Development and Characterization of Biodegradable Composite Films Based on Gelatin Derived from Beef, Pork and Fish Sources
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Film Preparation
2.3. Film Morphology
2.4. Film Thickness
2.5. Colour Measurement
2.6. Film Opacity
2.7. Mechanical Properties
2.8. Water Vapour Permeability (WVP)
2.9. Oxygen Permeability (OP)
2.10. Water Solubility of Gelatin Films
2.11. Attenuated Total Reflectance-Fourier Transform Infrared (ATR-FTIR) Spectroscopy
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Film Morphology

3.2. Film Thickness
| Samples | Thickness (μm) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Puncture Strength (N) | Elongation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4% | ||||
| Beef | 63.73 ± 8.31 d | 4.23 ± 0.88 f | 10.00 ± 1.61 d | 101.38 ± 9.92 c, d |
| Pork | 63.80 ± 3.94 d | 6.05 ± 0.19 e | 11.79 ± 0.21 c, d | 109.60 ± 11.53 c |
| Fish | 65.77 ± 2.90 d | 4.84 ± 0.11 f | 11.51 ± 1.10 c, d | 184.81 ± 4.91 a |
| 6% | ||||
| Beef | 85.13 ± 1.94 c | 2.41 ± 0.54 g | 12.69 ± 0.86 c | 141.04 ± 16.27 b |
| Pork | 55.10 ± 1.93 d | 7.59 ± 0.45 c | 20.68 ± 0.77 b | 93.37 ± 11.37 d |
| Fish | 66.87 ± 6.12 d | 6.56 ± 0.31 d, e | 20.15 ± 2.01 b | 139.78 ± 13.44 b |
| 8% | ||||
| Beef | 115.71 ± 3.73 a | 7.01 ± 0.69 c, d | 20.43 ± 2.44 b | 192.34 ± 11.86 a |
| Pork | 104.47 ± 7.71 b | 8.96 ± 0.26 b | 22.88 ± 0.76 a | 115.18 ± 8.26 c |
| Fish | 109.70 ± 5.77 a, b | 11.14 ± 0.84 a | 22.14 ± 2.16 a, b | 114.28 ± 7.79 c |
3.3. Colour Attributes and Opacity of Gelatin-Based Composite Films
| Samples | L | a | b+ | Opacity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4% | ||||
| Beef | 93.23 ± 0.08 b | −1.45 ± 0.04 e | 8.41 ± 0.13 b | 18.31 ± 0.37 i |
| Pork | 93.75 ± 0.04 a | −1.09 ± 0.03 b, c | 5.94 ± 0.07 c, d | 22.19 ± 0.05 h |
| Fish | 90.80 ± 0.55 e | −0.84 ± 0.07 a | 5.82 ± 0.07 c | 41.43 ± 0.03 d |
