Natural and Regenerated Cellulosic Microfibers Dominate Anthropogenic Particles Ingested by Commercial Fish Species from the Adriatic Sea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fish Sampling
2.3. Microfiber Extraction and Quantification
2.4. Microfiber Identification
2.5. Contamination Precautions
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
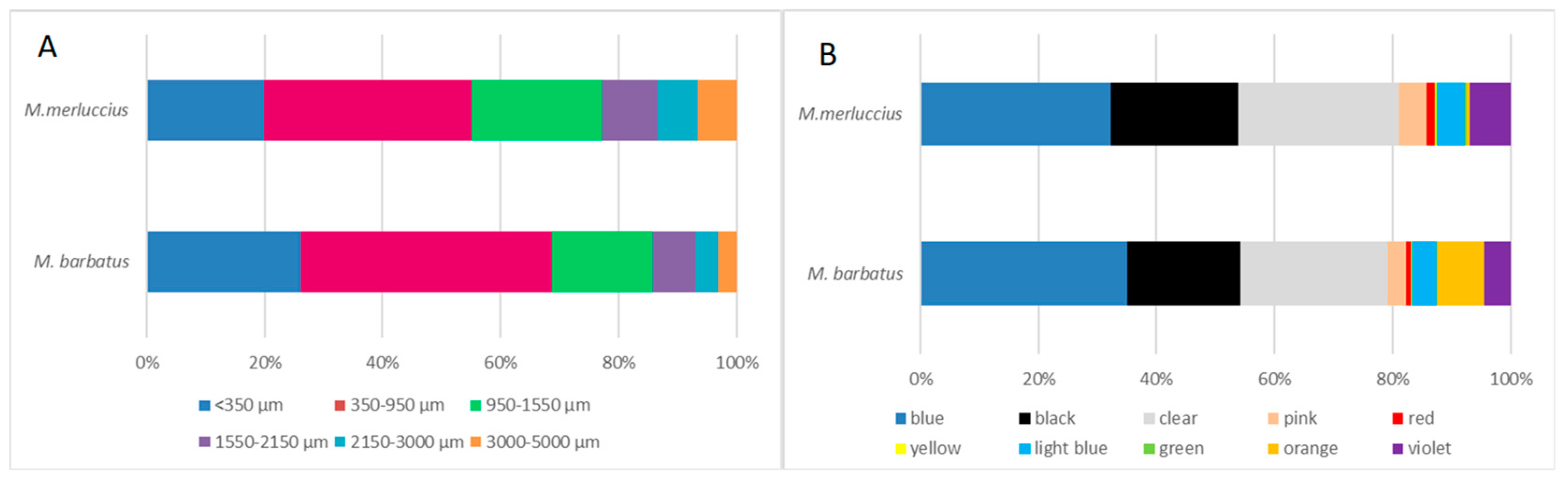
3.1. Microfibers in Fish
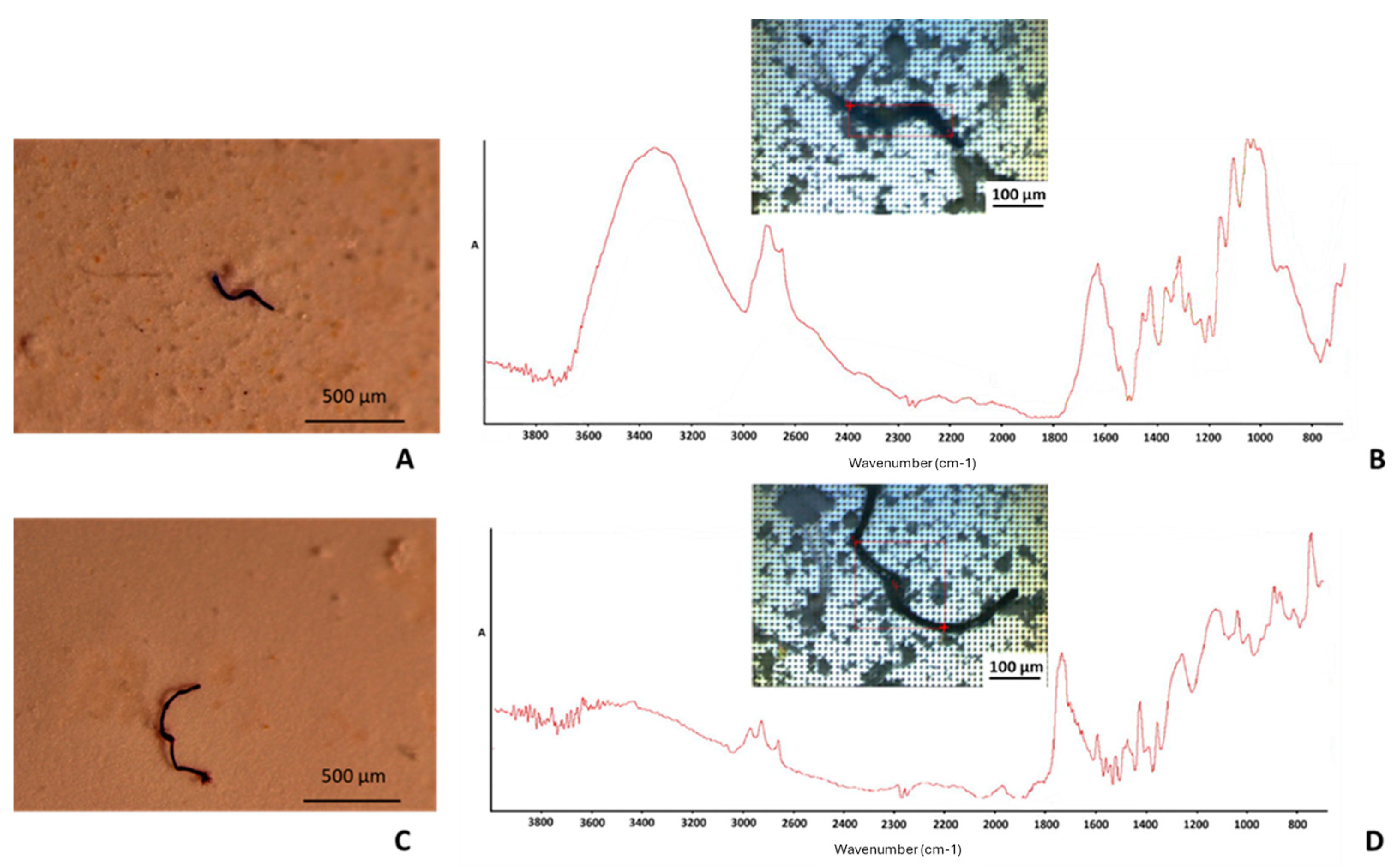
3.2. Microfiber Characterization
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GIT | Gastrointestinal tract |
| FAO-GFCM | General Fisheries Commission for the Mediterranean |
References
- Liu, J.; Yang, Y.; Ding, J.; Zhu, B.; Gao, W. Microfibers: A preliminary discussion on their definition and sources. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 29497–29501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avio, C.G.; Pittura, L.; d’Errico, G.; Abel, S.; Amorello, S.; Marino, G.; Regoli, F. Distribution and characterization of microplastic particles and textile microfibers in Adriatic food webs: General insights for biomonitoring strategies. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macieira, R.M.; Oliveira, L.A.S.; Cardozo-Ferreira, G.C.; Pimentel, C.R.; Andrades, R.; Gasparini, J.L.; Giarrizzo, T. Microplastic and artificial cellulose microfibers ingestion by reef fishes in the Guarapari Islands, southwestern Atlantic. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 167, 112371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Lu, Q.; Xing, Y.; Liu, K.; Ling, W.; Yang, J.; Zhao, D. Review of research on migration, distribution, biological effects, and analytical methods of microfibers in the environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 855, 158922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, S.; Rumi, S.S.; Hu, Y.; Abidi, N. Microfibers from synthetic textiles as a major source of microplastics in the environment: A review. Text Res. J. 2021, 91, 2136–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, Q.; An, L.; Wang, M.; Yang, Q.; Zhu, B.; Xu, Y. Microfiber pollution in the earth system. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2022, 260, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concato, M.; Panti, C.; Baini, M.; Galli, M.; Giani, D.; Fossi, M.C. Detection of anthropogenic fibres in marine organisms: Knowledge gaps and methodological issues. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 191, 114949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanton, T.; Johnson, M.; Nathanail, P.; MacNaughtan, W.; Gomes, R.L. Freshwater and airborne textile fibre populations are dominated by “natural”, not microplastic, fibres. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 666, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suaria, G.; Achtypi, A.; Perold, V.; Lee, J.R.; Pierucci, A.; Bornman, T.G.; Ryan, P.G. Microfibers in oceanic surface waters: A global characterization. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaay8493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodall, L.C.; Sanchez-Vidal, A.; Canals, M.; Paterson, G.L.; Coppock, R.; Sleight, V.; Thompson, R.C. The deep sea is a major sink for microplastic debris. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2014, 1, 140317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savoca, S.; Capillo, G.; Mancuso, M.; Faggio, C.; Panarello, G.; Crupi, R.; Spanò, N. Detection of artificial cellulose microfibers in Boops boops from the northern coasts of Sicily (Central Mediterranean). