Bacillus subtilis Synthesized Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (Fe3O4 NPs) Induced Metabolic and Anti-Oxidative Response in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) under Arsenic Stress
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Method and Plant Growth
2.2. Cellular Injury in Rice Plant
2.3. Photosynthetic Pigment
2.4. Metabolic Studies
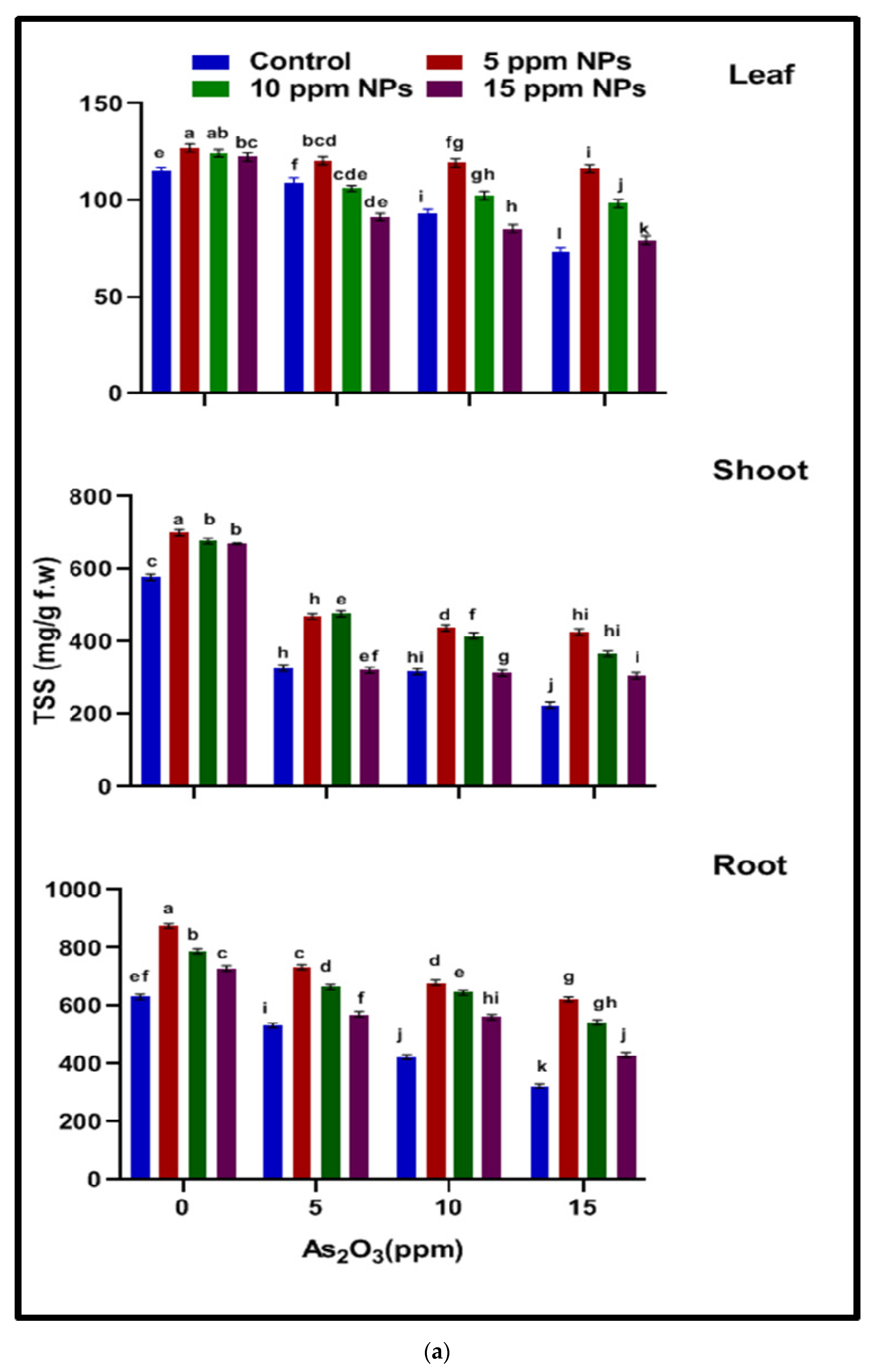
2.4.1. Total Soluble Sugar (TSS)
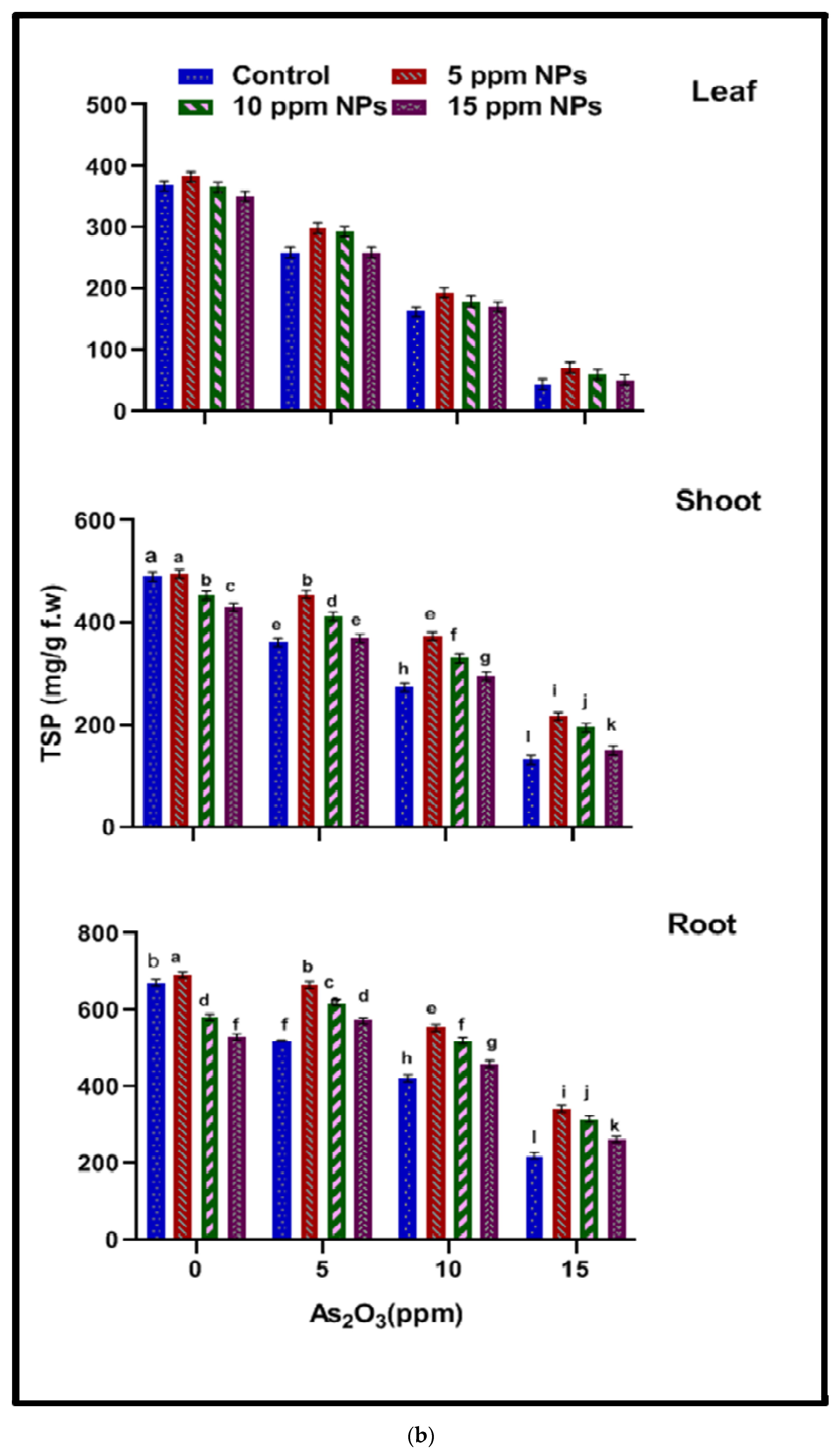
2.4.2. Total Soluble Protein (TSP)
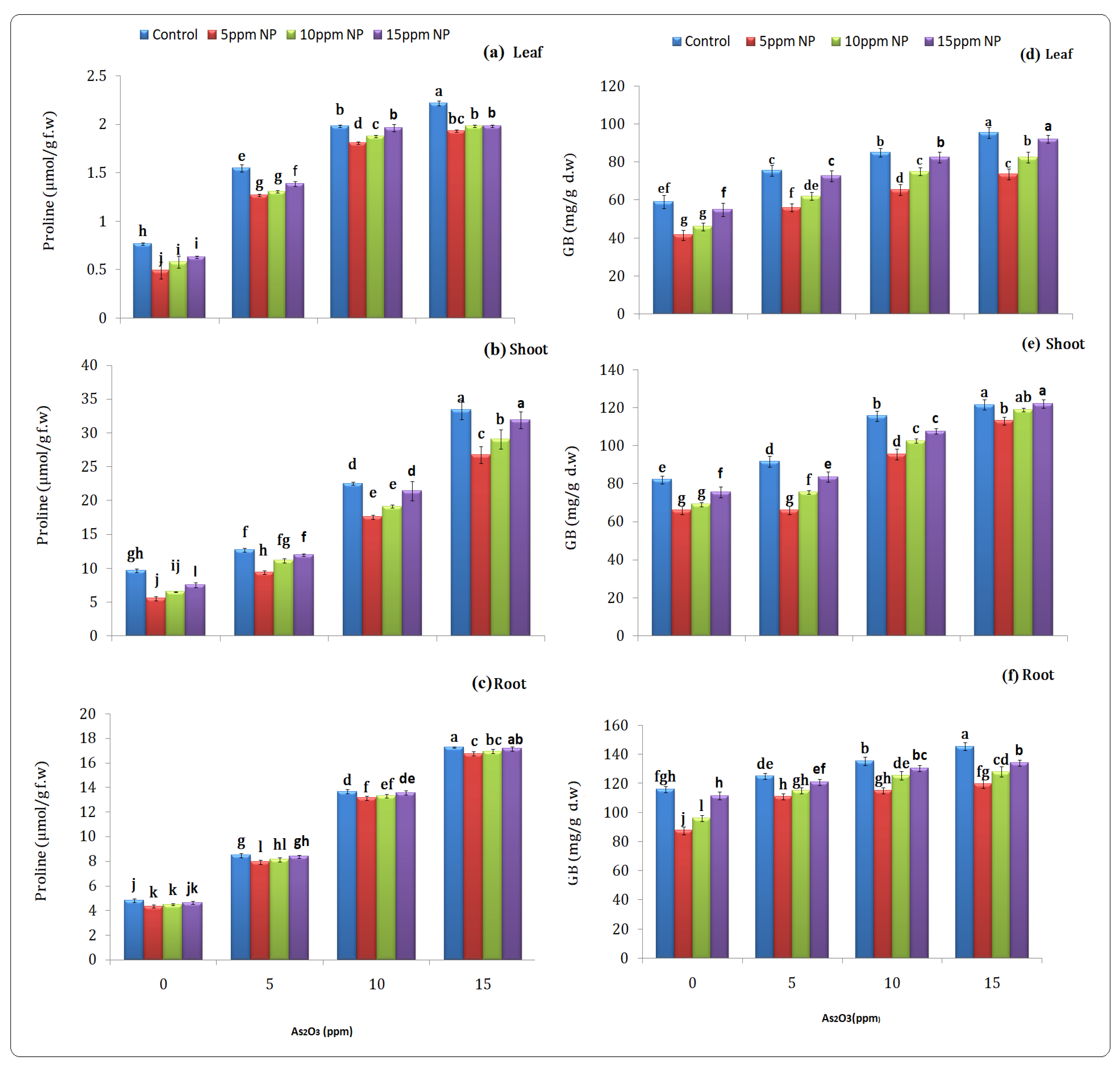
2.4.3. Stress Related Parameter (Proline)
2.4.4. Glycine Betain
2.5. Antioxidant (SOD, POD, CAT and APX) Determination
2.5.1. Superoxide Dismutase (SOD)
2.5.2. Peroxidase (POD)
2.5.3. Catalase (CAT)
2.5.4. Ascorbate Peroxidase (APX)
2.6. Stress Bio-Markers
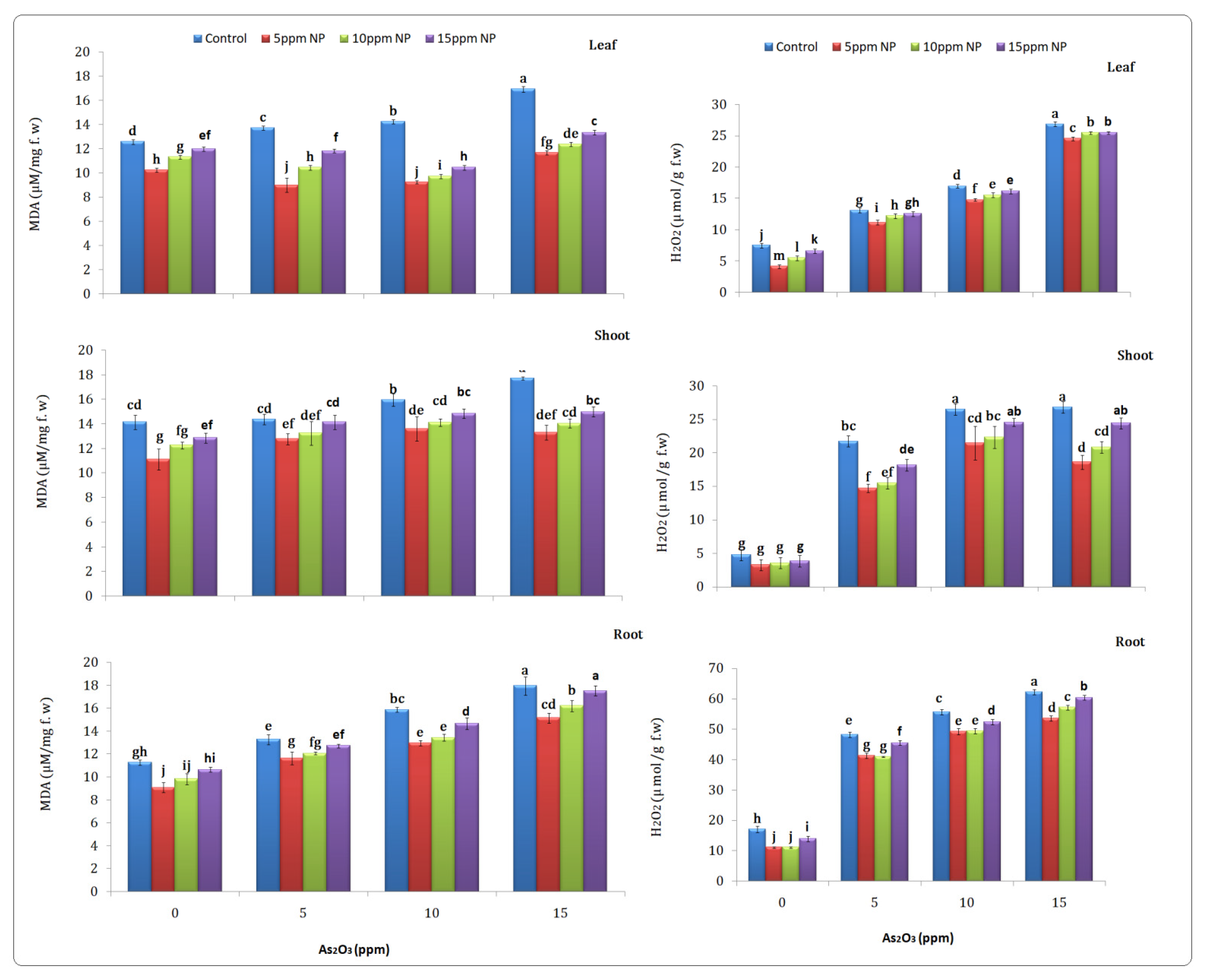
2.6.1. Malondialdehyde (MDA)
2.6.2. Hydrogen Peroxide
2.7. Determination of Arsenic Content in Plant Parts (Leaf, Shoot and Root)
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cell Injury
3.2. Total Chlorophyll Content
3.3. Metabolic Studies
3.3.1. Total Soluble Sugar (TSS)
3.3.2. Total Soluble Protein (TSP)
3.3.3. Stress-Related Parameter (Proline)
3.3.4. Glycine Betain
3.4. Antioxidant (SOD, POD, CAT and APX) Determination
3.5. Stree Bio-Markers
3.5.1. Malondialdehyde (MDA)
3.5.2. Hydrogen Peroxide
3.6. Determination of Arsenic Content in Plant Parts (Leaf, Shoot and Root)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gupta, S.; Thokchom, S.D.; Kapoor, R. Arbuscular mycorrhiza improves photosynthesis and restores alteration in sugar metabolism in Triticum aestivum L. grown in arsenic contaminated soil. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Akhtar, N.; Rehman, S.U.; Shujah, S.; Rha, E.S.; Jamil, M. Biosynthesized iron oxide nanoparticles (Fe3O4 NPs) mitigate arsenic toxicity in rice seedlings. Toxics 2020, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, N.; Khan, S.; Malook, I.; Rehman, S.U.; Jamil, M. Pb-induced changes in roots of two cultivated rice cultivars grown in lead-contaminated soil mediated by smoke. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 21298–21310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Li, X.; Guo, S.; Yang, L.; Li, D. Arsenic accumulation, speciation and bioavailability in rice cultivated in arsenic acid exposed soil. Plant. Soil Environ. 2021, 67, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Adeel, M.; Shakoor, N.; Guo, M.; Hao, Y.; Azeem, I.; Rui, Y. Application of nanoparticles alleviates heavy metals stress and promotes plant growth: An overview. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natasha, S.M.; Imran, M.; Khalid, S.; Murtaza, B.; Niazi, N.K.; Zhang, Y.; Hussain, I. Arsenic Environmental Contamination Status in South Asia. Arsen. Drink. Water Food 2020, 13–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgher, M.; Ahmed, S.; Sehar, Z.; Gautam, H.; Gandhi, S.G.; Khan, N.A. Hydrogen peroxide modulates activity and expression of antioxidant enzymes and protects photosynthetic activity from arsenic damage in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Hazar. Mater. 2021, 401, 123–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulick, D.; Samanta, S.; Sarkar, S.; Mukherjee, A.; Pattnaik, B.K.; Saha, S.; Santra, S.C. Arsenic contamination, impact and mitigation strategies in rice agro-environment: An inclusive insight. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 800, 149477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, X.; Zheng, F.; Norton, G.J.; Beesley, L.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, H.; Ding, Y. Physiological responses and transcriptome analyses of upland rice following exposure to arsenite and arsenate. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2021, 183, 104–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dien, D.C.; Thu, T.T.P.; Moe, K.; Yamakawa, T. Proline and carbohydrate metabolism in rice varieties (Oryza sativa L.) under various drought and recovery conditions. Plant. Physiol. Rep. 2019, 14, 376–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, B.; Das, S.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Biswas, A.K. Identification of arsenic-tolerant and arsenic-sensitive rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars on the basis of arsenic accumulation assisted stress perception, morpho-biochemical responses, and alteration in genomic template stability. Protoplasma 2019, 256, 193–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkhatib, R.; Alkhatib, B.; Abdo, N. Effect of Fe3O4 nanoparticles on seed germination in tobacco. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 2, 53568–53577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd El-Moneim, D.; Dawood, M.F.; Moursi, Y.S.; Farghaly, A.A.; Afifi, M.; Sallam, A. Positive and negative effects of nanoparticles on agricultural crops. Nanotechnol. Environ. Eng. 2021, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brar, R.S.; Kumar, A.; Simran jeet, K.A.U.R.; Sandip, S.A.H.A.