| 6% | ||||
| Beef | 92.40 ± 0.17 c | −1.65 ± 0.02 f | 9.67 ± 0.06 a | 40.27 ± 1.14 e |
| Pork | 93.80 ± 0.04 a | −0.82 ± 0.03 a | 5.32 ± 0.03 e | 22.75 ± 0.13 g |
| Fish | 92.54 ± 0.30 c | −0.89 ± 0.06 a | 5.52 ± 0.05 e | 50.80 ± 0.01 b |
| 8% | ||||
| Beef | 91.80 ± 0.41 d | −1.31 ± 0.14 d | 8.35 ± 0.63 b | 47.25 ± 0.04 c |
| Pork | 93.88 ± 0.02 a | −1.16 ± 0.03 c | 6.17 ± 0.03 c | 24.83 ± 0.15 f |
| Fish | 92.43 ± 0.02 c | −1.01 ± 0.05 b | 6.01 ± 0.08 c, d | 103.9 ± 0.07 a |
3.4. Mechanical Properties
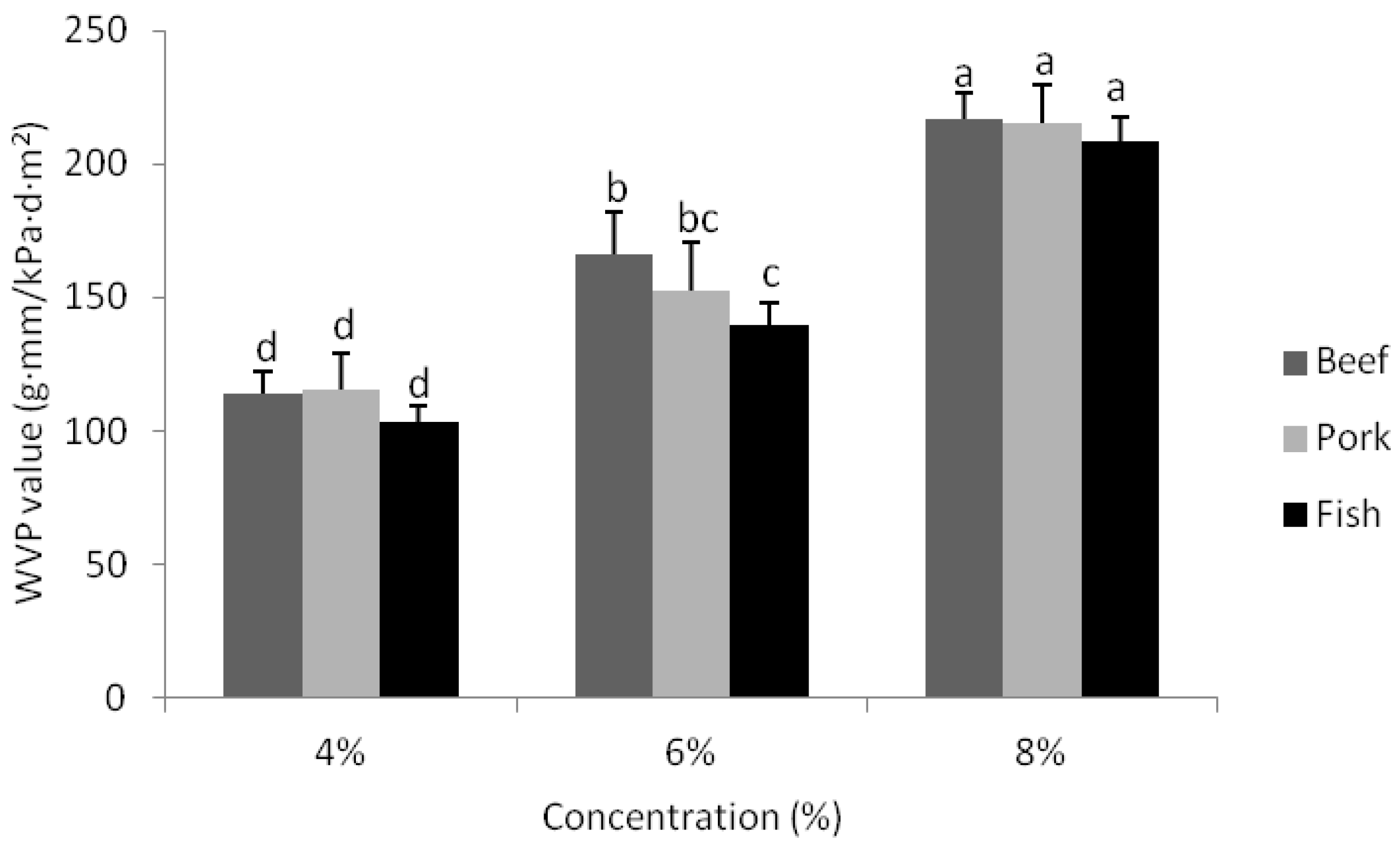
3.5. Water Permeability
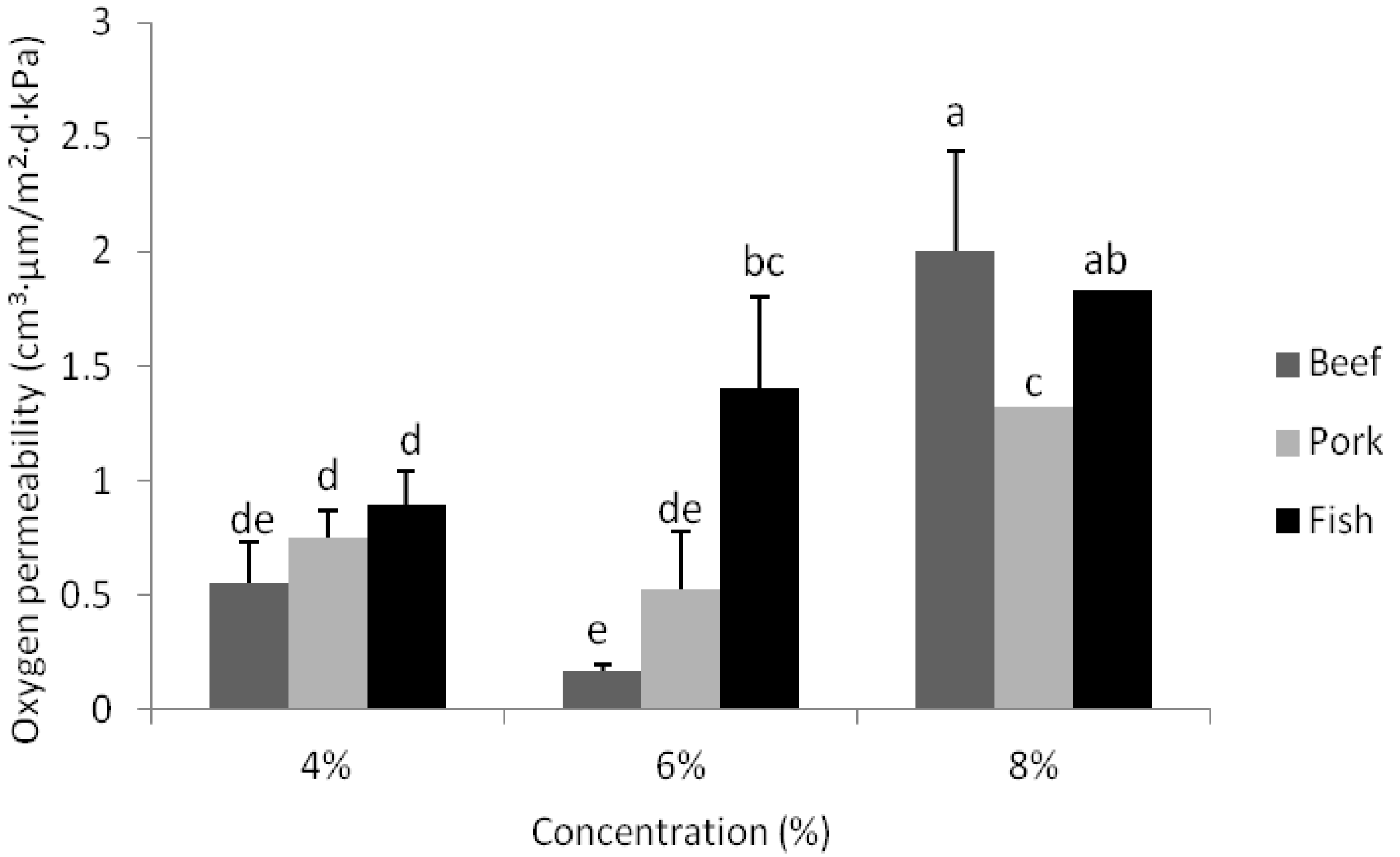
3.6. Oxygen Permeability
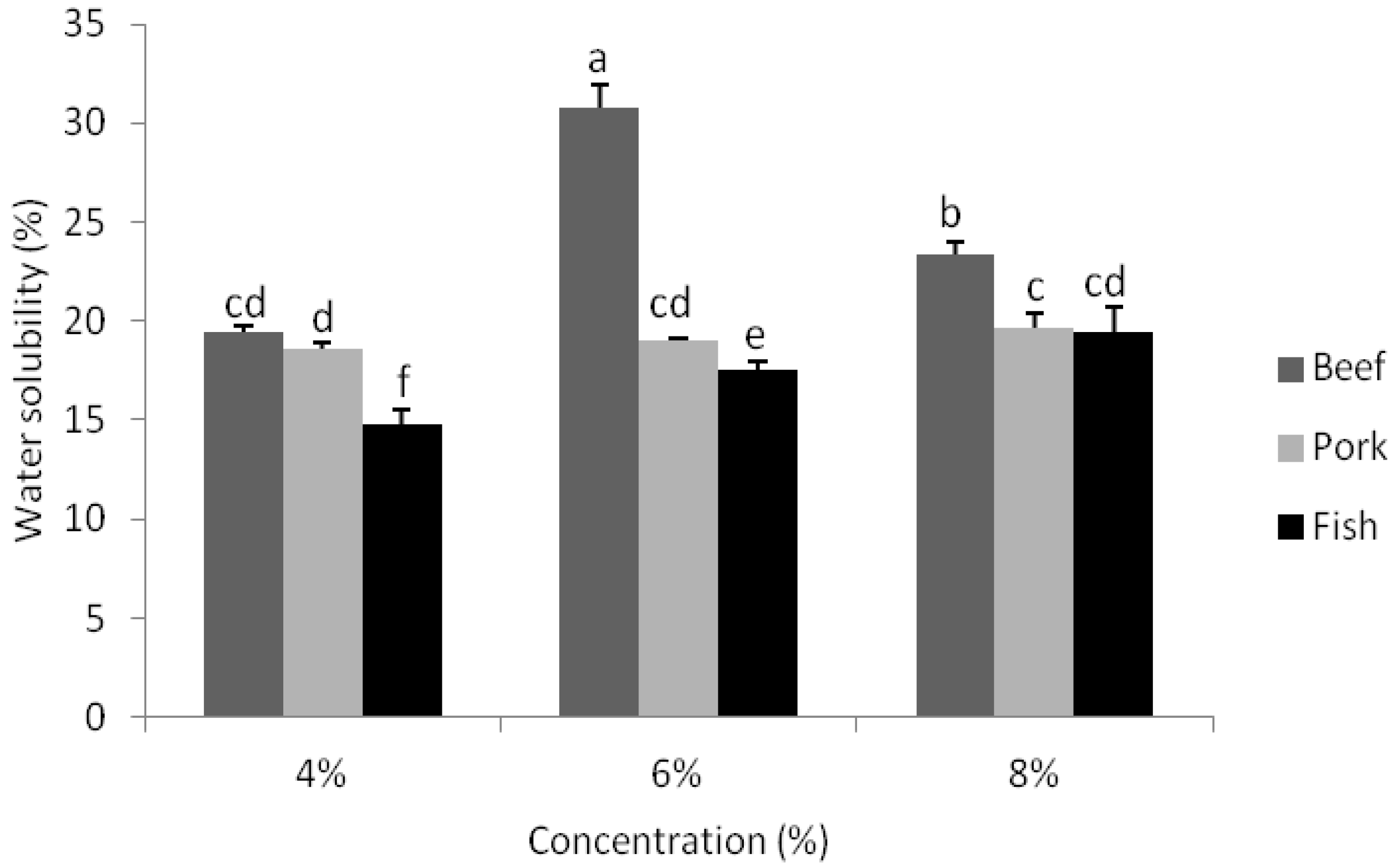
3.7. Water Solubility
3.8. FTIR Spectroscopy

4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pérez-Mateos, M.; Montero, P.; Gómez-Guillén, M.C. Formulation and stability of biodegradable films made from cod gelatin and sunflower oil blends. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, M.A.; Pinotti, A.; Martino, M.N.; Zaritzky, N.E. Characterization of composite hydrocolloid films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2004, 56, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertan, L.C.; Tanada-Palmu, P.S.; Siani, A.C.; Grosso, C.R.F. Effect of fatty acids and “Brazilian elemi” on composite films based on gelatin. Food Hydrocoll. 2005, 19, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Kerry, J.F.; Kerry, J.P. Effect of food ingredients and selected lipids on the physical properties of extruded edible films/casings. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 41, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourtoom, T.; Chinnan, M.S. Improvement of water barrier property of rice starch-chitosan composite film incorporated with lipids. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2009, 15, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Auty, M.A.E.; Kerry, J.F.; Kerry, J.P. Effect of pH and addition of corn oil on the properties of gelatin-based edible films. J. Food Eng. 2009, 90, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerqueira, M.A.; Souza, B.W.S.; Teixeira, J.A.; Vicente, A.A. Effect of glycerol and corn oil on physicochemical properties of polysaccharide films—A comparative study. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 27, 175–184. [Google Scholar]
- Taqi, A.; Askar, K.A.; Nagy, K.; Mutihac, L.; Stomatin, I. Effect of different concentrations of olive oil and oleic acid on the mechanical properties of albumen (egg white) edible films. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 12963–12972. [Google Scholar]
- Soradech, S.; Nunthanid, J.; Limmatvapirat, S.; Luangtana-anan, M. An approach for the enhancement of the mechanical properties and film coating efficiency of shellac by the formation of composite films based on shellac and gelatin. J. Food Eng. 2012, 108, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuq, B.; Gontard, N.; Cuq, J.-L.; Guilbert, S. Packaging films based on myofibrillar proteins: Fabrication, properties and applications. Nahrung 1998, 42, 260–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuq, B.; Aymard, C.; Cuq, J.-L.; Guilbert, S. Edible packaging films based on fish myofibrillar proteins: Formulation and functional properties. J. Food Sci. 1995, 60, 1369–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, S.; Wang, Y.; Tang, S.; Huang, C.; Jackson, M.G. Role of ferulic acid in preparing edible films from soy protein isolate. J. Food Eng. 2005, 70, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourtoom, T. Edible protein films: Properties enhancement. Int. Food Res. J. 2009, 16, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Vieira, M.G.A.; da Silva, M.A.; dos Santos, L.O.; Beppu, M.M. Natural-based plasticizers