Bioaccumulation and Mass Balance Analysis of Veterinary Antibiotics in an Agricultural Environment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Standards
2.2. Site Description and Sample Collection
2.3. Physicochemical Analysis of Samples
2.4. Antibiotic Extraction and Clean-Up Process
2.5. Instrumental Analysis
2.6. Method Validation
2.7. Mass Balance Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical Properties of Compost and Soil
3.2. Concentrations of Antibiotics in Manure-Based Compost and Soil
3.3. Concentrations of Bioaccumulated Antibiotics in Crops
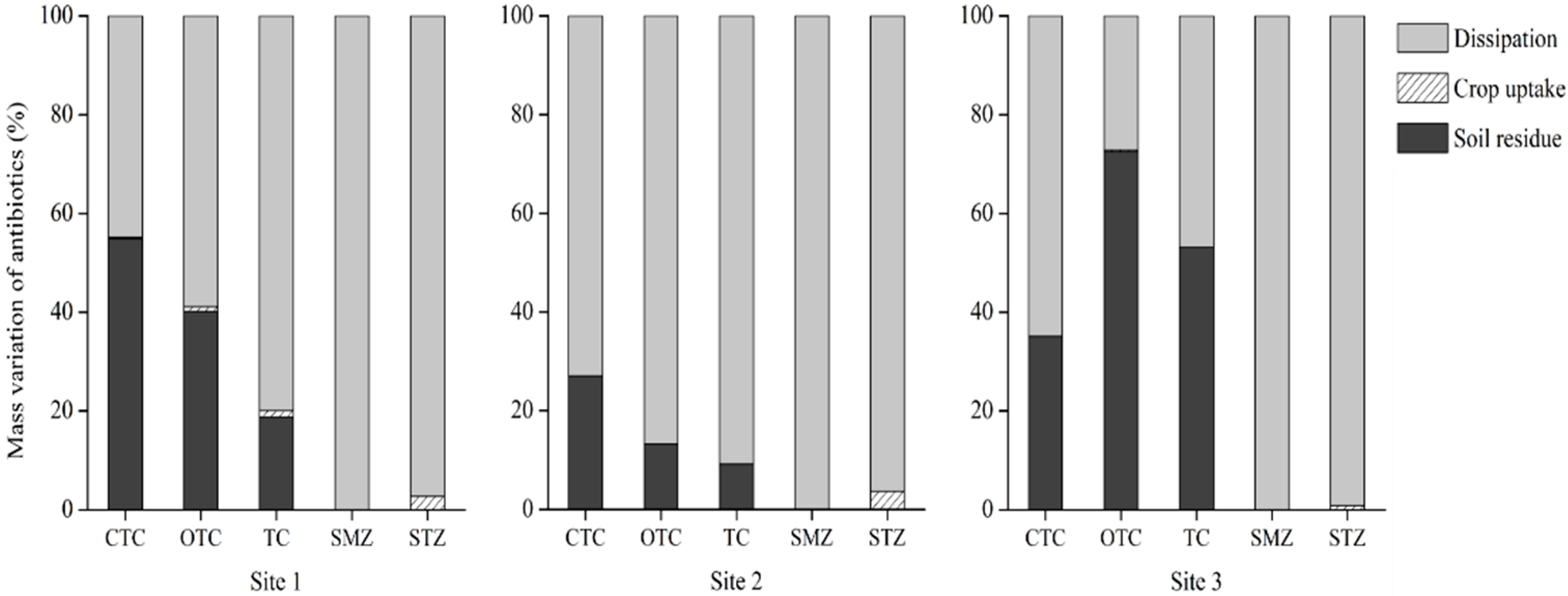
3.4. The Fate of Veterinary Antibiotics Based on Mass Balance Analysis in Soil
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hao, H.; Cheng, G.; Iqbal, Z.; Ai, X.; Hussain, H.I.; Huang, L.; Dai, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, Z. Benefits and risks of antimicrobial use in food-producing animals. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Boeckel, T.P.; Brower, C.; Gilbert, M.; Grenfell, B.T.; Levin, S.A.; Robinson, T.P.; Teillant, A.; Laxminarayan, R. Global trends in antimicrobial use in food animals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5649–5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Awad, Y.M.; Kim, K.R.; Kim, S.-C.; Kim, K.; Lee, S.R.; Lee, S.S.; Ok, Y.S. Monitoring Antibiotic Residues and Corresponding Antibiotic Resistance Genes in an Agroecosystem. J. Chem. 2015, 2015, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jjemba, P.K. The potential impact of veterinary and human therapeutic agents in manure and biosolids on plants grown on arable land: A review. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2002, 93, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larney, F.J.; Sullivan, D.M.; Buckley, K.E.; Eghball, B. The role of composting in recycling manure nutrients. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2006, 86, 597–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, M.; Chen, W.; Su, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, C. Fate of tetracyclines in swine manure of three selected swine farms in China. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 1047–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boy-Roura, M.; Mas-Pla, J.; Petrovic, M.; Gros, M.; Soler, D.; Brusi, D.; Menció, A. Towards the understanding of antibiotic occurrence and transport in groundwater: Findings from the Baix Fluvià alluvial aquifer (NE Catalonia, Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 1387–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kümmerer, K. Antibiotics in the aquatic environment–a review–part I. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 417–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillis, D.G.; Fletcher, J.; Solomon, K.R.; Sibley, P.K. Effects of ten antibiotics on seed germination and root elongation in three plant species. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2011, 60, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kong, W.; Zhu, Y.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Smith, F.; Yang, M. Uptake of oxytetracycline and its phytotoxicity to alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Environ. Pollut. 2007, 147, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Chu, L. Phytotoxicity of veterinary antibiotics to seed germination and root elongation of crops. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 126, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Jin, D.; Freitag, T.E.; Sun, W.; Yu, Q.; Fu, J.; Ma, J. A compositional shift in the soil microbiome induced by tetracycline, sulfamonomethoxine and ciprofloxacin entering a plant-soil system. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 212, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Ying, G.-G.; Tao, R.; Zhao, J.-L.; Yang, J.-F.; Zhao, L.-F. Effects of six selected antibiotics on plant growth and soil microbial and enzymatic activities. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1636–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chee-Sanford, J.C.; Aminov, R.; Krapac, I.J.; Garrigues-Jeanjean, N.; Mackie, R.I. Occurrence and diversity of tetracycline resistance genes in lagoons and groundwater underlying two swine production facilities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 1494–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luangtongkum, T.; Jeon, B.; Han, J.; Plummer, P.; Logue, C.M.; Zhang, Q. Antibiotic resistance in Campylobacter: Emergence, transmission and persistence. Futur. Microbiol. 2009, 4, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karthikeyan, K.; Meyer, M.T. Occurrence of antibiotics in wastewater treatment facilities in Wisconsin, USA. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 361, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biel-Maeso, M.; Corada-Fernández, C.; Lara-Martín, P.A. Monitoring the occurrence of pharmaceuticals in soils irrigated with reclaimed wastewater. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschall, N.; Topp, E.; Metcalfe, C.; Edwards, M.; Payne, M.; Kleywegt, S.; Russell, P.; Lapen, D. Pharmaceutical and personal care products in groundwater, subsurface drainage, soil, and wheat grain, following a high single application of municipal biosolids to a field. Chemosphere 2012, 87, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wu, L.; Liu, X.; Luo, Y. Residues and risks of veterinary antibiotics in protected vegetable soils following application of different manures. Chemosphere 2016, 152, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Chen, L.; Yen, H.; Sun, L.; Li, S.; Li, M.; Feng, Q.; Yang, L. Multimedia mass balance approach to characterizing the transport potential of antibiotics in soil-plant systems following manure application. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, A.M.; Williams, C.; Andrews, D.M.; Watson, J.E. Sorption and desorption behavior of four antibiotics at concentrations simulating wastewater reuse in agricultural and forested soils. Chemosphere 2022, 289, 133038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ter Laak, T.L.; Gebbink, W.A.; Tolls, J. Estimation of soil sorption coefficients of veterinary pharmaceuticals from soil properties. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2006, 25, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.Y.; Huwe, B. Effect of pH and soil structure on transport of sulfonamide antibiotics in agricultural soils. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 213, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blake, G.R.; Hartge, K. Bulk density. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 1 Physical and Mineralogical Method; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1986; Volume 5, pp. 363–375. [Google Scholar]
- Walkley, A.; Black, I.A. An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter, and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci. 1934, 37, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. EPA Method 1694: Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products in Water, Soil, Sediment, and Biosolids by HPLC/MS/MS; EPA-821-R-08-002; EPA: Washington, DA, USA, 2007.
