Suitability and Sensitivity of Golden Grey Mullet Chelon auratus (Risso, 1810) as a Reference Fish Species for Ecotoxicity Tests in the Black Sea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Laboratory Equipment
2.2. Organism Selection and Acquisition
2.3. Test Check-List
2.4. Parameter Monitoring
2.5. Data Processing and Calculation of LC50
2.6. Development of the Species Sensitivity Distribution (SSD) Curve
3. Results and Discussion-Protocol Design
3.1. Species Selection
3.2. Fish Collection and Acclimation
3.3. Fish Conditioning
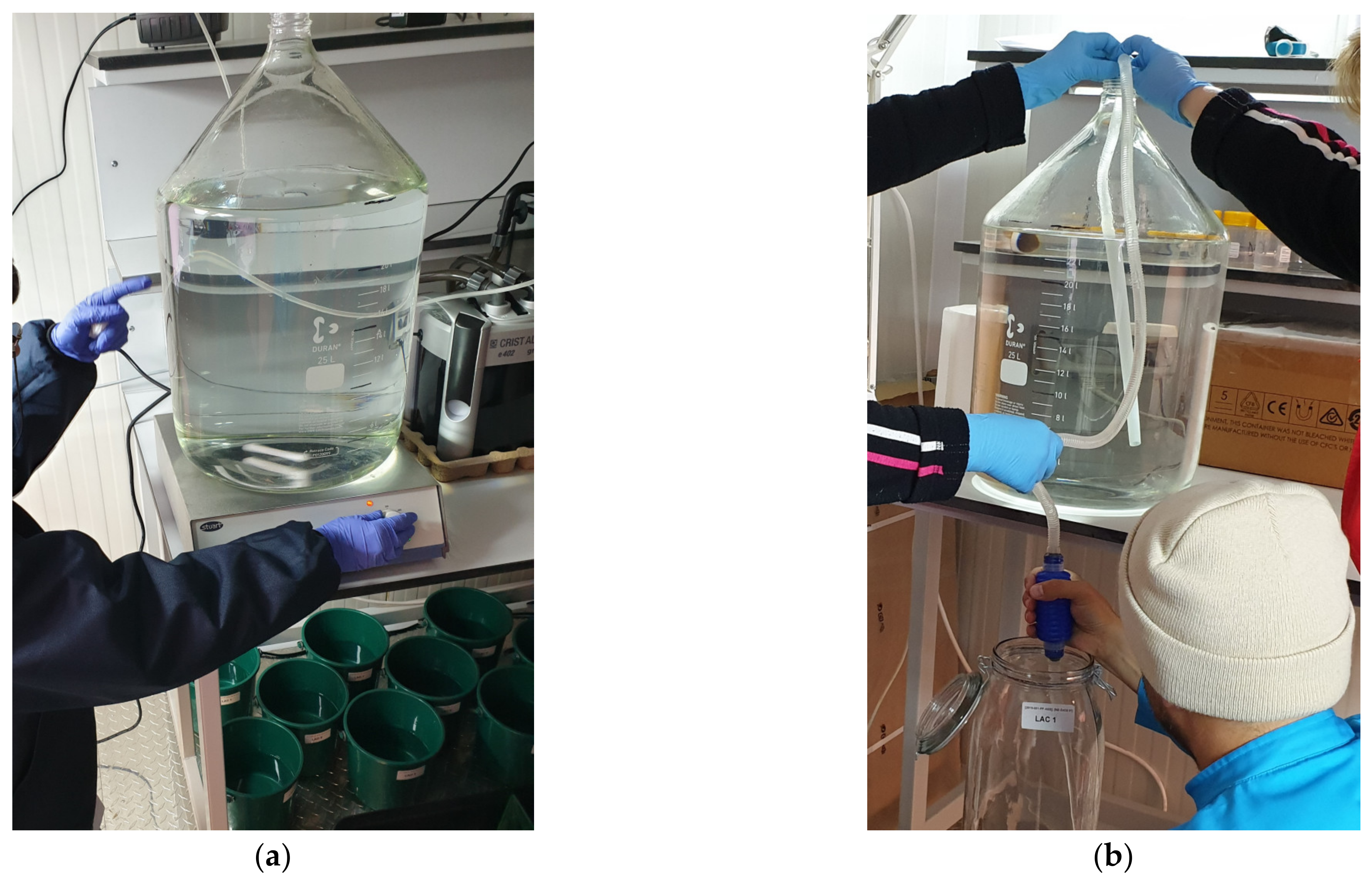
3.4. Dilution Water Preparation and Oxygenation
3.5. Fish Randomization
3.6. Acute Toxicity Testing
3.6.1. Reference Substance
3.6.2. Experimental Design
3.6.3. Test Substance Preparation and Administration
3.6.4. Parameter Monitoring
3.7. Mortality Observation and Euthanasia
3.8. Data Processing and Interpretation
3.9. Significant Results: LC50 Values
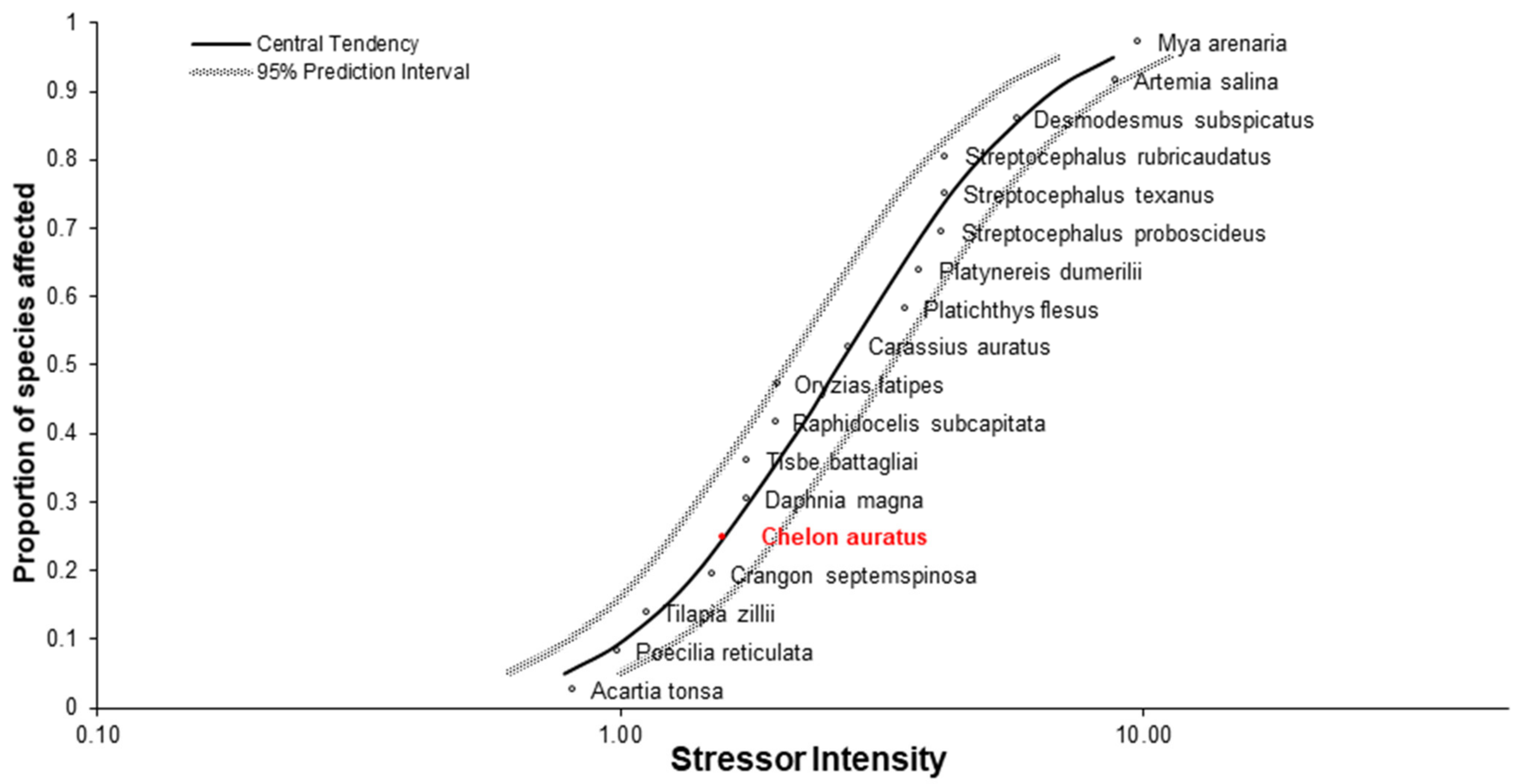
3.10. Sensitivity of C. auratus in Relation to Literature Data
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adams, W.J.; Rowland, C.D. Aquatic Toxicology Test Methods. In Handbook of Ecotoxicology, 2nd ed.; Hoffman, D.J., Ed.; Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003; Volume 3, pp. 19–44. [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard, J.B. Aquatic Toxicology: Past, Present, and Prospects. Environ. Health Perspect. 1993, 100, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, N. Aquatic Toxicity Tests. In Perspectives of Aquatic Toxicology; Jovanovic, B., Ed.; Iowa State University: Ames, IA, USA, 2019; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Rand, G.M. Fundamentals of Aquatic Toxicology, Effects, Environmental Fate, and Risk Assessment, 2nd ed.; Taylor and Francis: Washington, DC, USA, 1995; pp. 1–1148. [Google Scholar]
