Phenotypic and Genomic Insights into Schleiferilactobacillus harbinensis WU01, a Candidate Probiotic with Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial Activity Against ESKAPE (Enterococcus faecium, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Enterobacter) Pathogens
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Culture Conditions
2.2. Characterization of Probiotic Properties
2.2.1. Screening of Antipathogenic Activity
2.2.2. Acid Tolerance
2.2.3. Pepsin, Pancreatin, and Bile-Salt Tolerances
2.2.4. Auto-Aggregation
2.2.5. Cell-Surface Hydrophobicity
2.2.6. Adhesion to Human Intestinal Epithelial Cells
2.2.7. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.2.8. Susceptibility to Antibiotics
2.2.9. Hemolytic Test
2.3. Characterization of the Active Antimicrobial Substances of S. harbinensis WU01
2.3.1. Bacteriocin Screening
2.3.2. Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2) Production and Bile Salt Hydrolase (BSH) Activity
2.4. Genomic Analysis
2.4.1. DNA Isolation and WGS
2.4.2. Pangenome Analysis and Comparative Genomics
2.5. Computational Methods
2.5.1. System Preparation
2.5.2. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Bacterial Isolation and Identification
3.2. Characterization of Probiotic Properties
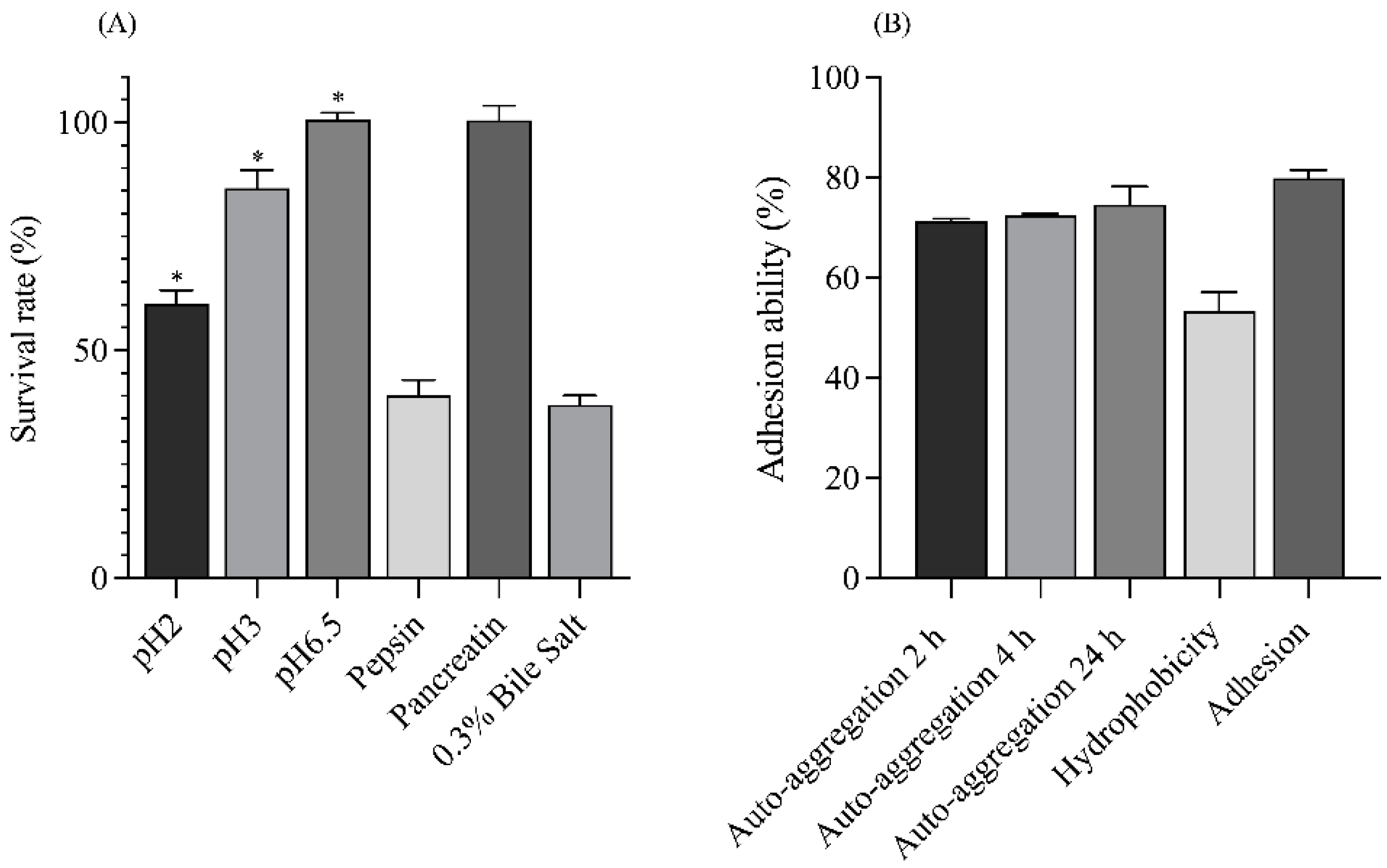
3.2.1. Stimulation of Gastrointestinal Tract (GIT) Tolerance
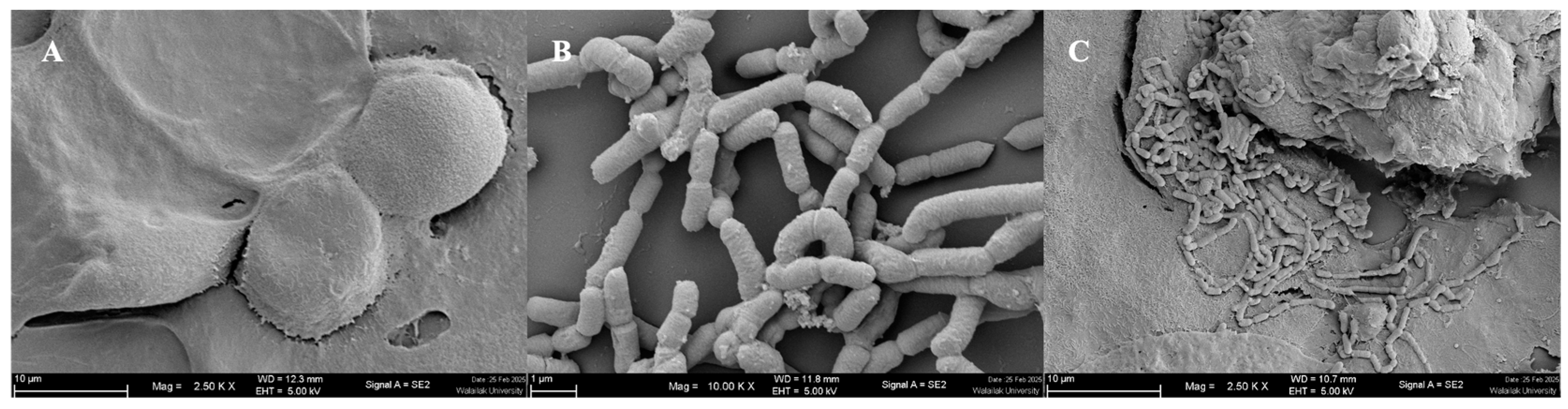
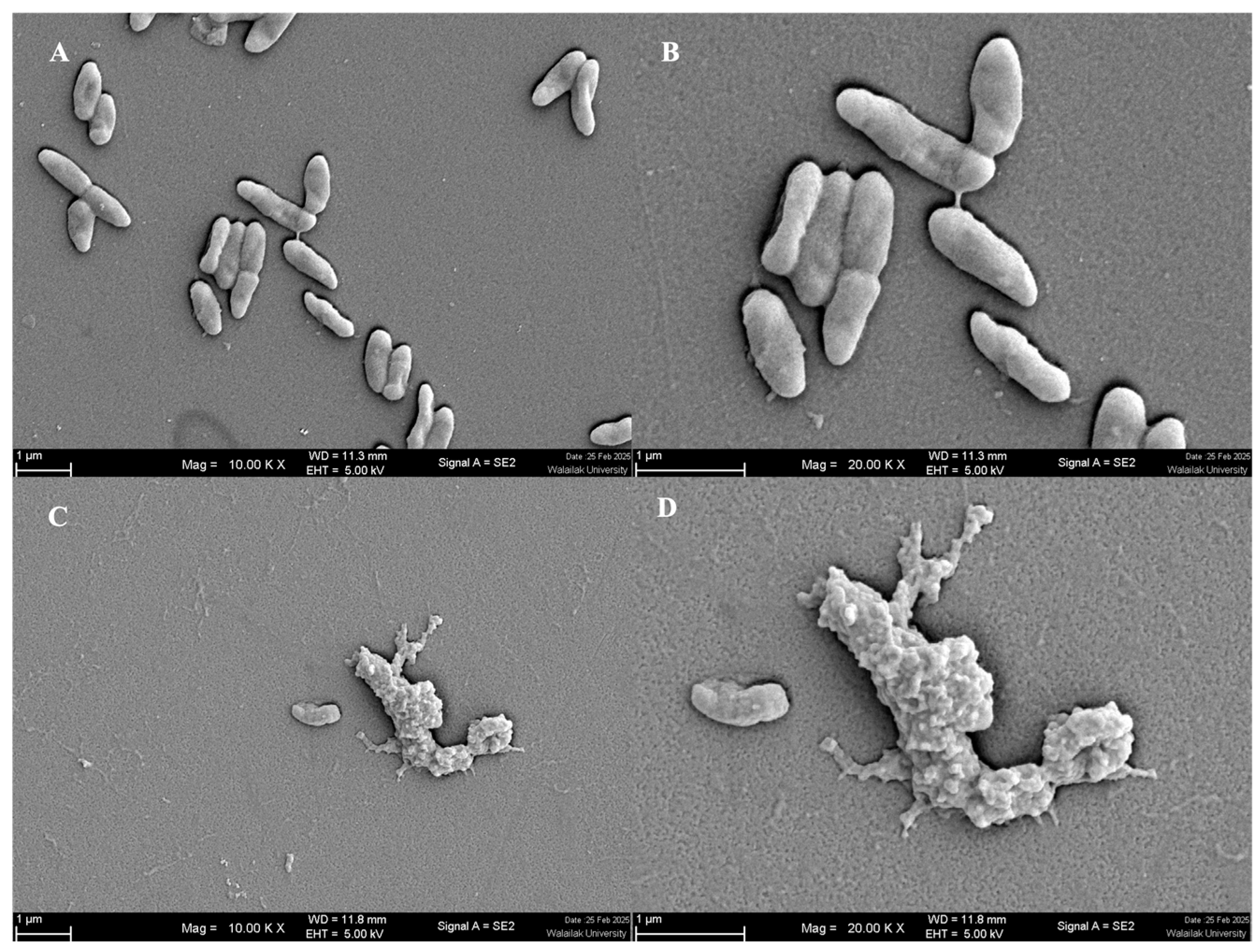
3.2.2. Auto-Aggregation and Enhancement of Adhesion Ability
3.2.3. Antibiotic Susceptibility and Hemolysis
3.3. Characterization of Antimicrobial Substances
3.3.1. Antimicrobial Activity
3.3.2. Production of Antimicrobial Substances
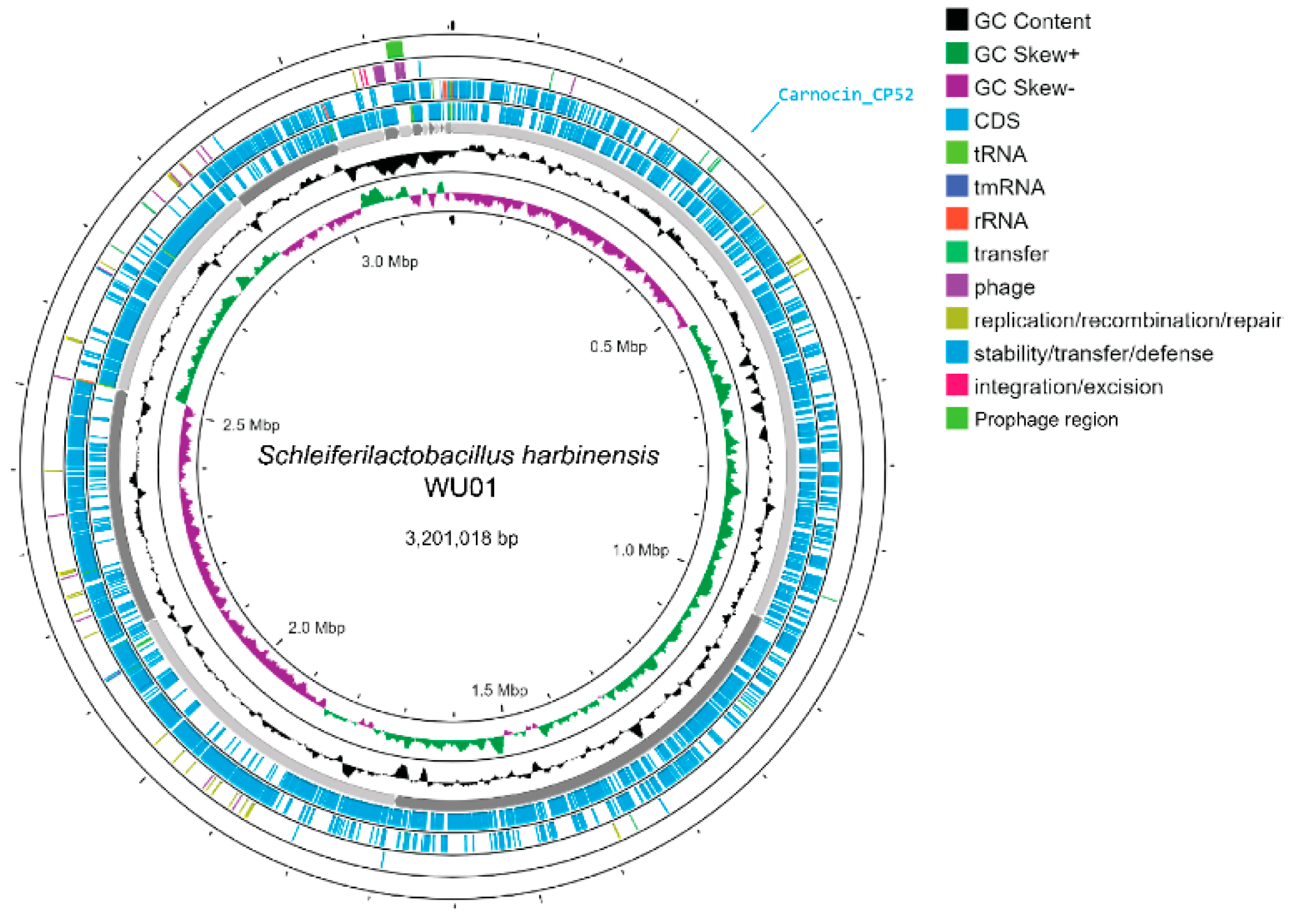
3.3.3. Genome Characteristics
3.3.4. In Silico Safety Evaluation
3.4. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MDR | Multidrug resistant |
| LAB | Lactic acid bacteria |
| WGS | Whole-genome sequencing |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| BSH | Bile Salt Hydrolase |
| ARGs | Antimicrobial-resistance genes |
| ANI | Average nucleotide identity |
References
