Effects of Planting Methods and Varieties on Rice Quality in Northern China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Methods for Measuring Indicators
2.3.1. Main Quality Indicators of Rice
2.3.2. Determination of the Eating Quality Value of Cooked Rice
2.3.3. Determination of the Viscosity of the RVA Profile of Rice
2.3.4. Temperature- and Light-Related Data
2.3.5. Data Processing and Statistics
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Processing Quality of Rice
3.2. Appearance Quality of Rice
3.3. Tasting Quality of Rice
3.4. Nutritional Quality of Rice
3.5. RVA of Rice
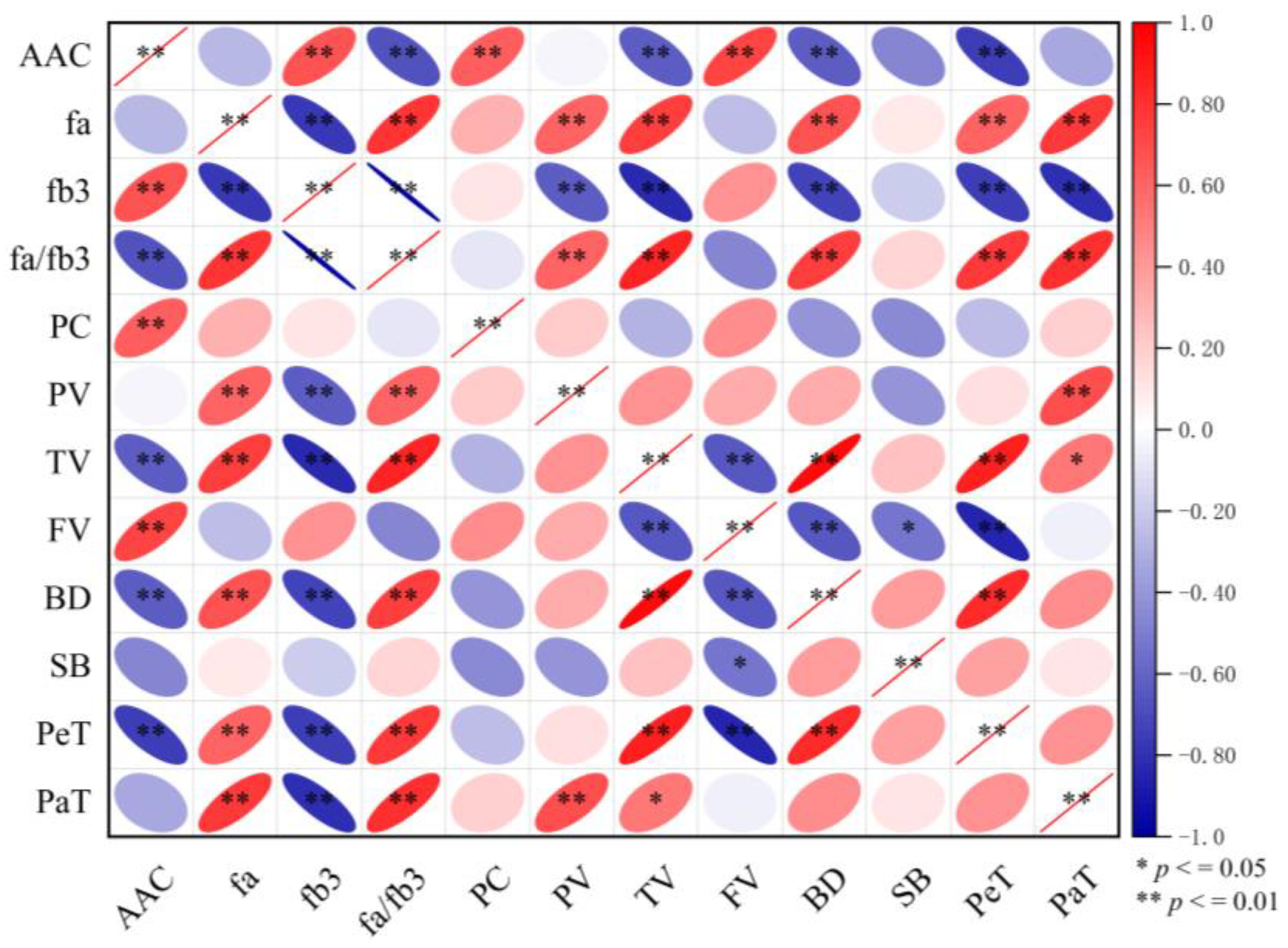
3.6. Correlation Between Nutritional Quality and RVA of Rice
3.7. Influence of Climatic Factors on Rice Quality and RVA Curves
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Planting Methods and Varieties on the Processing and Appearance Quality of Rice
4.2. Effects of Planting Methods and Varieties on the Tasting Quality, Nutritional Quality, and RVA of Rice
4.3. Correlation Between Nutritional Quality and RVA of Rice
4.4. Influence of Climatic Factors on Rice Quality
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Ma, Z.H.; Cheng, H.T.; Nitta, Y.; Aoki, N.; Chen, Y.; Chen, H.X.; Ohsugi, R.; Lyu, W.Y. Differences in Viscosity of Superior and Inferior Spikelets of Japonica Rice with Various Percentages of Apparent Amylose Content. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 4237–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, S.Y.; Luo, H.W.; Wu, F.D.; He, L.X.; Lai, R.F.; Tang, X.R. Organic cultivation induced regulation in yield formation, grain quality attributes, and volatile organic compounds of fragrant rice. Food Chem. 2023, 405, 134845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.T.; Yang, T.Z.; Cao, M.X.; Tang, H.; Shu, C.; Guo, P.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, Y.T. Effects of Artificial Direct Seeding and Artificial Transplanting on Rice Yield of Wuliangyou Huazhan. Fujian Agric. Sci. Technol. 2024, 55, 70. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.M.; Lee, H.T.; Lo, S.F.; Ho, T.D. How does rice cope with too little oxygen during its early life? New Phytol. 