Antibacterial Mechanism and Flavour Impact of Ultrasound and Plasma-Activated Water Combination on Aeromonas veronii in Crayfish
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparations
2.1.1. Bacterial Strain and Working Solution Preparations
2.1.2. Crayfish Collection and Preparation
2.2. US and PAW Preparations
2.3. Optimisation of Preparation Conditions for US-PAW
2.4. Sample Treatments
2.4.1. Bacterial Treatment
2.4.2. Antibiofilm Formation
2.4.3. Crayfish Inoculation and Treatment
2.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.6. Measurement of Cell Membrane Damage
2.6.1. Measurement of Cell Membrane Integrity
2.6.2. Electrical Conductivity
2.6.3. Leakage of Proteins and Nucleic Acids
2.6.4. Permeability Analysis of the Outer Membrane
2.7. Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and H2O2 Content
2.8. Antioxidant Enzyme Activities Assay
2.9. Analysis of Key Enzyme Activities and Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) Content in the Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle
2.10. Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS)
2.11. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
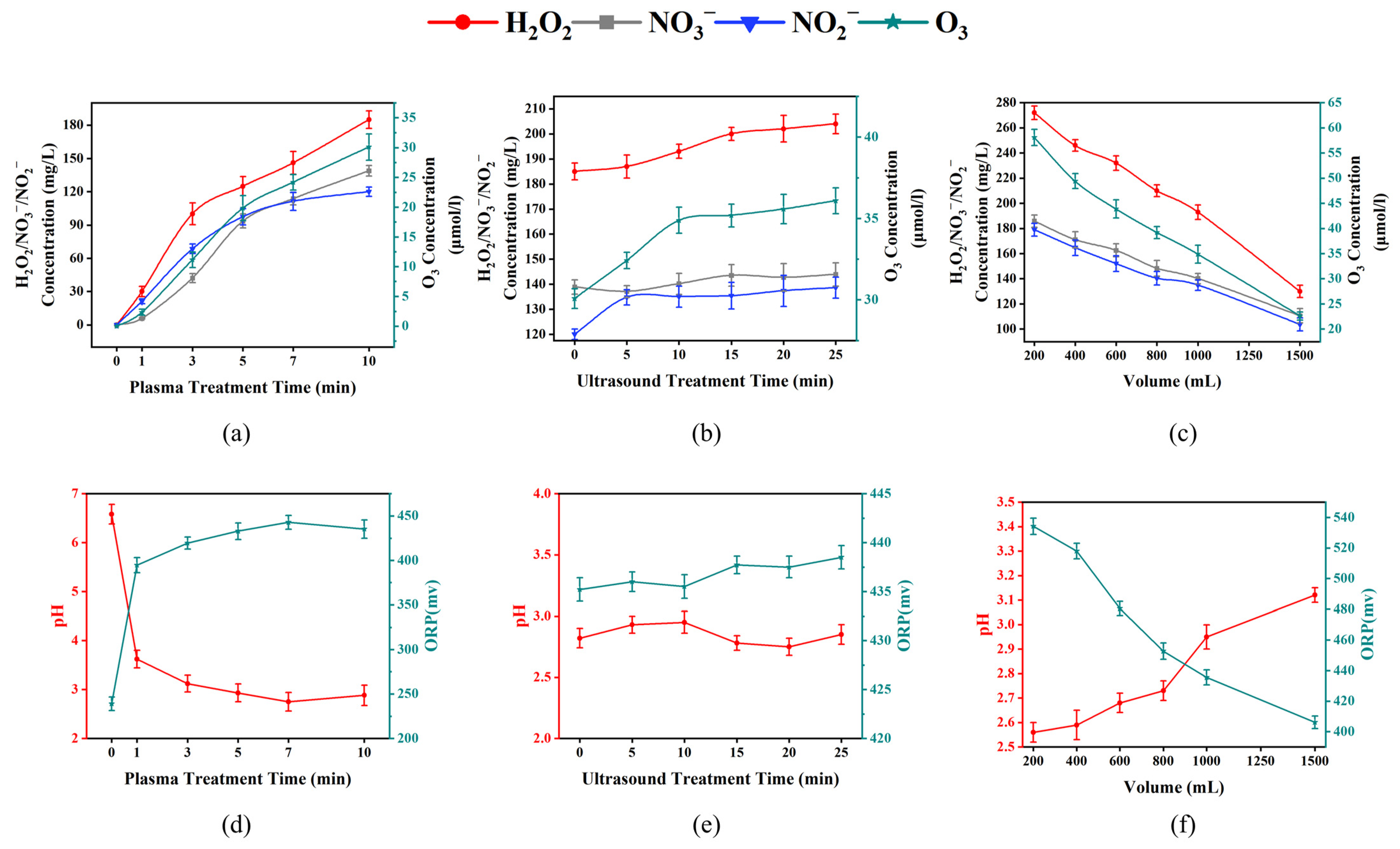
3.1. The Optimal Preparation Conditions for US-PAW
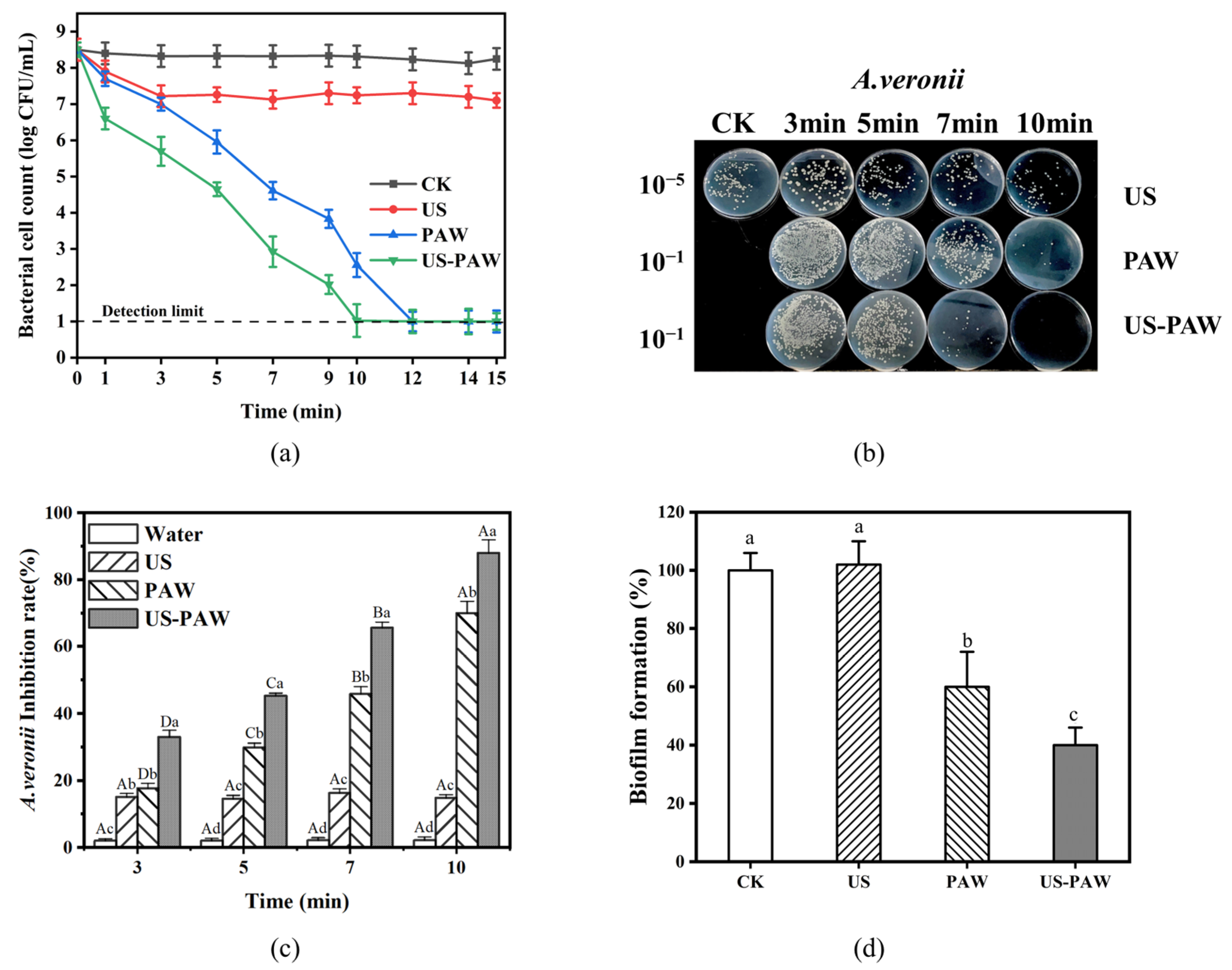
3.2. The Inactivation of A. veronii by US-PAW
3.3. Effect of US-PAW on the Regrowth Capacity of A. veronii Biofilm
3.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy Observations
3.5. Effects of US-PAW on the Cell Membrane
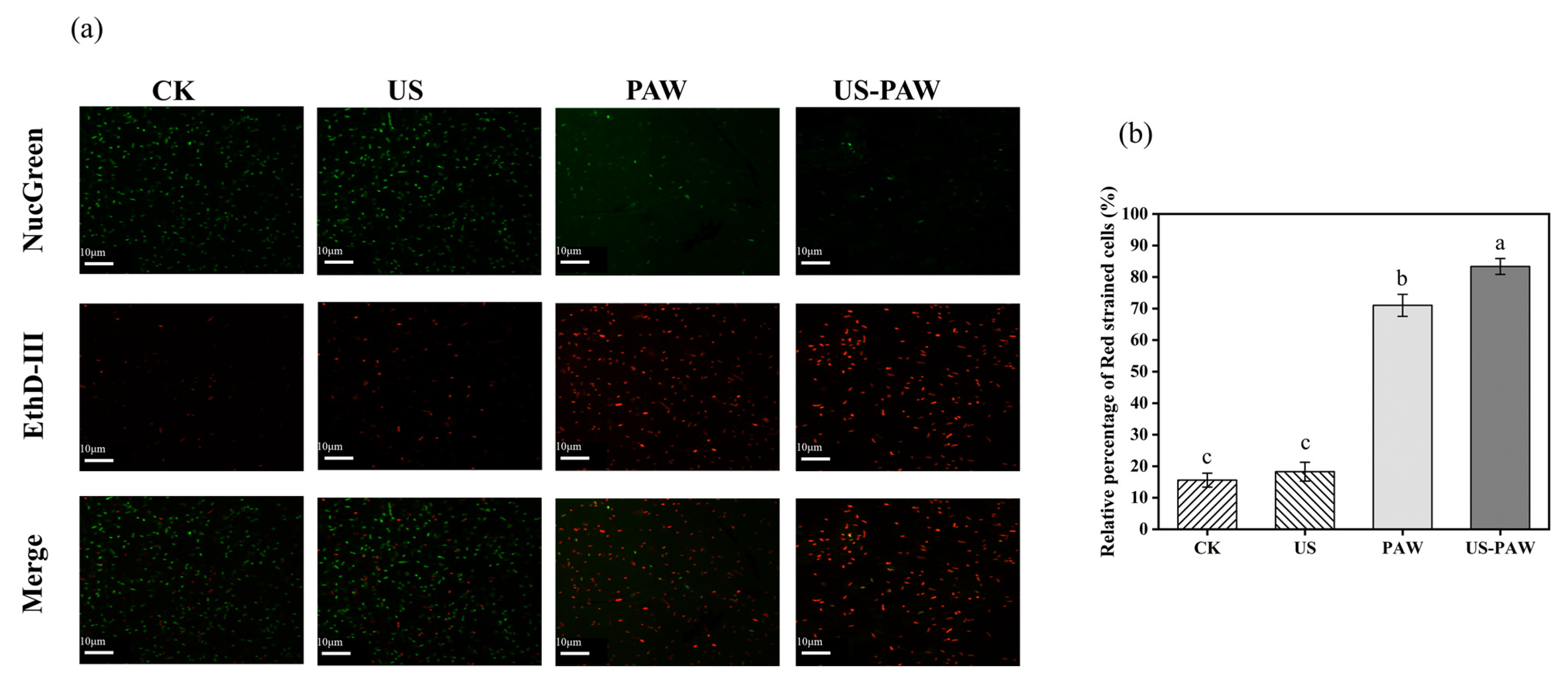
3.5.1. Cell Membrane Integrity
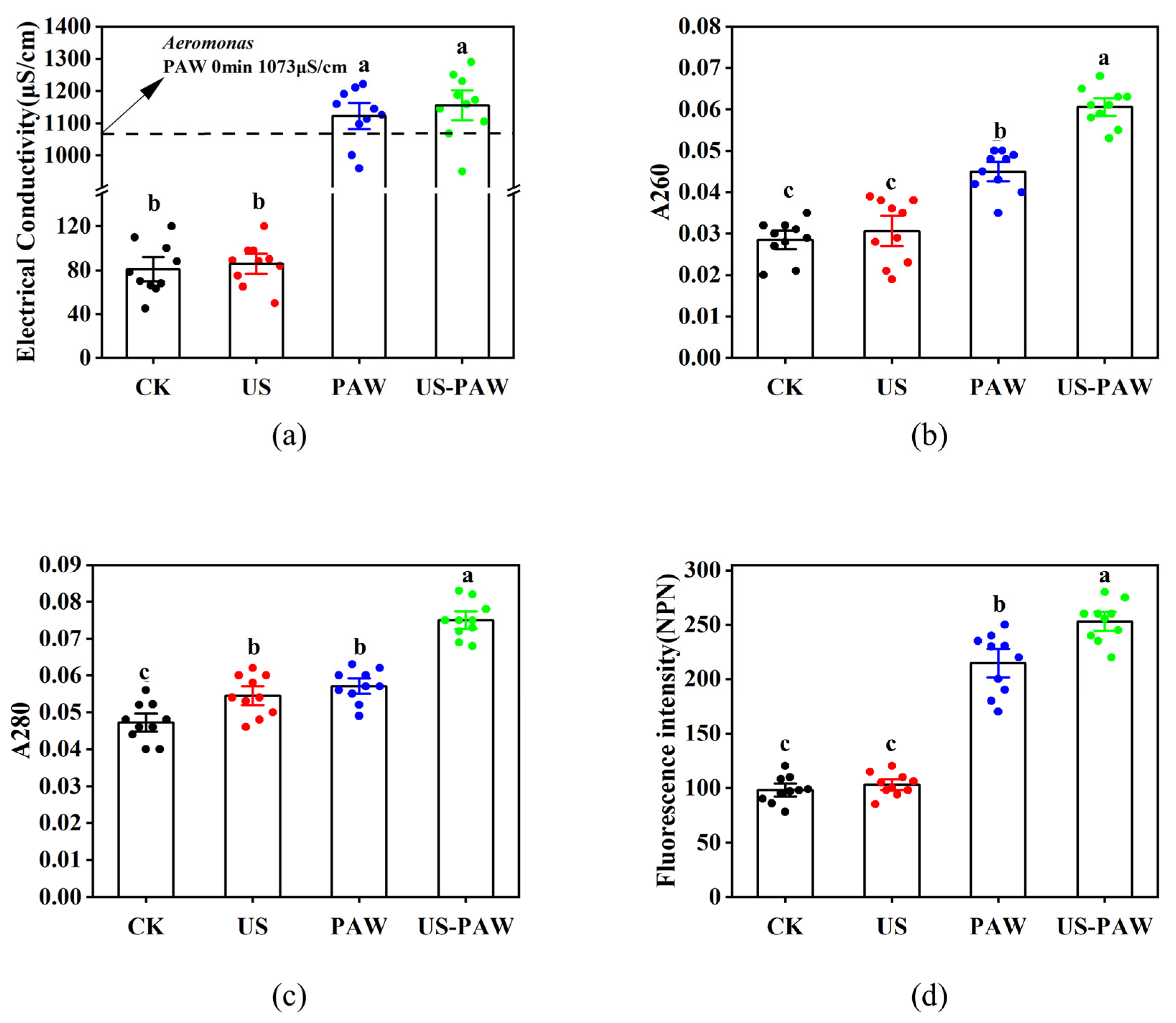
3.5.2. Electrical Conductivity of A. veronii Suspensions
3.5.3. Protein and Nucleic Acid Leakage
