Exposure to Environmentally Relevant Concentrations of Polystyrene Microplastics Increases Hexavalent Chromium Toxicity in Aquatic Animals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Microplastics
2.2. Rotifer Toxicity Test
2.3. Water Flea Toxicity Test
2.4. Amphipod Chronic Toxicity Test
2.5. Polychaete Acute Toxicity Test
2.6. Zebrafish Early Life Stage Test
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
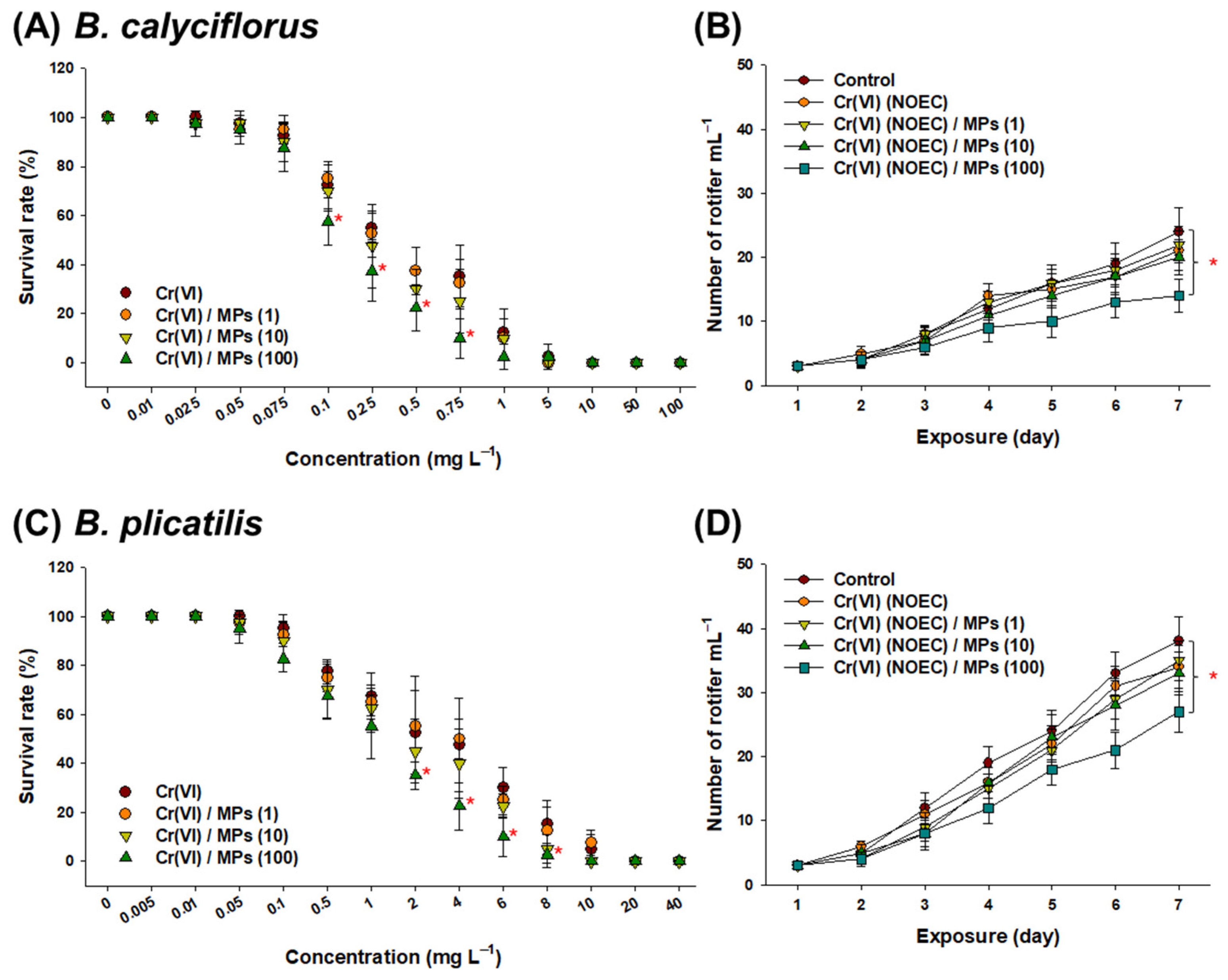
3.1. Effect of Cr(VI) and MP on Rotifer Survival
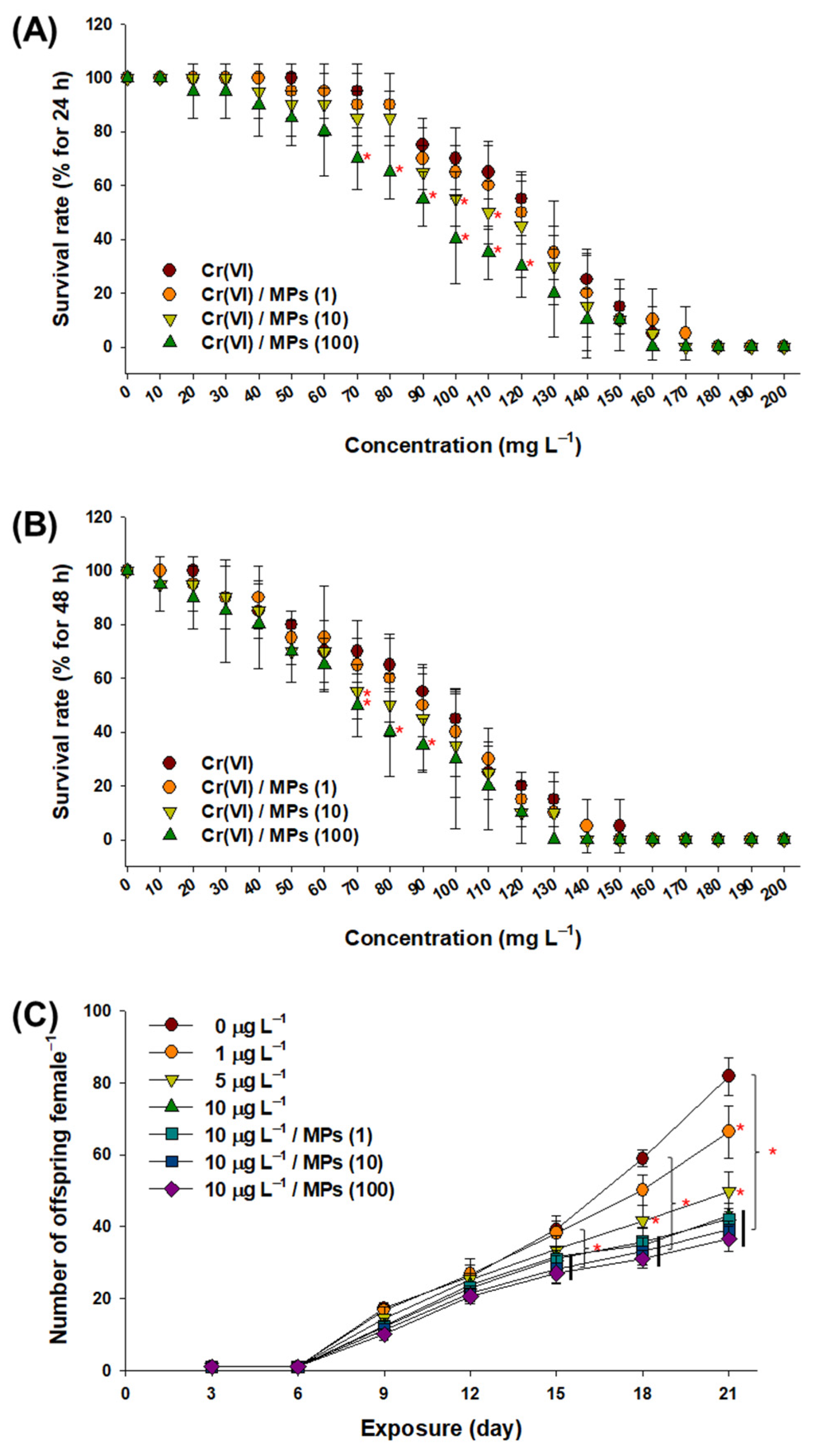
3.2. Effect of Cr(VI) and MPs on the Survival and Offspring Production of Water Fleas
3.3. Effect of Cr(VI) and MPs on the Survival Rate and Growth of Amphipods
3.4. Effect of Cr(VI) and MPs on the Survival and Burrowing Capacity of Polychaetes
3.5. Effect of Cr(VI) and MPs on the Survival of Zebrafish Embryos and Larvae
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Velma, V.; Vutukuru, S.S.; Tchounwou, P.B. Ecotoxicology of hexavalent chromium in freshwater fish: A critical review. Rev. Environ. Health 2009, 24, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DesMarias, T.L.; Costa, M. Mechanisms of chromium-induced toxicity. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2019, 14, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EPA. Health Advisory: Chromium; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1987.
- WHO. Chromium in Drinking Water. Background Document for Development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, B.-M.; Kim, B.; Nam, S.-E.; Eom, H.-J.; Lee, S.; Kim, K.; Rhee, J.-S. Reductive transformation of hexavalent chromium in ice decreases chromium toxicity in aquatic animals. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 3503–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourahmad, J.; Peter, J.B.; Jokar, F.; Daraei, B. Carcinogenic metal induced sites of reactive oxygen species formation in hepatocytes. Toxicol. Vitr. 2003, 17, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumschnabel, G.; Nawaz, M. Acute toxicity of hexavalent chromium in isolated teleost hepatocytes. Aquat. Toxicol. 2004, 70, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, J.D.; Filice, F.P.; Li, M.S.; Ding, Z. Tracking live-cell response to hexavalent chromium toxicity by using scanning electrochemical microscopy. ChemElectroChem 2017, 4, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, I.; Oliveira, R.; Lourenço, J.; Grisolia, C.K.; Mendo, S.; Soares, A.M.V.M. Biomarkers as a tool to assess effects of chromium (VI): Comparison of responses in zebrafish early life stages and adults. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2010, 152, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, S.; Yousafzai, A.M. Chromium toxicity in fish: A review article. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2017, 5, 1483–1488. [Google Scholar]