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, S. Impact of metal oxide nanoparticles on cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.): A physiological perspective. J. Cotton Res. 2021, 4, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Manzoor, N.; Ahmed, T.; Noman, M.; Shahid, M.; Nazir, M.M.; Ali, L.; Wang, G. Iron oxide nanoparticles ameliorated the cadmium and salinity stresses in wheat plants, facilitating photosynthetic pigments and restricting cadmium uptake. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 769, 145–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, M.; Nisar, S.; Gul, I.; Nawaz, U.; Irum, S.; Ahmad, S.; Alyemeni, M.N. Multi-element uptake and growth responses of Rice (Oryza sativa L.) to TiO2 nanoparticles applied in different textured soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 215, 112–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrouel, F.; Viennot, S.; Ottolenghi, L.; Gaillard, C.; Bourgeois, D. Nanoparticles as anti-microbial, anti-inflammatory, and remineralizing agents in oral care cosmetics: A review of the current situation. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Alidoust, D.; Wang, C. Effects of iron oxide nanoparticles on the mineral composition and growth of soybean (Glycine max L.) plants. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum 2020, 42, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, N.; Khan, S.; Rehman, S.U.; Rehman, Z.U.; Khatoon, A.; Rha, E.S.; Jamil, M. Synergistic effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles and bacteria reduce heavy metals toxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.) plant. Toxics 2021, 9, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansar, S.; Tabassum, H.; Aladwan, N.S.; Ali, M.N.; Almaarik, B.; Al Mahrouqi, S.; Alsubki, R. Eco friendly silver nanoparticles synthesis by Brassica oleracea and its antibacterial, anticancer and antioxidant properties. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tombuloglu, H.; Slimani, Y.; AlShammari, T.M.; Bargouti, M.; Ozdemir, M.; Tombuloglu, G.; Baykal, A. Uptake, translocation, and physiological effects of hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticles in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikari, K.; Mahato, G.R.; Chen, H.; Sharma, H.C.; Chandel, A.K.; Gao, B. Nanoparticles and their impacts on seed germination. In Plant Responses to Nanomaterials: Recent Interventions, and Physiological and Biochemical Responses; Singh, V.P., Singh, S., Tripathi, D.K., Prasad, S.M., Chauhan, D.K., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 21–31. [Google Scholar]
