Fine-Scale Strontium Isotope Mapping in Eastern China (Anhui Province) and Its Application in Food Traceability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Sample Collection
2.2.1. Plant and Water Samples for 87Sr/86Sr Analysis
2.2.2. Samples for Production Region Traceability
2.3. 87Sr/86Sr Determination
2.3.1. Specimen Preprocessing Procedures
2.3.2. Sample Digestion
2.3.3. Sr/Matrix Separation
2.3.4. ICP-MS and MC-ICP-MS Measurements
2.4. Creation of the Bioavailable 87Sr/86Sr Map
3. Results
3.1. Construction of a Bioavailable 87Sr/86Sr Map for Anhui Province
3.2. Application of Anhui Province’s 87Sr/86Sr Map in Food Geographical Origin Traceability
3.2.1. Paeonia ostii
3.2.2. Chaenomeles speciosa
3.2.3. Teas
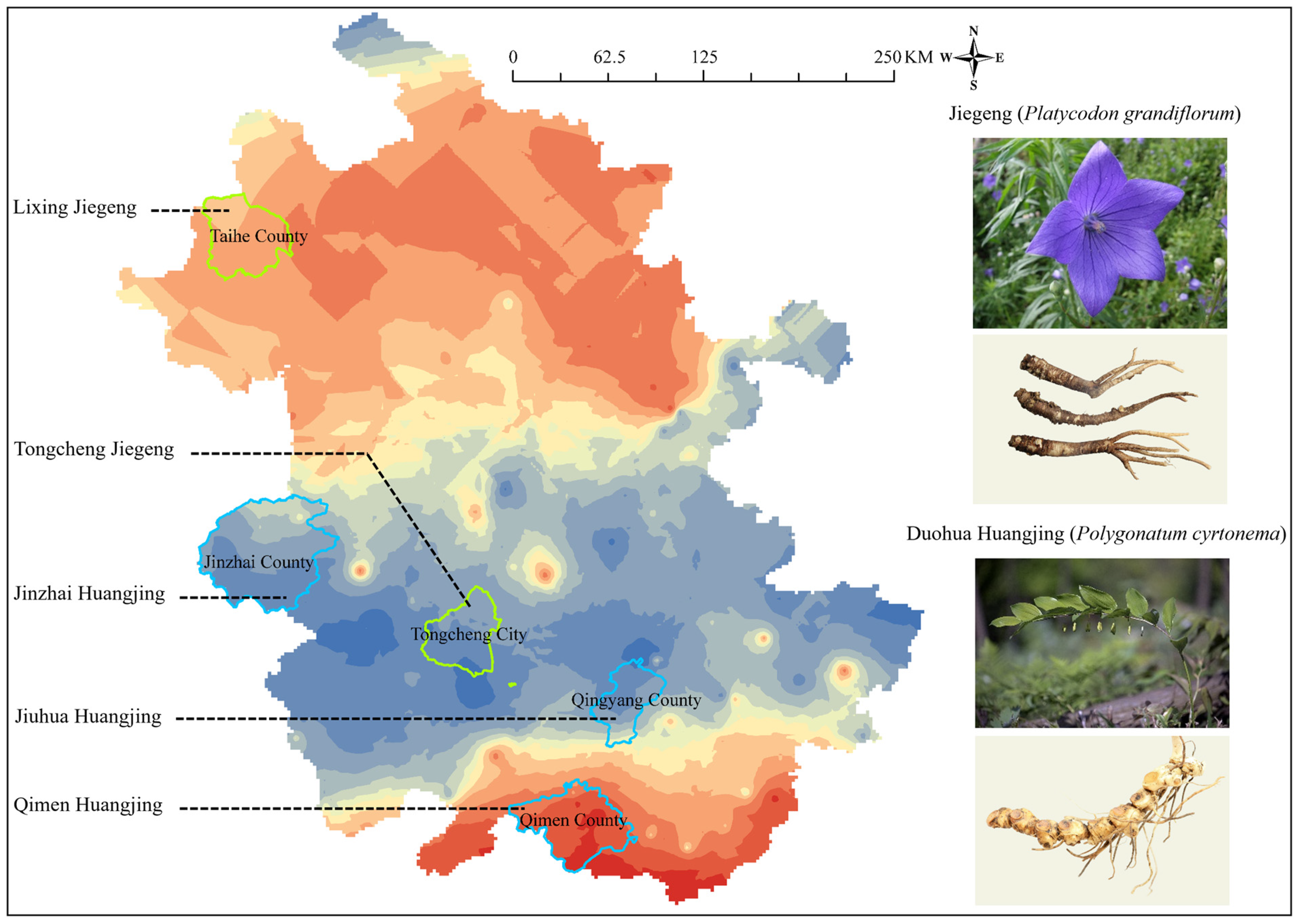
3.2.4. Platycodon grandiflorum
3.2.5. Polygonatum cyrtonema
4. Discussion
4.1. Construction of the First Fine-Scale 87Sr/86Sr Map of Anhui Province
4.2. Feasibility Analysis of Tracing Plant-Derived Food Production Areas Using the 87Sr/86Sr Map of Anhui Province
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GI | Geographical indication |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| RMSE | Root mean square error |
References
- Chen, X.; Zhang, T.; Wu, R.Q.; Zhang, X.Z.; Xie, H.Y.; Wang, S.J.; Zhang, H.; Ni, D.J.; Yu, Z.; Yang, Y.J.; et al. Intelligent geographical origin traceability of Pu-erh tea based on multispectral feature fusion. Food Chem. 2025, 492, 145375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrakopoulou, M.E.; Panteleli, E.; Vantarakis, A. Improved PCR-DGGE analysis by emulsion-PCR for the determination of food geographical origin: A case study on Greek PDO “avgotaracho Mesolonghiou”. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2021, 4, 746–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.P.; Yang, J.; Xiao, G.S.