Comprehensive Evaluation of Yunnan Potato Landraces: Agronomic, Sensory, and Nutritional Traits
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials and Field Management
2.2. Experimental Method
2.2.1. Phenotypic Trait Measurement
2.2.2. Quality Trait Measurement
- (1)
- Determination of Mineral Element Content
- (2)
- Starch Pasting Characteristics
- (3)
- Tuber Textural Characteristics
- (4)
- Sensory Evaluation
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Investigation of Agronomic Traits of Landraces
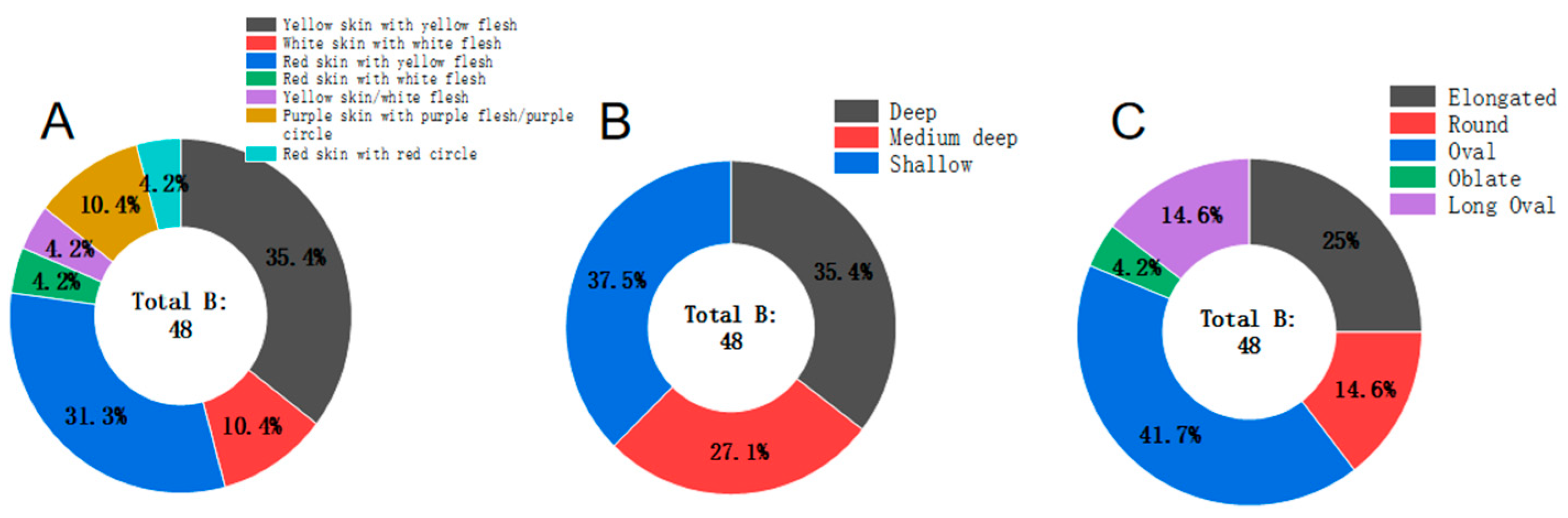
3.2. Tuber Characteristics of Landraces
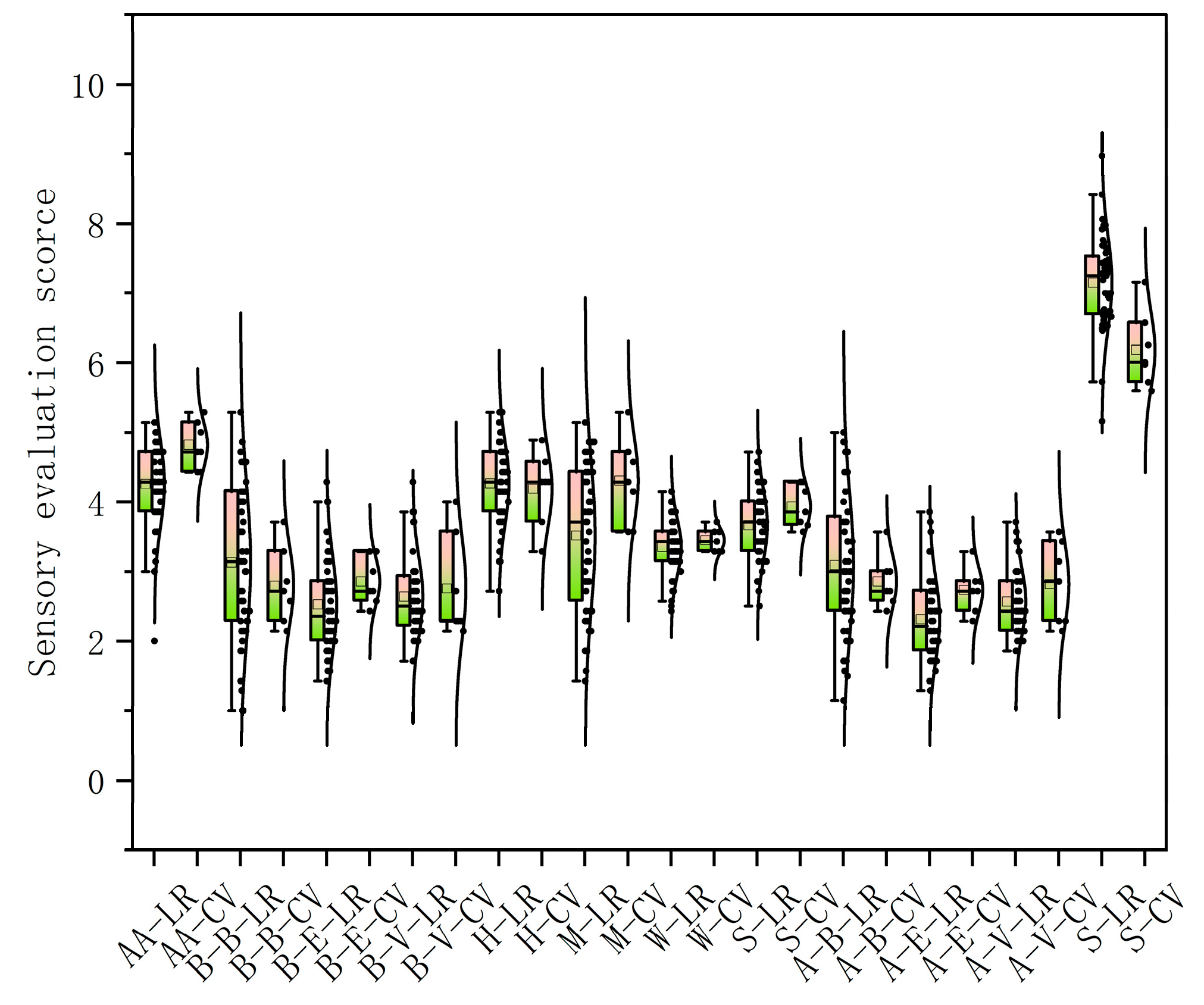
3.3. Diversity Analysis of Sensory Characteristics in Landraces
3.4. Diversity Analysis of Mineral Elements in Potato Landraces
3.5. Diversity Analysis of Starch Pasting Characteristics in Landraces
3.6. Diversity Analysis of Textural Characteristics in Landraces
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zeven, A.C. Landraces: A review of definitions and classifications. Euphytica 1998, 104, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Bian, X.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, M.; Xu, Y.; Bao, J.; Zhou, X. Mineral Contents Variation Among Cultivated and Local Potatoes. J. Nucl. Agric. Sci. 2018, 32, 2170–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.N. Research on Local Cultivars and Introduction of New Varieties in Tibet. Master’s Thesis, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing, China, 2013. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=YHRUfPYi6NO5THOIjVif2UJtH9ljGCahYX6kOu29HLI56L9QhOmThIgwDjXzD4vR4WrmcKE263R31KnxvdB1s43gqZl6Ce35Xf3cH30Kuw9EjfVIMaSNBWOxgUJ8SYTlO9Fdfkl39SdhMHfSnjNz8SeTrPaKhZP68DYyVNFTms1sMKf3xJFMxmNytV9ZnYMC3tIC-opXTwk=&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 16 January 2025).
