Analysis of Bacterial and Metabolic Diversity of Pickles in Different Karst Regions of Guizhou, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
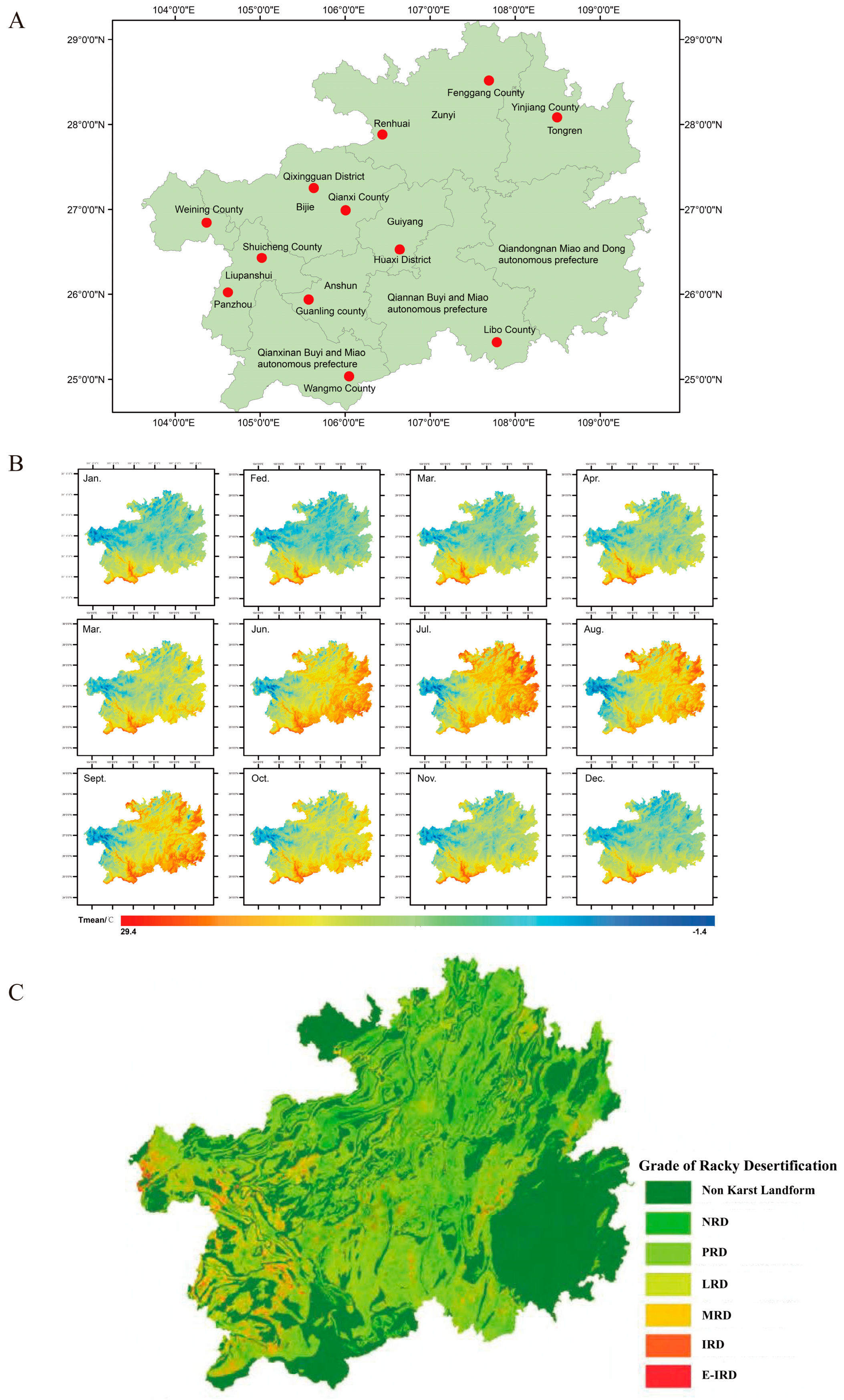
2.1. Pickle Sampling
2.2. PacBio Sequencing of Bacterial Communities
2.3. Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (UHPLC)-Mass Spectrometry (MS/MS) Analysis of Pickles
2.4. Multivariate Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
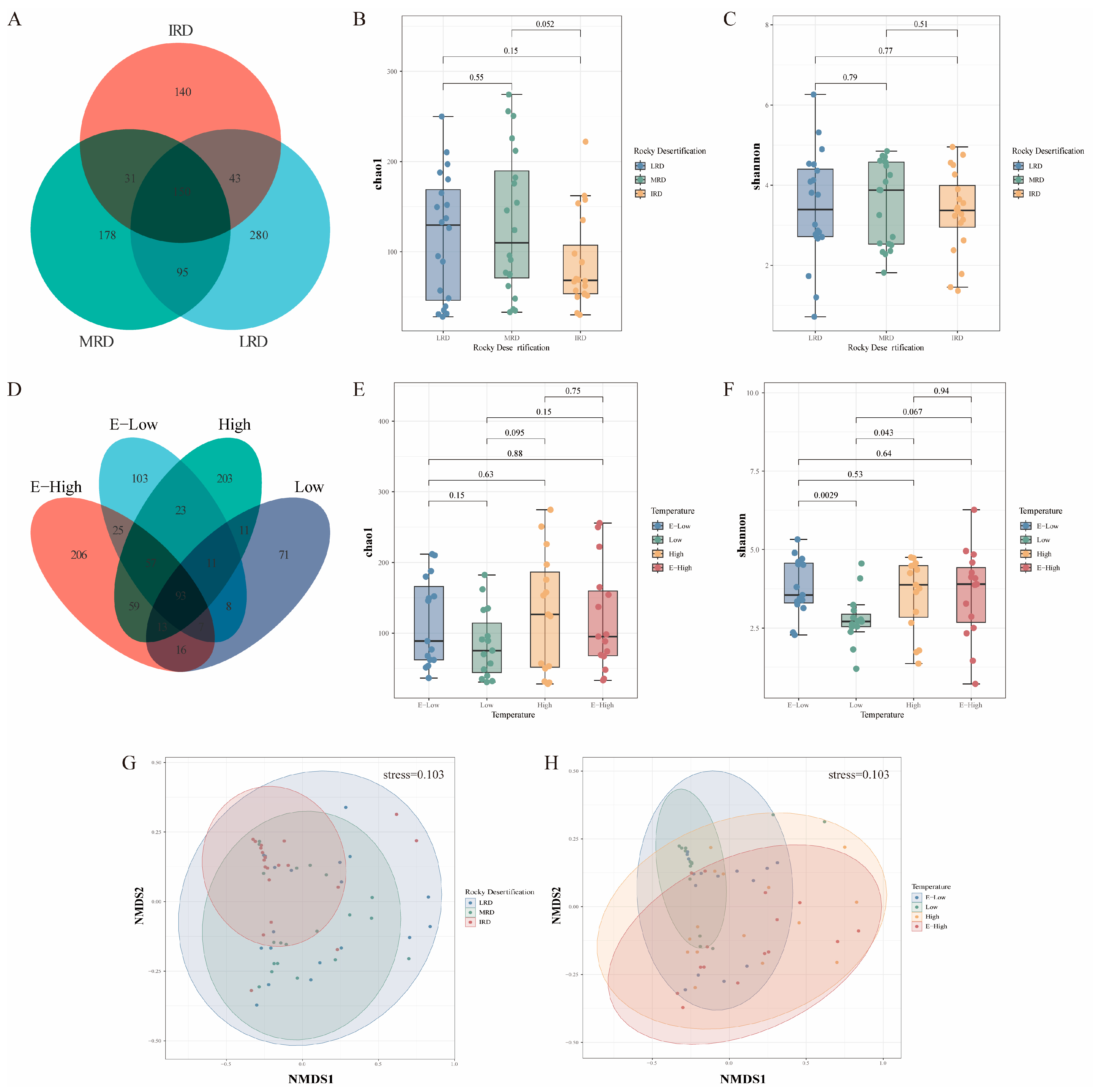
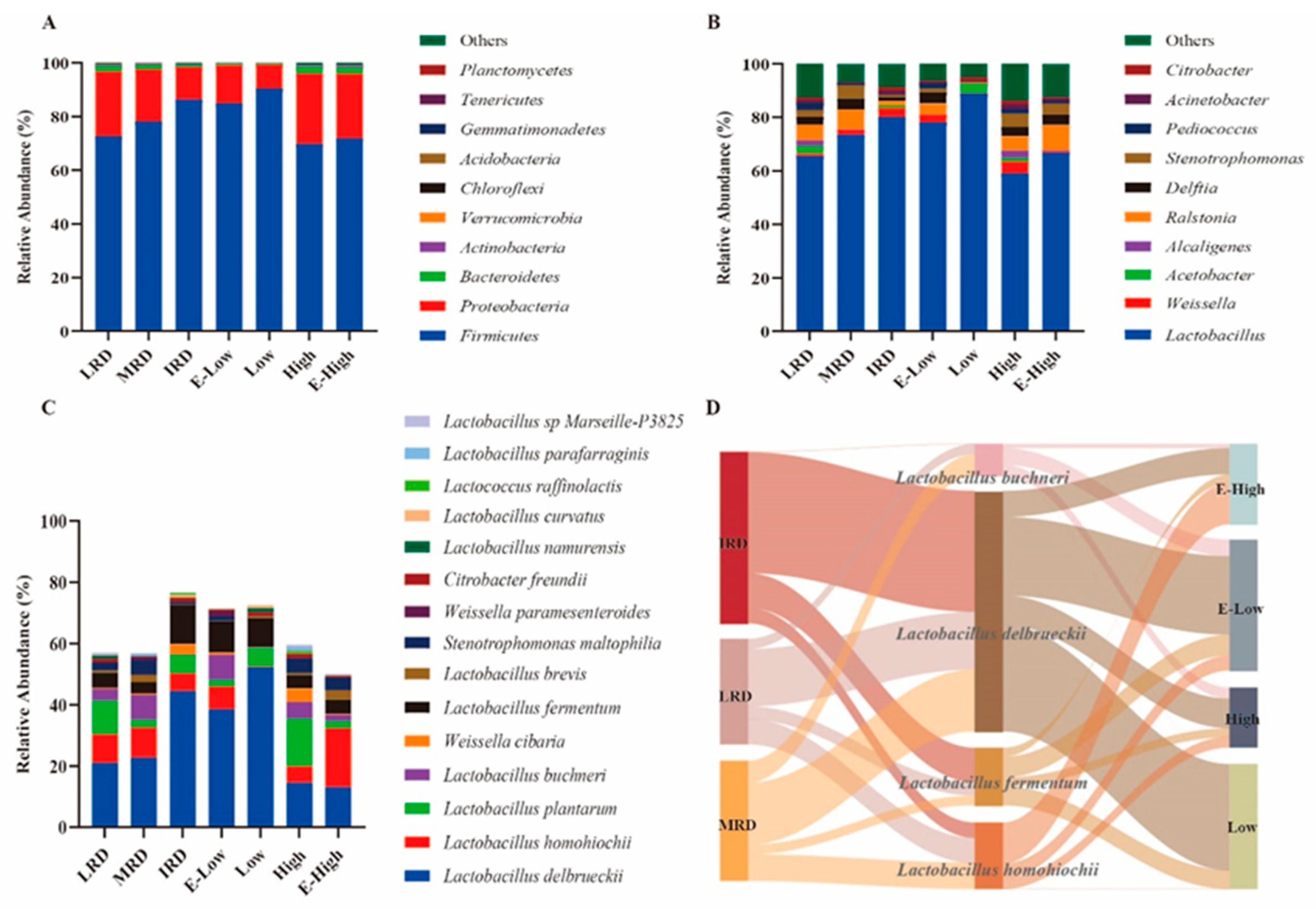
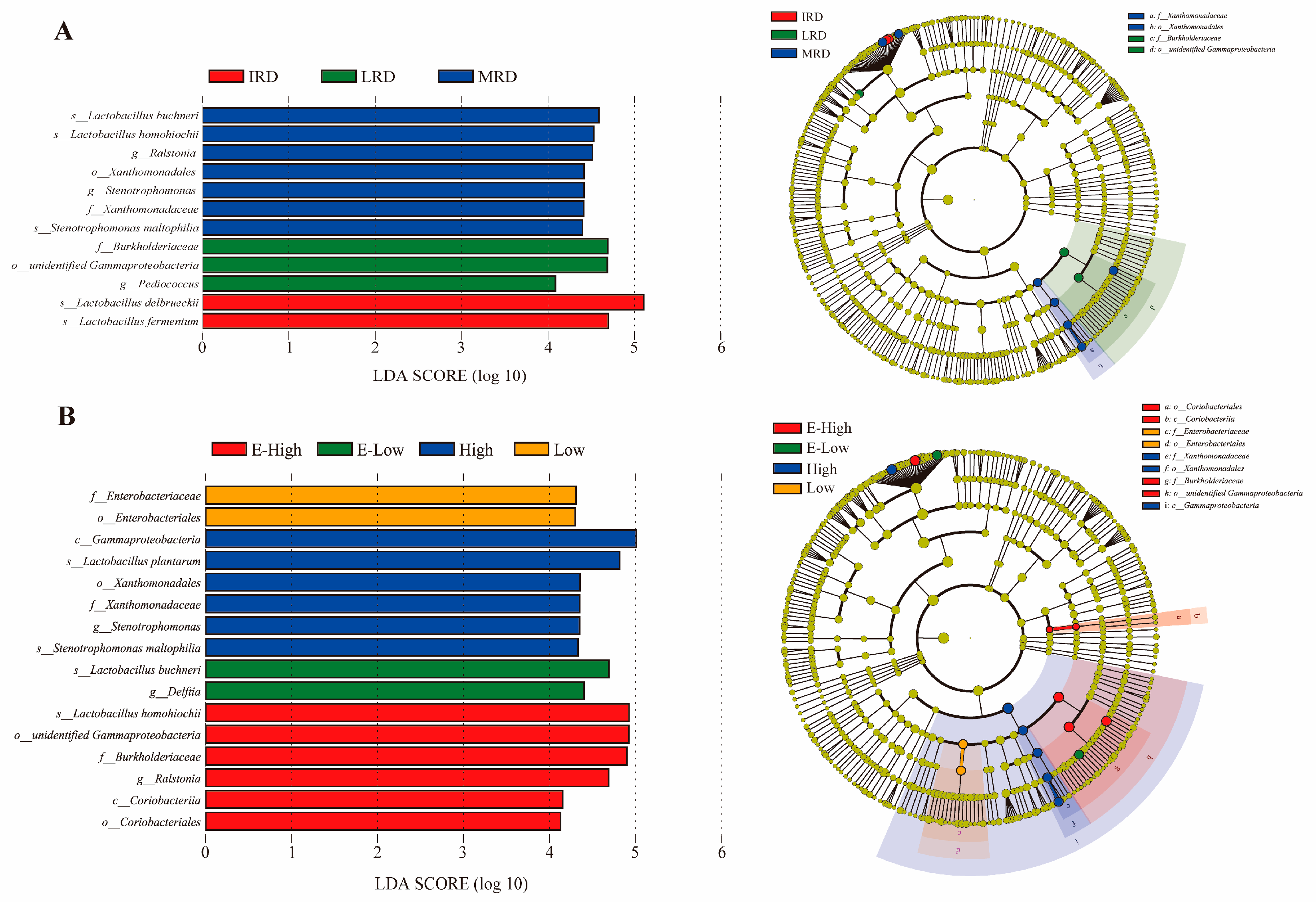
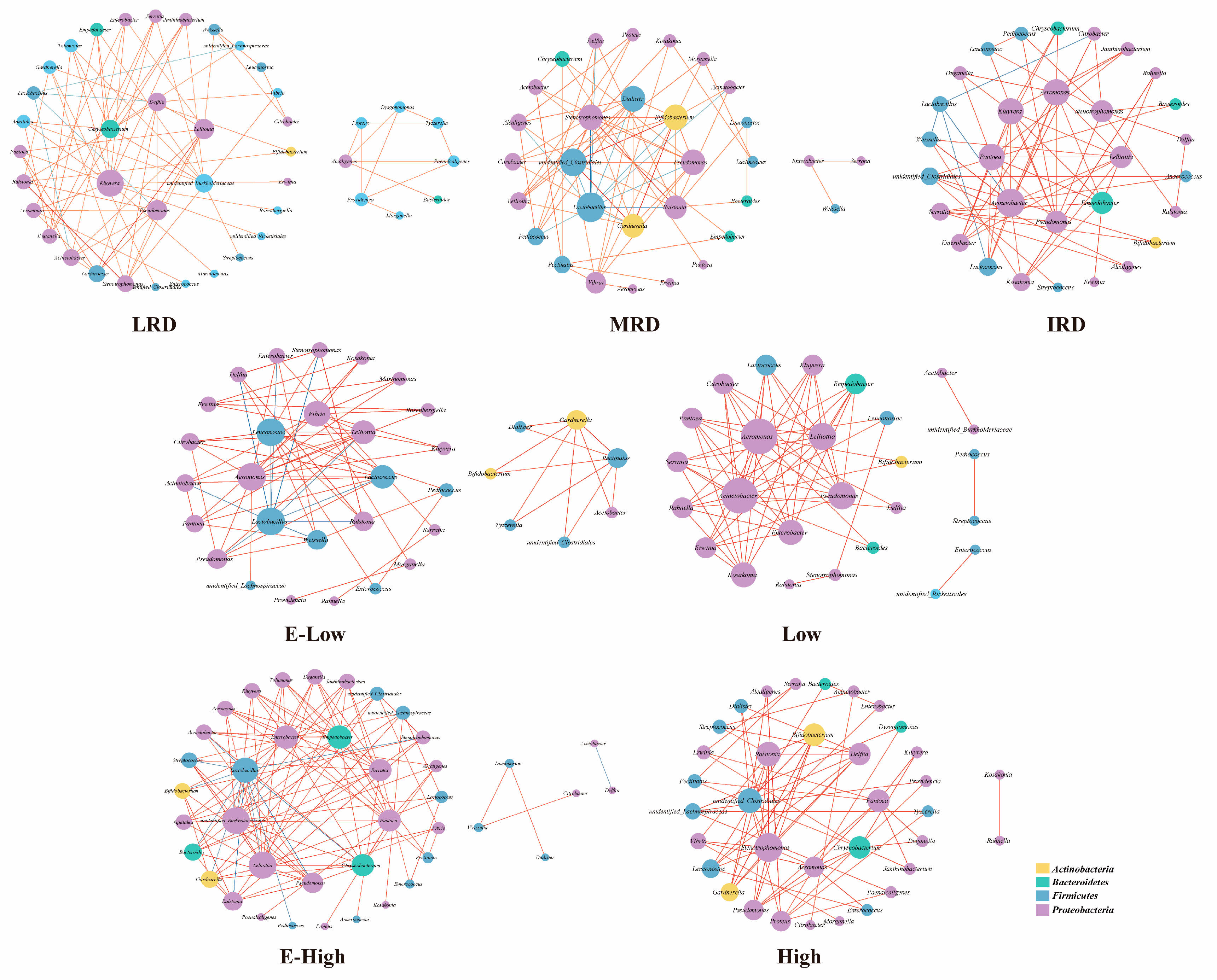
3.1. Bacterial Community Composition of Pickles
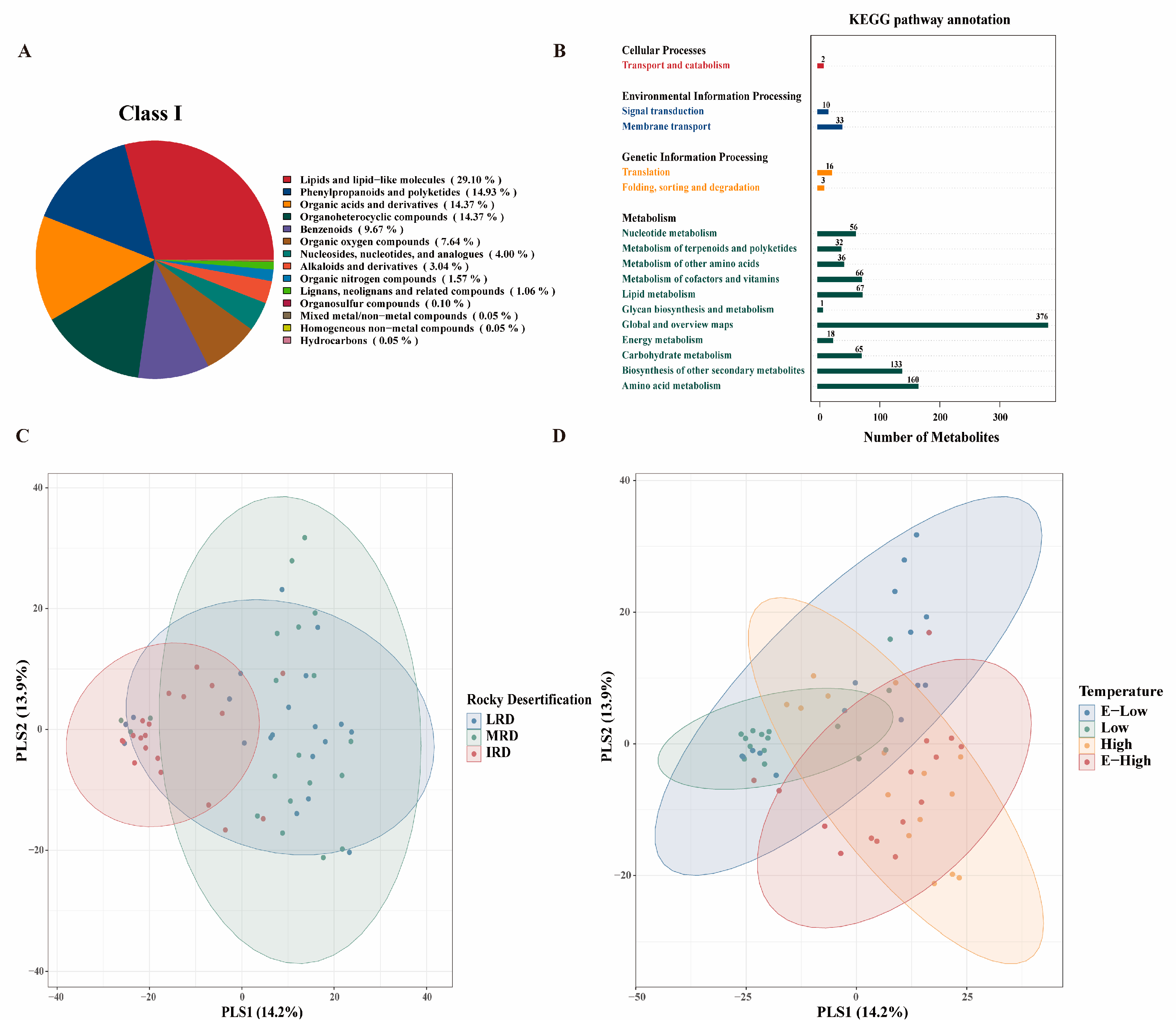
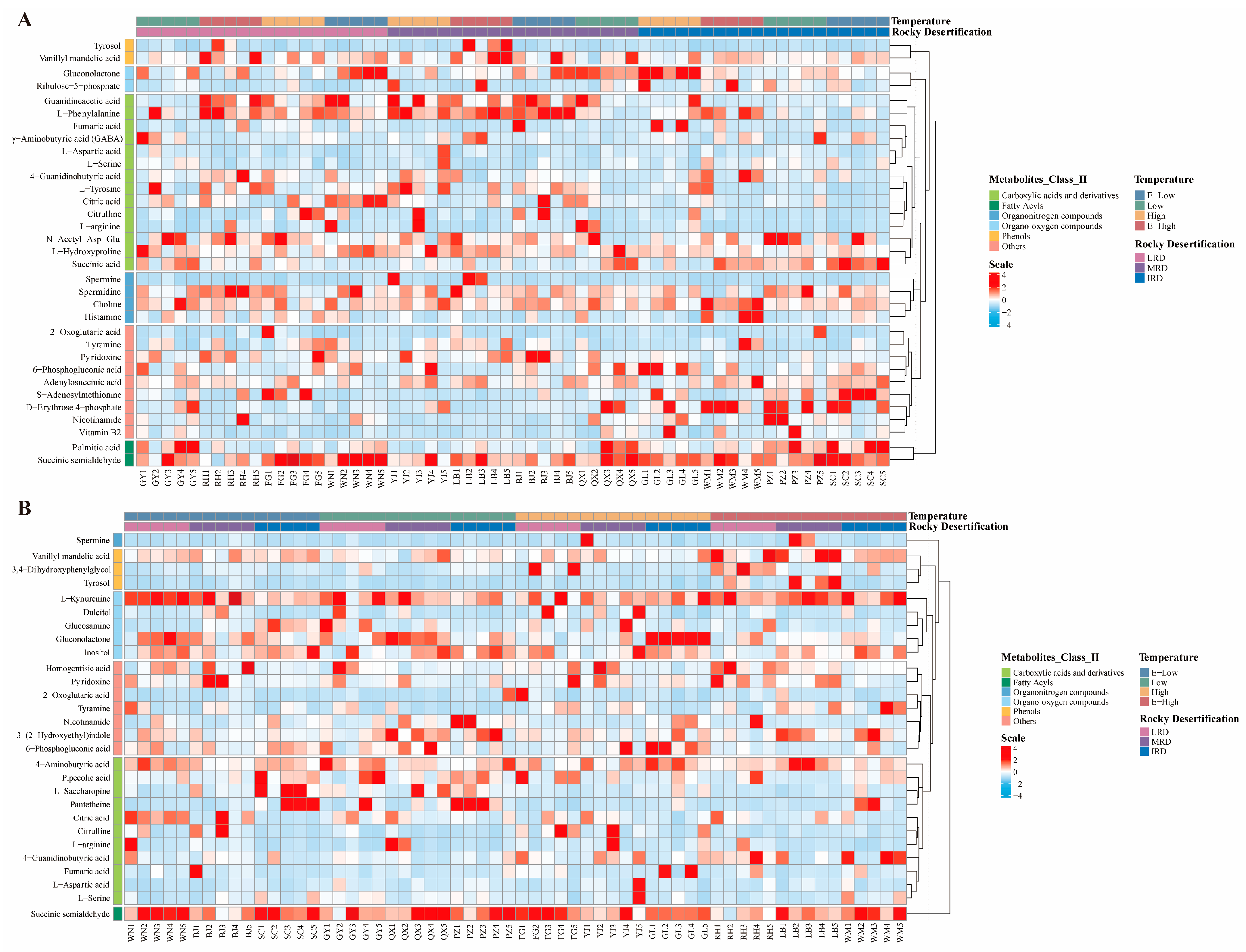
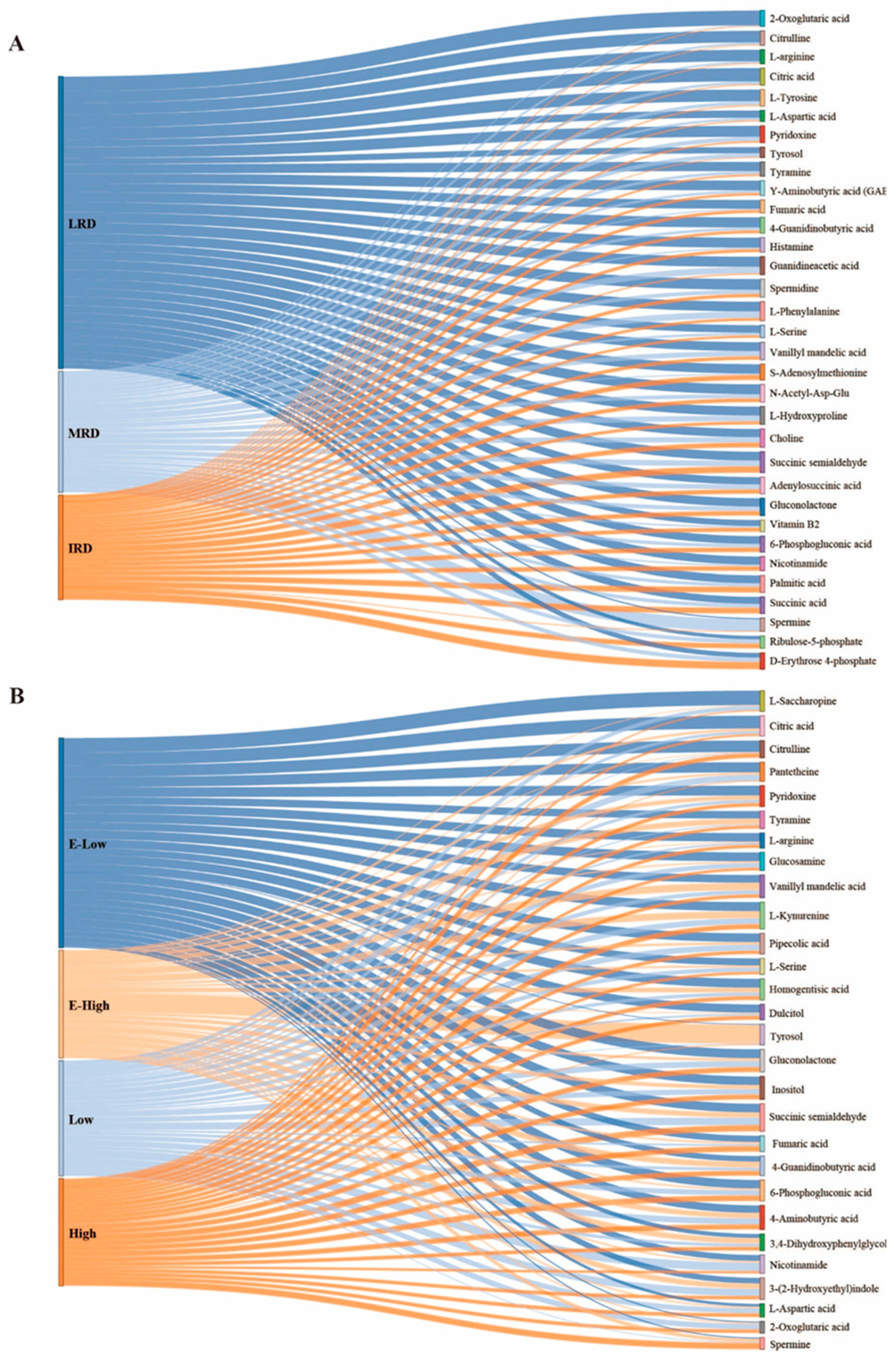
3.2. Metabolites of Pickles
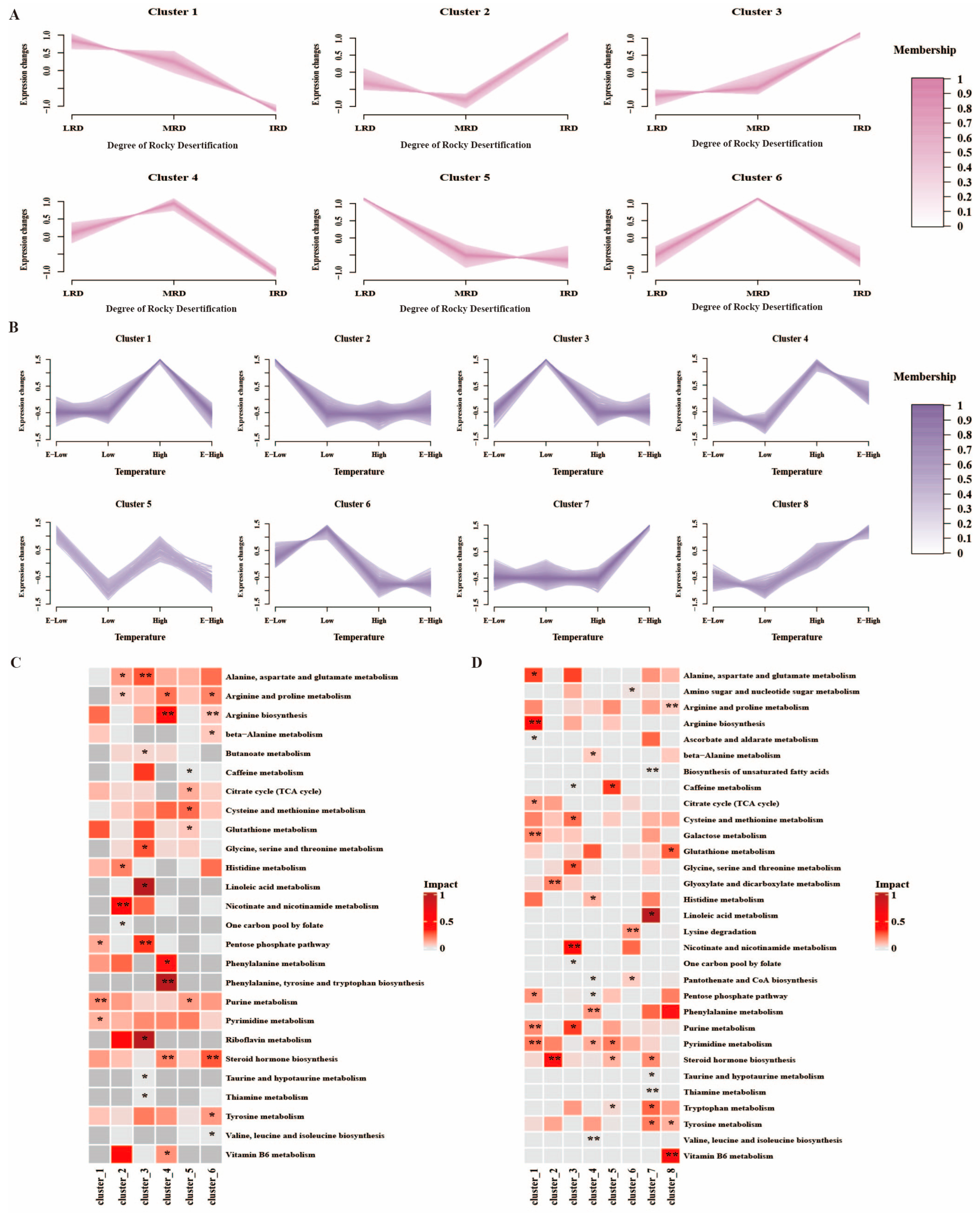
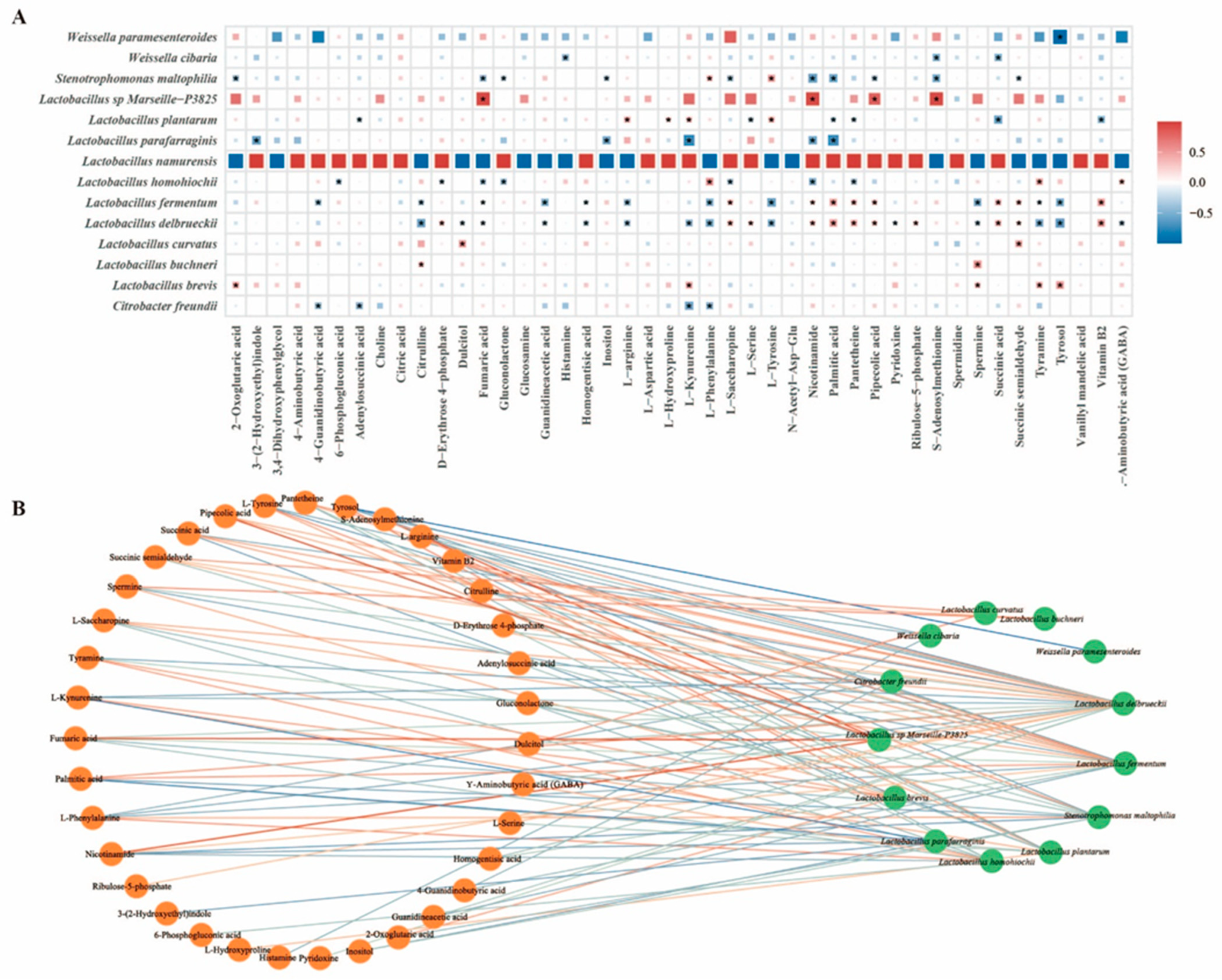
3.3. Combined Analysis of Bacterial Community and Metabolites in Pickles
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Behera, S.S.; El Sheikha, A.F.; Hammami, R.; Kumar, A. Traditionally fermented pickles: How the microbial diversity associated with their nutritional and health benefits? J. Funct. Foods 2020, 70, 103971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, C.; Kobayashi, M.; Kimoto-Nira, H. Novel exopolysaccharides produced by Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis, and the diversity of epsE genes in the exopolysaccharide biosynthesis gene clusters. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2013, 77, 2013–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.Y.; Zhang, L.; Wen, R.X.; Chen, Q.; Kong, B.H. Role of lactic acid bacteria in flavor development in traditional Chinese fermented foods: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 62, 2741–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Gupta, G.; Ahmad, T.; Kaur, B.; Hakeem, K.R. Tailoring cellular metabolism in lactic acid bacteria through metabolic engineering. J. Microbiol. Methods 2020, 170, 105862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Z.; Shang, Z.X.; Li, M.Q.; Zhang, X.T.; Ren, H.B.; Hu, X.S.; Yi, J.J. Effect of ripening and variety on the physiochemical quality and flavor of fermented Chinese chili pepper (Paojiao). Food Chem. 2022, 368, 130797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-E.; Seo, S.-H.; Kim, E.-J.; Na, C.-S.; Son, H.-S. Effects of different fermentation temperatures on metabolites of Kimchi. Food Biosci. 2018, 23, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Gao, M.; Zhang, Y.D.; Long, M.Z.; Wu, Y.J.; Li, X.N. Effects of disturbance to moss biocrusts on soil nutrients, enzyme activities, and microbial communities in degraded karst landscapes in southwest China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 152, 108065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.J.; Liu, Q.M.; Zhang, D.F. Karst rocky desertification in southwestern China: Geomorphology, landuse, impact and rehabilitation. Land Degrad. Dev 2010, 15, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Want, E.J.; Masson, P.; Michopoulos, F.; Wilson, I.D.; Theodoridis, G.; Plumb, R.S.; Shockcor, J.; Loftus, N.; Holmes, E.; Nicholson, J.K. Global metabolic profiling of animal and human tissues via UPLC-MS. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S. 1-km Monthly Mean Temperature Dataset for China (1901–2023); National Tibetan Plateau Data Center: Beijing, China, 2019; Available online: https://cstr.cn/18406.11.Meteoro.tpdc.270961 (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Heng, S.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y. Spatial Coupling Between Regional Green Urbanization and Rocky Desertification:A Case Study of Guizhou Province. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin (In Chinese). 2024, 33, 1905–1917. [Google Scholar]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, B.; Mei, Z.; Zeng, C.; Liu, S. MetaX: A flexible and comprehensive software for processing metabolomics data. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xiang, S.; Zhai, R.; Li, X.; Hu, M.; Wang, T.; Zhang, H.; Pan, L. Analysis of microbial and metabolic diversity in Jiangshui from Northwest China. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 43, e107222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Chen, H.; Wang, X.; Lin, X.P.; Ji, C.F.; Li, S.J.; Liang, H.P. Effects of different temperatures on bacterial diversity and volatile flavor compounds during the fermentation of suancai, a traditional fermented vegetable food from northeastern China. LWT 2020, 118, 108773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.Y.; Xiong, T.; Peng, Z.; Liu, C.G.; Huang, T.; Yu, H.; Xie, M.Y. Correlation between microbiota and flavours in fermentation of Chinese Sichuan Paocai. Food Res. Int. 2018, 114, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Peng, Z.; Huang, T.; Xiao, M.; Li, J.; Xie, M.; Xiong, T. Comparison of bacterial diversity in traditionally homemade paocai and Chinese spicy cabbage. Food Microbiol. 2019, 83, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Wu, Q.; Rao, C.J.; Chen, X.Y.; Wang, E.W.; Liang, X.C.; Yan, W.D. Characteristics and interactions of soil bacteria, phytocommunity and soil properties in rocky desertification ecosystems of Southwest China. CATENA 2023, 220, 106731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.D.; Chen, G.; Tang, Y.; Li, H.; Shen, W.X.; Wang, M.; Liu, S.L.; Qin, W.; Zhang, Q.S. Effects of temperature on paocai bacterial succession revealed by culture-dependent and culture-independent methods. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 317, 108463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.Y.; Shang, Z.C.; Chen, J.; Shen, Y.J.; Li, Z.J.; Huang, D.; Luo, H.B. Differences in structure, volatile metabolites, and functions of microbial communities in Nongxiangxing daqu from different production areas. LWT 2022, 166, 113784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Niu, C.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Chai, L.; Shi, J.; Xu, Z.; Li, Q. A Bottom-Up Approach to Develop a Synthetic Microbial Community Model: Application for Efficient Reduced-Salt Broad Bean Paste Fermentation. Appl. Environ. Microbio. 