Detecting Aquatic Pollution Using Histological Investigations of the Gills, Liver, Kidney, and Muscles of Oreochromis niloticus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Fish and Water Samples
2.2. Histopathological Procedure
2.2.1. Fixation
2.2.2. Dehydration
2.2.3. Infiltration and Embedding
2.2.4. Sectioning
2.2.5. Staining
2.2.6. Examination
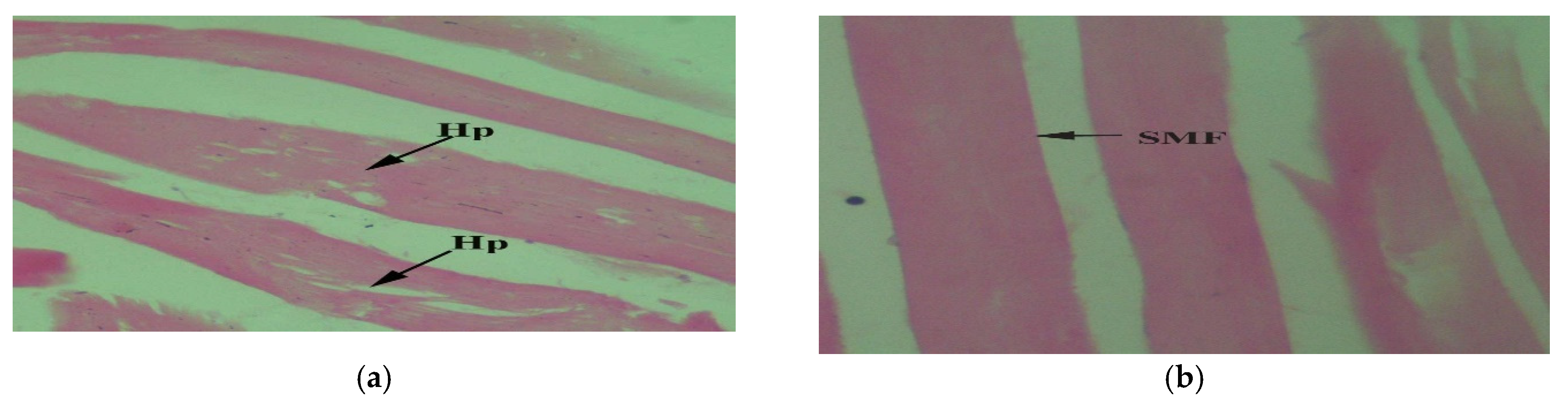
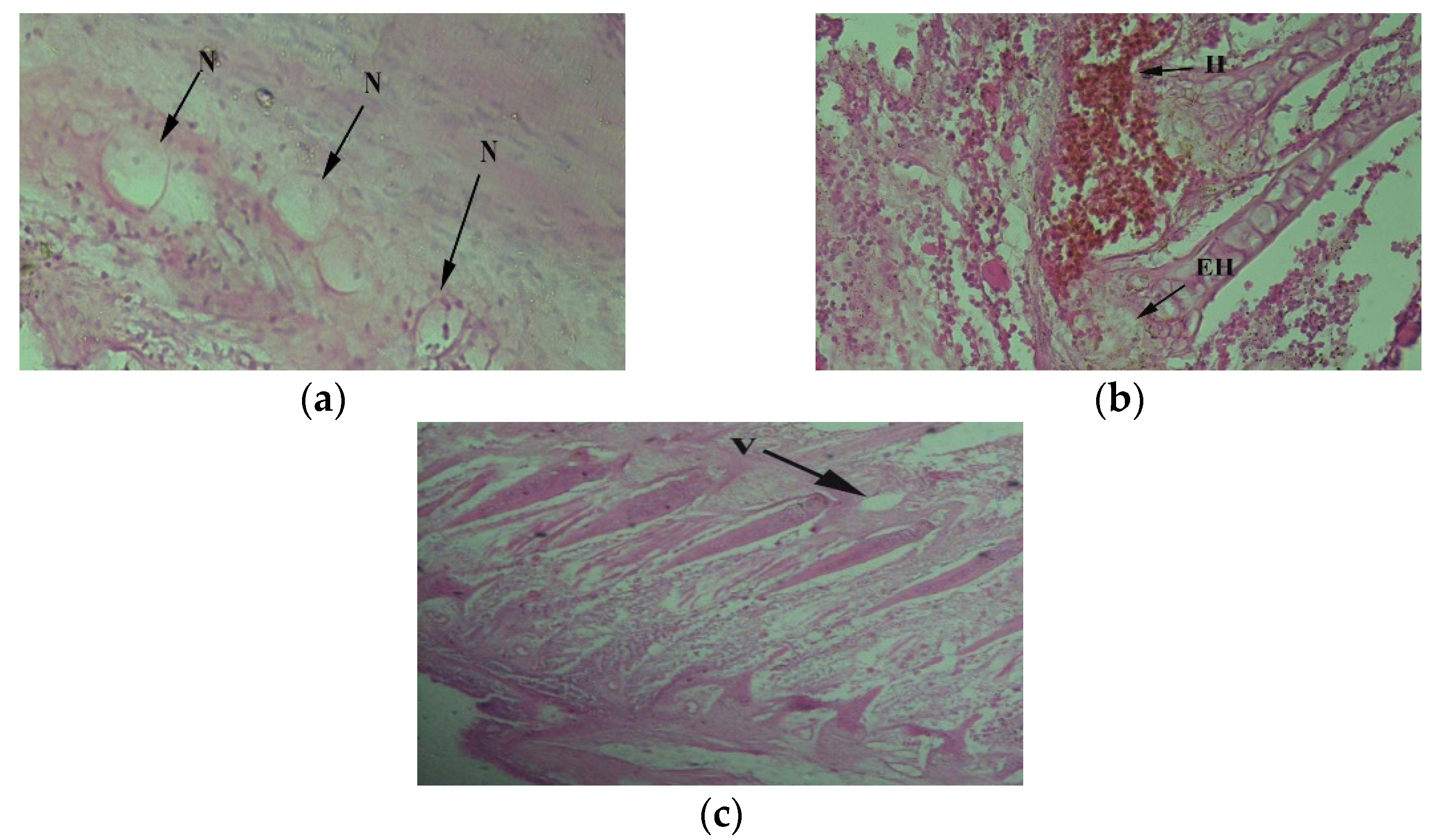
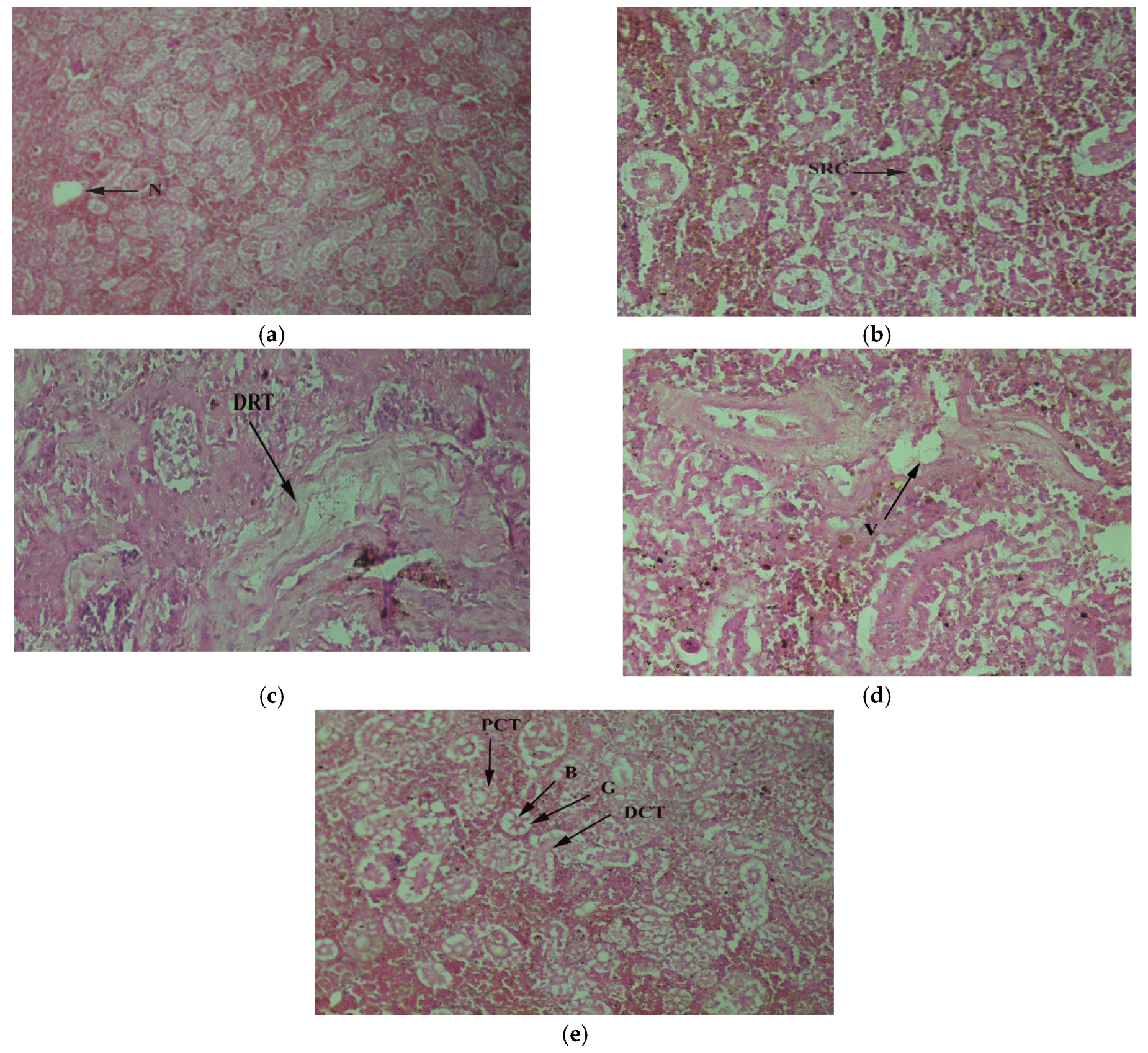
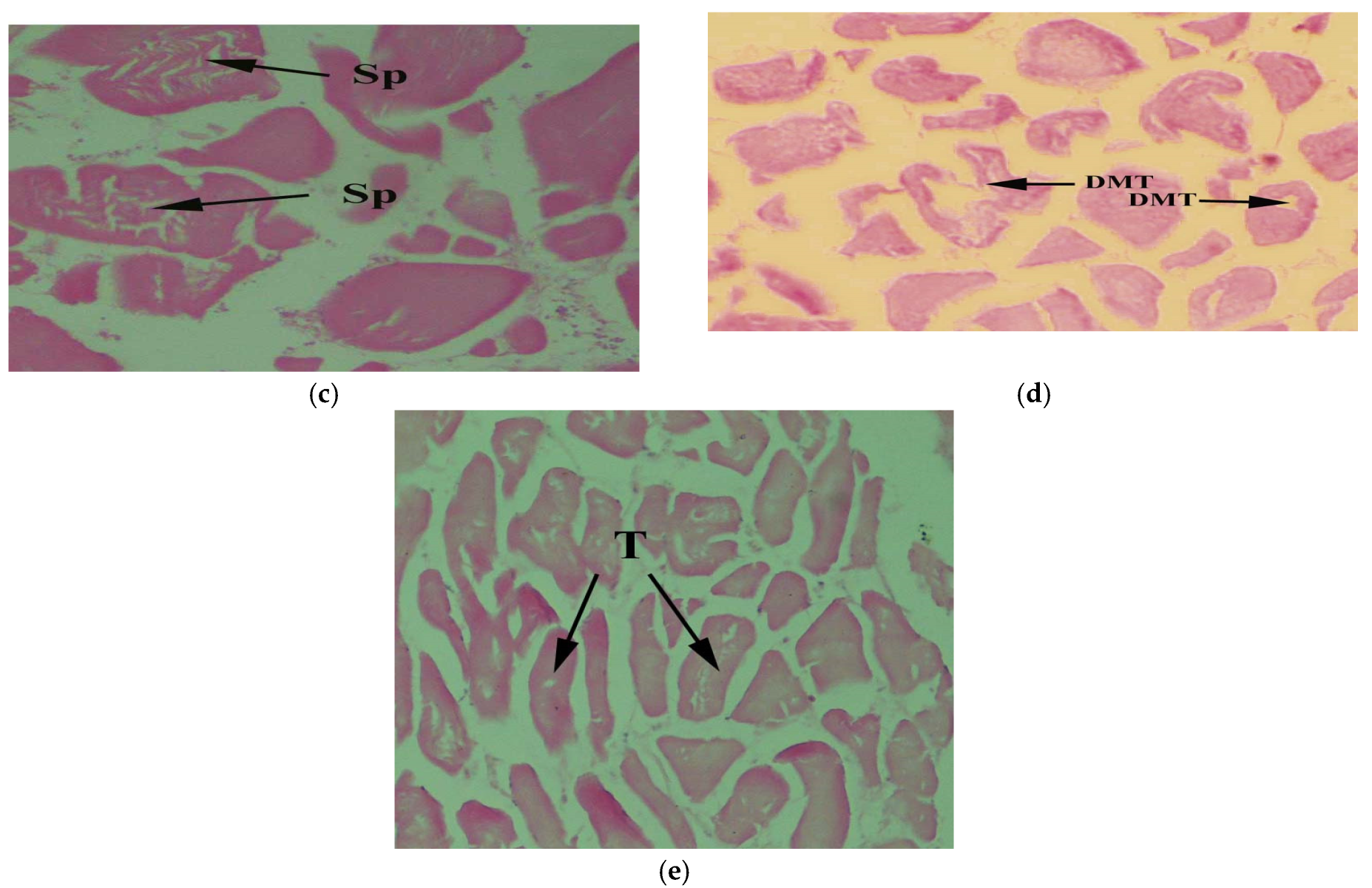
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thabet, I.A.; Tawadrous, W.E.; Samy, A.M. Pollution induced change of liver of Oreochromis niloticus: Metals accumulation and histopathological response. World J. Adv. Res. Rev. 2019, 2, 025–035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savassi, L.A.; Paschoalini, A.L.; Arantes, F.P.; Rizzo, E.; Bazzoli, N. Heavy metal contamination in a highly consumed Brazilian fish: Immunohistochemical and histopathological assessments. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brázová, T.; Šalamún, P.; Miklisová, D.; Šestinová, O.; Findoráková, L.; Hanzelová, V.; Oros, M. Transfer of Heavy Metals Through Three Components: Sediments, Plants and Fish in the Area with Previous Mining Activity. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 106, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodhe, W. Crystallization of eutrophication concepts in North Europe. In Eutrophication, Causes, Consequences; National Academy of Sciences: Washington, DC, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.K.E.; Kabir, S.; Jahan, A. A review on the distribution of Hg in the environment and its humanhealth impacts. