Improvement of Summer Green Tea Quality Through an Integrated Shaking and Piling Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Instruments
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Sensory Evaluation and Colorimetric Measurement
2.4. Non-Targeted Metabolomics Analysis by UPLC-Triple-TOF-MS
2.5. Identification of Metabolites
2.6. Statistical Analysis
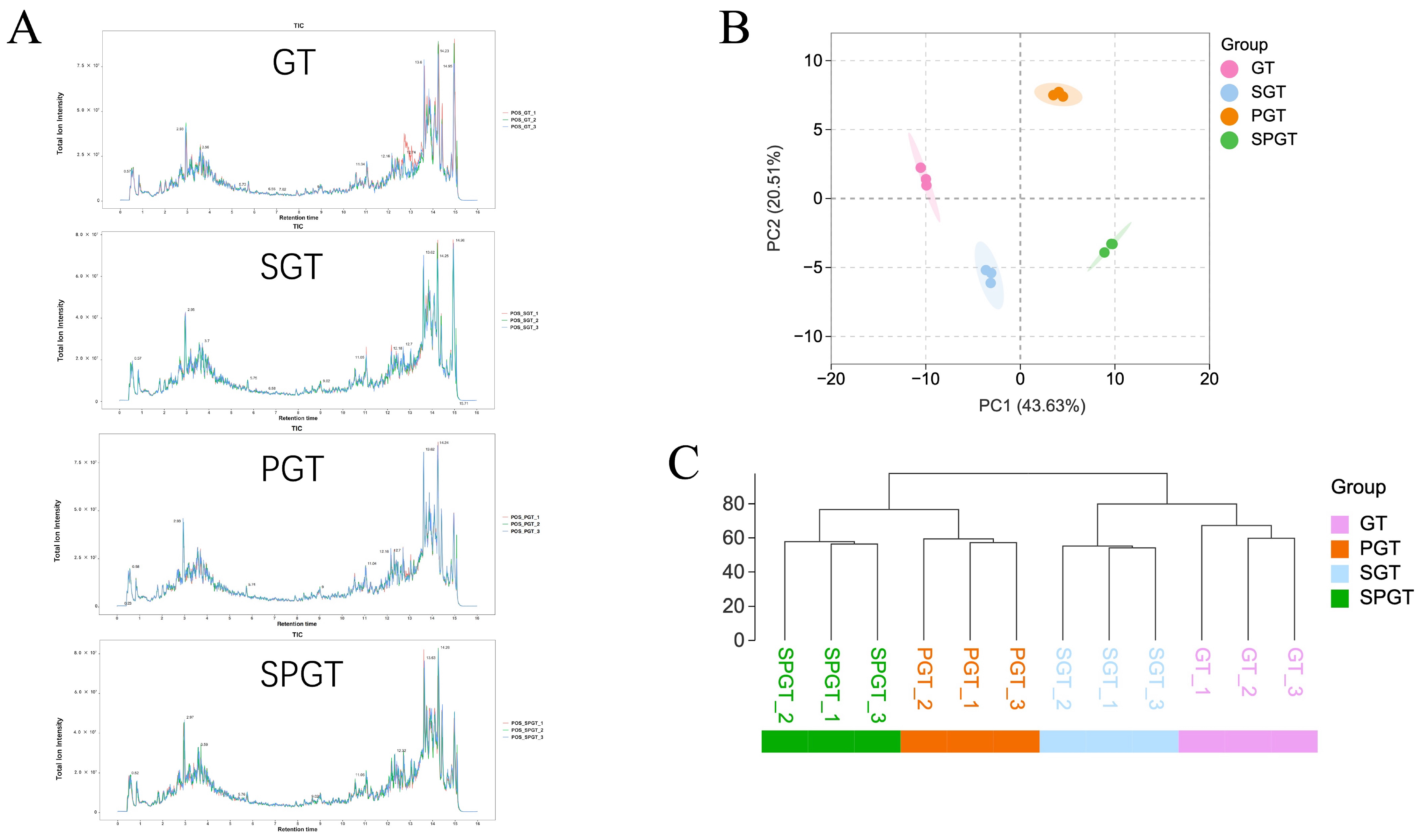
3. Results
3.1. Variations in Infusion Color and Taste Among GT, SGT, PGT, and SPGT
3.2. Overall Determination of NVMs Among GT, SGT, PGT, and SPGT
3.2.1. Amino Acids and Derivatives
3.2.2. Catechins, Procyanidins, and Tea Pigments
3.2.3. Flavonoids and Their Glycosides
3.2.4. Organic Acids
3.2.5. Soluble Sugars
3.2.6. Peptides and Nucleotides
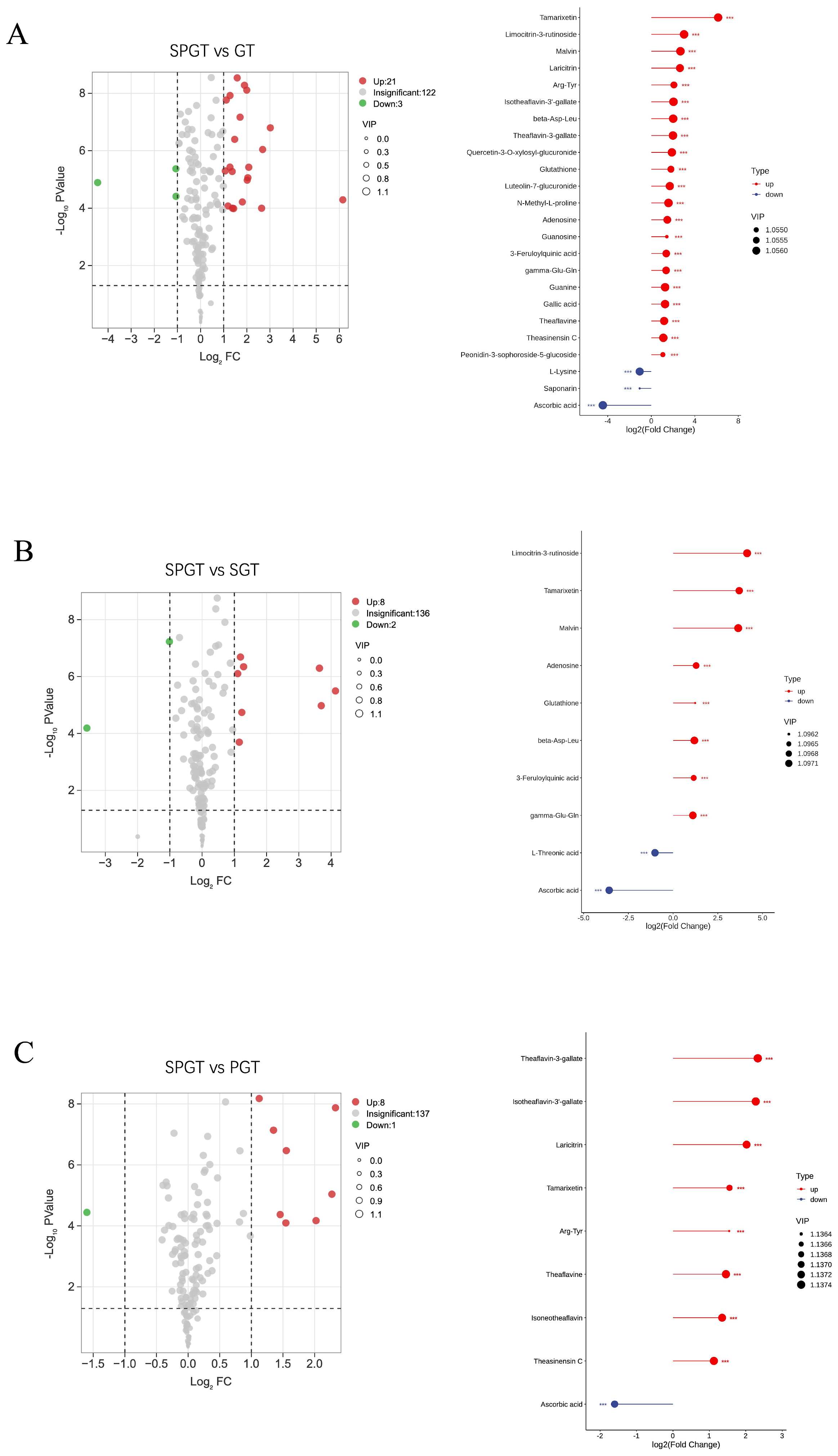
3.3. Characterization of Significant Changed NVMs Among GT, SGT, PGT, and SPGT
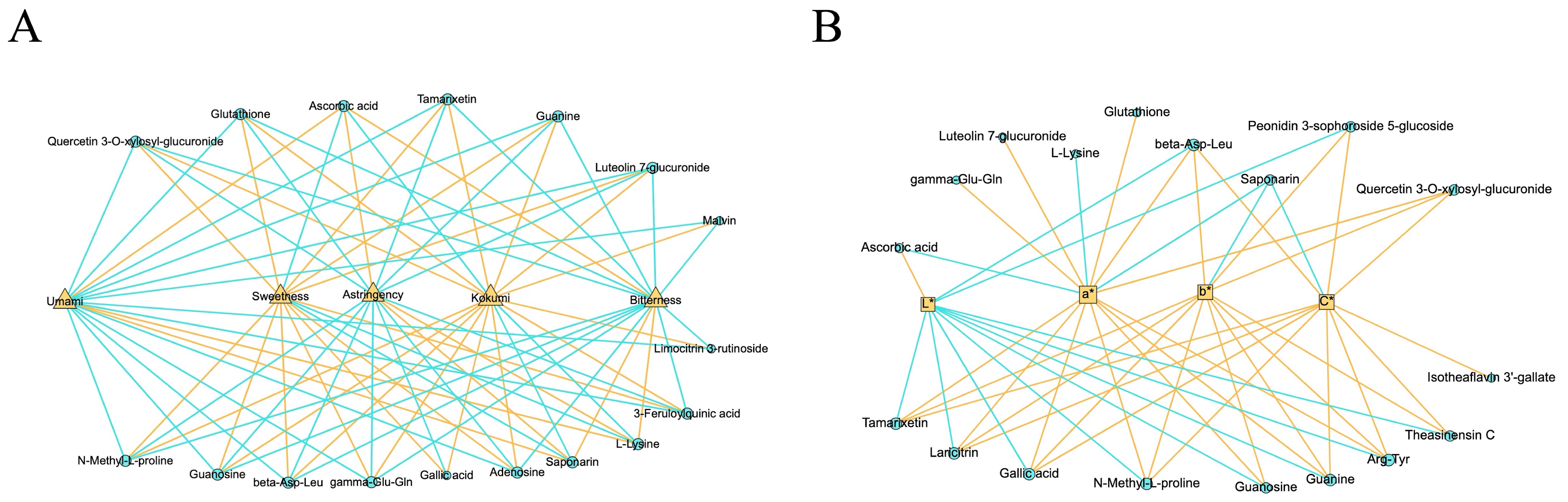
3.3.1. Taste-Related Differential NVMs
3.3.2. Color-Related Differential NVMs
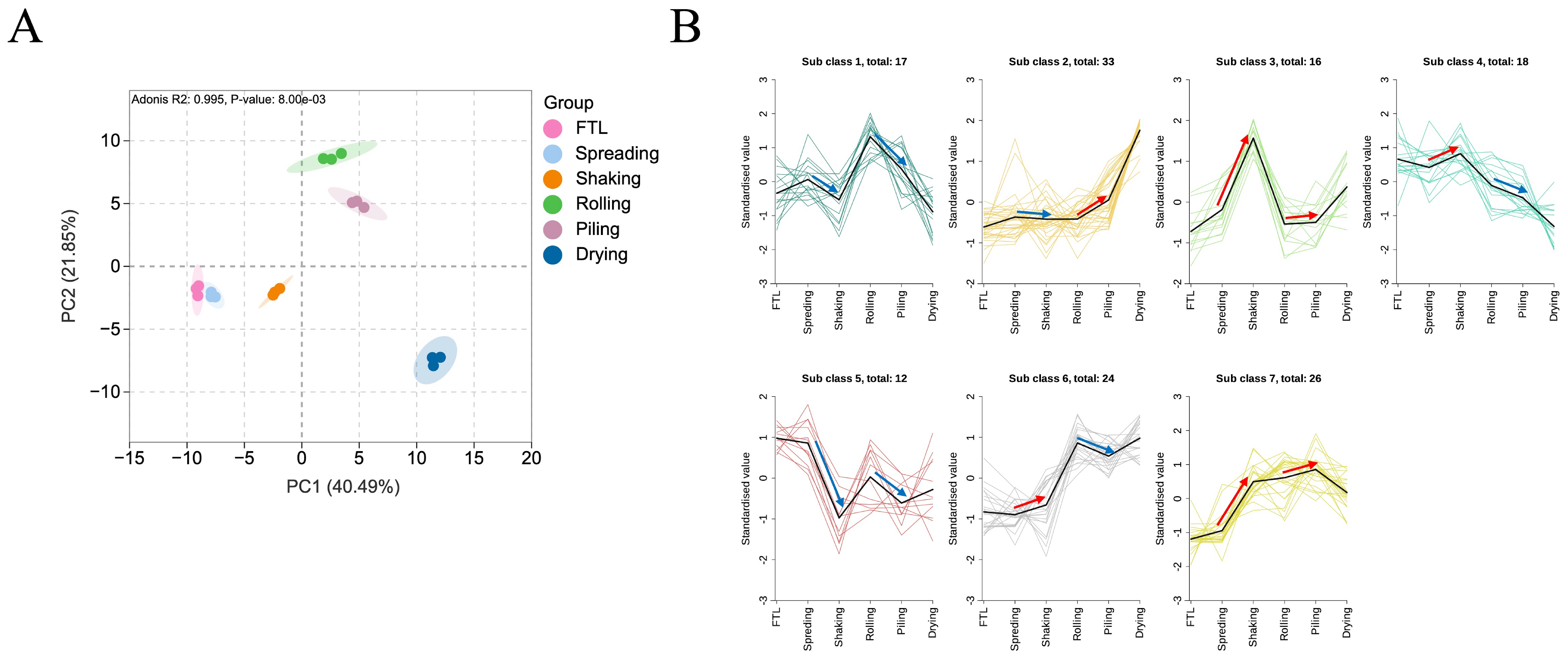
3.4. Dynamic Changes in NVMs During Integrated Shaking and Piling Process
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, J.; Dong, S.; Li, J.; Zhao, H. A comprehensive review on the effects of green tea and its components on the immune function. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2022, 11, 1143–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Luo, X.; Ho, C.; Li, D.; Guo, H.; Xie, Z. A new strategy for grading of Lu’an guapian green tea by combination of differentiated metabolites and hypoglycaemia effect. Food Res. Int. 2022, 159, 111639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, F.; Du, Q.; Yin, J. Quantitative analyses of the bitterness and astringency of catechins from green tea. Food Chem. 2018, 258, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cao, Q.; Granato, D.; Xu, Y.; Ho, C. Association between chemistry and taste of tea: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 101, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Ma, W.; Shi, J.; Peng, Q.; Lin, Z.; Lv, H. Comprehensive investigation on non-volatile and volatile metabolites in four types