2020, l86, e00306-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, M.Y.; Huang, T.; Huang, C.L.; Hardie, J.; Peng, Z.; Xie, M.Y.; Xiong, T. The microbial communities and flavour compounds of Jiangxi yancai, Sichuan paocai and Dongbei suancai: Three major types of traditional Chinese fermented vegetables. LWT 2020, 121, 108865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Du, H.; Zhang, H.; Fang, C.; Jin, G.; Chen, S.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Xu, Y. Geographically Associated Fungus-Bacterium Interactions Contribute to the Formation of Geography-Dependent Flavor during High-Complexity Spontaneous Fermentation. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e01844-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Li, A.; Cheng, L.; Chen, Q.; Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Huo, D. Deep Shotgun metagenomic and 16S rRNA analysis revealed the microbial diversity of lactic acid bacteria in traditional fermented foods of eastern Hainan, China. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 12938–12952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Kwak, H.S.; Jung, H.Y.; Kim, S.S. Microbial communities related to sensory attributes in Korean fermented soy bean paste (doenjang). Food Res. Int. 2016, 89, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, Z.X.; Ye, Z.; Li, M.Q.; Ren, H.B.; Cai, S.B.; Hu, X.S.; Yi, J.J. Dynamics of microbial communities, flavor, and physicochemical properties of pickled chayote during an industrial-scale natural fermentation: Correlation between microorganisms and metabolites. Food Chem. 2022, 377, 