2021, 229, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duart, V.M.; Garbuio, F.J.; Caires, E.F. Does direct-seeded rice performance improve upon lime and phosphogypsum use? ScienceDirect. Soil. Till. Res. 2021, 212, 105055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, M.A.; Mccouch, S.R.; Hall, R.D. Not just a grain of rice: The quest for quality. Trends Plant Sci. 2009, 14, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, A.; Ikeda, A.; Yonemaru, J.; Morita, S.; Yamamoto, Y. Relationships among the chalkiness, kernel size and endosperm cell morphology of rice kernels at different spikelet positions within a panicle. Plant Prod. Sci. 2018, 21, 225–232. [Google Scholar]
- Bautista, R.C.; Counce, P.A. An overview of rice and rice quality. Cereal Foods World 2020, 65, 52. [Google Scholar]
- Chandusingh, P.R.; Singh, N.K.; Prabhu, K.V.; Vinod, K.K.; Singh, A.K. Molecular mapping of quantitative trait loci for grain chalkiness in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Indian J. Genet. Plant Breed. 2013, 73, 244–251. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Xu, R.; Duan, P.; Li, Y. Control of grain size in rice. Plant Reprod. 2018, 31, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Pang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Z.; Chen, K.; Ali, J.; Ye, G.; Xu, J.; Li, Z. Genome-wide and gene-based association mapping for rice eating and cooking characteristics and protein content. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17203. [Google Scholar]
- Long, X.; Guan, C.; Wang, L.; Jia, L.; Fu, X.; Lin, Q.; Huang, Z.; Liu, C. Rice Storage Proteins: Focus on Composition, Distribution, Genetic Improvement and Effects on Rice Quality. Rice Sci. 2023, 30, 207–221. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, H.; Saito, S.I.; Taira, T. Selection for High Palatable Rice Lines by Use of Mido Meter and Rapid Visco Analyser. Jpn. J. Crop Sci. 2003, 72, 390394. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 1789-1999; High-Quality Paddy. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1999.
- NY147-88; Methods for Determination of Rice Quality. Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1988.