- Stephan, C.E. Methods for Acute Toxicity Tests with Fish, Macroinvertebrates, and Amphibians; Ecological Research Series, EPA-660/3–75–009; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Avenue, NW, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM. Conducting Acute Toxicity Tests on Materials with Fishes, Macroinvertebrates, and Amphibians. Book of Standards. Vol. 11. ASTM E729-96; American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- EC. Biological Test Method—Acute Lethality Test Using Rainbow Trout EPS 1/RM/Environmental Protection Series; Environment Canada: Ottawa, Ontario, Canada, 2007; pp. 1–66. [Google Scholar]
- US-EPAa. Methods for Measuring the Acute Toxicity of Effluents and Receiving Waters to Freshwater and Marine Organisms, 5th ed.; EPA-821-R-02-012; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Avenue, NW, USA, 2002; pp. 1–275. [Google Scholar]
- US-EPA-OCSPP850; Freshwater and Saltwater Fish Acute Toxicity Test, EPA 712-C-16-007; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency—Office of Chemical Safety and Pollution Prevention: Avenue, NW, USA, 2016; pp. 1–19.
- OECDa. Fish Toxicity Testing Framework. Environment, Health and Safety Publications Series on Testing and Assessment, 171. s.l.; Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development: Paris, France, 2012; pp. 1–174. [Google Scholar]
- OECDb. Test Guideline No. Fish Acute Toxicity Testing, OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2. s.l.; Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development: Paris, France, 2019; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Suhur, S.; Al-Naema, N.; Butler, J.D.; Febbo, E.J. Arabian Killifish (Aphanius dispar) Embryos: A Model Organism for the Risk Assessment of the Arabian Gulf Coastal Waters. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 34, 2898–2905. [Google Scholar]