132004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahri, S.; Zerrouk, N.; Aussel, C.; Moinard, C.; Crenn, P.; Curis, E.; Chaumeil, J.; Cynober, L.; Sfar, S. Citrulline: From metabolism to therapeutic use. Nutrition 2013, 29, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Tang, J.; Feng, Q.; Niu, Z.; Shen, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhou, S. Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA): A comprehensive review of dietary sources, enrichment technologies, processing effects, health benefits, and its applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 8852–8874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karković Marković, A.; Torić, J.; Barbarić, M.; Jakobušić Brala, C. Hydroxytyrosol, Tyrosol and Derivatives and Their Potential Effects on Human Health. Molecules 2019, 24, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, I.Y.; Jeong, C.S. Inhibitory Effects of 4-Guanidinobutyric Acid against Gastric Lesions. Biomol. Ther. 2012, 20, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostojic, S.M.; Premusz, V.; Nagy, D.; Acs, P. Guanidinoacetic acid as a novel food for skeletal muscle health. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 73, 104129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; He, W.; Wu, G. Hydroxyproline in animal metabolism, nutrition, and cell signaling. Amino Acids 2022, 54, 513–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parra, M.; Stahl, S.; Hellmann, H. Vitamin B6 and Its Role in Cell Metabolism and Physiology. Cells 2018, 7, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabie, M.A.; Siliha, H.; El-Saidy, S.; El-Badawy, A.A.; Malcata, F.X. Reduced