Rhus and Safflower Extracts as Potential Novel Food Antioxidant, Anticancer, and Antimicrobial Agents Using Nanotechnology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Plant Extracts
2.3. Metal Nanoparticles Synthesis
2.4. Instrumental Analysis for Metals Nanoparticles
2.5. Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) Measurement
2.6. Determination of Total Polyphenols Content
2.7. Determination of Total Flavonoids Content
2.8. Radical Scavenging Activity (RSA) Using DPPH Assay
2.9. Radical Scavenging Activity against ABTS•+
2.10. Microbial Susceptibility Testing
2.11. Potential Sulforhodamine B (SRB) Cell Cytotoxicity Assay
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
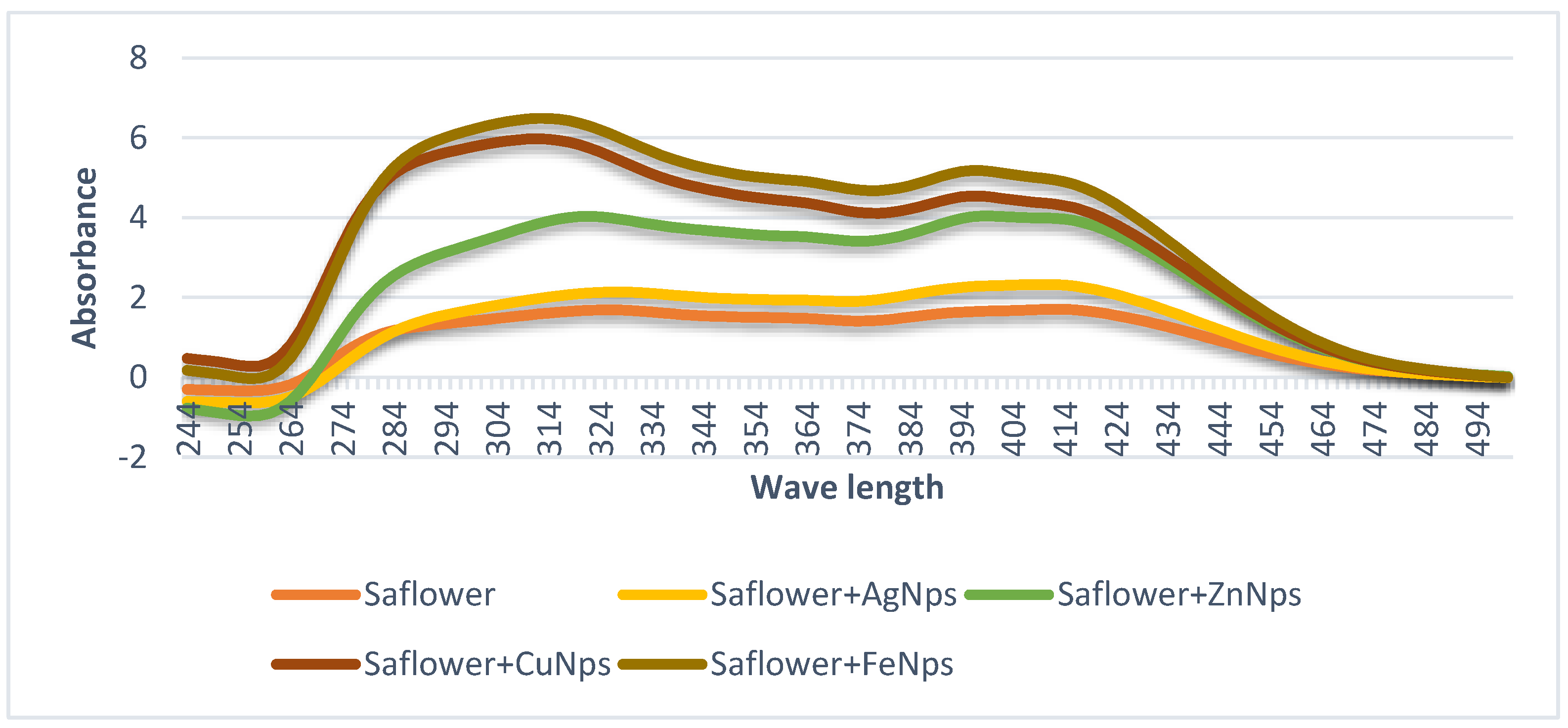
3.1. Nanoparticles Characteristics via UV-Vis Spectroscopy