- Hemmer, M.J.; Middaugh, D.P.; Comparetta, V. Comparative Acute Sensitivity of Larval Topsmelt, Atherinops affinis, and inland silverside, Menidia beryllina, to 11 chemicals. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1992, 11, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deloitte. The Contribution of Black Sea Oil & Gas Projects to the Development of the Romanian Economy; Deloitte Consultanta srl: Bucharest, Romania, 2019; pp. 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Brănoiu, G.H.; Frunzescu, D.; Nistor, I.; Jugastreanu, C.; Lungu, I.A. Is There a Future for Oil and Gas Exploration in Romania? In Proceedings of the GEOLINKS International Conference on GeoSciences Proceedings, Athens, Greece, 26–29 March 2019; pp. 183–191. [Google Scholar]
- Brănoiu, G.H. General Framework of Exploration and Production Activities in Romania; Ploiești Oil and Gas University: Ploiești, Romania, 2019; pp. 1–174. [Google Scholar]
- Stoica-Negulescu, E.R. Romanian Oil and Gas from Geophysics to Petroleum Systems; Vergiliu Publishing: Bucharest, Romania, 2015; pp. 1–97. [Google Scholar]
- Center for Environmental Fisheries and Aquaculture Science. Available online: https://www.cefas.co.uk/data-and-publications/ocns/#:~:text=The%20Offshore%20Chemical%20Notification%20Scheme,in%20the%20UK%20and%20Netherlands (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- US-EPAb. National Pollution Discharge Elimination System (NPDES) Permit Writers’ Manual; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Wastewater Management, Water Permits Division: Avenue, NW, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Access to European Union Law. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2008/105/oj (accessed on 16 March 2022).
