Gel Properties and Interaction Mechanism of Heat-Induced Lentinan–Chicken Myofibrillar Protein
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of LNT
2.3. MP Extraction
2.4. Preparation of LNT-MP Gels
2.5. Determination of Water-Holding Capacity (WHC) and Oil-Holding Capacity (OHC)
2.6. Determination of Rheological Characteristics
2.7. Determination of Microstructure
2.8. Determination of Texture
2.9. Determination of Particle Size and Zeta Potential
2.10. Determination of Endogenous Fluorescence
2.11. Determination of Surface Hydrophobicity
2.12. Determination of Free Sulfhydryl Content
2.13. Determination of Protein Solubility
2.14. Determination of Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.15. Determination of X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.16. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of LNT Addition on the Gel Properties of MPs
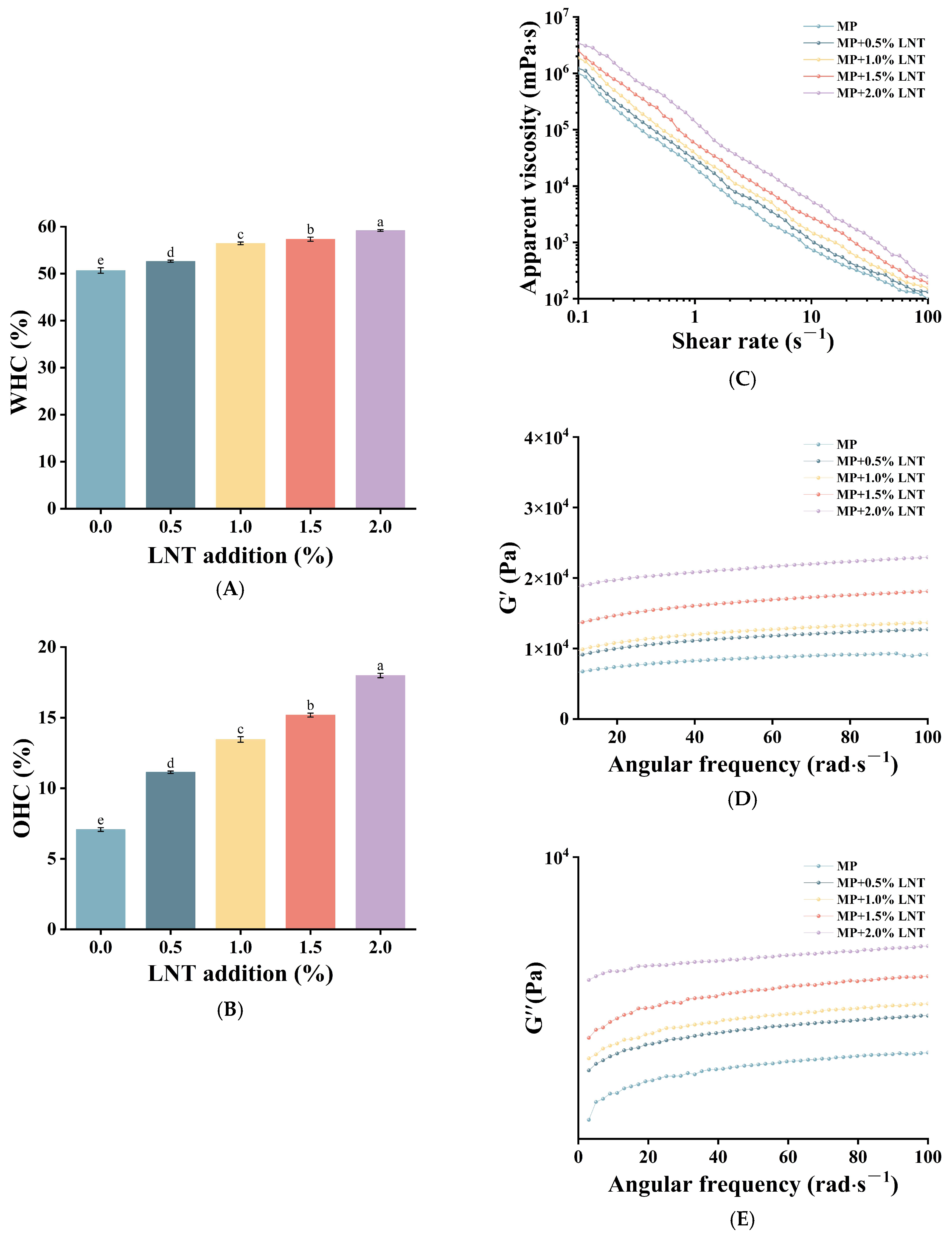
3.1.1. WHC and OHC Analysis
3.1.2. Rheological Analysis
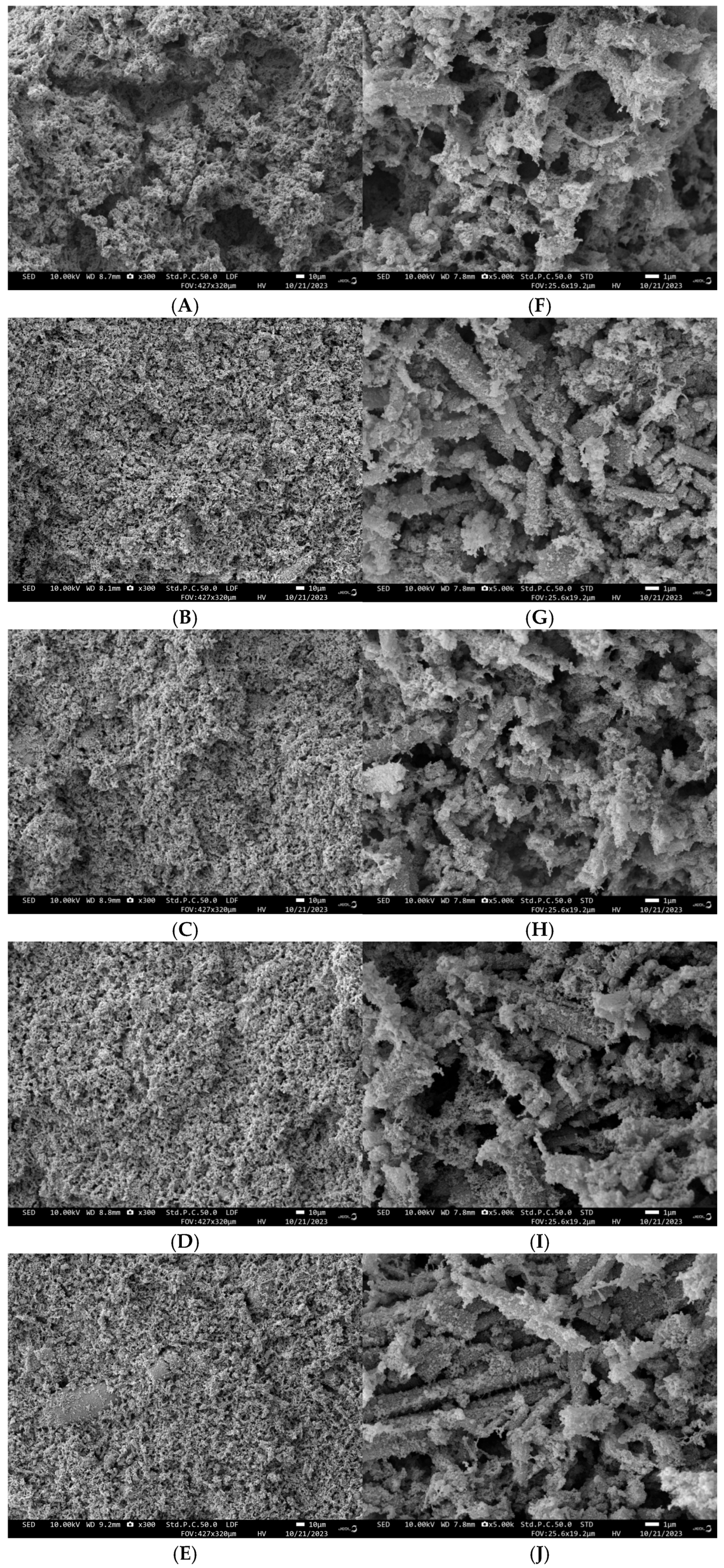
3.1.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy Analysis
3.1.4. Texture Analysis
3.2. Effect of LNT Addition on the Interaction Mechanism of LNT-MP Composite Gels
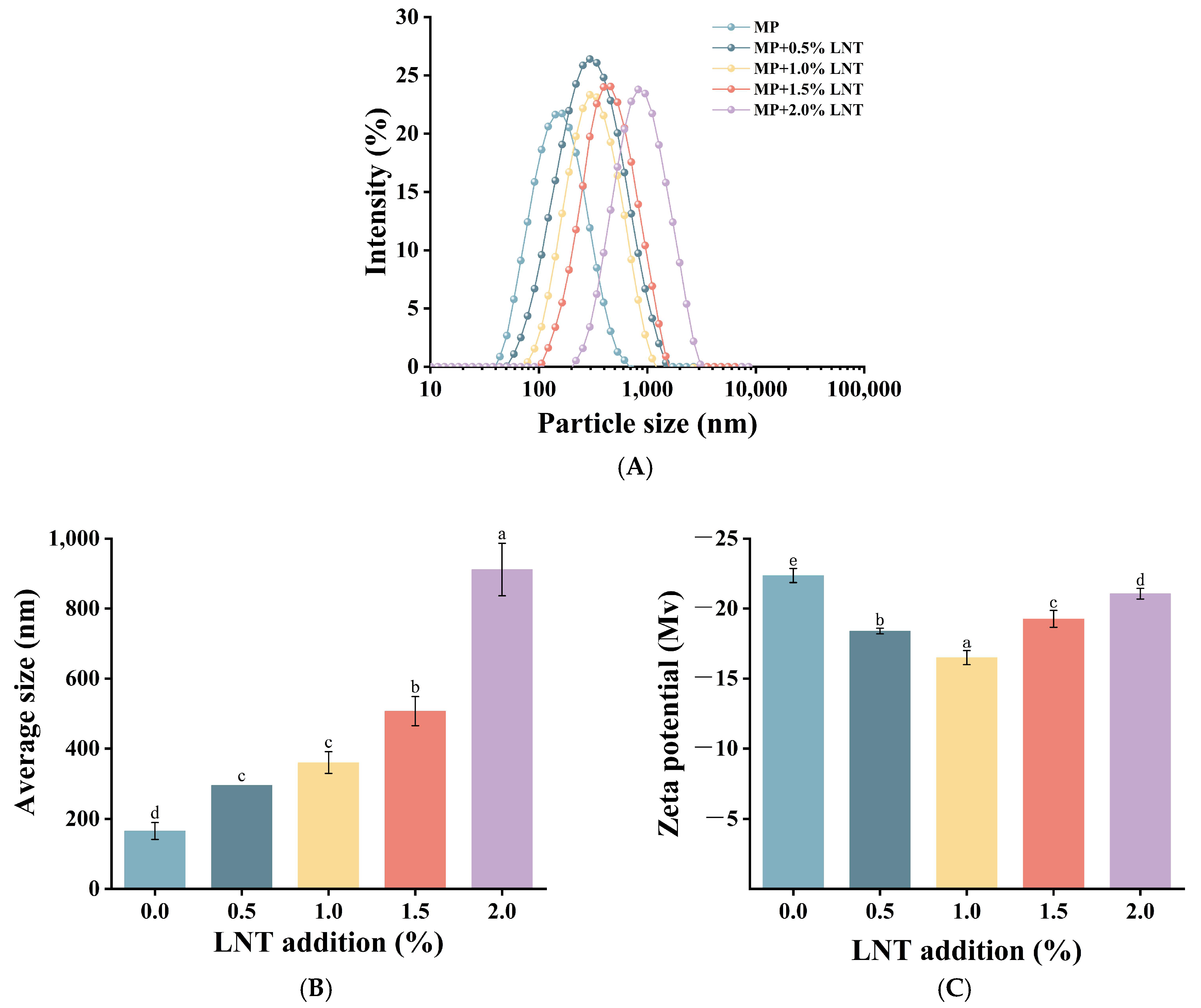
3.2.1. Particle Size and Zeta Potential Distribution Analysis
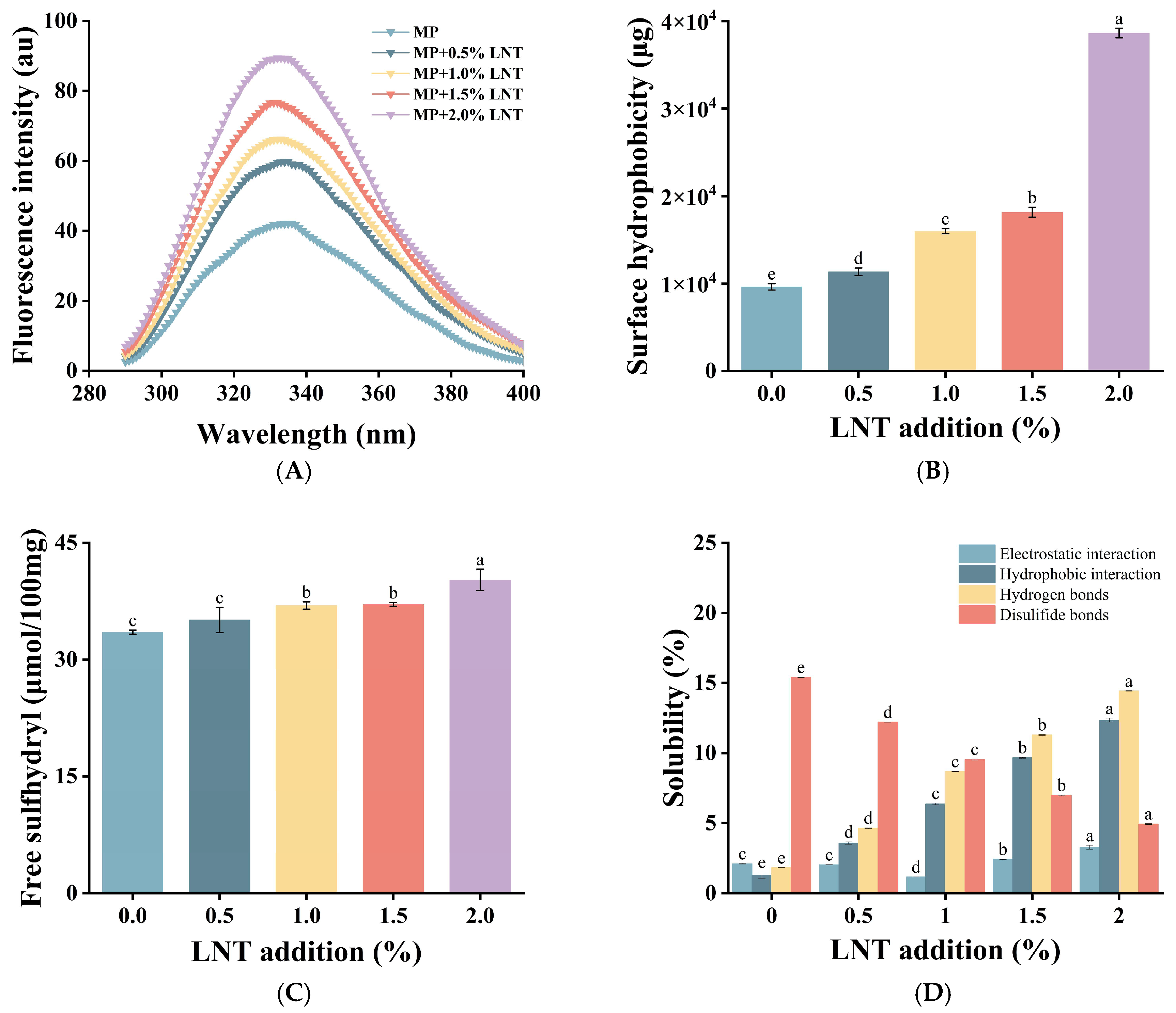
3.2.2. Endogenous Fluorescence Spectroscopy Analysis
3.2.3. Surface Hydrophobicity Analysis
3.2.4. Free Sulfhydryl Analysis
3.2.5. Solubility Analysis
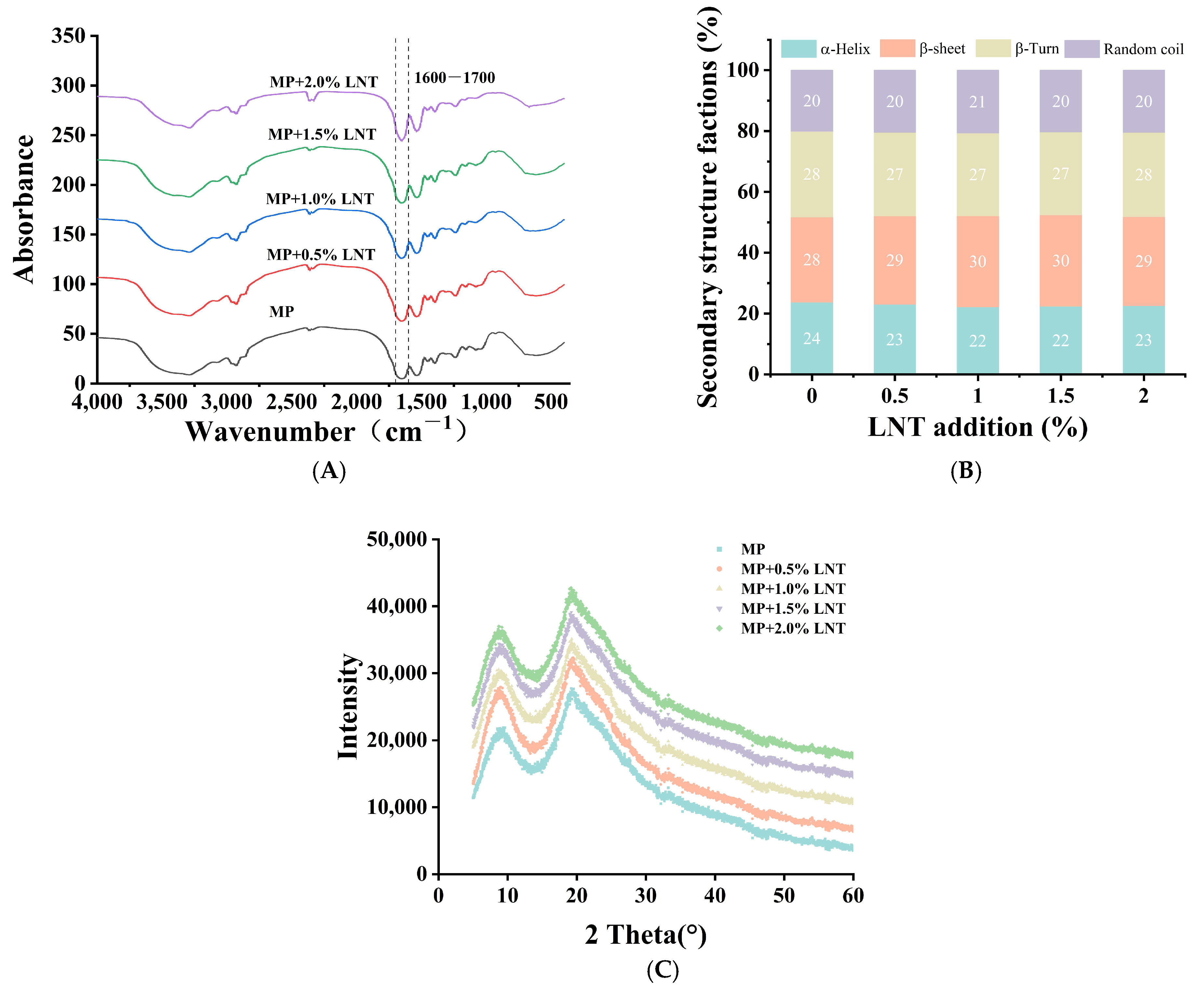
3.2.6. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Analysis
3.2.7. XRD Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, R.; Wang, S.; Li, K.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, S.; Zhao, D.; Bai, Y. Effect of chitooligosaccharides in inhibiting textural deterioration of chicken myofibril protein gel induced by high temperature. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 153, 110031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Cao, C.; He, J.; Kong, B.; Sun, F.; Liu, Q. Research Progress in the Regulatory Mechanism of Hydrocolloids on the Formation of Heat-Induced Myofibrillar Protein Gel. Food Sci. 2024, 45, 285–293. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Huang, W.; Feizollahi, E.; Roopesh, M.S.; Chen, L. Improvement of pea protein gelation at reduced temperature by atmospheric cold plasma and the gelling mechanism study. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2021, 67, 102567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Zha, X.