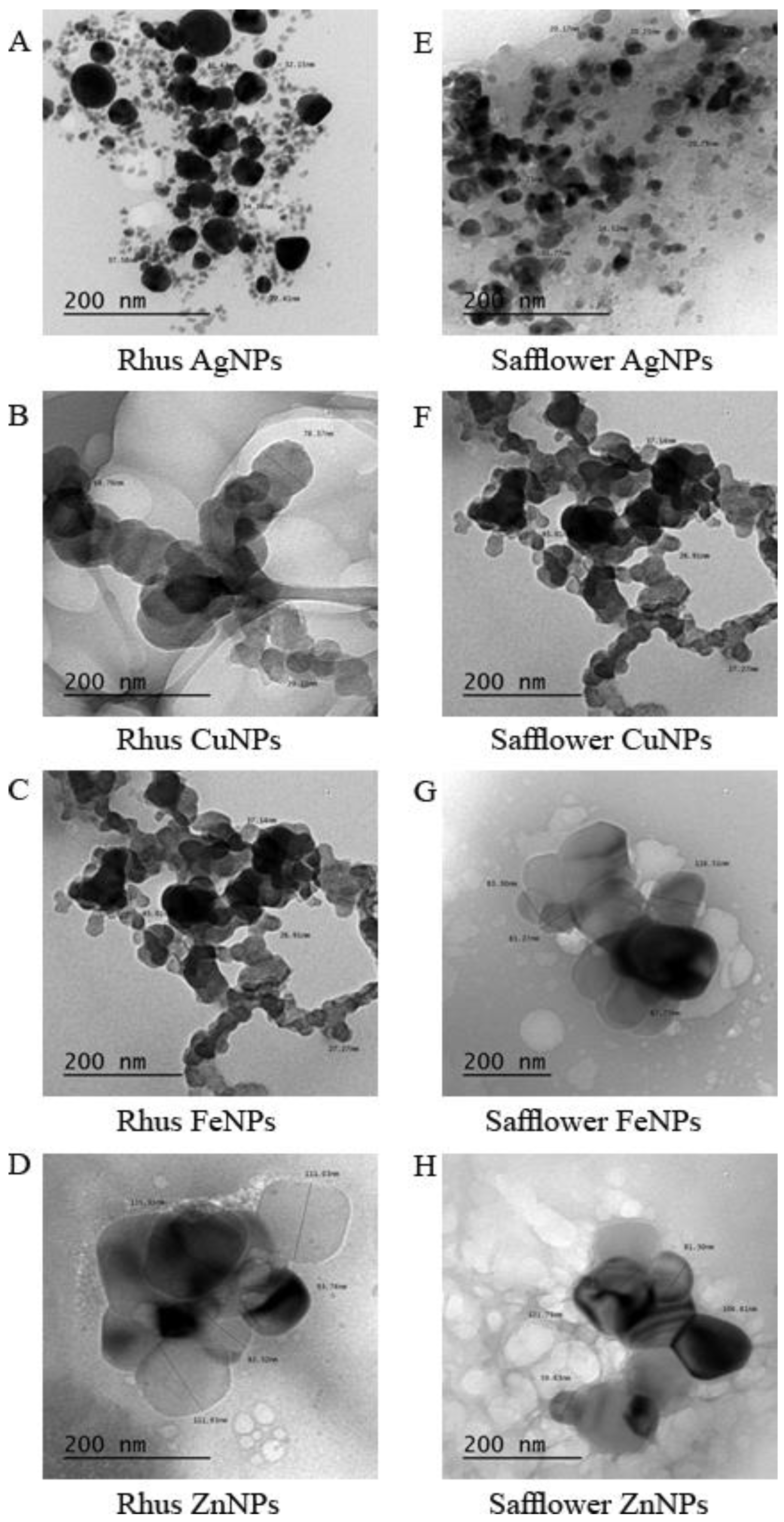
3.2. Nanoparticles Characteristic via Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
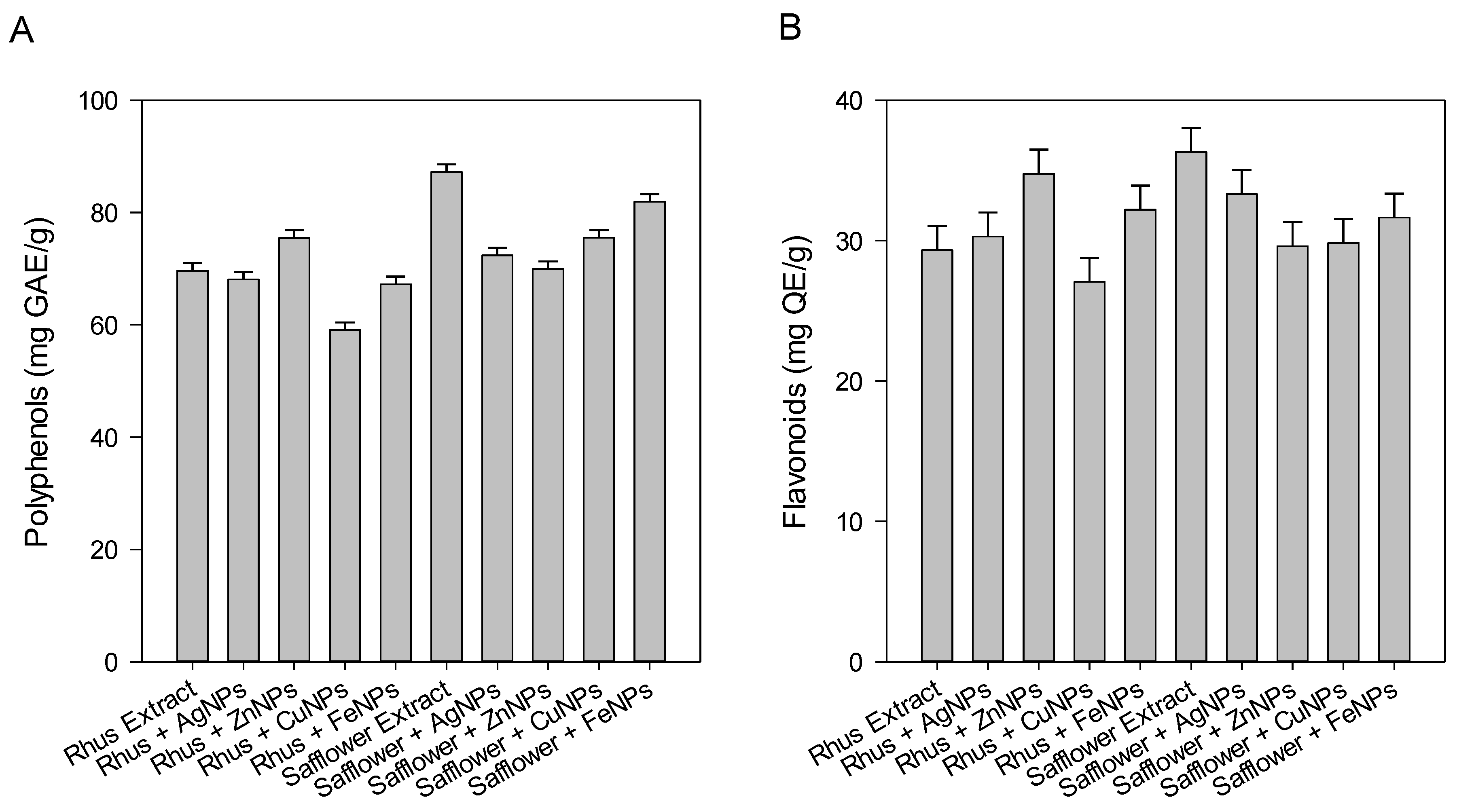
3.3. Determination of Total Polyphenolic and Flavonoid Contents
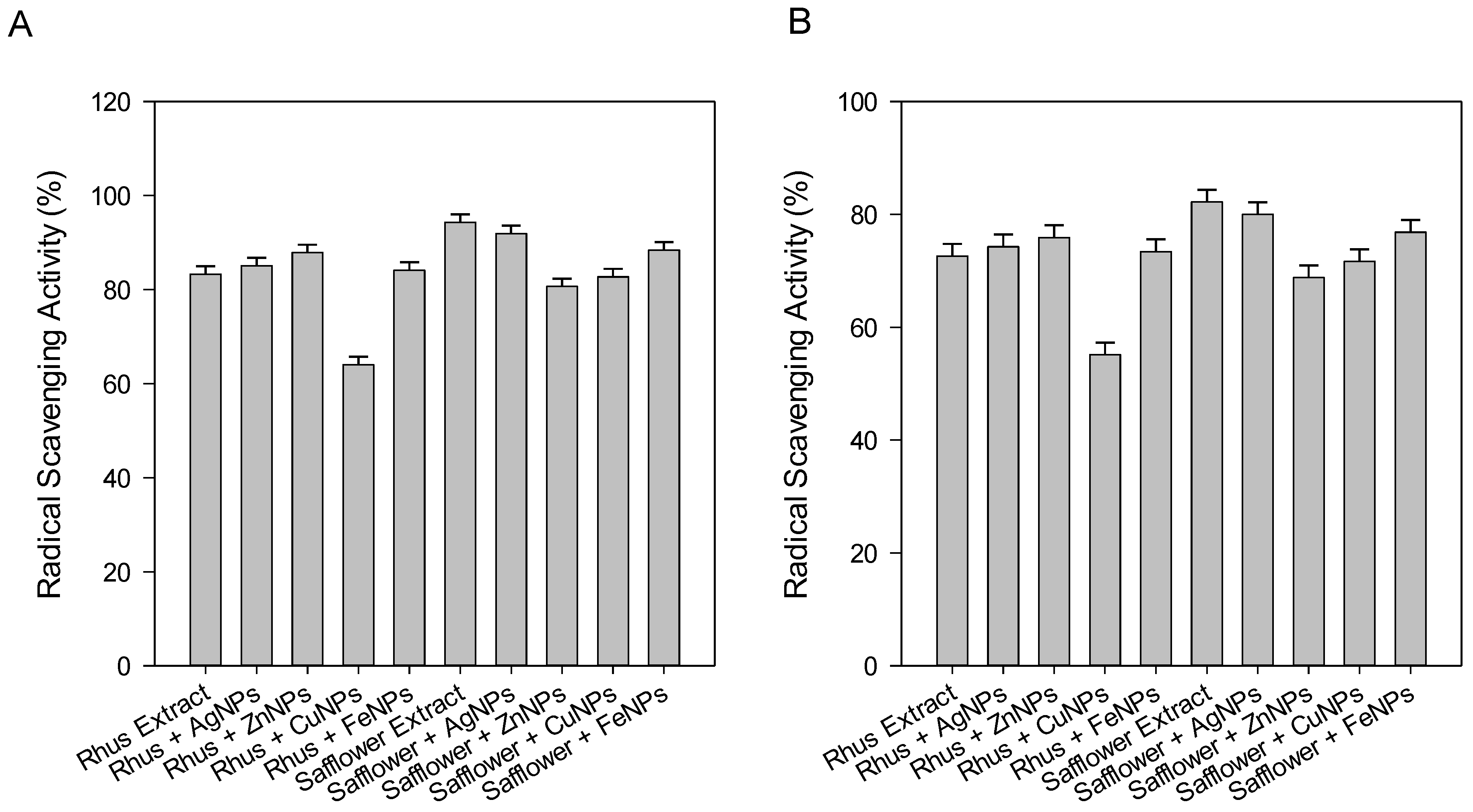
3.4. Antioxidant Activities of ABTS•+ and DPPH
3.5. Antimicrobial Activity
3.6. Potential Sulforhodamine B (SRB) Cell Cytotoxicity Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Devasenan, S.; Beevi, N.H.; Jayanthi, S. Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles by chemical reduction method and their antimicrobial activities. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 2016, 9, 571–576. Available online: https://sphinxsai.com/2016/ch_vol9_no5/2/(571-576)V9N5CT.pdf (accessed on 9 January 2019).
