Comprehensive Profiling of the Native and Modified Peptidomes of Raw Bovine Milk and Processed Milk Products
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Peptide Extraction
2.3. Tandem Mass Spectrometry
2.4. Data Processing
2.4.1. Unmodified Peptides
2.4.2. Modified Peptides
3. Results
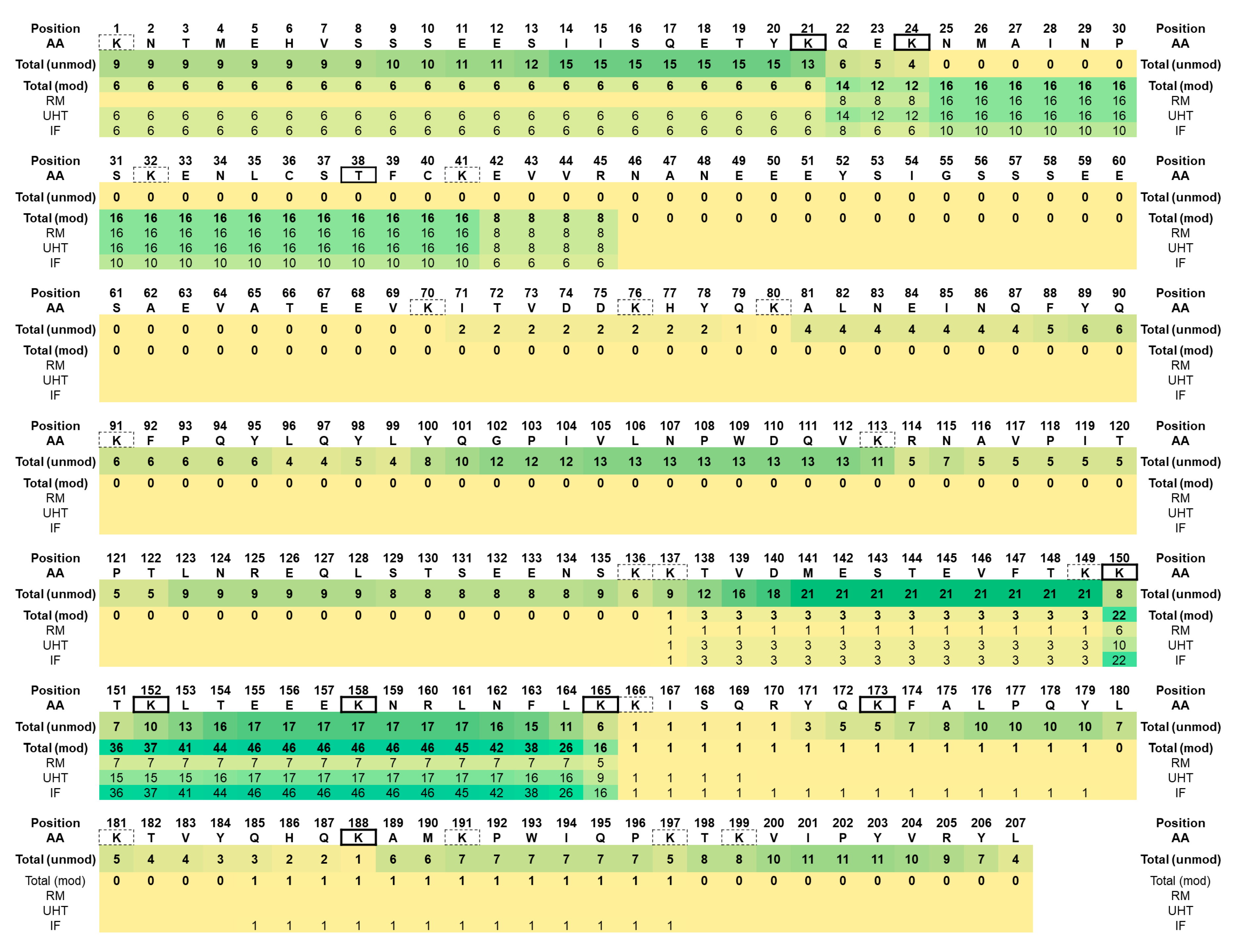
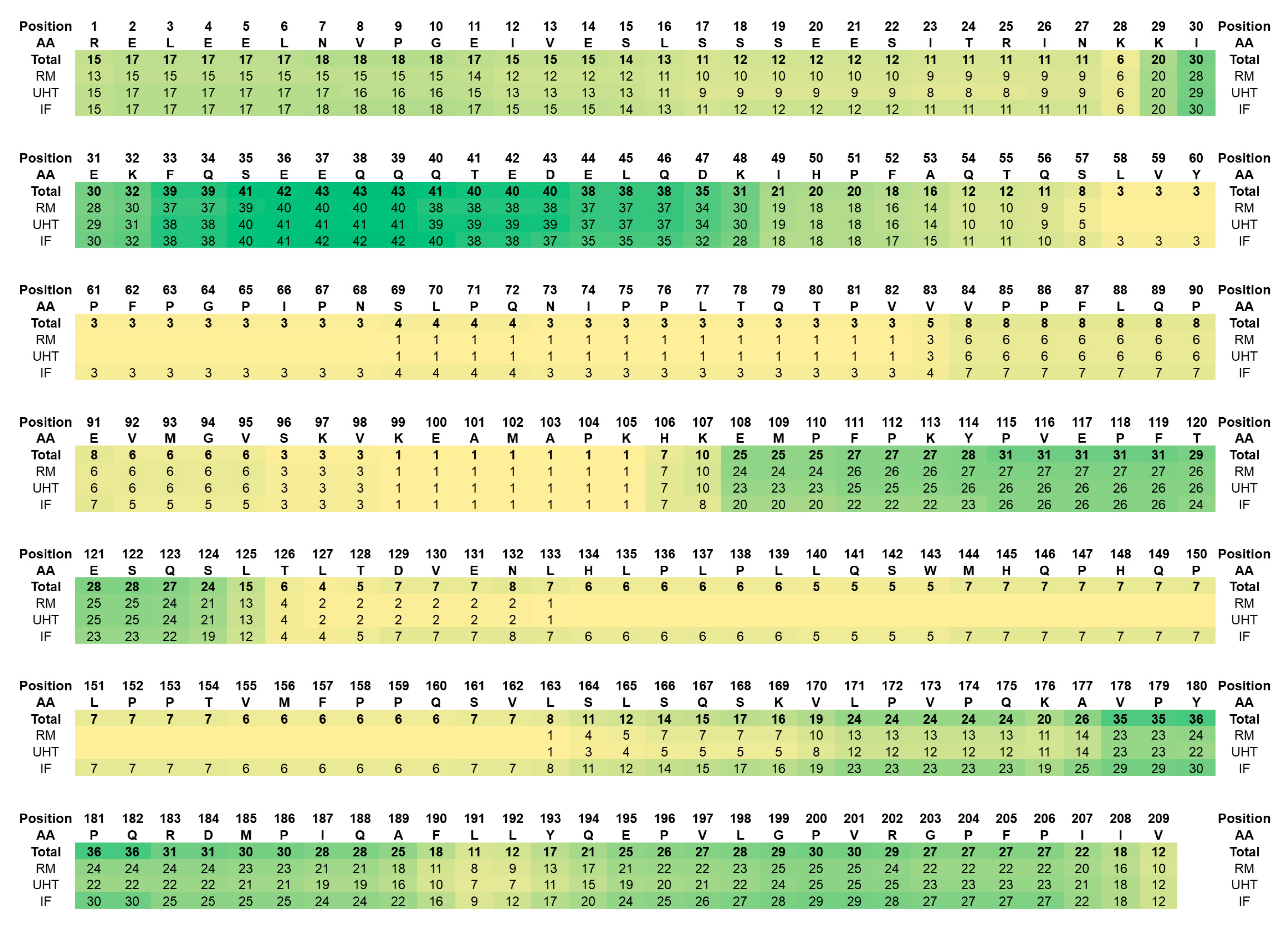
3.1. Native Peptidome
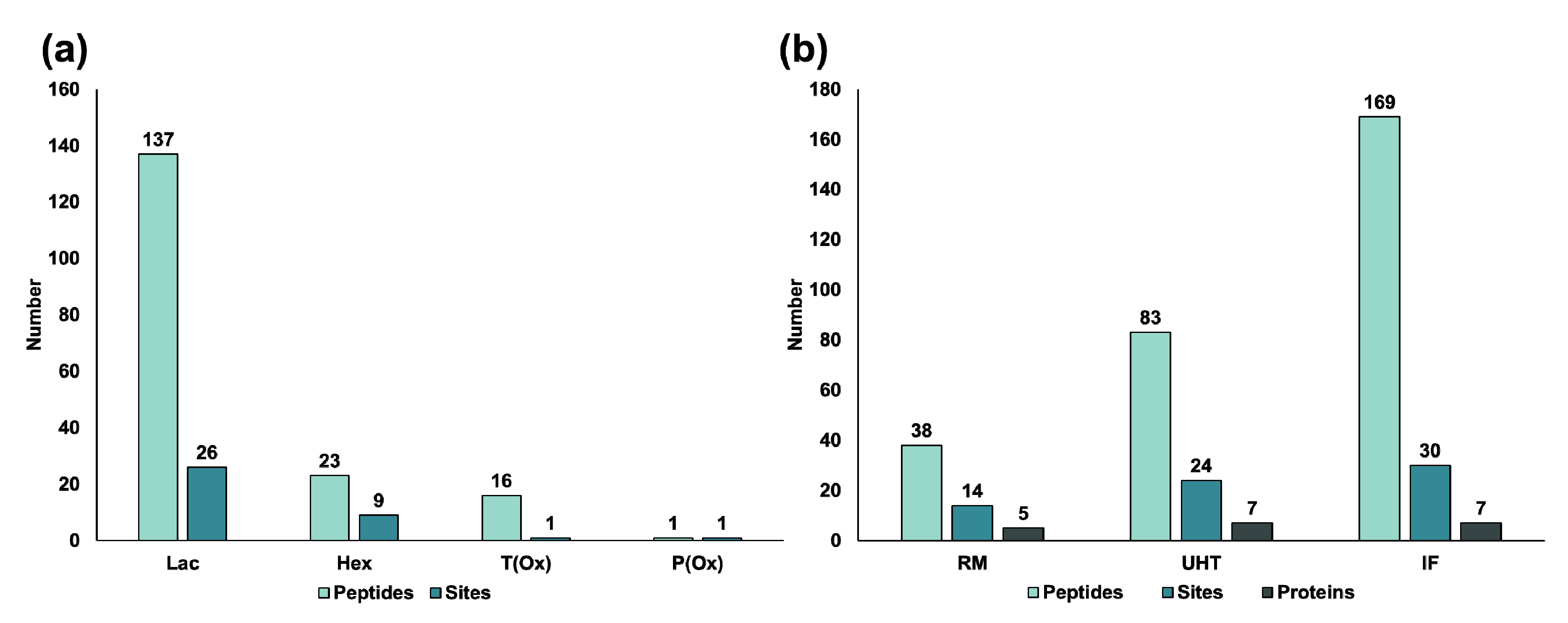
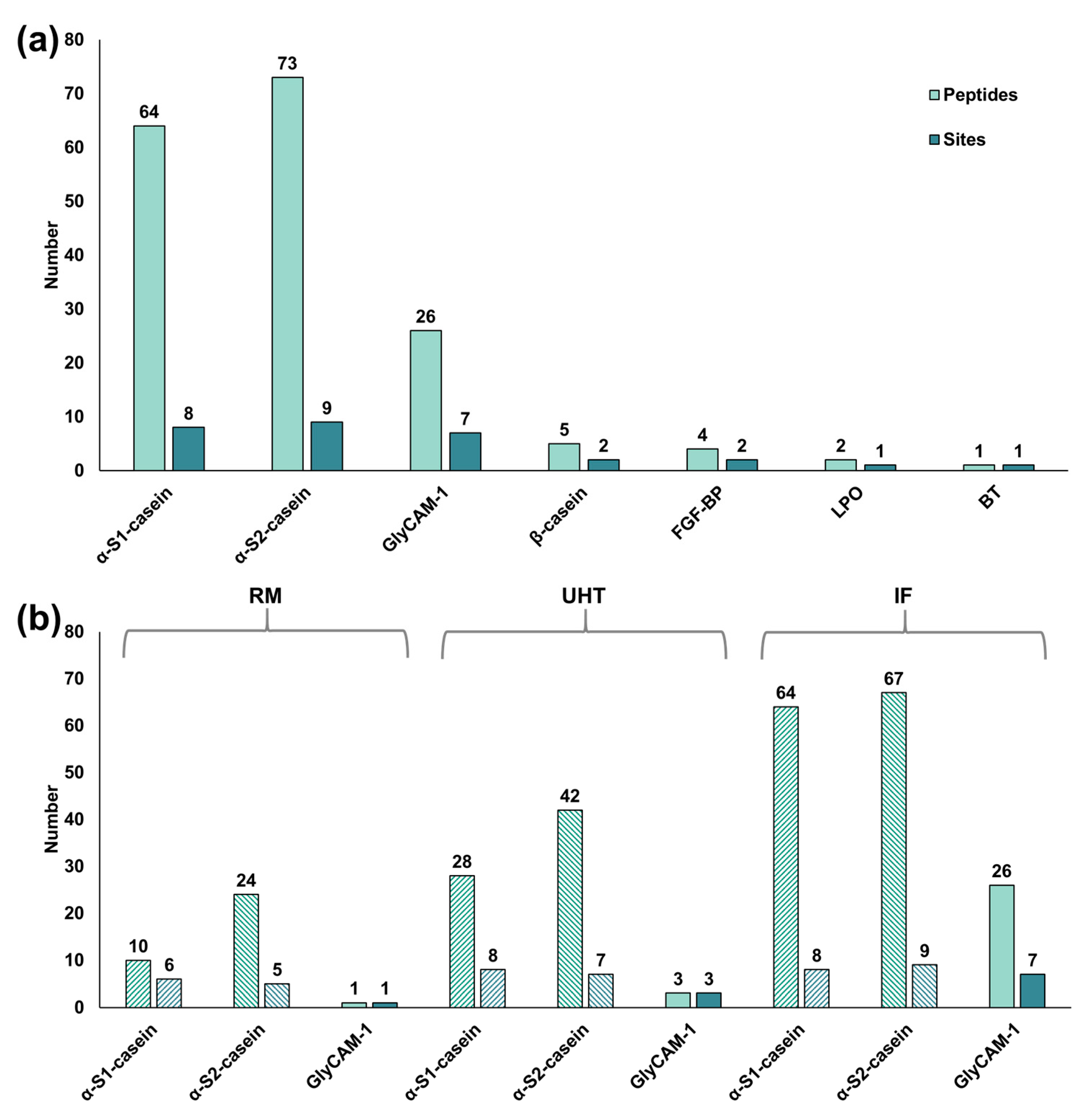
3.2. Non-Enzymatic Modifications in the Bovine Milk Peptidome
4. Discussion
4.1. Native Peptidome
4.2. Non-Enzymatic Modifications
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meisel, H. Biochemical properties of peptides encrypted in bovine milk proteins. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 12, 1905–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagpal, R.; Behare, P.; Rana, R.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, M.; Arora, S.; Morotta, F.; Jain, S.; Yadav, H. Bioactive peptides derived from milk proteins and their health beneficial potentials: An update. Food Funct. 2011, 2, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastian, E.D.; Brown, R.J. Plasmin in milk and dairy products: An update. Int. Dairy J. 1996, 6, 435–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Mahony, J.A.; Fox, P.F.; Kelly, A.L. Indigenous Enzymes of Milk. In Advanced Dairy Chemistry: Volume 1A: Proteins: Basic Aspects; McSweeney, P.L.H., Fox, P.F., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 337–385. ISBN 978-1-46-144713-9. [Google Scholar]
- Dallas, D.C.; Murray, N.M.; Gan, J. Proteolytic Systems in Milk: Perspectives on the Evolutionary Function within the Mammary Gland and the Infant. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia 2015, 20, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, A.L.; O’Flaherty, F.; Fox, P.F. Indigenous proteolytic enzymes in milk: A brief overview of the present state of knowledge. Int. Dairy J. 2006, 16, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, F.; Fedorova, M.; Ebner, J.; Hoffmann, R.; Pischetsrieder, M. Analysis of the endogenous peptide profile of milk: Identification of 248 mainly casein-derived peptides. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 5447–5462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallas, D.C.; Guerrero, A.; Parker, E.A.; Garay, L.A.; Bhandari, A.; Lebrilla, C.B.; Barile, D.; German, J.B. Peptidomic profile of milk of Holstein cows at peak lactation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansor, R.; Mullen, W.; Albalat, A.; Zerefos, P.; Mischak, H.; Barrett, D.C.; Biggs, A.; Eckersall, P.D. A peptidomic approach to biomarker discovery for bovine mastitis. J. Proteom. 2013, 85, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, A.; Dallas, D.C.; Contreras, S.; Bhandari, A.; Cánovas, A.; Islas-Trejo, A.; Medrano, J.F.; Parker, E.A.; Wang, M.; Hettinga, K.; et al. Peptidomic analysis of healthy and subclinically mastitic bovine milk. Int. Dairy J. 2015, 46, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallas, D.C.; Weinborn, V.; de Moura Bell, J.M.L.N.; Wang, M.; Parker, E.A.; Guerrero, A.; Hettinga, K.A.; Lebrilla, C.B.; German, J.B.; Barile, D. Comprehensive peptidomic and glycomic evaluation reveals that sweet whey permeate from colostrum is a source of milk protein-derived peptides and oligosaccharides. Food Res. Int. 2014, 63, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, A.T. Proteinases in normal bovine milk and their action on caseins. J. Dairy Res. 1983, 50, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, R.; Stevenson, C.D.; Guck, S.E.; Pillsbury, L.A.; Ismail, B.; Hayes, K.D. Effect of various heat treatments on plasminogen activation in bovine milk during refrigerated storage. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 44, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, M.G.; Hurley, M.J.; Larsen, L.B.; Heegaard, C.W.; Magboul, A.A.; Oliveira, J.C.; McSweeney, P.L.; Kelly, A.L. Thermal inactivation kinetics of bovine cathepsin D. J. Dairy Res. 2001, 68, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalabasmaz, S.; Dittrich, D.; Kellner, I.; Drewello, T.; Pischetsrieder, M. Identification of peptides reflecting the storage of UHT milk by MALDI-TOF-MS peptide profiling. J. Proteom. 2019, 207, 103444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Boekel, M. Effect of heating on Maillard reactions in milk. Food Chem. 1998, 62, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arena, S.; Renzone, G.; Novi, G.; Paffetti, A.; Bernardini, G.; Santucci, A.; Scaloni, A. Modern proteomic methodologies for the characterization of lactosylation protein targets in milk. Proteomics 2010, 10, 3414–3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siciliano, R.A.; Mazzeo, M.F.; Arena, S.; Renzone, G.; Scaloni, A. Mass spectrometry for the analysis of protein lactosylation in milk products. Food Res. Int. 2013, 54, 988–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milkovska-Stamenova, S.; Hoffmann, R. Identification and quantification of bovine protein lactosylation sites in different milk products. J. Proteom. 2016, 134, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milkovska-Stamenova, S.; Hoffmann, R. Hexose-derived glycation sites in processed bovine milk. J. Proteom. 2016, 134, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milkovska-Stamenova, S.; Hoffmann, R. Influence of storage and heating on protein glycation levels of processed lactose-free and regular bovine milk products. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wölk, M.; Milkovska-Stamenova, S.; Schröter, T.; Hoffmann, R. Influence of seasonal variation and processing on protein glycation and oxidation in regular and hay milk. Food Chem. 2020, 337, 127690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renzone, G.; Arena, S.; Scaloni, A. Proteomic characterization of intermediate and advanced glycation end-products in commercial milk samples. J. Proteom. 