Anxiety and Gene Expression Enhancement in Mice Exposed to Glyphosate-Based Herbicide
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Pesticide
2.3. Doses and Protocol of Exposure
2.4. Behavioral Tests
2.4.1. Open Field (OF)
2.4.2. Elevated Plus Maze (EPM)
2.5. IEG Immunofluorescence Detection
2.6. Image Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
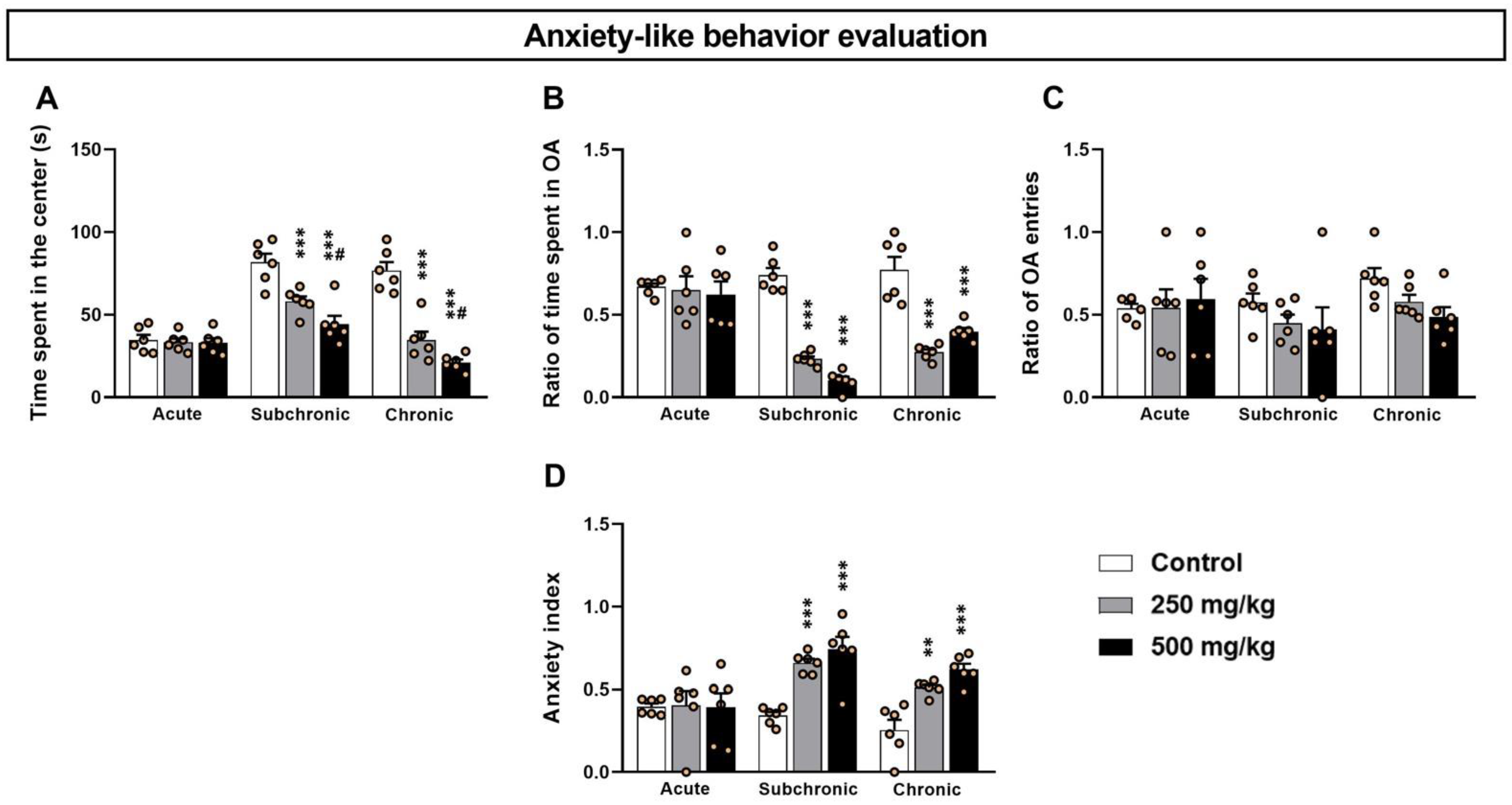
3.1. GBH-Exposed Mice Exhibit Higher Anxiety-like Levels in OF and EPM Tests
3.2. GBH-Exposed Mice Display Increased IEG Expression in the mPFC and the Amygdala
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 5-HT | Serotonin |
| BLA | Basolateral amygdala |
| CeA | Central amygdala |
| EPM | Elevated plus maze |
| GBH | Glyphosate-based herbicide |
| IEGs | Immediate early genes |
| IL | Infralimbic cortex |
| mPFC | medial prefrontal cortex |
| NOAEL | No-observed adverse effect level |
| NDS | Normal donkey serum |
| OA | Open arm |
| OF | Open field |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| pCREB | cAMP-responsive element-binding protein |
| PrLCx | Prelimbic cortex |
References
- Samsel, A.; Seneff, S. Glyphosate pathways to modern diseases V: Amino acid analogue of glycine in diverse proteins. J. Biol. Phys. Chem. 2016, 16, 9–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattani, D.; Cavalli, V.L.D.L.O.; Rieg, C.E.H.; Domingues, J.T.; Dal-Cim, T.; Tasca, C.I.; Silva, F.R.M.B.; Zamoner, A. Mechanisms underlying the neurotoxicity induced by glyphosate-based herbicide in immature rat hippocampus: Involvement of glutamate excitotoxicity. Toxicology 2014, 320, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, J.P.; Antoniou, M.N.; Blumberg, B.; Carroll, L.; Colborn, T.; Everett, L.G.; Hansen, M.; Landrigan, P.J.; Lanphear, B.P.; Mesnage, R.; et al. Concerns over use of glyphosate-based herbicides and risks associated with exposures: A consensus statement. Environ. Health 2016, 15, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallegos, C.E.; Bartos, M.; Gumilar, F.; Raisman-Vozari, R.; Minetti, A.; Baier, C.J. Intranasal glyphosate-based herbicide administration alters the redox balance and the cholinergic system in the mouse brain. NeuroToxicology 2020, 77, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bali, Y.A.; Ba-Mhamed, S.; Bennis, M. Behavioral and Immunohistochemical Study of the Effects of Subchronic and Chronic Exposure to Glyphosate in Mice. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyori, Y.; Nishida, M.; Shioda, K.; Suda, S.; Kato, S. Unilateral hippocampal infarction associated with an attempted suicide: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2014, 8, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baier, C.J.; Gallegos, C.E.; Raisman-Vozari, R.; Minetti, A. Behavioral impairments following repeated intranasal glyphosate-based herbicide administration in mice. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2017, 64, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayberg, H.S.; Liotti, M.; Brannan, S.K.; McGinnis, S.; Mahurin, R.K.; Jerabek, P.A.; Silva, J.A.; Tekell, J.L.; Martin, C.C.; Lancaster, J.L.; et al. Reciprocal limbic-cortical function and negative mood: Converging PET findings in depression and normal sadness. Am. J. Psychiatry 1999, 156, 675–682. [Google Scholar]