-Q.; Li, Q.-M.; Pan, L.-H.; Luo, J.-P. Research progress on polysaccharide/protein hydrogels: Preparation method, functional property and application as delivery systems for bioactive ingredients. Food Res. Int. 2021, 147, 110542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, C.; Qiao, Y.; Li, J.; Liang, G.; Yun, S.; Cao, J.; Cheng, Y.; Cheng, F.; Chang, M.; Meng, J.; et al. Research Progress on Structure and Function of Polysaccharides from Edible Fungi. J. Shanxi Agric. Sci. 2024, 52, 128–144. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, D.; Xu, J.; Tu, D.; Zhuang, W.; Tian, Y. Effect of polysaccharide concentration on heat-induced Tremella fuciformis polysaccharide-soy protein isolation gels: Gel properties and interactions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 262, 129782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Blecker, C.; Wei, X.; Xie, X.; Li, S.; Chen, L.; Zhang, D. Effects of different plant polysaccharides as fat substitutes on the gel properties, microstructure and digestion characteristics of myofibrillar protein. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 150, 109717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.S.; Shin, J.; Hong, S.; Gopal, J.; Oh, J.-W. Anticarcinogenic potential of the mushroom polysaccharide lentinan on gastric and colon cancer cells: Antiproliferative, antitumorigenic, Mu-2-related death-inducing gene, MUDENG ramifications. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2024, 135, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Ju, Y.; Li, J.; Yu, M. Antioxidant activities of polysaccharides from Lentinus edodes and their significance for disease prevention. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 50, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, H.; Shimura, T.; Mizoshita, T.; Kubota, E.; Mori, Y.; Mizushima, T.; Wada, T.; Ogasawara, N.; Tanida, S.; Sasaki, M.; et al. Lentinan with S-1 and paclitaxel for gastric cancer chemotherapy improve patient quality of life. Hepatogastroenterology 2009, 56, 547–550. [Google Scholar]
- Nakano, H.; Namatame, K.; Nemoto, H.; Motohashi, H.; Nishiyama, K.; Kumada, K. A multi-institutional prospective study of lentinan in advanced gastric cancer patients with unresectable and recurrent diseases: Effect on prolongation of survival and improvement of quality of life. Kanagawa Lentinan Research Group. Hepatogastroenterology 1999, 46, 2662–2668. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Wu, D.; Li, W.; Chen, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wan, J.; Yu, H.; Zhou, S.; Yang, Y. Structural elucidation and anti-inflammatory activity of a proteoglycan from spent substrate of Lentinula edodes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 224, 1509–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, S.; Hasan, M.; Ahmad, A.; Richards, S.-J.; Dietrich, B.; Wallace, M.; Tang, Q.; Smith, A.J.; Gibson, M.I.; Adams, D.J. Mechanical release of homogenous proteins from supramolecular gels. Nature 2024, 631, 544–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, C.; Christian, S.; Sylvie, D.-B.; Hardy, J. Structure and Technofunctional Properties of Protein-Polysaccharide Complexes: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1998, 38, 689–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Chen, J.; Hemar, Y.; Cui, B. Improvement of the rheological and textural properties of calcium sulfate-induced soy protein isolate gels by the incorporation of different polysaccharides. Food Chem. 2020, 310, 125983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, L.; Jia, F.; Wu, J.; Jin, W.; Zhao, W.; Cao, J.; Cheng, Y.; Shi, L.; Yun, S.; et al. Exploring the effect of pH-shifting on the gel properties and interaction of heat-induced Flammulina velutipes polysaccharide-porcine myofibrillar protein for improving the quality of Flammulina velutipes-pork patties. Food Chem. 2025, 465, 142187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Bai, X.; Li, Y.; Kong, B.; Nuerjiang, M.; Wu, K.; Li, Z.; Xia, X. Improvement on gel properties of myofibrillar protein from chicken patty with potato dietary fiber: Based on the change in myofibrillar protein structure and water state. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 230, 123228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, F.; Hamidian, Y.; Behrouzifar, F.; Mostafazadeh, R.; Ghorbani-HasanSaraei, A.; Alizadeh, M.; Mortazavi, S.-M.; Janbazi, M.; Naderi Asrami, P. An applicable method for extraction of whole seeds protein and its determination through Bradford’s method. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 164, 113053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Guo, J.; Wang, X.; Yang, K.; Wang, L.; Ma, J.