A Molecularly Imprinted Fluorescence Sensor for the Simultaneous and Rapid Detection of Histamine and Tyramine in Cheese
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Preparation of CdSe/ZnS Quantum Dots
2.3. Preparation of Imprinted Polymer Fluorescent Sensor with Histamine and Tyramine as Dual Templates
2.4. Detection of the Sensitivity of CdSe/ZnS-MIP to Biogenic Amines
2.5. Specific Detection of Structural Analogs by CdSe/ZnS-MIP
2.6. Application of CdSe/ZnS-MIP in Cheese Samples
3. Results and Discussion
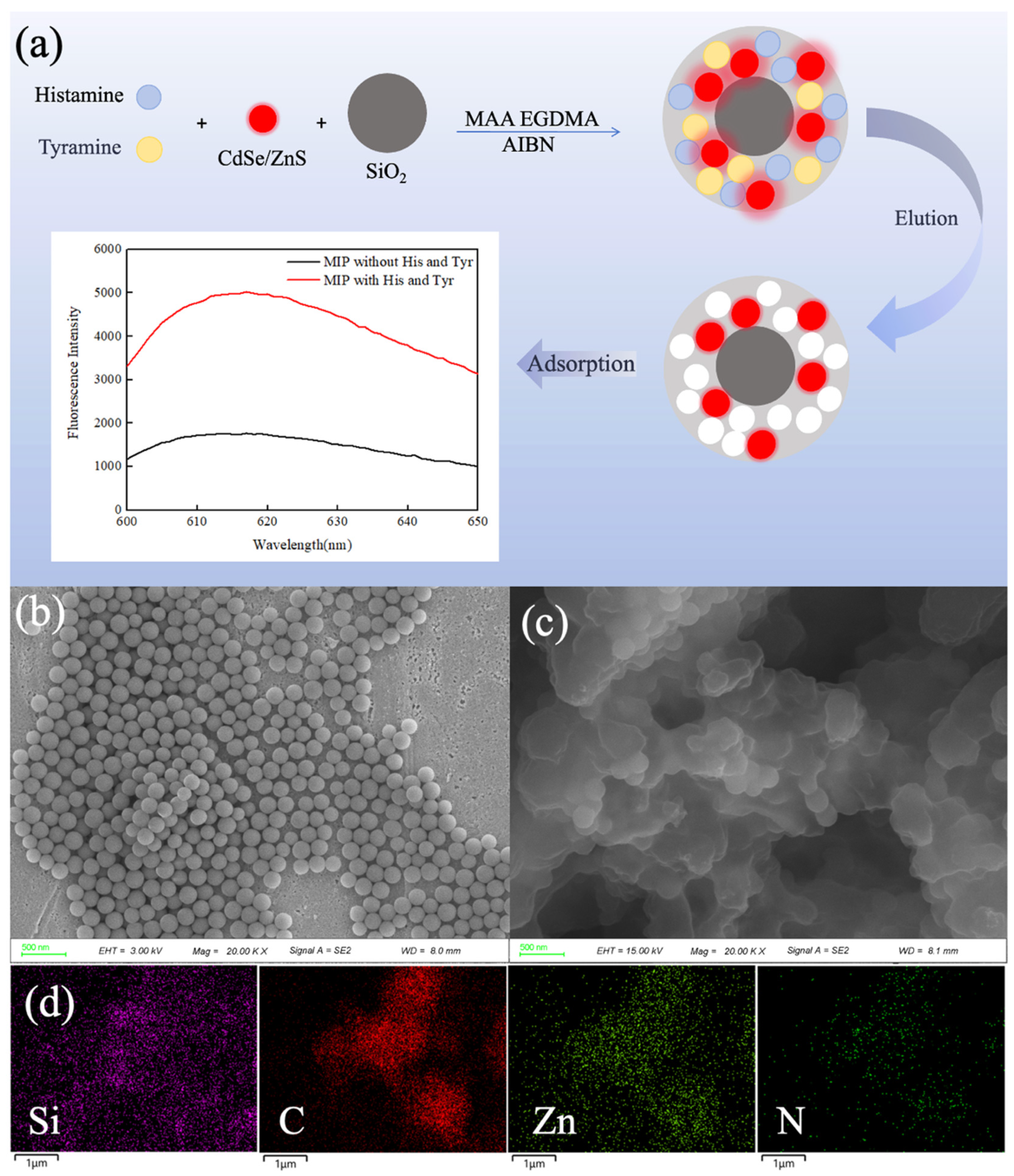
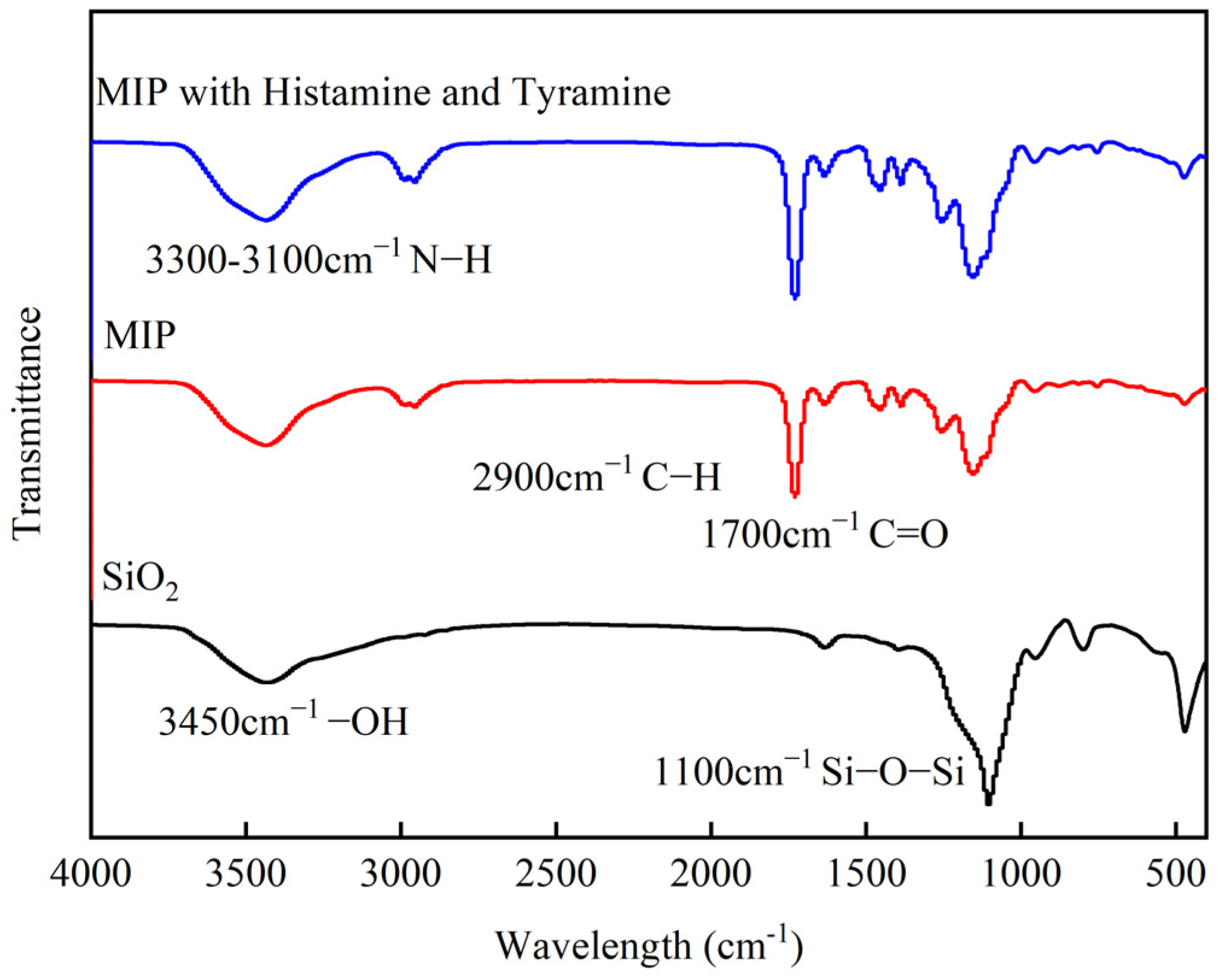
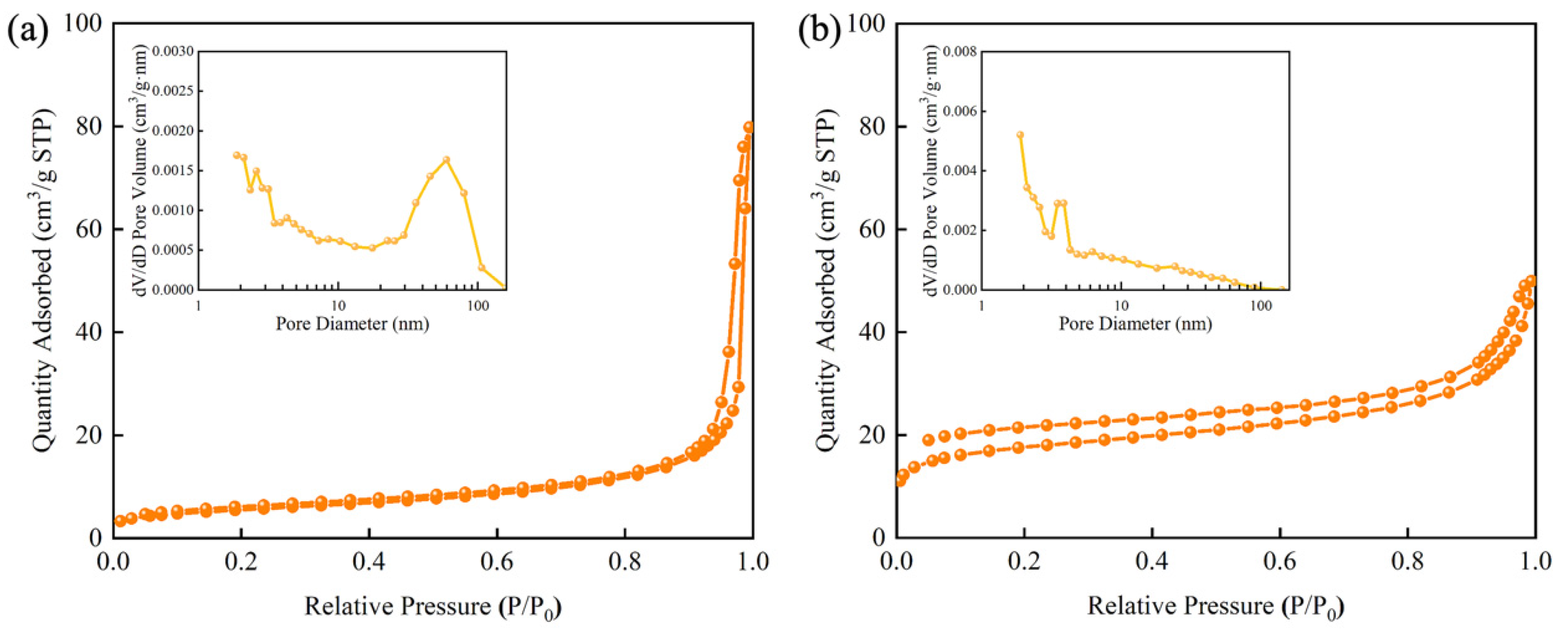
3.1. Preparation Principle and Characterizations of CdSe/ZnS-MIP
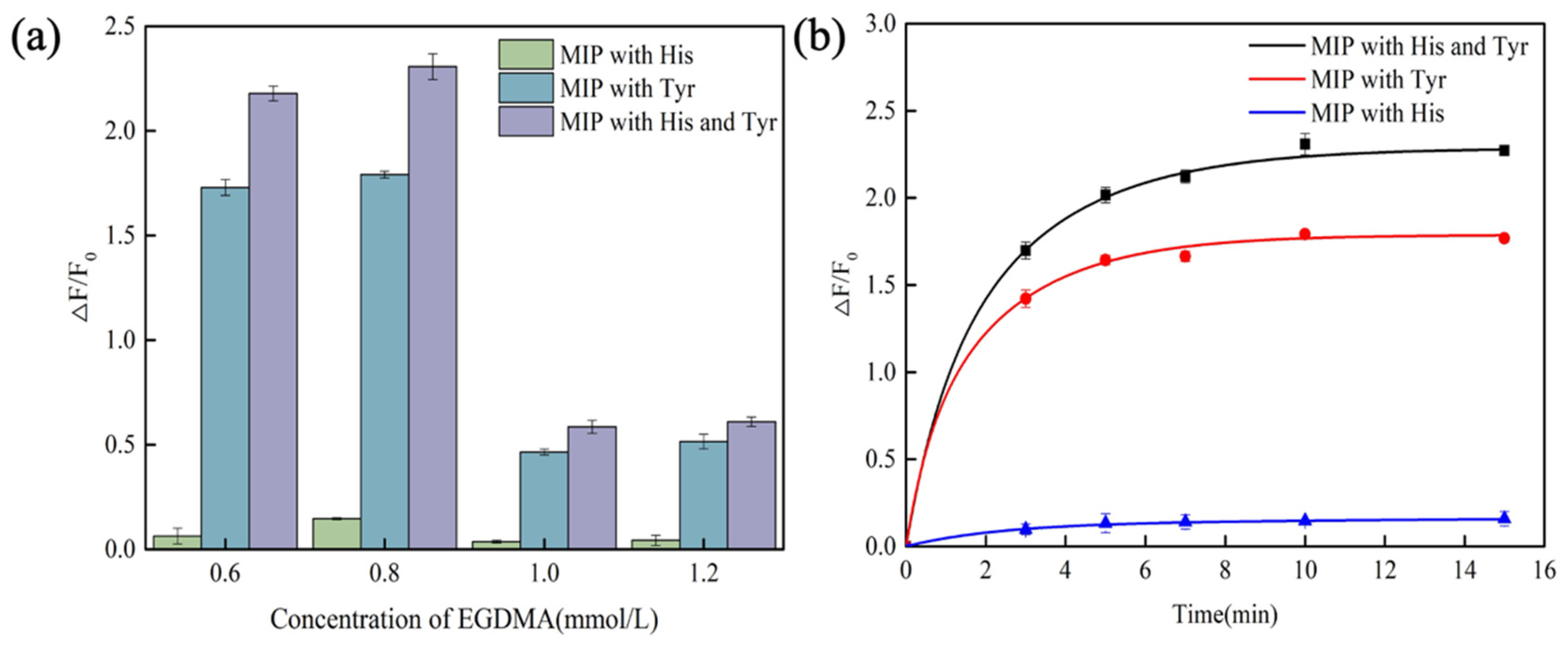
3.2. Optimization of Polymerization and Detection Conditions
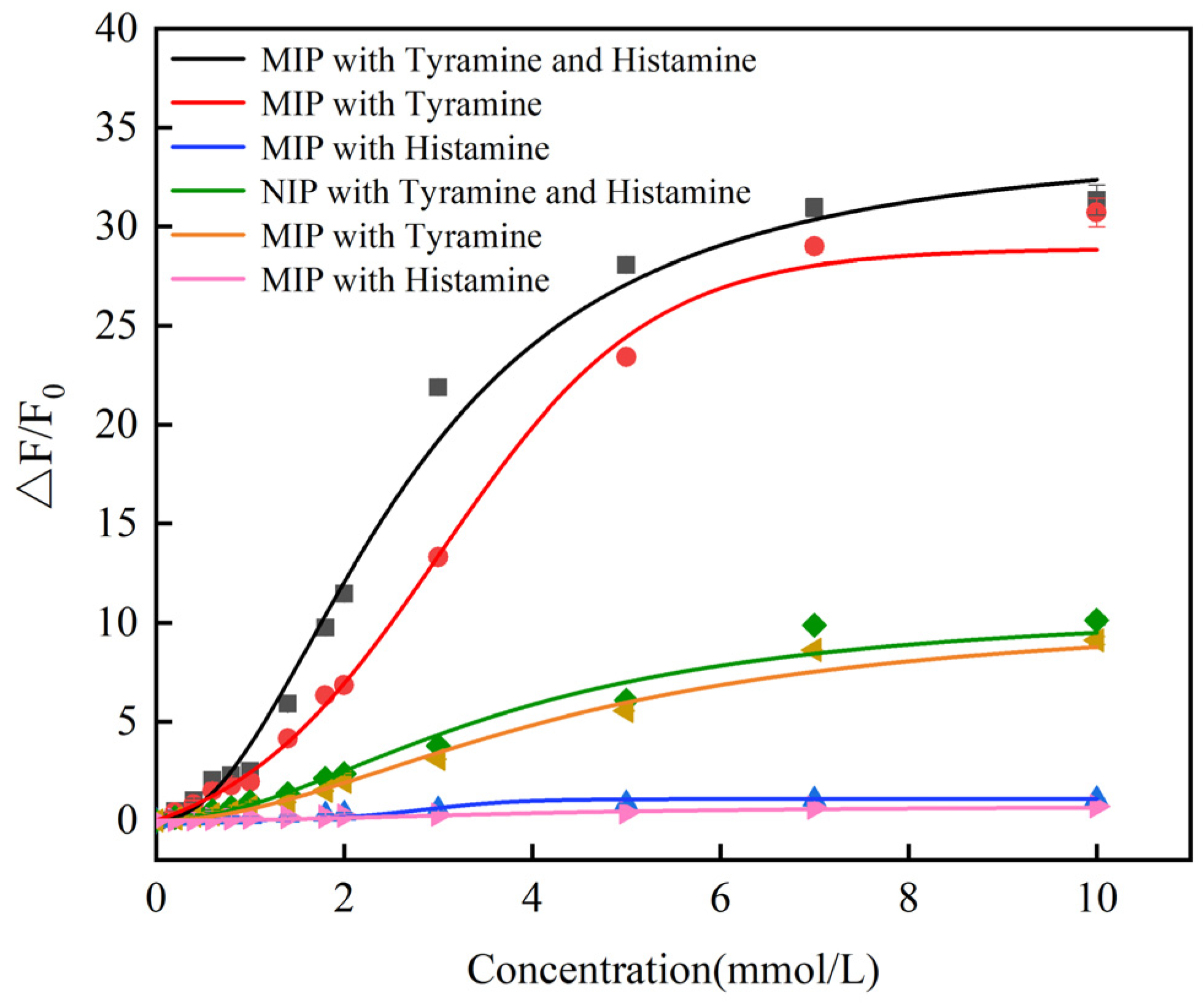
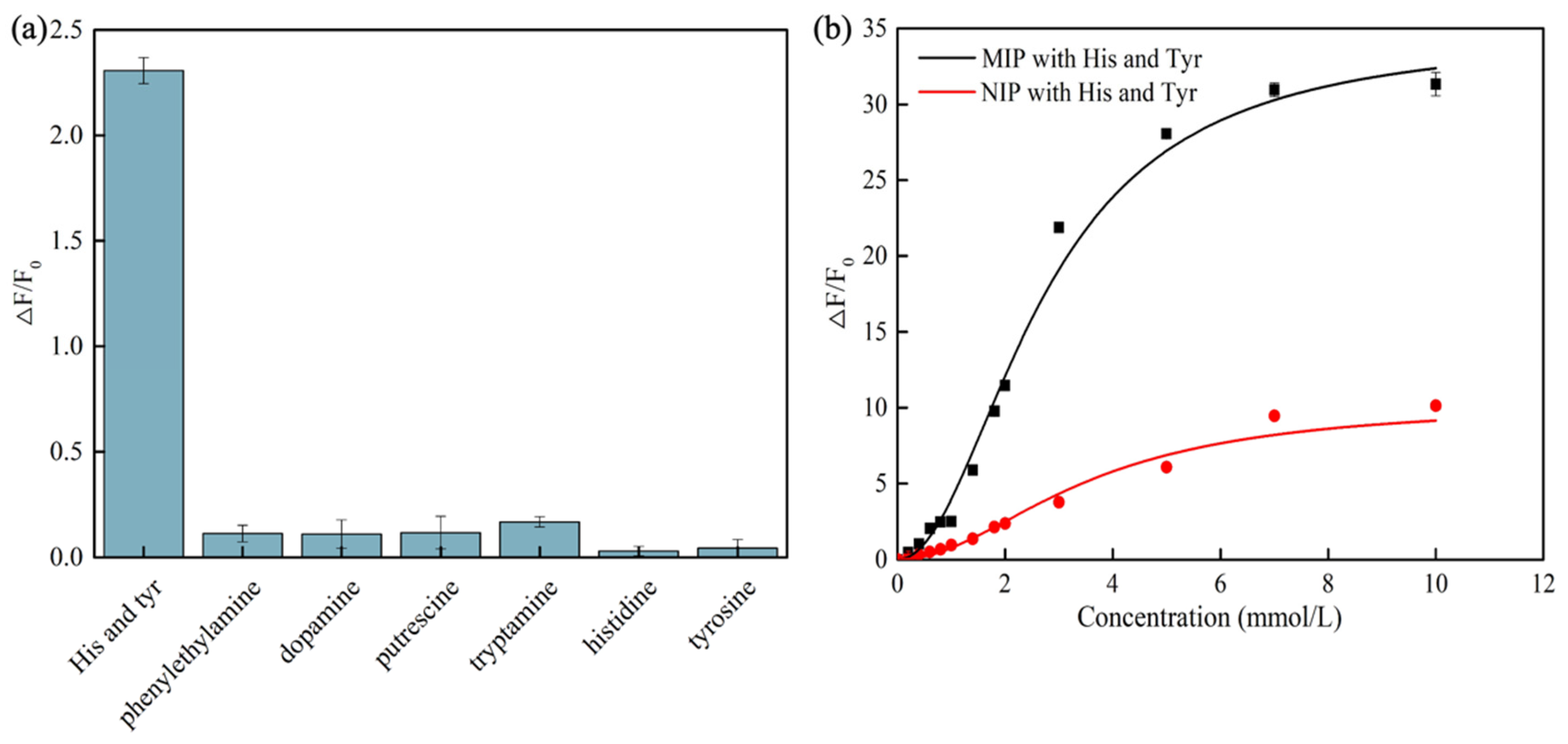
3.3. Sensitivity of CdSe/ZnS-MIP for Histamine and Tyramine
3.4. Selectivity and Stability of CdSe/ZnS-MIP for Histamine and Tyramine
3.5. Application of CdSe/ZnS-MIP in Cheese Samples
3.6. Comparison of CdSe/ZnS-MIP with Other Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tan, F.; Wang, B.; Li, L.; Yu, Q.; Cai, J.; Zhang, M. The Effect of Non-Saccharomyces Yeasts on Biogenic Amines in Sauvignon Blanc Wine and Gewürztraminer Wine. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 104153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves da Silva, A.; Franco, D.L.; Santos, L.D. A Simple, Fast, and Direct Electrochemical Determination of Tyramine in Brazilian Wines Using Low-Cost Electrodes. Food Control 2021, 130, 108369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dala-Paula, B.M.; Custódio, F.B.; Gloria, M.B. Health Concerns Associated with Biogenic Amines in Food and Interaction with Amine Oxidase Drugs. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2023, 54, 101090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishioh, M.; Nozu, T.; Miyagishi, S.; Igarashi, S.; Funayama, T.; Ueno, N.; Okumura, T. Brain Histamine Improves Colonic Hyperpermeability through the Basal Forebrain Cholinergic Neurons, Adenosine A2B Receptors and Vagus Nerve in Rats. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2024, 224, 116201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Wang, K.; Xue, X.; Wen, Q.; Qin, S.; Suo, Y.; Liang, M. The Effects of Different Processing Methods on the Levels of Biogenic Amines in Zijuan Tea. Foods 2022, 11, 1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aladhadh, M.; Nasser Binjawhar, D.; Abd El-Kader Ebrahim, H.N.E.-D.; Radhi, K.S.; Almatrafi, M.; Fayad, E.; Al-Saman, M.A.; Elsanhoty, R.M. Investigation of Biogenic Amine Levels and Microbiological Activity as Quality Markers in Some Dairy and Fish Products in Food Markets in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 19193–19202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iko Afé, O.H.; Saegerman, C.; Kpoclou, Y.E.; Douny, C.; Igout, A.; Mahillon, J.; Anihouvi, V.B.; Hounhouigan, D.J.; Scippo, M.-L. Contamination of Smoked Fish and Smoked-Dried Fish with Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Biogenic Amines and Risk Assessment for the Beninese Consumers. Food Control 2021, 126, 108089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Lin, X.; Liang, H.; Chen, Y.; Ji, C. Heterologous Expression of the Lactobacillus Sakei Multiple Copper Oxidase to Degrade Histamine and Tyramine at Different Environmental Conditions. Foods 2022, 11, 3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.; Xing, S.; Yao, G.; Yong, W.; Ling, Y.; Chu, B. Simultaneous Quantification of 14 Glucosinolates in Rapeseeds by Ultra High Performance Liquid Chromatography—Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Food Chem. 2025, 467, 142302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonomiya, J.; Li, K.S.; Babin, B.M.; Mulvihill, M.M. Covalent Library Screening by Targeted Mass Spectrometry for Rapid Binding Site Identification. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 3779–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkal, M.A.; Nardin, C. Pesticide Biosensors: Trends and Progresses. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2023, 415, 5899–5924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chafi, S.; Ballesteros, E. A Simple, Efficient, Eco-Friendly Sample Preparation Procedure for the Simultaneous Determination of Hormones in Meat and Fish Products by Gas Chromatography—Mass Spectrometry. Foods 2022, 11, 3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, S.A.; Jooyandeh, H. Investigation on the Effect of Persian Gum and Transglutaminase Enzyme on Some Physicochemical and Microstructural Characteristics of Low-Fat Ultrafiltrated Iranian White Cheese. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 12, 9810–9821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsenzadeh, E.; Ratautaite, V.; Brazys, E.; Ramanavicius, S.; Zukauskas, S.; Plausinaitis, D.; Ramanavicius, A. Application of Computational Methods in the Design of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers (Review). TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 171, 117480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.S.; Thotathil, V.; Zaidi, S.A.; Sheikh, H.; Mohamed, M.; Qureshi, A.; Sadasivuni, K.K. Picomolar or beyond Limit of Detection Using Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Electrochemical Sensors: A Review. Biosensors 2022, 12, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Dong, Q.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, Y. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers with Shape-Memorable Imprint Cavities for Efficient Separation of Hemoglobin from Blood. Biomacromolecules 2023, 24, 1233–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Li, A.; Zhang, A.; Wei, S.; Zhang, M.; Wu, Z.; Jung, K.; Boyer, C.; Liu, J. Enzyme Mimics Based on Molecular Imprinting Polymers: Applications and Perspective. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 499, 156433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Xu, W.; Xu, G.; Jia, Q. An Updated Overview of MOF@MIP in Drug Carrier and Drug Analysis: Construction, Application and Prospective. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 167, 117275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Shang, J.; Liu, S.; Tian, X.; Yao, X.; Liu, F.; Zhu, R.; Wang, Y.; Gao, R.; Wang, S. Preparation of Protein-Resistant Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymers as Solid-Phase Extraction Adsorbents via a One-Stone-Two-Birds Strategy for Selective Enrichment of Tetracycline in Milk. Talanta 2025, 287, 127678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, R.; Liao, D.; Yan, W.; Liang, W.; Zhi, J.; Guo, Y.; Dong, C.; Fan, L. Design an Efficient Molecularly Imprinted Photoelectrochemical Sensor for Detection of Butyl Benzyl Phthalate. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2025, 430, 137357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Sun, D.; Li, J.; Ostovan, A.; Wang, X.; Ma, J.; You, J.; Muhammad, T.; Chen, L.; Arabi, M. The Metal- and Covalent-Organic Frameworks-Based Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Composites for Sample Pretreatment. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 178, 117830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, D. A Novel Fluorescence Sensing Method Based on Quantum Dot-Graphene and a Molecular Imprinting Technique for the Detection of Tyramine in Rice Wine. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 3884–3889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Ashley, J.; Zhou, T.; Halder, A.; Sun, Y. A Facile Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Fluorometric Assay for Detection of Histamine. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 2365–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.-X.; Zhao, N.; Liu, J.-M.; Fang, G.