Encapsulation of Monascus Pigments Using Enzyme-Modified Yeast Protein–Polysaccharide Complex Pickering Emulsions to Increase Its Stability During Storage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Optimization of Experimental Conditions for Enzymatic Modification of YP
2.2.1. Degree of Hydrolysis (DH) Assay
2.2.2. Solubility
2.2.3. Emulsifying Activity Index (EAI) and Emulsion Stability Index (ESI)
2.3. Characterization of the Structural and Morphological Properties of EYP
2.3.1. Ultraviolet–Visible and Fluorescence Spectra
2.3.2. Particle Size Distribution
2.3.3. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.3.4. Gel Permeation Chromatography
2.3.5. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
2.3.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.4. Optimization of Experimental Conditions for the Preparation of YP– and EYP–Polysaccharide Complex Pickering Emulsions
2.5. Optimization of Experimental Conditions for the Preparation of MP-Loaded YP– and EYP–Polysaccharide Complex Pickering Emulsions
2.6. Characterization of Different MP-Loaded Complex Pickering Emulsions
2.7. Stability of Different MP-Loaded Complex Pickering Emulsions During Storage at Room Temperature
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effects of Different Enzymatic Modification Treatments on the DH, Solubility, EAI, and ESI of YP
3.2. Optimization of Experimental Conditions for Enzymatic Hydrolysis with Enzymatic Cross-Linking Modification of YP
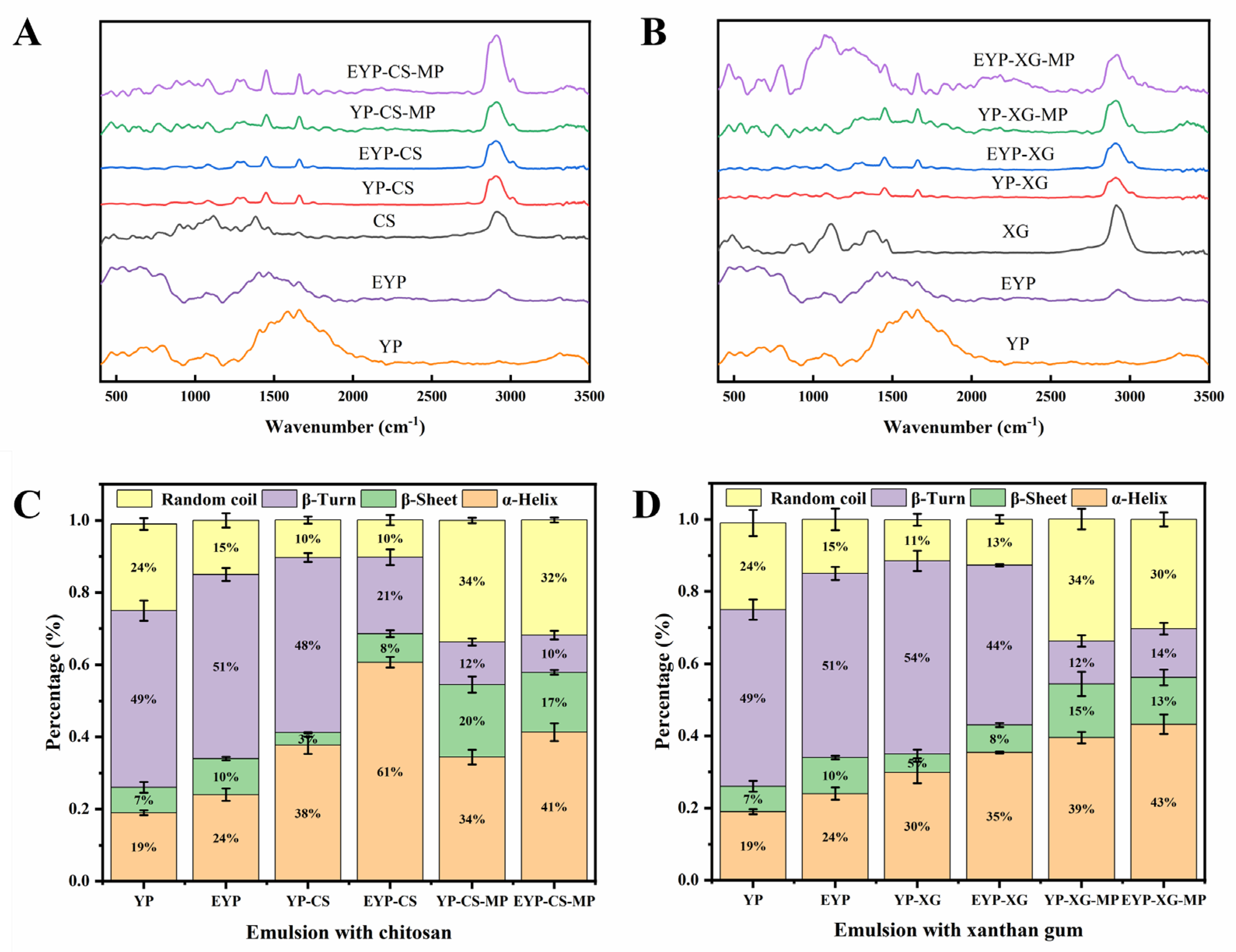
3.3. Structural and Morphological Properties of EYP
3.3.1. Ultraviolet–Visible and Fluorescence Spectra of YP and EYP Protein Solutions
3.3.2. Size Distribution of YP and EYP Protein Solutions
3.3.3. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy of YP and EYP Protein Solutions
3.3.4. Gel Permeation Chromatography of YP and EYP Protein Solutions
3.3.5. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis
3.3.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy of YP and EYP Protein Solutions
3.4. Optimization of the Preparing Process of YP– and EYP –Polysaccharide Complex Pickering Emulsions
3.5. Effects of MP Concentration on the Encapsulation Efficiency (EE) for MPs in YP– and EYP–Polysaccharide Complex Pickering Emulsions
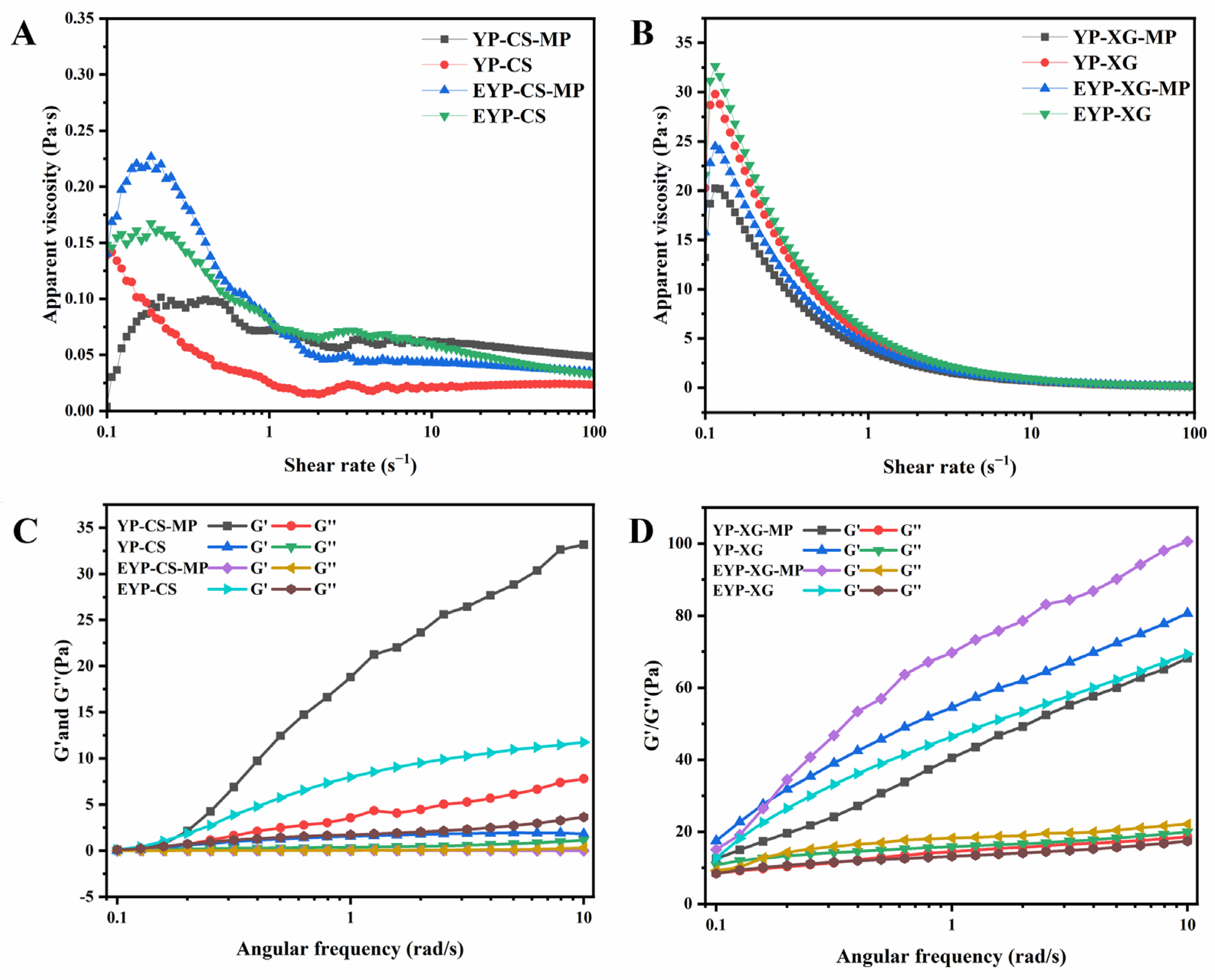
3.6. Rheological Properties of MP-Loaded Complex Pickering Emulsions
3.7. Raman Spectrum Analysis of MP-Loaded Complex Pickering Emulsions
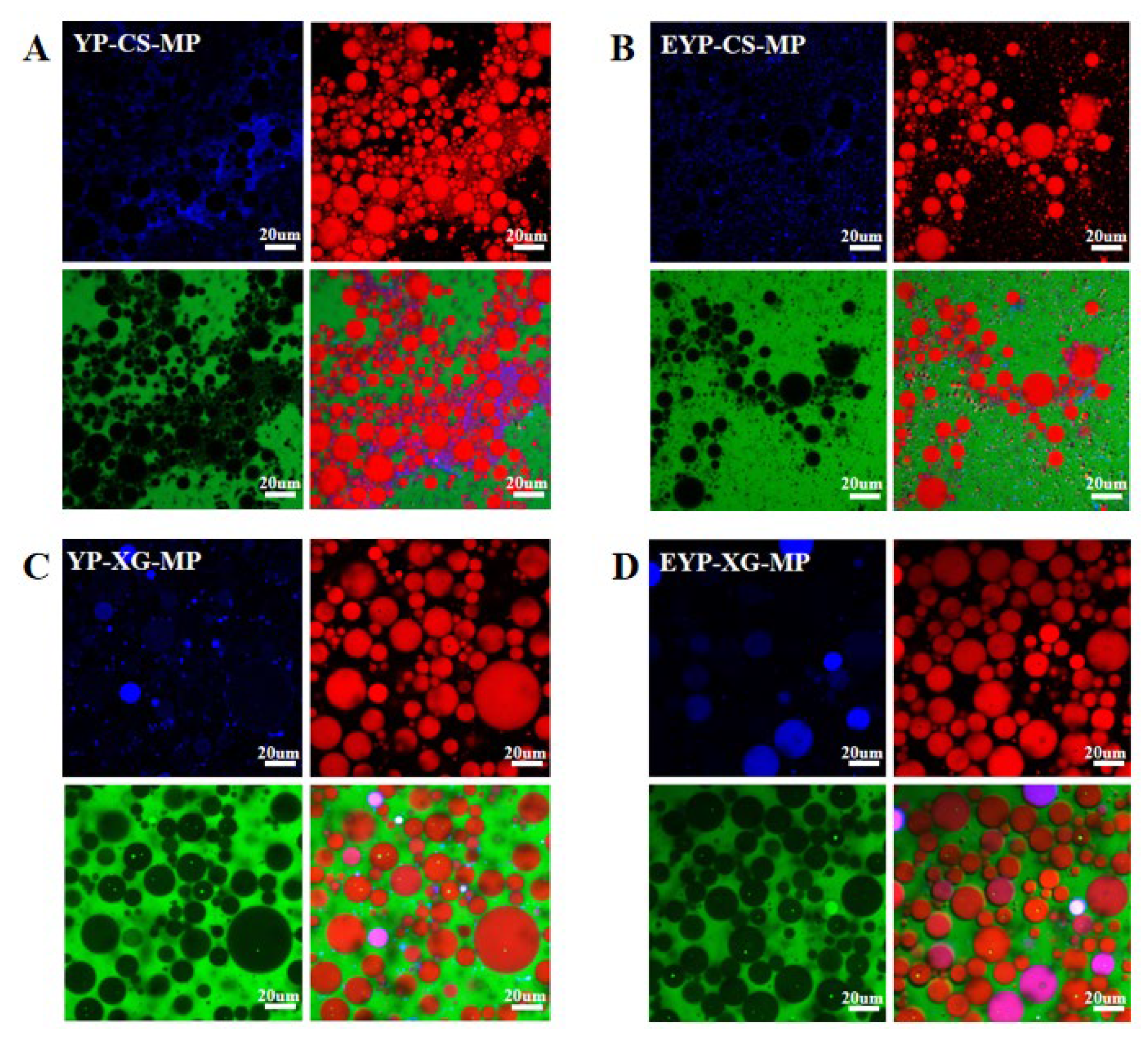
3.8. CC Analysis of MP-Loaded Complex Pickering Emulsions
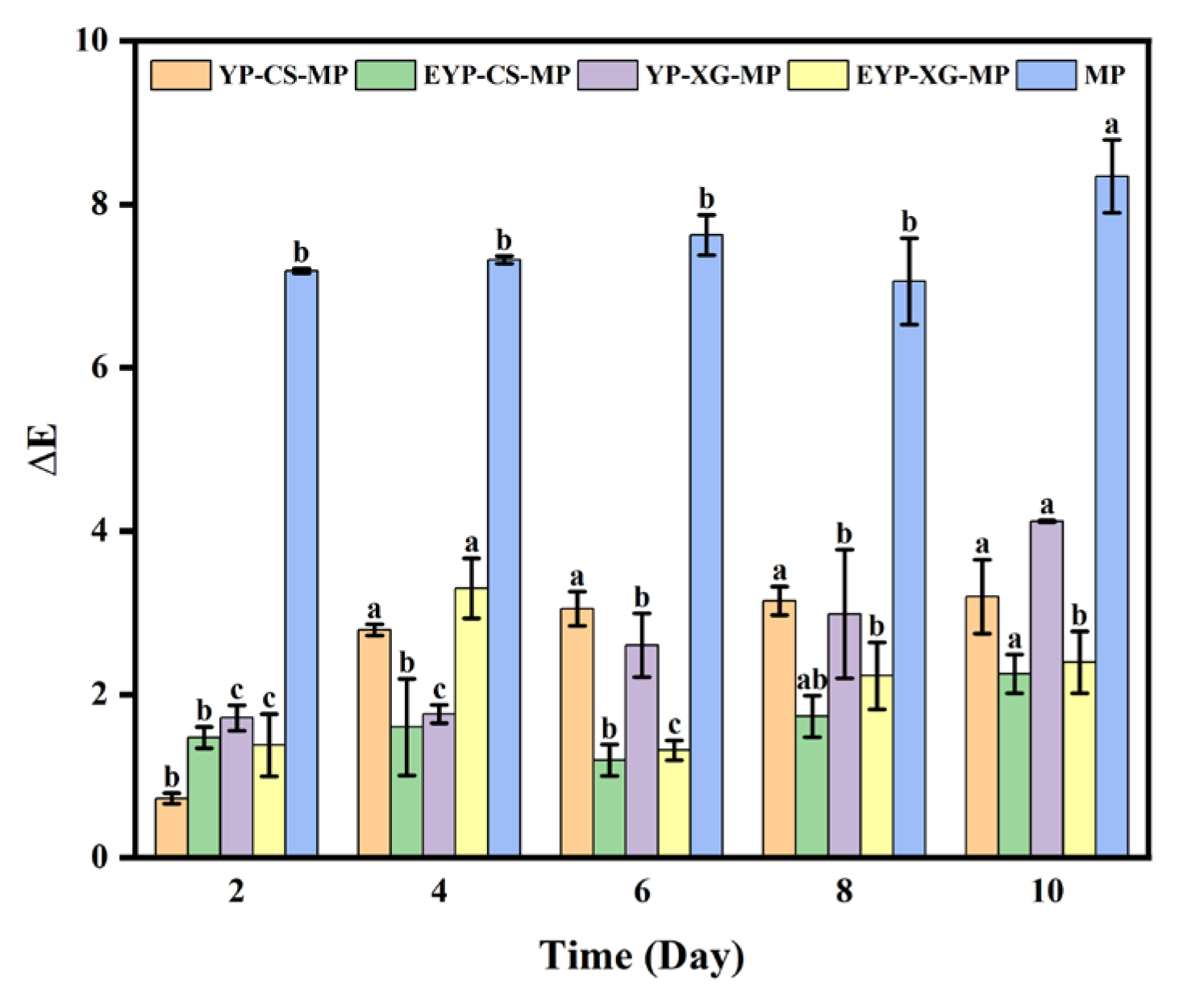
3.9. Effects of Storage Time on the Color Changes of MP-Loaded Complex Pickering Emulsions at Room Temperature
