Novel Endo-β-N-Acetylglucosaminidases Derived from Human Fecal Samples Selectively Release N-Glycans from Model Glycoproteins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Sample Origins
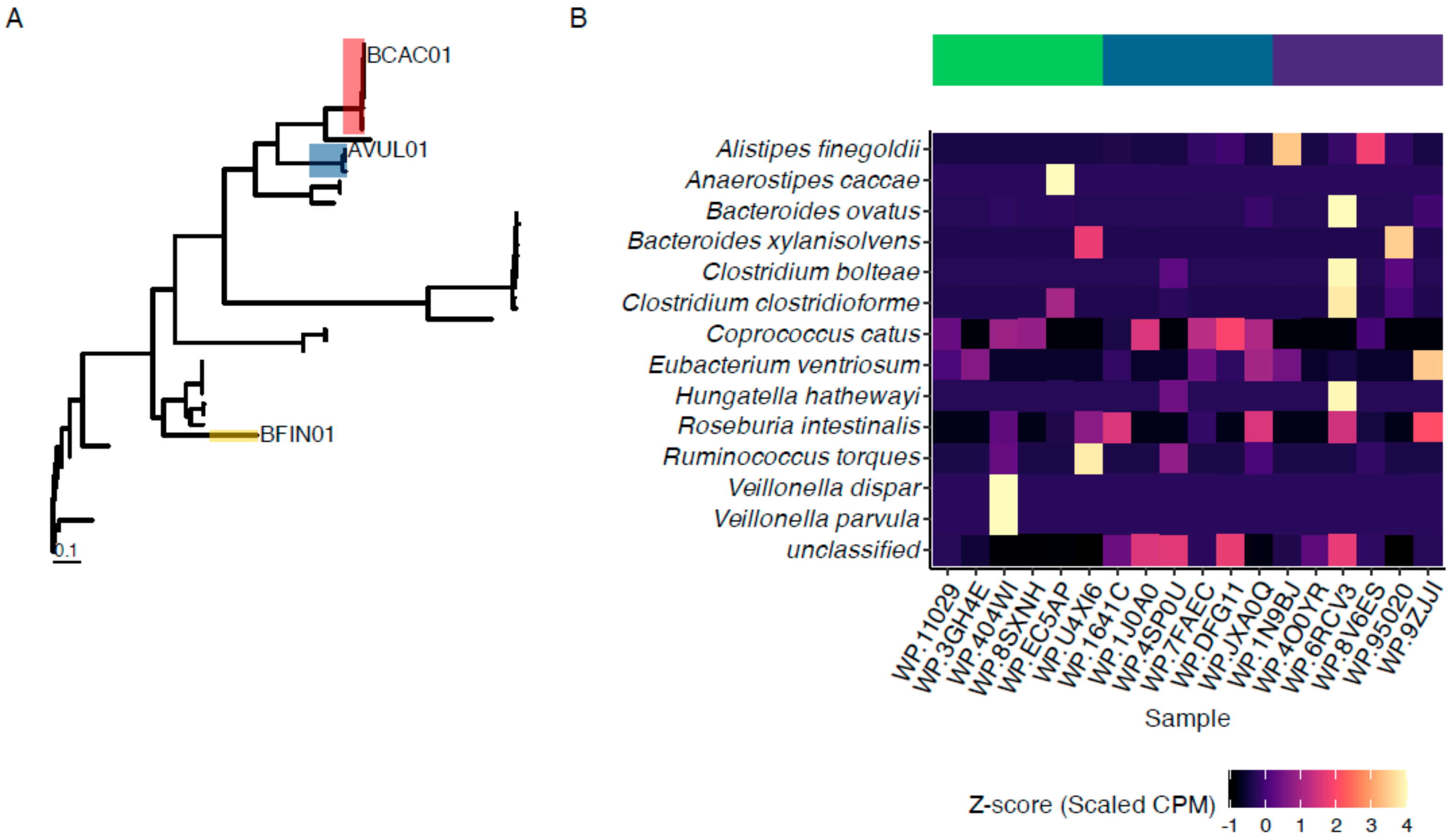
2.2. Sequencing and Identification of Endo-β-N-Acetylglucosaminidases
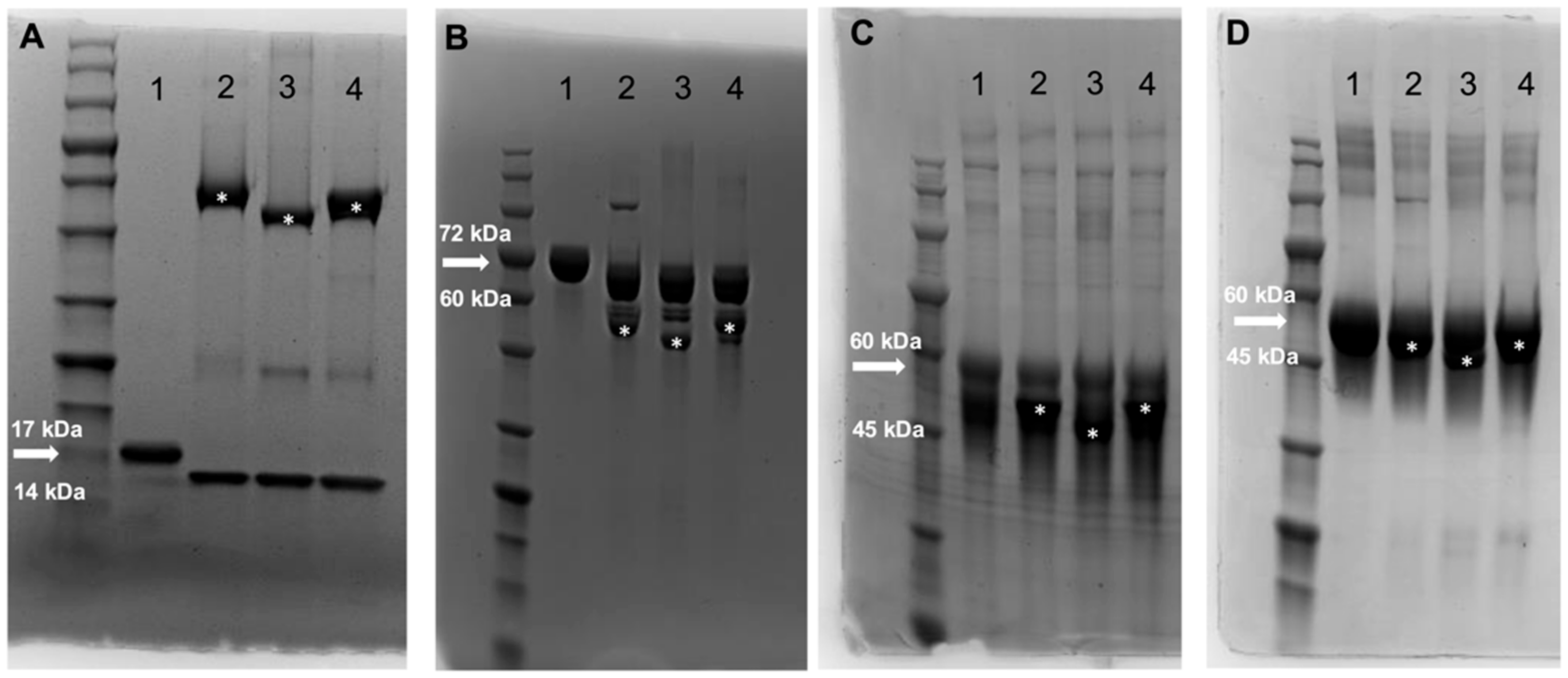
2.3. Cloning and Production of Candidate Enzymes
2.4. Comparison of N-Glycan Release by ENGases
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Identification and Production of Novel ENGases from Human Fecal Samples
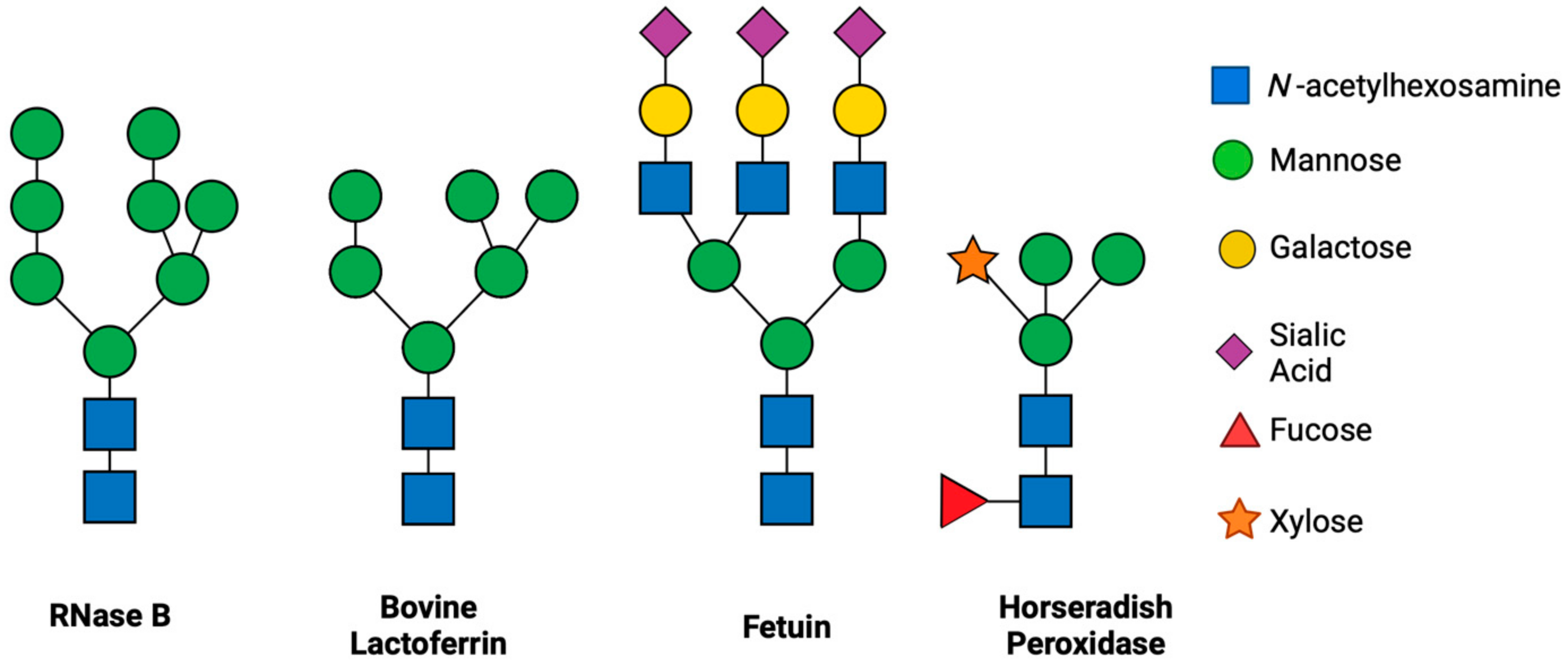
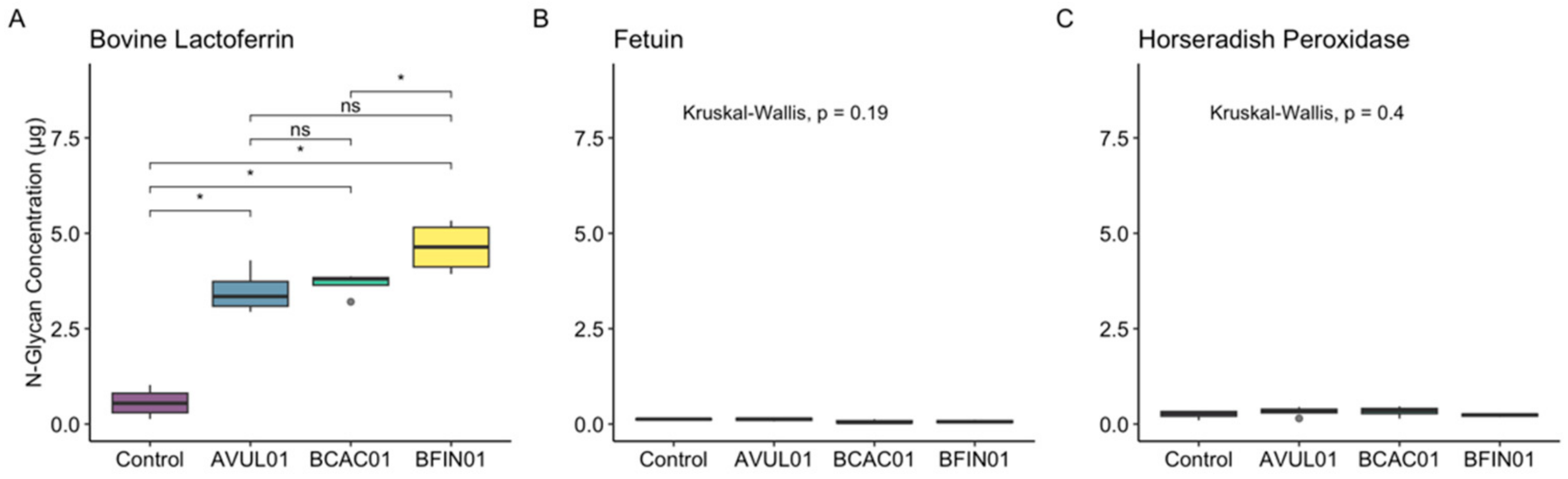
3.2. ENGases Display Catalytic Activity Exclusively on Oligomannose Glycoproteins
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berg, G.; Rybakova, D.; Fischer, D.; Cernava, T.; Vergès, M.-C.C.; Charles, T.; Chen, X.; Cocolin, L.; Eversole, K.; Corral, G.H.; et al. Microbiome Definition Re-Visited: Old Concepts and New Challenges. Microbiome 2020, 8, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holscher, H.D. Dietary Fiber and Prebiotics and the Gastrointestinal Microbiota. Gut Microbes 2017, 8, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koropatkin, N.M.; Cameron, E.A.; Martens, E.C. How Glycan Metabolism Shapes the Human Gut Microbiota. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makki, K.; Deehan, E.C.; Walter, J.; Bäckhed, F. The Impact of Dietary Fiber on Gut Microbiota in Host Health and Disease. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, M.S.; Seekatz, A.M.; Koropatkin, N.M.; Kamada, N.; Hickey, C.A.; Wolter, M.; Pudlo, N.A.; Kitamoto, S.; Terrapon, N.; Muller, A.; et al. A Dietary Fiber-Deprived Gut Microbiota Degrades the Colonic Mucus Barrier and Enhances Pathogen Susceptibility. Cell 2016, 167, 1339–1353.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windey, K.; De Preter, V.; Verbeke, K. Relevance of Protein Fermentation to Gut Health. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2012, 56, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolino, M.; Avcı, İ.; Kayili, H.M.; Duman, H.; Salih, B.; Karav, S.; Frese, S.A. Identification and Comparison of N-Glycome Profiles from Common Dietary Protein Sources. Food Chem. X 2025, 25, 102025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karav, S.; Le Parc, A.; Leite Nobrega de Moura Bell, J.M.; Frese, S.A.; Kirmiz, N.; Block, D.E.; Barile, D.; Mills, D.A. Oligosaccharides Released from Milk Glycoproteins Are Selective Growth Substrates for Infant-Associated Bifidobacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 3622–3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briliūtė, J.; Urbanowicz, P.A.; Luis, A.S.; Baslé, A.; Paterson, N.; Rebello, O.; Hendel, J.; Ndeh, D.A.; Lowe, E.C.; Martens, E.C.; et al. Complex N-Glycan Breakdown by Gut Bacteroides Involves an Extensive Enzymatic Apparatus Encoded by Multiple Co-Regulated Genetic Loci. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 1571–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitling, J.; Aebi, M. N-Linked Protein Glycosylation in the Endoplasmic Reticulum. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a013359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aebi, M. N-Linked Protein Glycosylation in the ER. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Res. 2013, 1833, 2430–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wang, H.; Gai, J.; Tian, X.; Zhang, X.; Lv, Y.; Jian, Y. Evolution of Protein N-Glycosylation Process in Golgi Apparatus Which Shapes Diversity of Protein N-Glycan Structures in Plants, Animals and Fungi. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagneux, P.; Panin, V.; Hennet, T.; Aebi, M.; Varki, A. Evolution of Glycan Diversity. In Essentials of Glycobiology; Varki, A., Cummings, R.D., Esko, J.D., Stanley, P., Hart, G.W., Aebi, M., Mohnen, D., Kinoshita, T., Packer, N.H., Prestegard, J.H., et al., Eds.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2022; ISBN 978-1-62182-421-3. [Google Scholar]