- Geyer, R.; Jambeck, J.R.; Law, K.L. Production, use, and fate of all plastics ever made. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frias, J.P.G.L.; Nash, R. Microplastics: Finding a consensus on the definition. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 138, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelmans, A.A.; Mohamed Nor, N.H.; Hermsen, E.; Kooi, M.; Mintenig, S.M.; De France, J. Microplastics in freshwaters and drinking water: Critical review and assessment of data quality. Water Res. 2019, 155, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Li, M. Interaction of microplastics and heavy metals: Toxicity, mechanisms, and environmental implications. In The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; He, D., Luo, Y., Eds.; Microplastics in Terrestrial Environments; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 95, pp. 185–195. [Google Scholar]
- González-Pleiter, M.; Tamayo-Belda, M.; Pulido-Reyes, G.; Amariei, G.; Leganés, F.; Rosal, R.; Fernández-Piñas, F. Secondary nanoplastics released from a biodegradable microplastic severely impact freshwater environments. Environ. Sci. Nano 2019, 6, 1382–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.K.; Hong, S.H.; Eo, S.; Jang, M.; Hang, G.M.; Isobe, A.; Shim, W.J. Horizontal and vertical distribution of microplastics in Korean coastal waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 12188–12197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, O.Y.; Kang, J.-H.; Hong, S.H.; Shim, W.J. Spatial distribution of microplastic in the surface waters along the coast of Korea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 155, 110729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galgani, F.; Leaute, J.P.; Moguedet, P.; Souplet, A.; Verin, Y.; Carpentier, A.; Goraguere, H.; Latrouitee, D.; Andralf, B.; Cadiou, Y.; et al. Litter on the sea floor along European coasts. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2000, 40, 516–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, I.A.; Clare, M.A. Dispersion, accumulation, and the ultimate fate of micro-plastics in deep-marine environments: A review and future directions. Front. Earth Sci. 2019, 7, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, D.K.; Galgani, F.; Thompson, R.C.; Barlaz, M. Accumulation and fragmentation of plastic debris in global environments. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 1985–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.C.; Olsen, Y.; Mitchell, R.P.; Davis, A.; Rowland, S.J.; John, A.W.G.; McGonigle, D.; Russell, A.E. Lost at sea: Where is all the plastic? Science 2004, 304, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wong, C.S.; Chen, D.; Lu, X.; Wang, F.; Zeng, E.Y. Interaction of toxic chemicals with microplastics: A critical review. Water Res. 2018, 139, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.L.; Thompson, R.C.; Galloway, T.S. The physical impacts of microplastics on marine organisms: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 178, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setälä, O.; Fleming-Lehtinen, V.; Lehtiniemi, M. Ingestion and transfer of microplastics in the planktonic food web. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 185, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, E.E.; Boxall, A.B. Microplastics in the aquatic environment: Evidence for or against adverse impacts and major knowledge gaps. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 37, 2776–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, F.; Adeyemi, J.A.; Bocato, M.Z.; Comas, A.; Campiglia, A. A critical viewpoint on current issues, limitations, and future research needs on micro- and nanoplastic studies: From the detection to the toxicological assessment. Environ. Res. 2020, 182, 109089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouin, T. Toward an improved understanding of the ingestion and trophic transfer of microplastic particles: Critical review and implications for future research. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2020, 39, 1119–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, L.A.; Turner, A.; Thompson, R.C. Interactions between trace metals and plastic production pellets under estuarine conditions. Mar. Chem. 2014, 167, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagat, J.; Zang, L.; Nishimura, N.; Shimada, Y. Zebrafish: An emerging model to study microplastic and nanoplastic toxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roda, J.F.B.; Lauer, M.M.; Risso, W.E.; Dos Reis Martinez, C.B. Microplastics and copper effects on the neotropical teleost Prochilodus lineatus: Is there any interaction? Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2020, 242, 110659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, D.; Felix, L.; Luzio, A.; Parra, S.; Cabecinha, E.; Bellas, J.; Monteiro, S.M. Toxicological effects induced on early life stages of zebrafish (Danio rerio) after an acute exposure to microplastics alone or co-exposed with copper. Chemosphere 2020, 261, 127748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Wang, M.; Chen, X.; Yang, C.; Wu, L. Combined toxicity of microplastics and cadmium on the zebrafish embryos (Danio rerio). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 743, 140638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, H.