Biological Responses of Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus as Influenced by Dietary Florfenicol
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Fish and Design
2.2. Florfenicol Diet Preparation and Dose Administration
2.3. Blood Sampling
2.4. Serum Biomarkers
2.5. Hematology and Hematological Indices
2.6. Erythrocyte Morphological Characters
2.7. Histopathology
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Feed Intake, Survival, and Biomass
3.2. Serum Biomarkers
3.3. Hematology and Hematological Indices
3.4. Blood Cell Morphological Alterations
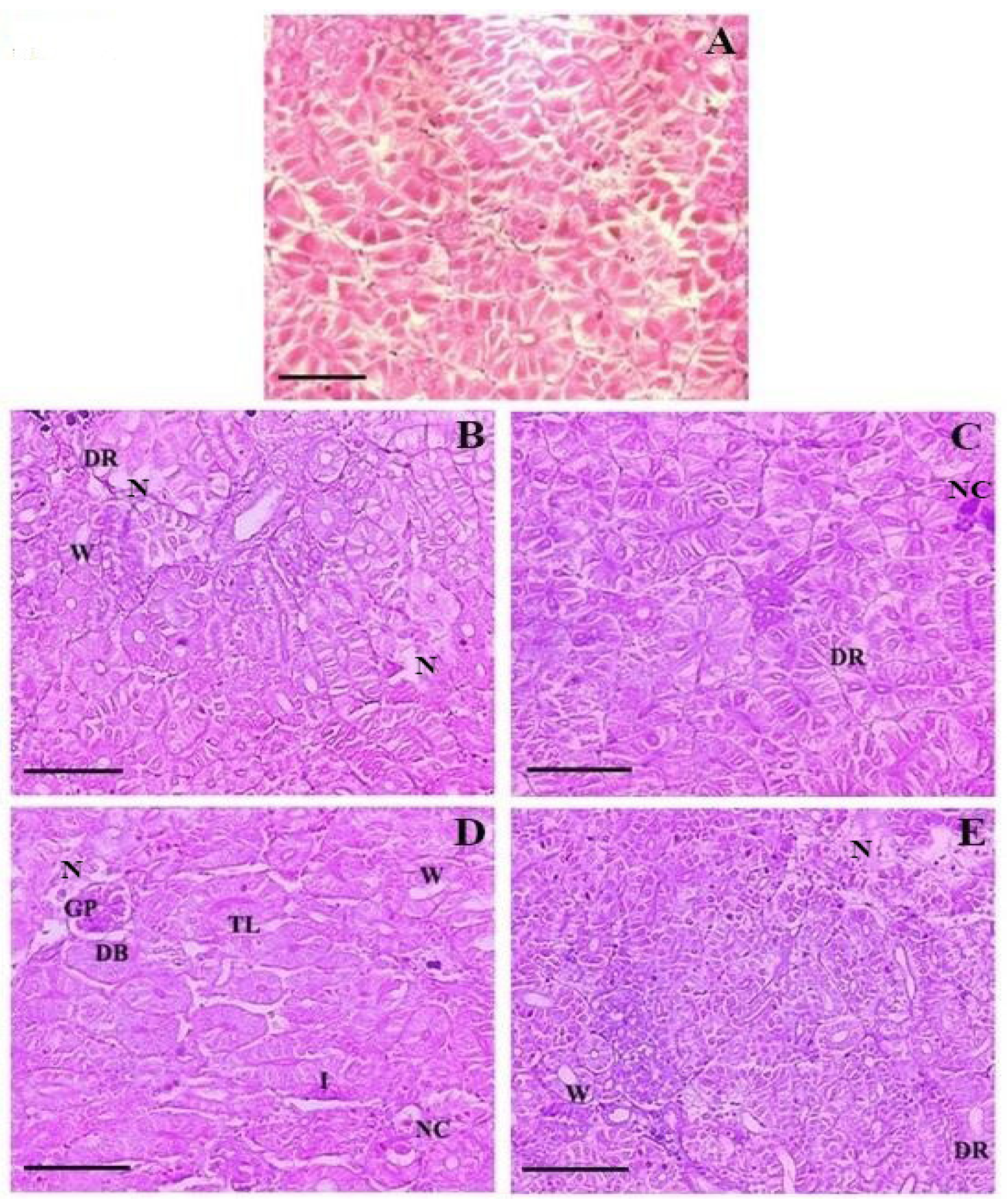
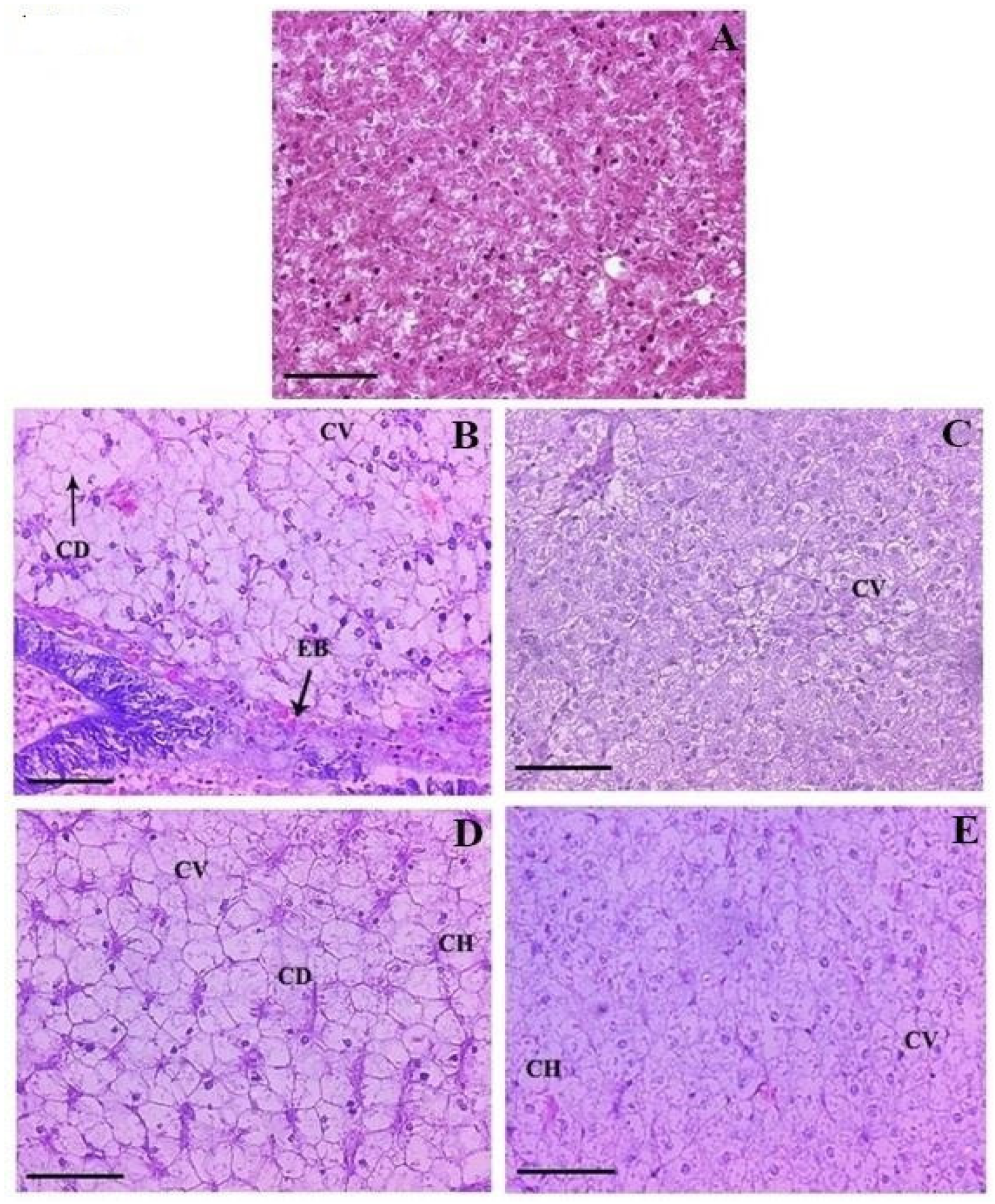
3.5. Histopathology
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- USFWS (United States Fish and Wildlife Services). Aquatic Animal Drug Approval Partnership Program; American Fisheries Society’s Fish Culture and Fish Health Sections, Association of Fish and Wildlife Agencies and Fisheries and Water Resources Policy Committee’s Drug Approval Working Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2015.