2015, 117, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalsgaard, T.K.; Nielsen, J.H.; Larsen, L.B. Proteolysis of milk proteins lactosylated in model systems. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2007, 51, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ames, J.M. Applications of the Maillard reaction in the food industry. Food Chem. 1998, 62, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guéraud, F.; Atalay, M.; Bresgen, N.; Cipak, A.; Eckl, P.M.; Huc, L.; Jouanin, I.; Siems, W.; Uchida, K. Chemistry and biochemistry of lipid peroxidation products. Free Radic. Res. 2010, 44, 1098–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stadtman, E.R.; Levine, R.L. Protein oxidation. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 899, 191–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henle, T. Protein-bound advanced glycation endproducts (AGEs) as bioactive amino acid derivatives in foods. Amino Acids 2005, 29, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milkovska-Stamenova, S.; Mnatsakanyan, R.; Hoffmann, R. Protein carbonylation sites in bovine raw milk and processed milk products. Food Chem. 2017, 229, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arena, S.; Renzone, G.; D’Ambrosio, C.; Salzano, A.M.; Scaloni, A. Dairy products and the Maillard reaction: A promising future for extensive food characterization by integrated proteomics studies. Food Chem. 2017, 219, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milkovska-Stamenova, S.; Hoffmann, R. Diversity of advanced glycation end products in the bovine milk proteome. Amino Acids 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wölk, M.; Schröter, T.; Hoffmann, R.; Milkovska-Stamenova, S. Profiling of Low-Molecular-Weight Carbonyls and Protein Modifications in Flavored Milk. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallas, D.; Nielsen, S.D. Milk Peptidomics to Identify Functional Peptides and for Quality Control of Dairy Products. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1719, 223–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassi, M.; Arena, S.; Scaloni, A. MALDI-TOF-MS Platform for Integrated Proteomic and Peptidomic Profiling of Milk Samples Allows Rapid Detection of Food Adulterations. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 6157–6171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huppertz, T.; Fox, P.F.; Kelly, A.L. The caseins: Structure, stability, and functionality. In Proteins in Food Processing, 2nd ed.; Yada, R.Y., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2018; pp. 49–92. ISBN 978-0-08-100722-8. [Google Scholar]
- Hurley, M.; Larsen, L.; Kelly, A.; McSweeney, P. The milk acid proteinase cathepsin D: A review. Int. Dairy J. 2000, 10, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, E.; Nielsen, S.D.; Abd-El Aal, S.; El-Leboudy, A.; Saleh, E.; LaPointe, G. Use of Mass Spectrometry to Profile Peptides in Whey Protein Isolate Medium Fermented by Lactobacillus helveticus LH-2 and Lactobacillus acidophilus La-5. Front. Nutr. 2019, 6, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, R.; Maire, J.-C.; Maynard, F.; Secretin, M.-C. Aspects of whey protein usage in infant nutrition, a brief review. Int. J. Food Sci Tech. 1999, 34, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnaillie, L.M.; Tomasula, P.M. Whey Protein Fractionation. In Whey Processing, Functionality and Health Benefits, 1st ed.; Onwulata, C., Huth, P.J., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Ames, IA, USA, 2008; pp. 15–38. ISBN 978-0-81-380384-5. [Google Scholar]