- Gan, S.N. Evaluation and Application of 18 Local Potato Variety Resources in Yunnan. Master’s Thesis, Yunnan Agricultural University, Kunming, China, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.Q.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Feng, L.H. Genetic Relationship between Potato Local Varieties and Some Cultivars of Sichuan Revealed by RAPD Analysis. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2010, 26, 40–44. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=YHRUfPYi6NMrvH8j1fS6UqqOYGy9DIYy4noECy9RSXvJLstueubEMJeH5zQe6Oj3c7PQCRu48B_kB9iCxNgcs-acuPbqoUNA26jCIcuB_Cr7TSd42TG67EprX-vKz-Goq7awXwXRCLxP-C7smHgvwS58dUZzDoth3gRsemii7g4WkVWxYDAroXMzBcK7maY9&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 16 January 2025).
- Sun, M.L.; Li, Y.H.; Li, X.P. The History Planting Systems and Native Variety Resoures of Potato in Yunnan. Agric. Hist. China 2004, 4, 13–17. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=YHRUfPYi6NN6_2_YhN4lMpWVNOIeNvwajrtb_gTSn1GHwUmue0uFaYPec1o8vu5tmBuqZr-zja5co_2ff3vQL2mu7FFQDDRKAvWmrieCRQyCWLTNuYOD8XGcM4sIsZds_I8n9PZPn9-GXGnX9KAXgBa33hFlagz8GLxsTC7M_pBJfx8Qi5AHB2Y_g2IOhrpi&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 16 January 2025).
- Wang, Y.; Rashid, M.A.R.; Li, X.; Yao, C.; Lu, L.; Bai, J.; Li, Y.; Xu, N.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, L.; et al. Collection and Evaluation of Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of Potato Landraces and Varieties in China. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thelen, K.; Prigge, V.; Kohlmorgen, A.; Muders, K.; Truberg, B.; Hartje, S.; Renner, J.; Stich, B. Variance and covariance components of agronomic and quality traits assessed in tetraploid potato and their implications on practical breeding. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 15, 1505193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, C.H.; Poole, G.H.; Parker, P.E.; Gottwald, T.R. Plant Disease Severity Estimated Visually, by Digital Photography and Image Analysis, and by Hyperspectral Imaging. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2010, 29, 59–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NY/T1653-2008; Agricultural Industry Standard of the People’s Republic of China. Determination of Mineral Elements in Veg-etables, Fruits and Derived Products by ICP-AES Method. Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2008. Available online: https://www.chinesestandard.net/PDF/English.aspx/NYT1653-2008?Redirect (accessed on 16 January 2025).
- Slepkov, A.D.; Ridsdale, A.; Pegoraro, A.F.; Moffatt, D.J.; Stolow, A. Multimodal CARS microscopy of structured carbohydrate biopolymers. Biomed. Opt. Express 2010, 1, 1347–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.H. Comparison and Evaluation of Cooking Edibility Qualities in Waxy and Non-waxy Proso Millet. Ph.D. Thesis, Northwest A&F University, Xianyang, China, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.L.; Yuan, J.L.; Duan, H.M.; Jiang, T.H.; Liu, L.L.; Zhang, F. Comprehensive Evaluation of Potato Tuber Texture. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2022, 55, 2278–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuker, A.; Maurya, N.K. Selection and Performance of Sensory Panelists: A Comprehensive Review of Factors Influencing Sensory Evaluation Outcomes. Nutr. Food Process. 2024, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, W.L.; Gao, Y.J.; Bai, J.M.; Li, X.P. Comprehensive Evaluation of Eating Traits of Diploid Potatoes, Molecular Plant Breeding. 2022. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/46.1068.S.20221018.0826.002 (accessed on 16 January 2025).
