Process Regulation of Microbial-Driven Aldehyde Metabolism in Sauce-Flavor Baijiu Fermentation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
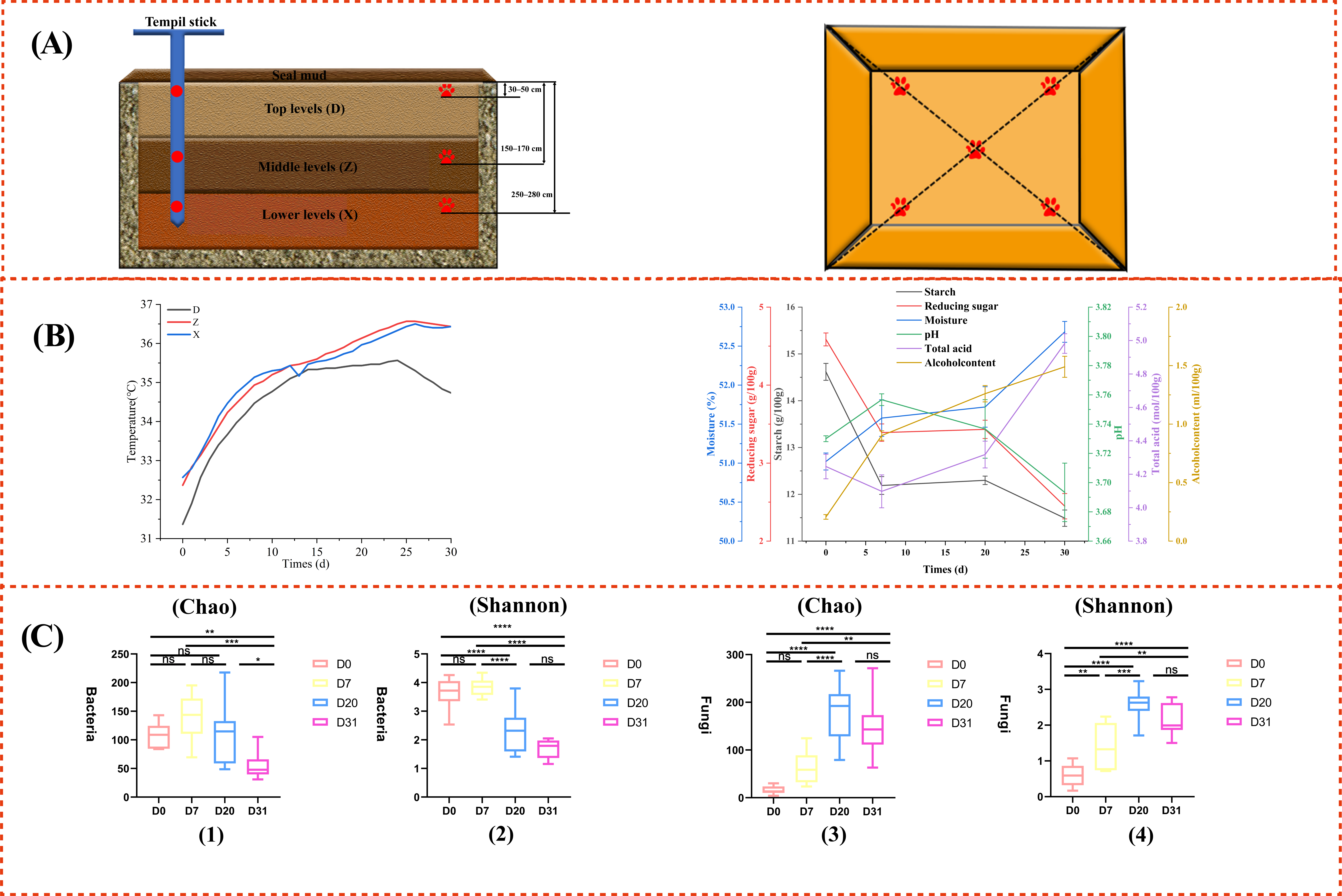
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Environmental and Physicochemical Factors Determination
2.3. Flavor Analysis
2.4. Analysis of the Microbial Community
2.5. Environmental Regulation During Pit Fermentation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical Factors in the Process of Pit Fermentation
3.2. Microbial Community Richness and Diversity During Pit Fermentation
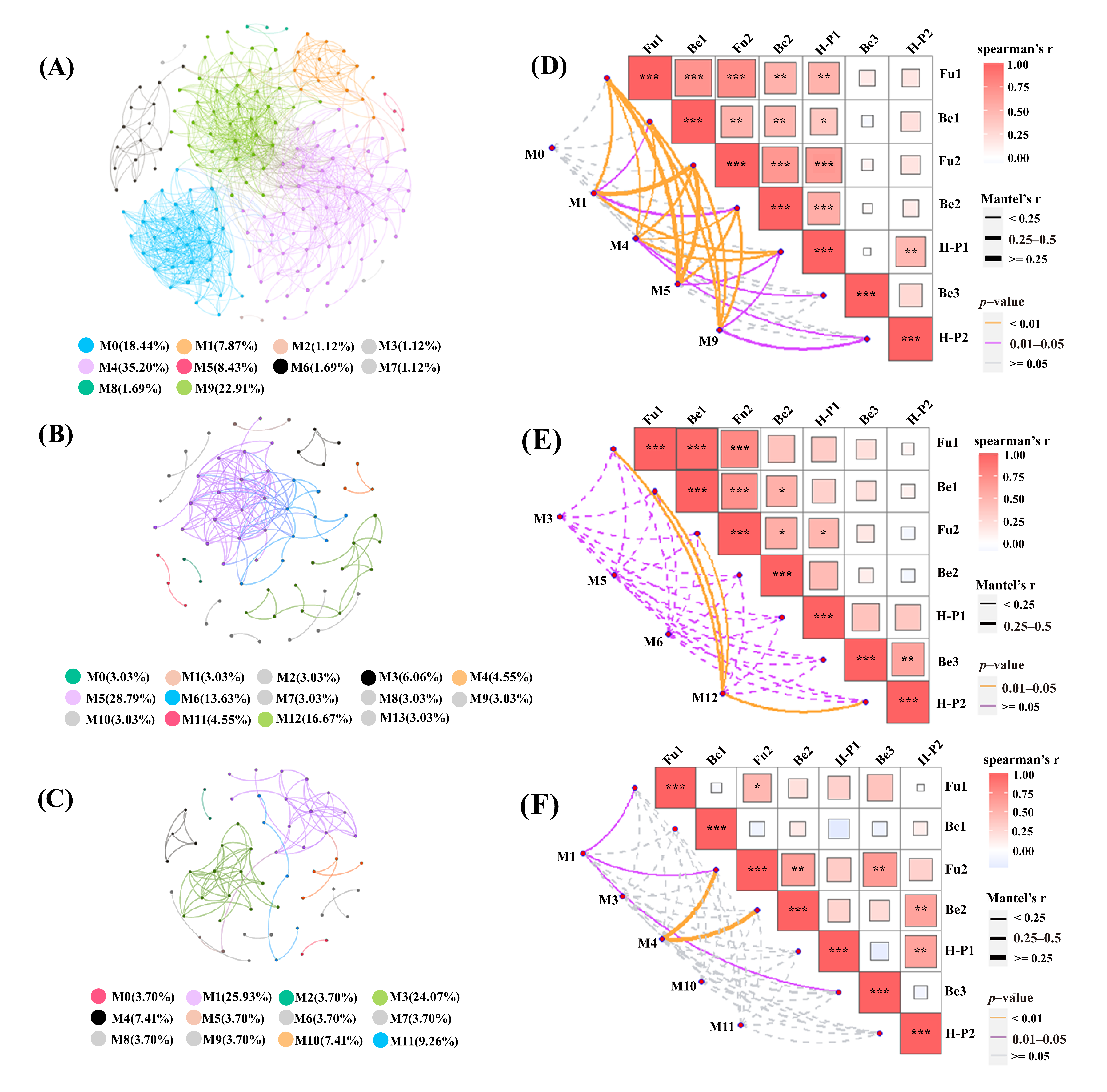
3.3. Microbial Composition and Succession of the Pit Fermentation Process
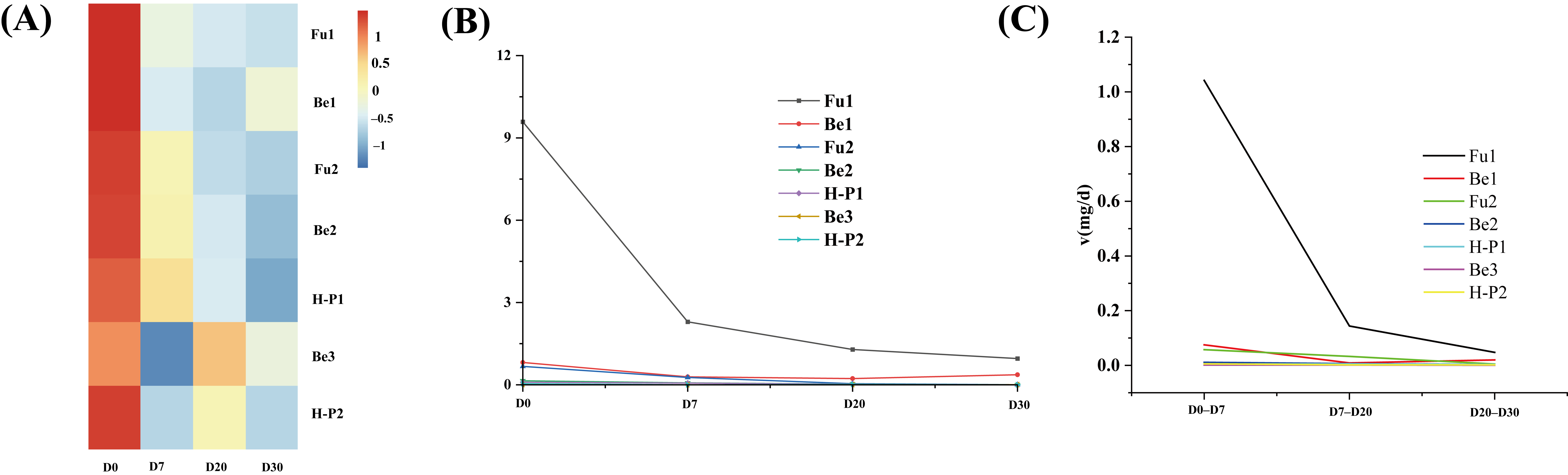
3.4. Dynamic Changes in Aldehyde Compounds During Pit Fermentation
3.5. Relationship Between Microorganisms and the Aldehyde of the Pit Fermentation Process
3.6. The Relationship Between Physicochemical Environment and Microorganisms Related with Aldehyde Synthesis
3.7. Environmental Regulation During Pit Fermentation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Wang, H.; Lu, H.; Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Xu, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, Y. Turning over fermented grains elevating heap temperature and driving microbial community succession during the heap fermentation of sauce-flavor baijiu. LWT 2022, 172, 114173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Z.; Li, X.; Sun, B. Flavor mystery of Chinese traditional fermented baijiu: The great contribution of ester compounds. Food Chem. 2022, 369, 130920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhu, L.; Wang, B.; Zheng, F.; Wang, G.; Chen, E.; Zhang, Y. Environmental factors induced metabolome shifts during Laobaigan-flavor Baijiu fermentation. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 123, 105570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Cheng, Y.; Huang, Y. Study on the drunkenness of Chinese Baijiu with representative flavor based on behavioral characteristics. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1014813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, Y. Mystery behind Chinese liquor fermentation. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 63, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Zhang, H.; Cao, Y.; Du, H.; Xu, Y. Heap fermentation modes of sauce-flavored Baijiu: Microbial metabolic differences and optimization strategies for mechanized fermentation. Food Biosci. 2025, 68, 106449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, H.; Min, W.; Zhu, H.; Wang, H.; Lu, H.; Li, X.; Xu, Y.; Li, W. Effect of Environmental Microorganisms on Fermentation Microbial Community of Sauce-Flavor baijiu. Foods 2023, 12, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Shu, N.; Hou, Q.; Tang, F.; Shan, C.; Yang, X.; Guo, Z. Insights into the Aroma Profile of Sauce-Flavor Baijiu by GC-IMS Combined with Multivariate Statistical Analysis. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2022, 2022, 4614330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, W.; Cao, X.; Cheng, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, T.; Wu, Q.; Xiang, P.; Shen, C.; Li, Q. Chinese Baijiu: The Perfect Works of Microorganisms. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 919044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Tian, Z.; Meng, W.; Li, Z. Microbial Diversity and Physicochemical Characteristics of the Maotai-Flavored Liquor Fermentation Process. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2020, 20, 4097–4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ding, Z.; Dong, W.; Li, W.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Ma, H.; Sun, B.; Li, X. Analysis of differences in microorganisms and aroma profiles between normal and off-flavor pit mud in Chinese strong-flavor Baijiu. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2024, 137, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.; Su, W.; Mu, Y.; Qi, Q.; Zhang, D. Study on the correlation between microbial communities with physicochemical properties and flavor substances in the Xiasha round of cave-brewed sauce-flavor Baijiu. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1124817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, J.; Yang, S.; Shen, Y.; Cheng, W.; Li, H.; Sun, J.; Huang, M.; Sun, B. What Are the Main Factors That Affect the Flavor of Sauce-Aroma Baijiu. Foods 2022, 11, 3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Zhao, D.; Sun, B. Research Progress on the Profile of Trace Components in Baijiu. Food Rev. Int. 2023, 39, 1666–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, E.; Zhang, C.; Lang, Y.; Li, X.; Hu, S.; Xu, Y.; Li, W.; Sun, B. Changes in Microbial Communities and Volatile Compounds during the Seventh Round of Sauce-Flavor baijiu Fermentation in Beijing Region. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2024, 82, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Quan, S.; Xia, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, W. Exploring the regulated effects of solid-state fortified Jiuqu and liquid-state fortified agent on Chinese Baijiu brewing. Food Res. Int. 2024, 179, 114024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Zou, W.; Shen, C.H.; Yang, J.G. Basic flavor types and component characteristics of Chinese traditional liquors: A review. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 4096–4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gernat, D.C.; Brouwer, E.; Ottens, M. Aldehydes as Wort Off-Flavours in Alcohol-Free Beers—Origin and Control. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2020, 13, 195–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehnhardt, F.; Nobis, A.; Skornia, A.; Becker, T.; Gastl, M. A Comprehensive Evaluation of Flavor Instability of Beer (Part 1): Influence of Release of Bound State Aldehydes. Foods 2021, 10, 2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.L.; Yu, Y.; Ramaswamy, H.S.; Zhu, S.M. Characterization of Chinese liquor aroma components during aging process and liquor age discrimination using gas chromatography combined with multivariable statistics. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 39671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakili, S.; Kivevele, T.; Kichonge, B.; Salifu, A.A.; King’ondu, C.K. Furfural from lignocellulose biomass a comprehensive review of hydrolysis methods production technologies and integration into the circular economy. Discov. Sustain. 2025, 6, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Hai, J.-q.; Wang, L.-y.; Long, X.-l. A study on the oxidation of toluene to benzaldehyde by air catalyzed by polyoxometalate loaded on activated carbon. Mol. Catal. 2023, 551, 113626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Maghrabey, M.H.; El-Shaheny, R.; El Hamd, M.A.; Al-Khateeb, L.A.; Kishikawa, N.; Kuroda, N. Aldehydes’ Sources, Toxicity, Environmental Analysis, and Control in Food. In Organic Pollutants: Toxicity and Solutions; Vasanthy, M., Sivasankar, V., Sunitha, T.G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 117–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Gao, Y.; Wang, L.; Yu, X.; Chen, S.; Xu, Y. Maillard reaction intermediates in Chinese Baijiu and their effects on Maillard reaction related flavor compounds during aging. Food Chem. X 2024, 22, 101356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Chen, S.; Xu, Y. Distilled beverage aging: A review on aroma characteristics, maturation mechanisms, and artificial aging techniques. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2023, 22, 502–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Su, W.; Mu, Y.; Mu, Y.; Jiang, L. Integrative Metagenomics–Metabolomics for Analyzing the Relationship Between Microorganisms and Non-volatile Profiles of Traditional Xiaoqu. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 617030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Wu, C.; Huang, J.; Zhou, R. Interphase microbial community characteristics in the fermentation cellar of Chinese Luzhou-flavor liquor determined by PLFA and DGGE profiles. Food Res. Int. 2015, 72, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloss Patrick, D.; Westcott Sarah, L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall Justine, R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister Emily, B.; Lesniewski Ryan, A.; Oakley Brian, B.; Parks Donovan, H.; Robinson Courtney, J.; et al. Introducing mothur: Open-Source, Platform-Independent, Community-Supported Software for Describing and Comparing Microbial Communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.J.; Zhu, H.M.; Ren, Z.Q.; Huang, Z.G.; Wei, C.H.; Deng, J. Characterization of Microbial Diversity and Community Structure in Fermentation Pit Mud of Different Ages for Production of Strong-Aroma Baijiu. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2020, 69, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Mu, Y.; Lv, X.; Chen, N.; Chen, L.; Wen, T.; Su, W. Analysis of fermentation characteristics in fermented grains across seven rounds of sauce-flavored Baijiu: Microbial communities structure, physicochemical parameters, volatile and non-volatile flavor compounds. Food Chem. X 2025, 25, 102228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Fan, G.; Fu, Z.; Wang, W.; Xu, Y.; Teng, C.; Zhang, C.; Yang, R.; Sun, B.; Li, X. Effects of fortification of Daqu with various yeasts on microbial community structure and flavor metabolism. Food Res. Int. 2020, 129, 108837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Shen, Y.; Chen, M.; Zhong, M.; Zhou, Y.; Luo, A. Characterisation of volatile compounds in Maotai flavour liquor during fermentation and distillation. J. Inst. Brew. 2019, 125, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.S.; Chong, M.N.; Poh, P.E.; Ocon, J.D.; Md Zoqratt, M.Z.H.; Lee, S.M. Impacts of morphological-controlled ZnO nanoarchitectures on aerobic microbial communities during real wastewater treatment in an aerobic-photocatalytic system. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 259, 113867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feranchuk, S.; Belkova, N.; Potapova, U.; Kuzmin, D.; Belikov, S. Evaluating the use of diversity indices to distinguish between microbial communities with different traits. Res. Microbiol. 2018, 169, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deepika, S.; Kothamasi, D. Plant hosts may influence arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal community composition in mangrove estuaries. Mycorrhiza 2021, 31, 699–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, R.; Zhang, C.; Li, X. Temporal Profile of the Microbial Community and Volatile Compounds in the Third-Round Fermentation of Sauce-Flavor baijiu in the Beijing Region. Foods 2024, 13, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Duan, Z.; Niu, J.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, C.; Li, W.; Li, X.; Sun, B. Spatial heterogeneity of microbiota and flavor across different rounds of sauce-flavor baijiu in Northern China. Food Chem. X 2023, 20, 100970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.-X.; Shi, W.; Huang, T.-C.; Mei, J.-L.; Lu, Z.-M.; Zhang, X.-J.; Yang, B.; Chen, X.-Y.; Wang, S.-T.; Shen, C.