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 306, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baig, J.A.; Kazi, T.G.; Arain, M.B.; Afridi, H.I.; Kandhro, G.A.; Sarfraz, R.A.; Jamal, M.K.; Shah, A.Q. Evaluation of arsenic and other physico-chemical parameters of surface and ground water of Jamshoro, Pakistan. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Kopp, F.; Chang, T.C.; Sataluri, A.; Chen, B.; Sivakumar, S.; Yu, H.; Xie, Y.; Mendell, J.T. Noncoding RNA NORAD regulates genomic stability by sequestering PUMILIO proteins. Cell 2016, 164, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fent, K.; Woodin, B.R.; Stegeman, J.J. Effects of triphenyltin and other organotins on hepatic monooxygenase system in fish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Pharmacol. Toxicol. Endocrinol. 1998, 121, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogiers, V.; Vercruysse, A. Hepatocyte cultures in drug metabolism and toxicological research and testing. In Cytochrome P450 Protocols; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 1998; pp. 279–294. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S.K.; Chakrabarty, D. The use of fish community structure as a measure of ecological degradation: A case study in two tropical rivers of India. Biosystems 2007, 90, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.; Shukla, S.P. Endosulfan effects on muscle malate dehydrogenase of the freshwater catfish Clarias batrachus. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2003, 56, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, J.; Gaines, K.F.; Boring, C.S.; Stephens, W.L.; Snodgrass, J.; Dixon, C.; Mcmahon, M.; Shukla, S.; Shukla, T.; Gochfeld, M. Metal levels in fish from the Savannah River: Potential hazards to fish and other receptors. Environ. Res. 2002, 89, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Salbu, B.; Heier, L.S.; Teien, H.C.; Lind, O.C.; Oughton, D.; Petersen, D.K.; Rosseland, B.O.; Skipperud, L.; Tollefsen, K.E. Early stress responses in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) exposed to environmentally relevant concentrations of uranium. Aquat. Toxicol. 2012, 112, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terra, B.F.; Araújo, F.G.; Calza, C.F.; Lopes, R.T.; Teixeira, T.P. Heavy metal in tissues of three fish species from different trophic levels in a tropical Brazilian river. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2007, 187, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzsimmons, K.; Martinez-Garcia, R.; Gonzalez-Alanis, P. Why tilapia is becoming the most important food fish on the planet. In Better science, better fish, better life. In Proceedings of the 9th International Symposium on Tilapia in Aquaculture, Shanghai Ocean University, Shanghai, China, 21–24 April 2011; Aqua Fish Collaborative Research Support Program: Corvallis, OR, USA; pp. 9–18.
- Hernandez-Sanchez, F.; Aguilera-Morales, M.E. Nutritional richness and importance of the consumption of tilapia in the Papaloapan Region. REDVET Rev. Elec. Vet. 2012, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Mjoun, K.; Rosentrater, K.; Brown, M.L. Tilapia: Profile and Economic Importance. 2019. Available online: http://openprairie.sdstate.edu/extensionfact/163 (accessed on 26 April 2019).
- Greenfield, B.K.; Teh, S.J.; Ross, J.R.M.; Hunt, J.; Zhang, G.; Davis, J.A.; Ichikawa, G.; Crane, D.; Hung, S.S.O.; Deng, D.; et al. Contaminant concentrations and histopathological effects in Sacramento splittail (Pogonichthys macrolepidotus). Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2008, 55, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wikipedia. 2019. Available online: https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Catfish (accessed on 27 May 2019).