- Duman, H.; Kaplan, M.; Arslan, A.; Sahutoglu, A.S.; Kayili, H.M.; Frese, S.A.; Karav, S. Potential Applications of Endo-β-N-Acetylglucosaminidases from Bifidobacterium longum Subspecies Infantis in Designing Value-Added, Next-Generation Infant Formulas. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 646275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funkhouser, J.D.; Aronson, N.N. Chitinase Family GH18: Evolutionary Insights from the Genomic History of a Diverse Protein Family. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barratt, M.J.; Nuzhat, S.; Ahsan, K.; Frese, S.A.; Arzamasov, A.A.; Sarker, S.A.; Islam, M.M.; Palit, P.; Islam, M.R.; Hibberd, M.C.; et al. Bifidobacterium infantis Treatment Promotes Weight Gain in Bangladeshi Infants with Severe Acute Malnutrition. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabk1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbe, J.; Sjögren, J.; Cosgrave, E.F.J.; Struwe, W.B.; Bober, M.; Olin, A.I.; Rudd, P.M.; Collin, M. EndoE from Enterococcus faecalis Hydrolyzes the Glycans of the Biofilm Inhibiting Protein Lactoferrin and Mediates Growth. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 91035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoog, E.C.; Castagna, V.F.; Omer, S.; Madigan, J.; Flagg, V.; Burrick, K.; Jiang, R.; Du, X.; Lönnerdal, B.; Schnitzler, A. Structure and Function of Fermentation-Derived Bovine Lactoferrin Produced from Komagataella phaffii. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2025, 103, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolino, M.; Duman, H.; Avcı, İ.; Kayili, H.M.; Petereit, J.; Zundel, C.; Salih, B.; Karav, S.; Frese, S.A. Proteomic and N-Glycomic Comparison of Synthetic and Bovine Whey Proteins and Their Effect on Human Gut Microbiomes. bioRxiv 2024, 2024.09.18.613515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores Martinez, K.E.; Bloszies, C.S.; Bolino, M.J.; Henrick, B.M.; Frese, S.A. Hemp Hull Fiber and Two Constituent Compounds, N-Trans-Caffeoyltyramine and N-Trans-Feruloyltyramine, Shape the Human Gut Microbiome in Vitro. Food Chem. X 2024, 23, 101611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushnell, B.; Rood, J.; Singer, E. BBMerge–Accurate Paired Shotgun Read Merging via Overlap. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurk, S.; Meleshko, D.; Korobeynikov, A.; Pevzner, P.A. metaSPAdes: A New Versatile Metagenomic Assembler. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 824–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, D.D.; Li, F.; Kirton, E.; Thomas, A.; Egan, R.; An, H.; Wang, Z. MetaBAT 2: An Adaptive Binning Algorithm for Robust and Efficient Genome Reconstruction from Metagenome Assemblies. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid Prokaryotic Genome Annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Zhang, H.; Wu, P.; Entwistle, S.; Li, X.; Yohe, T.; Yi, H.; Yang, Z.; Yin, Y. dbCAN-Seq: A Database of Carbohydrate-Active Enzyme (CAZyme) Sequence and Annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D516–D521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple Sequence Alignment with High Accuracy and High Throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and Applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic Local Alignment Search Tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beghini, F.; McIver, L.J.; Blanco-Míguez, A.; Dubois, L.; Asnicar, F.; Maharjan, S.; Mailyan, A.; Manghi, P.; Scholz, M.; Thomas, A.M.; et al. Integrating Taxonomic, Functional, and Strain-Level Profiling of Diverse Microbial Communities with bioBakery 3. eLife 2021, 10, e65088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karav, S.; Bell, J.M.L.N.D.M.; Le Parc, A.; Liu, Y.; Mills, D.A.; Block, D.E.; Barile, D. Characterizing the Release of Bioactive N-Glycans from Dairy Products by a Novel Endo-β-N-Acetylglucosaminidase. Biotechnol. Prog. 2015, 31, 1331–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuko, T.; Minami, A.; Iwasaki, N.; Majima, T.; Nishimura, S.