Rapid Simultaneous Determination of Three Synthetic Cannabinoids in Urine and Plasma of Rats Using Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents, Supplies, and Specimens
2.2. Animals and Treatment
2.3. Sample Preparation
2.4. LC-MS/MS Analysis
2.5. Method Validation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
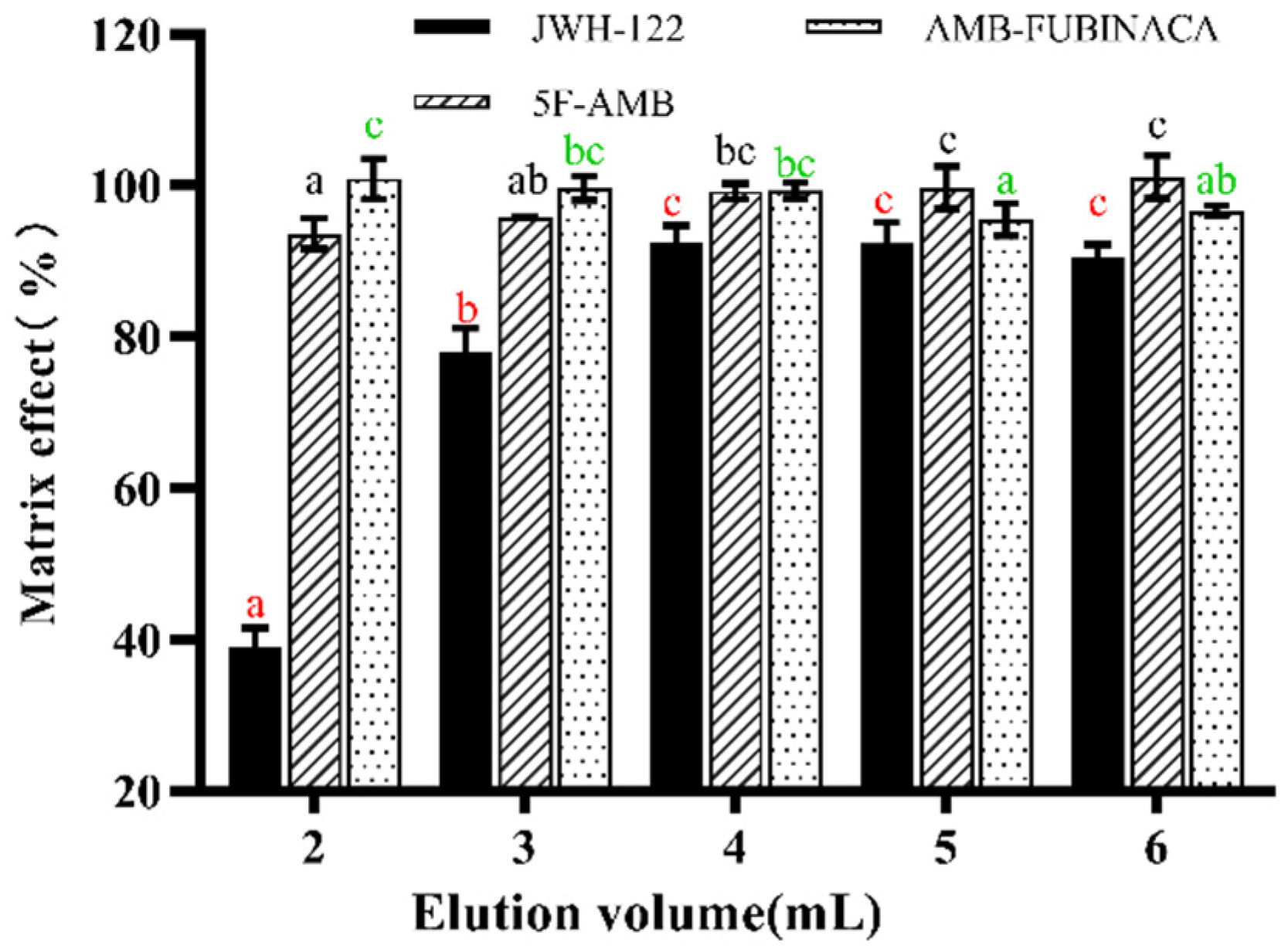
3.1. Extraction Conditions
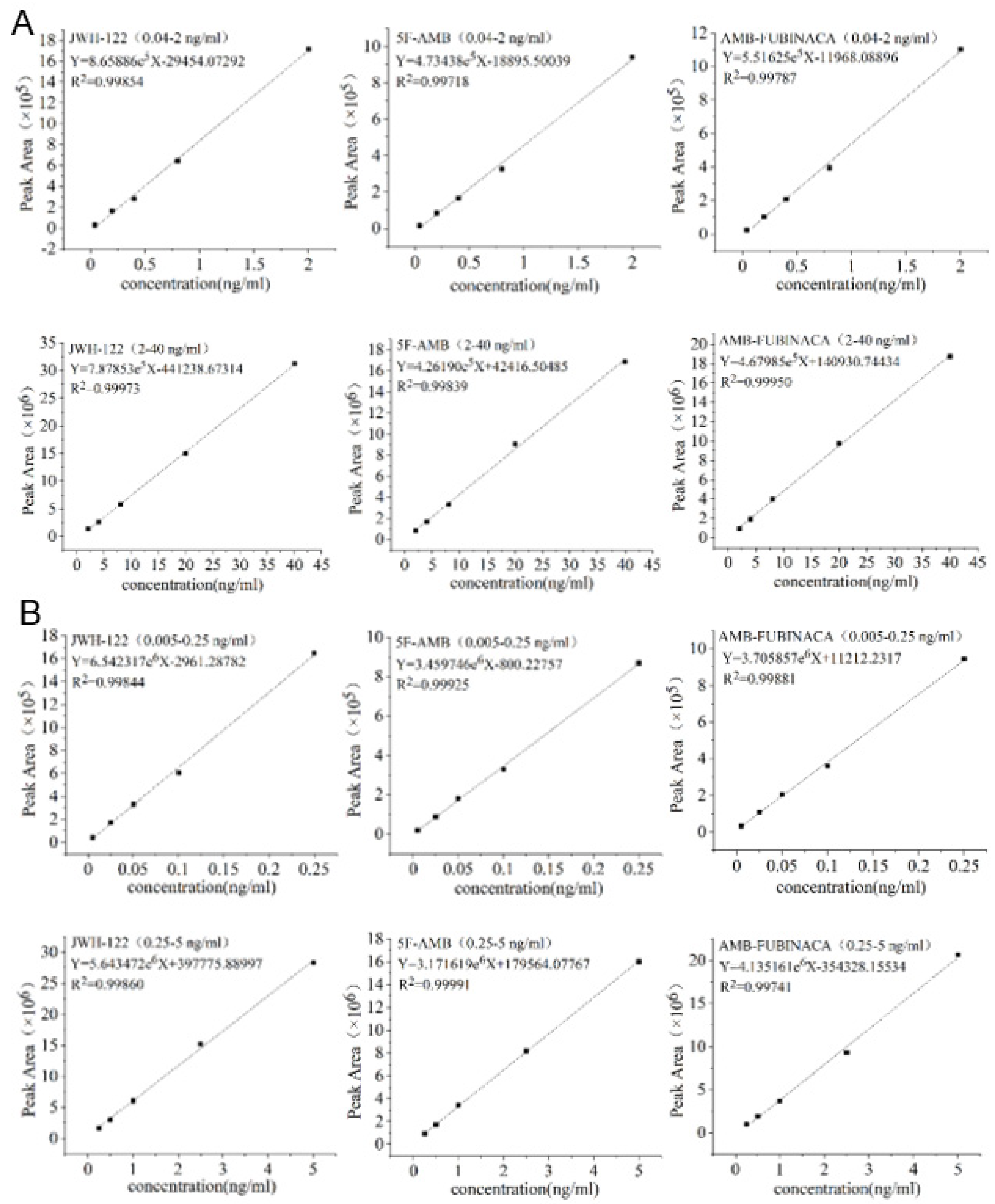
3.2. Method Validation
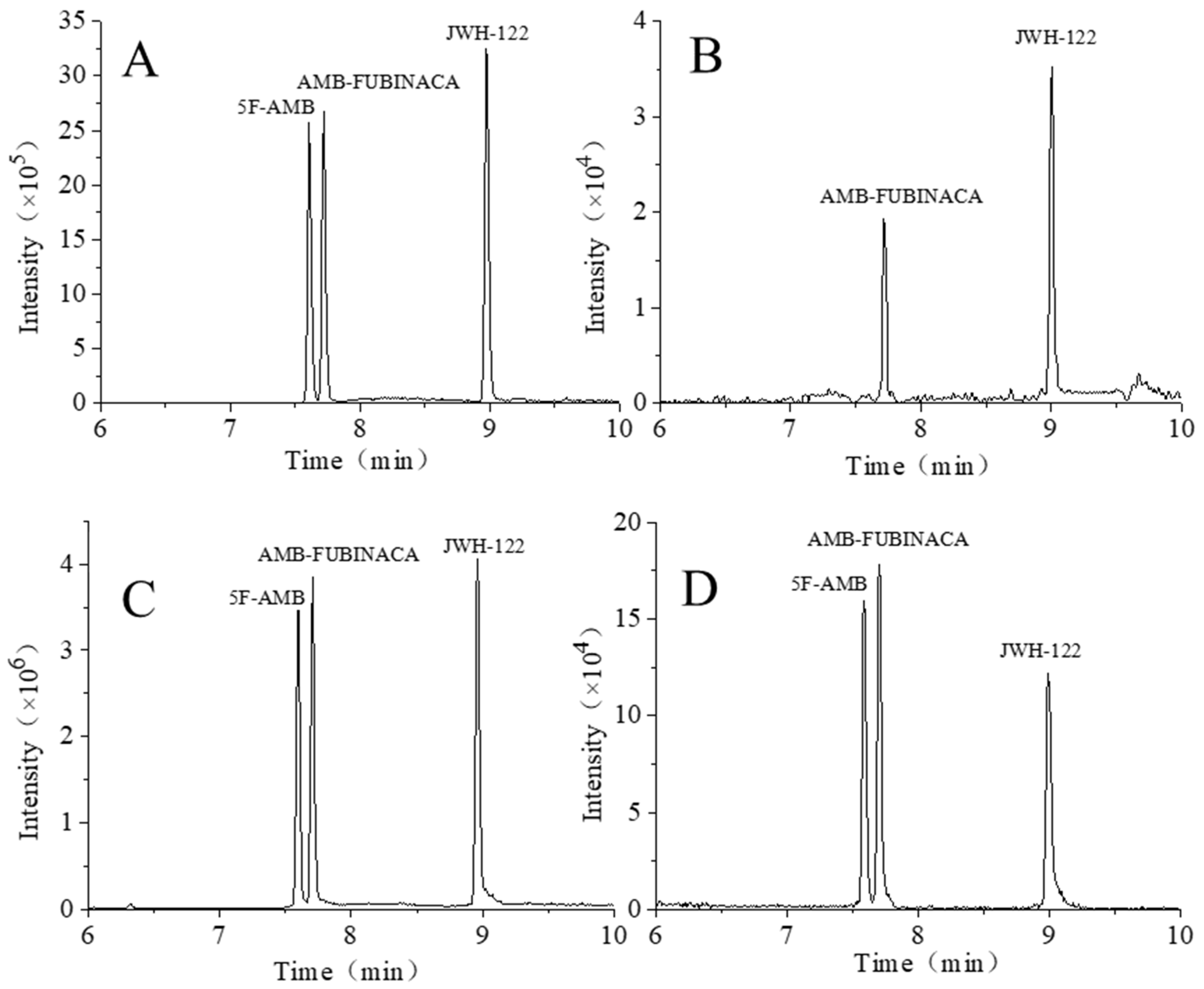
3.3. Sample Analysis of Synthetic Cannabinoids
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NPS | New Psychoactive Substance |
| EWS | Early Warning System |
| EMCDDA | European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction |
| JWH-122 | 4-methylnaphthalen-1-yl-(1-pentylindol-3-yl) methanone |
| 5F-AMB | methyl (1-(5-fluoropentyl)-1H-indazole-3-carbonyl)-L-valinate |
| AMB-FUBINACA | methyl 2-(1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-1H-indazole-3-carboxamido)-3-methylbutanoate |
| LC-MS/MS | liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry |
| JWH-018 | 1-Pentyl-3-(1-naphthoyl) indole |
| AKB-48 | N-(1-Adamantyl)-1-pentylindazole-3-carboxamide |
| MDMB-CHMINACA | indole carboxamides |
| LOD | limit of detection |
| LOQ | limit of quantitation |
References
- Huffman, J.; Dai, D.; Martin, B.R.; David, R.C. Synthesis and Pharmacology of Cannabimimetic Indoles. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1994, 4, 563–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurney, S.; Scott, K.S.; Kacinko, S.L.; Presley, B.C.; Logan, B.K. Pharmacology, Toxicology, and Adverse Effects of Synthetic Cannabinoid Drugs. Forensic. Sci. Rev. 2014, 26, 53–78 . Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26226970/ (accessed on 7 August 2022). [PubMed]