- Dziwulska-Hunek, A.; Kachel, M.; Gagoś, M.; Szymanek, M. Influence of silver nanoparticles, laser light and electromagnetic stimulation of seeds on germination rate and photosynthetic parameters in pumpkin (Cucurbitapepo L.) Leaves. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, N.; Khan, S.; Naveen, S.; Masood, S.; Khattak, M.R.; Malook, I.; Jamil, M. Effect of wastewater on physiological and biochemical characteristics of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Interciencia J. 2018, 43, 102–123. [Google Scholar]
- Khattak, M.R.; Jan, S.U.; Malook, I.; Khattak, S.R.; Akhtar, N.; Khan, S.; Jamil, M. Effects of halophilic bacteria on biochemical characteristics of rice cultivars under salinity stress conditions. In Saline Soil-Based Agriculture by Halo tolerant Microorganisms; Kumar, M., Etesami, H., Kumar, V., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 161–174. [Google Scholar]
- Akhtar, N.; Khan, S.; Rehman, S.U.; Rha, E.S.; Jamil, M. Combined Effect of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and Bacteria on Osmolytes and Antioxidative Parameters of Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Plant Grown in Heavy Metal-Contaminated Water. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2022, 2022, 4148765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, L.; Servin, A.D.; De La Torre-Roche, R.; Mukherjee, A.; Majumdar, S.; Hawthorne, J. Molecular response of crop plants to engineered nanomaterials. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 7198–7207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, F.D.; Attia, M.F.; Whitehead, D.C.; Alexis, F. Nanotechnology for Environmental Remediation: Materials and Applications. Molecules 2018, 23, 1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hammad, M.; Fortugno, P.; Hardt, S.; Kim, C.; Salamon, S.; Schmidt, T.C.; Wiggers, H. Large-scale synthesis of iron oxide/graphene hybrid materials as highly efficient photo-Fenton catalyst for water remediation. Environ. Technol. Innovat. 2021, 21, 101–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.A.; Gupta, M. Exposure of Brassica juncea (L.) to arsenic species in hydroponic medium: A comparative analysis in accumulation and biochemical and transcriptional alterations. Environ. Sci. Pollut. 2013, 10, 8141–8150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, P.; Adeel, M.; Guo, Z.; Chetwynd, A.J.; Ma, C.; Rui, Y. Physiological impacts of zero valent iron, Fe3O4 and Fe2O3 nanoparticles in rice plants and their potential as Fe fertilizers. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 116–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortella, G.; Rubilar, O.; Fincheira, P.; Pieretti, J.C.; Duran, P.; Lourenço, I.M.; Seabra, A.B. Bactericidal and Virucidal Activities of Biogenic Metal-Based Nanoparticles: Advances and Perspectives. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamim, H.; Miftahudin, M.; Setyaningsih, L. Cellular and Ultrastructure Alteration of Plant Roots in Response to MetalStress; Intech Open: London, UK, 2018; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Liang, L.; Li, W.; Ashraf, U.; Ma, L.; Tang, X.; Pan, S.; Tian, H.; Mo, Z. ZnO nanoparticle-based seed priming modulates early growth and enhances physio-biochemical and metabolic profiles of fragrant rice against cadmium toxicity. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, N.; Khan, S.; Rehman, S.U.; Jahangir, M.; Ahmad, R.; Rha, E.S.; Jamil, M. Remediating Effect Of Smoke Solution On Shoot Of Two Rice (Oryza Sativa L.) Cultivars under Lead Contaminated Water. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2020, 29, 10376–10391. [Google Scholar]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, L.S.; Waldren, R.P.; Teare, I.D. Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 1973, 39, 105–107. [Google Scholar]
- Beauchamp, C.; Fridovich, I. Superoxide dismutase: Improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. Anal. Biochem. 1971, 44, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velikova, V.; Yordanov, I.; Edreva, A. Oxidative stress and some antioxidant systems in acid rain-treated bean plants: Protective role of exogenous polyamines. Plant Sci. 2000, 151, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.F.; Meharg, A.A.; McGrath, S.P. Arsenic uptake and metabolism in plants. New Phytol. 2009, 181, 777–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiol, D.F.; Terrile, M.C.; Frik, J.; Mesas, F.A.; Álvarez, V.A.; Casalongué, C.A. Nanotechnology in plants: Recent advances and challenges. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2021, 96, 2095–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, P.M. Oligosaccharides. In Methods in Plant Biochemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1990; Volume 1, pp. 189–218. [Google Scholar]
- Hasanuzzaman, M.; Bhuyan, M.H.M.; Zulfiqar, F.; Raza, A.; Mohsin, S.M.; Mahmud, J.A.; Fotopoulos, V. Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant defense in plants under abiotic stress: Revisiting the crucial role of a universal defense regulator. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aebi, H. Chapter 13—Catalase in vitro. In Methods in Enzymology; Packer, L., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1984; Volume 105, pp. 121–126. [Google Scholar]
