Comparative Study on the Physical and Chemical Properties Influenced by Variations in Fermentation Bacteria Groups: Inoculating Different Fermented Mare’s Milk into Cow’s Milk
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Microbiota Diversity Detection
2.4. Determination of Water-Holding Capacity
2.5. Rheological Property Measurement
2.6. Determination of Texture Properties
2.7. pH Value and Titratable Acidity Measurement
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
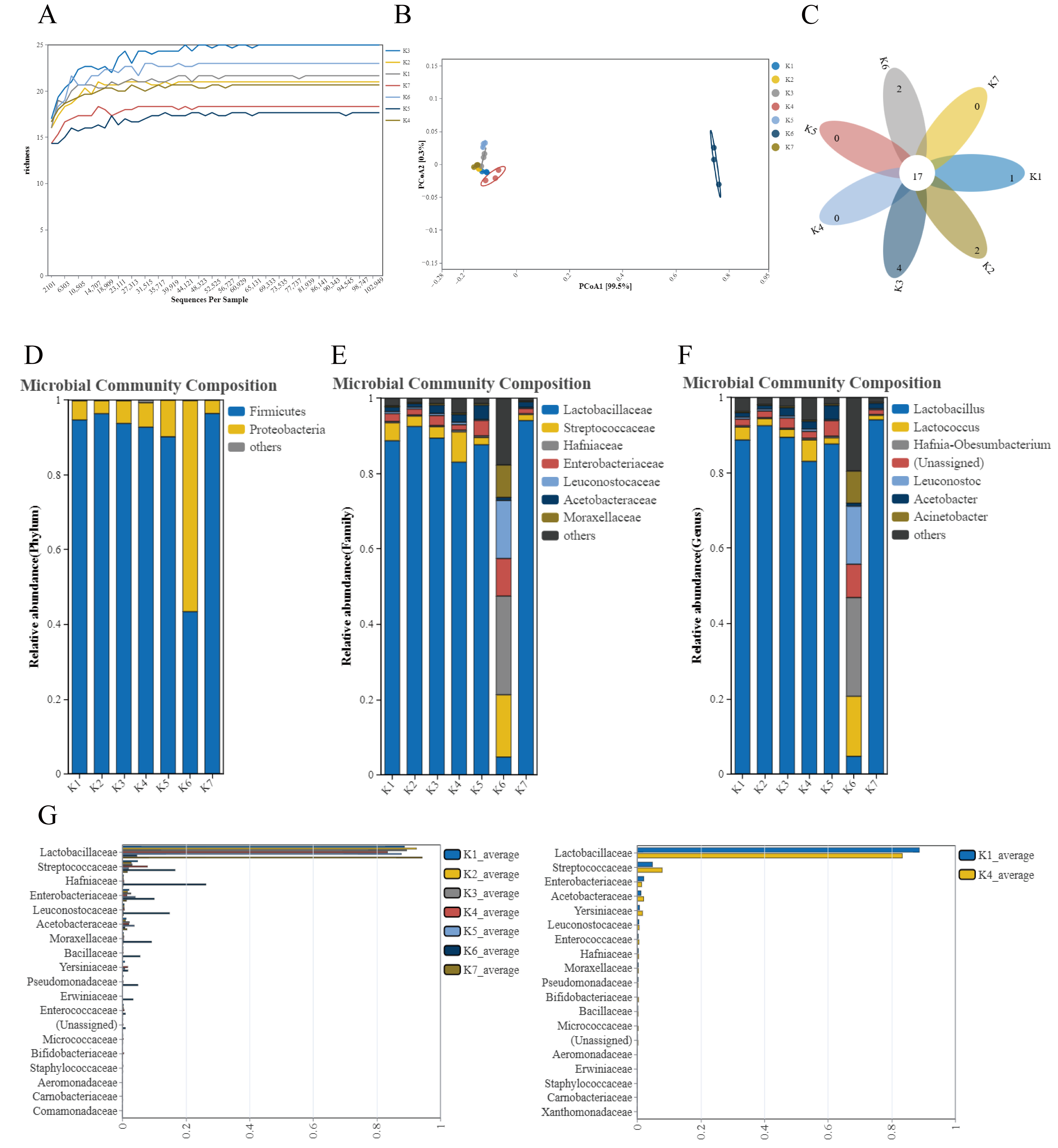
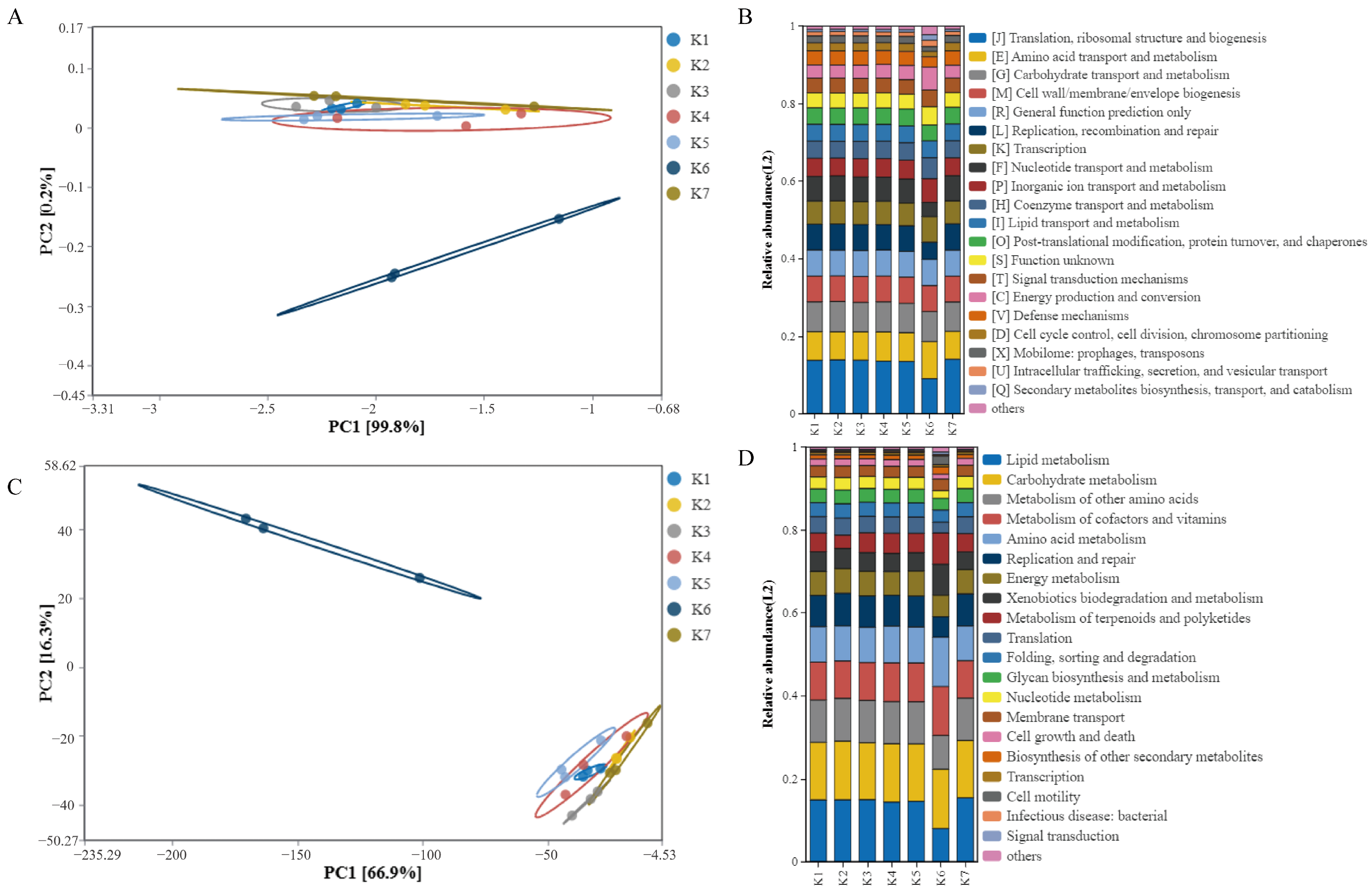
3.1. Microbiota Analysis and Functional Prediction Analysis
3.2. Description of Fermented Cow’s Milk Sample
3.3. pH and Titratable Acidity Analysis
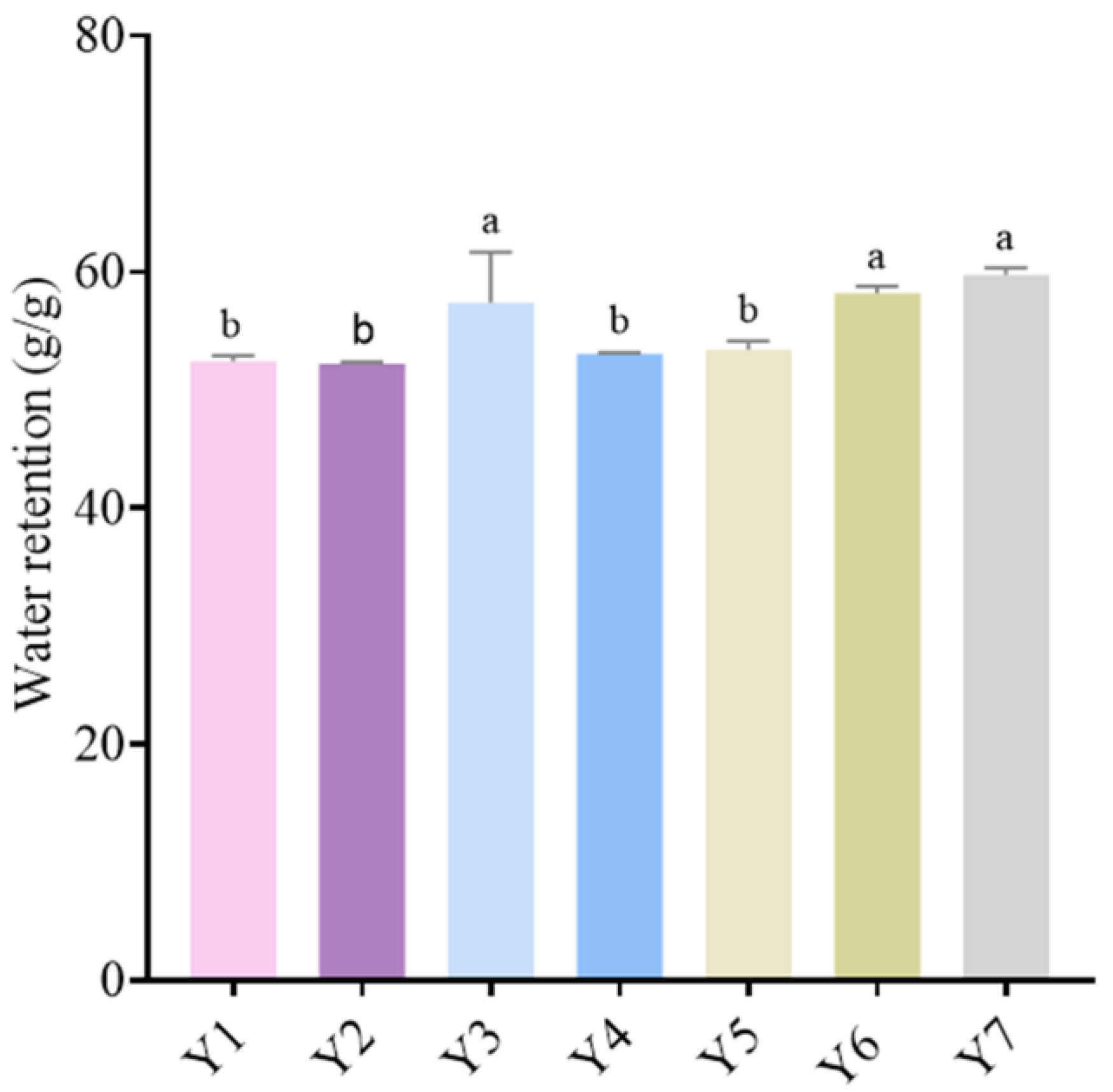
3.4. Water-Retention Analysis
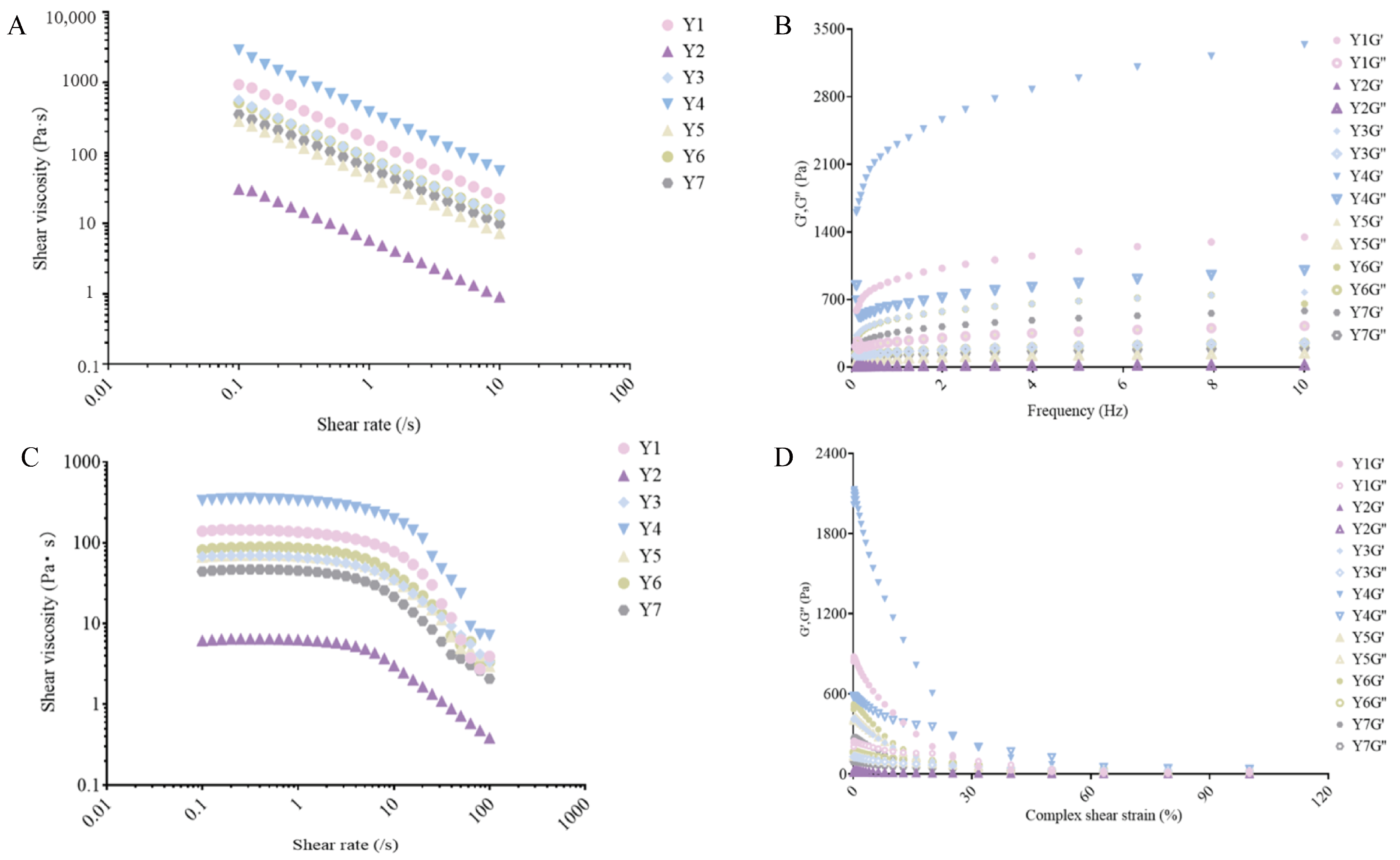
3.5. Rheological Analysis
3.6. Texture Characteristic Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, L.; Xu, W.; Li, C.; Guo, Y.; Chagan, I. Comparative study of physicochemical composition and microbial community of Khoormog, Chigee, and Airag, traditionally fermented dairy products from Xilin Gol in China. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 1564–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, A.; Jiang, Y.; Li, B.; Wang, T.; Zhao, J.; Liu, X.; Chen, W. Indigenous Chinese fermented dairy products: Microbial diversity, flavour, and health benefits. Int. Dairy J. 2022, 135, 105479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martuzzi, F.; Franceschi, P.; Formaggioni, P. Fermented Mare Milk and Its Microorganisms for Human Consumption and Health. Foods 2024, 13, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Askar, K.; Gerard, L.; Nawel, A.; Christian, M.; Gaukhar, K. Fermented mare milk product (Qymyz, Koumiss). Int. Dairy J. 2021, 119, 105065. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Y.; Chen, X.; Sun, Z.; Li, Y.; Chen, D.; Fang, S.; Chen, J. Exploring core microbiota responsible for the production of volatile flavor compounds during the traditional fermentation of Koumiss. LWT 2021, 135, 110049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Lyu, M.; Fukunaga, M.; Watanabe, S.; Iwatani, S.; Miyanaga, K.; Yamamoto, N. Lactobacillus johnsonii enhances the gut barrier integrity via the interaction between GAPDH and the mouse tight junction protein JAM-2. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 11021–11033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzaal, M.; Saeed, F.; Anjum, F.; Waris, N.; Husaain, M.; Ikram, A.; Ateeq, H.; Muhammad Anjum, F.; Suleria, H. Nutritional and ethnomedicinal scenario of koumiss: A concurrent review. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 6421–6428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Zhao, S.; Yan, B.; Zhou, X. Impact of Buckwheat Fermented Milk Combined with High-Fat Diet on Rats’ Gut Microbiota and Short-Chain Fatty Acids. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 3833–3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, R.; Choudhury, P.K. Bifidobacteria in Fermented Dairy Foods: A Health Beneficial Outlook. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2023, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Chen, L.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, G.; Jiang, T. Improved peptide generation from milk fermented by heat-shocked Lactobacillus helveticus. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 52, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, S.; Chen, L.; Chen, C.; Ren, X.; Zheng, Z.; Weng, L.; Ge, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, G.; et al. Immunomodulatory effects of L. helveticus WHH2580 fermented milk on an immunosuppressed murine model. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 99, 105353. [Google Scholar]
- Gölbaşι, G.; Akιn, N.; Çiğdem, K.G.; Demirci, T. Monitoring the changes in physicochemical, sensory properties and microbiota of village-type homemade yoghurts along three consecutive back-slopping procedures. Int. Dairy J. 2023, 143, 105663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byakika, S.; Mukisa, I.M. Microbial diversity, aflatoxin M1 contamination and potential lactic acid starters for commercially produced traditional fermented dairy beverages, a case of Bongo from Uganda. Int. Dairy J. 2024, 159, 106069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teichert, J.; Cais-Sokolinska, D.; Dankow, R.; Pikul, J.; Chudy, S.; Bierzunska, P.; Kaczynski, L.K. Color Stability of Fermented Mare’s Milk and a Fermented Beverage from Cow’s Milk Adapted to Mare’s Milk Composition. Foods 