- Scheidweiler, K.B.; Huestis, M.A. Simultaneous quantification of 20 synthetic cannabinoids and 21 metabolites, and semi-quantification of 12 alkyl hydroxy metabolites in human urine by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1327, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsohly, M.A.; Gul, W.; Wanas, A.S.; Amira, S.W.; Mohamed, M.R. Synthetic cannabinoids: Analysis and metabolites. Life Sci. 2014, 97, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaneto, M.S.; Wohlfarth, A.; Desrosiers, N.A.; Hartman, R.A.; Gorelick, D.A.; Huestis, M.A. Synthetic cannabinoids pharmacokinetics and detection methods in biological matrices. Drug Metab. Rev. 2015, 47, 124–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, M.; Diao, X.; Wohlfarth, A.; Scheidweiler, K.B.; Huestis, M.A. Metabolic profiling of new synthetic cannabinoids AMB and 5F-AMB by human hepatocyte and liver microsome incubations and high-resolution mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass. Sp. 2016, 30, 1067–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchiyama, N.; Shimokawa, Y.; Kawamura, M.; Hanajiri, R.K.; Hakamatsuka, T. Chemical analysis of a benzofuran derivative, 2-(2-ethylaminopropyl)benzofuran (2-EAPB), eight synthetic cannabinoids, five cathinone derivatives, and five other designer drugs newly detected in illegal products. Forensic. Toxicol. 2014, 32, 266–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobato-Freitas, C.; Brito-da-Costa, A.M.; Dinis-Oliveira, R.J.; Carmo, H.; Carvalho, F.; Silva, J.P.; Dias-da-Silva, D. Overview of Synthetic Cannabinoids ADB-FUBINACA and AMB-FUBINACA: Clinical, Analytical, and Forensic Implications. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, A.J.; Banister, S.D.; Irizarry, L.; Trecki, J.; Schwartz, M.; Gerona, R. "Zombie" Outbreak Caused by the Synthetic Cannabinoid AMB-FUBINACA in New York. New Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jager, A.; Warner, J.V.; Henman, M.; Ferguson, W.; Hall, A. LC-MS/MS method for the quantitation of metabolites of eight commonly-used synthetic cannabinoids in human urine-An Australian perspective. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life 2012, 897, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoes, S.S.; Silva, I.; Ajenjo, A.C.; Dias, M.J. Validation and application of an UPLC–MS/MS method for the quantification of synthetic cannabinoids in urine samples and analysis of seized materials from the Portuguese market. Forensic. Sci. Int. 2014, 243, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, C.; Murach, J.; Krueger, L.; Scharrenbroch, L.; Unger, M.; Madea, B.; Sydow, K. Simultaneous detection of 93 synthetic cannabinoids by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and retrospective application to real forensic samples. Drug Test Anal. 2017, 9, 721–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrance, H.J.; Aldlgan, A.A. Bioanalytical methods for the determination of synthetic cannabinoids and metabolites in biological specimens. TRAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 80, 444–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, A.L.; Chimalakonda, K.C.; Moran, C.L.; Keith, R.M.; Pandya, A.R.; James, L.P.; Kokes, C.; Moran, J.K. K2 Toxicity: Fatal Case of Psychiatric Complications Following AM2201 Exposure. J. Forensic. Sci. 2014, 58, 1676–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigdon, B.A.; Kennedy, P.; Corp, R.; Chemical, C. LC/MS/MS Analysis of Metabolites of Synthetic Cannabinoids JWH-018 and JWH-073 in Urine. Forensic. Toxicol. 2011, 52, 423–438. Available online: https://www.chromtech.net.au/pdf2/Clinical,%20Forensic%20%20Toxicology_Cannabinoids%20JWH-018%20and%20JWH-073%20in%20Urine_CFAN1383.pdf (accessed on 7 August 2022).