- Paithane, K.T.; Sonawane DLBandare, R.Y.; More, P.R. Histopathological changes due to induced dimethoate in the liver of freshwater fish Channa punctatus from River Shivana, Aurangabad (ms) India. Inter. Q. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 1, 213–217. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, P.M.; Diniz, M.S.; Caeiro, S.; Lobo, J.; Martins, M.; Ferreira, A.M.; Caetano, M.; Calos, T.A.D.; Costa, M.H. Histological biomarkers in liver and gills of juvenile Solea senegalensis exposed to contaminated estuarine sediments: A weighted indices approach. Aquat. Toxicol. 2009, 92, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwaiger, J.; Ferling, H.; Mallow, U.; Wintermayr, H.; Negele, R.D. Toxic effects of the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug diclofenac: Part I: Histopathological alterations and bioaccumulation in rainbow trout. Aquat. Toxicol. 2004, 68, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wester, P.W.; Canton, J.H. The usefulness of histopathology in aquatic toxicity studies. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Comp. Pharmaol. Toxicol. 1991, 100, 115–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, C.E. Water Quality in Warm Water Fish Ponds, 2nd ed.; Craft Master Printers Inc.: Opelika, AL, USA, 1981; pp. 213–264. [Google Scholar]
- Sultana, T.; Butt, K.; Sultana, S.; Al-Ghanim, K.A.; Mubashra, R.; Bashir, N.; Ahmed, Z.; Ashraf, A.; Mahboob, S. Histopathological changes in liver, gills and intestine of Labeo rohita inhabiting industrial waste contaminated water of River Ravi. Pak. J. Zool. 2016, 48, 172–1177. [Google Scholar]