3.10. The Storage Stability of MP-Loaded Complex Pickering Emulsions Under Refrigerating and Heating Conditions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, Y.L.; Shao, Y.C.; Chen, F.S. Monascus pigments. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 96, 1421–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhao, J.; Huang, Y.; Xin, Q.; Wang, Z. Diversifying of chemical structure of native Monascus pigments. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, B.; Li, X.; Hao, J.; Xu, D. Meat systems produced with Monascus pigment water-in-oil-in-water multiple emulsion as pork fat replacers. Food Chem. 2023, 402, 134080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, W.; Wang, P.; Li, J.; Lu, Y. Light stability and mechanism of monascus pigment under different lights. LWT 2024, 191, 115666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Zhu, J.; Gao, H.; Yao, H.; Zhai, C.; Nie, Y. Agriculture. An efficient method for improving the stability of Monascus pigments using ionic gelation. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 6190–6197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alouk, I.; Lv, W.; Chen, W.; Miao, S.; Chen, C.; Wang, Y.; Xu, D. Encapsulation of Monascus pigments in gel in oil in water (G/O/W) double emulsion system based on sodium caseinate and guar gum. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 285, 138232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z. Improving the color stability of red Monascus pigments by direct protein microgelation. Food Res. Int. 2025, 199, 115389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Zheng, B.; Che, Y.; Liu, G.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, S.; Cao, Y. The stability, microstructure, and microrheological properties of Monascus pigment double emulsions stabilized by polyglycerol polyricinoleate and soybean protein isolate. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 543421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Yu, W.; Gao, B.; Niu, Y.; Yu, L. Novel nanoparticle composed by Ovalbumin-OSA modified pectin-rutin for improving the stability of Monascus pigments. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 158, 110467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Huang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, L.; Yang, S.; Jin, R.; Lin, R.; Liu, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Effect of myosin-kappa carrageenan pickering emulsions on the quality of bighead carp surimi gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 161, 110890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Song, J.; Chen, S.; Fu, C.; Li, Z.; Weng, W.; Shi, L.; Ren, Z. Improving surimi gel quality by corn oligopeptide-chitosan stabilized high-internal phase Pickering emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 166, 111268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, P.; Wang, D.; Liang, R.