Evaluation of the Antioxidant, Antibacterial Activity and Volatile Components of Three Distinctive Apis cerana Honeys
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples of Honey
2.2. Experimental Materials
2.3. Experimental Procedure
2.3.1. Quantification of Total Phenolics
2.3.2. Evaluation of Antioxidant Activity
DPPH Radical Scavenging Assay
ABTS Radical Scavenging Assay
FRAP Reducing Power Assay
EC50 Calculation
- A0 is the absorbance of the blank control (sample-free).
- As is the absorbance of the sample solution containing honey at a specific mass concentration.
2.3.3. Evaluation of Antibacterial Activity
2.3.4. Analysis of Volatile Components
HS-SPME Extraction
GC-MS Instrumental Parameters
Compound Identification
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Total Polyphenols of Honey
3.2. Antioxidant Capacity
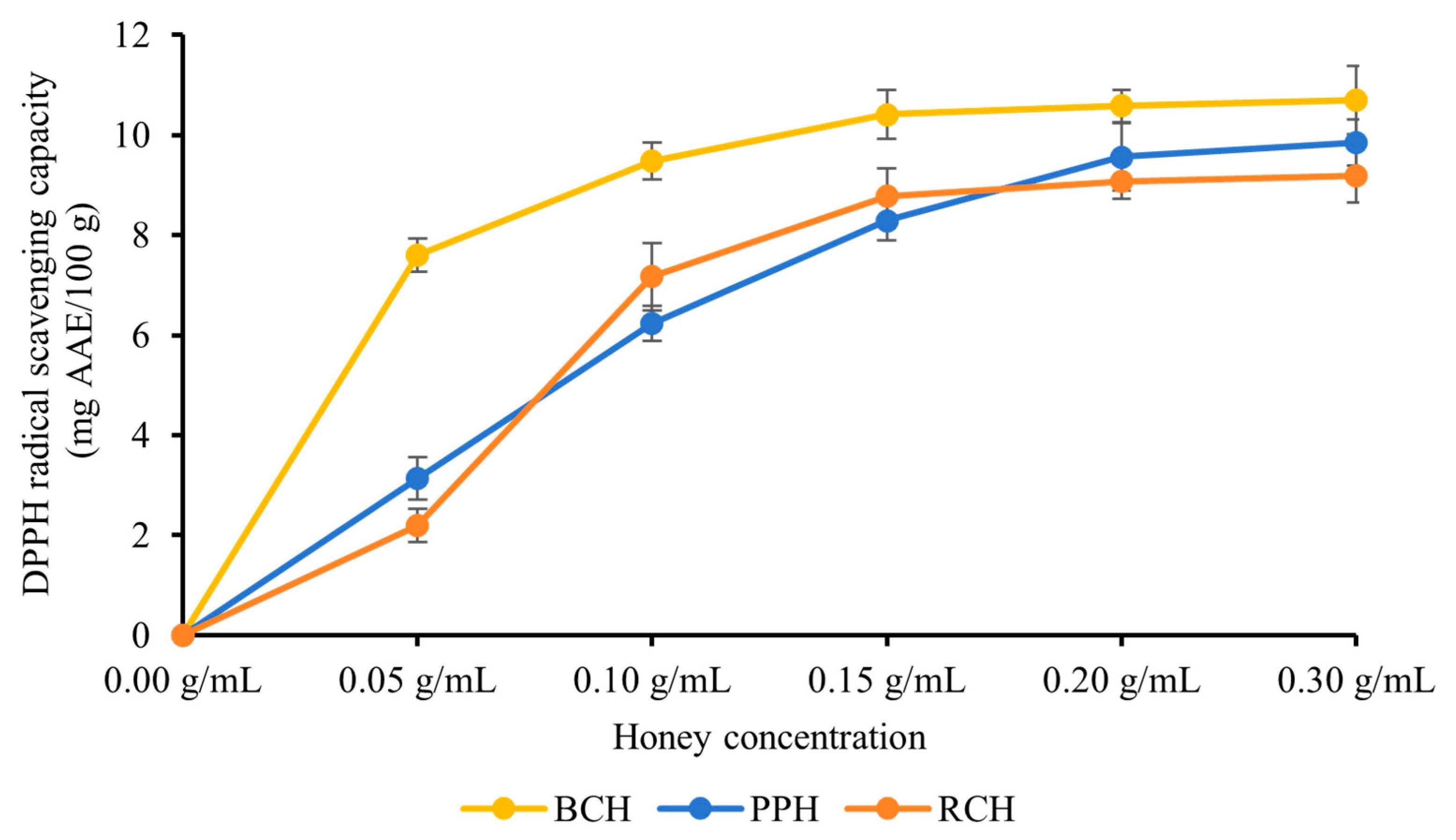
3.2.1. DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity
3.2.2. ABTS Radical Scavenging Activity
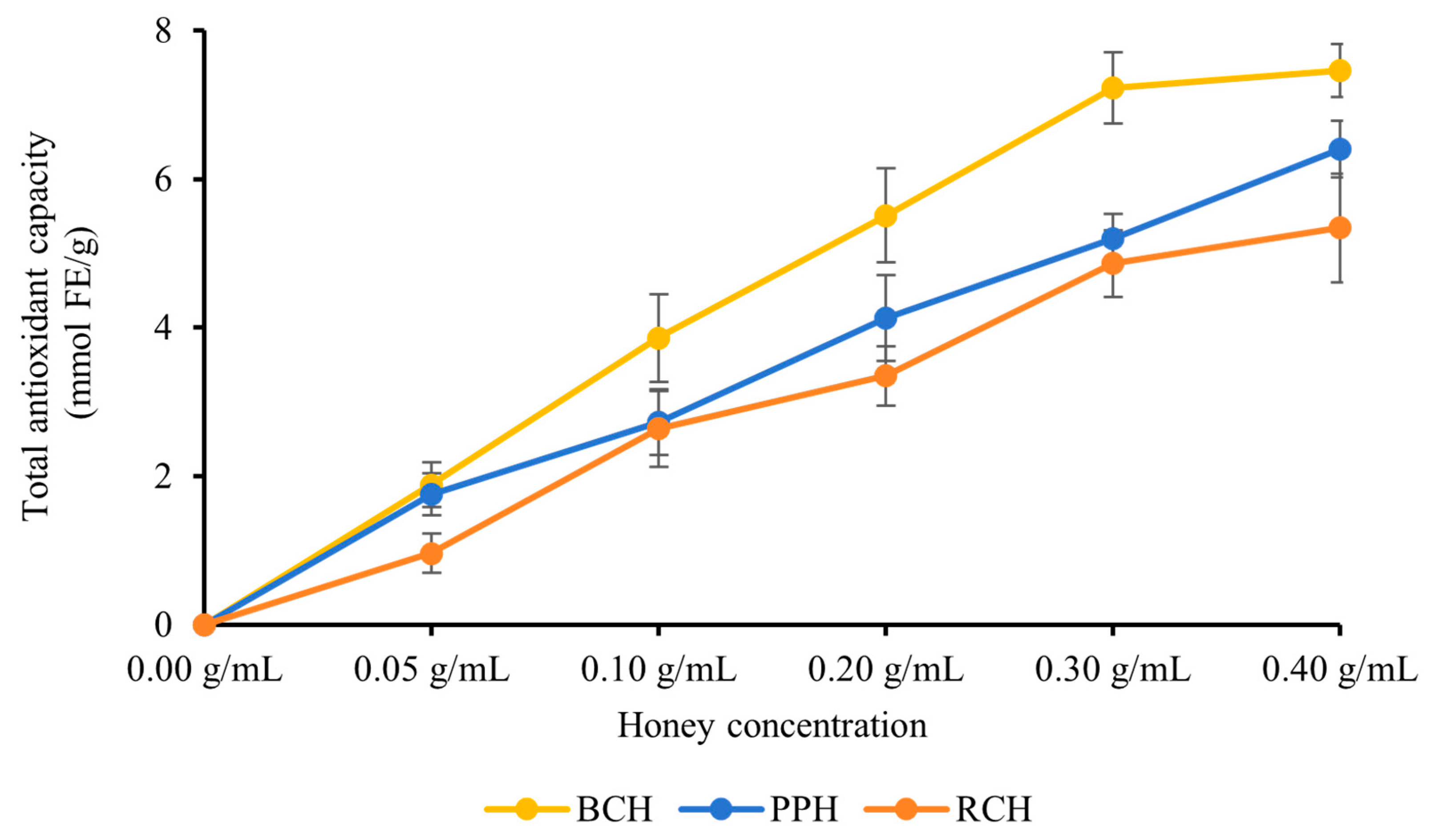
3.2.3. FRAP Assay
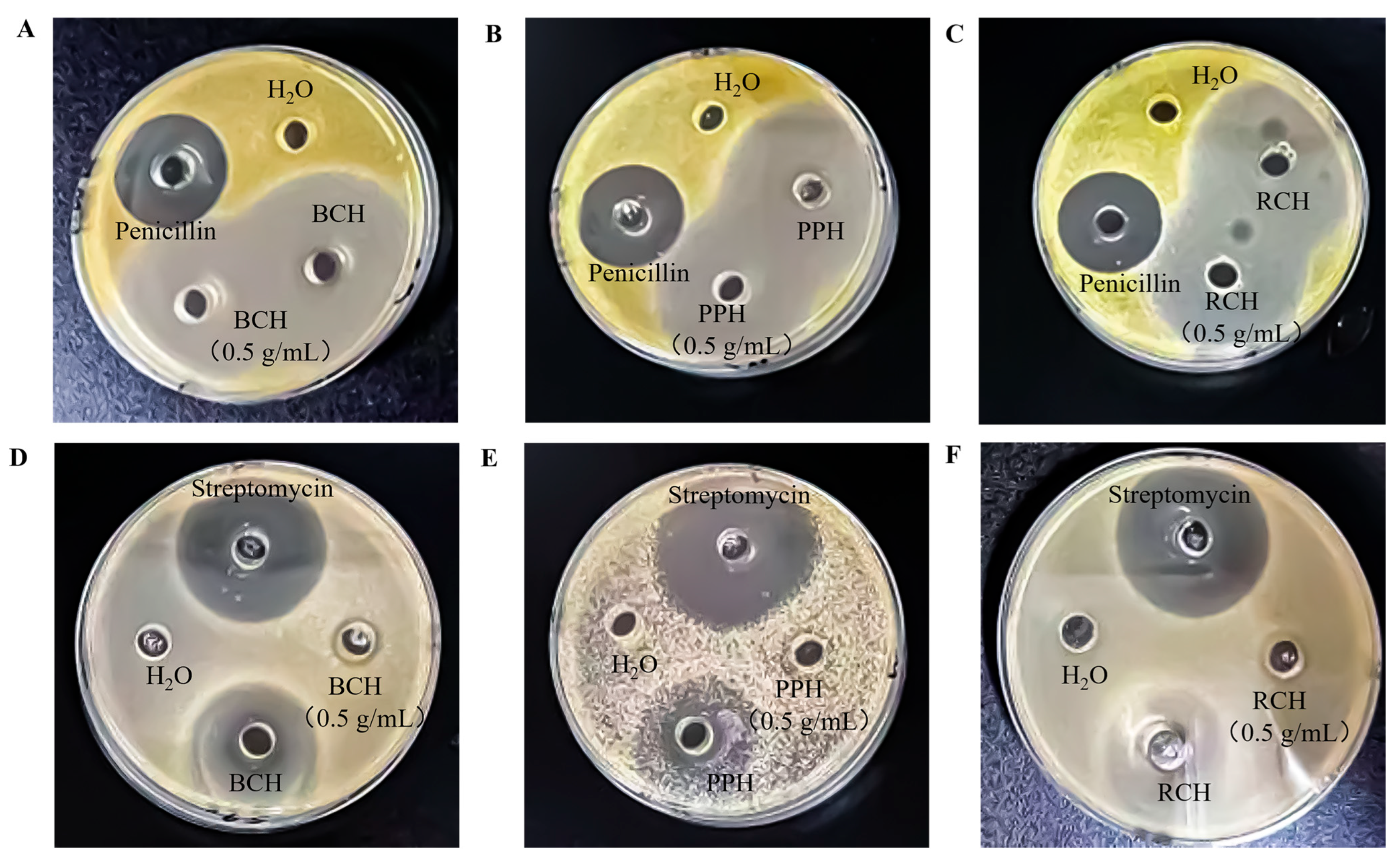
3.3. Antibacterial Activitys
3.4. Volatile Components Analysis
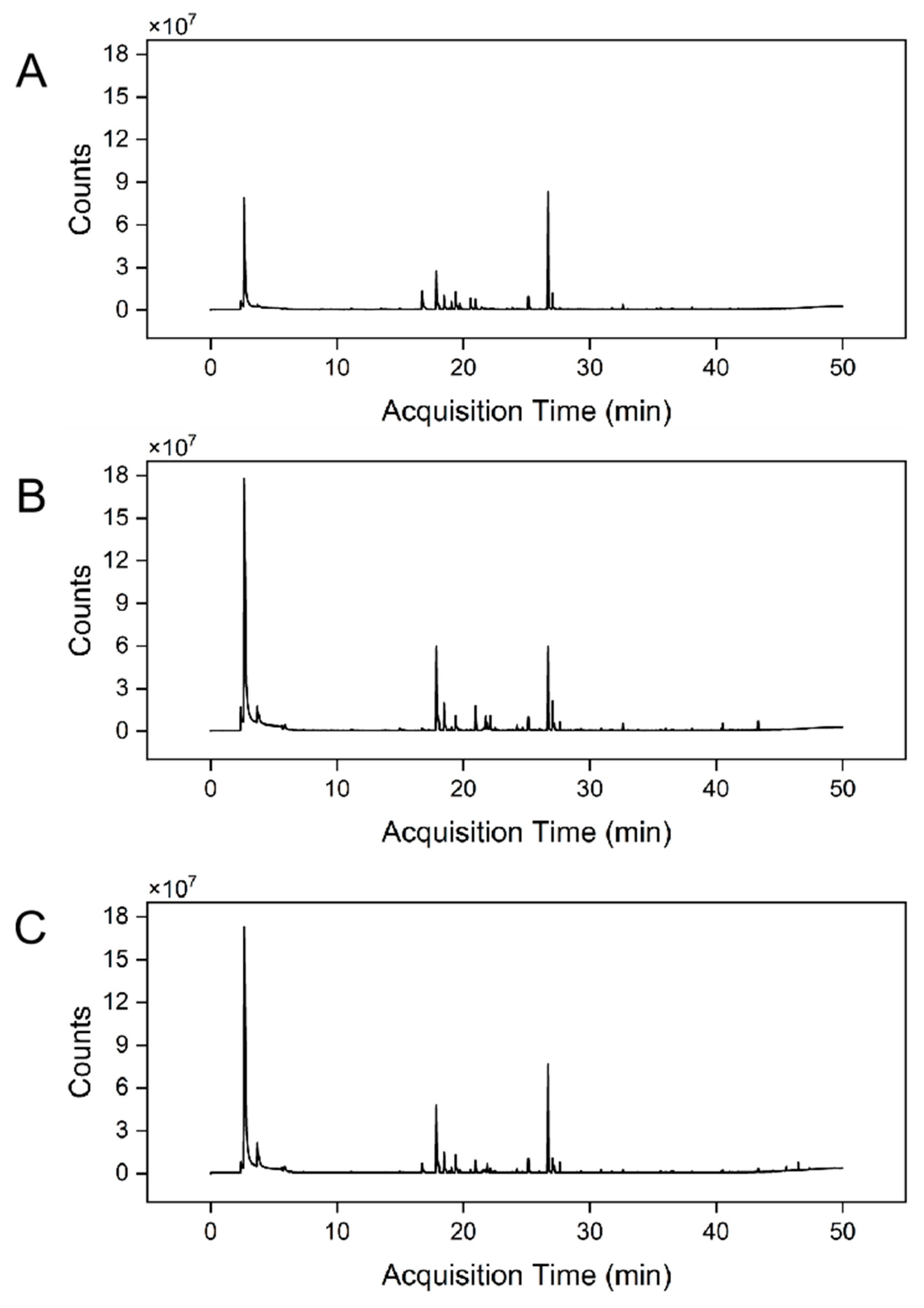
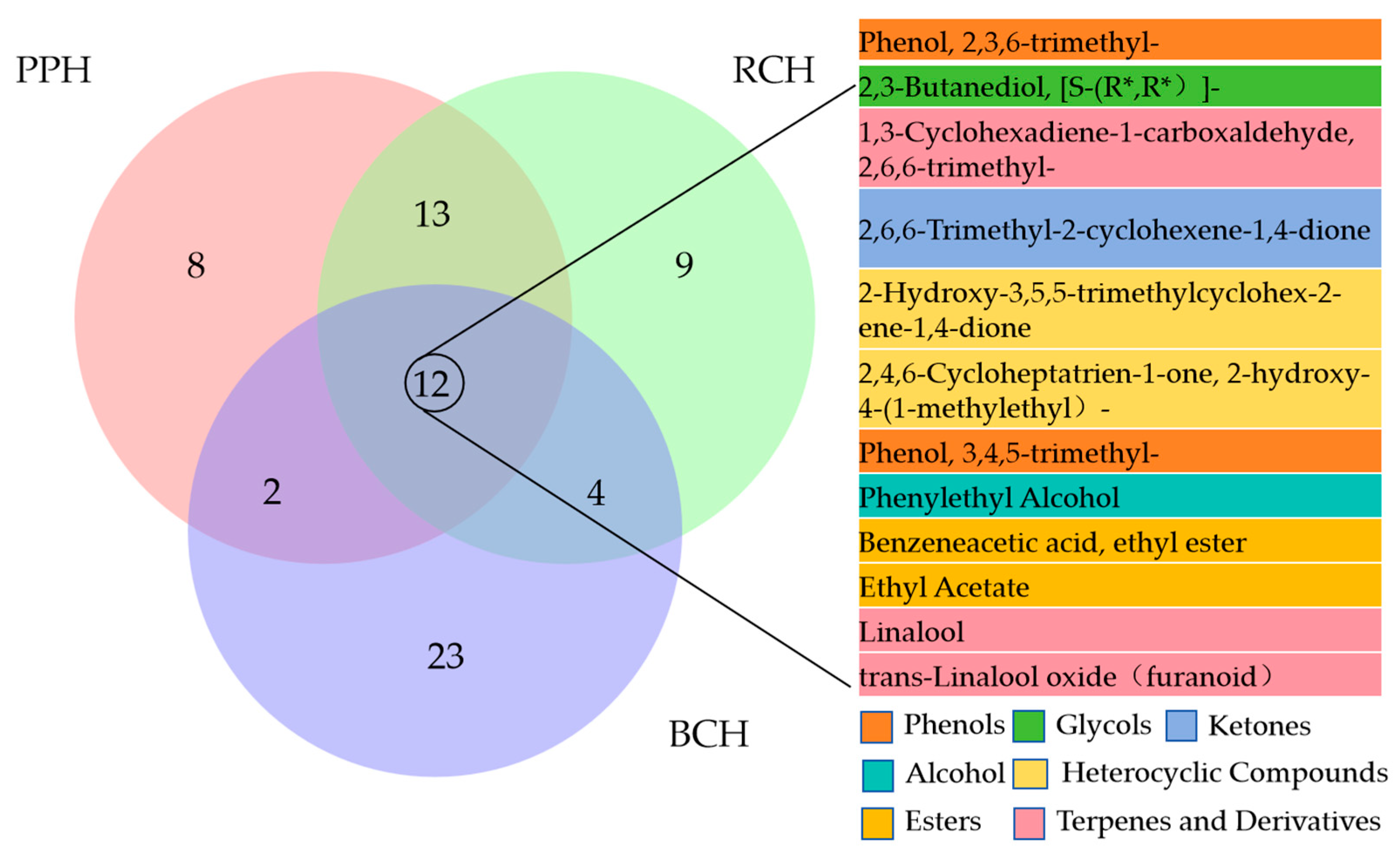
3.4.1. Profiling and Comparison of Volatile Compounds
3.4.2. Unique Volatile Compounds and Potential Chemical Markers
3.4.3. Bioactive Potential and Correlation Analysis of Key Volatile Compounds
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BCH | Bauhinia championii honey |
| PPH | Polygonum perfoliatum honey |
| RCH | Rhus chinensis honey |
| CFU | colony-forming units |
References