-J.; Haque, M.N.; Lee, S.; Rhee, J.-S. Exposure to metals premixed with microplastics increases toxicity through bioconcentration and impairs antioxidant defense and cholinergic response in a marine mysid. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 249, 109142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, C.-B.; Won, E.-J.; Kang, H.-M.; Lee, M.-C.; Hwang, D.-S.; Hwang, U.K.; Zhou, B.; Souissi, S.; Lee, S.-J.; Lee, J.-S. Microplastic size-dependent toxicity, oxidative stress induction, and p-JNK and p-p38 activation in the monogonont rotifer (Brachionus koreanus). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 8849–8857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Xu, W.; Gu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, L.; Gu, L.; Huang, Y.; Lyu, K.; Yang, Z. Small-sized microplastics negatively affect rotifers: Changes in the key life-history traits and rotifer-phaeocystis population dynamics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 9241–9251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jemec, A.; Horvat, P.; Kunej, U.; Bele, M.; Kržan, A. Uptake and effects of microplastic textile fibers on freshwater crustacean Daphnia magna. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziajahromi, S.; Kumar, A.; Neale, P.A.; Leusch, F.D.L. Impact of microplastic beads and fibers on waterflea (Ceriodaphnia dubia) survival, growth, and reproduction: Implications of single and mixture exposures. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 13397–13406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Rhee, J.-S. Biochemical and physiological responses of the water flea Moina macrocopa to microplastics: A multigenerational study. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 2021, 17, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, S.Y.; Bruce, T.F.; Bridges, W.C.; Klaine, S.J. Responses of Hyalellaazteca to acute and chronic microplastic exposures. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 34, 2564–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iannilli, V.; Pasquali, V.; Setini, A.; Corami, F. First evidence of microplastics ingestion in benthic amphipods from Svalbard. Environ. Res. 2019, 179, 108811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamieson, A.J.; Brooks, L.S.R.; Reid, W.D.K.; Piertney, S.B.; Narayanaswamy, B.E.; Linley, T.D. Microplastics and synthetic particles ingested by deep-sea amphipods in six of the deepest marine ecosystems on Earth. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 180667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, M.A.; Niven, S.J.; Galloway, T.S.; Rowland, S.J.; Thompson, R.C. Microplastic moves pollutants and additives to worms, reducing functions linked to health and biodiversity. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, 2388–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, J.; Chan, K.Y.K. Microplastics reduced posterior segment regeneration rate of the polychaete Perinereis aibuhitensis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 129, 782–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.S.S.; Oliveira, M.; Lopéz, D.; Martins, M.; Figueira, E.; Pires, A. Do nanoplastics impact the ability of the polychaeta Hediste diversicolor to regenerate? Ecol. Indic. 2020, 110, 105921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchi, S.; Bianchi, J.; Scalici, M.; Fabroni, F.; Tomassetti, P. Field evidence for microplastic interactions in marine benthic invertebrates. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, K.; Qiao, R.; An, H.; Zhang, Y. Influence of microplastics on the accumulation and chronic toxic effects of cadmium in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Chemosphere 2018, 202, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, D.; Félix, L.; Luzio, A.; Parra, S.; Bellas, J.; Monteiro, S.M. Single and combined acute and subchronic toxic effects of microplastics and copper in zebrafish (Danio rerio) early life stages. Chemosphere 2021, 277, 130262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsang, Y.Y.; Mak, C.W.; Liebich, C.; Lam, S.W.; Sze, E.T.-P.; Chan, K.M. Microplastic pollution in the marine waters and sediments of Hong Kong. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 115, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Bai, H.; Chen, B.; Sun, X.; Qu, K.; Xia, B. Microplastic pollution in North Yellow Sea, China: Observations on occurrence, distribution and identification. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Zhu, L.; Wang, T.; Li, D. Suspended microplastics in the surface water of the Yangtze estuary system, China: First observations on occurrence, distribution. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 86, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nel, H.A.; Froneman, P.W. A quantitative analysis of microplastic pollution along the south-eastern coastline of South Africa. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 101, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colton, J.B.; Burns, B.R.; Knapp, F.D. Plastic particles in surface waters of the Northwestern Atlantic. Science 1974, 185, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA. Methods for Measuring the Toxicity and Bioaccumulation of Sediment-Associated Contaminants with Freshwater Invertebrates, 2nd ed.; Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2000; EPA/600/R–99/064.