2020, 9, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyash, M.; Abu-Jdayil, B.; Itsaranuwat, P.; Almazrouei, N.; Galiwango, E.; Esposito, G.; Hunashal, Y.; Hamed, F.; Najjar, Z. Exopolysaccharide produced by the potential probiotic Lactococcus garvieae C47: Structural characteristics, rheological properties, bioactivities and impact on fermented camel milk. Food Chem. 2020, 333, 127418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, J.; Safian, M.M.; Luo, Y.; Guo, Z.; Mu, G. Fabrication of Delivery Gels with Micellar Casein Concentrates (MCC) Using Microfiltration Embedding Lactobacillus Rhamnosus GG (LGG): Effect of Temperature on Structure, Rheological Behavior, and Texture. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 7498–7508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Feng, K.; Jin, J.; Safian Murad, M.; Mu, G.; Wu, X. Comparison on properties between normal and A2 bovine milk fermented using commercial bacteria mixed with/without two probiotics from human milk. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 216, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redondo-Useros, N.; Gheorghe, A.; Diaz-Prieto, L.E.; Villavisencio, B.; Marcos, A.; Nova, E. Associations of Probiotic Fermented Milk (PFM) and Yogurt Consumption with Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus Components of the Gut Microbiota in Healthy Adults. Nutrients 2019, 11, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Cai, X.; Liu, X.; Lai, G.; Guan, X.; Chen, B.; Wang, Q. Lactobacillus fermentum B153 from human colostrum modulates intestinal immunity and gut microbiota in obese mice model. J. Funct. Foods 2025, 125, 106662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, T.; Wang, D.; Wu, S.; Jin, R.; Ren, W.; Sun, T. Profiles of Volatile Flavor Compounds in Milk Fermented with Different Proportional Combinations of Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus. Molecules 2017, 22, 1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Song, L.; Han, D.; Han, P.; Bai, F. Microbiological and Physicochemical Dynamics in Traditional and Industrial Fermentation Processes of Koumiss. Fermentation 2024, 10, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.N.; Tang, S.H.; Ren, R.; Gong, J.X.; Chen, Y.M. Metabolomic profile of milk fermented with Streptococcus thermophilus cocultured with Bifidobacterium animalis ssp. lactis, Lactiplantibacillus plantarum, or both during storage. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 8493–8505. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; Gu, Y.; Lv, Z.; Wang, L. The exopolysaccharides produced by Leuconostoc mesenteroides XR1 and its effect on silk drawing phenomenon of yoghurt. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 262, 129952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, L.A.; Lopes Neto, J.H.P.; Cardarelli, H.R. Exopolysaccharides produced by Lactobacillus plantarum: Technological properties, biological activity, and potential application in the food industry. Ann. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.; Liang, M.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Renye, J.A., Jr.; Qi, P.X.; Ren, D. Characterization of an exopolysaccharide (EPS-3A) produced by Streptococcus thermophilus ZJUIDS-2-01 isolated from traditional yak yogurt. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 192, 1331–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelicaen, R.; Weckx, S.; Gonze, D.; De Vuyst, L. Application of comparative genomics of Acetobacter species facilitates genome-scale metabolic reconstruction of the Acetobacter ghanensis LMG 23848(T) and Acetobacter senegalensis 108B cocoa strains. Front Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1060160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Wittouck, S.; Salvetti, E.; Franz, C.; Harris, H.M.B.; Mattarelli, P.; O’Toole, P.W.; Pot, B.; Vandamme, P.; Walter, J.; et al. A taxonomic note on the genus Lactobacillus: Description of 23 novel genera, emended description of the genus Lactobacillus Beijerinck 1901, and union of Lactobacillaceae and Leuconostocaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 2782–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.Q.; Liu, T.J.; Sadiq, F.A.; Gu, J.S.; Zhang, G.H. Insights into the microbial diversity and community dynamics of Chinese traditional fermented foods from using high-throughput sequencing approaches. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2017, 18, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.; Jin, H.; Kwok, L.Y.; Lv, R.; Zhao, Z.; Bilige, M.; Sun, Z.; Liu, W.; Zhang, H. Intraspecific microdiversity and ecological drivers of lactic acid bacteria in naturally fermented milk ecosystem. Sci. Bull. 2023, 68, 2405–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Lv, M.; Shao, Z.; Hungwe, M.; Wang, J.; Bai, X.; Xie, J.; Wang, Y.; Geng, W. Metabolism Characteristics of Lactic Acid Bacteria and the Expanding Applications in Food Industry. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 612285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, H.; Saier, M.H., Jr. Comparative Genomics of the Transport Proteins of Ten Lactobacillus Strains. Genes 2020, 11, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshwal, G.K.; Tiwari, S.; Kumar, A.; Raman, R.K.; Kadyan, S. Review on factors affecting and control of post-acidification in yoghurt and related products. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 109, 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Wu, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Weng, P.; Miao, Y. Effects of Inoculated Starter of Lactic Acid Bacteria on Quality and Microbial Diversity of Pickled Wax Gourd in Eastern Zhejiang. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2017, 41, e12833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushell, F.M.L.; Tonner, P.D.; Jabbari, S.; Schmid, A.K.; Lund, P.A. Synergistic Impacts of Organic Acids and pH on Growth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A Comparison of Parametric and Bayesian Non-parametric Methods to Model Growth. Front Microbiol. 2018, 9, 3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziarno, M.; Zaręba, D.; Ścibisz, I.; Kozłowska, M. Texture and water holding capacity of oat drinks fermented with lactic acid bacteria, bifidobacteria and Propionibacterium. Int. J. Food Prop. 2023, 27, 106–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, S.; Khetra, Y.; Dularia, C.; Meena, G.S.; Arora, S. Symbiotic fermentation study of Acetobacter orientalis and lactic acid bacteria for lactobionic acid enriched yoghurt production. Food Biosci. 