-I.; Lee, Y.C. Carbohydrate Analysis by a Phenol-Sulfuric Acid Method in Microplate Format. Anal. Biochem. 2005, 339, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kruskal, W.H.; Wallis, W.A. Use of Ranks in One-Criterion Variance Analysis. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1952, 47, 583–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcoxon, F. Individual Comparisons by Ranking Methods. In Breakthroughs in Statistics: Methodology and Distribution; Kotz, S., Johnson, N.L., Eds.; Springer Series in Statistics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1992; pp. 196–202. ISBN 978-1-4612-4380-9. [Google Scholar]
- Kassambara, A. Ggpubr: “ggplot2” Based Publication Ready Plots. 2022. Available online: https://rpkgs.datanovia.com/ggpubr/ (accessed on 10 January 2025).
- Kassambara, A. Rstatix: Pipe-Friendly Framework for Basic Statistical Tests. 2022. Available online: https://rdrr.io/cran/rstatix/ (accessed on 10 January 2025).
- Trastoy, B.; Du, J.J.; Klontz, E.H.; Li, C.; Cifuente, J.O.; Wang, L.-X.; Sundberg, E.J.; Guerin, M.E. Structural Basis of Mammalian High-Mannose N-Glycan Processing by Human Gut Bacteroides. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prien, J.M.; Ashline, D.J.; Lapadula, A.J.; Zhang, H.; Reinhold, V.N. The High Mannose Glycans from Bovine Ribonuclease B Isomer Characterization by Ion Trap MS. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2009, 20, 539–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanesh Kumar, B.S.; Mattad, S. Comprehensive Analysis of Lactoferrin N-Glycans with Site-Specificity from Bovine Colostrum Using Specific Proteases and RP-UHPLC-MS/MS. Int. Dairy J. 2021, 119, 104999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marie, A.