Smartphone Video Imaging Combined with Machine Learning: A Cost-Effective Method for Authenticating Whey Protein Supplements
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
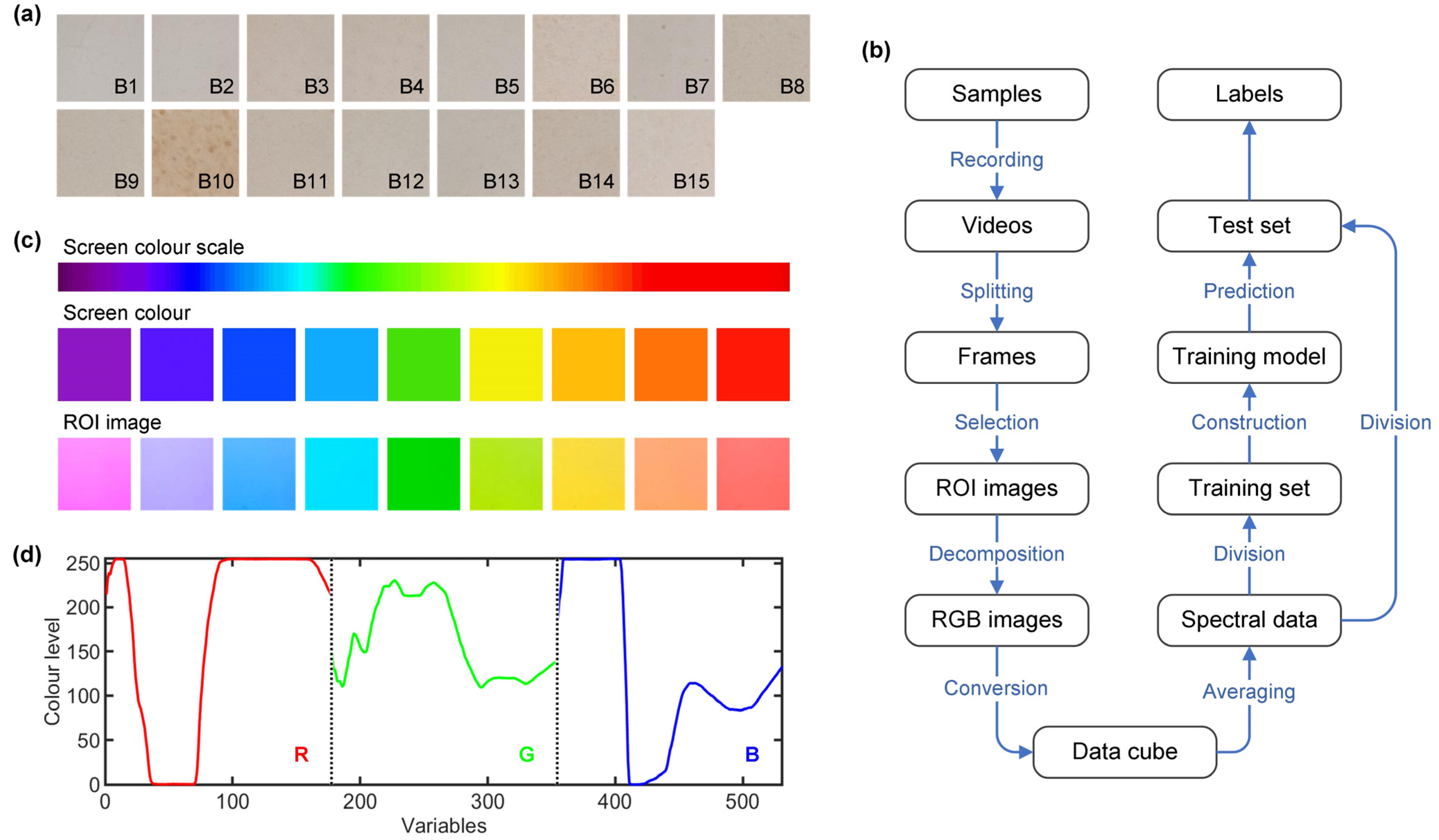
2.2. Measurements
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
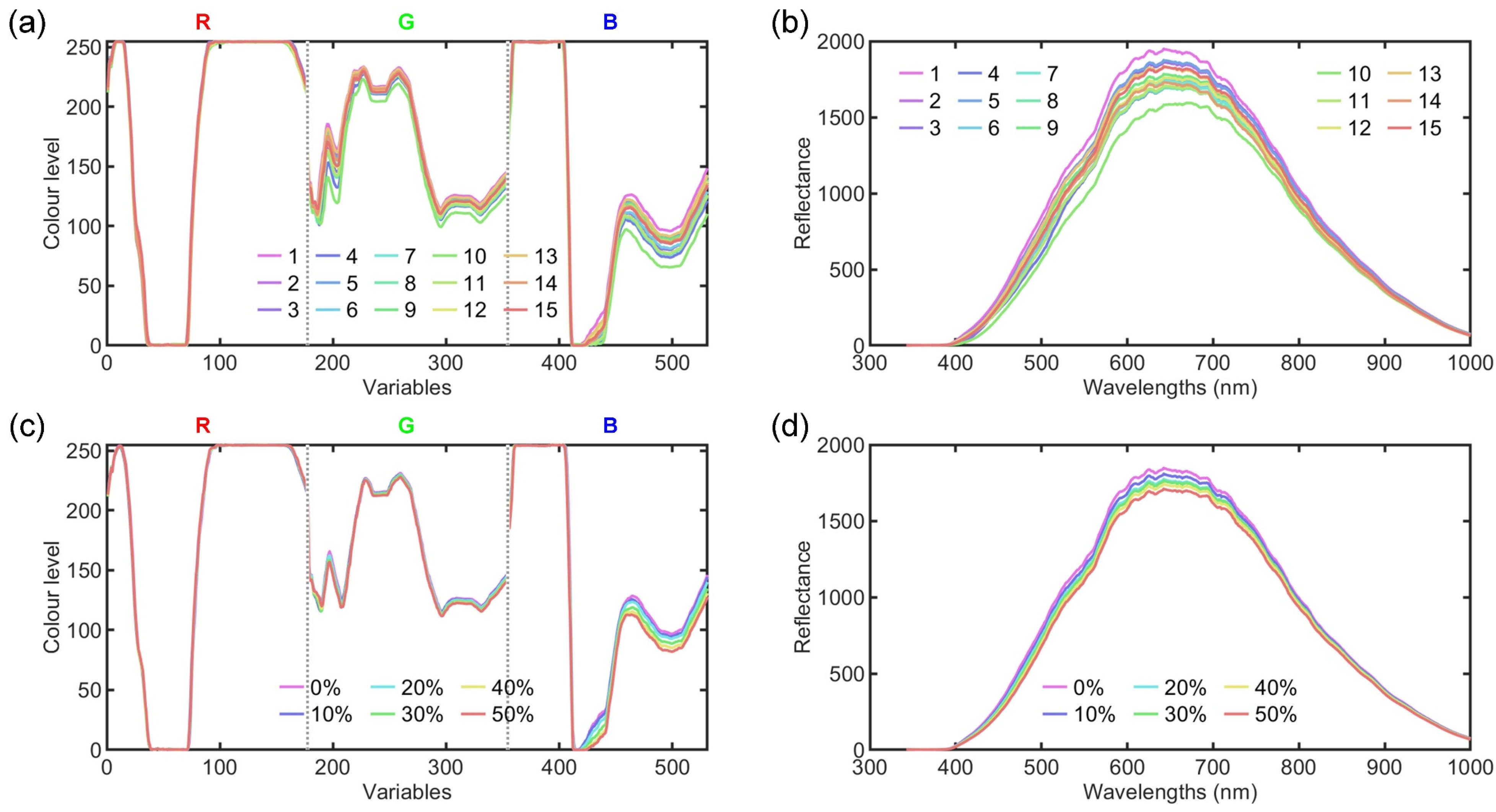
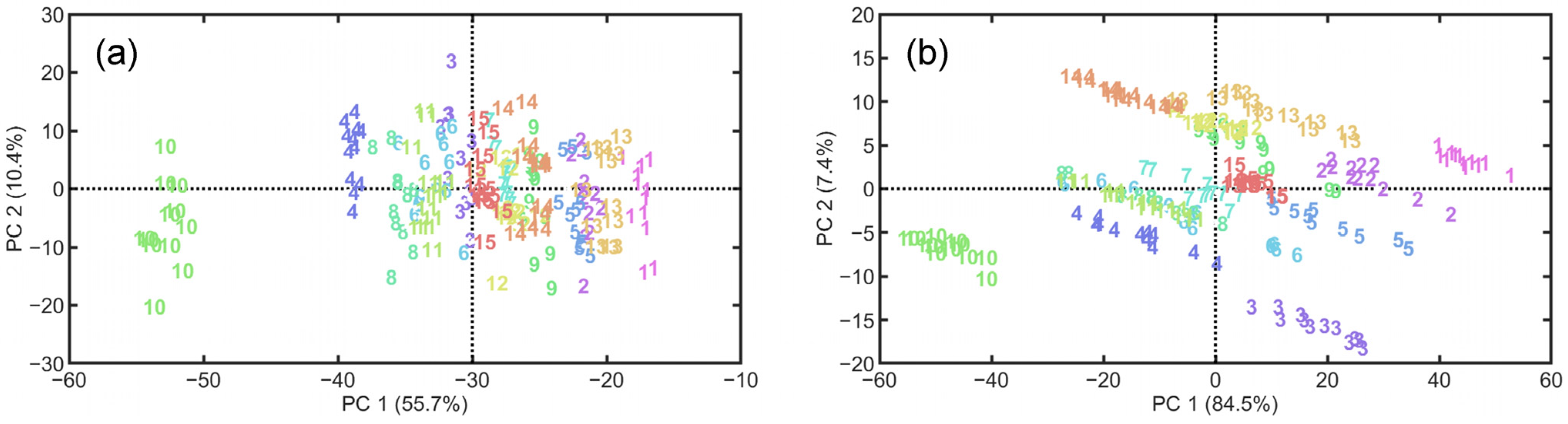
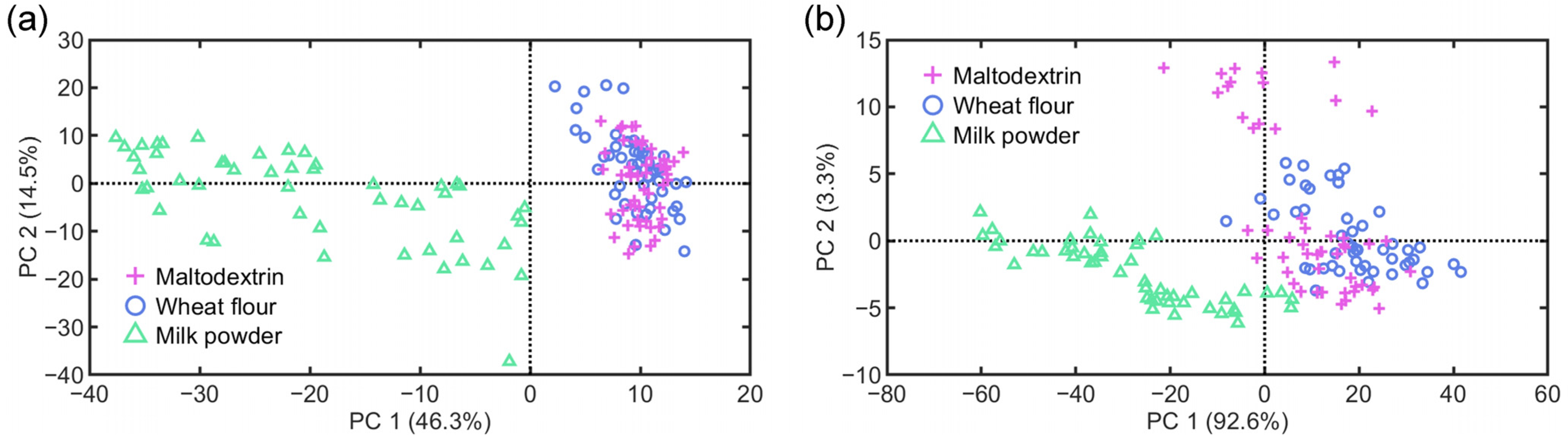
3.1. Data Description
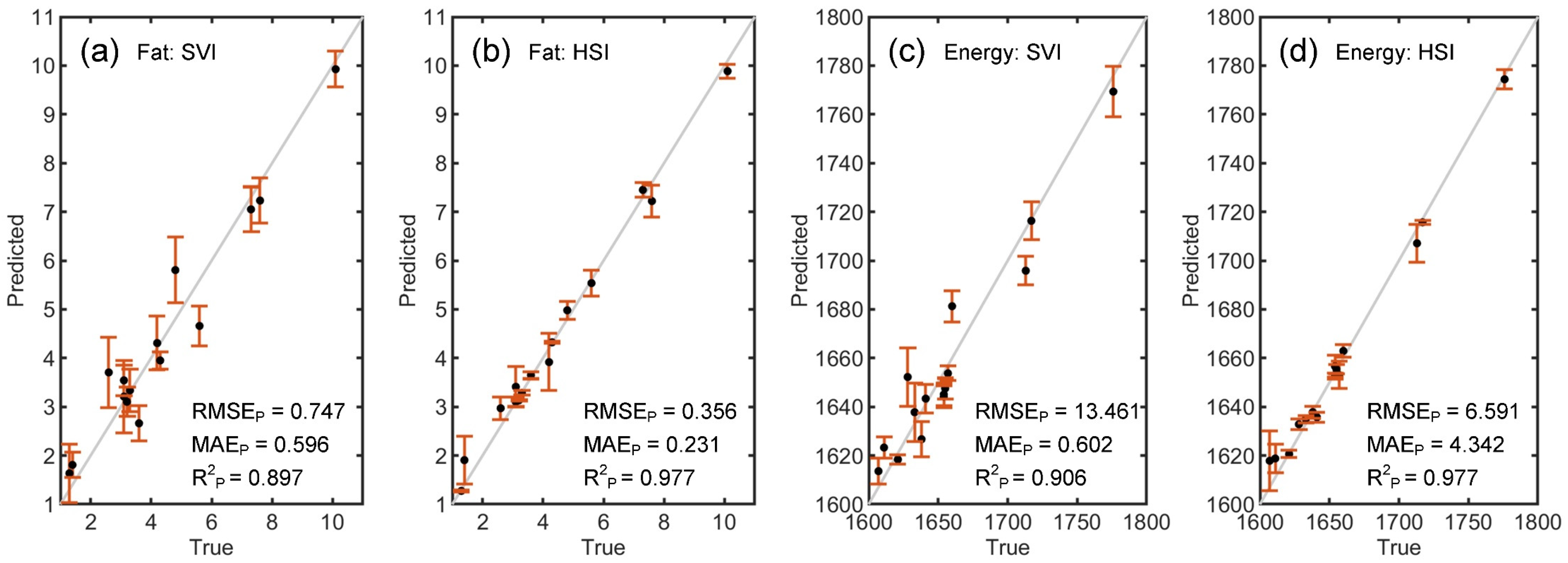
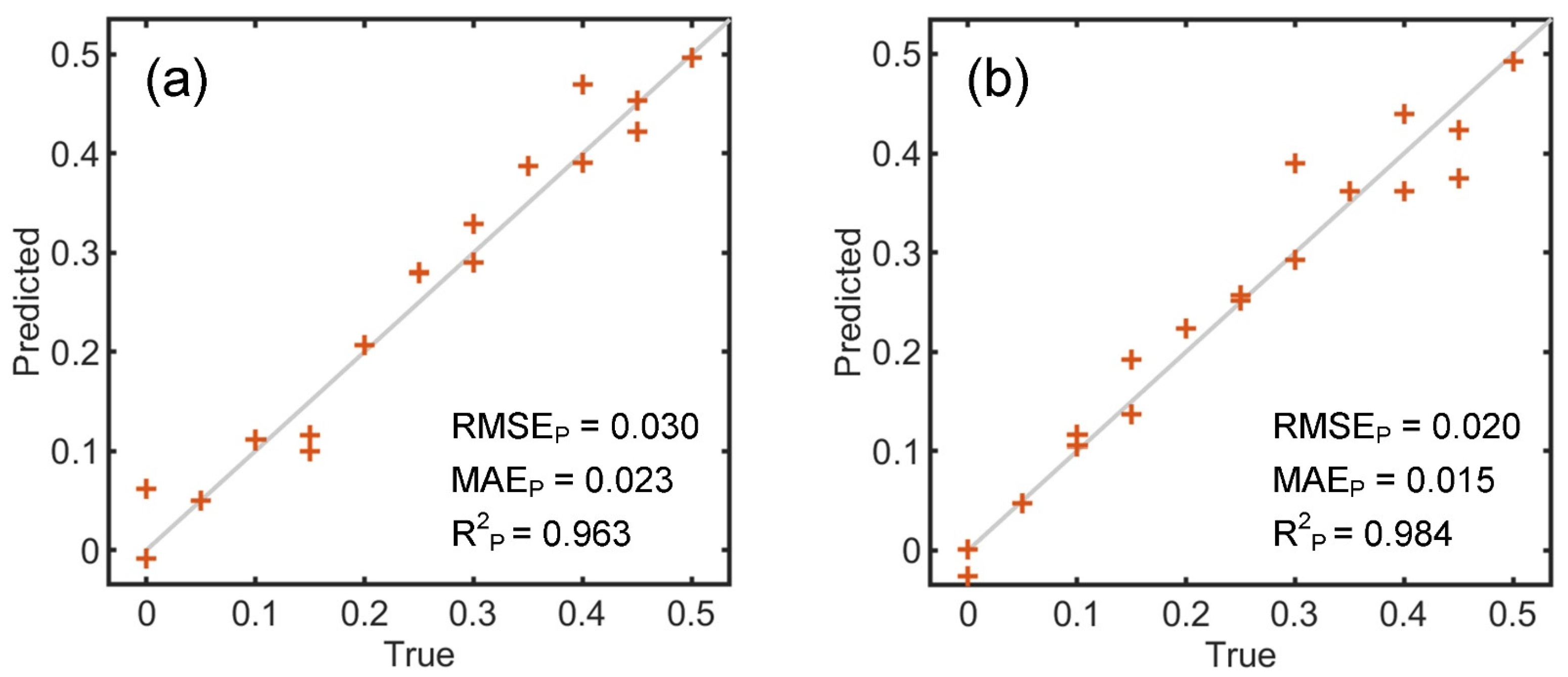
3.2. WPC Authentication
3.3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, T.; Tan, S.Y.; Mutilangi, W.; Aykas, D.P.; Rodriguez-Saona, L.E. Authentication of Whey Protein Powders by Portable Mid-Infrared Spectrometers Combined with Pattern Recognition Analysis. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, C2111–C2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, C.G.; Andrade, J.; Ranquine, T.; de Moura, I.N.; da Rocha, R.A.; Furtado, M.A.M.; Bell, M.J.V.; Anjos, V. Characterization and Detection of Adulterated Whey Protein Supplements Using Stationary and Time-Resolved Fluorescence Spectroscopy. LWT 2018, 97, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Sun, D.