- Fukui, H.; Fujihara, Y.; Kano, T. In vitro and in vivo antibacterial activities of florfenicol, a new fluorinated analogue of thiamphenicol, against fish pathogens. Fish Pathol. 1987, 22, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limbu, S.M.; Chen, L.Q.; Zhang, M.L.; Du, Z.Y. A global analysis on the systemic effects of antibiotics in cultured fish and their potential human health risk: A review. Rev. Aquacult. 2021, 13, 1015–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization). The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2020-Sustainability in Action; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gaikowski, M.P.; Wolf, J.C.; Endris, R.G.; Gingerich, W.H. Safety of Aquaflor (florfenicol, 50% type A medicated article), administered in feed to channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus. Toxicol. Pathol. 2003, 31, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardhan, A.; Abraham, T.J.; Singha, J.; Saha, S.; Sarker, S.; Patil, P.K. The effects of extended feeding of florfenicol coated medicated diets on the safety, serum biomarkers and blood cells morphology of Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus (L.). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 39914–39927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto, E.; Kidd, S.; Gaunt, P.S.; Endris, R. Efficacy of florfenicol for control of mortality associated with Francisella noatunensis subsp. oriental in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.). J. Fish Dis. 2013, 36, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambili, T.R.; Saravanan, M.; Ramesh, M.; Abhijith, D.B.; Poopal, R.K. Toxicological effects of the antibiotic oxytetracycline to an Indian major carp Labeo rohita. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2013, 64, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, M.; Thilagavathi, T.; Rathika, R.; Poopal, R.K. Antioxidant status, biochemical, and hematological responses in a cultivable fish Cirrhinus mrigala exposed to an aquaculture antibiotic Sulfamethazine. Aquaculture 2018, 491, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omoregie, E.; Oyebanji, S.M. Oxytetracycline-induced blood disorder in juvenile Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus (Trewavas). J. World Aquac. Soc. 2002, 33, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umamaheswari, S.; Renuka, S.S.; Ramesh, M.; Poopal, R.K. Chronic amoxicillin exposure affects Labeo rohita: Assessment of hematological, ionic compounds, biochemical, and enzymological activities. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondera, E.; Bojarski, B.; Ługowska, K.; Kot, B.; Witeska, M. Effects of oxytetracycline and gentamicin therapeutic doses on hematological, biochemical and hematopoietic parameters in Cyprinus carpio juveniles. Animals 2020, 10, 2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botelho, R.G.; Christofoletti, C.A.; Correia, J.E.; Ansoar, Y.; Olinda, R.A.; Tornisielo, V.L. Genotoxic responses of juvenile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) exposed to florfenicol and oxytetracycline. Chemosphere 2015, 132, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, R.J. Fish Pathology, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Trinder, P. Determination of blood glucose using an oxidase-peroxidase system with a non-carcinogenic chromogen. J. Clin. Pathol. 