- Palma-Morales, M.; Huertas, J.R.; Rodríguez-Pérez, C.A. Comprehensive Review of the Effect of Honey on Human Health. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tlak Gajger, I.; Dar, S.A.; Ahmed, M.M.M.; Aly, M.M.; Vlainić, J. Antioxidant Capacity and Therapeutic Applications of Honey: Health Benefits, Antimicrobial Activity and Food Processing Roles. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.M.; Rahaman, M.S.; Islam, M.R.; Rahman, F.; Mithi, F.M.; Alqahtani, T.; Almikhlafi, M.A.; Alghamdi, S.Q.; Alruwaili, A.S.; Hossain, M.S.; et al. Role of Phenolic Compounds in Human Disease: Current Knowledge and Future Prospects. Molecules 2021, 27, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatipamula, V.B.; Kukavica, B. Phenolic Compounds as Antidiabetic, Anti-Inflammatory, and Anticancer Agents and Improvement of Their Bioavailability by Liposomes. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2021, 39, 926–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masad, R.J.; Haneefa, S.M.; Mohamed, Y.A.; Al-Sbiei, A.; Bashir, G.; Fernandez-Cabezudo, M.J.; Al-Ramadi, B.K. The Immunomodulatory Effects of Honey and Associated Flavonoids in Cancer. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Ding, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; He, J.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, P.; Gong, X. Evaluation of the Antioxidant Activities and Phenolic Profile of Shennongjia Apis cerana Honey through a Comparison with Apis mellifera Honey in China. Molecules 2023, 28, 3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiassi, M.C.E.V.; de Souza, V.R.; Lago, A.M.T.; Carvalho, G.R.; Curi, P.N.; Guimarães, A.S.; Queiroz, F. Quality of Honeys from Different Botanical Origins. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 4167–4177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Cheng, N.; He, L.; Peng, G.; Liu, Q.; Ma, T.; Cao, W. Hepatoprotective Effects of the Honey of Apis cerana Fabricius on Bromobenzene-Induced Liver Damage in Mice. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Nie, J. Revealing the Key Antioxidant Compounds and Potential Action Mechanisms of Bauhinina championii Honey Based on Non-Targeted Metabolomics, Mineralogical Analysis and Physicochemical Characterization. Food Chem. 2025, 477, 143456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zeng, Y.; Sun, G.; Yu, S.; Xu, Y.; He, C.; Li, Z.; Jin, S.; Qin, X. Polygonum perfoliatum L., an Excellent Herbal Medicine Widely Used in China: A Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 581266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Lang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Song, M.; Jiang, A.; Li, N.; Chen, L. Dynamic Variation in the Aroma Characteristics of Rhus chinensis Honey at Different Stages after Capping. Food Chem. 2024, 449, 139226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, G.; Francisco, V.; Lopes, M.C.; Cruz, M.T.; Batista, M.T. Intracellular Signaling Pathways Modulated by Phenolic Compounds: Application for New Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Discovery. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 2876–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acevedo, F.; Torres, P.; Oomah, B.D.; de Alencar, S.M.; Massarioli, A.P.; Martín-Venegas, R.; Albarral-Ávila, V.; Burgos-Díaz, C.; Ferrer, R.; Rubilar, M. Volatile and Non-Volatile/Semi-Volatile Compounds and In Vitro Bioactive Properties of Chilean Ulmo (Eucryphia cordifolia Cav.) Honey. Food Res. Int. 2017, 94, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaškonienė, V.; Venskutonis, P.R. Floral