biogenic amine contents in sauerkraut via addition of selected lactic acid bacteria. Food Chem. 2011, 129, 1778–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doeun, D.; Davaatseren, M.; Chung, M.S. Biogenic amines in foods. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 26, 1463–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dala-Paula, B.M.; Custódio, F.B.; Gloria, M.B. Health concerns associated with biogenic amines in food and interaction with amine oxidase drugs. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2023, 54, 101090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieber, C.S.; Packer, L. S-Adenosylmethionine: Molecular, biological, and clinical aspects-an introduction1,2,3. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 76, 1148S–1150S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carta, G.; Murru, E.; Banni, S.; Manca, C. Palmitic Acid: Physiological Role, Metabolism and Nutritional Implications. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.X.; Wu, B.B.; Zhao, W.T.; Pang, X.L.; Lao, F.; Liao, X.J.; Wu, J.H. Correlation between autochthonous microbial communities and key odorants during the fermentation of red pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Food Microbiol. 2020, 91, 103510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.; Qian, Y.; Tao, Y.; She, X.; Li, Y.L.; Chen, X.; Guo, S.Y.; Xiang, W.L.; Liu, L.; Du, H.J.; et al. Characterization of the microbial communities and their correlations with chemical profiles in assorted vegetable Sichuan pickles. Food Control 2020, 113, 107174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Jiang, S.; Chen, J.; Ma, C.; Huo, D.