-Z.; Wang, S. Ultra-Stable UiO-66 Involved Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Specific and Sensitive Determination of Tyramine Based on Quartz Crystal Microbalance Technology. Polymers 2020, 12, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Ma, Y.; Liao, Y.; Wang, F.; Liu, H. Fabrication of Fluorescence Probe Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymers on Red Emissive Biomass-Derived Carbon Dots Coupled with Smartphone Readout for Tyramine Determination in Fermented Meat Products. Microchim. Acta 2024, 191, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Tian, X.; Xu, X. A Molecular Imprinted Ratiometric Fluorescence Sensor Based on Blue/Orange MXene Quantum Dots for Visual Detection of Histamine. Food Chem. 2024, 460, 140519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB5009.208-2016; Determination of Biogenic Amines in Food. National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China, State Administration for Market Regulation: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Wang, G.-L.; Jiao, H.-J.; Zhu, X.-Y.; Dong, Y.-M.; Li, Z.-J. Enhanced Fluorescence Sensing of Melamine Based on Thioglycolic Acid-Capped CdS Quantum Dots. Talanta 2012, 93, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.-H.; Fang, G.-Z.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Zhang, D.-D.; Liu, J.-M.; Wang, S. Fluorescent Sensing Probe for the Sensitive Detection of Histamine Based on Molecular Imprinting Ionic Liquid-Modified Quantum Dots. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 2585–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Yao, A.; Ding, Y.; Leng, Q.; Teng, F.; Zhao, L.; Sun, R.; Bu, H. A Dual-Template Imprinted Polymer Based on Amino-Functionalized Zirconium-Based Metal–Organic Framework for Delivery of Doxorubicin and Phycocyanin with Synergistic Anticancer Effect. Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 170, 111161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Huang, S. Comparison on Binding Interactions of Quercetin and Its Metal Complexes with Calf Thymus DNA by Spectroscopic Techniques and Viscosity Measurement. J. Mol. Recognit. 