-W.; Pu, H.; Wei, Q. Principles and Applications of Spectroscopic Techniques for Evaluating Food Protein Conformational Changes: A Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 67, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Rosa, A.R.; Leone, F.; Cheli, F.; Chiofalo, V. Fusion of Electronic Nose, Electronic Tongue and Computer Vision for Animal Source Food Authentication and Quality Assessment—A Review. J. Food Eng. 2017, 210, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdoğan, G.; Lin, X.; Sun, D.-W. Rapid and Noninvasive Sensory Analyses of Food Products by Hyperspectral Imaging: Recent Application Developments. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 111, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukacs, M.; Bazar, G.; Pollner, B.; Henn, R.; Kirchler, C.G.; Huck, C.W.; Kovacs, Z. Near Infrared Spectroscopy as an Alternative Quick Method for Simultaneous Detection of Multiple Adulterants in Whey Protein-Based Sports Supplement. Food Control 2018, 94, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.S.; Nascimento, M.H.; Barbosa, L.L.; Campos, L.C.G.; Singh, M.N.; Martin, F.L.; Romão, W.; Filgueiras, P.R.; Barauna, V.G. Detection and Quantification Using ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy of Whey Protein Concentrate Adulteration with Wheat Flour. LWT 2022, 172, 114161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxton, R.; McDougal, O.M. Whey Protein Powder Analysis by Mid-Infrared Spectroscopy. Foods 2021, 10, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Kim, M.S.; Chao, K.; Qin, J.; Lim, J.; Lee, H.; Garrido-Varo, A.; Pérez-Marín, D.; Ying, Y. Detection of Melamine in Milk Powders Based on NIR Hyperspectral Imaging and Spectral Similarity Analyses. J. Food Eng. 2014, 124, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.H.; Sun, D.W. Fourier Transform Infrared and Raman and Hyperspectral Imaging Techniques for Quality Determinations of Powdery Foods: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 104–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobari Moghaddam, H.; Tamiji, Z.; Amini, M.; Khoshayand, M.R.; Kobarfrad, F.; Sadeghi, N.; Hajimahmoodi, M. Development of Non-Destructive Methods for the Assessment of Authenticity of Sports Whey Protein Supplements. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2024, 41, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Géa Neves, M.; Poppi, R.J.; Breitkreitz, M.C. Authentication of Plant-Based