- Yildirim, Y.; Gonulalan, Z.; Narin, I.; Soylak, M. Evaluation of trace heavy metal levels of some fish species sold at retail in Kayseri, Turkey. Environ. Monit. Asses. 2019, 149, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaishankar, M.; Seten, T.T.; Anbalagan, N.; Mathew, B.; Beeregowda, K.N. Toxicity, mechanism and health effects of some heavy metals. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2014, 7, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, N.; Biswas, A.K.; Qureshi, T.A.; Borana, K.; Virha, R. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in fish tissues of a freshwater lake of Bhopal. Environ. Monit. Asses. 2014, 160, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javed, M. comparison of selected heavy metals toxicity in the planktonic biota of the river Ravi. Indian J. Biol. Sci. 2004, 1, 59–62. [Google Scholar]
- Yancheva, V.; Velcheva, I.; Stoyanova, S.; Georgieva, E. Histological biomarkers in fish as a tool in ecological risk assessment and monitoring programs: A review. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2016, 14, 47–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramudu, K.R.; Dash, G. Histopathological alterations in the vital organs of Indian Major Carps with parasitic infestation in fish farms West Bengal, India. Drug Dev. Ther. 2015, 6, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallatt, J. Fish gill structural changes induced by toxicants and other irritants: A statistical review. Can. J. Fish Aquat. Sci. 1985, 42, 630–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, C.; Fontainhas-Fernandes, A.; Monteiro, S.M.; Salgado, M.A. Histopathological gill changes in wild leaping grey mullet (Liza saliens) from the Esmoriz-Paramos coastal lagoon, Portugal. Environ. Toxicol. 