- Sofo, A.; Scopa, A.; Nuzzaci, M.; Vitti, A. Ascorbate peroxidase and catalase activities and their genetic regulation inplants subjected to drought and salinity stresses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 13561–13578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashraf, I.; Ahmad, F.; Sharif, A.; Altaf, A.R.; Teng, H. Heavy metals assessment in water, soil, vegetables and their associated health risks via consumption of vegetables, district Kasur, Pakistan. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janero, D.R. Malondialdehyde and thiobarbituric acid-reactivity as diagnostic indices of lipid peroxidation and peroxidative tissue injury. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1990, 9, 515–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nankano, Y.; Asada, K. Hydrogen-peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol. 1980, 1, 867–877. [Google Scholar]
- Praveen, A.; Khan, E.; Ngiimei, S.; Perwez, M.; Sardar, M.; Gupta, M. Iron Oxide Nanoparticles as Nano-adsorbents: A Possible Way to Reduce Arsenic Phytotoxicity in Indian Mustard Plant (Brassica juncea L.). J. Plant Growth Regul. 2018, 37, 612–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabnam, N.; Kim, M.; Kim, H. Iron(III) oxide nanoparticles alleviate arsenic induceds tunting in Vigna radiata. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 183, 109496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joardar, J.C.; Afrin, N.; Halder, M. Arsenics tress on photosynthesis and growth in Ipomoeaaquatica. Plant. Sci. Today 2019, 6, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Lu, J.; Zhao, H.; Liu, M.; Nechitaylo, G.S.; Glushchenko, N.N. New insights in to the cellular responses to iron nanoparticles in Capsicum annuum. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chowdhury, S.R.; Yanful, E.K.; Pratt, A.R. Arsenic removal from aqueous solutions by mixed magnetite-maghemite nanoparticles. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 64, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahakham, W.; Sarmah, A.K.; Maensiri, S.; Theerakulpisut, P. Nanopriming technology for enhancing germination and starch metabolism of aged rice seeds using phytosynthesized silver nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rivero-Montejo, S.D.J.; Vargas-Hernandez, M.; Torres-Pacheco, I. Nanoparticles as Novel Elicitors to Improve Bioactive Compounds in Plants. Agriculture 2021, 11, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torasso, N.; Vergara-Rubio, A.; Rivas-Rojas, P.; Huck-Iriart, C.; Larrañaga, A.; Fernández-Cirelli, A.; Cerveny, S.; Goyanes, S. Enhanc in garsenic adsorption via excellent dispersion of iron oxide nanoparticles in side poly (vinyl alcohol) nanofibers. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, S.S.; Fouda, A. Green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles and their prospective biotechnological applications: An overview. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2021, 199, 344–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, S.; Usmani, Z.; Atanasov, A.G.; Singh, V.K.; Singh, N.P.; Abdel-Azeem, A.M.; Prasad, R.; Gupta, G.; Bhargava, A. Biological nano factories: Using living forms for metal nanoparticle synthesis. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2021, 21, 245–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahid, M.; Khalid, S.; Bibi, I.; Khalid, S.; Masood, N.; Qaisrani, S.A.; Niazi, N.K.; Dumat, C. Arsenic- induced oxidative stress in Brassica oleracea: Multi variate and literature data analyses of physiological parameters, applied levels and plant organ type. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 44, 1827–1839. [Google Scholar]
- Samanta, S.; Banerjee, A.; Roychoudhury, A. Melatonin application differentially modulates the enzymes associated with antioxidative machinery and ascorbate-glutathione cycle during arsenate exposure in indica rice varieties. Plant Biol. 2021, 23, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Treatments (Leaf) | Chlorophyll (a) | Chlorophyll (b) | Total Pigments | Carotenoids | ||||
| (mg/g) | (mg/g) | (mg/g) | (µg/g) | |||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| Control | 3.78 | 0.01 e | 2.44 | 0.03 e | 6.22 | 6.22 c | 1.54 | 0.00 e |
| 5 ppmNP | 4.45 | 0.03 a | 2.85 | 0.04 bc | 7.3 | 7.33 a | 1.83 | 0.01 a |
| 10 ppmNP | 4.35 | 0.35 b | 2.85 | 0.03 a | 7.2 | 7.23 a | 1.78 | 0.00 b |
| 15 ppmNP | 4.25 | 0.04 c | 2.75 | 0.03 ab | 7 | 6.66 b | 1.69 | 0.01 c |
| C + 5(As) | 2.86 | 0.03 h | 2.34 | 0.04 e | 5.2 | 5.23 e | 1.23 | 0.01 j |
| 5 + 5(As) | 3.85 | 0.03 d | 2.85 | 0.03 a | 6.7 | 6.73 b | 1.57 | 0.01 d |
| 5 + 10(As) | 3.76 | 0.03 e | 2.65 | 0.04 cd | 6.41 | 6.41 c | 1.46 | 0.01 f |
| 5 + 15(As) | 3.65 | 0.03 f | 2.55 | 0.03 d | 6.2 | 6.23 c | 1.38 | 0.01 g |
| C + 10(As) | 2.56 | 0.03 i | 1.55 | 0.03 h | 4.11 | 4.11 h | 1.1 | 0.01 m |
| 10 + 5(As) | 3.63 | 0.03 f | 1.95 | 0.03 f | 5.58 | 5.57 d | 1.32 | 0.01 h |
| 10 + 10(As) | 3.13 | 0.03 g | 1.85 | 0.04 g | 4.98 | 4.97 f | 1.28 | 0.00 i |
| 10 + 15(As) | 2.85 | 0.03 h | 1.75 | 0.03 g | 4.6 | 4.63 g | 1.22 | 0.02 j |
| C + 15(As) | 2.05 | 0.03 l | 1.15 | 0.04 k | 3.2 | 3.23 j | 0.66 | 0.01 o |
| 15 + 5(As) | 2.46 | 0.03 g | 1.34 | 0.04 i | 3.8 | 3.76 i | 1.18 | 0.01 k |
| 15 + 10(As) | 2.25 | 0.04 k | 1.25 | 0.04 ij | 2.5 | 2.46 k | 1.12 | 0.00 l |
| 15 + 15(As) | 2.06 | 0.01 l | 1.16 | 0.03 jk | 1.22 | 1.22 l | 0.98 | 0.01 n |