- Adejumo, S.A.; Ogundiran, M.B.; Togun, A.O. Soil amendment with compost and crop growth stages influenced heavy metal uptake and distribution in maize crop grown on lead-acid battery waste contaminated soil. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 4809–4819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambone, F.; Genevini, P.; Adani, F. The effects of short-term compost application on soil chemical properties and on nutritional status of maize plant. Compost Sci. Util. 2007, 15, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Wu, G.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Liu, W.; Meng, J.; Liu, H.; Yu, X.; Jiang, G. Effects of cattle manure compost combined with chemical fertilizer on topsoil organic matter, bulk density and earthworm activity in a wheat–maize rotation system in Eastern China. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 156, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, T.J.; Han, K.J.; Muir, J.P.; Weindorf, D.C.; Lastly, L. Dairy manure compost effects on corn silage production and soil properties. Agron. J. 2008, 100, 1541–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frimpong, K.A.; Abban-Baidoo, E.; Marschner, B. Can combined compost and biochar application improve the quality of a highly weathered coastal savanna soil? Heliyon 2021, 7, e07089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, T.J.; Muir, J.P. Dairy manure compost improves soil and increases tall wheatgrass yield. Agron. J. 2006, 98, 1090–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whalen, J.K.; Chang, C.; Clayton, G.W.; Carefoot, J.P. Cattle manure amendments can increase the pH of acid soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 962–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Luo, Y.; Wu, L.; Huang, Y.; Christie, P. Residues and potential ecological risks of veterinary antibiotics in manures and composts associated with protected vegetable farming. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 5908–5918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, M.; Wu, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, H.; Ma, J. Occurrence of trace elements and antibiotics in manure-based fertilizers from the Zhejiang Province of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 559, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Dong, Y.H.; Wang, H. Residues of veterinary antibiotics in manures from feedlot livestock in eight provinces of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, Y.B.; Zakaria, M.P.; Latif, P.A.; Saari, N. Degradation of veterinary antibiotics and hormone during broiler manure composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 131, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolliver, H.; Gupta, S.; Noll, S. Antibiotic degradation during manure composting. J. Environ. Qual. 2008, 37, 1245–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvam, A.; Wong, J. Degradation of antibiotics in livestock manure during composting. Curr. Dev. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2017, 267–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.B.; Zakaria, M.P.; Latif, P.A.; Saari, N. Occurrence of veterinary antibiotics and progesterone in broiler manure and agricultural soil in Malaysia. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 488, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albero, B.; Tadeo, J.L.; Escario, M.; Miguel, E.; Pérez, R.A. Persistence and availability of veterinary antibiotics in soil and soil-manure systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 1562–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; He, T.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, L.; Shang, B.; Li, Z.; Wang, R. Occurrence of seventeen veterinary antibiotics and resistant bacterias in manure-fertilized vegetable farm soil in four provinces of China. Chemosphere 2019, 215, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamscher, G.; Pawelzick, H.T.; Höper, H.; Nau, H. Different behavior of tetracyclines and sulfonamides in sandy soils after repeated fertilization with liquid manure. Environ. Toxic. Chem. 2005, 24, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conde-Cid, M.; Ferreira-Coelho, G.; Fernandez-Calvino, D.; Nunez-Delgado, A.; Fernandez-Sanjurjo, M.J.; Arias-Estevez, M.; Alvarez-Rodriguez, E. Single and simultaneous adsorption of three sulfonamides in agricultural soils: Effects of pH and organic matter content. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 744, 140872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.; Li, S.; Sun, L. Bioaccumulation of antibiotics in crops under long-term manure application: Occurrence, biomass response and human exposure. Chemosphere 2019, 219, 882–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yu, H.; Xu, S.; Hua, R. Uptake of three sulfonamides from contaminated soil by pakchoi cabbage. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 92, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, E.L.; Nason, S.L.; Karthikeyan, K.G.; Pedersen, J.A. Root Uptake of Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Product Ingredients. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 525–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, M.; Chu, L.M. Fate of antibiotics in soil and their uptake by edible crops. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599–600, 500–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolliver, H.; Kumar, K.; Gupta, S. Sulfamethazine uptake by plants from manure-amended soil. J. Environ. Qual. 2007, 36, 1224–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Zhou, Q.; Luo, Y. Occurrence and source analysis of typical veterinary antibiotics in manure, soil, vegetables and groundwater from organic vegetable bases, northern China. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 2992–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolliver, H.; Gupta, S. Antibiotic losses in leaching and surface runoff from manure-amended agricultural land. J. Environ. Qual. 2008, 37, 1227–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiele-Brun, S.; Peters, D. Photodegradation of pharmaceutical antibiotics on slurry and soil surfaces. Landbauforsch. Volkenrode 2007, 57, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Topp, E.; Chapman, R.; Devers-Lamrani, M.; Hartmann, A.; Marti, R.; Martin-Laurent, F.; Sabourin, L.; Scott, A.; Sumarah, M. Accelerated biodegradation of veterinary antibiotics in agricultural soil following long-term exposure, and isolation of a sulfamethazine-degrading Microbacterium sp. J. Environ. Qual. 2013, 42, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-C.; Davis, J.G.; Truman, C.C.; Ascough II, J.C.; Carlson, K. Simulated rainfall study for transport of veterinary antibiotics–mass balance analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 175, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuzig, R.; Höltge, S.; Brunotte, J.; Berenzen, N.; Wogram, J.; Schulz, R. Test-plot studies on runoff of sulfonamides from manured soils after sprinkler irrigation. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2005, 24, 777–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kivits, T.; Broers, H.P.; Beeltje, H.; Van Vliet, M.; Griffioen, J. Presence and fate of veterinary antibiotics in age-dated groundwater in areas with intensive livestock farming. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 988–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, D.; Yang, D.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, Y.; He, Y.; Luo, L.; Zhou, Y. Current progress in the adsorption, transport and biodegradation of antibiotics in soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 251, 109598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karcı, A.; Balcıoğlu, I.A. Investigation of the tetracycline, sulfonamide, and fluoroquinolone antimicrobial compounds in animal manure and agricultural soils in Turkey. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 4652–4664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, J.; Chen, H.; Wei, S.; Gu, J. Antibiotic contamination in animal manure, soil, and sewage sludge in Shenyang, northeast China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 5077–5086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-Y.; Lim, J.-E.; Kim, S.-C.; Kim, K.-R.; Kwon, O.-K.; Yang, J.-E.; Ok, Y.-S. Transport of selected veterinary antibiotics (tetracyclines and sulfonamides) in a sandy loam soil: Laboratory-scale soil column experiments. J. Korean Soc. Environ. Eng. 2009, 31, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Wang, H. Adsorption behavior of antibiotic in soil environment: A critical review. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2015, 9, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Li, C.; Dolhi, J.M.; Li, S.; He, J.; Qiao, M. Characteristics of oxytetracycline sorption and potential bioavailability in soils with various physical–chemical properties. Chemosphere 2012, 87, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Hu, C.; Deng, D.; Li, Y.; Luo, L. Factors affecting sorption behaviors of tetracycline to soils: Importance of soil organic carbon, pH and Cd contamination. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 197, 110572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sassman, S.A.; Lee, L.S. Sorption of three tetracyclines by several soils: Assessing the role of pH and cation exchange. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 7452–7459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueroa, R.A.; Leonard, A.; MacKay, A.A. Modeling tetracycline antibiotic sorption to clays. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Veterinary Antibiotics | R2 | Recovery (%) | Method Detection Limit (ng/kg) | Limit of Quantification (ng/kg) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manure-Based Compost | Soil | Crop | Manure-Based Compost | Soil | Crop | Manure-Based Compost | Soil | Crop | ||
| CTC | 0.9971 | 79.8 | 72.9 | 101.8 | 4.0 | 2.9 | 4.6 | 12.8 | 9.3 | 14.7 |
| OTC | 0.9992 | 105.8 | 110.0 | 89.9 | 10.4 | 8.7 | 4.0 | 33.0 | 27.6 | 12.8 |
| TC | 0.9982 | 66.3 | 111.9 | 105.9 | 3.3 | 8.2 | 1.5 | 10.5 | 26.3 | 4.7 |
| SMZ | 0.9995 | 108.5 | 81.4 | 80.3 | 2.1 | 2.9 | 1.2 | 6.5 | 9.2 | 3.7 |
| SMX | 0.9987 | 83.8 | 62.8 | 76.7 | 10.6 | 11.9 | 0.7 | 33.6 | 37.8 | 2.4 |
| STZ | 0.9993 | 59.1 | 58.8 | 64.4 | 4.5 | 3.6 | 1.1 | 14.3 | 11.3 | 3.2 |
| Sampling Sites | pH | EC | OM |
|---|---|---|---|
| dS/m | (%) | ||
| Site 1 | 9.90 ± 0.03 a | 39.0 ± 0.66 c | 90.3 ± 0.59 a |
| Site 2 | 8.71 ± 0.02 c | 70.5 ± 0.68 a | 78.7 ± 6.40 b |
| Site 3 | 9.68 ± 0.01 b | 55.4 ± 1.85 b | 78.2 ± 1.29 b |