- Aggarwal, R.; Mahajan, P.; Pandiya, S.; Bajaj, A.; Verma, S.K.; Yadav, P.; Kharat, A.S.; Khan, A.U.; Dua, M.; Johri, A.K. Antibiotic resistance: A global crisis, problems and solutions. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 50, 896–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, W.R.; Arias, C.A. ESKAPE pathogens: Antimicrobial resistance, epidemiology, clinical impact and therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 598–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Tanwar, M.; Singh, T.P.; Sharma, S.; Sharma, P. An escape from ESKAPE pathogens: A comprehensive review on current and emerging therapeutics against antibiotic resistance. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 279, 135253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. Expert consensus document. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokoena, M.P. Lactic Acid Bacteria and Their Bacteriocins: Classification, Biosynthesis and Applications against Uropathogens: A Mini-Review. Molecules 2017, 22, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, R.H.; Zendo, T.; Sonomoto, K. Multiple bacteriocin production in lactic acid bacteria. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2022, 134, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehily, S.R.; Basnayake, C.; Wright, E.K.; Yao, C.K.; Godsell, J.; Gibson, P.R.; Kamm, M.A. Probiotics: Are they beneficial? Intern. Med. J. 2024, 54, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.F.; Sohail, A.; Ghazanfar, S.; Ahmad, A.; Riaz, A.; Abbasi, K.S.; Ibrahim, M.S.; Uzair, M.; Arshad, M. Recent Innovations in Non-dairy Prebiotics and Probiotics: Physiological Potential, Applications, and Characterization. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2023, 15, 239–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Wittouck, S.; Salvetti, E.; Franz, C.; Harris, H.M.B.; Mattarelli, P.; O’Toole, P.W.; Pot, B.; Vandamme, P.; Walter, J.; et al. A taxonomic note on the genus Lactobacillus: Description of 23 novel genera, emended description of the genus Lactobacillus Beijerinck 1901, and union of Lactobacillaceae and Leuconostocaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 2782–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.-n.; Han, Y.; Zhou, Z.-j. Lactic acid bacteria in traditional fermented Chinese foods. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amara, A.; Shibl, A. Role of Probiotics in health improvement, infection control and disease treatment and management. Saudi Pharm. J. 2015, 23, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, M.; Seto, Y.; Hao, D.H.; Teshima, T.; Sun, Y.B.; Kabuki, T.; Yao, L.B.; Nakajima, H. Lactobacillus harbinensis sp. nov., consisted of strains isolated from traditional fermented vegetables ’Suan cai’ in Harbin, Northeastern China and Lactobacillus perolens DSM 12745. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 28, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, M.; Castilho, N.P.A.; Todorov, S.D.; Nero, L.A. Beneficial properties of lactic acid bacteria naturally present in dairy production. BMC Microbiol. 2018, 18, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colares, H.C.; Guimarães, G.M.; Couto, C.A.P.; Gil, P.O.; Santos, S.; Silva, T.N.L.; de Carvalho, I.L.Q.; da Fonseca, F.G.; Gagnon, M.; Roy, D.; et al. Optimization of bioprocess of Schleiferilactobacillus harbinensis Ca12 and its viability in frozen Brazilian berries (Açai, Euterpe oleracea Mart.). Braz. J. Microbiol. 2021, 52, 2271–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Wu, Z.; Dong, S.; Wang, Q.; Zhong, Q. Simulated Gastrointestinal Digestion and Fecal Fermentation Characteristics of Exopolysaccharides Synthesized by Schleiferilactobacillus harbinensis Z171. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 19748–19765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wu, Z.; Pan, Y.; Luo, D.; Zhong, Q. Effects of different stress conditions on the production, bioactivities, physicochemical and structural characteristics of exopolysaccharides synthetized by Schleiferilactobacillus harbinensis Z171. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 257, 128675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sornsenee, P.; Singkhamanan, K.; Sangkhathat, S.; Saengsuwan, P.; Romyasamit, C. Probiotic Properties of Lactobacillus Species Isolated from Fermented Palm Sap in Thailand. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2021, 13, 957–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigam, A.; Kumar, A.; Iyengar, M.H.V.; Bhola, N. In-vitro Screening of antibacterial activity of lactic acid bacteria against common enteric pathogens. J. Biomed. Sci. 2012, 1. [Google Scholar]