2021, 34, e2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luliński, P.; Janczura, M.; Sobiech, M.; Giebułtowicz, J. Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Nano-Conjugates for Effective Extraction of Food Components—A Model Study of Tyramine Determination in Craft Beers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi Falah Langeroodi, S.; Kazemipour, M.; Eslaminejad, T.; Naghipour, A.; Ansari, M. Molecular Imprinted Polymer with Dorzolamide for Contact Lens Applications Assisted by Computational and Experimental Design. React. Funct. Polym. 2022, 178, 105355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larasati, L.; Dendy, D.; Lestari, W.W.; Suharbiansah, R.S.R.; Firdaus, M.; Masykur, A.; Wibowo, F.R. Rapid and Facile Electrochemical Synthesis of MIL-101(Fe)-NH2 and Its Curcumin Loading and Release Studies. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. 2024, 34, 4039–4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, B.; Tian, L.; Ali, Z.; Zhang, Q. Fabrication and Characterization of Glutathione-Imprinted Polymers on Fibrous SiO2 Microspheres with High Specific Surface. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 327, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Kim, I.Y.; Lakhi, K.S.; Srivastava, P.; Naidu, R.; Vinu, A. Single Step Synthesis of Activated Bio-Carbons with a High Surface Area and Their Excellent CO2 Adsorption Capacity. Carbon 2017, 116, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, Y.; Úsuga, B.A.; Campos, C.H.; Alderete, J.B.; Jiménez, V.A. NanoMIPs Design for Fucose and Mannose Recognition: A Molecular Dynamics Approach. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 2048–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Soto, M.J.; Haupt, K.; Gonzato, C. Synthesis of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers by Photo-Iniferter Polymerization under Visible Light. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 4830–4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyann, L.; Ariff, Z.M.; Shafiq, M.D.; Shuib, R.K.; Musa, M.S. Investigating the Effect of Methacrylic Acid on the Properties of Waterborne Epoxy-Acrylate Core-Shell Emulsion, Film and Coating. Prog. Org. Coat. 2024, 187, 108096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yuan, M.; Xu, F.; Cao, H.; Hao, L.; Yu, J.; Chen, J.; Wu, Z. Rapid Determination of Histamine in Cheese by Employing Fluorescence Enhancement of Quantum Dots-Molecularly Imprinted Polymer. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 126, 105867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayerdurai, V.; Cieplak, M.; Noworyta, K.R.; Gajda, M.; Ziminska, A.; Sosnowska, M.; Piechowska, J.; Borowicz, P.; Lisowski, W.; Shao, S.; et al. Electrochemical Sensor for Selective Tyramine Determination, Amplified by a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Film. Bioelectrochemistry 2021, 138, 107695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-F.; Lin, Z.-Z.; Hong, C.-Y.; Huang, Z.-Y. Histamine Detection in Fish Samples Based on Indirect Competitive ELISA Method Using Iron-Cobalt Co-Doped Carbon Dots Labeled Histamine Antibody. Food Chem. 2021, 345, 128812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horemans, F.; Alenus, J.; Bongaers, E.; Weustenraed, A.; Thoelen, R.; Duchateau, J.; Lutsen, L.; Vanderzande, D.; Wagner, P.; Cleij, T.J. MIP-Based Sensor Platforms for the Detection of Histamine in the Nano- and Micromolar Range in Aqueous Media. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 148, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample | Spiked/(mg/kg) | Found/(mg/kg) | RSD (%) | HPLC/ (mg/kg) | RSD(%) | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | - | - | 15.31 ± 0.22 | 1.42 | - |
| 2 | 318 | 320.97 ± 11.98 | 3.73 | 311.57 ± 2.88 | 0.92 | 103.02 ± 3.85 |
| 3 | 636 | 651.53 ± 36.38 | 5.58 | 655.06 ± 29.82 | 4.55 | 99.46 ± 5.55 |
| 4 | 954 | 1006.3 ± 62.02 | 6.16 | 992.05 ± 43.25 | 4.4 | 101.44 ± 6.25 |