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, F.J.L. Lycopene-loaded bilayer emulsions stabilized by whey protein isolate and chitosan. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 151, 112122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, X.; Yu, S.; Cui, Y.; Tong, Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Han, J.; Zhu, H.; Wang, S. Stability of electrostatically stabilized emulsions and its encapsulation of astaxanthin against environmental stresses: Effect of sodium caseinate-sugar beet pectin addition order. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2024, 9, 100821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Yu, W.; Gao, B.; Niu, Y.; Yu, L. A novel emulsifier for Pickering emulsion composed of whey protein and OSA-pectin loaded with Monascus pigments. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 295, 139490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timira, V.; Chen, X.; Zhou, P.; Wu, J.; Wang, T.; Safety, F. Potential use of yeast protein in terms of biorefinery, functionality, and sustainability in food industry. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2024, 23, e13326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Xia, S.; Song, J.; Hou, Y.; Hao, T.; Shen, S.; Li, K.; Xue, C.; Jiang, X. Yeast protein as a novel protein source: Processing, functional properties, and potential applications in foods. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2024, 93, 103606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Song, J.; Li, K.; Hao, T.; Ma, C.; Shen, S.; Jiang, X.; Xue, C.; Xue, Y. Yeast protein-based meat analogues: Konjac glucomannan induces the fibrous structure formation by modifying protein structure. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 142, 108798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Xiong, J.; Li, P.; Ma, C.; Zhao, X.; Cai, W.; Kong, Y.; Huang, Q. Emulsified sausages with yeast protein as an animal fat replacer: Effects on nutritional composition, spatial structure, gel performance, and sensory quality. Meat Sci. 2024, 210, 109433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Yang, R.; Chen, R.; Liu, C.; Sha, X.; Li, K.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Y. Enhanced O/W emulsion stability and betanin protection using yeast protein and chitooligosaccharide: Comparative insights from complex coacervation and layer-by-layer methods. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 147, 109409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Xia, S.; Song, J.; Hou, Y.; Hao, T.; Shen, S.; Li, K.; Xue, C.; Jiang, X. Yeast protein as a novel dietary protein source: Comparison with four common plant proteins in physicochemical properties. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2023, 7, 100555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikbakht Nasrabadi, M.; Sedaghat Doost, A.; Mezzenga, R. Modification approaches of plant-based proteins to improve their techno-functionality and use in food products. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 118, 106789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, F.; Xu, F.; Zhong, F. Improvement of the encapsulation capacity and emulsifying properties of soy protein isolate through controlled enzymatic hydrolysis. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 138, 108444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Deng, D.; Yang, X.; Zhang, L.; Ma, X.; He, L.; Ma, G.; Li, S.; Li, H. Bovine liver hydrolysates based on six proteases: Physicochemical properties, emulsification characteristics, antioxidant capacity assessment, and peptide identification. LWT 2024, 208, 116718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Li, Y.; Xie, L.; Sun, H.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, F. Effects of enzymatic cross-linking combined with ultrasound on the oil adsorption capacity of chickpea protein. Food Chem. 2022, 383, 132641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Zhang, J.; Hu, A.; Guo, F.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Q. Effect of transglutaminase and laccase on pea protein gel properties compared to that of soybean. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 156, 110314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Tanidjaja, I.; Damodaran, S. Nanostructure and functionality of enzymatically repolymerized whey protein hydrolysate. Food Chem. 2018, 256, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, B. Effect of limited hydrolysis with endopeptidase on bitterness properties of wheat gluten hydrolysates. LWT 2024, 198, 115988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinlschmidt, P.; Schweiggert-Weisz, U.; Brode, V.; Eisner, P. Enzyme assisted degradation of potential soy protein allergens with special emphasis on the technofunctionality and the avoidance of a bitter taste formation. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 68, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domokos-Szabolcsy, É.; Alshaal, T.; Elhawat, N.; Kovács, Z.; Kaszás, L.; Béni, Á.; Kiss, A.J.P. Enhanced Oligopeptide and Free Tryptophan Release from Chickpea and Lentil Proteins: A Comparative Study of Enzymatic Modification with Bromelain, Ficin, and Papain. Plants 2024, 13, 3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Li, Z.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Song, H.; Pan, W.; Chen, W.; Xiong, W.; Yang, L.; Huang, Z. Umami-enhancing effect of Agaricus bisporus-pork bone stocks based on the EUC value and sensory evaluation. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2024, 38, 101033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.-D.; Hu, B.; Gao, P.; Yin, J.-J.; Wang, S.; Yang, Y.; Tan, L.; Hu, C.-R.; He, D.-P.; Zhong, W.J.F. Synthesis and Characterization of Emulsifiers Based on the Maillard Reaction and Its Application in Stabilized DHA Algal Oil Nanoemulsions. Foods 2024, 13, 1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Li, Y.; Li, P.; Zhao, J.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, B.; Ni, L.; Li, H.; Xi, Y.; et al. Encapsulation of roast beef flavor by soy protein isolate/chitosan complex Pickering emulsions to improve its releasing properties during the processing of plant-based meat analogues. Food Chem. 2024, 450, 139313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Huang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, L.; Yang, S.; Jin, R.; Lin, R.; Liu, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Novel Pickering emulsions using polysaccharide-myosin complexes: Effect of polysaccharide types. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 157, 110469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, X.; Gao, J.; Lu, J.; Ma, C.; Lv, J.; Adhikari, B.; Wang, B. Preparation and drying of water-in-oil-in-water (W/O/W) double emulsion to encapsulate soy peptides. Food Res. Int. 2021, 141, 110148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.N.; Ishwarya, S.P.; Nisha, P. Nanoemulsion Versus Microemulsion Systems for the Encapsulation of Beetroot Extract: Comparison of Physicochemical Characteristics and Betalain Stability. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2021, 14, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wu, Y.-R.; Li, J.; Zhou, Q.; Yu, Z.-Y.; Liu, Y.-N.; Zheng, M.-M.; Zhou, Y.-B.; Liu, K. Comparison of Alternative Protein Hydrogels for Delivering Myricetin: Interaction Mechanism and Stability Evaluation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 8784–8797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghribi, A.M.; Gafsi, I.M.; Sila, A.; Blecker, C.; Danthine, S.; Attia, H.; Bougatef, A.; Besbes, S. Effects of enzymatic hydrolysis on conformational and functional properties of chickpea protein isolate. Food Chem. 2015, 187, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfandiary, R.; Hunjan, J.S.; Lushington, G.H.; Joshi, S.B.; Middaugh, C.R. Temperature dependent 2nd derivative absorbance spectroscopy of aromatic amino acids as a probe of protein dynamics. Protein Sci. A Publ. Protein Soc. 2009, 18, 2603–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Errity, C.; Jacquier, J.-C. Fabrication and characterization of industrially stable whey protein nanogels via thermal denaturation and calcium interaction. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 159, 110641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tintor, Đ.; Ninković, K.; Milošević, J.; Polović, N.