2007, 22, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, A.A.; Alwan, S.F. Histopathological changes in gills, liver and kidney of fresh water fish, Tilapia zillii, exposed to aluminum. Int. Pharm. Life Sci. 2012, 3, 2071–2081. [Google Scholar]
- Jaidka, A.; Hundal, S.S. Histological changes in gills and liver of fishes in River Sutlej as an effect of Buddha Nullah pollution at Ludhian. Int. J. Life Sci. 2016, 5, 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, S.; Khera, K.S.; Kondal, J.K. Heavy metal induced histopathological alterations in liver, muscle and kidney of freshwater cyprinid, Labeo rohita (Hamilton). J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2018, 6, 2137–2144. [Google Scholar]
- Dane, H.; Sisman, T.A. Histopathological study on the freshwater fish species chub (Squalius cephalus) in the Karasu River, Turkey. Turk. J. Zool. 2017, 41, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilak, K.S.; Rao, D.K.; Veeraiah, K. Effects of chlorpyrifos on histopathology of the fish Catla catl. J. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Monit. 2005, 15, 127–140. [Google Scholar]
- Thophon, S.; Kruatrachue, M.; Upatham, E.S.; Pokethitiyook, P.; Sahaphong, S.; Jaritkhuan, S. Histopathological alterations of white seabass, Lates calcarifer, in acute and subchronic cadmium exposure. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 121, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokote, M. Digestive system. In An Atlas of Histology—Normal and Pathological Features Commercial Deltamethrin on the Structure of the Gill; Hibiya, T., Ed.; Kodansha Ltd.: Tokyo, Japan, 1982; pp. 74–93. [Google Scholar]