-L.; Ray, S.; Ivanov, A.R. Highly-Sensitive Label-Free Deep Profiling of N-Glycans Released from Biomedically-Relevant Samples. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurosaka, A.; Yano, A.; Itoh, N.; Kuroda, Y.; Nakagawa, T.; Kawasaki, T. The Structure of a Neural Specific Carbohydrate Epitope of Horseradish Peroxidase Recognized by Anti-Horseradish Peroxidase Antiserum. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 4168–4172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Cai, Z.P.; Gu, X.Q.; Ma, H.Y.; Du, Y.M.; Huang, K.; Voglmeir, J.; Liu, L. Discovery and Characterization of a Novel Extremely Acidic Bacterial N-Glycanase with Combined Advantages of PNGase F and A. Biosci. Rep. 2014, 34, e00149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouch, L.I.; Urbanowicz, P.A.; Baslé, A.; Cai, Z.-P.; Liu, L.; Voglmeir, J.; Melo Diaz, J.M.; Benedict, S.T.; Spencer, D.I.R.; Bolam, D.N. Plant N-Glycan Breakdown by Human Gut Bacteroides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2208168119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeze, H.H.; Kranz, C. Endoglycosidase and Glycoamidase Release of N-Linked Glycans. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2010, 89, 17.13A.1–17.13A.25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trastoy, B.; Klontz, E.; Orwenyo, J.; Marina, A.; Wang, L.-X.; Sundberg, E.J.; Guerin, M.E. Structural Basis for the Recognition of Complex-Type N-Glycans by Endoglycosidase S. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameleers, L.; Gaenssle, L.A.; Bertran-Llorens, S.; Pijning, T.; Jurak, E. Polysaccharide Utilization Loci Encoded DUF1735 Likely Functions as Membrane-Bound Spacer for Carbohydrate Active Enzymes. FEBS Open Bio 2024, 14, 1133–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuskin, F.; Lowe, E.C.; Temple, M.J.; Zhu, Y.; Cameron, E.A.; Pudlo, N.A.; Porter, N.T.; Urs, K.; Thompson, A.J.; Cartmell, A.; et al. Human Gut