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Z.M.; Bai, W.D.; Zeng, X.F.; Dong, H. A comprehensive overview of emerging techniques and chemometrics for authenticity and traceability of animal-derived food. Food Chem. 2023, 402, 134216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, R.A. Strontium isotopes from the earth to the archaeological skeleton: A review. J. Archaeol. Method Theory 2006, 13, 135–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baffi, C.; Trincherini, P.R. Food traceability using the 87Sr/86Sr isotopic ratio mass spectrometry. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2016, 242, 1411–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capo, R.C.; Stewart, B.W.; Chadwick, O.A. Strontium isotopes as tracers of ecosystem processes: Theory and methods. Geoderma 1998, 82, 197–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britton, K.; Le Corre, M.; Willmes, M.; Moffat, I.; Grün, R.; Mannino, M.A.; Woodward, S.; Jaouen, K. Sampling plants and malacofauna in 87Sr/86Sr bioavailability studies: Implications for isoscape mapping and reconstructing of past mobility patterns. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 8, 579473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, E.; Evans, J.A.; Madgwick, R. Strontium (87Sr/86Sr) mapping: A critical review of methods and approaches. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 216, 103593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmes, M.; Bataille, C.P.; James, H.J.; Moffat, I.; McMorrow, L.; Kinsley, L.; Armstrong, R.A.; Eggins, S.; Grün, R. Mapping of bioavailable strontium isotope ratios in France for archaeological provenance studies. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 90, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, T.; Yamashita, K.; Ando, A.; Kusaka, S.; Saitoh, Y. Geographic variation of Sr and S isotope ratios in bottled waters in Japan and sources of Sr and S. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frei, R.; Frei, K.M.; Kristiansen, S.M.; Jessen, S.; Schullehner, J.; Hansen, B. The link between surface water and groundwater-based drinking water-strontium isotope spatial distribution patterns and their relationships to Danish sediments. Appl. Geochem. 2020, 121, 104698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snoeck, C.; Ryan, S.; Pouncett, J.; Pellegrini, M.; Claeys, P.; Wainwright, A.N.; Mattielli, N.; Lee-Thorp, J.A.; Schulting, R.J. Towards a biologically available strontium isotope baseline for Ireland. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 712, 136248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, W.J.; Ryu, J.S.; Kim, R.H.; Min, J.S. First strontium isotope map of groundwater in South Korea: Applications for identifying the geographical origin. Geosci. J. 2021, 25, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Tang, Z.H. The first large-scale bioavailable Sr isotope map of China and its implication for provenance studies. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020, 210, 103353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.T.; Wu, Q. Resource management and application of geographical indication products in Anhui Province. China Stand. 2025, 154–156. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.H.; Han, X.J.; Jiang, Y.L.; Ren, A.Y.; Yang, Z.Y.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Wang, M.; Yang, B.; Yin, M.Z.; Peng, H.S.; et al. Study on strontium isotope characteristics in plants: Providing reference for food production area traceability. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 20745–20755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomsen, E.; Andreasen, R. Agricultural lime disturbs natural strontium isotope variations: Implications for provenance and migration studies. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaav8083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetelat, B.; Liu, C.Q.