- Oruna-Concha, M.J.; Duckham, S.C.; Ames, J.M. Comparison of Volatile Compounds Isolated from the Skin and Flesh of Four Potato Cultivars after Baking. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 2414–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobson, G.; Griffiths, D.W.; Davies, H.V.; McNicol, J.W. Comparison of Fatty Acid and Polar Lipid Contents of Tubers from Two Potato Species, Solanum tuberosum and Solanum phureja. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 6306–6314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansky, S.H. Genotypic and Environmental Contributions to Baked Potato Flavor. Am. J. Potato Res. 2008, 85, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschner, M.; Erikson, K. Manganese. Adv. Nutr. Int. Rev. J. 2017, 8, 520–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musso, C.G. Magnesium metabolism in health and disease. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2009, 41, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Institute of Medicine (IOM). Food and Nutrition Board. In Dietary Reference Intakes: Calcium, Phosphorus, Magnesium, Vitamin D and Fluorideexternal Link Disclaimer; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andre, C.M.; Ghislain, M.; Bertin, P.; Oufir, M.; Herrera, M.D.R.; Hoffmann, L.; Hausman, J.-F.; Larondelle, A.Y.; Evers, D. Andean Potato Cultivars (Solanum tuberosum L.) as a Source of Antioxidant and Mineral Micronutrients. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 366–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, K.A.; Magnuson, B.A.; Tschirgi, M.L.; Smith, B. Determining the Geographic Origin of Potatoes with Trace Metal Analysis Using Statistical and Neural Network Classifiers. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 1568–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
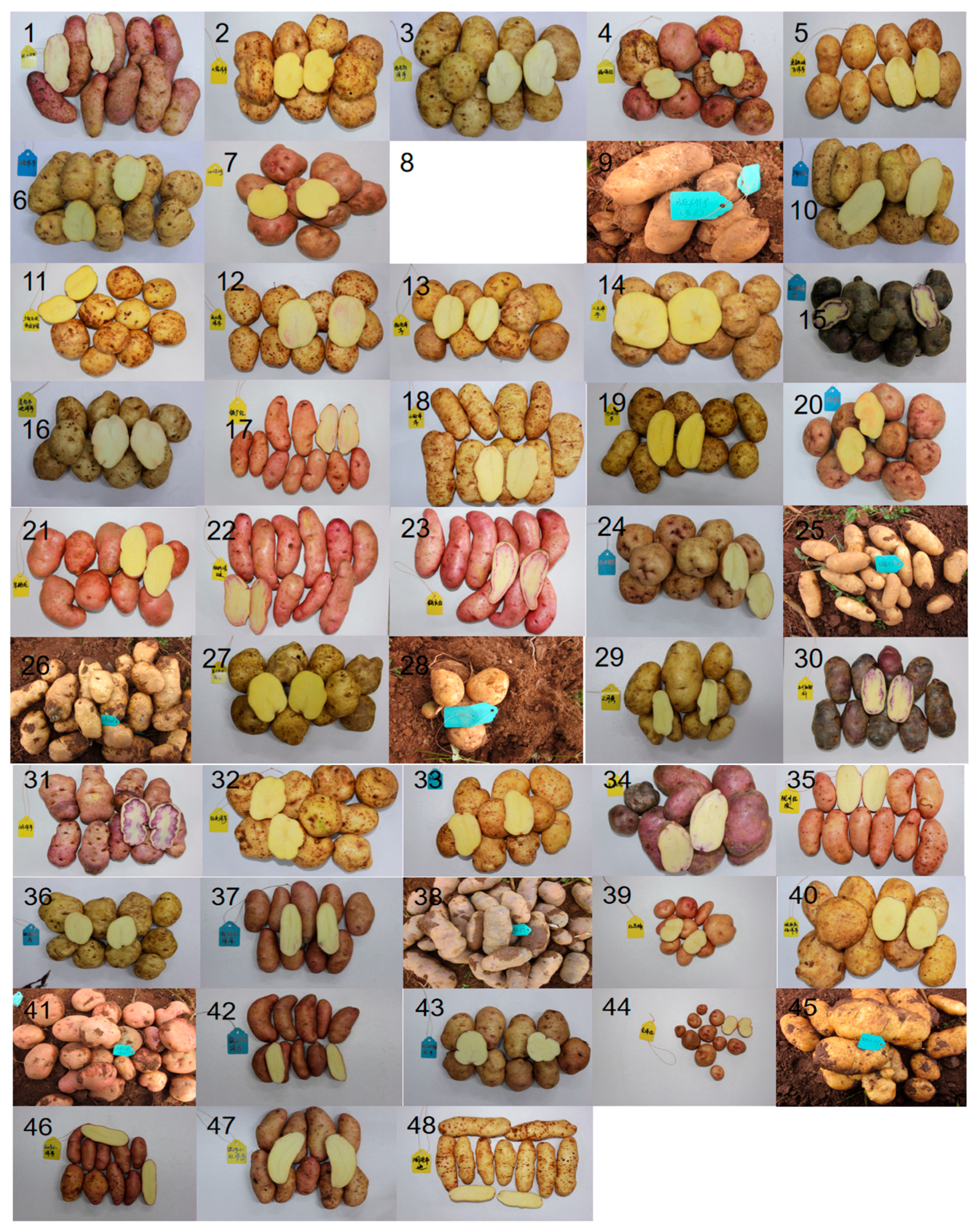
| No. | Variety Name | No | Variety Name | No | Variety Name | No | Variety Name | No | Variety Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Haoziyangyu | 12 | Gongshanduyangyu | 23 | Heqinghong | 34 | Dongchuanmuduo | 45 | Yaoziyangyu |
| 2 | Dawoyangyu | 13 | Lincangyangyu | 24 | Hongdayanjing | 35 | Longchuanhongpi | 46 | Honghexiaoyangyu |