- El-Refai, A.A.; Ghoniem, G.A.; El-Khateeb, A.Y.; Hassaan, M.M. Eco-friendly synthesis of metal nanoparticles using ginger and garlic extracts as biocompatible novel antioxidant and antimicrobial agents. J. Nanostructure Chem. 2018, 8, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattanayak, M.; Nayak, P. Ecofriendly green synthesis of iron nanoparticles from various plants and spices extract. Int. J. Plant Anim. Environ. Sci. 2013, 3, 68–78. Available online: http://www.ijpaes.com/admin/php/uploads/277_pdf.pdf (accessed on 9 January 2019).
- Abu-Reidah, I.M.; Jamous, R.M.; Ali-Shtayeh, M.S. Phytochemistry, pharmacological properties and industrial applications of Rhus coriaria L. (sumac). Jordan J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A.; Ferk, F.; Simić, T.; Brantner, A.; Dušinská, M.; Kundi, M.; Hoelzl, C.; Nersesyan, A.; Knasmüller, S. DNA-protective effects of sumach (Rhus coriaria L.), a common spice: Results of human and animal studies. Mutat. Res. Fundam. Mol. Mech. Mutagenesis 2009, 661, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, L.H.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.Z. Rapid determination of volatile constituents in safflower from Xinjiang and Henan by ultrasonic-assisted solvent extraction and GC-MS. J. Pharm. Anal. 2011, 1, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, H.L.; Nagatsu, A.; Sakakibara, J. Novel antioxidants from safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) oil cake. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1996, 44, 874–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, H.L.; Nagatsu, A.; Watanabe, T.; Okuyama, H. Antioxidative compounds isolated from safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) oil cake. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1997, 45, 1910–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shebis, Y.; Iluz, D.; Kinel-Tahan, Y.; Dubinsky, Z.; Yehoshua, Y. Natural antioxidants: Function and sources. Food Nutr. Sci. 2013, 4, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakayama, S.; Kusaka, K.; Kanehira, T.; Yamada, Y.; Kawazu, K.; Kobayashi, A. Kinobeon A, a novel red pigment produced in safflower tissue culture systems. Z. Nat. C 1994, 49, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erichsen-Brown, C. Medicinal and Other Uses of North American Plants: A Historical Survey with Special Reference to the Eastern Indian Tribes; Courier Corporation: North Chelmsford, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Nascimento, G.G.; Locatelli, J.; Freitas, P.C.; Silva, G.L. Antibacterial activity of plant extracts and phytochemicals on antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2000, 31, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, G.; McCutcheon, A.; Farmer, S.; Towers, G.; Hancock, R. Antimicrobial constituents of Rhus glabra. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1994, 42, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deve, A.S.; Kumaresan, K.; Rapheal, V.S. Extraction process optimization of polyphenols from Indian Citrus sinensis as novel antiglycative agents in the management of diabetes mellitus. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2014, 13, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.; Tahiliani, S.; Jain, N.; Priyadarshi, R.; Chhangani, S.; Purohit, S.; Joshi, P. Cynodon dactylon leaf extract assisted green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their anti-microbial activity. Adv. Sci. Eng. Med. 2013, 5, 858–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shahaby, O.; El-Zayat, M.; Salih, E.; El-Sherbiny, I.; Reicha, F. Evaluation of antimicrobial activity of water infusion plant-mediated silver nanoparticles. J. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2013, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.N.S.; Agarwala, M. Phytochemical analysis of some medicinal plants. J. Phytol. 2011, 3, 10–14. Available online: http://updatepublishing.com/journal/index.php/jp/article/view/2737 (accessed on 9 January 2019).
- Li, J.-E.; Fan, S.-T.; Qiu, Z.-H.; Li, C.; Nie, S.-P. Total flavonoids content, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of extracts from Mosla chinensis Maxim. cv. Jiangxiangru. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 64, 1022–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodouleas, D.C.; Fotakis, C.; Nikokavoura, A.; Papadopoulos, K.; Calokerinos, A.C. Modified DPPH and ABTS assays to assess the antioxidant profile of untreated oils. Food Anal. Methods 2015, 8, 1294–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaidhani, S.; Singh, A.; Kumari, S.; Lavekar, G.; Juvekar, A.; Sen, S.; Padhi, M. Evaluation of some plant extracts for standardization and anticancer activity. Indian J. Tradit. Knowl. 2013, 12, 682–687. Available online: https://nopr.niscair.res.in/handle/123456789/22175 (accessed on 9 January 2019).
