Education level b | 0.612 | ||
| ≤Elementary school | 5 (26.3) | 54 (40.3) | |
| Middle school | 3 (15.8) | 22 (16.4) | |
| High school | 7 (36.8) | 35 (26.1) | |
| ≥College | 4 (21.1) | 23 (17.2) | |
| Exposure prior to hospitalization | <0.001 | ||
| Ever | 13 (59.1) | 21 (15.0) | |
| Non (first exposure during hospitalization) | 9 (40.9) | 119 (85.0) | |
| Disease after hospitalization | 0.450 | ||
| Lung disease development | 15 (68.2) | 106 (75.7) | |
| Not development | 7 (31.8) | 34 (24.3) | |
| HD exposure characteristics b | |||
| Exposure proximity | 0.523 | ||
| <1 m | 18 (81.8) | 114 (86.4) | |
| ≥1 m | 4 (18.2) | 18 (13.6) | |
| Exposure direction | 1.000 | ||
| Toward the face | 19 (86.4) | 117 (87.3) | |
| Toward the other sides | 3 (13.6) | 17 (12.7) | |
| Daily exposure time | 0.665 | ||
| <24 h | 11 (50.0) | 40 (33.3) | |
| 24 h (whole day) | 11 (50.0) | 80 (66.7) | |
| Exposure duration (month) | 30.35 ± 34.66 | 24.68 ± 20.69 | 0.297 |
| Cumulative exposure time (h) | 11,772.0 ± 11,148.70 | 15,227.7 ± 21,205.10 | 0.275 |
| Indoor air concentration c (μg/m3) | 524.7 ± 690.80 | 637.7 ± 553.10 | 0.588 |
| Characteristics | Hospital Exposure only (n = 142) | Non-Hospital Exposure only (n = 5699) | p-Value a |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) b | 60.31 ± 21.62 | 32.29 ± 25.29 | <0.001 |
| ≤6 | 11 (7.8) | 1980 (34.7) | <0.001 |
| 7–19 | 5 (3.5) | 302 (5.3) | |
| 20–64 | 49 (34.5) | 2724 (47.8) | |
| ≥65 | 77 (54.2) | 693 (12.2) | |
| Sex | 0.229 | ||
| Male | 82 (59.1) | 2916 (51.2) | |
| Female | 60 (40.9) | 2754 (48.3) | |
| Unknown | 0 (0.0) | 29 (0.5) | |
| Survival status | <0.001 | ||
| Survivor | 50 (35.2) | 4600 (80.7) | |
| Death | 92 (64.8) | 1099 (19.3) | |
| Cigarette smoking b | <0.001 | ||
| Never smoker | 12 (9.2) | 216 (4.3) | |
| Former smoker | 47 (35.9) | 1000 (20.1) | |
| Current smoker | 72 (55.0) | 3760 (75.6) | |
| Education level b | 0.001 | ||
| ≤Elementary school | 52 (44.8) | 1533 (34.0) | |
| Middle school | 17 (14.7) | 484 (10.7) | |
| High school | 31 (26.7) | 1055 (23.4) | |
| ≥College | 16 (13.8) | 1436 (31.9) | |
| HD exposure characteristics b | <0.001 | ||
| Exposure proximity | |||
| <1 m | 108 (87.1) | 3751 (66.7) | |
| ≥1 m | 16 (12.9) | 1871 (33.3) | <0.001 |
| Exposure direction | |||
| Toward the face | 110 (85.9) | 3790 (68.4) | |
| Toward the other sides | 18 (14.1) | 1748 (31.6) | |
| Daily exposure time | <0.001 | ||
| <24 h | 21 (18.8) | 4597 (82.8) | |
| 24 h (whole day) | 91 (81.3) | 953 (17.2) | |
| Exposure duration (month) | 14.01 ± 26.75 | 29.25 ± 29.39 | <0.001 |
| Cumulative exposure time (h) | 7601.40 ± 16,658.30 | 10,193.20 ± 13,487.80 | 0.116 |
| Indoor air concentration c (μg/m3) | 314.40 ± 249.50 | 956.00 ± 4017.30 | <0.001 |
| Adjusted indoor air concentration d (μg/m3) | 8490.7 ± 7116.2 | 3933.4 ± 12,115.8 | 0.012 |
| Adjusted indoor air concentration e (μg/m3) | 3438 ± 2798.1 | 1977.4 ± 5791.7 | 0.037 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.; Han, K.; Yoon, J.; Jo, E.-K.; Yang, W.; Choi, Y.-H. New-Onset and Exacerbation of Lung Diseases after Short-Term Exposures to Humidifier Disinfectant during Hospitalization. Toxics 2022, 10, 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10070371
Lee S, Han K, Yoon J, Jo E-K, Yang W, Choi Y-H. New-Onset and Exacerbation of Lung Diseases after Short-Term Exposures to Humidifier Disinfectant during Hospitalization. Toxics. 2022; 10(7):371. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10070371
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Seula, Kyunghee Han, Jeonggyo Yoon, Eun-Kyung Jo, Wonho Yang, and Yoon-Hyeong Choi. 2022. "New-Onset and Exacerbation of Lung Diseases after Short-Term Exposures to Humidifier Disinfectant during Hospitalization" Toxics 10, no. 7: 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10070371
APA StyleLee, S., Han, K., Yoon, J., Jo, E.-K., Yang, W., & Choi, Y.-H. (2022). New-Onset and Exacerbation of Lung Diseases after Short-Term Exposures to Humidifier Disinfectant during Hospitalization. Toxics, 10(7), 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10070371