- CLSI. Methods for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing of Anaerobic Bacteria, 29th ed.; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Leite, A.M.; Miguel, M.A.; Peixoto, R.S.; Ruas-Madiedo, P.; Paschoalin, V.M.; Mayo, B.; Delgado, S. Probiotic potential of selected lactic acid bacteria strains isolated from Brazilian kefir grains. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 3622–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.L.; Kato, N.; Matsumiya, Y.; Liu, C.X.; Kato, H.; Watanabe, K. Identification of and hydrogen peroxide production by fecal and vaginal lactobacilli isolated from Japanese women and newborn infants. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 3062–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zeng, X.; Mo, Y.; Smith, K.; Guo, Y.; Lin, J. Identification and characterization of a bile salt hydrolase from Lactobacillus salivarius for development of novel alternatives to antibiotic growth promoters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 8795–8802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chukamnerd, A.; Jeenkeawpiam, K.; Chusri, S.; Pomwised, R.; Singkhamanan, K.; Surachat, K. BacSeq: A User-Friendly Automated Pipeline for Whole-Genome Sequence Analysis of Bacterial Genomes. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzer, M.; Marz, M. De novo transcriptome assembly: A comprehensive cross-species comparison of short-read RNA-Seq assemblers. Gigascience 2019, 8, giz039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevich, A.; Saveliev, V.; Vyahhi, N.; Tesler, G. QUAST: Quality assessment tool for genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1072–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterhouse, R.M.; Seppey, M.; Simao, F.A.; Manni, M.; Ioannidis, P.; Klioutchnikov, G.; Kriventseva, E.V.; Zdobnov, E.M. BUSCO Applications from Quality Assessments to Gene Prediction and Phylogenomics. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.L.; Mullet, J.; Hindi, F.; Stoll, J.E.; Gupta, S.; Choi, M.; Keenum, I.; Vikesland, P.; Pruden, A.; Zhang, L. mobileOG-db: A Manually Curated Database of Protein Families Mediating the Life Cycle of Bacterial Mobile Genetic Elements. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 88, e0099122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starikova, E.V.; Tikhonova, P.O.; Prianichnikov, N.A.; Rands, C.M.; Zdobnov, E.M.; Ilina, E.N.; Govorun, V.M. Phigaro: High-throughput prophage sequence annotation. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 3882–3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malberg Tetzschner, A.M.; Johnson, J.R.; Johnston, B.D.; Lund, O.; Scheutz, F. In Silico Genotyping of Escherichia coli Isolates for Extraintestinal Virulence Genes by Use of Whole-Genome Sequencing Data. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e01269-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolaia, V.; Kaas, R.S.; Ruppe, E.; Roberts, M.C.; Schwarz, S.; Cattoir, V.; Philippon, A.; Allesoe, R.L.; Rebelo, A.R.; Florensa, A.F.; et al. ResFinder 4.0 for predictions of phenotypes from genotypes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 3491–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couvin, D.; Bernheim, A.; Toffano-Nioche, C.; Touchon, M.; Michalik, J.; Néron, B.; Rocha, E.P.C.; Vergnaud, G.; Gautheret, D.; Pourcel, C. CRISPRCasFinder, an update of CRISRFinder, includes a portable version, enhanced performance and integrates search for Cas proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W246–W251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Heel, A.J.; de Jong, A.; Song, C.X.; Viel, J.H.; Kok, J.; Kuipers, O.P. BAGEL4: A user-friendly web server to thoroughly mine RiPPs and bacteriocins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W278–W281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, A.J.; Cummins, C.A.; Hunt, M.; Wong, V.K.; Reuter, S.; Holden, M.T.G.; Fookes, M.; Falush, D.; Keane, J.A.; Parkhill, J. Roary: Rapid large-scale prokaryote pan genome analysis. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3691–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stothard, P.; Grant, J.R.; Van Domselaar, G. Visualizing and comparing circular genomes using the CGView family of tools. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 20, 1576–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST plus: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.; Ouk Kim, Y.; Park, S.C.; Chun, J. OrthoANI: An improved algorithm and software for calculating average nucleotide identity. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 1100–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Park, S.; Choi, Y.K.; Im, W. CHARMM-GUI Membrane Builder: Past, Current, and Future Developments and Applications. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2023, 19, 2161–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.; Kim, T.; Iyer, V.G.; Im, W. CHARMM-GUI: A web-based graphical user interface for CHARMM. J. Comput. Chem. 2008, 29, 1859–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case, D.A.; Aktulga, H.M.; Belfon, K.; Ben-Shalom, I.Y.; Berryman, J.T.; Brozell, S.R.; Cerutti, D.S.; Cheatham, T.E., III; Cisneros, G.A.; Cruzeiro, V.W.D.; et al. AMBER 2022; University of California: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Suez, J.; Zmora, N.; Segal, E.; Elinav, E. The pros, cons, and many unknowns of probiotics. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 716–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribera, C.; Sánchez-Ortí, J.V.; Clarke, G.; Marx, W.; Mörkl, S.; Balanzá-Martínez, V. Probiotic, prebiotic, synbiotic and fermented food supplementation in psychiatric disorders: A systematic review of clinical trials. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2024, 158, 105561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ábrahám, Á.; Islam, M.N.; Gazdag, Z.; Khan, S.A.; Chowdhury, S.; Kemenesi, G.; Akter, S. Bacterial Metabarcoding of Raw Palm Sap Samples from Bangladesh with Nanopore Sequencing. Foods 2024, 13, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terpou, A.; Papadaki, A.; Lappa, I.K.; Kachrimanidou, V.; Bosnea, L.A.; Kopsahelis, N. Probiotics in Food Systems: Significance and Emerging Strategies Towards Improved Viability and Delivery of Enhanced Beneficial Value. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baick, S.C.; Kim, C.H. Assessment of Characteristics and Functional Properties of Lactobacillus Species Isolated from Kimchi for Dairy Use. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2015, 35, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.Y.; Koon, S.S.; Padam, B.S.; Chye, F.Y. Evaluation of probiotic potential of lactic acid bacteria isolated from traditional Malaysian fermented Bambangan (Mangifera pajang). CyTA J. Food 2015, 13, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, X.; Chen, Q.; Ju, X.; Liu, H.; Chen, W.; Xue, Z. A tolerant lactic acid bacteria, Lactobacillus paracasei, and its immunoregulatory function. Can. J. Microbiol. 