and biopolymer films: A review. Eur. Polym. J. 2011, 47, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamper, S.L.; Fennema, O. Water vapour permeability of edible bilayer films. J. Food Sci. 1984, 49, 1478–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilbert, S. Technology and Application of Edible Protective Film. In Food Packaging and Preservation: Theory and Practice; Mathlouthi, M., Ed.; Elsevier Science Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 1986; pp. 371–394. [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin, E.A.; Nisperos-Carriedo, N.O.; Baker, R.A. Use of edible coatings to preserve quality of lightly (and slightly) processed products. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1995, 35, 509–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutter, C.N. Opportunities for bio-based packaging technologies to improve the quality and safety of fresh and further processed muscle foods. Meat Sci. 2006, 74, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekthamasut, K.; Akesowan, A. Effect of vegetable oils on physical characteristics of edible konjac film. AU J. Technol. 2001, 5, 22–28. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, M.; Ishizaki, S.; Suzuki, T.; Takai, R. Water vapour permeability of edible films prepared from fish water soluble proteins as affected by lipid type. J. Tokyo Univ. Fish. 2001, 87, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Gennadios, A.H.; Bradenburg, A.H.; Weller, C.L.; Testin, R.F. Effect of pH on properties of wheat gluten and soy protein isolate films. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1993, 41, 1835–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, R.; Chen, H. Functional properties of edible films using whey protein concentrate. J. Dairy Sci. 1995, 78, 1673–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banker, G.S. Film coating theory and practice. J. Pharm. Sci. 1996, 55, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anker, M.; Stading, M.; Hermansson, A.M. Relationship between the microstructure and the mechanical and barrier properties of whey protein films. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 3806–3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nur Hanani, Z.A.; Roos, Y.H.; Kerry, J.P. Use of beef, pork and fish gelatin sources in the manufacture of films and assessment of their composition and mechanical properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 29, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gontard, N.; Guilbert, S.; Cuq, J.-L. Edible wheat gluten films: Influence of main process variables on film properties using response surface methodology. J. Food Sci. 1992, 57, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gontard, N.; Guilbert, S. Bio Packaging: Technology and Properties of Edible and/or Biodegradable Material of Agricultural Origin. In Food Packaging and Preservation; Mthlouthi, M., Ed.; Blakie Academic and Professional: London, UK, 1994; pp. 159–181. [Google Scholar]
- American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM), Standard Test Methods for Tensile Properties of Thin Plastic Sheeting. Standard Designation: D882. In Annual Book of American Standards Testing Methods; ASTM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1985; pp. 182–188.
- McHugh, T.H.; Avena-Bustillos, R.; Krochta, J.M. Hydrophilic edible films: Modified procedure for water vapour permeability and explanation of thickness effects. J. Food Sci. 1993, 58, 899–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM). Standard Test Methods for Water Vapour Transmission of Materials. Designation: E96-90. In Annual Book of American Standards Testing Methods Standard; ASTM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1990; pp. 834–841.