- Nakamura, S.; Satoh, H.; Ohtsubo, K.I. Development of formulae for estimating amylose content, amylopectin chain length distribution, and resistant starch content based on the iodine absorption curve of rice starch. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2015, 79, 443–455. [Google Scholar]
- Hanashiro, I.; Abe, J.I.; Hizukuri, S. A periodic distribution of the chain length of amylopectin as revealed by high-performance anion-exchange chromatography. Carbohydr. Res. 1996, 283, 151–159. [Google Scholar]
- American Association of Cereal Chemists (AACC). Methods 61-02 for RVA, 9th ed.; AACC: St. Paul, MN, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Q.; Zhang, C. Data Processing System (DPS) software with experimental design, statistical analysis and data mining developed for use in entomological research. Insect Sci. 2013, 20, 254–260. [Google Scholar]
- Shimoyanagi, R.; Abo, M.; Shiotsu, F. Higher temperatures during grain filling affect grain chalkiness and rice nutrient contents. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.X.; Zheng, J.K.; Zhu, Y.C.; Wang, G.X. Effect of Atmospheric Phenomena Factors on the Milling Quality and the Appearance Quality of Medium India Hybrid Rice During the Period from Full Heading to Maturity. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2003, 27, 73–77. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gong, D.; Dai, G.; Chen, Y.; Yu, G. Optimal tillage depths for enhancing rice yield, quality and lodging resistance in the rice production systems of northeast China. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15739. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, L.; Yang, T.; Li, R.; Ma, L.; Feng, Y.; Li, Y. Grain Yield, Rice Seedlings and Transplanting Quantity in Response to Decreased Sowing Rate Under Precision Drill Sowing. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Peng, S.; Visperas, R.M.; Sanico, A.L.; Zhu, Q.; Gu, S. Grain filling pattern and cytokinin content in the grains and roots of rice plants. Plant Growth Regul. 2000, 30, 261–270. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, B.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Yang, J. Changes in Activities of the Key Enzymes Related to Starch Synthesis in Rice Grains During Grain Filling and Their Relationships with the Filling Rate and Cooking Quality. Agric. Sci. China 2005, 4, 26–33. [Google Scholar]
- Sui, M.; Shi, G.H.; Que, B.C.; Huang, Y.Q.; Li, G.; Quan, M.L.; Tang, L. Relationship Between Grain Shape and Quality Trait of Shennong Rice New Lines with High Yield. J. Shenyang Agric. Univ. 2014, 45, 655–660. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, R.; Jiang, L.; Zheng, J.; Wang, T.; Hong, Z. Genetic bases of rice grain shape: So many genes, so little known. Trends Plant Sci. 2012, 18, 218–226. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zhang, H.C.; Gong, J.L.; Chang, Y.; Dai, Q.G.; Huo, Z.Y.; Xu, K.; Wei, H.Y.; Gao, H. Influence of Planting Methods on Grain-Filling Properties of Super Rice. Acta Agron. Sin. 2011, 37, 1631–1641. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, J.; Xu, F.; Han, C.; Qiu, S.; Ge, J. Effects of planting methods on yield and quality of different types of japonica rice in northern Jiangsu plain, China. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 2624–2635. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, J. Rice: Eating Quality. In Encyclopedia of Food Grains, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 166–175. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, M.; Fitzgerald, M.A. Proteins in Rice Grains Influence Cooking Properties! J. Cereal Sci. 2002, 36, 285–294. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, Z.; Huo, Z.; Dai, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, M.; Wu, P.; Qian, H.; Cao, W.; Hu, Y.; Guo, B. Effect of Mechanical Transplanting with Pothole Seedlings on Grain Quality of Different Types of Rice in Rice-Wheat Rotation System. Acta Agron. Sin. 2017, 43, 581–595. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, J.Y.; Ji, G.M.; Zhang, J.F.; Luo, D.Q.; Zhang, F.; Li, L.J.; Jiang, M.J.; Zhu, D.W.; Li, M. Variety Screening and Characterization Analysis of Storage Stability of Eating Quality of Rice. Foods 2024, 13, 4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allahgholipour, M.; Ali, J.; Alinia, F.; Nagamine, T.; Kojima, Y. Relationship between rice grain amylose and pasting properties for breeding better quality rice varieties. Plant Breed. 2006, 125, 357–362. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, Z.; Li, J.; Xu, K.; Dai, Q.; Wei, H.; Gong, J.; Zhang, H. Effect of Planting Methods on Quality of Different Growth and Development Types of Japonica Rice Under High-Yielding Cultivation Condition. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2012, 45, 3932–3945. [Google Scholar]
- Dou, Z.; Tang, S.; Li, G.; Liu, Z.; Ding, C.; Chen, L.; Wang, S.; Ding, Y. Application of Nitrogen Fertilizer at Heading Stage Improves Rice Quality Under Elevated Temperature During Grain-Filling Stage. Crop Sci. 2017, 57, 2183–2192. [Google Scholar]
- Hori, K.; Suzuki, K.; Iijima, K.; Ebana, K. Variation in cooking and eating quality traits in Japanese rice germplasm accessions. Breed. Sci. 2016, 66, 309–318. [Google Scholar]