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, J. Unique Microbial Diversity and Metabolic Pathway Features of Fermented Vegetables from Hainan, China. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, X.; Xu, D.; Wang, P.; Chen, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, G.; Zhang, M.; Li, P.; Chen, C. Analysis of Bacterial and Metabolic Diversity of Pickles in Different Karst Regions of Guizhou, China. Foods 2025, 14, 1324. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081324
Huang X, Xu D, Wang P, Chen C, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Lu G, Zhang M, Li P, Chen C. Analysis of Bacterial and Metabolic Diversity of Pickles in Different Karst Regions of Guizhou, China. Foods. 2025; 14(8):1324. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081324
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Xiaokang, Duhan Xu, Pan Wang, Cheng Chen, YuJia Wang, Yubo Zhang, Guangrou Lu, Mingjie Zhang, Ping Li, and Chao Chen. 2025. "Analysis of Bacterial and Metabolic Diversity of Pickles in Different Karst Regions of Guizhou, China" Foods 14, no. 8: 1324. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081324
APA StyleHuang, X., Xu, D., Wang, P., Chen, C., Wang, Y., Zhang, Y., Lu, G., Zhang, M., Li, P., & Chen, C. (2025). Analysis of Bacterial and Metabolic Diversity of Pickles in Different Karst Regions of Guizhou, China. Foods, 14(8), 1324. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081324