| Treatments (Shoot) | Chlorophyll (a) | Chlorophyll (b) | Total Pigments | Carotenoids | ||||
| (mg/g) | (mg/g) | (mg/g) | (µg/g) | |||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| Control | 3.35 | 0.04 d | 1.55 | 0.04 g | 4.9 | 6.22 c | 1.34 | 0.04 c |
| 5 ppmNP | 3.85 | 0.03 a | 2.42 | 0.01 a | 6.27 | 7.33 a | 1.47 | 0.01 a |
| 10 ppmNP | 3.55 | 0.04 b | 2.39 | 0.00 ab | 6.15 | 7.23 a | 1.41 | 0.02 b |
| 15 ppmNP | 3.45 | 0.03 c | 2.36 | 0.01 b | 5.81 | 6.66 b | 1.36 | 0.01 c |
| C + 5(As) | 3.25 | 0.04 e | 2.11 | 0.00 f | 5.36 | 5.23 e | 1.27 | 0.01 d |
| 5 + 5(As) | 3.54 | 0.04 b | 2.28 | 0.01 c | 5.82 | 6.73 b | 1.45 | 0.02 a |
| 5 + 10(As) | 3.45 | 0.04 c | 2.24 | 0.02 d | 5.85 | 6.41 c | 1.34 | 0.02 c |
| 5 + 15(As) | 3.25 | 0.04 e | 2.17 | 0.06 e | 5.42 | 6.23 c | 1.3 | 0.05 c |
| C + 10(As) | 2.14 | 0.04 i | 1.2 | 0.01 jk | 3.6 | 4.11 h | 1.17 | 0.02 f |
| 10 + 5(As) | 2.45 | 0.03 f | 1.36 | 0.02 h | 3.81 | 5.57 d | 1.34 | 0.02 c |
| 10 + 10(As) | 2.35 | 0.04 g | 1.27 | 0.01 i | 3.62 | 4.97 f | 1.23 | 0.01 e |
| 10 + 15(As) | 2.25 | 0.04 h | 1.24 | 0.04 ij | 3.49 | 4.63 g | 1.21 | 0.02 e |
| C + 15(As) | 1.74 | 0.04 k | 1.11 | 0.01 m | 2.85 | 3.23 j | 0.55 | 0.03 j |
| 15 + 5(As) | 2.35 | 0.03 g | 1.24 | 0.02 ij | 3.59 | 3.76 i | 0.87 | 0.01 g |
| 15 + 10(As) | 2.15 | 0.04 i | 1.16 | 0.01 kl | 3.31 | 2.46 k | 0.78 | 0.01 h |
| 15 + 15(As) | 2.05 | 0.04 j | 1.15 | 0.04 lm | 3.2 | 1.22 l | 0.73 | 0.02 i |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, S.; Akhtar, N.; Rehman, S.U.; Shujah, S.; Rha, E.S.; Jamil, M. Bacillus subtilis Synthesized Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (Fe3O4 NPs) Induced Metabolic and Anti-Oxidative Response in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) under Arsenic Stress. Toxics 2022, 10, 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100618
Khan S, Akhtar N, Rehman SU, Shujah S, Rha ES, Jamil M. Bacillus subtilis Synthesized Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (Fe3O4 NPs) Induced Metabolic and Anti-Oxidative Response in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) under Arsenic Stress. Toxics. 2022; 10(10):618. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100618
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Sehresh, Nazneen Akhtar, Shafiq Ur Rehman, Shaukat Shujah, Eui Shik Rha, and Muhammad Jamil. 2022. "Bacillus subtilis Synthesized Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (Fe3O4 NPs) Induced Metabolic and Anti-Oxidative Response in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) under Arsenic Stress" Toxics 10, no. 10: 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100618