- Balindong, J.L.; Ward, R.M.; Liu, L.; Rose, T.J.; Pallas, L.A.; Ovenden, B.W.; Snell, P.J.; Waters, D.L.E. Rice grain protein composition influences instrumental measures of rice cooking and eating quality. J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 79, 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Lu, W.; Lu, F.; Cheng, H.; Ma, Z.; Chen, H. Effect of Panicle Type and Endosperm Composition on Viscoelasticity of Cooked Rice. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2019, 40, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, T.Q.; Jiang, W.; Ham, T.H.; Chu, S.H.; Koh, H.J. Comparison of grain quality traits between japonica rice cultivars from Korea and Yunnan province of China. J. Crop Sci. Biotechnol. 2008, 11, 135–140. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, J.; Zhang, X.; Cuf, Z.; Kusutani, A.; Matsue, Y. Correlation between Evaluation of Palatability by Sensory Test and Physicochemical Properties in Chinese japonica–type Rice. J. Fac. Agric. Kyushu Univ. 2016, 61, 53–58. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Sheng, W.; Jun, W.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Q.; Deng, Q. Differential expressions among five Waxy alleles and their effects on the eating and cooking qualities in specialty rice cultivars. J. Integr. Agric. 2015, 14, 1153–1162. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Zhao, L.; Chen, T.; Zhao, Q.; Zhou, L.; Yao, S.; Zhao, C.; Wang, C. Correlation Analyses of Amylose Contents and Srarch RVA Profiles of New Rice Varieties (Lines) Carrying Wx-mq Gene. Acta Agric. Bor. Sin. 2013, 28, 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Chen, D.; He, L.; Wang, T.; Ren, W. Correlation of taste values with chemical compositions and rapid visco analyser profiles of 36 indica rice (Oryza sativa L.) varieties. Food Chem. 2021, 349, 129176. [Google Scholar]
- Thitisaksakul, M.; Jiménez, R.C.; Arias, M.C.; Beckles, D.M. Effects of environmental factors on cereal starch biosynthesis and composition. J. Cereal Sci. 2012, 56, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, A.; Lee, H.J.; Hamaker, B.R.; Janaswamy, S. Effects of Ripening Temperature on Starch Structure and Gelatinization, Pasting, and Cooking Properties in Rice (Oryza sativa). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 3085–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.B.; Liu, D.H.; Zhong, M.; Wang, Y.Y. Research Progress of Climate Factor on Quality Formation and Influence Mechanism in Rice. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2019, 58, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Zhou, L.; Zhu, Z.; Lu, H.; Zhou, X.; Qian, Y.; Li, Q.; Lu, Y.; Gu, M.; Liu, Q. Characterization of Grain Quality and Starch Fine Structure of Two Japonica Rice (Oryza sativa) Cultivars with Good Sensory Properties at Different Temperatures during the Filling Stage. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 4048–4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Tetlow, I.J.; Nawaz, S.; Iqbal, A.; Mubin, M.; Nawaz ul Rehman, M.S.; Butt, A.; Lightfoot, D.A.; Maekawa, M. Effect of high temperature on grain filling period, yield, amylose content and activity of starch biosynthesis enzymes in endosperm of basmati rice. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 2237–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Zhu, P.; Sui, Z.; Bao, J. Physicochemical properties of starches from diverse rice cultivars varying in apparent amylose content and gelatinisation temperature combinations. Food Chem. 2015, 172, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.J.; Fu, W.Q.; Chang, Q.; Zheng, B.D.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, H.L. Moisture distribution model describes the effect of water content on the structural properties of lotus seed resistant starch. Food Chem. 2019, 286, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q.; Zheng, B.D.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, H.L. A comprehensive review of the factors influencing the formation of retrograded starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 186, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
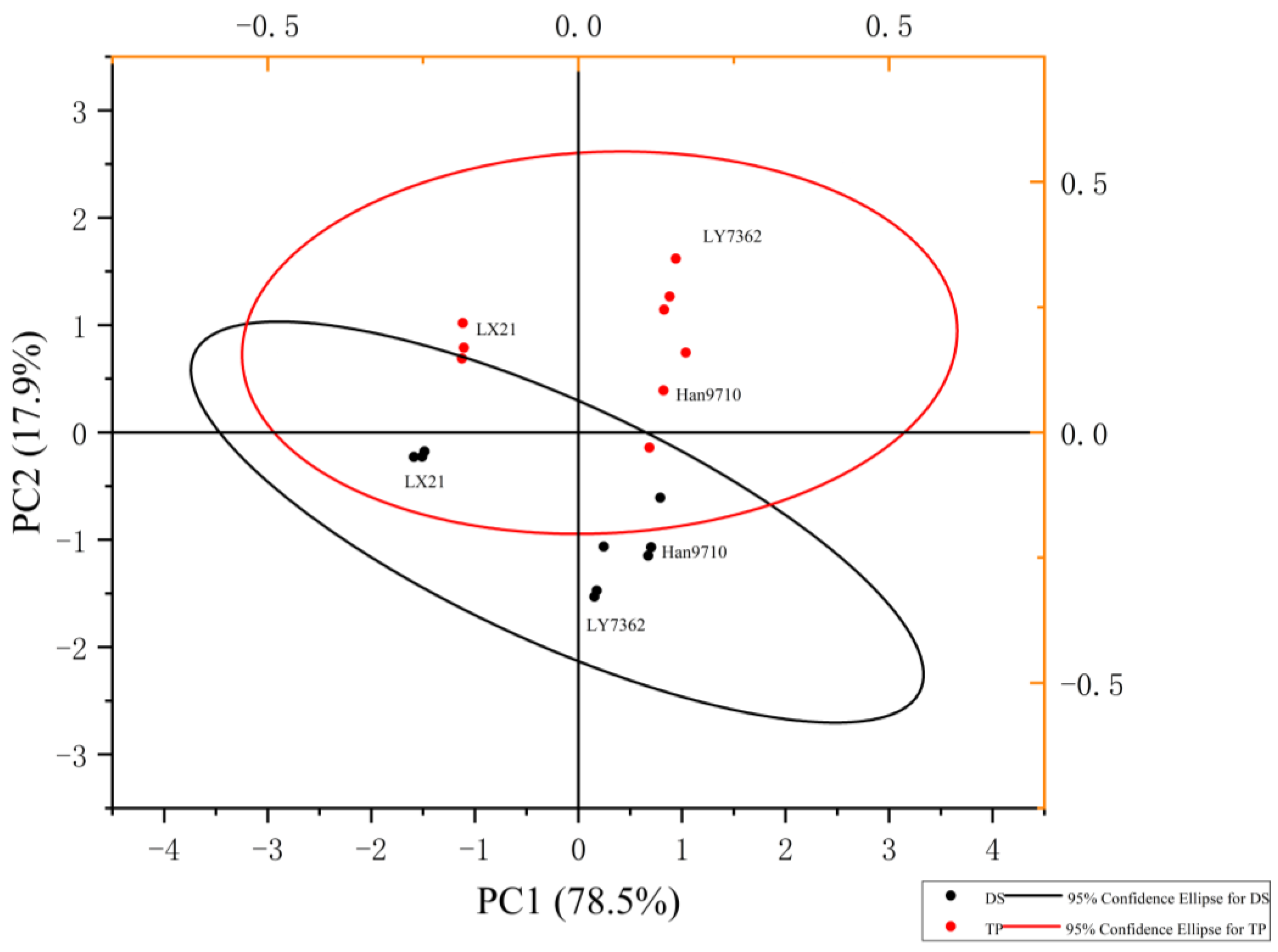
| PM | V | SS | ES | FHS | MS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP | LX21 | 4/15 | 7/12 | 8/7 | 9/29 |
| H9710 | 4/15 | 7/10 | 8/3 | 9/26 | |
| LY7362 | 4/15 | 7/16 | 8/15 | 10/1 | |
| DS | LX21 | 4/27 | 7/20 | 8/11 | 10/1 |
| H9710 | 4/27 | 7/17 | 8/8 | 9/30 | |
| LY7362 | 4/27 | 7/26 | 8/20 | 10/5 |
| Items | V | BRR (%) | MRR (%) | HRR (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP | LX21 | 0.81ab | 0.71a | 68.09a |
| H9710 | 0.81a | 0.71a | 64.21b | |
| LY7362 | 0.81ab | 0.68a | 60.40d | |
| DS | LX21 | 0.81ab | 0.71a | 68.97a |
| H9710 | 0.81ab | 0.68a | 63.39bc | |
| LY7362 | 0.81b | 0.69a | 61.17cd | |
| LSD (0.05) | 0.01 | 0.04 | 2.56 | |
| PM | ||||
| TP | 0.81a | 0.70a | 64.23a | |
| DS | 0.81a | 0.69a | 64.51a | |
| V | ||||
| LX21 | 0.81ab | 0.71a | 68.53a | |
| H9710 | 0.81a | 0.69ab | 63.80b | |
| LY7362 | 0.81b | 0.68b | 60.78c | |
| Analysis of variance | ||||
| PM | NS | NS | NS | |
| V | NS | * | ** | |
| PM × V | NS | NS | NS |
| Items | V | GL (mm) | GW (mm) | GL/W | CGR (%) | CH (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP | LX21 | 5.80a | 2.50d | 2.32a | 0.85c | 1.55c |
| H9710 | 4.70c | 2.70b | 1.74c | 1.59b | 3.51a | |
| LY7362 | 4.60d | 2.60c | 1.77b | 2.06a | 3.65a | |
| DS | LX21 | 5.80a | 2.50d | 2.32a | 0.23d | 0.45d |
| H9710 | 4.80b | 2.80a | 1.71d | 1.37b | 2.36b | |
| LY7362 | 4.70c | 2.70b | 1.74c | 0.83c | 1.30c | |
| LSD (0.05) | 0.02 | <0.01 | 0.01 | 0.29 | 0.57 | |
| PM | ||||||
| TP | 5.04b | 2.60b | 1.94a | 1.50a | 2.90a | |
| DS | 5.10a | 2.67a | 1.92b | 0.81b | 1.37b | |
| V | ||||||
| LX21 | 5.80a | 2.50c | 2.32a | 0.54b | 1.00c | |
| H9710 | 4.75b | 2.75a | 1.73c | 1.48a | 2.94a | |
| LY7362 | 4.65c | 2.65b | 1.75b | 1.45a | 2.48b | |
| Analysis of variance | ||||||
| PM | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | |
| V | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | |
| PM × V | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| Items | V | A | H | Ss | DB | T |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP | LX21 | 7.03a | 6.03d | 7.03a | 7.07a | 71.67a |
| H9710 | 6.43c | 6.67a | 6.73c | 6.53cd | 67.67b | |
| LY7362 | 6.60b | 6.47b | 6.90ab | 6.80b | 70.33ab | |
| DS | LX21 | 6.93a | 6.33c | 6.77bc | 6.63bc | 70.33ab |
| H9710 | 6.30c | 6.33c | 6.00e | 6.70bc | 68.00b | |
| LY7362 | 6.33c | 6.53b | 6.53d | 6.43d | 69.00ab | |
| LSD (0.05) | 0.16 | 0.11 | 0.15 | 0.19 | 3.08 | |
| PM | ||||||
| TP | 6.69a | 6.39a | 6.89a | 6.80a | 69.89a | |
| DS | 6.52b | 6.40a | 6.43b | 6.59b | 69.11a | |
| V | ||||||
| LX21 | 6.98a | 6.18b | 6.90a | 6.85a | 71.00a | |
| H9710 | 6.37b | 6.50a | 6.37c | 6.62b | 67.83c | |
| LY7362 | 6.47b | 6.50a | 6.72b | 6.62b | 69.67b | |
| Analysis of variance | ||||||
| PM | * | NS | ** | * | NS | |
| V | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | |
| PM × V | NS | ** | ** | ** | NS |
| Items | V | AAC% | fa | fb3 | fa/fb3 | PC% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP | LX21 | 19.10ab | 31.95ab | 6.39b | 5.00c | 7.67a |
| H9710 | 17.22d | 32.14a | 5.06d | 6.35a | 7.27abc | |
| LY7362 | 19.67a | 31.85b | 6.86a | 4.65d | 7.43ab | |
| DS | LX21 | 17.58cd | 31.48c | 6.74a | 4.68d | 6.20bc |
| H9710 | 16.74d | 32.08a | 5.39c | 5.95b | 6.04c | |
| LY7362 | 18.40bc | 31.76b | 7.00a | 4.54d | 6.90abc | |
| LSD (0.05) | 0.91 | 0.20 | 0.26 | 0.20 | 1.26 | |
| PM | ||||||
| TP | 18.66a | 31.98a | 6.11b | 5.33a | 7.46a | |
| DS | 17.57b | 31.77b | 6.38a | 5.06b | 6.38a | |
| V | ||||||
| LX21 | 18.34b | 31.71b | 6.57b | 4.84b | 6.94ab | |
| H9710 | 16.98c | 32.11a | 5.23c | 6.15a | 6.66b | |
| LY7362 | 19.04a | 31.80b | 6.93a | 4.59c | 7.17a | |
| Analysis of variance | ||||||
| PM | * | * | * | * | NS | |
| V | ** | ** | ** | ** | * | |
| PM × V | NS | ** | NS | NS | * |
| Items | V | PV/cP | TV/cP | FV/cP | BD/cP | SB/cP | PeT (min) | PaT/°C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP | LX21 | 3572.67a | 1585.00bc | 1870.33a | 3142.67d | 1607.67ab | 5.67c | 71.02a |
| H9710 | 3542.67ab | 2058.33a | 1424.33c | 3538.33b | 1580.00b | 6.13a | 71.77a | |
| LY7362 | 3495.33ab | 1668.33bc | 1841.00a | 3235.33cd | 1500.33c | 5.69c | 69.63b | |
| DS | LX21 | 3409.67b | 1506.00c | 1650.00b | 3089.67d | 1596.67ab | 5.71c | 69.37b |
| H9710 | 3124.00c | 2151.33a | 1427.33c | 3801.00a | 1649.67a | 6.11a | 71.02a | |
| LY7362 | 2800.00d | 1724.33b | 1375.67c | 3337.33c | 1646.33ab | 5.93b | 68.85b | |
| LSD (0.05) | 136.98 | 203.39 | 56.89 | 167.04 | 68.73 | 0.17 | 1.22 | |
| PM | ||||||||
| TP | 3508.33a | 1770.56a | 1711.89a | 3305.44a | 1562.67b | 5.83a | 70.81a | |
| DS | 3139.78b | 1793.89a | 1484.33b | 3409.33a | 1630.89a | 5.92a | 69.74b | |
| V | ||||||||
| LX21 | 3266.83b | 1545.5c | 1760.17a | 3116.17c | 1602.17a | 5.69c | 70.19b | |