1969, 22, 158–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaylova, V.; Ilkova, P. Photometric determination of micro amounts of calcium with arsenazo III. Anal. Chim. Acta 1971, 53, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenfeld, R.G.; Lewellan, C.J. A colourimetric method for determination of serum chloride. Clin. Chem. 1964, 10, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junge, W.; Wilke, B.; Halabi, A.; Klein, G. Determination of reference intervals for serum creatinine, creatinine excretion and creatinine clearance with an enzymatic and a modified Jaffe method. Clin. Chim. Acta 2004, 344, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, D.W.; Maynard, J.E.; Emery, G.; Webster, H. Transaminase activities in serum of long-term hemodialysis patients. Clin. Chem. 1972, 18, 1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, L.; Müller, M.; Schumann, G.; Weidemann, G.; Klein, G.; Lunau, S.; Pick, K.H.; Sonntag, O. Consensus of DGKL and VDGH for interim reference intervals on enzymes in serum Consensus of DGKL and VDGH on preliminary reference ranges for serum enzymes. Lab. Med. 2005, 29, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, K.R. Fish hematology and associated disorders. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2015, 18, 83–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshina, M.M.; de Angelis, D.D.F.; Marin-Morales, M.A. Induction of micronucleus and nuclear alterations in fish (Oreochromis niloticus) by a petroleum refinery effluent. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2008, 656, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojarski, B.; Witeska, M. Blood biomarkers of herbicide, insecticide, and fungicide toxicity to fish—A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 19236–19250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowker, J.D.; Carty, D.; Bowman, M.P. The safety of Aquaflor (50% florfenicol) administered in feed to fingerling yellow perch. N. Am. J. Aquac. 2013, 75, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elia, A.C.; Pacini, N.; Fioravanti, M.L.; Dörr, A.J.M.; Zaccaroni, A.; Parmeggiani, A.M.; Gustinelli, A.; Mordenti, O.; Abete, M.C.; Prearo, M. Assessment of detoxifying markers for florfenicol in rainbow trout liver. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2016, 28, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardhan, A.; Abraham, T.J.; Singha, J.; Sar, T.K.; Rajisha, R.; Krishna, E.K.N.; Kumar, K.A.; Patil, P.K. Histopathological aberrations and oxidative stress responses in Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus as influenced by dietary florfenicol and its metabolites. Aquaculture 2022, 10, 738447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julinta, R.B.; Abraham, T.J.; Roy, A.; Singha, J.; Boda, S.; Patil, P.K. Dietary influences of oxytetracycline on the growth and serum biomarkers of Oreochromis niloticus (L.). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 186, 109752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Han, Z.; Li, C.; Lv, L.; Cheng, Z.; Liu, S. Florfenicol induces more severe hemotoxicity and immunotoxicity than equal doses of chloramphenicol and thiamphenicol in Kunming mice. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2016, 38, 472–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidi, L.R.; Santos, F.A.; Ribeiro, A.C.S.; Fernandes, C.; Silva, L.H.; Gloria, M.B.A. Quinolones and tetracyclines in aquaculture fish by a simple and rapid LC-MS/MS method. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 1232–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaskó, K.; Shagina, L.V.; Györgyi, S.; Lev, A.A. The mode of action of some antibiotics on red blood cell membranes. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 1986, 6, 625–636. [Google Scholar]
- Er, A.; Dik, B. The effects of florfenicol on the values of serum tumor necrosis factor and other biochemical markers in lipopolysaccharide-induced endotoxemia in brown trout. Mediat, Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 464373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, M.; Sujitha, M.; Anila, P.A.; Ren, Z.; Poopal, R.K. Responses of Cirrhinus mrigala to second-generation fluoroquinolone (ciprofloxacin) toxicity: Assessment of antioxidants, tissue morphology, and inorganic ions. Environ. Toxicol. 2021, 36, 887–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Getchell, R.G.; Wooster, G.A.; Craigmill, A.L.; Bowser, P.R. Oxytetracycline residues in four species of fish after 10-day oral dosing in feed. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2004, 16, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iftikhar, N.; Hashmi, I. Assessment of immunohematological, hematological and biochemical responses in cultivable fish Cyprinus carpio exposed to an antibiotic sulfamethoxazole (SMX). J. Water Health 2021, 19, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiroma, L.S.; Bottoli, C.B.G.; Jonsson, C.M.; Queiroz, S.C. Exposure of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) to the antibiotic florfenicol in water: Determination of the bioconcentration factor and the withdrawal period. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 39026–39034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lis, M.; Szczypka, M.; Suszko, A.; Switala, M.; Obminska-Mrukowicz, B. The effect of florfenicol on lymphocyte subsets and humoral immune response in mice. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2011, 14, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reda, R.M.; Ibrahim, R.E.; Ahmed, E.N.G.; El-Bouhy, Z.M. Effect of oxytetracycline and florfenicol as growth promoters on the health status of cultured Oreochromis niloticus. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2013, 39, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Adawy, M.; El-Aziz, M.A.; El-Shazly, K.; Ali, N.G.; El-Magd, M.A. Dietary propionic acid enhances antibacterial and immunomodulatory effects of oxytetracycline on Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 34200–34211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahjahan, M.; Uddin, M.; Bain, V.; Haque, M. Increased water temperature altered hemato-biochemical parameters and structure of peripheral erythrocytes in striped catfish Pangasianodon hypophthalmus. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 44, 1309–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaikowski, M.P.; Wolf, J.C.; Schleis, S.M.; Tuomari, D.; Endris, R.G. Safety of florfenicol administered in feed to tilapia (Oreochromis sp.). Toxicol. Pathol. 2013, 41, 639–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chico, V.; Puente-Marin, S.; Nombela, I.; Ciordia, S.; Mena, M.C.; Carracedo, B.; Villena, A.; Mercado, L.; Coll, J.; Ortega-Villaizan, M.D.M. Shape-shifted red blood cells: A novel red blood cell stage? Cells 2018, 7, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, K.; Sarter, M.; De Souza, N.R.; De Campo, L.; Whitten, A.E.; Kuchel, P.W.; Garvey, C.J.; Stadler, A.M. Effect of red blood cell shape changes on haemoglobin interactions and dynamics: A neutron scattering study. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2020, 7, 201507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffar, A.; Hussain, R.; Ahmad, N.; Ghafoor, R.; Akram, M.W.; Khan, I.; Khan, A. Evaluation of hemato-biochemical, antioxidant enzymes as biochemical biomarkers and genotoxic potential of glyphosate in freshwater fish (Labeo rohita). Chem. Ecol. 2021, 37, 646–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, I.Z.; Bibi, A.; Shahid, S.; Ghazanfar, M. Exposure to sub-acute doses of fipronil and buprofezin in combination or alone induces biochemical, hematological, histopathological and genotoxic damage in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 179, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Oost, R.; Beyer, J.; Vermeulen, N.P. Fish bioaccumulation and biomarkers in environmental risk assessment: A review. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2003, 13, 57–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Han, C.; Cui, Y.; Li, S.; Jin, G.; Shi, W.; Bao, Y. Florfenicol causes excessive lipid peroxidation and apoptosis induced renal injury in broilers. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 207, 111282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julinta, R.B.; Abraham, T.J.; Roy, A.; Singha, J.; Bardhan, A.; Sar, T.K.; Patil, P.K.; Kumar, K.A. Safety of emamectin benzoate administered in feed to Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus (L.). Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 75, 103348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, J.C.; Wheeler, J.R. A critical review of histopathological findings associated with endocrine and non-endocrine hepatic toxicity in fish models. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 197, 60–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, J.C.; Wolfe, M.J. A brief overview of nonneoplastic hepatic toxicity in fish. Toxicol. Pathol. 2005, 33, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Moneim, A.M.; Al-Kahtani, M.A.; Elmenshawy, O.M. Histopathological biomarkers in gills and liver of Oreochromis niloticus from polluted wetland environments, Saudi Arabia. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Wang, Z.; Gao, B.; Liu, P.; Li, J. Effects of florfenicol on the antioxidant status, detoxification system and biomolecule damage in the swimming crab (Portunus trituberculatus). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 143, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, J.M.; Qureshi, T.A.; Shah, T.; Shah, Q.A.; Arain, M.A.; Bhutto, Z.A.; Saeed, M.; Siyal, F.A. Impact of therapeutic and high doses of florfenicol on kidney and liver functional indicators in goat. Vet. World 2016, 9, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Qu, Y.; Li, S.; Feng, K.; Cai, W.; Yin, H.; Wang, S.; Liu, W.; Wang, A.; Deng, Y. Florfenicol restructured the microbial interaction network for wastewater treatment by microbial electrolysis cells. Environ. Res. 2020, 183, 109145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Xie, X.; Feng, F.; Huang, S.; Sun, Y. Impact of acyl-homoserine lactones on the response of nitrogen cycling in sediment to florfenicol stress. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 785, 147294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

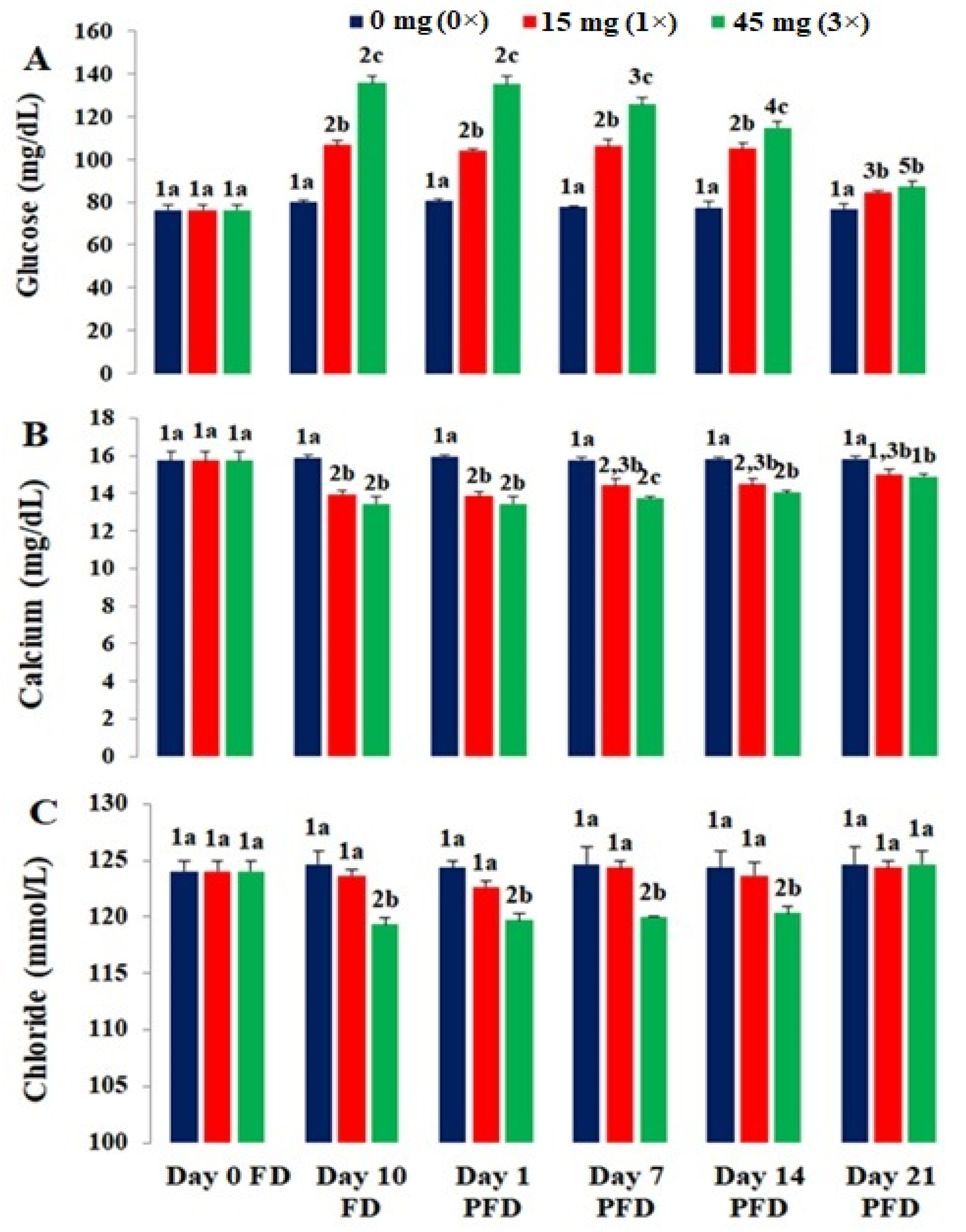


| Serum Biomarkers | Kits Used | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Glucose | Glucose test kit, GOD FS 10′ (Diasys Diagnostic Systems, Germany) | [15] |
| Calcium | Calcium test kit, AS FS (Diasys Diagnostic Systems, Germany) | [16] |
| Chloride | Chloride test kit, 21 FS (Diasys Diagnostic Systems, Germany) | [17] |
| Creatinine | Creatinine test kit, Modified Jaffe’s Reaction, Initial rate assay (Span Diagnostics Ltd., India) | [18] |
| ALT 1 | ERBA SGPT Kit, IFCC Method, Kinetic (Erba Manheim, Germany) | [19] |
| AST 2 | ERBA SGOT Kit, IFCC Method, Kinetic (Erba Manheim, Germany) | [19] |
| ALP 3 | Alkaline Phosphatase Kit, FS IFCC 37 °C (Diasys Diagnostic Systems, Germany) | [20] |
| Behavioral Changes a | Percentage of Fish | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 10 FD | Day 21 PFD | |||||
| 0× | 1× | 3× | 0× | 1× | 3× | |
| Gasping for air | 0.00 (0) | 7.50 (9) | 11.67 (14) | 0.00 (0) | 2.50 (3) | 4.17 (5) |
| Lethargy | 0.00 (0) | 0.00 (0) | 1.67 (2) | 0.00 (0) | 0.00 (0) | 0.00 (0) |
| Excessive epidermal mucus secretion | 0.00 (0) | 4.17 (5) | 10.83 (13) | 0.00 (0) | 0.00 (0) | 0.83 (1) |
| Residing at tank bottom * | 0.00 (0) | 8.33 (10) | 9.17 (11) | 0.00 (0) | 0.00 (0) | 0.00 (0) |
| Biomarkers | PD | Day 10 FD | Day 21 PFD | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0× | 1× | 3× | 0× | 1× | 3× | ||
| TEC (×106 cells mm−3) | 1.73 ± 0.06 * | 1.70 ± 0.06 1a * | 1.19 ± 0.03 1b | 1.14 ± 0.06 1b | 1.73 ± 0.05 1a * | 1.36 ± 0.05 2b | 1.26 ± 0.04 2c |
| TC (×105 cells mm−3) | 1.26 ± 0.12 * | 1.28 ± 0.03 1a * | 1.89 ± 0.02 1b | 1.96 ± 0.06 1c | 1.26 ± 0.02 1a * | 1.31 ± 0.01 2a | 1.37 ± 0.02 2a |
| TLC (×104 cells mm−3) | 3.09 ± 0.05 * | 3.08 ± 0.03 1a * | 10.33 ± 0.05 1b | 11.85 ± 0.04 1c | 3.09 ± 0.06 1a * | 9.13 ± 0.05 2b | 9.41 ± 0.10 2b |
| LC (%) | 65.36 ± 0.22 * | 65.58 ± 1.20 1a * | 86.57 ± 1.46 1b | 88.88 ± 0.59 1c | 64.95 ± 1.19 1a * | 73.32 ± 1.00 2b | 78.20 ± 1.39 2c |