- CoStat. Statistical Software Version 6.450: CoHort Software, 798 Light houseAve, PMB 320; CoStat: Monterey, CA, USA, 2017; Available online: http://www.cohort.com/costst.html (accessed on 9 January 2019).
- Duncan, D.B. Multiple range and multiple F tests. Biometrics 1955, 11, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliakbarlu, J.; Mohammadi, S.; Khalili, S. A study on antioxidant potency and antibacterial activity of water extracts of some spices widely consumed in Iranian diet. J. Food Biochem. 2014, 38, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorova, E.; Revina, A. Synthesis of metallic nanoparticles in reverse micelles in the presence of quercetin. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2000, 168, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Patil, S.; Ahire, M.; Kitture, R.; Kale, S.; Pardesi, K.; Cameotra, S.S.; Bellare, J.; Dhavale, D.D.; Jabgunde, A. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Dioscorea bulbifera tuber extract and evaluation of its synergistic potential in combination with antimicrobial agents. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Reidah, I.M.; Ali-Shtayeh, M.S.; Jamous, R.M.; Arráez-Román, D.; Segura-Carretero, A. HPLC–DAD–ESI-MS/MS screening of bioactive components from Rhus coriaria L.(Sumac) fruits. Food Chem. 2015, 166, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sroka, Z.; Cisowski, W. Hydrogen peroxide scavenging, antioxidant and anti-radical activity of some phenolic acids. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2003, 41, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, A.; Kerr, D.J.; Gescher, A.; Chipman, J.K. Antioxidant effects of isoflavonoids and lignans, and protection against DNA oxidation. Free Radic. Res. 1999, 31, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, T.; Liu, F.; Wang, Z. Antioxidative activity of natural products from plants. Life Sci. 2000, 66, 709–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, V.; Patil, A.; Phatak, A.; Chandra, N. Free radicals, antioxidants and functional foods: Impact on human health. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2010, 4, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birben, E.; Sahiner, U.M.; Sackesen, C.; Erzurum, S.; Kalayci, O. Oxidative stress and antioxidant defense. World Allergy Organ. J. 2012, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butovich, I.A.; Lukyanova, S.M. Inhibition of lipoxygenases and cyclooxygenases by linoleyl hydroxamic acid: Comparative in vitro studies. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 1284–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viji, V.; Helen, A. Inhibition of lipoxygenases and cyclooxygenase-2 enzymes by extracts isolated from Bacopa monniera (L.) Wettst. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 118, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Samples | Inhibition Zone (IZ) of Bacterial Strains (mm) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gram-Negative Bacteria | Gram-Positive Bacteria | Candida albicans | ||||