| H9710 | 3534.00a | 2104.83a | 1425.83c | 3669.67a | 1614.83a | 6.12a | 71.39a | |
| LY7362 | 3171.33c | 1696.33b | 1608.33b | 3286.33b | 1573.33a | 5.81b | 69.24c | |
| Analysis of variance | ||||||||
| PM | ** | NS | ** | NS | * | NS | * | |
| V | ** | ** | ** | ** | NS | ** | ** | |
| PM × V | ** | NS | ** | * | * | ** | NS |
| Tems | V | Daily Mean Temperature (°C) | Daily Highest Temperature (°C) | Daily Lowest Temperature (°C) | Daily Mean Temperature Difference (°C) | Daily Mean Light Hours (h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP | LX21 | 21.18 | 26.63 | 15.73 | 10.90 | 6.44 |
| H9710 | 21.61 | 26.87 | 16.35 | 10.51 | 6.02 | |
| LY7362 | 20.09 | 26.48 | 14.63 | 11.54 | 7.12 | |
| DS | LX21 | 20.37 | 26.42 | 15.19 | 10.95 | 6.66 |
| H9710 | 21.07 | 26.58 | 15.55 | 11.03 | 6.59 | |
| LY7362 | 20.20 | 25.70 | 13.44 | 12.13 | 7.54 |
| Rice Quality Character | Daily Mean Temperature (°C) | Daily Highest Temperature (°C) | Daily Lowest Temperature (°C) | Daily Mean Temperature Difference (°C) | Daily Mean Light Hours (h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AAC% | −0.44 | −0.18 | −0.40 | 0.41 | 0.44 |
| fa | 0.63 ** | 0.34 | 0.50 * | −0.35 | −0.47 * |
| fb3 | −0.75 ** | −0.45 | −0.75 ** | 0.69 ** | 0.77 ** |
| fa/fb3 | 0.75 ** | 0.44 | 0.73 ** | −0.67 ** | −0.75 ** |
| PC% | 0.09 | 0.06 | 0.05 | −0.01 | −0.07 |
| PV/cP | 0.49 * | 0.63 ** | 0.75 ** | −0.63 ** | −0.66 ** |
| TV/cP | 0.52 * | 0.24 | 0.37 | −0.26 | −0.36 |
| FV/cP | −0.17 | 0.21 | 0.12 | −0.10 | −0.03 |
| BD/cP | 0.44 | 0.19 | 0.26 | −0.13 | −0.22 |
| SB/cP | 0.29 | −0.06 | −0.04 | 0.12 | 0.06 |
| PeT (min) | 0.50 * | 0.14 | 0.26 | −0.16 | −0.27 |
| PaT/°C | 0.81 ** | 0.60 ** | 0.82 ** | −0.69** | −0.78 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; He, N.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Zheng, W.; Ma, D.; Wang, H.; Tang, Z. Effects of Planting Methods and Varieties on Rice Quality in Northern China. Foods 2025, 14, 1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071093
Wang L, Zhang L, He N, Wang C, Zhang Y, Ma Z, Zheng W, Ma D, Wang H, Tang Z. Effects of Planting Methods and Varieties on Rice Quality in Northern China. Foods. 2025; 14(7):1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071093
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Lili, Liying Zhang, Na He, Changhua Wang, Yuanlei Zhang, Zuobin Ma, Wenjing Zheng, Dianrong Ma, Hui Wang, and Zhiqiang Tang. 2025. "Effects of Planting Methods and Varieties on Rice Quality in Northern China" Foods 14, no. 7: 1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071093
APA StyleWang, L., Zhang, L., He, N., Wang, C., Zhang, Y., Ma, Z., Zheng, W., Ma, D., Wang, H., & Tang, Z. (2025). Effects of Planting Methods and Varieties on Rice Quality in Northern China. Foods, 14(7), 1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071093