Bacteroidetes Can Utilize Yeast Mannan through a Selfish Mechanism. Nature 2015, 517, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karav, S. Application of a Novel Endo-β-N-Acetylglucosaminidase to Isolate an Entirely New Class of Bioactive Compounds: N-Glycans. In Enzymes in Food Biotechnology; Kuddus, M., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 389–404. ISBN 978-0-12-813280-7. [Google Scholar]
- Martens, E.C.; Kelly, A.G.; Tauzin, A.S.; Brumer, H. The Devil Lies in the Details: How Variations in Polysaccharide Fine-Structure Impact the Physiology and Evolution of Gut Microbes. J. Mol. Biol. 2014, 426, 3851–3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bolino, M.; Haththotuwe Gamage, N.; Duman, H.; Abiodun, O.; De Mello, A.S.; Karav, S.; Frese, S.A. Novel Endo-β-N-Acetylglucosaminidases Derived from Human Fecal Samples Selectively Release N-Glycans from Model Glycoproteins. Foods 2025, 14, 1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081288
Bolino M, Haththotuwe Gamage N, Duman H, Abiodun O, De Mello AS, Karav S, Frese SA. Novel Endo-β-N-Acetylglucosaminidases Derived from Human Fecal Samples Selectively Release N-Glycans from Model Glycoproteins. Foods. 2025; 14(8):1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081288
Chicago/Turabian StyleBolino, Matthew, Nadini Haththotuwe Gamage, Hatice Duman, Odunayo Abiodun, Amilton S. De Mello, Sercan Karav, and Steven A. Frese. 2025. "Novel Endo-β-N-Acetylglucosaminidases Derived from Human Fecal Samples Selectively Release N-Glycans from Model Glycoproteins" Foods 14, no. 8: 1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081288
APA StyleBolino, M., Haththotuwe Gamage, N., Duman, H., Abiodun, O., De Mello, A. S., Karav, S., & Frese, S. A. (2025). Novel Endo-β-N-Acetylglucosaminidases Derived from Human Fecal Samples Selectively Release N-Glycans from Model Glycoproteins. Foods, 14(8), 1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081288