- Snell, T.W.; Persoone, G. Acute toxicity bioassay using rotifers. I. A test for brackish and marine environments with Brachionus plicatilis. Aquat. Toxicol. 1989, 14, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snell, T.W.; Moffat, B.D.; Janssen, C.; Persoone, G. Acute toxicity tests using rotifers. IV. Effects of cyst age, temperature, and salinity on the sensitivity of Brachionus calyciflorus. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1991, 21, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD (Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development). Guidelines for Testing of Chemicals. Proposal for Updated Guideline 211, Daphnia magna Reproduction Test. Revisted Draft Document; OECD: Paris, France, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- ISO (International Organisation for Standardization). Water Quality ± Determination of the Mobility of Daphnia magna Straus (Cladocera, Crustacea); ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Besser, J.M.; Brumbaugh, W.G.; Kemble, N.E.; May, T.W.; Ingersoll, C.G. Effects of sediment characteristics on the toxicity of chromium (III) and chromium (VI) to the amphipod, Hyalella azteca. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 6210–6216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, M.N.; Nam, S.-E.; Eom, H.-J.; Kim, S.-K.; Rhee, J.-S. Exposure to sublethal concentrations of zinc pyrithione inhibits growth and survival of marine polychaete through induction of oxidative stress and DNA damage. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 156, 111276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD (Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development). Fish Embryo Toxicity Test. Organization for Economic Co-Operation and Development; OECD: Paris, France, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Strähle, U.; Scholz, S.; Geisler, R.; Greiner, P.; Hollert, H.; Rastegar, S.; Schumacher, A.; Selderslaghs, I.; Weiss, C.; Witters, H.; et al. Zebrafish embryos as an alternative to animal experiments--a commentary on the definition of the onset of protected life stages in animal welfare regulations. Reprod. Toxicol. 2012, 33, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, L.A.; Turner, A.; Thompson, R.C. Adsorption of trace metals to plastic resin pellets in the marine environment. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 160, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luís, L.G.; Ferreira, P.; Fonte, E.; Oliveira, M.; Guilhermino, L. Does the presence of microplastics influence the acute toxicity of chromium(VI) to early juveniles of the common goby (Pomatoschistus microps)? A study with juveniles from two wild estuarine populations. Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 164, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, L.; Hua, T.; Li, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wang, W.; You, Z.; Wang, H.; Li, M. The mechanism for adsorption of Cr(VI) ions by PE microplastics in ternary system of natural water environment. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 257, 113440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, W.; Zuo, Q.; Abdelkader, A.; Xi, K.; Heynderickx, P.M.; Kim, K.H. The potential of microplastics as adsorbents of sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate and chromium in an aqueous environment. Environ. Res. 2021, 197, 111057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stohs, S.J.; Bagchi, D. Oxidative mechanisms in the toxicity of metal ions. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1995, 18, 321–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vroom, R.J.; Koelmans, A.A.; Besseling, E.; Halsband, C. Aging of microplastics promotes their ingestion by marine zooplankton. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, F.; Cowie, P.R. Plastic contamination in the decapod crustacean Nephrops norvegicus (Linnaeus, 1758). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1207–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eom, H.-J.; Nam, S.-E.; Rhee, J.-S. Polystyrene microplastics induce mortality through acute cell stress and inhibition of cholinergic activity in a brine shrimp. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 2020, 16, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-H.; Lee, S.; Rhee, J.-S. Consistent exposure to microplastics induces age-specific physiological and biochemical changes in a marine mysid. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 162, 111850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reish, D.J.; Gerlinger, T.V. A review of the toxicological studies with polychaetous annelids. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1997, 60, 584–607. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W.S.; Cho, H.-J.; Kim, E.; Huh, Y.H.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, B.; Kang, T.; Lee, J.-S.; Jeong, J. Bioaccumulation of polystyrene nanoplastics and their effect on the toxicity of Au ions in zebrafish embryos. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 3173–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ge, J.; Yu, X. Bioavailability and toxicity of microplastics to fish species: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 189, 109913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, G.; Venkateswara Rao, J.; Srikanth, K. Oxidative stress and changes in locomotor behavior and gill morphology of Gambusia affinis exposed to chromium. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2006, 88, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochman, C.M.; Hentschel, B.T.; Teh, S.J. Long-term sorption of metals is similar among plastic types: Implications for plastic debris in aquatic environments. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85433. [Google Scholar]



| MPs Conc. (Particles L−1) | Cr(VI) Conc. (mg L−1) | Cumulative Mortality (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | 96 h | 120 h | 144 h | ||
| 0 | 0 | 3 | 6 | 10 | 11 | 13 | 13 |
| 21 | 7 | 10 | 18 | 22 | 25 | 31 | |
| 49 | 11 | 15 | 19 | 24 | 29 | 33 | |
| 75 | 15 | 21 | 26 | 29 | 35 | 42 | |
| 93 | 17 | 22 | 31 | 39 | 60 | 72 | |
| 116 | 19 | 22 | 36 | 43 | 68 | 92 | |
| 120 | 22 | 25 | 40 | 51 | 79 | 96 | |
| 1 | 0 | 3 | 6 | 7 | 11 | 13 | 13 |
| 21 | 8 | 11 | 15 | 21 | 26 | 32 | |
| 49 | 13 | 13 | 18 | 25 | 33 | 36 | |
| 75 | 17 | 18 | 24 | 31 | 39 | 49 | |
| 93 | 15 | 19 | 33 | 39 | 65 | 79 | |
| 116 | 21 | 24 | 39 | 46 | 78 | 96 | |
| 120 | 26 | 26 | 43 | 56 | 86 | 97 | |
| 10 | 0 | 3 | 6 | 10 | 11 | 13 | 13 |
| 21 | 7 | 13 | 19 | 26 | 28 | 33 | |
| 49 | 11 | 17 | 18 | 26 | 29 | 35 | |
| 75 | 14 | 19 | 26 | 28 | 36 | 46 | |
| 93 | 18 | 25 | 31 | 36 | 65 | 81 | |
| 116 | 24 | 29 | 42 | 44 | 82 | 97 | |
| 120 | 24 | 25 | 39 | 51 | 85 | 99 | |
| 100 | 0 | 3 | 6 | 10 | 11 | 13 | 13 |
| 21 | 10 | 13 | 15 | 22 | 42 | 44 | |
| 49 | 14 | 14 | 17 | 22 | 32 | 39 | |
| 75 | 18 | 21 | 29 | 32 | 42 | 49 | |
| 93 | 19 | 26 | 33 | 35 | 69 | 83 | |
| 116 | 22 | 26 | 35 | 49 | 86 | 96 | |
| 120 | 25 | 26 | 39 | 58 | 86 | 99 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.; Haque, M.N.; Lee, S.; Lee, D.-H.; Rhee, J.-S. Exposure to Environmentally Relevant Concentrations of Polystyrene Microplastics Increases Hexavalent Chromium Toxicity in Aquatic Animals. Toxics 2022, 10, 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100563
Kim J, Haque MN, Lee S, Lee D-H, Rhee J-S. Exposure to Environmentally Relevant Concentrations of Polystyrene Microplastics Increases Hexavalent Chromium Toxicity in Aquatic Animals. Toxics. 2022; 10(10):563. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100563
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jaehee, Md. Niamul Haque, Somyeong Lee, Do-Hee Lee, and Jae-Sung Rhee. 2022. "Exposure to Environmentally Relevant Concentrations of Polystyrene Microplastics Increases Hexavalent Chromium Toxicity in Aquatic Animals" Toxics 10, no. 10: 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100563
APA StyleKim, J., Haque, M. N., Lee, S., Lee, D.-H., & Rhee, J.-S. (2022). Exposure to Environmentally Relevant Concentrations of Polystyrene Microplastics Increases Hexavalent Chromium Toxicity in Aquatic Animals. Toxics, 10(10), 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100563