- Erol, E.Y.; Yeter, O.; Alpertunga, B. Validation of JWH-018 and its metabolites in blood and urine by UPLC–MS/MS: Monitoring in forensic cases. Forensic. Sci. Int. 2015, 248, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matuszewski, B.K.; Constanzer, M.L.; Chavez-Eng, C.M. Strategies for the Assessment of Matrix Effect in Quantitative Bioanalytical Methods Based on HPLC−MS/MS. ScAnal Chem. 2003, 75, 3019–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Li, L.; Ye, Y.; Zheng, L.; Jiang, Y. Simultaneous determination of major phytocannabinoids, their main metabolites, and common synthetic cannabinoids in urine samples by LC-MS/MS. J. Chromatogr. B 2016, 1033–1034, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneisel, S.; Speck, M.; Moosmann, B.; Corneillie, T.M.; Butlin, N.G.; Auwärter, V. LC/ESI-MS/MS method for quantification of 28 synthetic cannabinoids in neat oral fluid and its application to preliminary studies on their detection windows. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 4691–4706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, N.C.; Poole, C.F. Mechanistic study of the sorption properties of OASIS HLB and its use in solid-phase extraction. Chromatographia 2002, 56, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.; Schäffer, A.; Smith, K. Equilibrium partitioning of organic compounds to OASIS HLB as a function of compound concentration, pH, temperature and salinity. Chemosphere 2017, 174, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Diehl, D.M.; Trammell, B.; Brousmiche, D.; Woods, E.; Gara, J.; Iraneta, P.C.; Karn, S.; Walter, T.; Xu, Y.; et al. A Novel, Mixed-Mode Weak Cation Exchange SPE Sorbent: Oasis WCX. LC-GC Eur. 2004, 22, 57–58. Available online: https://www.waters.com/webassets/cms/library/docs/wa40491.pdf (accessed on 7 August 2022).