- Bat, L.; Şahin, F.; Öztekin, A. Toxic Metal Amounts in Chelon auratus (Risso, 1810): A Potential Risk for Consumer’s Health. J. Aquac. Mar. Biol. 2018, 7, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basar, E.; Sivri, N.; Ugurlu, O.; Zulal Sonmez, V. Potential Impact of Oil Spill Damage around the Planned Oil Rigs at the Black Sea. Indian J. Mar. Sci. 2018, 47, 2198–2206. [Google Scholar]
- Krajnović-Ozretić, M.; Ozretić, B. The ALA-D Activity Test in Lead-Exposed Grey Mullet Mugil auratus. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1980, 3, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu-Olayan, A.H.; Thomas, B.V. Assessment on Biocides Bioaccumulation in Mullet Liza klunzingeri in Kuwaiti Waters, off the Arabian Gulf. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2006, 2, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hariharan, G.; Purvaja, R.; Ramesh, R. Environmental Safety Level of Lead (Pb) Pertaining to Toxic Effects on Grey Mullet (Mugil cephalus) and Tiger Perch (Terapon jarbua). Environ. Toxicol. 2016, 31, 24–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaz, E.; Elahe, E.; Kasalkhe, N. Acute Toxicity and the Effects of Copper Sulphate [CuSO4.5H2O] on the Behavior of the Gray Mullet (Mugil cephalus). Int. J. Sci. Res. Environ. Sci. Toxicol. 2018, 3, 771–778. [Google Scholar]
- Parrino, V.; De Marco, G.; Minutoli, R.; Lo Paro, G.; Giannetto, A.; Cappello, T.; De Plano, L.M.; Cecchini, S.; Fazio, F. Effects of Pesticides on Chelon labrosus (Risso, 1827) Evaluated by Enzymatic Activities along the North-Eastern Sicilian Coastlines (Italy). Eur. Zool. J. 2021, 88, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, C.E.; Shehadeh, Z.H. (Eds.) Review of Breeding and Propagation Techniques for Grey Mullet, Mugil cephalus L.; ICLARM Studies and Reviews: Manilla, Philippines, 1980; pp. 1–87. [Google Scholar]
- Crosetti, D.; Cataudella, S. The Mullets; Novotny, C.E., Nash, A.J., Eds.; World Animal Sciences—Production of Aquatic Animals (Fishes C8); Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1995; pp. 253–268. [Google Scholar]
- Niță, V.; Nenciu, M.; Nicolae, C.G. Experimental Rearing of the Golden Grey Mullet Liza aurata (Risso, 1810) in a Recirculating System at the Black Sea. Agric. Life Life Agric. Conf. Proc. 2018, 1, 149–154. [Google Scholar]
- NIMRD. Internal Reports. Current State of the Romanian Marine and Coastal Environment; National Instutute for Marine Research and Development “Grigore Antipa“: Constanta, Romania, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- AAT Bioquest. Quest Graph™ LC50 Calculator. Available online: https://www.aatbio.com/tools/lc50-calculator (accessed on 9 March 2022).
- Abbot, W.S. A Method of Computing the Effectiveness of an Insecticide. J. Econ. Entomol. 1925, 18, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US-EPAc. ECOTOX User Guide: ECOTOXicology Knowledgebase System, Version 5.3; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Avenue, NW, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Neter, J.; Wasserman, W.; Kutner, M.H. Applied Linear Statistical Models; Homewood, Irwin: Boston, MA, USA, 1990; pp. 1–1184. [Google Scholar]
- Posthuma, L.; Suter, G.W., II; Traas, T.P. Species Sensitivity Distributions in Ecotoxicology; Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; pp. 1–587. [Google Scholar]
- US-EPAd Methods/Indicators for Determining when Metals are the Cause of Biological Impairments of Rivers Streams: Species Sensitivity Distributions Chronic Exposure-Response Relationships from Laboratory Data; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), Office of Research and Development, National Center for Environmental Assessment: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2005.