- Maharajan, A.; Kitto, M.R.; Paruruckumani, P.S.; Ganapiriya, V. Histopathology biomarker responses in Asian sea bass, Lates calcarifer (Bloch) exposed to Copper. J. Basic Appl. Zool. 2016, 77, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassif, E.; Mourad, M.H.; Haredi, A.M.M.; Tanekhy, M. Biochemical and Histopathological Changes in Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus at Lake Edku. Alex. J. Vet. Sci. 2017, 55, 40–51. [Google Scholar]
- Rajeshkumar, S.; Karunamurthy, D.; Halley, G.; Munuswamy, N. An integrated use of histological and ultra-structural biomarkers in Mugil cephalus for assessing heavy metal pollution in east Berbice-Corentyne, Guyana. Int. J. Bioassays 2015, 4, 4541–4554. [Google Scholar]
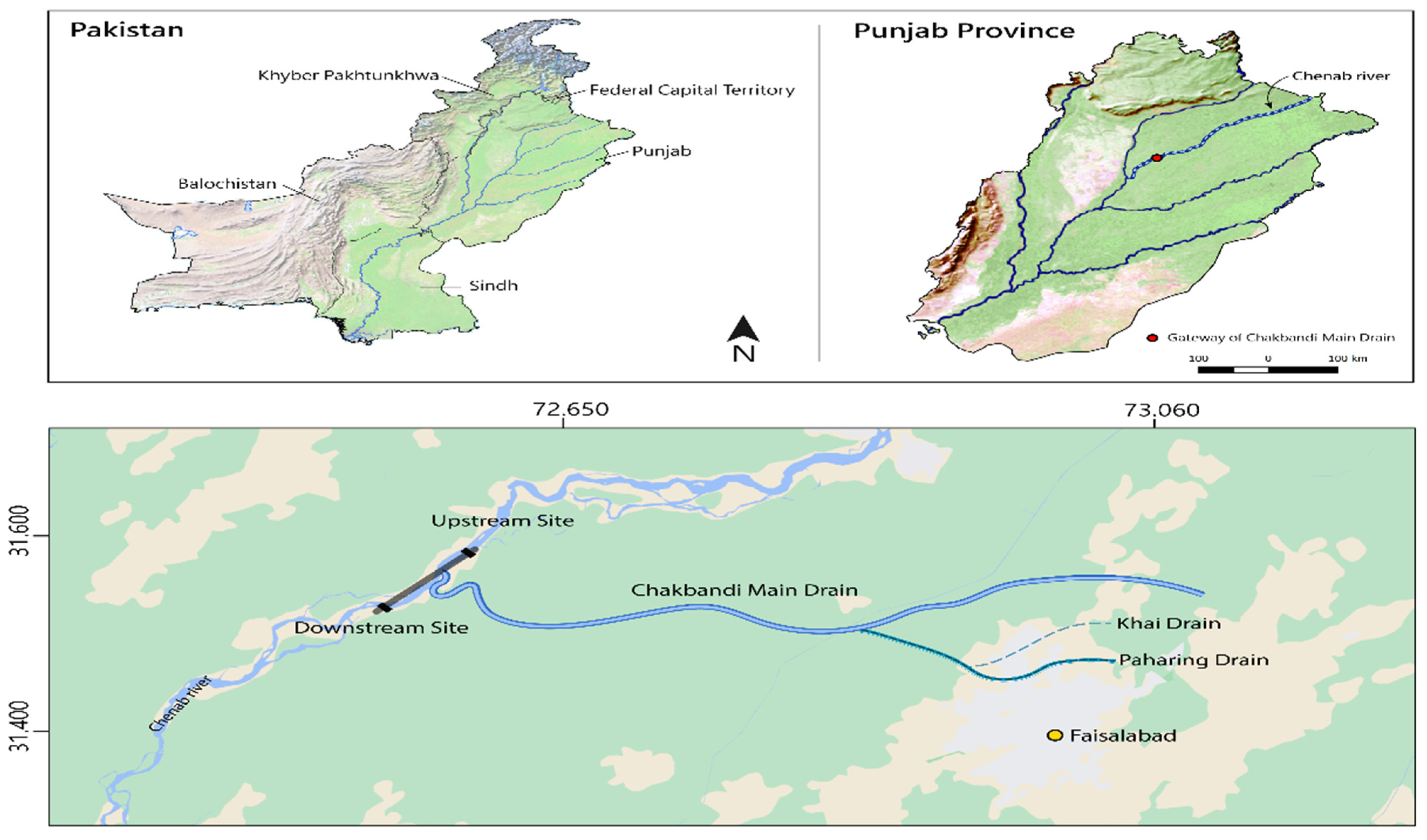



| Water Quality Parameters (mg/L) | Downstream Gateway of CMD | Upstream Gateway of CMD | Permissible Limits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lead | 2.975 ± 0.06 c | 0.15 ± 0.02 a | D: 0.05 mg/L, P: ** |
| Copper | 2.002 ± 0.07 a | 0.84 ± 0.08 b | D: 0.05 mg/L, P: 1.5 mg/L |
| Cadmium | 0.26 ± 0.02 a | 0.022 ± 0.0 b | D: 0.01 mg/L, P: ** |
| Mercury | 1.445 ± 0.03 b | 0.011 ± 0.0 c | D: 0.001 mg/L, P: ** |
| Cobalt | 0.979 ± 0.003 b | 0.833 ± 0.05 a | D: 0.05 mg/L |
| Tin | 0.488 ± 0.01 a | 0.019 ± 0.0 b | D: 0.01 mg/L, P: ** |
| Chromium | 0.676 ± 0.04 a | 0.28 ± 0.05 b | D: 0.05 mg/L, P: ** |
| Zinc | 0.54 ± 0.03 c | 0.19 ± 0.03 b | D: 5 mg/L, P: 15 mg/L |
| Manganese | 2.73 ± 0.1 b | 1.81± 0.06 a | D: 0.1 mg/L, P: 0.3 mg/L |
| Sulphates | 442 ± 5.71 a | 346± 6.93 c | D: <400 mg/L, P: 400 mg/L |
| Salinity | 1909 ± 7.68 a | 412 ± 3.02 b | P: <100 mg/L |
| Phenols | 2.31 ± 0.03 b | 0.68 ± 0.04 c | D: 0.001 mg/L, P: 0.002 mg/L |
| Conductivity (µS/cm) | 3.31 ± 0.02 b | 1.29 ± 0.07 a | D: 2.1 µS/cm, P: 2.1 µS/cm |