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 691, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ergas, M.; Figueroa, D.; Paschke, K.; Urbina, M.A.; Navarro, J.M.; Vargas-Chacoff, L. Cellulosic and microplastic fibers in the Antarctic fish Harpagifer antarcticus and Sub-Antarctic Harpagifer bispinis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 194, 115380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capillo, G.; Savoca, S.; Panarello, G.; Mancuso, M.; Branca, C.; Romano, V.; Spanò, N. Quali-quantitative analysis of plastics and synthetic microfibers found in demersal species from Southern Tyrrhenian Sea (Central Mediterranean). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 150, 110596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savoca, S.; Matanović, K.D.; Angelo, G.; Vetri, V.; Anselmo, S.; Bottari, T.; Mancuso, M.; Kužir, S.; Spanò, N.; Capillo, G.; et al. Ingestion of plastic and non-plastic microfibers by farmed gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) and common carp (Cyprinus carpio) at different life stages. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 782, 146851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, J.I.; Liu, H.; Wang, D.; Lee, Y.H.; Lee, J.S.; An, Y.J. Critical review of environmental impacts of microfibers in different environmental matrices. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 251, 109196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santonicola, S.; Volgare, M.; Cocca, M.; Dorigato, G.; Giaccone, V.; Colavita, G. Impact of Fibrous Microplastic Pollution on Commercial Seafood and Consumer Health: A Review. Animals 2023, 13, 1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giani, D.; Baini, M.; Galli, M.; Casini, S.; Fossi, M.C. Microplastics occurrence in edible fish species (Mullus barbatus and Merluccius merluccius) collected in three different geographical sub areas of the Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 140, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Nguyen, B.; You, J.B.; Karakolis, E.; Sinton, D.; Rochman, C. Identification of microfibers in the environment using multiple lines of evidence. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 11877–11887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santonicola, S.; Volgare, M.; Rossi, F.; Castaldo, R.; Cocca, M.; Colavita, G. Detection of fibrous microplastics and natural microfibers in fish species (Engraulis encrasicolus, Mullus barbatus and Merluccius merluccius) for human consumption from the Tyrrhenian sea. Chemosphere 2024, 363, 142778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggio, T.; Lo Brutto, S.; Garoia, F.; Tinti, F.; Arculeo, M. Microsatellite analysis of red mullet Mullus barbatus (Perciformes, Mullidae) reveals the isolation of the Adriatic Basin in the Mediterranean Sea. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2009, 66, 1883–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candelma, M.; Marisaldi, L.; Bertotto, D.; Radaelli, G.; Gioacchini, G.; Santojanni, A.; Carnevali, O. Aspects of reproductive biology of the European hake (Merluccius merluccius) in the Northern and Central Adriatic Sea (GSA 17-Central Mediterranean Sea). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistri, M.; Sfriso, A.A.; Casoni, E.; Nicoli, M.; Vaccaro, C.; Munari, C. Microplastic accumulation in commercial fish from the Adriatic Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 174, 113279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bošković, N.; Joksimović, D.; Bajt, O. Microplastics in fish and sediments from the Montenegrin coast (Adriatic Sea): Similarities in accumulation. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 850, 158074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittura, L.; Nardi, A.; Cocca, M.; De Falco, F.; d’Errico, G.; Mazzoli, C.; Regoli, F. Cellular disturbance and thermal stress response in mussels exposed to synthetic and natural microfibers. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 981365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spedicato, M.T.; Zupa, W.; Carbonara, P.; Fiorentino, F.; Follesa, M.C.; Galgani, F.; Thasitis, I. Spatial distribution of marine macro-litter on the seafloor in the northern Mediterranean Sea: The MEDITS initiative. Sci. Mar. 2019, 83, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorica, B.; Ezgeta-Balić, D.; Vidjak, O.; Vuletin, V.; Šestanović, M.; Isajlović, I.; Harrod, C. Diet Composition and isotopic analysis of nine important fisheries resources in the Eastern Adriatic Sea (Mediterranean). Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 609432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossi, M.C.; Pedà, C.; Compa, M.; Tsangaris, C.; Alomar, C.; Claro, F.; Baini, M. Bioindicators for monitoring marine litter ingestion and its impacts on Mediterranean biodiversity. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 1023–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Romeu, O.; Constenla, M.; Carrassón, M.; Campoy-Quiles, M.; Soler-Membrives, A. Are anthropogenic fibres a real problem for red mullets (Mullus barbatus) from the NW Mediterranean? Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 139336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volgare, M.; Santonicola, S.; Cocca, M.; Avolio, R.; Castaldo, R.; Errico, M.E.; Gentile, G.; Raimo, G.; Gasperi, M.; Colavita, G. A versatile approach to evaluate the occurrence of microfibers in mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capone, A.; Petrillo, M.; Misic, C. Ingestion and elimination of anthropogenic fibres and microplastic fragments by the European anchovy (Engraulis encrasicolus) of the NW Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Biol. 2020, 167, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercogliano, R.; Santonicola, S.; Raimo, G.; Gasperi, M.; Colavita, G. Extraction and identification of microplastics from mussels: Method development and preliminary results. Ital. J. Food Saf. 2021, 10, 9264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J.; Roux, C.; Wiggins, K.G. Forensic Examination of Fibres; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Prata, J.C.; Castro, J.L.; da Costa, J.P.; Duarte, A.C.; Cerqueira, M.; Rocha-Santos, T. An easy method for processing and identification of natural and synthetic microfibers and microplastics in indoor and outdoor air. MethodsX 2020, 7, 100762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Directive 2008/56/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 17 June 2008 Establishing a Framework for Community Action in the Field of Marine Environmental Policy (Marine Strategy Framework Directive-MSFD). Off. J. Eur. Union 2008, 164, 19–40.