| EC * | PV * | KP * | BS * | SA * | CA * | |
| Rhus Extract | 0.00 ± 0.00 b** | 12.80 ± 0.47 a | 7.00 ± 0.47 ab | 0.00 ± 0.00 b | 0.00 ± 0.00 b | 7.70 ± 0.47 ab |
| Rhus + AgNPs | 10.70 ± 0.47 ab | 8.40 ± 0.47 ab | 9.80 ± 0.47 ab | 9.50 ± 0.47 ab | 8.20 ± 0.47 ab | 11.40 ± 0.47 ab |
| Rhus + ZnNPs | 7.60 ± 0.47 ab | 7.20 ± 0.47 ab | 0.00 ± 0.00 b | 7.30 ± 0.47 ab | 7.70 ± 0.47 ab | 0.00 ± 0.00 b |
| Rhus + CuNPs | 8.70 ± 0.47 ab | 7.60 ± 0.47 ab | 7.50 ± 0.47 ab | 8.40 ± 0.47 ab | 0.00 ± 0.00 ab | 7.80 ± 0.47 ab |
| Rhus + FeNPs | 8.50 ± 0.47 ab | 0.00 ± 0.00 b | 8.20 ± 0.47 ab | 7.60 ± 0.47 ab | 8.50 ± 0.47 ab | 8.00 ± 0.47 ab |
| Safflower Extract | 9.40 ± 0.47 ab | 8.30 ± 0.47 ab | 7.50 ± 0.47 ab | 8.00 ± 0.47 ab | 8.20 ± 0.47 ab | 15.40 ± 0.47 a |
| Safflower + AgNPs | 10.50 ± 0.47 ab | 13.70 ± 0.47 a | 14.50 ± 0.47 a | 9.20 ± 0.47 ab | 14.30 ± 0.47 a | 9.20 ± 0.47 ab |
| Safflower + ZnNPs | 8.50 ± 0.47 ab | 0.00 ± 0.00 b | 7.70 ± 0.47 ab | 7.50 ± 0.47 ab | 7.60 ± 0.47 ab | 7.30 ± 0.47 ab |
| Safflower + CuNPs | 9.40 ± 0.47 ab | 12.50 ± 0.47 a | 13.00 ± 0.47 a | 11.40 ± 0.47 ab | 8.20 ± 0.47 ab | 9.40 ± 0.47 ab |
| Safflower + FeNPs | 7.50 ± 0.47 ab | 12.60 ± 0.47 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 b | 0.00 ± 0.00 b | 16.80 ± 0.47 a | 9.50 ± 0.47 ab |
| Samples | Conc. (µg mL−1) | Cancer Cell Inhibition % | IC50 (µg mL−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caco | HEPG2 | T47D | Caco | HEPG2 | T47D | ||
| Rhus Extract | 100 | 6.28 ± 0.53 p* | 10.34 ± 0.87 s | 17.71 ± 1.23 p | 1405.67 ± 17.14 a | 1093.46 ± 11.37 a | 1055.24 ± 12.27 a |
| Rhus Extract | 250 | 12.24 ± 1.10 mn | 15.23 ± 0.74 r | 22.37 ± 0.92 o | |||
| Rhus Extract | 500 | 19.72 ± 1.37 l | 26.98 ± 1.13 o | 30.72 ± 1.45 m | |||
| Rhus + AgNPs | 100 | 7.97 ± 0.82 op | 23.77 ± 0.81 p | 24.22 ± 1.11 o | 1147.89 ± 13.75 b | 720.49 ± 9.89 b | 567.38 ± 9.14 e |
| Rhus + AgNPs | 250 | 11.17 ± 0.98 n | 32.32 ± 1.91 m | 29.33 ± 1.87 mn | |||
| Rhus + AgNPs | 500 | 23.99 ± 1.47 k | 46.20 ± 2.50 i | 40.94 ± 2.12 l | |||
| Rhus + ZnNPs | 100 | 9.04 ± 0.70 o | 30.18 ± 1.35 n | 27.47 ± 1.76 n | 1005.16 ± 10.52 e | 676.17 ± 8.21 c | 538.07 ± 10.78 d |
| Rhus + ZnNPs | 250 | 13.31 ± 0.96 mn | 36.59 ± 1.81 hl | 32.12 ± 1.30 m | |||
| Rhus + ZnNPs | 500 | 27.19 ± 1.10 j | 48.34 ± 1.57 h | 43.26 ± 2.04 l | |||
| Rhus + CuNPs | 100 | 18.65 ± 0.93 l | 66.49 ± 2.72 d | 47.44 ± 2.73 k | 721.91 ± 9.89 e | 169.52 ± 5.53 f | 3.58 ± 0.06 i |
| Rhus + CuNPs | 250 | 25.06 ± 1.23 jk | 71.83 ± 3.14 c | 52.55 ± 2.81 j | |||
| Rhus + CuNPs | 500 | 38.94 ± 1.51 g | 91.06 ± 4.26 b | 66.94 ± 3.12 g | |||
| Rhus + FeNPs | 100 | 5.83 ± 0.27 p | 35.52 ± 1.41 l | 31.19 ± 2.02 m | 926.05 ± 11.31 d | 443.45 ± 9.25 d | 342.33 ± 9.43 h |