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Wang, Q.L.; Li, S.L.; Li, J.; Wang, B.L. Geochemistry of the dissolved load of the Changjiang Basin rivers: Anthropogenic impacts and chemical weathering. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2008, 72, 4254–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Zheng, H.B.; Tada, R.; Wu, W.H.; Irino, T.; Yang, S.Y.; Saito, K. Tracing Sr isotopic composition in space and time across the Yangtze River basin. Chem. Geol. 2014, 388, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, C.Q. Strontium isotopic compositions of dissolved and suspended loads from the main channel of the Yangtze River. Chemosphere 2007, 69, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.H.; Sun, M.Z.; Ji, X.; Qu, S.Y. Sr isotopic characteristics and fractionation during weathering of a small granitic watershed system in the Jiuhua Mountains (eastern China). J. Hydrol. 2019, 568, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.F.; Ji, J.P.; Shi, C. Water geochemistry of the Chaohu Lake Basin rivers, China: Chemical weathering and anthropogenic inputs. Appl. Geochem. 2011, 26, S379–S383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senila, M. Recent advances in the determination of major and trace elements in plants using inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry. Molecules 2024, 29, 3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durante, C.; Bertacchini, L.; Cocchi, M.; Manzini, D.; Marchetti, A.; Rossi, M.C.; Sighinolfi, S.; Tassi, L. Development of 87Sr/86Sr maps as targeted strategy to support wine quality. Food Chem. 2018, 255, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.C.; Chung, C.H.; You, C.F.; Chiang, Y.H. Determination of 87Sr/86Sr and δ88/86Sr ratios in plant materials using MC-ICP-MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, D.; Kieffer, B.; Maerschalk, C.; Barling, J.; De Jong, J.; Williams, G.A.; Hanano, D.; Pretorius, W.; Mattielli, N.; Scoates, J.S.; et al. High-precision isotopic characterization of USGS reference materials by TIMS and MC-ICP-MS. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2006, 7, Q08006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.Z.; Zhang, Y.L.; Yu, R.; Li, J.; Niu, L.X. Comparison of different extraction methods for seed oil from the ‘Fengdan’ peony cultivar. Food Sci. 2017, 38, 136–141. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.B.; Nam, Y.A.; Kim, H.S.; Hayes, A.W.; Lee, B.M. α-Linolenic acid: Nutraceutical, pharmacological and toxicological evaluation. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 70, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, F. Omega-3 fatty acids and marine oils in cardiovascular and general health: A critical overview of controversies and realities. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 19, 797–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agency AHMSAB. “Huangshan Maofeng” and “Lu’an Guapian” of Anhui Province Selected into the First Batch of National Geographical Indication Protection Projects. 2024. Available online: https://amr.ah.gov.cn/xwdt/dszc/150158511.html (accessed on 12 September 2025). (In Chinese)
- Zhang, S.N.; Chai, X.Y.; Hou, G.G.; Zhao, F.L.; Meng, Q.G. Platycodon grandiflorum (Jacq.) A. DC.: A review of phytochemistry, pharmacology, toxicology and traditional use. Phytomedicine 2022, 106, 154422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.Y.; Wang, W.M.; Wang, N.; Shi, L.; Wu, R.N. Research progress of Platycodon grandiflorum functionality and food development. Food Res. Dev. 2022, 43, 199–206. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.J.; Pu, W.T.; Song, Q.Y.; Ye, B.H.; Shi, X.X.; Chen, Y.W.; Yu, Y.F.; Li, H.B. Traditional processing can enhance the medicinal effects of Polygonatum cyrtonema by inducing significant chemical changes in the functional components in its rhizomes. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.D.; Li, C.L.; Li, C.S.; Sun, R.R.; Li, Y.; Yao, G.F. Research progress of Polygonatum functional components. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2021, 49, 16–18. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.T.; Liu, Y.J.; Jiang, Y.F.; Xie, J.Q.; Pan, X.H.; Liu, J.J.; Si, J.P. Status of Polygonati Rhizome industry and suggestion for its sustainable development. China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2018, 43, 2831–2835. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Adams, S.; Grün, R.; McGahan, D.; Zhao, J.X.; Feng, Y.X.; Nguyen, A.; Willmes, M.; Quaresimin, M.; Lobsey, B.; Collard, M.; et al. A strontium isoscape of north-east Australia for human provenance and repatriation. Geoarchaeology 2019, 34, 231–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesson, L.A.; Tipple, B.J.; Mackey, G.N.; Hynek, S.A.; Fernandez, D.P.; Ehleringer, J.R. Strontium isotopes in tap water from the coterminous USA. Ecosphere 2012, 3, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogewerff, J.A.; Reimann, C.; Ueckermann, H.; Frei, R.; Frei, K.M.; van Aswegen, T.; Stirling, C.; Reid, M.; Clayton, A.; Ladenberger, A. Bioavailable 87Sr/86Sr in European soils: A baseline for provenancing studies. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 672, 1033–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Tang, Z.H.; Dong, X.X. Distribution of strontium isotopes in river waters across the Tarim Basin: A map for migration studies. J. Geol. Soc. 2018, 175, 967–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Wei, L.; Chen, H.; Yang, X.; Kang, L.; Hao, Q.; Zhou, L.; Zhan, Z.L.; Liu, Z.; Yang, J.; et al. Combining stable C, N, O, H, Sr isotope and multi-element with chemometrics for identifying the geographical origins and farming patterns of Huangjing herb. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 102, 103972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.Y.; Zhang, J.C.; Wang, L.S.; Jin, G.; Zhang, A. Signature of Sr isotope ratios and the contents of elements as a tool to distinguish wine regions in China. Food Chem. 2024, 446, 138812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, F.; Yuan, Y.W.; Li, C.L.; Lyu, C.G.; Wan, X.F.; Nie, J.; Li, H.Y.; Yang, J.; Guo, L.P. Stable isotopic and elemental characteristics with chemometrics for the geographical origin authentication of dendrobium officinale at two spatial scales. LWT 2022, 167, 113871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
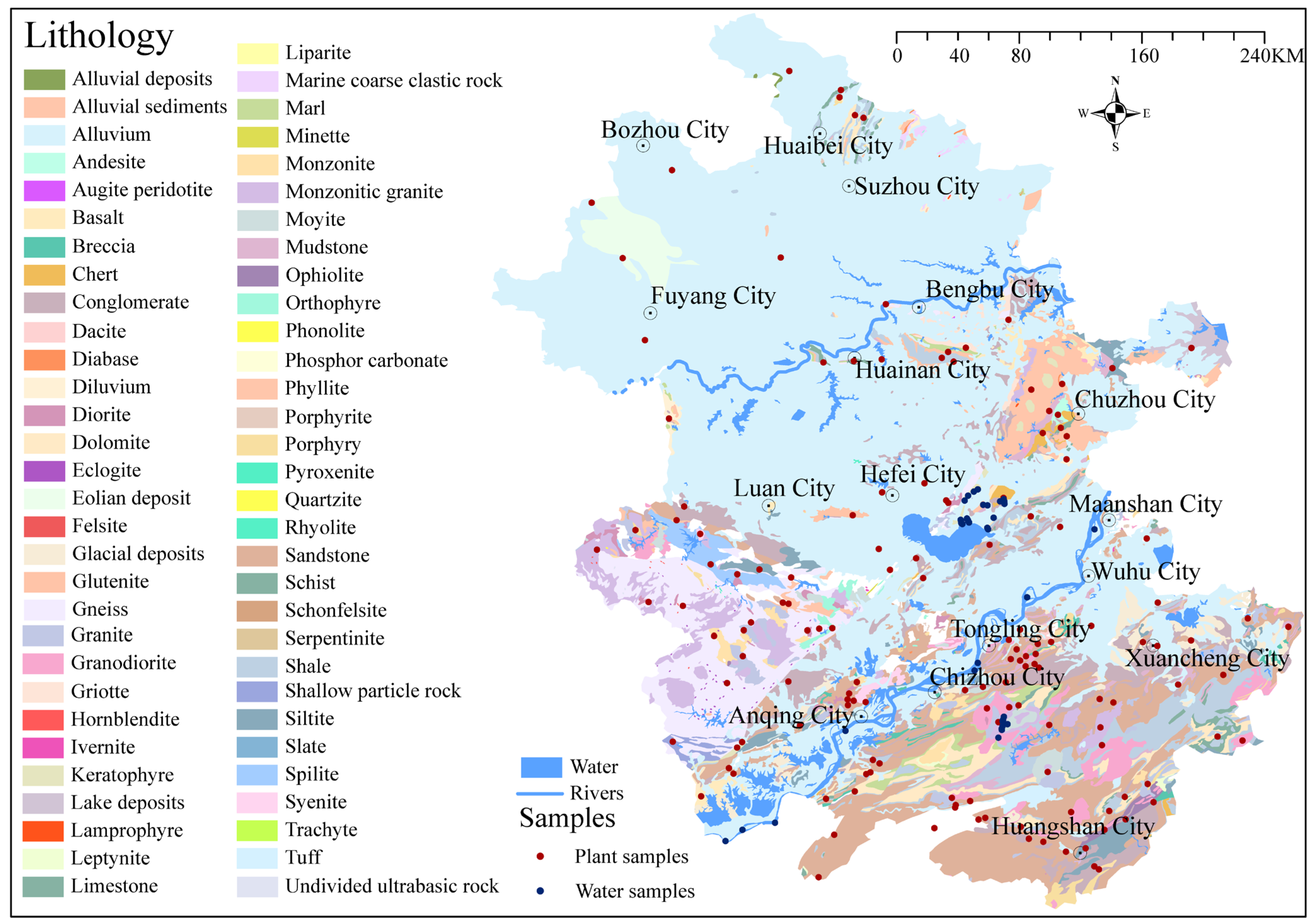
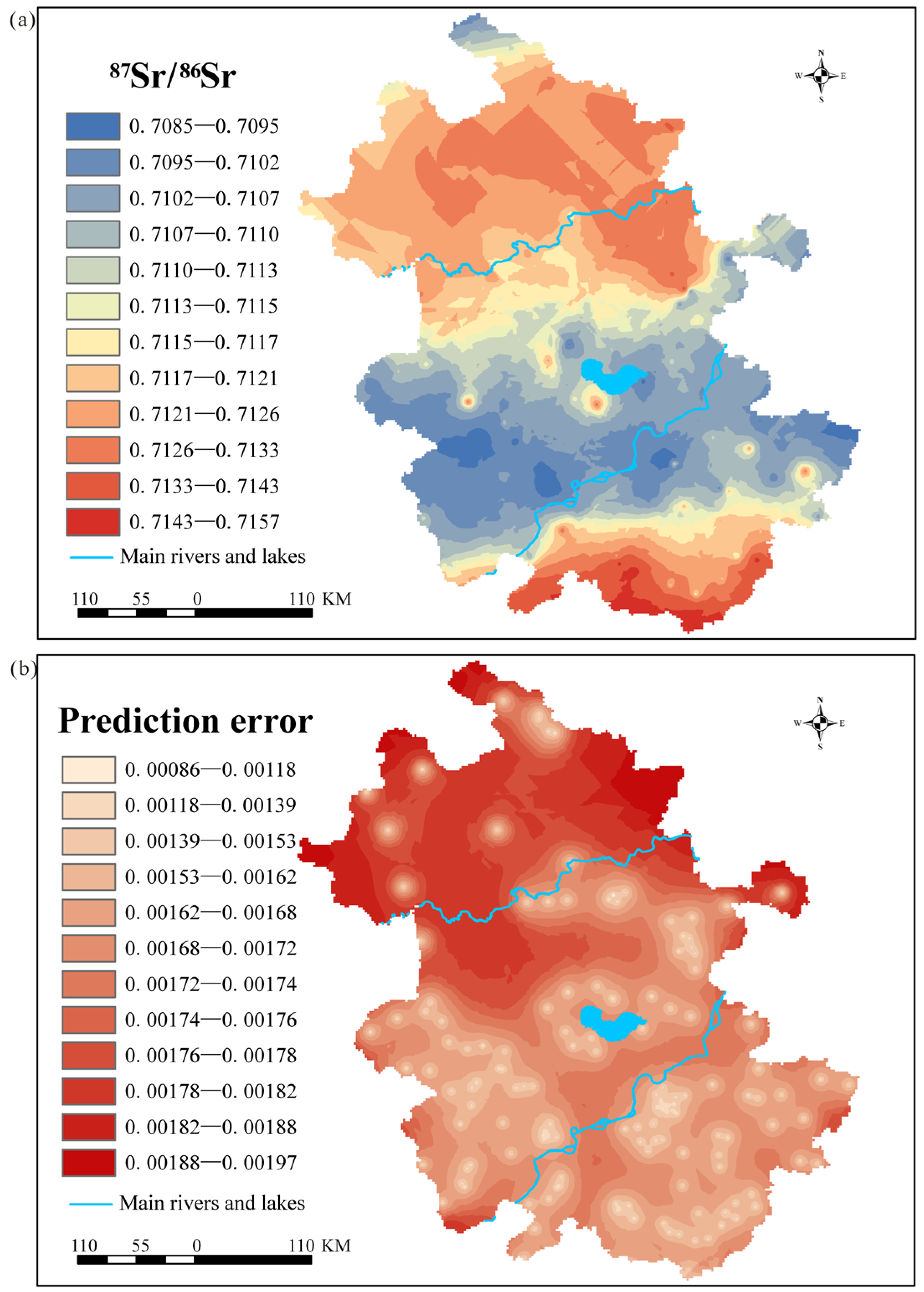
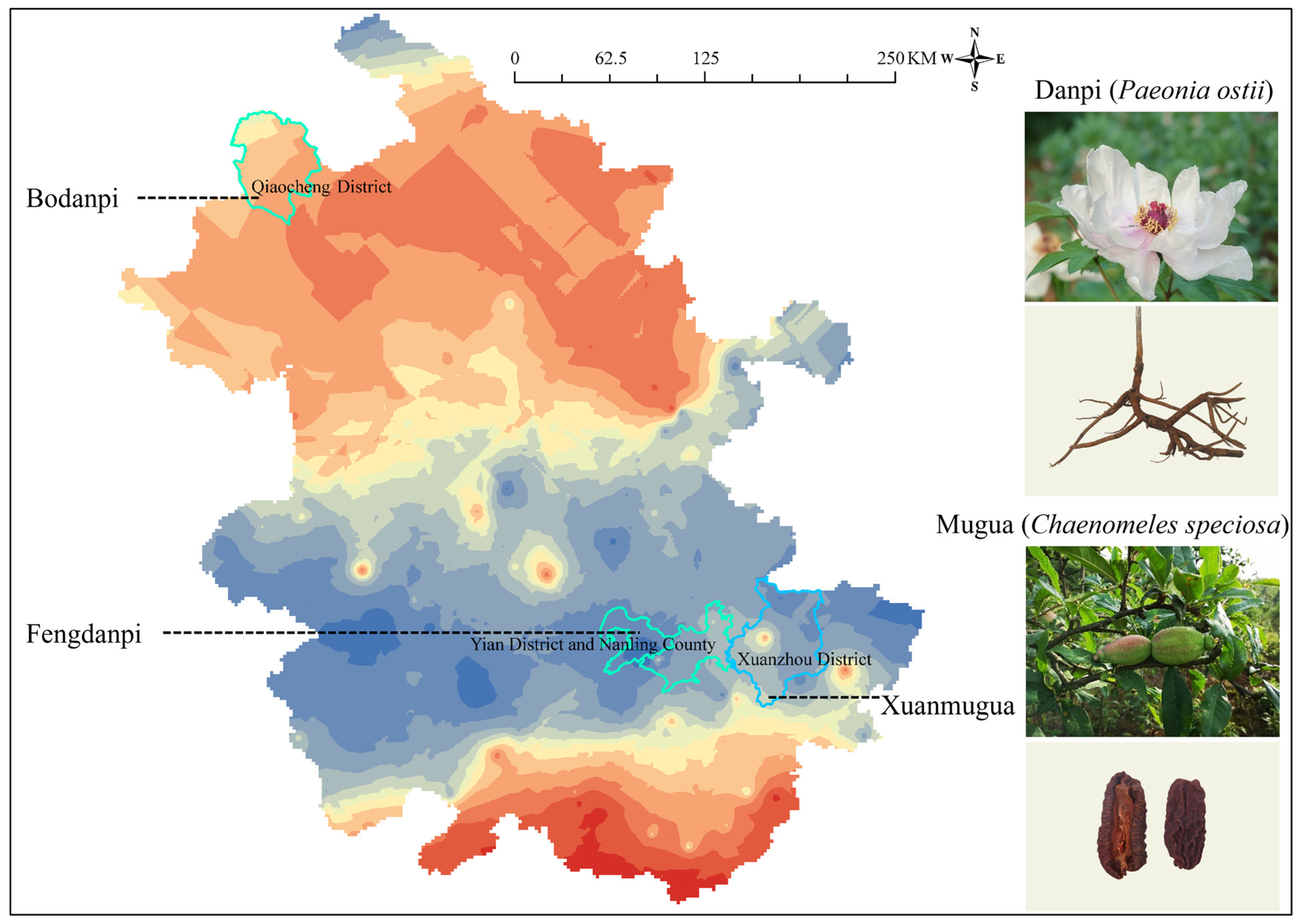
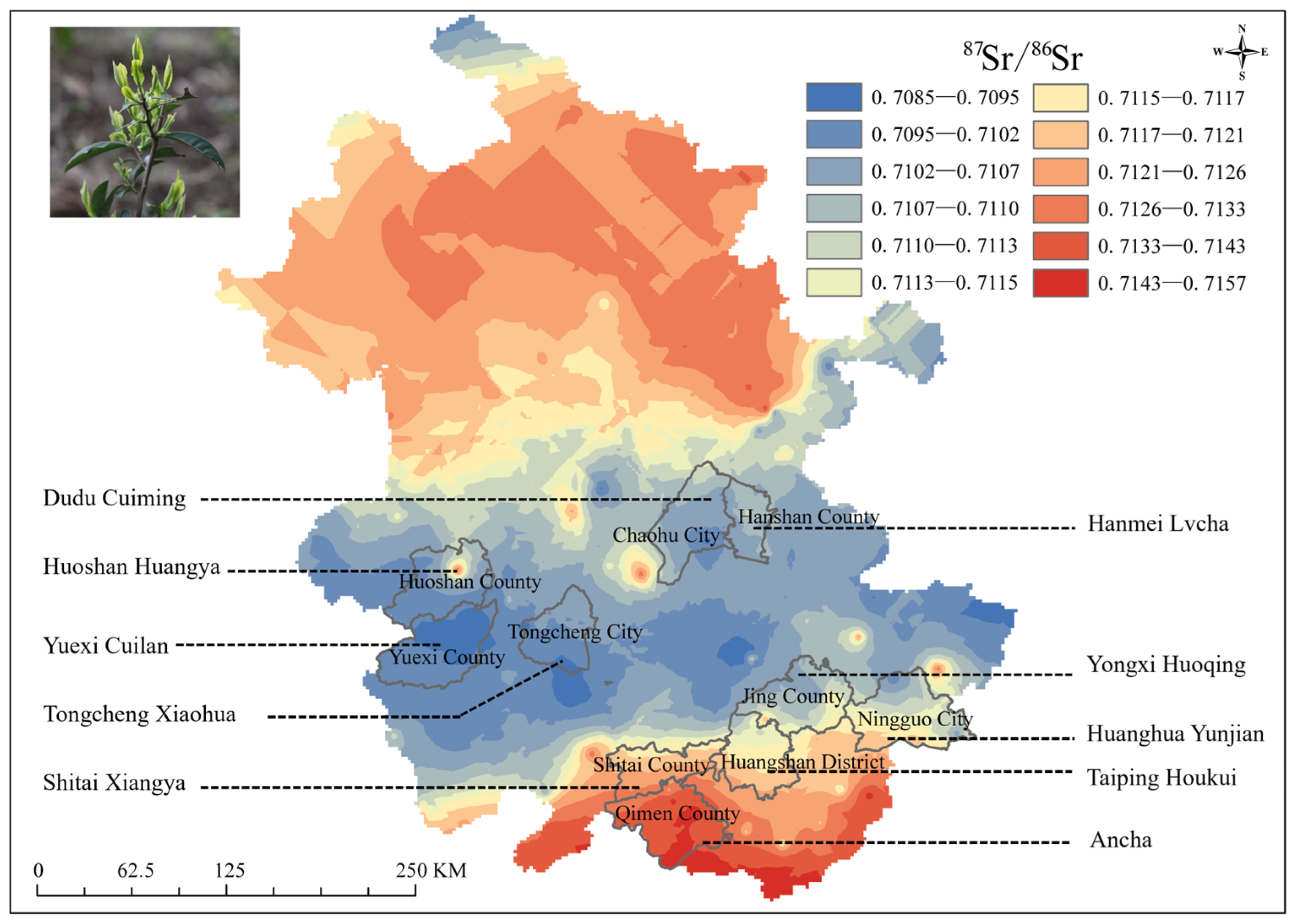
| Location | Main Bedrock | Latitude and Longitude | Minimum 87Sr/86Sr | Maximum 87Sr/86Sr | Mean 87Sr/86Sr ± SD (n) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hefei City | Alluvium, Conglomerate, Porphyrite | 31.861 N, 117.282 E | 0.7081 | 0.7146 | 0.7106 ± 0.002 (n = 13) |
| Chuzhou City | Phyllite, Shale | 32.247 N, 118.340 E | 0.7084 | 0.7184 | 0.7123 ± 0.003 (n = 15) |
| Chizhou City | Dolomite, Limestone, Sandstone | 29.693 N, 117.568 E | 0.7094 | 0.7176 | 0.7117 ± 0.002 (n = 15) |
| Xuancheng City | Alluvium, Dolomite, Mudstone, Sandstone | 30.932 N, 118.756 E | 0.7087 | 0.7145 | 0.7110 ± 0.002 (n = 17) |
| Huangshan City | Conglomerate, Granodiorite, Ophiolite, Sandstone, Shale | 30.298 N, 118.142 E | 0.7101 | 0.7216 | 0.7143 ± 0.003 (n = 21) |
| Lu’an City | Conglomerate, Gneiss, Sandstone | 31.728 N, 116.488 E | 0.7091 | 0.7149 | 0.7107 ± 0.002 (n = 15) |
| Anqing City | Alluvium, Diorite, Gneiss, Granite, Monzonite, Sandstone | 30.506 N, 117.038 E | 0.7073 | 0.7120 | 0.7096 ± 0.001 (n = 22) |
| Tongling City | Alluvium, Sandstone | 30.818 N, 117.764 E | 0.7083 | 0.7102 | 0.7091 ± 0.001 (n = 8) |
| Maanshan City | Alluvium | 31.706 N, 118.526 E | 0.7102 | 0.7118 | 0.7111 ± 0.0007 (n = 3) |
| Wuhu City | Sandstone | 31.361 N, 118.434 E | 0.7086 | 0.7132 | 0.7106 ± 0.002 (n = 5) |