- Yawney, J.; Treacy, S.; Hindmarsh, K.W.; Burczynski, F.J. A general screening method for acidic, neutral, and basic drugs in whole blood using the Oasis MCX column. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2002, 6, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Berg, T.; Kaur, L.; Risnes, A.; Havig, S.M.; Karinen, R. Determination of a selection of synthetic cannabinoids and metabolites in urine by UHPSFC-MS/MS and by UHPLC-MS/MS. Drug Test Anal. 2016, 8, 708–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, M.; Yang, W.; Choi, H.; Chang, H.; Lee, S.; Kim, E.; Chunga, H. Monitoring of urinary metabolites of JWH-018 and JWH-073 in legal cases. Forensic. Sci. Int. 2013, 23, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaneto, M.S.; Scheidweiler, K.B.; Gandhi, A.; Wohlfarth, A.; Klette, K.L.; Martin, T.M.; Huestis, M.A. Quantitative urine confirmatory testing for synthetic cannabinoids in randomly collected urine specimens. Drug Test Anal. 2015, 7, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlfarth, A.; Scheidweiler, K.B.; Chen, X.; Liu, H.; Huestis, M.A. Qualitative Confirmation of 9 Synthetic Cannabinoids and 20 Metabolites in Human Urine Using LC-MS/MS and Library Search. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 3730–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, B.; Cho, H.S.; Kim, J.; Sim, J.; Seol, I.; Baeck, S.K.; In, S.; Shin, D.H.; Kim, E. Simultaneous determination of synthetic cannabinoids and their metabolites in human hair using LC-MS/MS and application to human hair. Forensic. Sci. Int. 2020, 306, 110058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damon, B.; Anna, T.; Richard, S. A Fast and Comprehensive Analysis of 32 Synthetic Cannabinoids Using Agilent Triple Quadrupole LC–MS-MS. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2017, 1, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
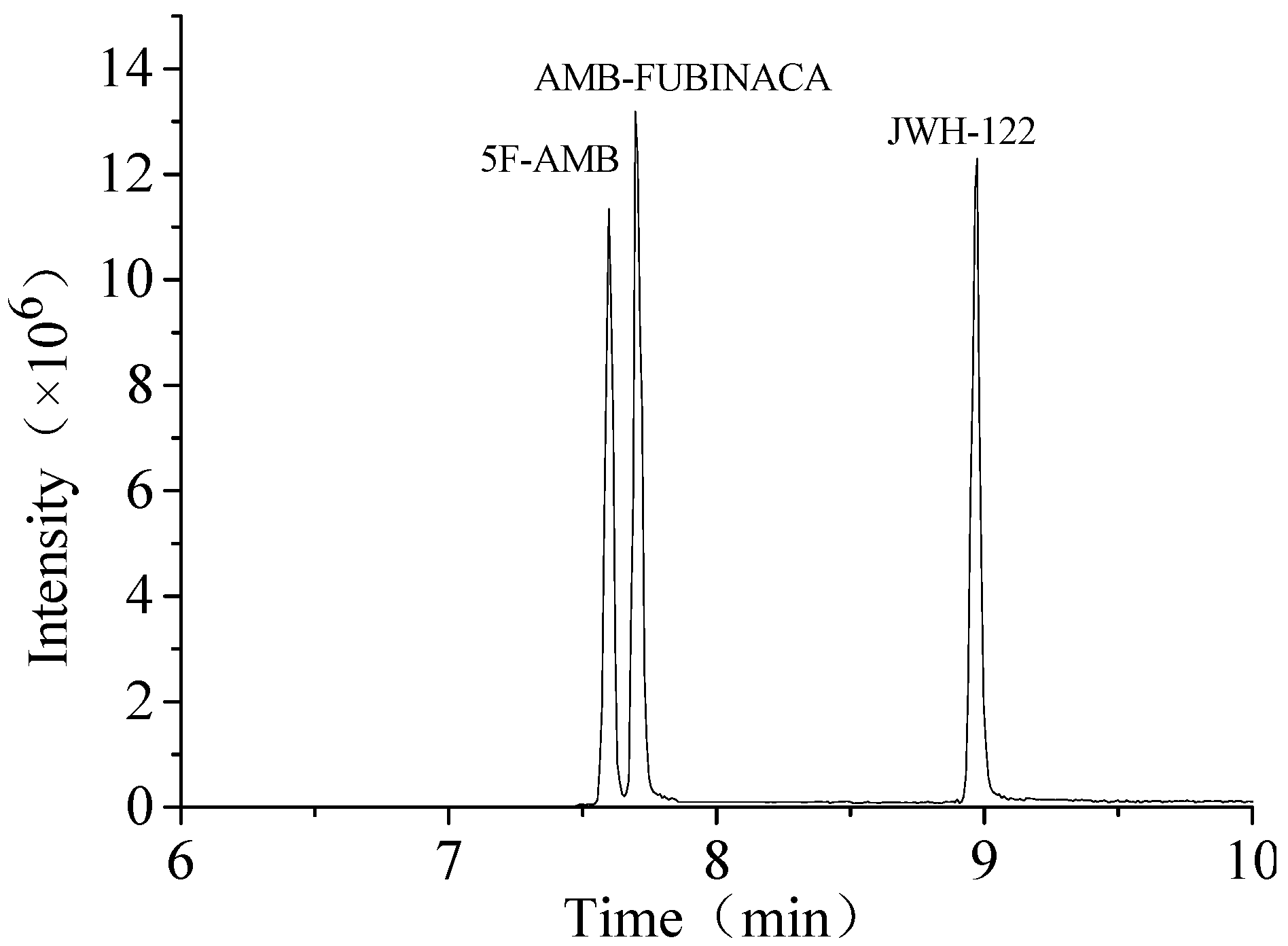
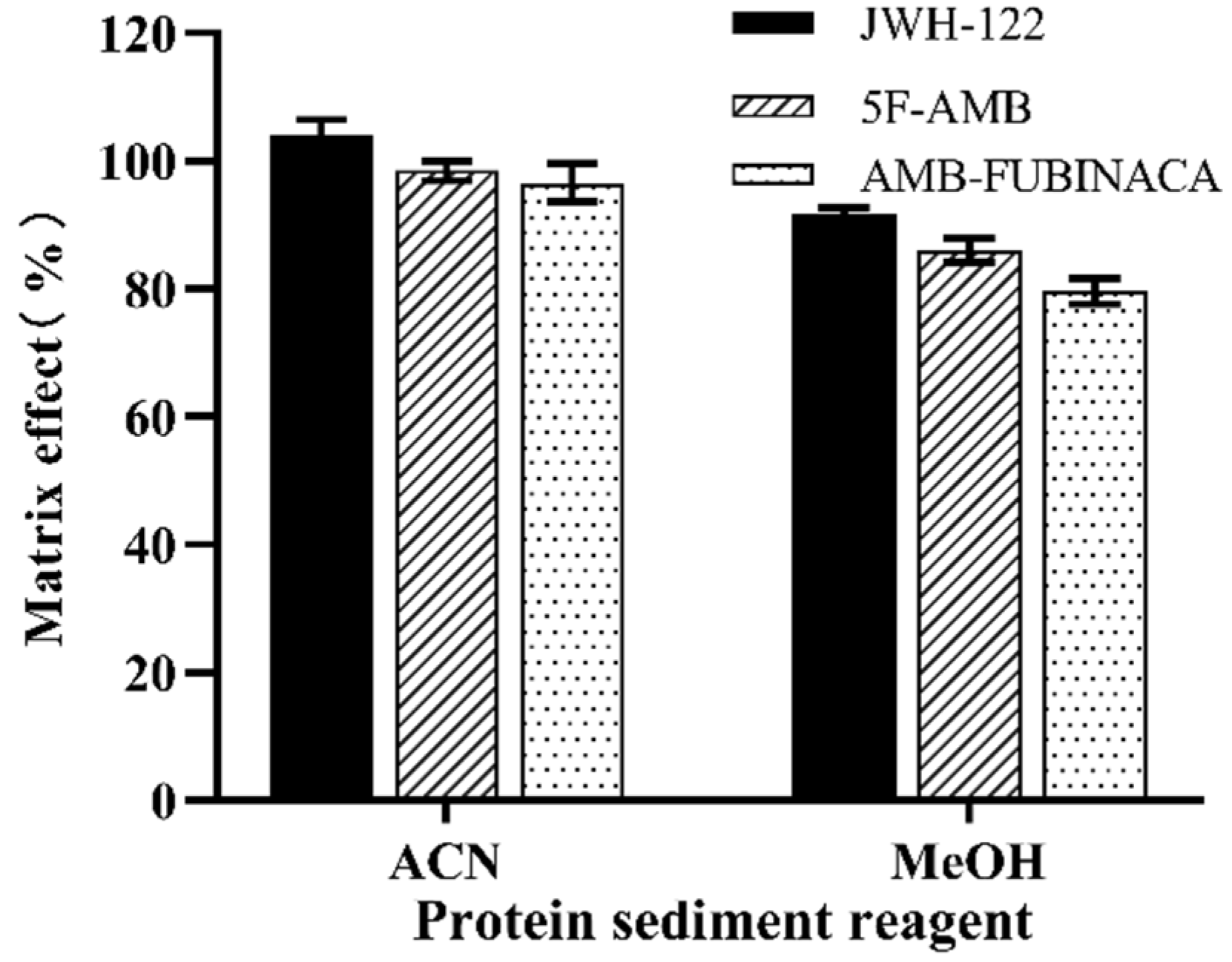

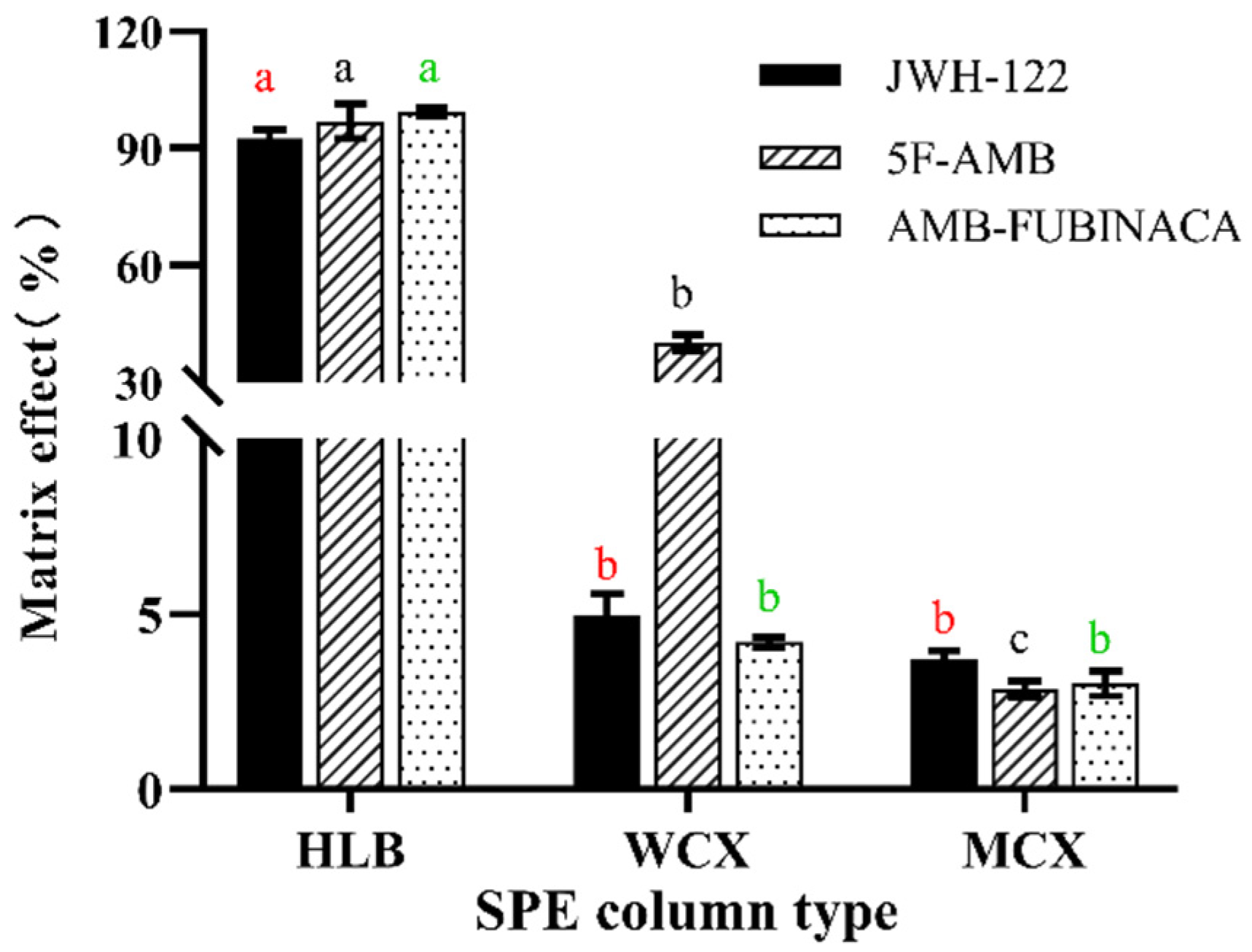
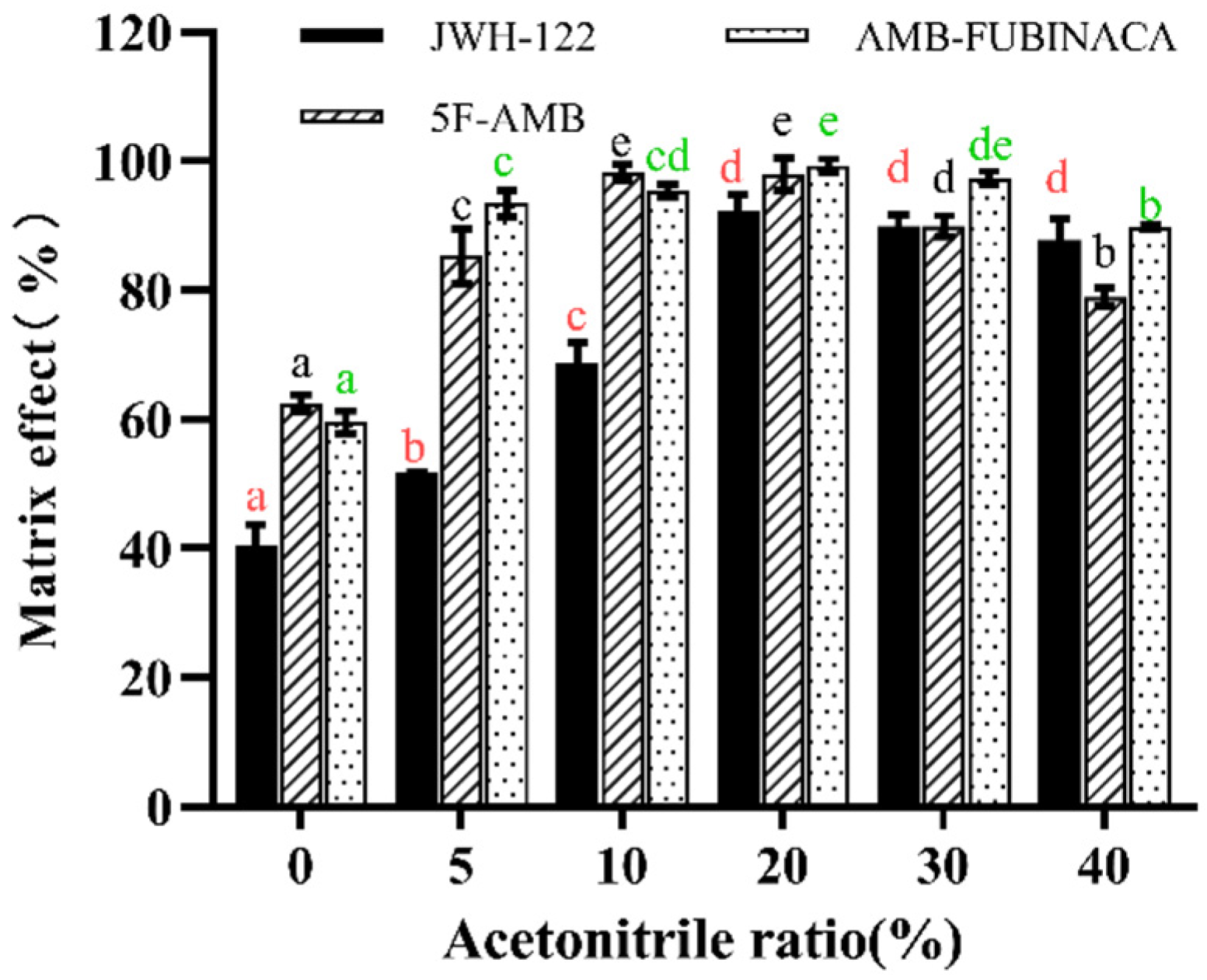
| (A) | |
| Factor | Type of protein precipitation reagent |
| 1 | Acetonitrile |
| 2 | Methanol |
| Factor | Volume of acetonitrile to plasma |
| 1 | 1:1 |
| 2 | 1:2 |
| 3 | 1:3 |
| 4 | 1:4 |
| 5 | 1:5 |
| (B) | |
| Factor | Type of SPE column |
| 1 | Oasis HLB |
| 2 | Oasis WCX |
| 3 | Oasis MCX |
| Factor | Proportion of extract solution (%) |
| 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 5 |
| 3 | 10 |
| 4 | 20 |
| 5 | 30 |
| 6 | 40 |
| Factor | Elution reagent volume (mL) |
| 1 | 2 |
| 2 | 3 |
| 3 | 4 |
| 4 | 5 |
| 5 | 6 |
| Compound Name | Precursor Ion (m/z) | Product Ion A (m/z) | Product Ion B (m/z) | DP (V) | CE (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JWH-122 | 356.2 | 169.2 | 214.2 | 32/32 | 176/177 |
| 5F-AMB | 364.2 | 233.2 | 304.2 | 32/21 | 72/71 |
| AMB-FUBINACA | 384.2 | 253.2 | 324.2 | 30/23 | 80/61 |
| Compound Name | Linear Range (ng/mL) | Correlation Coefficient | LOD (ng/mL) | LOQ (ng/mL) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasma | Urine | Plasma | Urine | Plasma | Urine | Plasma | Urine | |
| JWH-122 | 0.04–2 | 0.005–0.25 | 0.99854 | 0.99844 | 0.003 | 0.0003 | 0.012 | 0.00125 |