Markers in Honey of Various Botanical and Geographic Origins: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2010, 9, 620–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Zhao, H.; Sun, J.; Guo, J.; Wu, L.; Xue, X.; Cao, W. ICP-MS-Based Ionomics Method for Discriminating the Geographical Origin of Honey of Apis cerana Fabricius. Food Chem. 2021, 354, 129568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belay, A.; Solomon, W.K.; Bultossa, G.; Adgaba, N.; Melaku, S. Botanical origin, colour, granulation, and sensory properties of the Harenna forest honey, Bale, Ethiopia. Food Chem. 2015, 167, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilczyńska, A. Effect of Filtration on Colour, Antioxidant Activity and Total Phenolics of Honey. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 57, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida-Muradian, L.B.; Barth, O.M.; Dietemann, V.; Eyer, M.; Freitas, A.S.; Martel, A.-C.; Marcazzan, G.L.; Marchese, C.M.; Mucignat-Caretta, C.; Pascual-Maté, A.; et al. Standard Methods for Apis mellifera Honey Research. J. Apic. Res. 2020, 59, 1–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balázs, V.L.; Nagy-Radványi, L.; Bencsik-Kerekes, E.; Koloh, R.; Szabó, D.; Kocsis, B.; Kocsis, M.; Farkas, Á. Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Effect of Unifloral Honeys against Bacteria Isolated from Chronic Wound Infections. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhou, S.; Wu, C.; Xu, X.; Zhu, X. Evaluation of Litchi Honey Quality in Southern China. Foods 2025, 14, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gośliński, M.; Nowak, D.; Kłębukowska, L. Antioxidant Properties and Antimicrobial Activity of Manuka Honey versus Polish Honeys. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tananaki, C.; Rodopoulou, M.-A.; Dimou, M.; Kanelis, D.; Liolios, V. The Total Phenolic Content and Antioxidant Activity of Nine Monofloral Honey Types. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulea, A.; Obiștioiu, D.; Cocan, I.; Alexa, E.; Negrea, M.; Neacșu, A.G.; Hulea, C.; Pascu, C.; Costinar, L.; Iancu, I.; et al. Diversity of Monofloral Honey Based on the Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Potential. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulsen-Silva, E.; Gordillo-Fuenzalida, F.; Velásquez, P.; Llancalahuen, F.M.; Carvajal, R.; Cabaña-Brunod, M.; Otero, M.C. Antimicrobial, Antioxidant, and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Monofloral Honeys from Chile. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majewska, E.; Drużyńska, B.; Derewiaka, D.; Ciecierska, M.; Pakosz, P. Comparison of Antioxidant Properties and Color of Selected Polish Honeys and Manuka Honey. Foods 2024, 13, 2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.Z.; Han, L.Y.; Li, S.S.; Zheng, H.Q.; Hu, F.L. Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Properties of Three Monofloral Kinds of Honey from Medicinal Plants. Food Ferment. Ind. 2024, 50, 100–108. [Google Scholar]
- Adgaba, N.; Al-Ghamdi, A.; Sharma, D.; Tadess, Y.; Alghanem, S.M.; Ali Khan, K.; Ansari, M.J.; Mohamed, G.K.A. Physico-Chemical, Antioxidant and Anti-Microbial Properties of Some Ethiopian Mono-Floral Honeys. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 2366–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Estellé, M.; Hernández-González, V.; Saurina, J.; Núñez, O.; Sentellas, S. Characterization and Classification of Spanish Honeydew and Blossom Honeys Based on Their Antioxidant Capacity. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.L.; Lim, L.Y.; Hammer, K.; Hettiarachchi, D.; Locher, C. Determination of Antioxidant and Antibacterial Activities of Honey-Loaded Topical Formulations: A Focus on Western Australian Honeys. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorlíński, M.; Nowak, D.; Pawłowska, A.; Wojtasiak, R.; Gasiński, A. Antibacterial Activity of Polish Honeys against Selected Pathogenic Bacteria Including Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 137, 110438. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez-Suarez, J.M.; Gasparrini, M.; Forbes-Hernandez, T.Y.; Mazzoni, L.; Giampieri, F. The Composition and Biological Activity of Honey: A Focus on Manuka Honey. Foods 2014, 3, 420–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manyi-Loh, C.E.; Ndip, R.N.; Clarke, A.M. Volatile compounds in honey: A review on their involvement in aroma, botanical origin determination and potential biomedical activities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 9514–9532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyuncu, G. Determination of volatile compounds of Turkish commercial monofloral honeys by Headspace-solid phase microextraction/gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and sensory evaluation. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2025, 60, vvaf151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrouz, S.; Hosseini, M.; Rezaee, R.; Boskabady, M.H.; Asgharzadeh, F.; Gholamnezhad, Z. Cedrol ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced systemic inflammation and lung injury in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2025, 1003, 177952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample Name | Botanical Origin | Geographical Origin | Collection Time | Color | Average Pollen Percentage (%) | Physical State |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PPH | Polygonum perfoliatum | Hechi City, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China | July 2025 | Amber | 75.35 ± 5.20 | Liquid |
| RCH | Rhus chinensis Mill. | August 2025 | Light amber | 78.68 ± 3.82 | ||
| BCH | Bauhinia championii (Benth.) Benth | September 2025 | Dark amber | 83.40 ± 6.15 |
| Sample Name | Correlation Coefficient (R2) | EC50 (g/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| BCH | 0.994 | 0.015 ± 0.002 a |
| PPH | 0.959 | 0.185 ± 0.012 b |
| RCH | 0.938 | 0.207 ± 0.018 b |
| Sample Name | Correlation Coefficient (R2) | EC50 (g/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| BCH | 0.9946 | 0.689 ± 0.118 a |
| PPH | 0.8753 | 0.720 ± 0.075 b |
| RCH | 0.9988 | 0.880 ± 0.212 c |
| Specimen | Inhibition Zone Size (mm) | |
|---|---|---|
| S. aureus | E. coli | |
| PPH (undiluted) | 49.36 ± 0.80 a | 30.15 ± 0.42 a |
| BCH (undiluted) | 50.21 ± 0.40 a | 18.23 ± 0.14 b |
| RCH (undiluted) | 47.15 ± 0.56 b | 27.18 ± 0.50 c |
| PPH (0.5 g/mL) | 38.03 ± 0.80 d | 14.02 d |
| BCH (0.5 g/mL) | 37.15 ± 0.70 d | 10.14 ± 0.88 e |
| RCH (0.5 g/mL) | 40.23 ± 0.20 c | 10.13 ± 0.62 e |
| Penicillin | 28.16 ± 0.44 e | |
| Streptomycin | 36 ± 0.70 f | |
| Water | - | - |
| Honey Type | Core Chemical Families | Potential Key Markers | Inferred Dominant Aroma |
|---|---|---|---|
| BCH | Esters (floral) Terpenoids (mono-, oxygenated) Green-leaf volatiles | Phenethyl acetate (3R,6S)-2,2,6-trimethyl-6-vinyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-3-ol 1,3,8-p-Menthatriene (Z)-3-Hexen-1-ol acetate | Rich floral–fruity with subtle woody and green-leaf notes |