2014, 60, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slizewska, K.; Chlebicz-Wojcik, A. Growth Kinetics of Probiotic Lactobacillus Strains in the Alternative, Cost-Efficient Semi-Solid Fermentation Medium. Biology 2020, 9, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Melo Pereira, G.V.; de Oliveira Coelho, B.; Magalhães Júnior, A.I.; Thomaz-Soccol, V.; Soccol, C.R. How to select a probiotic? A review and update of methods and criteria. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 2060–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Zhang, R.; Tian, X.; Zhou, X.; Pan, X.; Wong, A. Assessing the risk of probiotic dietary supplements in the context of antibiotic resistance. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokatlı, M.; Gülgör, G.; Bağder Elmacı, S.; Arslankoz İşleyen, N.; Özçelik, F. In vitro properties of potential probiotic indigenous lactic acid bacteria originating from traditional pickles. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 315819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Shi, J.; Zhang, L.; Ding, Z.; Qu, X.; Cui, H. Class IIa bacteriocins: Diversity and new developments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 16668–16707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandasamy, S.; Lee, K.H.; Yoo, J.; Yun, J.; Kang, H.B.; Kim, J.E.; Oh, M.H.; Ham, J.S. Whole genome sequencing of Lacticaseibacillus casei KACC92338 strain with strong antioxidant activity, reveals genes and gene clusters of probiotic and antimicrobial potential. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1458221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wang, W. Protective effects of potential probiotics Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus SN21-1 and Lactiplantibacillus plantarum SN21-2 against Salmonella typhimurium infection in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 104207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbin, S.; Mathieu, F.; Brulé, F.; Branlant, C.; Lefebvre, G.; Lebrihi, A. Characteristics and genetic determinants of bacteriocin activities produced by Carnobacterium piscicola CP5 isolated from cheese. Curr. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Bacteria | S. harbinensis WU01 |
|---|---|
| E. faecium | ++ |
| E. faecalis DMST 4736 | +++ |
| S. aureus subsp. aureus ATCC 6538 | +++ |
| MRSA | ++ |
| K. pneumoniae | ++ |
| A. baumannii | ++ |
| P. aeruginosa | +++ |
| Enterobacter spp. | ND |
| E. coli DMST4212 | +++ |