| 2–40 | 0.25–5 | 0.99973 | 0.99860 | |||||
| 5F-AMB | 0.04–2 | 0.005–0.25 | 0.99781 | 0.99925 | 0.004 | 0.0005 | 0.016 | 0.002 |
| 2–40 | 0.25–5 | 0.99839 | 0.99991 | |||||
| AMB-FUBINACA | 0.04–2 | 0.005–0.25 | 0.99787 | 0.99881 | 0.004 | 0.0004 | 0.012 | 0.0015 |
| 2–40 | 0.25–5 | 0.99950 | 0.99741 | |||||
| Compound Name | Intra-Day Precision (%) | Inter-Day Precision (%) | Recovery (%) | Matrix Effect (%) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasma | Urine | Plasma | Urine | Plasma | Urine | Plasma | Urine | |||||||||||||||||
| A | B | C | D | E | F | A | B | C | D | E | F | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | G | H | I | |
| JWH-122 | 9.0 | 5.9 | 7.6 | 4.0 | 4.5 | 2.8 | 8.0 | 8.1 | 3.8 | 8.1 | 5.4 | 5.5 | 96.5 | 100.2 | 102.5 | 95.1 | 98.7 | 101.6 | 95.1 | 95.9 | 92.8 | 118.0 | 93.4 | 97.6 |
| 5F-AMB | 6.4 | 3.1 | 1.5 | 3.8 | 3.8 | 3.1 | 8.6 | 6.4 | 4.2 | 6.7 | 4.9 | 3.9 | 98.7 | 97.6 | 95.4 | 92.0 | 100.4 | 96.6 | 89.1 | 86.0 | 88.5 | 113.6 | 99.4 | 95.7 |
| AMB-FUBINACA | 2.3 | 3.4 | 1.3 | 6.7 | 6.1 | 4.4 | 4.6 | 4.4 | 3.0 | 7.8 | 6.7 | 8.8 | 106.8 | 102.3 | 98.2 | 97.9 | 98.3 | 102.0 | 93.9 | 82.6 | 92.2 | 101.0 | 95.4 | 96.6 |
| Compound Name | Plasma | Urine | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 72 h | 2 h | 4 h | 8 h | 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | ||||||||
| Concentration (ng/mL) | RSD (%) | Concentration (ng/mL) | RSD (%) | Concentration (ng/mL) | RSD (%) | Concentration (ng/mL) | RSD (%) | Concentration (ng/mL) | RSD (%) | Concentration (ng/mL) | RSD (%) | Concentration (ng/mL) | RSD (%) | |
| JWH-122 | 0.08 | 4.38 | 0.20 | 5.51 | 0.12 | 8.66 | 0.09 | 7.60 | 0.06 | 14.36 | 0.02 | 16.36 | 0.01 | 13.22 |