| Rhus + FeNPs | 250 | 14.38 ± 0.81 m | 45.13 ± 1.84 ij | 40.94 ± 1.90 l | |||
| Rhus + FeNPs | 500 | 27.19 ± 1.09 j | 59.02 ± 2.08 e | 52.55 ± 2.71 j | |||
| Safflower Extract | 100 | 24.84 ± 1.19 jk | 14.38 ± 0.82 r | 44.34 ± 2.23 l | 615.77 ± 7.43 f | 202.29 ± 5.35 e | 707.75 ± 10.10 b |
| Safflower Extract | 250 | 32.27 ± 1.32 i | 22.92 ± 1.07 p | 52.88 ± 1.84 j | |||
| Safflower Extract | 500 | 44.34 ± 1.56 e | 37.87 ± 0.91 k | 65.70 ± 3.16 g | |||
| Safflower + AgNPs | 100 | 37.84 ± 1.22 gh | 30.40 ± 1.12 n | 58.22 ± 2.40 i | 282.09 ± 8.51 h | 18.24 ± 0.80 h | 359.21 ± 9.71 g |
| Safflower + AgNPs | 250 | 49.91 ± 1.74 d | 44.28 ± 1.64 j | 72.11 ± 3.21 f | |||
| Safflower + AgNPs | 500 | 62.45 ± 1.85 c | 59.23 ± 2.04 e | 85.99 ± 3.80 d | |||
| Safflower + ZnNPs | 100 | 41.09 ± 1.31 f | 33.60 ± 1.83 m | 62.49 ± 2.70 h | 261.52 ± 7.27 i | 7.18 ± 0.67 i | 386.49 ± 7.61 f |
| Safflower + ZnNPs | 250 | 49.91 ± 1.87 d | 45.35 ± 2.32 ij | 71.04 ± 3.01 f | |||
| Safflower + ZnNPs | 500 | 62.45 ± 2.23 c | 54.96 ± 1.95 f | 90.26 ± 3.83 e | |||
| Safflower + CuNPs | 100 | 65.23 ± 1.92 b | 67.78 ± 2.27 d | 83.85 ± 2.94 d | 3.12 ± 0.81 j | 1.11 ± 0.04 j | 1.42 ± 0.07 j |
| Safflower + CuNPs | 250 | 66.77 ± 2.34 b | 70.98 ± 2.70 c | 93.47 ± 3.52 b | |||
| Safflower + CuNPs | 500 | 89.33 ± 3.28 a | 97.68 ± 3.44 a | 98.94 ± 4.03 a | |||
| Safflower + FeNPs | 100 | 26.23 ± 1.27 jk | 19.72 ± 0.98 q | 48.61 ± 2.81 k | 498.32 ± 9.34 g | 99.61 ± 8.72 g | 487.45 ± 8.48 e |
| Safflower + FeNPs | 250 | 35.98 ± 1.81 h | 32.53 ± 1.23 m | 62.49 ± 0.87 h | |||
| Safflower + FeNPs | 500 | 49.91 ± 2.09 d | 50.69 ± 1.80 g | 76.38 ± 0.82 e | |||
| LSD (p < 0.05) | 1.95 | 1.40 | 2.62 | 3.40 | 1.51 | 9.42 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ibrahim, F.Y.; EL-Khateeb, A.Y.; Mohamed, A.H. Rhus and Safflower Extracts as Potential Novel Food Antioxidant, Anticancer, and Antimicrobial Agents Using Nanotechnology. Foods 2019, 8, 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8040139
Ibrahim FY, EL-Khateeb AY, Mohamed AH. Rhus and Safflower Extracts as Potential Novel Food Antioxidant, Anticancer, and Antimicrobial Agents Using Nanotechnology. Foods. 2019; 8(4):139. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8040139
Chicago/Turabian StyleIbrahim, Faten Y., Ayman Y. EL-Khateeb, and Azza H. Mohamed. 2019. "Rhus and Safflower Extracts as Potential Novel Food Antioxidant, Anticancer, and Antimicrobial Agents Using Nanotechnology" Foods 8, no. 4: 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8040139
APA StyleIbrahim, F. Y., EL-Khateeb, A. Y., & Mohamed, A. H. (2019). Rhus and Safflower Extracts as Potential Novel Food Antioxidant, Anticancer, and Antimicrobial Agents Using Nanotechnology. Foods, 8(4), 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8040139