- Zaharia, T.; Niță, V.; Nenciu, M. Background of Romanian Marine Aquaculture; CD Press Publishing: Bucharest, Romania, 2017; pp. 1–273. ISBN 978-606-528-393-0. [Google Scholar]
- Barton, B.A. Stress in Fishes: A Diversity of Responses with Particular Reference to Changes in Circulating Corticosteroids. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2002, 42, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AVMA. Guidelines for the Euthanasia of Animals; American Veterinary Medical Association: Schaumburg, IL, USA, 2013; pp. 1–102. ISBN 978-1-882691-21-0. [Google Scholar]
- Niţă, V.; Nenciu, M. Biological and Ethological Response of Black Sea Golden Grey Mullet (Chelon auratus Risso, 1810) Fries to Different Salinities and Temperatures. Turkish J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2020, 20, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasshoff, K.; Kremling, K.; Ehrhardt, M. Methods of Seawater Analysis; Wiley-VCH: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1999; pp. 1–599. [Google Scholar]
- Strickland, J.D.H.; Parsons, T.R. A Practical Handbook of Seawater Analysis; Fisheries Research Board of Canada: Andrews, NB, Canada, 1972; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- IAEA-MELa. Training Manual on the Measurement of Organochlorine and Petroleum Hydrocarbons in Environmental Samples; Marine Environmental Studies Laboratory: Monaco, Principality of Monaco, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- IAEA-MELb. Training Manual on the Measurement of Heavy Metals in Environmental Samples; Marine Environmental Studies Laboratory: Monaco, Principality of Monaco, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Suresh, K. An Overview of Randomization Techniques: An Unbiased Assessment of Outcome in Clinical Research. J. Hum. Reprod. Sci. 2011, 4, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Random Lists. Available online: https://www.randomlists.com/random-numbers?min=1&max=120&qty=120&dup=false (accessed on 17 January 2022).
- Zagorc-Koncan, J.; Zgajnar Gotvajn, A.; Tisler, T. Hazard Identification for 3,5-Dichlorophenol in the Aquatic Environment. Cell Mol. Biol. Lett. 2002, 7, 381–382. [Google Scholar]
- ISO-Water Quality. Marine Algal Growth Inhibition Test with Skeletonema sp. and Phaeodactylum tricornutum. 2016. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/66657.html (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- ISO-Water Quality—Determination of Acute Lethal Toxicity to Marine Copepods (Copepoda, Crustacea). 1999. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/25162.html (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- Devillers, J.; Meunier, T.; Chambon, P. Usefulness of the Dosage-Effect-Time Relation in Ecotoxicology for Determination of Different Chemical Classes of Toxicants. Tech. Sci. Munic. 1985, 80, 329–334. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, S.; Furay, V.J.; Layiwola, P.J.; Menezes-Filho, J.A. Evaluation of the Toxicity and Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationships (QSAR) of Chlorophenols to the Copepodit Stage of a Marine Copepod (Tisbe battagliai) and Two Species of Benthic Flatfish, Flounder (Platichthys flesus) and Sole (Solea solea). Chemosphere 1994, 28, 825–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, J.-H.; Lin, K.-H.; Wang, Y.-S. Acute Lethal Toxicity of Environmental Pollutants to Aquatic Organisms. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2002, 52, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigeoka, T.; Yamagata, T.; Minoda, T.; Yamauchi, F. Acute Toxicity and Hatching Inhibition of Chlorophenols to Japanese Medaka, Oryzias latipes, and Structure-Activity Relationships. Eisei Kagaku 1988, 34, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takuo, K.; Kobayashi, K. Acute Toxicity and Structure-Activity Relationships of Chlorophenols in Fish. Water Res. 1996, 30, 387–392. [Google Scholar]
- Sebaugh, J.L. Guidelines for Accurate EC50/IC50 Estimation. Pharm. Stat. 2011, 10, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romanian Ministry of Environment and Water Management. Order No. 161/2006 Regarding the Ecological Status of Surface Water Bodies. Available online: https://legislatie.just.ro/Public/DetaliiDocument/72574 (accessed on 12 March 2022).





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niță, V.; Nenciu, M.; Coatu, V. Suitability and Sensitivity of Golden Grey Mullet Chelon auratus (Risso, 1810) as a Reference Fish Species for Ecotoxicity Tests in the Black Sea. Toxics 2022, 10, 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10050222
Niță V, Nenciu M, Coatu V. Suitability and Sensitivity of Golden Grey Mullet Chelon auratus (Risso, 1810) as a Reference Fish Species for Ecotoxicity Tests in the Black Sea. Toxics. 2022; 10(5):222. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10050222
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiță, Victor, Magda Nenciu, and Valentina Coatu. 2022. "Suitability and Sensitivity of Golden Grey Mullet Chelon auratus (Risso, 1810) as a Reference Fish Species for Ecotoxicity Tests in the Black Sea" Toxics 10, no. 5: 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10050222
APA StyleNiță, V., Nenciu, M., & Coatu, V. (2022). Suitability and Sensitivity of Golden Grey Mullet Chelon auratus (Risso, 1810) as a Reference Fish Species for Ecotoxicity Tests in the Black Sea. Toxics, 10(5), 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10050222