- Bessa, F.; Frias, J.; Kögel, T.; Lusher, A.; Andrade, J.M.; Antunes, J.; Gerdts, G. Harmonized protocol for monitoring microplastics in biota. Deliverable 4.3 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon-Sánchez, L.; Grelaud, M.; Garcia-Orellana, J.; Ziveri, P. River Deltas as hotspots of microplastic accumulation: The case study of the Ebro River (NW Mediterranean). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 687, 1186–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laglbauer, B.J.; Franco-Santos, R.M.; Andreu-Cazenave, M.; Brunelli, L.; Papadatou, M.; Palatinus, A. Macrodebris and microplastics from beaches in Slovenia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 89, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catarci, C. The Seafood Market in Italy Globefish; Research Program; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2008; Volume 92, p. 44. [Google Scholar]
- Cocci, P.; Gabrielli, S.; Pastore, G.; Minicucci, M.; Mosconi, G.; Palermo, F.A. Microplastics accumulation in gastrointestinal tracts of Mullus barbatus and Merluccius merluccius is associated with increased cytokine production and signaling. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, T.; Pelamatti, T.; Avio, C.G.; Camedda, A.; Costantini, M.L.; de Lucia, G.A.; Matiddi, M. One is not enough: Monitoring microplastic ingestion by fish needs a multispecies approach. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 184, 114133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onay, H.; Karslı, B.; Minaz, M.; Dalgıç, G. Seasonal monitoring of microplastic pollution in the Southeast Black Sea: An example of red mullet (Mullus barbatus) gastrointestinal tracts. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 191, 114886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabanilles, P.; Acle, S.; Arias, A.; Masiá, P.; Ardura, A.; Garcia-Vazquez, E. Microplastics risk into a three-link food chain inside european hake. Diversity 2022, 14, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muns-Pujadas, L.; Dallarés, S.; Constenla, M.; Padrós, F.; Carreras-Colom, E.; Grelaud, M.; Soler-Membrives, A. Revealing the capability of the European hake to cope with micro-litter environmental exposure and its inferred potential health impact in the NW Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Environ. Res. 2023, 186, 105921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atamanalp, M.; Köktürk, M.; Uçar, A.; Duyar, H.A.; Özdemir, S.; Parlak, V.; Alak, G. Microplastics in tissues (brain, gill, muscle and gastrointestinal) of Mullus barbatus and Alosa immaculata. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 81, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liboiron, F.; Ammendolia, J.; Saturno, J.; Melvin, J.; Zahara, A.; Richárd, N.; Liboiron, M. A zero percent plastic ingestion rate by silver hake (Merluccius bilinearis) from the south coast of Newfoundland, Canada. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 131, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santini, S.; De Beni, E.; Martellini, T.; Sarti, C.; Randazzo, D.; Ciraolo, R.; Cincinelli, A. Occurrence of Natural and Synthetic Micro-Fibers in the Mediterranean Sea: A Review. Toxics 2022, 10, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gago, J.; Carretero, O.; Filgueiras, A.V. Viñas, LSynthetic microfibers in the marine environment: A review on their occurrence in seawater and sediments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 127, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parliament. EU Strategy for Sustainable and Circular Textiles 2023. Available online: https://www.europarl.europa.eu/doceo/document/TA-9-2023-0215_EN.pdf (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Bai, C.L.; Liu, L.Y.; Hu, Y.B.; Zeng, E.Y.; Guo, Y. Microplastics: A review of analytical methods, occurrence and characteristics in food, and potential toxicities to biota. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Basantes, M.F.; Conesa, J.A.; Fullana, A. Microplastics in honey, beer, milk and refreshments in Ecuador as emerging contaminants. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Mean Length (cm) ± SD | Mean Weight (g) ± SD | Mean GIT Weight (g) ± SD | |