| 3 | Luojibaiyangyu | 14 | Erwuyangyu | 25 | Xiaonuoyang | 36 | Tiekeyangyu | 47 | Lianghexiaohongyangyu |
| 4 | Gezanhong | 15 | Dongchuanxiaowuyangyu | 26 | Xinluliang1 | 37 | Nandianhong | 48 | Lancangbendiyangyu |
| 5 | Hutiaoxiabaiyyangyu | 16 | Jinggubendiyangyu | 27 | Dongchuanshekuaiyangyu | 38 | Zihuayangyu | 49 | YS505 |
| 6 | Wakeyangyu | 17 | Tiechanghong | 28 | Chaomila | 39 | Hongmanan | 50 | YS702 |
| 7 | Gama2 | 18 | Xiaoziyangyu | 29 | Sanyuehuang | 40 | Weixiqingfuyangyu | 51 | Cooperation88 |
| 8 | Tachenghongyangyu | 19 | Hebayangyu | 30 | Dongchuanmajiaogan | 41 | Laojiayangyu(Xinping) | 52 | YS304 |
| 9 | Banna1 | 20 | Kaihuayangyu | 31 | Xiaowuyyangyu | 42 | Yingjianghongyu | 53 | Qingshu9 |
| 10 | Guangnanbaipi | 21 | Zaofenlong | 32 | Zilaiyangyu | 43 | Nujiangxiaonuoyangyu | 54 | YS401 |
| 11 | Guangnanbaipi1 | 22 | Banna1(hongpi) | 33 | Baihuayyangyu | 44 | Huizehong | 55 | Yunxuan2 |
| Landraces | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Standard Deviation | Minimum | Maximum | Coefficient of Variation/% | |
| Appearance acceptability | 4.26 | 0.61 | 2.00 | 5.14 | 14.39 |
| Pre-tasting buttery flavor | 3.13 | 1.10 | 1.00 | 5.29 | 35.27 |
| Pre-tasting earthy flavor | 2.52 | 0.68 | 1.43 | 4.29 | 26.99 |
| Pre-tasting boiled vegetable flavor | 2.64 | 0.56 | 1.71 | 4.29 | 21.20 |
| Hardness | 4.27 | 0.59 | 2.71 | 5.29 | 13.79 |
| Mealiness | 3.51 | 1.05 | 1.43 | 5.14 | 29.86 |
| Waxiness | 3.35 | 0.40 | 2.43 | 4.14 | 11.96 |
| Stickiness | 3.67 | 0.51 | 2.50 | 4.71 | 13.83 |
| Post-tasting buttery flavor | 3.09 | 1.03 | 1.14 | 5.00 | 33.42 |
| Post-tasting earthy flavor | 2.31 | 0.59 | 1.29 | 3.86 | 25.44 |
| Post-tasting boiled vegetable flavor | 2.57 | 0.48 | 1.86 | 3.71 | 18.63 |
| Overall score | 7.15 | 0.66 | 5.16 | 8.97 | 9.28 |
| Commercial varieties | |||||
| Appearance acceptability | 4.82 | 0.34 | 4.43 | 5.28 | 7.00 |
| Pre-tasting buttery flavor | 2.80 | 0.55 | 2.14 | 3.71 | 19.76 |
| Pre-tasting earthy flavor | 2.86 | 0.34 | 2.43 | 3.28 | 11.90 |
| Pre-tasting boiled vegetable flavor | 2.76 | 0.74 | 2.14 | 4.00 | 26.73 |
| Hardness | 4.19 | 0.53 | 3.29 | 4.89 | 12.71 |
| Mealiness | 4.31 | 0.62 | 3.57 | 5.28 | 14.39 |