| Biogenic Amines | Method | Sensor | Detection Time (min) | LOD | Detected Sample | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Histamine | Fluorescence spectroscopy | o-phthaldialdehyde-MIP | 240 | 1.8 μmoL/L | Milk | [23] |
| Histamine | Fluorescence spectroscopy | MXene-MIP | 20 | 21.9 nmoL/L | Fish | [26] |
| Tyramine | Electrochemical measurements | MIP | - | 159 μmoL/L | Cheese | [41] |
| Histamine | ELISA | mimic enzyme labeled with histamine antibody | 190 | 0.50 mg/kg | Fish | [42] |
| Histamine | Quartz crystal microbalance | MIP | 20 | 5 nmoL/L | Tunny | [43] |
| Histamine | Fluorescence spectroscopy | QDs-Ionic liquids -MIP | 390 | 110 μmoL/L | Fish | [29] |
| Histamine and Tyramine | Fluorescence spectroscopy | CdSe/ZnS-MIP | 10 | 14.57 μmoL/L | Cheese | This method |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Wu, Z.; Cao, H.; Ye, T.; Hao, L.; Yu, J.; Yuan, M.; Xu, F. A Molecularly Imprinted Fluorescence Sensor for the Simultaneous and Rapid Detection of Histamine and Tyramine in Cheese. Foods 2025, 14, 1475. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091475
Li X, Wu Z, Cao H, Ye T, Hao L, Yu J, Yuan M, Xu F. A Molecularly Imprinted Fluorescence Sensor for the Simultaneous and Rapid Detection of Histamine and Tyramine in Cheese. Foods. 2025; 14(9):1475. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091475
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xinpei, Zhiwei Wu, Hui Cao, Tai Ye, Liling Hao, Jinsong Yu, Min Yuan, and Fei Xu. 2025. "A Molecularly Imprinted Fluorescence Sensor for the Simultaneous and Rapid Detection of Histamine and Tyramine in Cheese" Foods 14, no. 9: 1475. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091475
APA StyleLi, X., Wu, Z., Cao, H., Ye, T., Hao, L., Yu, J., Yuan, M., & Xu, F. (2025). A Molecularly Imprinted Fluorescence Sensor for the Simultaneous and Rapid Detection of Histamine and Tyramine in Cheese. Foods, 14(9), 1475. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091475