|---|---|---|---|
| M. barbatus (50) | 10.96 ± 0.58 | 25.27 ± 5.07 | 1.25 ± 0.23 |
| M. merluccius (50) | 18.64 ± 1.16 | 58.85 ± 10.93 | 1.68 ± 0.93 |
| M. barbatus | M. merluccius | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Median | Range | Mean ± SD | Median | Range | |
| Number of MFs/GIT in all individuals examined | 5.90 ± 8.84 | 2.00 | - | 6.98 ± 12.10 | 2.00 | - |
| Number of MFs/GIT in individuals containing MFs | 8.19 ± 9.62 | 3.50 | 1–42 | 10.26 ± 13.52 | 6.50 | 1–67 |
| Number of MFs/g w.w. of GIT | 4.65 ± 6.57 | 1.42 | 0.66–28 | 5.02 ± 8.17 | 1.11 | 0.40–36.25 |
| Number of MFs/g w.w. of individual | 0.23 ± 0.33 a | 0.07 | 0.02–1.45 | 0.12 ± 0.22 a | 0.02 | 0.01–1.17 |
| Wavenumber (cm−1) | Assignment |
|---|---|
| Polyester | |
| 1714 | C=O stretching |
| 1447 | aromatic ring of C=C |
| 1249 | C–O–C stretching |
| 1092 | O=C–O–C stretching |
| 1014 | O=C–O–C stretching |
| 720 | heterocyclic aromatic ring |
| Cellulose | |
| 3600 to 3200 | OH-stretching |
| 2918 | CH2 asymmetrical stretching |
| 2850 | CH2 symmetrical stretching |
| 1735 | C=O stretching |
| 1638 | amide I |
| 1422 | CH2 scissoring |
| 1150 | Anti-symmetrical C-O-C stretching |
| 1100 | anti-symmetric C-O-C in-plane stretching |
| 1057 | C-O-C in-plane stretching |
| 1030 | C-O stretch |
| Number of Samples | Sampling Area | Frequency of Ingestion | Average Number of Microfibers/GIT | % of Natural/Artificial Microfibers | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 M. barbatus | Adriatic Sea | 72% | 5.9 | 78% | Current study |
| 8 M. barbatus | Adriatic Sea | 100% | 5.37 | >80% | [2] |
| 21 M. barbatus | Tyrrhenian Sea | 14.28% | 0.3 | - | [13] |
| 118 M. barbatus | Catalan coast | 50% | 1.48 | 57% | [28] |
| 50 M. barbatus | Tyrrhenian Sea | 62% | 8.3 | 58% | [19] |
| 50 M. merluccius | Adriatic Sea | 68% | 6.9 | 82% | Current study |
| 10 M. merluccius | Adriatic Sea | 60% | 2 | >80% | [2] |
| 82 M. merluccius | Catalan coast | 66% | 1.39 | 77.8% | [43] |
| 50 M. merluccius | Tyrrhenian Sea | 72% | 8.9 | 68% | [19] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santonicola, S.; Volgare, M.; Olivieri, F.; Cocca, M.; Colavita, G. Natural and Regenerated Cellulosic Microfibers Dominate Anthropogenic Particles Ingested by Commercial Fish Species from the Adriatic Sea. Foods 2025, 14, 1237. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071237
Santonicola S, Volgare M, Olivieri F, Cocca M, Colavita G. Natural and Regenerated Cellulosic Microfibers Dominate Anthropogenic Particles Ingested by Commercial Fish Species from the Adriatic Sea. Foods. 2025; 14(7):1237. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071237
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantonicola, Serena, Michela Volgare, Federico Olivieri, Mariacristina Cocca, and Giampaolo Colavita. 2025. "Natural and Regenerated Cellulosic Microfibers Dominate Anthropogenic Particles Ingested by Commercial Fish Species from the Adriatic Sea" Foods 14, no. 7: 1237. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071237
APA StyleSantonicola, S., Volgare, M., Olivieri, F., Cocca, M., & Colavita, G. (2025). Natural and Regenerated Cellulosic Microfibers Dominate Anthropogenic Particles Ingested by Commercial Fish Species from the Adriatic Sea. Foods, 14(7), 1237. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071237