of green teas obtained from the same tea cultivar of Longjing 43 (Camellia sinensis var. sinensis) using the widely targeted metabolomics. Food Chem. 2022, 394, 133501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, S.; Kumazawa, K.; Masuda, H.; Henze, A.; Hofmann, T. Molecular and sensory studies on the umami taste of Japanese green tea. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 2688–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Yin, X.; Wu, H.; Zhao, M.; Huang, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, T.; Ning, J. Improving the flavor of summer green tea (Camellia sinensis L.) using the yellowing process. Food Chem. 2022, 388, 32982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Cai, M.; Zhang, X.; Feng, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Li, L.; Jin, G.; Fan, S.; Lu, L. Impact of spreading time on flavor quality in Duyun Maojian summer green tea. LWT 2024, 214, 117103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Ouyang, W.; Chen, M.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, J.; Hua, J.; Yuan, H. Effects of electromagnetic roller-hot-air–steam triple-coupled fixation on reducing the bitterness and astringency and improving the flavor quality of green tea. Food Chem. X 2023, 19, 100844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Qu, F.; Wang, P.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Z.; Han, Y.; Zhang, X. Characterization analysis of flavor compounds in green teas at different drying temperature. LWT 2022, 161, 113394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Liang, G.; Li, Z.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Research Progress on Application of Oolong Tea Green-making Technology in Tea Processing. Mod. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2024, 5, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhuang, J.; Feng, X.; Lv, H.; Feng, J.; Ye, S.; Tian, W.; Pan, G.; Chen, P.; et al. Another inner truth of shaking: Water migration and transformation-advanced physicochemical alterations in tea leaves. Food Chem. 2025, 467, 