Đ. Gaining insight into protein structure via ATR-FTIR spectroscopy. Vib. Spectrosc. 2024, 134, 103726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Li, S.-Y.; He, Y.-Y.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Zhao, Y.-Y.; Du, M.-T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.-T.; Bai, Y.-H. Application of ultrasound-assisted alkaline extraction for improving the solubility and emulsifying properties of pale, soft, and exudative (PSE)-like chicken breast meat protein isolate. LWT 2022, 172, 114234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can Karaca, A.; Tan, C.; Assadpour, E.; Jafari, S.M. Recent advances in the plant protein-polyphenol interactions for the stabilization of emulsions. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 335, 103339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Sun, Y.; Tang, X.; Cui, Y.; Meng, D.; Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Guo, H.; Chen, H.; Yang, R. The interaction mechanism and the functionality of yeast protein with hydrophilic and hydrophobic bioactive molecules. Food Biosci. 2023, 52, 102448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, N.; Ma, H.; Ding, Y.; Lu, F.; Guo, L.; Zhang, X.; Gu, C. Effect of slit dual-frequency ultrasonic emulsification technology on the stability of walnut emulsions. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2022, 82, 105876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pöri, P.; Nisov, A.; Nordlund, E. Enzymatic modification of oat protein concentrate with trans- and protein-glutaminase for increased fibrous structure formation during high-moisture extrusion processing. LWT 2022, 156, 113035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Wang, Y.; Cao, W.; Yan, Y.; Guo, F.; Li, J.; Li, W. Stability and gastrointestinal behavior of curcumin-loaded emulsion stabilized by multi-conformation soy proteins: Influence of oil volume fraction. Food Chem. 2024, 440, 138215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Luo, L.; Liu, C.; McClements, D.J. Utilization of anionic polysaccharides to improve the stability of rice glutelin emulsions: Impact of polysaccharide type, pH, salt, and temperature. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 64, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Luo, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Liu, S.J.F.H. Concentrated O/W Pickering emulsions stabilized by soy protein/cellulose nanofibrils: Influence of pH on the emulsification performance. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 108, 106025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Gong, T.; Hou, Y.; Yang, X.; Guo, Y. Alginate-stabilized thixotropic emulsion gels and their applications in fabrication of low-fat mayonnaise alternatives. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 146, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Fan, L.; Li, J. Biopolymer-based pickering high internal phase emulsions: Intrinsic composition of matrix components, fundamental characteristics and perspective. Food Res. Int. 2023, 165, 112458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Cao, J.; Li, L.; Yang, X. Enhancing stability and performance of emulsion stabilized by soy protein isolate nanofiber—polysaccharide complexes. LWT 2024, 205, 116495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Wang, J.; Tan, C.; Ying, R.; Wu, X.; Otto, J.L. Modulating the functional properties of protein-stabilized pickering emulsion by inulin, xanthan gum and chitosan. Food Biosci. 2023, 55, 103063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, L.; Abdolmaleki, K.; Nayebzadeh, K.; Bahmaei, M. Characterization of sodium caseinate/Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose concentrated emulsions: Effect of mixing ratio, concentration and wax addition. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 128, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Y.; Mi, H.; Yi, S.; Gao, R.; Li, X.; Li, J. Effects of chickpea protein-stabilized Pickering emulsion on the structure and gelling properties of hairtail fish myosin gel. Food Chem. 2023, 417, 135821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Yang, J.; Shao, G.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Yang, L.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Zhu, D.; Li, Y.; et al. pH-induced conformational changes and interfacial dilatational rheology of soy protein isolated/soy hull polysaccharide complex and its effects on emulsion stabilization. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 109, 106075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, S.; Xin, L.; Zhang, L.; Yang, L.; Wang, P.; Liu, H. Exploring the influence of different enzymes on soy hull polysaccharide emulsion stabilization: A study on interfacial behavior and structural changes. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, K.; Yin, X.; Ma, J.; Li, Z.; Sun, W.; Han, M. Effect of low-frequency magnetic field on the gel properties of pork myofibrillar proteins. Food Chem. 2019, 274, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.X.; Deng, T.Y.; Wang, C.; Mi, H.B.; Yi, S.M.; Li, X.P.; Li, J.R. Effect of hydrocolloids on gel properties and protein secondary structure of silver carp surimi. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 2252–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, K.; Yu, X.; Gao, C.; Yang, Y.; Tang, X.; Feng, X. Effects of quinoa protein Pickering emulsion on the properties, structure and intermolecular interactions of myofibrillar protein gel. Food Chem. 2022, 394, 133456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavasoli, S.; Liu, Q.; Jafari, S.M. Development of Pickering emulsions stabilized by hybrid biopolymeric particles/nanoparticles for nutraceutical delivery. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 124, 107280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| MP Concentration | Encapsulation Efficiency (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YP–CS | EYP–CS | YP–XG | EYP–XG | |
| 0.10% (w/v) | 76.33 ± 0.02 d | 71.00 ± 0.12 e | 56.45 ± 0.25 l | 52.52 ± 1.1 m |
| 0.15% (w/v) | 79.34 ± 0.89 b | 79.73 ± 1.01 b | 62.99 ± 0.4f g | 58.60 ± 0.3 k |
| 0.20% (w/v) | 78.09 ± 0.5 c | 81.18 ± 0.18 a | 62.21 ± 0.11g h | 62.79 ± 0.24 fg |
| 0.25% (w/v) | 78.97 ± 0.07 b | 79.20 ± 0.7 b | 63.39 ± 0.19 f | 61.03 ± 0.49 i |
| 0.30% (w/v) | 76.56 ± 0.91 d | 76.18 ± 0.02 d | 61.36 ± 0.52 hi | 59.66 ± 0.05 g |
| Sample | tanδ | I850/I830 | I760/I1003 |
|---|---|---|---|
| YP–CS | 0.23 ± 0.00 ef | 2.06 ± 0.01 a | 0.37 ± 0.06 d |
| EYP–CS | 0.25 ± 0.04 de | 1.98 ± 0.06 a | 0.43 ± 0.06 d |
| YP–CS–MP | 0.20 ± 0.01 f | 0.56 ± 0.09 c | 1.29 ± 0.03 c |
| EYP–CS–MP | 0.88 ± 0.05 a | 1.18 ± 0.10 b | 1.02 ± 0.09 c |
| YP–XG | 0.29 ± 0.00 cd | 1.23 ± 0.03 b | 3.66 ± 0.08 a |
| EYP–XG | 0.28 ± 0.00 cd | 1.34 ± 0.14 b | 1.92 ± 0.03 b |
| YP–XG–MP | 0.36 ± 0.00 b | 0.22 ± 0.08 d | 1.37 ± 0.07 c |
| EYP–XG–MP | 0.29 ± 0.04 c | 0.44 ± 0.02 cd | 1.74 ± 0.13 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Z.; Zhao, J.; Liu, S.; Liu, M.; Zeng, X.; Li, H.; Xi, Y.; Li, J. Encapsulation of Monascus Pigments Using Enzyme-Modified Yeast Protein–Polysaccharide Complex Pickering Emulsions to Increase Its Stability During Storage. Foods 2025, 14, 1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081366
Zhao Z, Zhao J, Liu S, Liu M, Zeng X, Li H, Xi Y, Li J. Encapsulation of Monascus Pigments Using Enzyme-Modified Yeast Protein–Polysaccharide Complex Pickering Emulsions to Increase Its Stability During Storage. Foods. 2025; 14(8):1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081366
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Ziyan, Jinling Zhao, Sirong Liu, Mengxuan Liu, Xiangquan Zeng, He Li, Yu Xi, and Jian Li. 2025. "Encapsulation of Monascus Pigments Using Enzyme-Modified Yeast Protein–Polysaccharide Complex Pickering Emulsions to Increase Its Stability During Storage" Foods 14, no. 8: 1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081366
APA StyleZhao, Z., Zhao, J., Liu, S., Liu, M., Zeng, X., Li, H., Xi, Y., & Li, J. (2025). Encapsulation of Monascus Pigments Using Enzyme-Modified Yeast Protein–Polysaccharide Complex Pickering Emulsions to Increase Its Stability During Storage. Foods, 14(8), 1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081366