- Su, M.-Y.; Broadhurst, M.; Liu, C.-P.; Gathercole, J.; Cheng, W.-L.; Qi, X.-Y.; Clerens, S.; Dyer, J.M.; Day, L.; Haigh, B. Comparative analysis of human milk and infant formula derived peptides following in vitro digestion. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 1895–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benkerroum, N. Antimicrobial peptides generated from milk proteins: A survey and prospects for application in the food industry. A review. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2010, 63, 320–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meltretter, J.; Wüst, J.; Pischetsrieder, M. Comprehensive analysis of nonenzymatic post-translational β-lactoglobulin modifications in processed milk by ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 6971–6981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, Y.; Lönnerdal, B. Effects of different industrial heating processes of milk on site-specific protein modifications and their relationship to in vitro and in vivo digestibility. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 4175–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wölk, M.; Milkovska-Stamenova, S.; Hoffmann, R. Comprehensive Profiling of the Native and Modified Peptidomes of Raw Bovine Milk and Processed Milk Products. Foods 2020, 9, 1841. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9121841
Wölk M, Milkovska-Stamenova S, Hoffmann R. Comprehensive Profiling of the Native and Modified Peptidomes of Raw Bovine Milk and Processed Milk Products. Foods. 2020; 9(12):1841. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9121841
Chicago/Turabian StyleWölk, Michele, Sanja Milkovska-Stamenova, and Ralf Hoffmann. 2020. "Comprehensive Profiling of the Native and Modified Peptidomes of Raw Bovine Milk and Processed Milk Products" Foods 9, no. 12: 1841. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9121841
APA StyleWölk, M., Milkovska-Stamenova, S., & Hoffmann, R. (2020). Comprehensive Profiling of the Native and Modified Peptidomes of Raw Bovine Milk and Processed Milk Products. Foods, 9(12), 1841. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9121841