| Waxiness | 3.45 | 0.17 | 3.29 | 3.71 | 5.03 |
| Stickiness | 3.93 | 0.30 | 3.57 | 4.28 | 7.69 |
| Post-tasting buttery flavor | 2.86 | 0.38 | 2.43 | 3.57 | 13.23 |
| Post-tasting earthy flavor | 2.73 | 0.32 | 2.29 | 3.28 | 11.85 |
| Post-tasting boiled vegetable flavor | 2.82 | 0.59 | 2.14 | 3.57 | 20.86 |
| Overall score | 6.18 | 0.54 | 5.59 | 7.16 | 8.75 |
| Landraces | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Standard Deviation | Minimum | Maximum | Coefficient of Variation/% | |
| Zinc (mg/kg) | 2.48 | 0.48 | 1.69 | 4.10 | 19.36 |
| Phosphorus (mg/kg) | 501.05 | 92.04 | 340.00 | 671.50 | 18.37 |
| Iron (mg/kg) | 16.08 | 6.00 | 3.80 | 35.45 | 37.32 |
| Manganese (mg/kg) | 2.00 | 0.48 | 1.07 | 2.99 | 23.91 |
| Magnesium (mg/kg) | 237.55 | 37.70 | 136.13 | 345.50 | 15.87 |
| Calcium (mg/kg) | 43.92 | 9.24 | 30.40 | 69.70 | 21.04 |
| Copper (mg/kg) | 1.51 | 0.71 | 0.59 | 4.20 | 46.67 |
| Boron (mg/kg) | 0.71 | 0.26 | 0.00 | 1.21 | 37.02 |
| Commercial varieties | |||||
| Zinc (mg/kg) | 2.53 | 0.67 | 1.68 | 3.61 | 26.47 |
| Phosphorus (mg/kg) | 527.64 | 111.46 | 396.00 | 711.50 | 21.12 |
| Iron (mg/kg) | 16.85 | 9.55 | 8.58 | 37.20 | 56.64 |
| Manganese (mg/kg) | 1.76 | 0.14 | 1.46 | 1.89 | 7.94 |
| Magnesium (mg/kg) | 238.93 | 22.21 | 206.50 | 270.00 | 9.30 |
| Calcium (mg/kg) | 45.16 | 8.26 | 36.95 | 61.25 | 18.29 |
| Copper (mg/kg) | 1.58 | 0.97 | 0.56 | 3.66 | 61.26 |
| Boron (mg/kg) | 0.86 | 0.41 | 0.19 | 1.30 | 47.36 |
| Landraces | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Standard Deviation | Minimum | Maximum | Coefficient of Variation/% | |
| PV/RVU | 12,368.27 | 1008.74 | 9995.00 | 14,607.00 | 8.16 |
| TV/RVU | 2027.56 | 887.26 | 895.00 | 4267.00 | 43.76 |
| BD/RVU | 10,340.71 | 1224.87 | 6678.00 | 12,523.00 | 11.85 |
| FV/RVU | 4130.02 | 418.11 | 3400.00 | 5348.00 | 10.12 |
| SB/RVU | 2102.46 | 759.52 | 515.00 | 3277.00 | 36.13 |
| PT/°C | 67.19 | 1.91 | 62.60 | 70.30 | 2.85 |
| Commercial varieties | |||||
| PV/RVU | 12,354.43 | 1056.37 | 11,467.00 | 14,286.00 | 8.55 |
| TV/RVU | 1886.43 | 310.52 | 1407.00 | 2424.00 | 16.46 |
| BD/RVU | 10,468.00 | 1036.95 | 9272.00 | 12,223.00 | 9.91 |
| FV/RVU | 3954.86 | 418.47 | 3384.00 | 4514.00 | 10.58 |
| SB/RVU | 2068.43 | 545.81 | 960.00 | 2644.00 | 26.39 |