| Fuyang City | Alluvium | 32.869 N, 115.861 E | 0.7116 | 0.7122 | 0.7118 ± 0.0002 (n = 4) |
| Huainan City | Limestone | 32.133 N, 116.542 E | 0.7112 | 0.7127 | 0.7119 ± 0.0006 (n = 3) |
| Suzhou City | Shale | 34.053 N, 117.222 E | 0.7114 | 0.7137 | 0.7124 ± 0.0008 (n = 5) |
| Bozhou City | Alluvium | 33.863 N, 115.734 E | — | — | 0.7124 ± 0.0000 (n = 2) |
| Bengbu City | Gneiss | 32.924 N, 117.363 E | — | — | 0.7106 ± 0.0000 (n = 1) |
| Method | Transformation | Trend Removal | Variogram Model | Search Neighborhood | Sectors | RMSE | MAE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ordinary kriging | Box–Cox | 3 | Exponential | Standard Min: 2 Max: 5 | 4 | 0.00166 | 0.00164 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Wang, M.; Jiang, Y.; Han, X.; Ren, A.; He, J.; Yin, M.; Zhao, Y.; Peng, H. Fine-Scale Strontium Isotope Mapping in Eastern China (Anhui Province) and Its Application in Food Traceability. Foods 2026, 15, 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods15010033
Wang M, Jiang Y, Han X, Ren A, He J, Yin M, Zhao Y, Peng H. Fine-Scale Strontium Isotope Mapping in Eastern China (Anhui Province) and Its Application in Food Traceability. Foods. 2026; 15(1):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods15010033
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Mei, Yunlu Jiang, Xiaojing Han, Aoyu Ren, Jiahui He, Minzhen Yin, Yujiao Zhao, and Huasheng Peng. 2026. "Fine-Scale Strontium Isotope Mapping in Eastern China (Anhui Province) and Its Application in Food Traceability" Foods 15, no. 1: 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods15010033
APA StyleWang, M., Jiang, Y., Han, X., Ren, A., He, J., Yin, M., Zhao, Y., & Peng, H. (2026). Fine-Scale Strontium Isotope Mapping in Eastern China (Anhui Province) and Its Application in Food Traceability. Foods, 15(1), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods15010033