| PPH | Sesquiterpenes Terpene ketones Nitrogen-containing heterocycles | Cedrol Pyrazole-4-carboxaldehyde, 1-ethyl-5-methyl- 1-(1a,2,3,5,6a,6b-hexahydro-3,3,6a-trimethyloxireno[g]benzofuran-5-yl)- | Woody-herbal tone complemented by medicinal notes |
| RCH | Fatty acid ethyl esters Aromatic derivatives | Octanoic acid ethyl ester Tetradecanoic acid ethyl ester Benzaldehyd | Mellow fruity-sweet with almond-nutty notes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Zhang, C.; Lu, C.; Jiang, X.; Yuan, B.; Hu, F.; Niu, D. Evaluation of the Antioxidant, Antibacterial Activity and Volatile Components of Three Distinctive Apis cerana Honeys. Foods 2026, 15, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods15010024
Wang H, Zhang C, Lu C, Jiang X, Yuan B, Hu F, Niu D. Evaluation of the Antioxidant, Antibacterial Activity and Volatile Components of Three Distinctive Apis cerana Honeys. Foods. 2026; 15(1):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods15010024
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Haibo, Cuiping Zhang, Caoyang Lu, Xiasen Jiang, Bin Yuan, Fuliang Hu, and Defang Niu. 2026. "Evaluation of the Antioxidant, Antibacterial Activity and Volatile Components of Three Distinctive Apis cerana Honeys" Foods 15, no. 1: 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods15010024
APA StyleWang, H., Zhang, C., Lu, C., Jiang, X., Yuan, B., Hu, F., & Niu, D. (2026). Evaluation of the Antioxidant, Antibacterial Activity and Volatile Components of Three Distinctive Apis cerana Honeys. Foods, 15(1), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods15010024