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, W. The direct current magnetic field improved the water retention of low-salt myofibrillar protein gel under low temperature condition. LWT 2021, 151, 112034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Lu, K.; Piao, X.; Song, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhou, R.; Gao, P.; Khong, H.Y. Collagens for surimi gel fortification: Type-dependent effects and the difference between type I and type II. Food Chem. 2023, 407, 135157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiong, A.Y.J.; Crawford, S.; Jones, N.C.; McKinley, G.H.; Batchelor, W.; van’t Hag, L. Pea and soy protein isolate fractal gels: The role of protein composition, structure and solubility on their gelation behaviour. Food Struct. 2024, 40, 100374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yuan, K.; Zhang, H.; Luo, S.; Wang, S.; Yang, X.; Guo, Y. Regulation on gel textures of Nicandra physalodes (Linn.) Gaertn. pectin by its synergistic interaction with sodium alginate. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 134, 108047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Fu, L.; Zhao, Y.-Y.; Xue, S.-W.; Wang, P.; Xu, X.-L.; Bai, Y.-H. Use of high-intensity ultrasound to improve emulsifying properties of chicken myofibrillar protein and enhance the rheological properties and stability of the emulsion. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 98, 105275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Yang, L.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, H.; Wang, H.; Su, A. Modulation of the conformation, water distribution, and rheological properties of low-salt porcine myofibrillar protein gel influenced by modified quinoa protein. Food Chem. 2024, 455, 139902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhao, J.; Guo, F.; Wang, Y. Enhanced gelling properties and hydration capacity of ginkgo seed proteins by genipin cross-linking. Food Chem. 2023, 399, 133924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellman, G.L. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1959, 821, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.; Rosebrough, N.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R. Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 1931, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Pang, X.; Lu, J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, S.; Lv, J. Effect of high intensity ultrasound pretreatment on functional and structural properties of micellar casein concentrates. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 47, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandal, K.; Jindal, R. β-Cyclodextrin mediated controlled release of phenothiazine from pH-responsive pectin and pullulan-based hydrogel optimized through experimental design. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 278, 135045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, H.; Stepanova, T.; Kondratiuk, N.; Nie, Y.; Li, B. Effects of Agaricus bisporus on gel properties of chicken myofibrillar protein. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 5532–5541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, L.; Lan, G.; Wang, Y.; Xie, S.; Cai, S.; Liu, Q.; Chen, P.; Xie, F. Mastering textural control in multi-polysaccharide gels: Effect of κ-carrageenan, konjac glucomannan, locust bean gum, low-acyl gellan gum, and sodium alginate. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 254, 127885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Li, N.; Zhang, W.; Guo, Y.; Yu, D.; Cheng, J.; Wang, L. Construction of hemp seed protein isolate-phosphatidylcholine stablized oleogel-in-water gel system and its effect on structural properties and oxidation stability. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Ju, X.; Wang, Z.; He, R. Study of monoglycerides enriched with unsaturated fatty acids at sn-2 position as oleogelators for oleogel preparation. Food Chem. 2021, 354, 129534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroso, N.G.; Okuro, P.K.; Ribeiro, A.P.B.; Cunha, R.L. Tailoring Properties of Mixed-Component Oleogels: Wax and Monoglyceride Interactions Towards Flaxseed Oil Structuring. Gels 2020, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuomo, F.; Cofelice, M.; Lopez, F. Rheological Characterization of Hydrogels from Alginate-Based Nanodispersion. Polymers 2019, 11, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizarraga, M.S.; Piante Vicin, D.D.; González, R.; Rubiolo, A.; Santiago, L.G. Rheological behaviour of whey protein concentrate and λ-carrageenan aqueous mixtures. Food Hydrocoll. 2006, 205, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Meng, Z.; Hu, J.; Li, Q.; Dong, Y.; Cai, C.; Zhu, Y. Impact of Flammulina velutipes polysaccharide on properties and structural changes of pork myofibrillar protein during the gel process in the absence or presence of oxidation. Food Chem. 2024, 450, 139300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, K.; Wu, D.; Gong, H.; Guo, L.; Ma, J.; Sun, W. Study on the interaction and gel properties of pork myofibrillar protein with konjac polysaccharides. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 104, 2284–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Shen, M.; Jiang, L.; Song, Q.; Liu, S.; Xie, J. Influence of Mesona blumes polysaccharide on the gel properties and microstructure of acid-induced soy protein isolate gels. Food Chem. 2020, 313, 126125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjonu, R.; Doran, G.; Torley, P.; Agboola, S. Whey protein peptides as components of nanoemulsions: A review of emulsifying and biological functionalities. J. Food Eng. 2014, 122, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Zhao, M.; McClements, D.J. Improving the stability of wheat protein-stabilized emulsions: Effect of pectin and xanthan gum addition. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 43, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Huang, X.; Shi, L.; Liu, S.; Yang, S.; Hao, G.; Qiu, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Characteristics and potential application of myofibrillar protein from golden threadfin bream (Nemipterus virgatus) complexed with chitosan. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 240, 124380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Dong, Q.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, F.; Liu, F. Bifunctional Inhibitor Lentinan Inhibits Fibrillogenesis of Amyloid-β Protein and α-Synuclein and Alleviates Their Cytotoxicity: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2024, 15, 3437–3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, C.; Liang, X.; Xu, Y.; Kong, B.; Sun, F.; Liu, H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Q.; Wang, H. Effects and mechanisms of different κ-carrageenan incorporation forms and ionic strength on the physicochemical and gelling properties of myofibrillar protein. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 257, 128659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Li, S.; Yang, Y.; Feng, X.; Tang, X.; Chen, Y. Mechanisms of inulin addition affecting the properties of chicken myofibrillar protein gel. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 131, 107843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walayat, N.; Tang, W.; Wang, X.; Yi, M.; Guo, L.; Ding, Y.; Liu, J. Effective role of konjac oligosaccharide against oxidative changes in silver carp proteins during fluctuated frozen storage. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 131, 107761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Fu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Guo, W.; Hu, R.; Liu, X. Effects of different ph on properties of heat-induced Auricularia auricula-judae polysaccharide-whey protein isolate composite gels. Food Struct. 