| MC (%) | 4.53 ± 0.38 * | 4.54 ± 0.32 1a * | 2.23 ± 0.15 1b | 1.13 ± 0.06 1c | 4.57 ± 0.33 1a * | 3.87 ± 0.06 2b | 2.70 ± 0.53 1c |
| Hb (g dL−1) | 4.97 ± 0.32 * | 4.97 ± 0.21 1a * | 4.20 ± 0.17 1b | 3.53 ± 0.25 1c | 5.01 ± 0.25 1a * | 4.64 ± 0.35 2b | 3.77 ± 0.15 1c |
| Ht (%) | 19.09 ± 0.33 * | 19.12 ± 0.65 1a * | 18.25 ± 0.79 1a | 16.41 ± 0.44 1b | 19.53 ± 0.31 1a * | 18.62 ± 0.53 1a | 17.60 ± 0.14 2b |
| MCV (10−15 L) | 112.79 ± 0.99 * | 112.78 ± 2.50 1a * | 143.41 ± 9.93 1b | 153.48 ± 9.04 1c | 113.01 ± 5.17 1a * | 137.25 ± 1.12 2b | 140.13 ± 4.04 2c |
| MCH (10−12 g) | 28.81 ± 1.59 * | 29.03 ± 1.29 1a * | 30.95 ± 2.06 1a | 35.32 ± 3.90 1b | 29.13 ± 2.13 1a * | 29.98 ± 2.29 1a | 32.44 ± 1.76 2b |
| MCHC (g dL−1) | 25.13 ± 1.62 * | 25.78 ± 0.19 1a * | 21.11 ± 2.51 1b | 20.82 ± 1.69 1b | 25.48 ± 1.69 1a * | 22.02 ± 2.25 2b | 21.84 ± 1.75 2b |
| Major Histopathological Changes | 1× | 3× | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 10 FD | Day 21 PFD | Day 10 FD | Day 21 PFD | |
| Kidney | ||||
| Degeneration of renal tubular epithelium | 1.38 ± 0.11 1a | 0.48 ± 0.24 2a | 1.54 ± 0.10 1b | 0.97 ± 0.10 2b |
| Necrotized renal tubule | 1.18 ± 0.11 1a | 0.37 ± 0.21 2a | 1.28 ± 0.10 1a | 1.14 ± 0.10 2b |
| Glomerulopathy with dilated Bowman’s space | 0.43 ± 0.15 1a | 0.19 ± 0.07 2a | 1.17 ± 0.10 1b | 1.05 ± 0.13 2b |
| Nephrocalcinosis | 0.78 ± 0.28 1a | 1.02 ± 0.13 2a | 1.21 ± 0.07 1b | 1.11 ± 0.07 2a |
| Thickening of lumen lining | 0.00 ± 0.00 1a | 0.00 ± 0.00 1a | 0.43 ± 0.08 1b | 0.00 ± 0.00 1a |
| Inflamed renal tubule | 0.00 ± 0.00 1a | 0.00 ± 0.00 1a | 1.11 ± 0.15 1b | 0.62 ± 0.34 2b |
| Widening of lumen | 1.23 ± 0.13 1a | 0.82 ± 0.27 2a | 1.13 ± 0.14 1b | 0.52 ± 0.16 2b |
| Liver | ||||
| Glycogen type vacuolation | 4.59 ± 0.05 1a | 1.46 ± 0.04 2a | 4.67 ± 0.02 1b | 2.54 ± 0.04 2b |
| Cytoplasmic vacuolation | 1.31 ± 0.07 1a | 1.27 ± 0.10 1a | 1.42 ± 0.07 1b | 1.28 ± 0.13 2a |
| Cytoplasmic degeneration | 1.04 ± 0.14 1a | 1.00 ± 0.10 1a | 1.11 ± 0.09 1a | 1.09 ± 0.07 1a |
| Cellular hypertrophy | 1.01 ± 0.07 1a | 0.86 ± 0.19 2a | 1.44 ± 0.10 1b | 1.08 ± 0.07 2b |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bardhan, A.; Abraham, T.J.; Das, R.; Patil, P.K. Biological Responses of Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus as Influenced by Dietary Florfenicol. Toxics 2022, 10, 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100571
Bardhan A, Abraham TJ, Das R, Patil PK. Biological Responses of Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus as Influenced by Dietary Florfenicol. Toxics. 2022; 10(10):571. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100571
Chicago/Turabian StyleBardhan, Avishek, Thangapalam J. Abraham, Ratnapriya Das, and Prasanna K. Patil. 2022. "Biological Responses of Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus as Influenced by Dietary Florfenicol" Toxics 10, no. 10: 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100571
APA StyleBardhan, A., Abraham, T. J., Das, R., & Patil, P. K. (2022). Biological Responses of Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus as Influenced by Dietary Florfenicol. Toxics, 10(10), 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100571