Protein Powders and Classification of Adulterants as Whey, Soy Protein, and Wheat Using FT-NIR in Tandem with OC-PLS and PLS-DA Models. Food Control 2022, 132, 108489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meenu, M.; Cai, Q.; Xu, B. A Critical Review on Analytical Techniques to Detect Adulteration of Extra Virgin Olive Oil. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 91, 391–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danezis, G.P.; Tsagkaris, A.S.; Camin, F.; Brusic, V.; Georgiou, C.A. Food Authentication: Techniques, Trends & Emerging Approaches. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 85, 123–132. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, J.; Pereira, C.G.; de Almeida Junior, J.C.; Viana, C.C.R.; de Oliveira Neves, L.N.; da Silva, P.H.F.; Bell, M.J.V.; dos Anjos, V.d.C. FTIR-ATR Determination of Protein Content to Evaluate Whey Protein Concentrate Adulteration. LWT 2019, 99, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.; Meng, Y.; Wang, K.; Huang, W.; Li, N.; Liu, T.C.-Y. Rapid Detection of Adulterants in Whey Protein Supplement by Raman Spectroscopy Combined with Multivariate Analysis. Molecules 2019, 24, 1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinia Zaukuu, J.-L.; Aouadi, B.; Lukács, M.; Bodor, Z.; Vitális, F.; Gillay, B.; Gillay, Z.; Friedrich, L.; Kovacs, Z. Detecting Low Concentrations of Nitrogen-Based Adulterants in Whey Protein Powder Using Benchtop and Handheld NIR Spectrometers and the Feasibility of Scanning through Plastic Bag. Molecules 2020, 25, 2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Yun, Y.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, C.; Tang, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z. Authentication and Quality Assessment of Whey Protein-Based Sports Supplements Using Portable near-Infrared Spectroscopy and Hyperspectral Imaging. Food Res. Int. 2025, 203, 115807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Wang, H.; Yun, Y. Smartphone Video Imaging: A Versatile, Low-Cost Technology for Food Authentication. Food Chem. 2025, 462, 140911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Song, Z.; Vincent, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z. Quantification of Extra Virgin Olive Oil Adulteration Using Smartphone Videos. Talanta 2020, 216, 120920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Wei, X.; Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Tang, X.; Kong, X. Rapid and Low-Cost Detection of Saffron (Crocus sativus L.) Adulteration Using Smartphone Videos and Spectral Data Fusion Strategy. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 135, 106691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Yun, Y.; Wang, H.; Hou, Z.; Wang, Z. Smartphone Detection of Minced Beef Adulteration. Microchem. J. 2021, 164, 106088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Jiang, N.; Wang, H.; Vincent, J. Use of Smartphone Videos and Pattern Recognition for Food Authentication. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 304, 127247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Song, Z.; Yue, X.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z. Siamese Network-Based Spectral Reconstruction for Rapid Identification of Fire-Retardant Coatings. Measurement 2025, 242, 116074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 5009.5; National Food Safety Standard: Determination of Protein in Foods. National Standardization Management Committee of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB/Z 21922; Fundamental Terminology and Definition of Nutritional Component in Foods. National Standardization Management Committee of China: Beijing, China, 2008.