- Drevets, W.C. Neuroimaging and neuropathological studies of depression: Implications for the cognitive-emotional features of mood disorders. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2001, 11, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juranek, J.; Johnson, C.P.; Prasad, M.R.; Kramer, L.A.; Saunders, A.; Filipek, P.A.; Swank, P.R.; Cox, C.S.; Ewing-Cobbs, L. Mean diffusivity in the amygdala correlates with anxiety in pediatric TBI. Brain Imaging Behav. 2012, 6, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Keele, N.B. The role of serotonin in impulsive and aggressive behaviors associated with epilepsy-like neuronal hyperexcitability in the amygdala. Epilepsy Behav. 2005, 7, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, L.; Lasher, B.K.; Young, K.A.; Keele, N.B. Depletion of serotonin in the basolateral amygdala elevates glutamate receptors and facilitates fear-potentiated startle. Transl. Psychiatry 2013, 3, e298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciccarelli, A.; Calza, A.; Santoru, F.; Grasso, F.; Concas, A.; Sassoè-Pognetto, M.; Giustetto, M. Morphine withdrawal pro-duces ERK-dependent and ERK-independent epigenetic marks in neurons of the nucleus accumbens and lateral septum. Neuropharmacology 2013, 70, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flavell, S.W.; Greenberg, M.E. Signaling Mechanisms Linking Neuronal Activity to Gene Expression and Plasticity of the Nervous System. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 31, 563–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, M.-A.; Ares, I.; Rodríguez, J.-L.; Martínez, M.; Martínez-Larrañaga, M.-R.; Anadón, A. Neurotransmitter changes in rat brain regions following glyphosate exposure. Environ. Res. 2018, 161, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.C.; Vacek, T.; Lanier, D.L.; Dewsbury, D.A. Open-field behavior in muroid rodents. Behav. Biol. 1976, 17, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bali, Y.A.; Ba-M’Hamed, S.; Elhidar, N.; Nafis, A.; Soraa, N.; Bennis, M. Glyphosate based- herbicide exposure affects gut microbiota, anxiety and depression-like behaviors in mice. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2018, 67, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handley, S.L.; Mithani, S. Effects of alpha-adrenoceptor agonists and antagonists in a maze-exploration model of ?fear?-motivated behaviour. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Exp. Pathol. Pharmakol. 1984, 327, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomassy, G.S.; Morello, N.; Calcagno, E.; Giustetto, M. Developmental abnormalities of cortical interneurons precede symptoms onset in a mouse model of Rett syndrome. J. Neurochem. 2014, 131, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, T.J.; Burke, D.; Bewersdorf, J.; Booth, M.J. Adaptive optics enables 3D STED microscopy in aberrating specimens. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 20998–21009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccarelli, A.; Giustetto, M. Role of ERK signaling in activity-dependent modifications of histone proteins. Neuropharmacol. 2014, 80, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizzo, R.; Lamarca, A.; Sassoè-Pognetto, M.; Giustetto, M. Structural Bases of Atypical Whisker Responses in a Mouse Model of CDKL5 Deficiency Disorder. Neurosci. 2019, 445, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ait-Bali, Y.; Ba-M’hamed, S.; Gambarotta, G.; Sassoè-Pognetto, M.; Giustetto, M.; Bennis, M. Pre- and postnatal exposure to glyphosate-based herbicide causes behavioral and cognitive impairments in adult mice: Evidence of cortical ad hippocampal dysfunction. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 1703–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faria, M.; Bedrossiantz, J.; Ramírez, J.R.R.; Mayol, M.; García, G.H.; Bellot, M.; Prats, E.; Garcia-Reyero, N.; Gómez-Canela, C.; Gómez-Oliván, L.M.; et al. Glyphosate targets fish monoaminergic systems leading to oxidative stress and anxiety. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calhoon, G.G.; Tye, K.M. Resolving the neural circuits of anxiety. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 1394–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-H.; Lee, L.-T.; Yang, Y.K. Serotonin and Mental Disorders: A Concise Review on Molecular Neuroimaging Evidence. Clin. Psychopharmacol. Neurosci. 2014, 12, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hébert, C.; Habimana, A.; Élie, R.; Reader, T.A. Effects of chronic antidepressant treatments on 5-HT and NA transporters in rat brain: An autoradiographic study. Neurochem. Int. 2000, 38, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesch, K.-P.; Waider, J. Serotonin in the Modulation of Neural Plasticity and Networks: Implications for Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Neuron 2012, 76, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajos, M. In vivo inhibition of neuronal activity in the rat ventromedial prefrontal cortex by midbrain-raphe nuclei: Role of 5-HT1A receptors. Neuropharmacology 2003, 45, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, L.; Keele, N.B. P-chlorophenylalanine increases glutamate receptor 1 transcription in rat amygdala. NeuroReport 2011, 22, 758–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.A.; Morris, A.P.; McGlone, F.; Abbott, D.F.; Mattingley, J.B. Amygdala Responses to Fearful and Happy Facial Expressions under Conditions of Binocular Suppression. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 2898–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gammie, S.C.; Nelson, R.J. cFOS and pCREB activation and maternal aggression in mice. Brain Res. 2001, 898, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaleghzadeh-Ahangar, H.; Khodagholi, F.; Shaerzadeh, F.; Haghparast, A. Modulatory role of the intra-accumbal CB1 receptor in protein level of the c-fos and pCREB/CREB ratio in the nucleus accumbens and ventral tegmental area in extinc-tion and morphine seeking in the rats. Brain Res. Bull. 2018, 142, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemzadeh, Z.; Sardari, M.; Javadi, P.; Rezayof, A. Expression