| 5F-AMB | ND | / | 8.68 | 9.96 | 1.11 | 9.17 | 0.72 | 9.61 | 0.14 | 6.08 | 0.03 | 12.20 | 0.01 | 13.86 |
| AMB-FUBINACA | 0.05 | 8.42 | 3.38 | 4.39 | 0.41 | 10.06 | 0.19 | 3.92 | 0.10 | 12.80 | 0.03 | 14.45 | ND | / |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ke, X.; Tian, Y.; He, D.; Mu, P.; Wan, X.; Zhang, L.; Jia, W.; Wang, Q.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, Y. Rapid Simultaneous Determination of Three Synthetic Cannabinoids in Urine and Plasma of Rats Using Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Toxics 2022, 10, 619. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100619
Ke X, Tian Y, He D, Mu P, Wan X, Zhang L, Jia W, Wang Q, Fan Y, Zhang Y. Rapid Simultaneous Determination of Three Synthetic Cannabinoids in Urine and Plasma of Rats Using Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Toxics. 2022; 10(10):619. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100619
Chicago/Turabian StyleKe, Xing, Yimei Tian, Dandan He, Pengqian Mu, Xuzhi Wan, Lange Zhang, Wei Jia, Qiao Wang, Yilei Fan, and Yu Zhang. 2022. "Rapid Simultaneous Determination of Three Synthetic Cannabinoids in Urine and Plasma of Rats Using Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry" Toxics 10, no. 10: 619. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100619
APA StyleKe, X., Tian, Y., He, D., Mu, P., Wan, X., Zhang, L., Jia, W., Wang, Q., Fan, Y., & Zhang, Y. (2022). Rapid Simultaneous Determination of Three Synthetic Cannabinoids in Urine and Plasma of Rats Using Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Toxics, 10(10), 619. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100619