3.5.4. Permeability of the Outer Membrane
3.6. Generation of ROS and H2O2
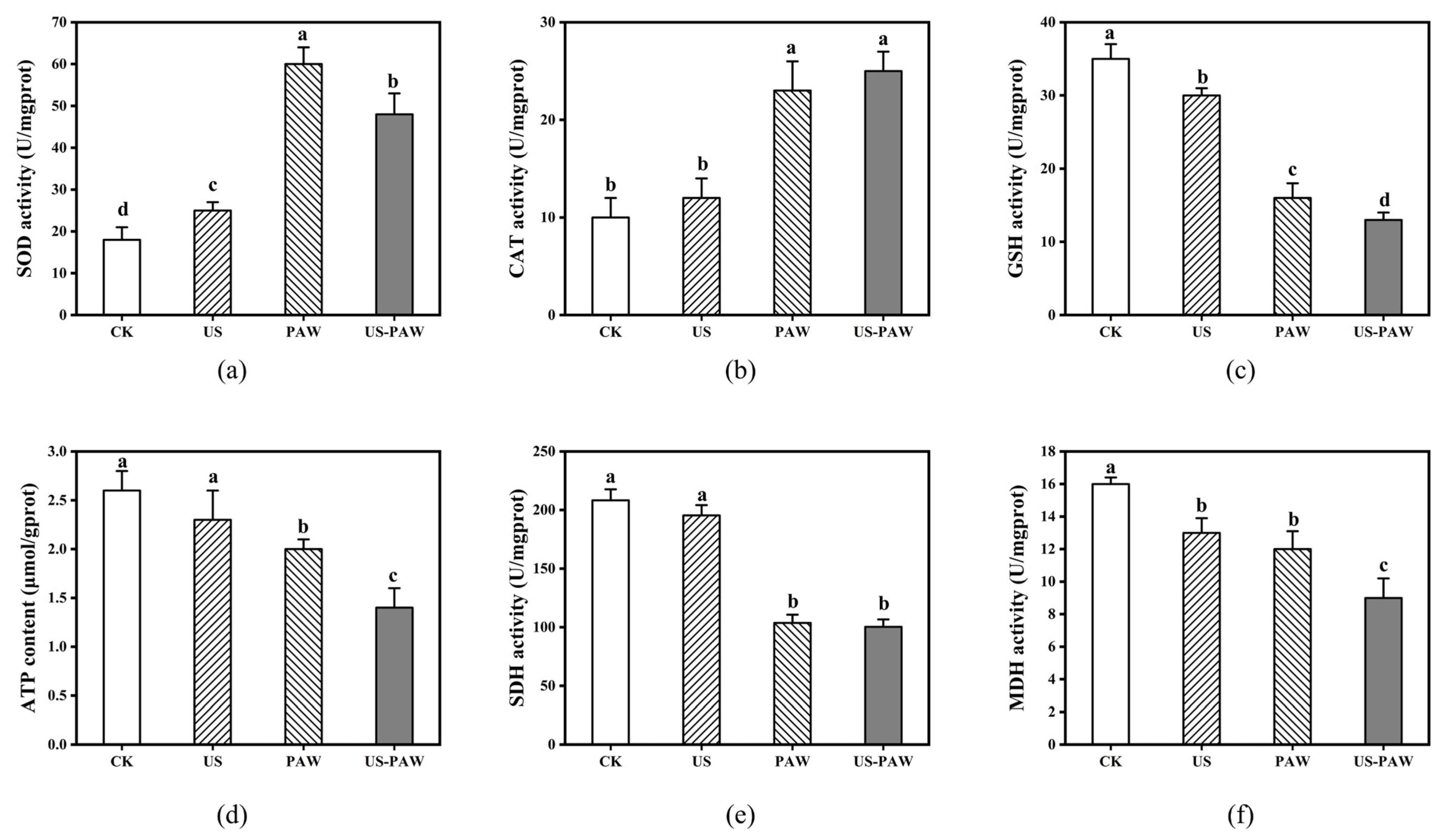
3.7. Effects of US-PAW on the Intracellular Antioxidant Enzyme System
3.8. Effects of US-PAW on the Energy Metabolic System
3.9. Effects of US-PAW on Crayfish During Storage at 4 °C
3.9.1. Antibacterial Effects on Crayfish
3.9.2. Effect of US-PAW on Volatile Flavour Compounds of Crayfish
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| A.veronii | Aeromonas veronii |
| CAT | Catalase |
| CK | Untreated |
| CLSM | Confocal laser scanning microscope |
| GC-MS | Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| H2O2 | Hydrogen peroxide |
| MDH | Malate dehydrogenase |
| NPN | N-Phenyl-1-naphthylamine |
| ORP | Oxidation–reduction potential |
| PAW | Plasma-activated water |
| RNS | Reactive nitrogen species |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SDH | Succinate dehydrogenase |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| TCA | Tricarboxylic acid cycle |
| TVBN | Total volatile basic nitrogen |
| US | Ultrasound |
| US-PAW | Ultrasound combined with plasma-activated water |
References
- Qin, L.R.; Wu, