Environmental Hazards of Nanobiomaterials (Hydroxyapatite-Based NMs)—A Case Study with Folsomia candida—Effects from Long Term Exposure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Organisms
2.2. Test Soil
2.3. Test Materials, Synthesis and Characterization
2.4. Spiking Procedure
2.5. Test Procedure
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Materials’ Characterization
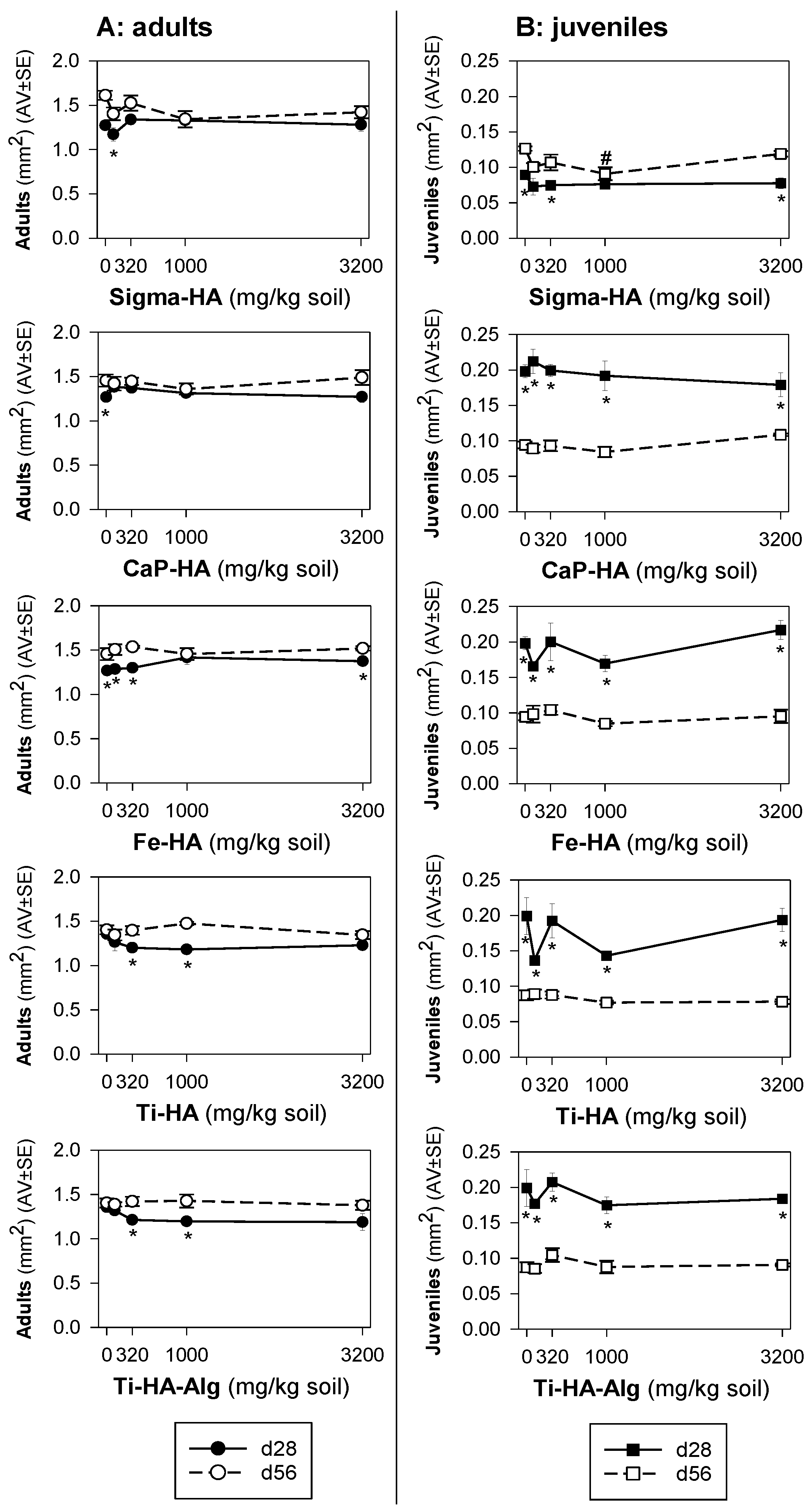
3.2. Toxicity Tests
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Melchor-Martínez, E.M.; Torres Castillo, N.E.; Macias-Garbett, R.; Lucero-Saucedo, S.L.; Parra-Saldívar, R.; Sosa-Hernández, J.E. Modern World Applications for Nano-Bio Materials: Tissue Engineering and COVID-19. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 597958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccirillo, C.; Castro, P.L. Calcium hydroxyapatite-based photocatalysts for environment remediation: Characteristics, performances and future perspectives. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 193, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besinis, A.; Van Noort, R.; Martin, N. Infiltration of demineralized dentin with silica and hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. Dent. Mater. 2012, 28, 1012–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioku, K. Tailored bioceramics of calcium phosphates for regenerative medicine. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2010, 118, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sopyan, I.; Mel, M.; Ramesh, S.; Khalid, K.A. Porous hydroxyapatite for artificial bone applications. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2007, 8, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, B.; Mondal, S.; Mondal, A.; Mandal, N. Fish scale derived hydroxyapatite scaffold for bone tissue engineering. Mater. Charact. 2016, 121, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surmeneva, M.A.; Mukhametkaliyev, T.M.; Khakbaz, H.; Surmenev, R.A.; Bobby Kannan, M. Ultrathin film coating of hydroxyapatite (HA) on a magnesium-calcium alloy using RF magnetron sputtering for bioimplant applications. Mater. Lett. 2015, 152, 280–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surmeneva, M.A.; Ivanova, A.A.; Tian, Q.; Pittman, R.; Jiang, W.; Lin, J.; Liu, H.H.; Surmenev, R.A. Bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cell response to the RF magnetron sputter deposited hydroxyapatite coating on AZ91 magnesium alloy. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 221, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Yang, J.; Liu, W.; Yan, Y.; Wang, Y. Hydroxyapatite as a passivator for safe wheat production and its impacts on soil microbial communities in a Cd-contaminated alkaline soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 404, 124005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nery, É.M.; Martinez, R.M.; Velasco, M.V.R.; Baby, A.R. A short review of alternative ingredients and technologies of inorganic UV filters. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2021, 20, 1061–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Rahaman, M.N.; Brown, R.F.; Day, D.E. Evaluation of BSA protein release from hollow hydroxyapatite microspheres into PEG hydrogel. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 2245–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swain, S.K.; Sarkar, D. Study of BSA protein adsorption/release on hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 286, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Wang, K.; Tian, J.; Shu, Y.; Yang, J.; Xiao, W.; Li, B.; Liao, X. Hierarchical porous hydroxyapatite fibers with a hollow structure as drug delivery carriers. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 19079–19085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzo, B.; Sidoti, M.C.; Roveri, N.; Tampieri, A.; Sandri, M.; Bertolazzi, L.; Galbusera, F.; Dubini, G.; Vena, P.; Contro, R. Controlled drug delivery from porous hydroxyapatite grafts: An experimental and theoretical approach. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2005, 25, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerasuriya, D.R.K.; Wijesinghe, W.P.S.L.; Rajapakse, R.M.G. Encapsulation of anticancer drug copper bis(8-hydroxyquinoline) in hydroxyapatite for pH-sensitive targeted delivery and slow release. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 71, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, J.S.; Appleford, M.; Ong, J.L.; Wenke, J.C.; Kim, J.M.; Choi, S.H.; Oh, D.S. Porous hydroxyapatite scaffold with three-dimensional localized drug delivery system using biodegradable microspheres. J. Control. Release 2011, 153, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truc, L.N.T.; Hong, S.; No, K. Evaluation of the Role of Hydroxyapatite in TiO2/Hydroxyapatite Photocatalytic Materials. In Photocatalysts-Applications and Attributes; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bogya, E.S.; Czikó, M.; Barabás, R.; Csavdari, A.A. Influence of synthesis method of nano-hydroxyapatite-based materials on cadmium sorption processes. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2014, 11, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lin, S.; Lu, X.-Q.; Chen, Z. Removal of Pb(II) from water using synthesized kaolin supported nanoscale zero-valent iron. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 163, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, D.S.; Santos, A.M.C.; Neves, G.A.; Menezes, R.R. A brief review on hydroxyapatite production and use in biomedicine. Ceramica 2019, 65, 282–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panseri, S.; Cunha, C.; D’Alessandro, T.; Sandri, M.; Giavaresi, G.; Marcacci, M.; Hung, C.T.; Tampieri, A. Intrinsically superparamagnetic Fe-hydroxyapatite nanoparticles positively influence osteoblast-like cell behaviour. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2012, 10, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panseri, S.; Montesi, M.; Sandri, M.; Iafisco, M.; Adamiano, A.; Ghetti, M.; Cenacchi, G.; Tampieri, A. Magnetic Labelling of Mesenchymal Stem Cells with Iron-Doped Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles as Tool for Cell Therapy. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2016, 12, 909–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Ong, K.J.; Ede, J.D.; Stafford, J.L.; Ng, K.W.; Goss, G.G.; Loo, S.C.J. Evaluating the Toxicity of Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles in Catfish Cells and Zebrafish Embryos. Small 2013, 9, 1734–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pappus, S.A.; Ekka, B.; Sahu, S.; Sabat, D.; Dash, P.; Mishra, M. A toxicity assessment of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles on development and behaviour of Drosophila melanogaster. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2017, 19, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundschuh, M.; Filser, J.; Lüderwald, S.; McKee, M.S.; Metreveli, G.; Schaumann, G.E.; Schulz, R.; Wagner, S. Nanoparticles in the environment: Where do we come from, where do we go to? Environ. Sci. Eur. 2018, 30, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalvo, D.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Degryse, F. Efficacy of Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles as Phosphorus Fertilizer in Andisols and Oxisols. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2015, 79, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, B.; Römbke, J.; Amorim, M.J.B. On the importance of longer-term exposure to stressors—A critical review and proposal for multigenerational testing in standard soil invertebrates. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 854, 158680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. 232 Test No. 232: Collembolan Reproduction Test in Soil. In OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2; Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development: Paris, France, 2016; ISBN 9789264264601. [Google Scholar]
- Guimarães, B.; Maria, V.L.; Römbke, J.; Amorim, M.J.B. Multigenerational exposure of Folsomia candida to ivermectin—Using avoidance, survival, reproduction, size and cellular markers as endpoints. Geoderma 2019, 337, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, B.; Maria, V.L.; Römbke, J.; Amorim, M.J.B. Exposure of Folsomia candida (Willem 1902) to teflubenzuron over three generations—Increase of toxicity in the third generation. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 134, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landi, E.; Logroscino, G.; Proietti, L.; Tampieri, A.; Sandri, M.; Sprio, S. Biomimetic Mg-substituted hydroxyapatite: From synthesis to in vivo behaviour. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2008, 19, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tampieri, A.; D’Alessandro, T.; Sandri, M.; Sprio, S.; Landi, E.; Bertinetti, L.; Panseri, S.; Pepponi, G.; Goettlicher, J.; Bañobre-López, M.; et al. Intrinsic magnetism and hyperthermia in bioactive Fe-doped hydroxyapatite. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 843–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamiano, A.; Sangiorgi, N.; Sprio, S.; Ruffini, A.; Sandri, M.; Sanson, A.; Gras, P.; Grossin, D.; Francès, C.; Chatzipanagis, K.; et al. Biomineralization of a titanium-modified hydroxyapatite semiconductor on conductive wool fibers. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 7608–7621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OECD. Guidance on Sample Preparation and Dosimetry for the Safety Testing of Manufactured Nanomaterials. In Series on the Safety of Manufactured Nanomaterials No. 36; Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development: Paris, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SigmaPlot 12.0 Statistical Package for the Social Sciences—SigmaPlot for Windows, Systat Software Inc.: Chicago, IL, USA, 2011.
- Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Han, R.; Wei, W. Enhanced tetracycline adsorption onto hydroxyapatite by Fe(III) incorporation. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 247, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Fang, Z.; Zheng, L.; Cheng, W.; Tsang, P.E.; Fang, J.; Zhao, D. Remediation of lead contaminated soil by biochar-supported nano-hydroxyapatite. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 132, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanh, N.T.; Bich, P.T.N.; Thao, H.T.T. Acute and subchronic oral toxicity assessment of calcium hydroxyapatite-alginate in animals. Vietnam J. Chem. 2019, 57, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tampieri, A.; Sandri, M.; Sprio, S. Physical Solar Filter Consisting of Substituted Hydroxyapatite in an Organic Matrix. 2022. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/US10813856B2/en (accessed on 4 October 2022).

| Test Material | Composition | Size | Surface Charge (mV) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DLS (nm) | X-ray sedimen-tography (μm) | ELS ζ potential | ||
| Sigma-HA | n/a | 2441 | n/a | 1.35 |
| CaP-HA | Ca = 34 a, P = 16 a, Ca/P =1.64 a (mol/mol) | 320 | d90 = 1.83 b, d50 = 1.22 b, d10 = 0.38 b | −19.6 |
| Fe-HA | Ca = 23 a, P = 15 a, Fe = 10 a, (Ca + Fe)/P= 1.64 a (mol/mol) | 164 | d90 = 1.45, d50 = 1.16, d10 = 0.87 | −19.3 |
| Ti-HA | Ca= 37 a, P = 14.6 a, Ti = 4.5 a, (Ca + Ti)/(P + Ti)= 1.49 mol/mol a. | 242 | d90 = 1.54, d50 = 0.29 | −9.11 |
| Ti-HA-Alg | Ca/P = 1.60 mol a; (Ca + Ti)/(P + Ti)= 1.49 mol/mol a; Ti/Ca = 15 (mol%) a. Ti/P = 23.2 (mol%) a. HA: Alg= 90:10 b | n/a | n/a | n/a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guimarães, B.; Gomes, S.I.L.; Campodoni, E.; Sandri, M.; Sprio, S.; Blosi, M.; Costa, A.L.; Amorim, M.J.B.; Scott-Fordsmand, J.J. Environmental Hazards of Nanobiomaterials (Hydroxyapatite-Based NMs)—A Case Study with Folsomia candida—Effects from Long Term Exposure. Toxics 2022, 10, 704. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10110704
Guimarães B, Gomes SIL, Campodoni E, Sandri M, Sprio S, Blosi M, Costa AL, Amorim MJB, Scott-Fordsmand JJ. Environmental Hazards of Nanobiomaterials (Hydroxyapatite-Based NMs)—A Case Study with Folsomia candida—Effects from Long Term Exposure. Toxics. 2022; 10(11):704. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10110704
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuimarães, Bruno, Susana I. L. Gomes, Elisabetta Campodoni, Monica Sandri, Simone Sprio, Magda Blosi, Anna L. Costa, Mónica J. B. Amorim, and Janeck J. Scott-Fordsmand. 2022. "Environmental Hazards of Nanobiomaterials (Hydroxyapatite-Based NMs)—A Case Study with Folsomia candida—Effects from Long Term Exposure" Toxics 10, no. 11: 704. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10110704
APA StyleGuimarães, B., Gomes, S. I. L., Campodoni, E., Sandri, M., Sprio, S., Blosi, M., Costa, A. L., Amorim, M. J. B., & Scott-Fordsmand, J. J. (2022). Environmental Hazards of Nanobiomaterials (Hydroxyapatite-Based NMs)—A Case Study with Folsomia candida—Effects from Long Term Exposure. Toxics, 10(11), 704. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10110704