- Papkovsky, D.P.; Papkovskaia, N.; Smyth, A.; Kerry, J. Phosphorescent sensor approach for non-destructive measurement of oxygen in packaged foods: Optimisation of disposable oxygen sensors and their characterization over a wide temperature range. Anal. Lett. 2000, 33, 1755–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, L.; Holmes, J.; Kerry, J.F.; Kerry, J.P. Assessment of film-forming potential and properties of protein and polysaccharide-based biopolymer films. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 42, 1128–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kester, J.J.; Fennema, O. Edible films and coatings: A review. Food Technol. 1986, 40, 47–56. [Google Scholar]
- Greener, I.K.; Fennema, O. Evaluation of edible bilayer films for use as moisture barriers for food. J. Food Sci. 1989, 54, 1400–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Paulson, A.T. Effects of lipids on mechanical and moisture barrier properties of edible gellan film. Food Res. Int. 2000, 33, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, N.B.; Mohana, F.J.; O’Riordan, E.D.; O’Sullivan, M. Effects of soya oil and glycerol on physical properties of composite WPI films. J. Food Eng. 2002, 51, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pommet, M.; Redl, A.; Morel, M.-H.; Guilbert, S. Study of wheat gluten plasticization with fatty acids. Polymer 2003, 44, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Weller, C.L.; Hamouz, F.; Cuppet, S.L.; Schnepf, M. Development and applications of multicomponent edible coatings and films: A review. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2002, 44, 347–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carvalho, R.A.; Grosso, A.R.F. Characterization of gelatin based films modified with transglutaminase, glyoxal and formaldehyde. Food Hydrocoll. 2004, 18, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gontard, N.; Duchez, C.; Cuq, J.-L.; Guilbert, S. Edible composite films of wheat and lipids: Water vapour permeability and other physical properties. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 1994, 29, 39–50. [Google Scholar]
- Hoque, M.S.; Benjakul, S.; Prodpran, T. Effect of heat treatment of film-forming solution on the properties of film from cuttlefish (Sepia pharaonis) skin gelatine. J. Food Eng. 2010, 96, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongjareonrak, A.; Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Tanaka, M. Antioxidative activity and properties of fish skin gelatine films incorporated with BHT and α-tocopherol. Food Hydrocoll. 2008, 22, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aewsiri, T.; Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W. Functional properties of gelatin from cuttlefish (Sepia pharaonis) skin as affected by bleaching using hydrogen peroxide. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muyonga, J.H.; Cole, C.G.B.; Duodu, K.G. Characterization of acid soluble collagen from skins of young and adult Nile perch (Lates niloticus). Food Chem. 2004, 85, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pranoto, Y.; Lee, C.M.; Park, H.J. Characterizations of fish gelatin films added with gellan and κ-carrageenan. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 40, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakimes, I.; Wellner, N.; Smith, A.C.; Wilson, R.H.; Farhat, I.; Mitchell, J. Mechanical properties with respect to water content of gelatin films in glassy state. Polymer 2005, 46, 12577–12585. [Google Scholar]
- Vlachos, N.; Skopelitis, Y.; Psaroudaki, M.; Konstantinidou, V.; Chatzilazarou, A.; Tegou, E. Applications of Fourier transform-infrared spectroscopy to edible oils. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 573-574, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Nur Hanani, Z.A.; Beatty, E.; Roos, Y.H.; Morris, M.A.; Kerry, J.P. Development and Characterization of Biodegradable Composite Films Based on Gelatin Derived from Beef, Pork and Fish Sources. Foods 2013, 2, 1-17. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods2010001
Nur Hanani ZA, Beatty E, Roos YH, Morris MA, Kerry JP. Development and Characterization of Biodegradable Composite Films Based on Gelatin Derived from Beef, Pork and Fish Sources. Foods. 2013; 2(1):1-17. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods2010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleNur Hanani, Zainal A., Eddie Beatty, Yrjo H. Roos, Mick A. Morris, and Joseph P. Kerry. 2013. "Development and Characterization of Biodegradable Composite Films Based on Gelatin Derived from Beef, Pork and Fish Sources" Foods 2, no. 1: 1-17. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods2010001
APA StyleNur Hanani, Z. A., Beatty, E., Roos, Y. H., Morris, M. A., & Kerry, J. P. (2013). Development and Characterization of Biodegradable Composite Films Based on Gelatin Derived from Beef, Pork and Fish Sources. Foods, 2(1), 1-17. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods2010001