| Sampling Sites | Soil Texture | Soil pH | EC dS/m | OM (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| March | Spetember | March | Spetember | March | Spetember | ||
| Site 1 | Sandy loam | 5.10 ± 0.01 a | 5.30 ± 0.05 a | 0.24 ± 0.01 a | 0.52 ± 0.01 b | 2.10 ± 0.04 a | 3.32 ± 0.06 b |
| Site 2 | Sandy loam | 5.43 ± 0.02 a | 7.00 ± 0.02 b | 0.37 ± 0.02 a | 0.94 ± 0.04 b | 2.65 ± 0.13 a | 3.47 ± 0.04 b |
| Site 3 | Sandy clay loam | 6.25 ± 0.02 a | 7.40 ± 0.09 b | 0.38 ± 0.03 a | 0.45 ± 0.02 b | 1.91 ± 0.06 a | 2.61 ± 0.04 b |
| Sampling Sites | Concentrations of Veterinary Antibiotics (Mean ± SD, μg/kg) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTC | OTC | TC | SMZ | SMX | STZ | |
| Site 1 | 24.38 ± 1.55 b | 8.06 ± 0.69 c | 7.41 ± 0.72 b | 3.52 ± 0.06 c | BLD | 27.94 ± 2.86 b |
| Site 2 | 7.85 ± 0.52 c | 29.53 ± 1.30 b | 4.87 ± 0.14 c | 5.02 ± 0.72 b | BLD | 19.60 ± 1.85 c |
| Site 3 | 234.19 ± 1.80 a | 38.08 ± 3.08 a | 44.93 ± 2.49 a | 28.14 ± 1.29 a | BLD | 187.49 ± 1.56 a |
| Date | Sampling Sites | Concentrations of Veterinary Antibiotics (Mean ± SD, μg/kg) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTC | OTC | TC | SMZ | SMX | STZ | ||
| March | Site 1 | 4.68 ± 0.54 c | 2.54 ± 0.05 c | 3.46 ± 0.49 c | BLD | BLD | BLD |
| Site 2 | 8.03 ± 1.28 b | 7.32 ± 0.31 b | 5.09 ± 0.72 b | BLD | BLD | BLD | |
| Site 3 | 13.08 ± 0.14 a | 10.56 ± 0.85 a | 7.74 ± 0.55 a | BLD | BLD | BLD | |
| September | Site 1 | 2.64 ± 0.30 b | 1.04 ± 0.06 b | 0.66 ± 0.11 b | BLD | BLD | BLD |
| Site 2 | 2.18 ± 0.19 b | 0.99 ± 0.09 b | 0.52 ± 0.01 b | BLD | BLD | BLD | |
| Site 3 | 5.23 ± 0.06 a | 7.87 ± 0.33 a | 4.29 ± 0.50 a | BLD | BLD | BLD | |
| Plant Part | Crops | Antibiotic Concentrations (Mean ± SD, μg/kg) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTC | OTC | TC | SMZ | SMX | STZ | ||
| Edible parts | Perilla | 24.71 ± 1.51 | 23.60 ± 0.46 | 39.57 ± 1.27 | BLD | BLD | 4.85 ± 0.25 |
| Maize | BLD | BLD | BLD | BLD | BLD | 1.88 ± 0.39 | |
| Soybean | BLD | 12.72 ± 0.84 | BLD | BLD | BLD | 3.72 ± 0.23 | |
| Stem | Perilla | 9.62 ± 1.22 | 19.48 ± 3.23 | 34.50 ± 5.32 | BLD | BLD | 2.91 ± 0.09 |
| Maize | BLD | BLD | BLD | BLD | BLD | 1.30 ± 0.02 | |
| Soybean | BLD | 10.91 ± 1.78 | BLD | BLD | BLD | 3.13 ± 0.58 | |
| Root | Perilla | 4.60 ± 0.31 | 6.75 ± 1.10 | 20.79 ± 3.67 | BLD | BLD | 1.95 ± 0.56 |
| Maize | BLD | BLD | BLD | BLD | BLD | 1.05 ± 0.07 | |
| Soybean | BLD | 9.90 ± 0.19 | BLD | BLD | BLD | 3.07 ± 0.47 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.-W.; Hong, Y.-K.; Yang, J.-E.; Kwon, O.-K.; Kim, S.-C. Bioaccumulation and Mass Balance Analysis of Veterinary Antibiotics in an Agricultural Environment. Toxics 2022, 10, 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10050213
Kim J-W, Hong Y-K, Yang J-E, Kwon O-K, Kim S-C. Bioaccumulation and Mass Balance Analysis of Veterinary Antibiotics in an Agricultural Environment. Toxics. 2022; 10(5):213. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10050213
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jin-Wook, Young-Kyu Hong, Jae-E. Yang, Oh-Kyung Kwon, and Sung-Chul Kim. 2022. "Bioaccumulation and Mass Balance Analysis of Veterinary Antibiotics in an Agricultural Environment" Toxics 10, no. 5: 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10050213
APA StyleKim, J.-W., Hong, Y.-K., Yang, J.-E., Kwon, O.-K., & Kim, S.-C. (2022). Bioaccumulation and Mass Balance Analysis of Veterinary Antibiotics in an Agricultural Environment. Toxics, 10(5), 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10050213