142338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Qu, L.; Yu, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, C.; Zhu, X.; Lin, Q.; Niu, L.; Yu, Y.; Lin, Q.; et al. Targeted quantitative metabolomic and flavor objective quantification technique reveal the impact mechanism of shaking on black tea quality and non-volatile metabolites. Food Chem. 2024, 458, 140226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Yang, S.; Pan, Y.; Zhou, S.; Ma, S.; Ou, C.; Fan, F.; Gong, S.; Chen, P.; Chu, Q. Yellow tea: More than turning green leaves to yellow. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 7836–7853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Hao, J.; Zhou, J.; He, C.; Yu, Z.; Chen, S.; Chen, Y.; Ni, D. Pile-fermentation of dark tea: Conditions optimization and quality formation mechanism. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 166, 113753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, M.; Luo, S.; Ning, M.; Chen, Y.; Tan, L.; Tang, X.; Liu, X.; Zheng, L.; Saarloos, A.; et al. Multi-Omics analysis reveals the sensory quality and fungal communities of Tibetan teas produced by wet- and dry-piling fermentation. Food Res. Int. 2025, 201, 115690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Li, T.; Xu, S.; Ni, T.; Deng, W.; Ning, J. The profile of dynamic changes in yellow tea quality and chemical composition during yellowing process. LWT 2021, 139, 110792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Z.; Li, S.; Tao, M.; He, W.; Shu, Z.; Wang, S.; Liu, Z. Effect of shaking and piling processing on improving the aroma quality of green tea. Food Res. Int. 2025, 201, 115624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 23776-2018; Methodology for Sensory Evaluation of Tea [National Standard]. Standardization Administration of China. China Standards Press: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Cao, Q.; Wang, F.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Yin, J.; Li, L.; Xu, Y. Effects of brewing water on the sensory attributes and physicochemical properties of tea infusions. Food Chem. 2021, 364, 13023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Deng, G.; Fan, Y.; Wang, W.; Yu, T.; Wei, Y.; Gao, J.; Ning, J.; Wang, Y. The processing of shaking and standing improves the taste quality of summer black tea. Food Res. Int. 2025, 201, 115545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Yin, X.