analysis of hippocampal and amygdala CREB-BDNF sig-naling pathway in nicotine-induced reward under stress in rats. Brain Res. 2020, 1741, 146885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Widjaja, S.; Xu, J.; Shepherd, R.K. Cochlear Implants Stimulate Activity-Dependent CREB Pathway in the Deaf Auditory Cortex: Implications for Molecular Plasticity Induced by Neural Prosthetic Devices. Cereb. Cortex 2007, 18, 1799–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baho, E.; Di Cristo, G. Neural activity and neurotransmission regulate the maturation of the innervation field of cortical. GABAergic interneurons in an age-dependent manner. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didier, S.; Sauvé, F.; Domise, M.; Buée, L.; Marinangeli, C.; Vingtdeux, V. AMP-activated Protein Kinase Controls Immediate Early Genes Expression Following Synaptic Activation Through the PKA/CREB Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, C.; Rudolph-Correia, S.; Sheng, M. Developmentally Regulated NMDA Receptor-Dependent Dephosphorylation of cAMP Response Element-Binding Protein (CREB) in Hippocampal Neurons. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 3529–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijholt, I.; Blank, T.; Ahi, J.; Spiess, J. In vivo CREB phosphorylation mediated by dopamine and NMDA receptor activation in mouse hippocampus and caudate nucleus. Gene Expr. Patterns 2002, 1, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altieri, S.C.; Garcia-Garcia, A.L.; Leonardo, E.D.; Andrews, A.M. Rethinking 5-HT1AReceptors: Emerging Modes of Inhibitory Feedback of Relevance to Emotion-Related Behavior. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2013, 4, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, A.; Bocchio, M.; Bannerman, D.; Sharp, T.; Capogna, M. Control of Amygdala Circuits by 5-HT Neurons via 5-HT and Glutamate Cotransmission. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 1785–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ait bali, Y.; Kaikai, N.-e.; Ba-M’hamed, S.; Sassoè-Pognetto, M.; Giustetto, M.; Bennis, M. Anxiety and Gene Expression Enhancement in Mice Exposed to Glyphosate-Based Herbicide. Toxics 2022, 10, 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10050226
Ait bali Y, Kaikai N-e, Ba-M’hamed S, Sassoè-Pognetto M, Giustetto M, Bennis M. Anxiety and Gene Expression Enhancement in Mice Exposed to Glyphosate-Based Herbicide. Toxics. 2022; 10(5):226. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10050226
Chicago/Turabian StyleAit bali, Yassine, Nour-eddine Kaikai, Saadia Ba-M’hamed, Marco Sassoè-Pognetto, Maurizio Giustetto, and Mohamed Bennis. 2022. "Anxiety and Gene Expression Enhancement in Mice Exposed to Glyphosate-Based Herbicide" Toxics 10, no. 5: 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10050226
APA StyleAit bali, Y., Kaikai, N.-e., Ba-M’hamed, S., Sassoè-Pognetto, M., Giustetto, M., & Bennis, M. (2022). Anxiety and Gene Expression Enhancement in Mice Exposed to Glyphosate-Based Herbicide. Toxics, 10(5), 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10050226