-H.; et al. Overproduction of organic acids affects the microbial community succession and flavor metabolism during Baijiu fermentation. LWT 2024, 213, 117093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Rao, W.; Hu, S.; Zhu, S.; Ouyang, L.; Zhou, J. Study on the relationship between microbial community succession and physicochemical factors in the fermentation of rice-flavor Baijiu based on high-throughput and redundancy analysis techniques. LWT 2024, 213, 117031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Qiu, S.; Lv, Y.; Li, D. Exploring the controllability of the Baijiu fermentation process with microbiota orientation. Food Res. Int. 2023, 173, 113249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Fan, Y.; Lu, T.; Kang, J.; Pang, X.; Han, B.; Chen, J. Composition and Metabolic Functions of the Microbiome in Fermented Grain during Light-Flavor Baijiu Fermentation. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yang, F.; Han, Y.; Yang, C.; Qin, X.; Zheng, H.; Chen, L.; Lu, J.; Zhang, C.; Lu, F.; et al. Aldehyde metabolism in Maotai-flavor Baijiu: Insights from integrated metagenomic and metaproteomic analyses. Food Res. Int. 2025, 221, 117518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, T.; Mu, Y.; Qi, Q.; Ren, T.; Su, W. Analysis of microbial community succession and its metabolic characteristics in the first and second rounds of cave-brewed sauce-flavor Baijiu. Food Biosci. 2024, 60, 104485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, D.; Xu, L.; Wang, C. Diversity of the microbial community and antioxidant activity during fermentation of red raspberry Enzymes. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, F.; Tan, Y.; Lv, X.; Chen, L.; Yang, F.; Wang, H.; Du, H.; Wang, L.; Xu, Y. Microbial Community Succession and Its Environment Driving Factors During Initial Fermentation of Maotai-Flavor Baijiu. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 669201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Chen, B.; Cheng, W.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Hu, J.; Luo, H.; Huang, D.; Tong, W.; Zhang, Y. Process Regulation of Microbial-Driven Aldehyde Metabolism in Sauce-Flavor Baijiu Fermentation. Foods 2026, 15, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods15010017
Chen B, Cheng W, Li Y, Yang Y, Hu J, Luo H, Huang D, Tong W, Zhang Y. Process Regulation of Microbial-Driven Aldehyde Metabolism in Sauce-Flavor Baijiu Fermentation. Foods. 2026; 15(1):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods15010017
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Bo, Wei Cheng, Yiyun Li, Ying Yang, Jixiang Hu, Huibo Luo, Dan Huang, Wenhua Tong, and Yadong Zhang. 2026. "Process Regulation of Microbial-Driven Aldehyde Metabolism in Sauce-Flavor Baijiu Fermentation" Foods 15, no. 1: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods15010017
APA StyleChen, B., Cheng, W., Li, Y., Yang, Y., Hu, J., Luo, H., Huang, D., Tong, W., & Zhang, Y. (2026). Process Regulation of Microbial-Driven Aldehyde Metabolism in Sauce-Flavor Baijiu Fermentation. Foods, 15(1), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods15010017