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, J.; Li, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ning, J. Metabolomics analysis reveals the mechanism underlying the improvement in the color and taste of yellow tea after optimized yellowing. Food Chem. 2023, 428, 136785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Liu, P.; Guo, G.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; Le, T.; Yin, J.; Ni, D.; Jiang, H. Profiling of dynamic changes in non-volatile metabolites of shaken black tea during the manufacturing process using targeted and non-targeted metabolomics analysis. LWT 2022, 156, 113010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Kuan, Y.; Sheu, F. Revealing the roles of solar withering and shaking processes on oolong tea manufacturing from transcriptome and volatile profile analysis. Food Res. Int. 2025, 201, 115586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.C. Biochemistry of Tea, 3rd ed.; China Agricultural Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2003; pp. 9, 15–16. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, J.; Taylor, A. Analysis of proanthocyanidins by high-performance gel permeation chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 995, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, K.; Gu, L. Absorption and metabolism of proanthocyanidins. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 7, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Huang, X.; Liu, S.; Liu, J.; Guo, Y.; Sun, Y.; Lin, J.; Guo, Y.; Wei, S. Understanding the formation mechanism of oolong tea characteristic non-volatile chemical constitutes during manufacturing processes by using integrated widely-targeted metabolome and DIA proteome analysis. Food Chem. 2020, 310, 125941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Fang, S.; Jin, G.; Ni, T.; Hou, Z.; Li, T.; Deng, W.; Ning, J. Effects of two yellowing process on colour, taste and nonvolatile compounds of bud yellow tea. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 2931–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharbert, S.; Hofmann, T. Molecular Definition of Black Tea Taste by Means of Quantitative Studies, Taste Reconstitution, and Omission Experiments. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 5377–5384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; An, J.; Bo, N.; Li, R.; Chen, Q.; Sha, G.; Liang, Z.; Guan, Y.; Zhao, L.; Wang, W.; et al. Changes and metabolic mechanisms of organic acids in the fermentation of pu-erh tea. LWT 2024, 203, 116304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Shen, S.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Hua, J.; Yuan, H. Novel insight into the effect of fermentation time on quality of Yunnan congou black tea. LWT 2022, 155, 112939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; He, C.; Yu, X.; Zhou, J.; Ran, W.; Chen, Y.; Ni, D. Effects of red-light withering on the taste of black tea as revealed by non-targeted metabolomics and transcriptomics analysis. LWT 2021, 147, 111620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Dai, X.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, S.; Dai, Q.; Jiang, X.; Xia, T. Evaluation of astringent taste of green tea through mass spectrometry-based targeted metabolic profiling of polyphenols. Food Chem. 2020, 305, 12507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tang, B.; Gao, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, F.; Yin, J.; Zeng, L.; Zhou, W.; Xu, Y. Impact of heat treatment on the flavor stability of Longjing green tea beverages: Metabolomic insights and sensory correlations. Food Res. Int. 2024, 193, 114867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Wang, J.; Yuan, H. Comparison on the quality of black tea prepared by different freezing and shaking processes. Mod. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 39, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, M.