2023, 53, 102612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ke, C.; Li, L. Physicochemical, rheological and digestive characteristics of soy protein isolate gel induced by lactic acid bacteria. J. Food Eng. 2021, 292, 110243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, E.R.; dos Anjos Pinto, C.B.; Stephani, R.; Fernandes de Carvalho, A.; Perrone, Í.T. Effect of adding different types of soluble fibre to high-protein yoghurts on water holding capacity, particle size distribution, apparent viscosity, and microstructure. Int. Dairy J. 2023, 141, 105609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Wang, Z.; Yu, Z.; Gao, Z.; Mu, G.; Wu, X. Influence on physical properties and digestive characters of fermented coconut milk with different loading proportion of skimmed coconut drink using Lactiplantibacillus plantarum MWLp-4 from human milk mixing with commercial bacteria. Food Biosci. 2023, 53, 102598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoxha, R.; Evstatieva, Y.; Nikolova, D. Physicochemical, Rheological, and Sensory Characteristics of Yogurt Fermented by Lactic Acid Bacteria with Probiotic Potential and Bioprotective Properties. Foods 2023, 12, 2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, E.; Watanabe, R.; Ichimura, T.; Ishida, T.; Kimura, K. Effect of lactose hydrolysis on the milk-fermenting properties of Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus 2038 and Streptococcus thermophilus 1131. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 1454–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenzuela, J.A.; Vazquez, L.; Rodriguez, J.; Florez, A.B.; Vasek, O.M.; Mayo, B. Phenotypic, Technological, Safety, and Genomic Profiles of Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid-Producing Lactococcus lactis and Streptococcus thermophilus Strains Isolated from Cow’s Milk. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Li, H.; Ma, H.; Wang, P.; Mao, X.; Liu, R.; Fang, B.; Chen, J.; Zhu, L.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Grainy properties of post–heating fermented milk with different particle sizes. LWT 2024, 198, 116003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.; Shen, X.; Hou, J.; Guo, M. Effects of polymerized whey protein prepared directly from cheese whey as fat replacer on physiochemical, texture, microstructure and sensory properties of low-fat set yogurt. LWT 2019, 115, 108268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodziak, A.; Krol, J.; Barlowska, J.; Teter, A.; Florek, M. Changes in the Physicochemical Parameters of Yoghurts with Added Whey Protein in Relation to the Starter Bacteria Strains and Storage Time. Animals 2020, 10, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wa, Y.; Chanyi, R.M.; Nguyen, H.T.H.; Gu, R.; Day, L.; Altermann, E. Extracellular Polysaccharide Extraction from Streptococcus thermophilus in Fermented Milk. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e02280-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delikanli, B.; Ozcan, T. Improving the Textural Properties of Yogurt Fortified with Milk Proteins. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2017, 41, e13101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Song, W.; Liu, T.; Xu, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, D.; Li, H.; Yu, J. Developing novel synbiotic yoghurt with Lacticaseibacillus paracasei and lactitol: Investigation of the microbiology, textural and rheological properties. Int. Dairy J. 2022, 135, 105475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kong, F.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, S.; Mu, G.; Wu, X. Comparative Study on the Physical and Chemical Properties Influenced by Variations in Fermentation Bacteria Groups: Inoculating Different Fermented Mare’s Milk into Cow’s Milk. Foods 2025, 14, 1328. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081328
Kong F, Zhao Q, Wang S, Mu G, Wu X. Comparative Study on the Physical and Chemical Properties Influenced by Variations in Fermentation Bacteria Groups: Inoculating Different Fermented Mare’s Milk into Cow’s Milk. Foods. 2025; 14(8):1328. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081328
Chicago/Turabian StyleKong, Fanyu, Qing Zhao, Shengyuan Wang, Guangqing Mu, and Xiaomeng Wu. 2025. "Comparative Study on the Physical and Chemical Properties Influenced by Variations in Fermentation Bacteria Groups: Inoculating Different Fermented Mare’s Milk into Cow’s Milk" Foods 14, no. 8: 1328. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081328
APA StyleKong, F., Zhao, Q., Wang, S., Mu, G., & Wu, X. (2025). Comparative Study on the Physical and Chemical Properties Influenced by Variations in Fermentation Bacteria Groups: Inoculating Different Fermented Mare’s Milk into Cow’s Milk. Foods, 14(8), 1328. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081328