| S. typhi DMST 22842 | + |
| S. enteritidis DMST 15676 | +++ |
| S. flexneri DMST 44237 | ++ |
| Features | S. harbinensis WU01 |
|---|---|
| Genome size (bp.) | 3,201,018 |
| Contigs | 28 |
| GC content (%) | 53.31% |
| N50 | 453,387 |
| L50 | 3 |
| Number of CDS | 2993 |
| tRNA | 63 |
| rRNA | 4 |
| tmRNA | 1 |
| Bacteriocin-like encoding gene | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Romyasamit, C.; Surachat, K.; Pattaranggoon, N.C.; Suksabay, P.; Permpoon, U.; Nam, T.-G.; Sornsenee, P. Phenotypic and Genomic Insights into Schleiferilactobacillus harbinensis WU01, a Candidate Probiotic with Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial Activity Against ESKAPE (Enterococcus faecium, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Enterobacter) Pathogens. Foods 2025, 14, 1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071161
Romyasamit C, Surachat K, Pattaranggoon NC, Suksabay P, Permpoon U, Nam T-G, Sornsenee P. Phenotypic and Genomic Insights into Schleiferilactobacillus harbinensis WU01, a Candidate Probiotic with Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial Activity Against ESKAPE (Enterococcus faecium, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Enterobacter) Pathogens. Foods. 2025; 14(7):1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071161
Chicago/Turabian StyleRomyasamit, Chonticha, Komwit Surachat, Nawanwat C. Pattaranggoon, Pinkanok Suksabay, Uttapol Permpoon, Tae-Gyu Nam, and Phoomjai Sornsenee. 2025. "Phenotypic and Genomic Insights into Schleiferilactobacillus harbinensis WU01, a Candidate Probiotic with Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial Activity Against ESKAPE (Enterococcus faecium, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Enterobacter) Pathogens" Foods 14, no. 7: 1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071161
APA StyleRomyasamit, C., Surachat, K., Pattaranggoon, N. C., Suksabay, P., Permpoon, U., Nam, T.-G., & Sornsenee, P. (2025). Phenotypic and Genomic Insights into Schleiferilactobacillus harbinensis WU01, a Candidate Probiotic with Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial Activity Against ESKAPE (Enterococcus faecium, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Enterobacter) Pathogens. Foods, 14(7), 1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071161