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Q.; Khan, I. Yellow tea (Camellia sinensis L.), a promising Chinese tea: Processing, chemical constituents and health benefits. Food Res. Int. 2018, 107, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Cao, Y.; Pan, Y.; Mei, S.; Zhang, G.; Chu, Q.; Chen, P. Sensory-Guided Identification and Characterization of Kokumi-Tasting Compounds in Green Tea (Camellia sinensis L.). Molecules 2022, 27, 5677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuninaka, A. Studies on Taste of Ribonucleic Acid Derivatives. Nippon Nōgei Kagakukaishi 1960, 34, 489–492. [Google Scholar]
- Kimoto, E.; Tanaka, H.; Ohmoto, T.; Choami, M. Analysis of the transformation products of dehydro-L-ascorbic acid by ion-pairing high performance liquid chromatography. Anal. Biochem. 1993, 214, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, K.; Fujii, A.; Senda, Y.; Iwashina, T. Greenish blue flower colour of Strongylodon macrobotrys. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2010, 38, 630–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 14456.1-2017; Green Tea—Part 1: Basic Requirements [National Standard]. Standardization Administration of China. China Standards Press: Beijing, China, 2017.


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tu, Z.; Li, S.; Xu, A.; Yu, Q.; Cao, Y.; Tao, M.; Wang, S.; Liu, Z. Improvement of Summer Green Tea Quality Through an Integrated Shaking and Piling Process. Foods 2025, 14, 1284. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071284
Tu Z, Li S, Xu A, Yu Q, Cao Y, Tao M, Wang S, Liu Z. Improvement of Summer Green Tea Quality Through an Integrated Shaking and Piling Process. Foods. 2025; 14(7):1284. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071284
Chicago/Turabian StyleTu, Zheng, Sixu Li, Anan Xu, Qinyan Yu, Yanyan Cao, Meng Tao, Shanshan Wang, and Zhengquan Liu. 2025. "Improvement of Summer Green Tea Quality Through an Integrated Shaking and Piling Process" Foods 14, no. 7: 1284. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071284
APA StyleTu, Z., Li, S., Xu, A., Yu, Q., Cao, Y., Tao, M., Wang, S., & Liu, Z. (2025). Improvement of Summer Green Tea Quality Through an Integrated Shaking and Piling Process. Foods, 14(7), 1284. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071284