| Hardness | 576.19 ± 8.12 c | 207.42 ± 4.42 b | P: 120–170 mg/L P: ** |
| BOD | 76.94 ± 0.39 c | 43.7± 0.07 a | † D: 30 mg/L, P: ** |
| COD | 193.95 ± 1.93 c | 70.4 ± 0.22 a | † D: 250 mg/L, P: ** |
| TSS | 308 ± 2.44 a | 209 ± 5.21 c | D: 100mg/L, P: ** |
| TDS | 2411 ± 6.87 a | 1318 ± 8.01 b | D: 500 mg/L, P: 2000 mg/L |
| pH | 11.8 ± 0.25 a | 8.0 ± 0.07 b | D: 6.5–8.5, P: ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shahid, S.; Sultana, T.; Sultana, S.; Hussain, B.; Al-Ghanim, K.A.; Al-Bashir, F.; Riaz, M.N.; Mahboob, S. Detecting Aquatic Pollution Using Histological Investigations of the Gills, Liver, Kidney, and Muscles of Oreochromis niloticus. Toxics 2022, 10, 564. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100564
Shahid S, Sultana T, Sultana S, Hussain B, Al-Ghanim KA, Al-Bashir F, Riaz MN, Mahboob S. Detecting Aquatic Pollution Using Histological Investigations of the Gills, Liver, Kidney, and Muscles of Oreochromis niloticus. Toxics. 2022; 10(10):564. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100564
Chicago/Turabian StyleShahid, Sana, Tayyaba Sultana, Salma Sultana, Bilal Hussain, Khalid Abdullah Al-Ghanim, Fahad Al-Bashir, Mian Nadeem Riaz, and Shahid Mahboob. 2022. "Detecting Aquatic Pollution Using Histological Investigations of the Gills, Liver, Kidney, and Muscles of Oreochromis niloticus" Toxics 10, no. 10: 564. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100564
APA StyleShahid, S., Sultana, T., Sultana, S., Hussain, B., Al-Ghanim, K. A., Al-Bashir, F., Riaz, M. N., & Mahboob, S. (2022). Detecting Aquatic Pollution Using Histological Investigations of the Gills, Liver, Kidney, and Muscles of Oreochromis niloticus. Toxics, 10(10), 564. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100564