- Mehmood, T.; Ahmed, B. The Diversity in the Applications of Partial Least Squares: An Overview. J. Chemom. 2016, 30, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Afgan, M.S.; Yun, Y.; Wang, H.; Cui, J.; Gu, W.; Hou, Z.; Wang, Z. Spectral Knowledge-Based Regression for Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy Quantitative Analysis. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 205, 117756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhong, W.; Jiang, C.; Li, Z.; Peng, X.; Cheng, H. Key Performance Index Estimation Based on Ensemble Locally Weighted Partial Least Squares and Its Application on Industrial Nonlinear Processes. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2020, 203, 104031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, M.; Rayens, W. Partial Least Squares for Discrimination. J. Chemom. 2003, 17, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.-B.; Zhu, Q.-Y.; Siew, C.-K. Extreme Learning Machine: Theory and Applications. Neurocomputing 2006, 70, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Yan, F.; Yang, G.; Chen, H.; Song, Z. Quantitative Analysis of Sinters Using Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) Coupled with Kernel-Based Extreme Learning Machine (K-ELM). Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 1074–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Shu, H.; Tang, H.; Zhang, H. Spectra Data Classification with Kernel Extreme Learning Machine. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2019, 192, 103815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| B1 | B2 | B3 | B4 | B5 | B6 | B7 | B8 | B9 | B10 | B11 | B12 | B13 | B14 | B15 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fat (g/100 g) | 3.3 | 3.1 | 4.3 | 7.3 | 3.2 | 3.1 | 5.6 | 7.6 | 3.6 | 10.1 | 4.8 | 2.6 | 1.4 | 4.2 | 1.3 |
| Energy (kJ/100 g) | 1657 | 1633 | 1655 | 1717 | 1654 | 1607 | 1654 | 1713 | 1638 | 1776 | 1660 | 1628 | 1611 | 1641 | 1621 |
| Analyte | Measurement | Model | RMSECV | MAECV | R2CV | RMSEP | MAEP | R2P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fat | SVI | PLSR | 0.774 | 0.628 | 0.889 | 0.916 | 0.760 | 0.845 |
| (g/100 g) | K-ELM | 0.633 | 0.535 | 0.926 | 0.747 | 0.596 | 0.897 | |
| HSI | PLSR | 0.569 | 0.463 | 0.940 | 0.589 | 0.482 | 0.936 | |
| K-ELM | 0.298 | 0.218 | 0.984 | 0.356 | 0.231 | 0.977 | ||
| Energy | SVI | PLSR | 15.111 | 12.415 | 0.881 | 17.567 | 14.128 | 0.840 |
| (kJ/100 g) | K-ELM | 12.769 | 10.691 | 0.915 | 13.460 | 10.602 | 0.906 | |
| HSI | PLSR | 12.661 | 10.350 | 0.917 | 13.390 | 11.094 | 0.907 | |
| K-ELM | 5.887 | 4.185 | 0.982 | 6.591 | 4.342 | 0.977 |
| RMSECV | MAECV | R2CV | RMSEP | MAEP | R2P | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVI | PLSR | 0.039 | 0.031 | 0.940 | 0.032 | 0.024 | 0.959 |
| K-ELM | 0.040 | 0.032 | 0.937 | 0.030 | 0.023 | 0.963 | |
| HSI | PLSR | 0.026 | 0.018 | 0.973 | 0.034 | 0.024 | 0.951 |
| K-ELM | 0.030 | 0.023 | 0.963 | 0.020 | 0.015 | 0.984 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, X.; Du, W.; Song, W.; Gu, W.; Kong, X. Smartphone Video Imaging Combined with Machine Learning: A Cost-Effective Method for Authenticating Whey Protein Supplements. Foods 2025, 14, 1277. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071277
Tang X, Du W, Song W, Gu W, Kong X. Smartphone Video Imaging Combined with Machine Learning: A Cost-Effective Method for Authenticating Whey Protein Supplements. Foods. 2025; 14(7):1277. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071277
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Xuan, Wenjiao Du, Weiran Song, Weilun Gu, and Xiangzeng Kong. 2025. "Smartphone Video Imaging Combined with Machine Learning: A Cost-Effective Method for Authenticating Whey Protein Supplements" Foods 14, no. 7: 1277. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071277
APA StyleTang, X., Du, W., Song, W., Gu, W., & Kong, X. (2025). Smartphone Video Imaging Combined with Machine Learning: A Cost-Effective Method for Authenticating Whey Protein Supplements. Foods, 14(7), 1277. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071277