2023, 36, 100317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Tu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Xin, X.; Hu, H.; Qiu, W.; Ruan, D.; Zhao, Y. Mechanism of ultrasound and tea polyphenol assisted ultrasound modification of egg white protein gel. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 81, 105857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resendiz-Vazquez, J.A.; Ulloa, J.A.; Urías-Silvas, J.E.; Bautista-Rosales, P.U.; Ramírez-Ramírez, J.C.; Rosas-Ulloa, P.; González-Torres, L. Effect of high-intensity ultrasound on the technofunctional properties and structure of jackfruit (Artocarpus heterophyllus) seed protein isolate. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 37, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Kang, S.; Liu, Y.; Guo, X.; Li, M.; Xu, H. Effect and mechanism of calcium ions on the gelation properties of cellulose nanocrystals-whey protein isolate composite gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silventoinen, P.; Sozer, N. Impact of Ultrasound Treatment and pH-Shifting on Physicochemical Properties of Protein-Enriched Barley Fraction and Barley Protein Isolate. Foods 2020, 9, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yuan, X.; Kang, Z.; Zhu, M.; Ma, H. High-pressure processing influences the conformation, water distribution, and gel properties of pork myofibrillar proteins containing Artemisia sphaerocephala Krasch gum. Food Chem. X 2022, 14, 100320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Gu, Y.; Zhu, J. Design and characterization of low salt myofibrillar protein-sugar beet pectin double-crosslinked gels pretreated by ultrasound and konjac glucomannan: Conformational and gelling properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 141, 108717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-J.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Li, L.; Zheng, J.; Wang, C.; Lai, B.; Yan, J.-N.; Wu, H.-T. Gelation and film-forming properties of ternary composite gels constructed by scallop (Patinopecten yessoensis) protein hydrolysates, SDS, and polysaccharides. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 154, 110080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Wang, J.; Xu, J.; Sun, X.; Li, P.; Fan, Y. Construction of chitosan-gelatin polysaccharide-protein composite hydrogel via mechanical stretching and its biocompatibility in vivo. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 264, 130357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekala, S.; Saldaña, M.D.A. Lentil protein concentrate + pectin gels dried with SC-CO2: Influence of protein-polysaccharide interactions on the characteristics of aerogels. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2023, 201, 106006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Yang, X.; Yin, S.; Li, R.; Zhang, S.; Li, L. Gelation behaviour of Auricularia polytricha polysaccharides-whey protein isolate. J. Food Eng. 2024, 377, 112079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| LNT Addition (%) | Cohesiveness (Ratio) | Springiness (mm) | Gumminess (N) | Chewiness (mJ) | Hardness (N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.21 ± 0.01 d | 1.56 ± 0.01 d | 0.43 ± 0.01 d | 0.69 ± 0.01 e | 1.83 ± 0.01 d |
| 0.5 | 0.22 ± 0.003 d | 1.74 ± 0.02 c | 0.50 ± 0.01 c | 0.91 ± 0.01 d | 1.87 ± 0.01 d |
| 1 | 0.24 ± 0.003 c | 1.75 ± 0.01 c | 0.57 ± 0.01 b | 1.02 ± 0.01 c | 1.93 ± 0.02 c |
| 1.5 | 0.26 ± 0.003 b | 1.85 ± 0.01 b | 0.59 ± 0.003 b | 1.06 ± 0.01 b | 2.60 ± 0.02 b |
| 2 | 0.31 ± 0.01 a | 2.03 ± 0.01 a | 0.62 ± 0.003 a | 1.15 ± 0.01 a | 2.75 ± 0.02 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, K.; Ren, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Cheng, Y.; Yun, S.; Cheng, F.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, L.; Chang, M.; et al. Gel Properties and Interaction Mechanism of Heat-Induced Lentinan–Chicken Myofibrillar Protein. Foods 2025, 14, 1614. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091614
Li K, Ren Y, Li Y, Li L, Cheng Y, Yun S, Cheng F, Zhao W, Zhao L, Chang M, et al. Gel Properties and Interaction Mechanism of Heat-Induced Lentinan–Chicken Myofibrillar Protein. Foods. 2025; 14(9):1614. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091614
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Kexin, Ya Ren, Yong Li, Liang Li, Yanfen Cheng, Shaojun Yun, Feier Cheng, Wenfei Zhao, Li Zhao, Mingchang Chang, and et al. 2025. "Gel Properties and Interaction Mechanism of Heat-Induced Lentinan–Chicken Myofibrillar Protein" Foods 14, no. 9: 1614. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091614
APA StyleLi, K., Ren, Y., Li, Y., Li, L., Cheng, Y., Yun, S., Cheng, F., Zhao, W., Zhao, L., Chang, M., Cao, J., & Feng, C. (2025). Gel Properties and Interaction Mechanism of Heat-Induced Lentinan–Chicken Myofibrillar Protein. Foods, 14(9), 1614. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091614