| PT/°C | 68.10 | 0.44 | 67.70 | 68.70 | 0.65 |
| Landraces | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Standard Deviation | Minimum | Maximum | Coefficient of Variation/% | |
| Hardness/N | 630.96 | 229.67 | 178.28 | 1139.73 | 0.36 |
| Peak load/N | 734.00 | 252.22 | 281.63 | 1596.68 | 0.34 |
| Springiness/mm | 0.60 | 0.14 | 0.29 | 0.85 | 0.23 |
| Cohesiveness/ratio | 0.16 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.42 | 0.49 |
| Gumminess/N | 101.40 | 56.23 | 15.66 | 276.80 | 0.55 |
| Chewiness/mj | 58.72 | 35.54 | 11.04 | 183.32 | 0.61 |
| Commercial varieties | |||||
| Hardness/N | 504.86 | 180.76 | 201.19 | 762.37 | 0.36 |
| Peak load/N | 545.29 | 225.56 | 148.18 | 758.26 | 0.41 |
| Springiness/mm | 0.51 | 0.16 | 0.23 | 0.69 | 0.32 |
| Cohesiveness/ratio | 0.18 | 0.10 | 0.07 | 0.36 | 0.53 |
| Gumminess/N | 90.24 | 53.15 | 12.85 | 166.63 | 0.59 |
| Chewiness/mj | 43.50 | 26.80 | 3.24 | 93.85 | 0.62 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Yao, C.; He, J.; Zhang, L.; Bai, J.; Li, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, B.; Li, X.; Pan, Z.; et al. Comprehensive Evaluation of Yunnan Potato Landraces: Agronomic, Sensory, and Nutritional Traits. Foods 2025, 14, 1298. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081298
Wang Y, Yao C, He J, Zhang L, Bai J, Li Y, Zhou J, Zhao B, Li X, Pan Z, et al. Comprehensive Evaluation of Yunnan Potato Landraces: Agronomic, Sensory, and Nutritional Traits. Foods. 2025; 14(8):1298. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081298
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ying, Chunguang Yao, Jitian He, Lei Zhang, Jianming Bai, Yanshan Li, Jinhua Zhou, Beilei Zhao, Xianping Li, Zhechao Pan, and et al. 2025. "Comprehensive Evaluation of Yunnan Potato Landraces: Agronomic, Sensory, and Nutritional Traits" Foods 14, no. 8: 1298. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081298
APA StyleWang, Y., Yao, C., He, J., Zhang, L., Bai, J., Li, Y., Zhou, J., Zhao, B., Li, X., Pan, Z., & Yang, W. (2025). Comprehensive Evaluation of Yunnan Potato Landraces: Agronomic, Sensory, and Nutritional Traits. Foods, 14(8), 1298. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081298





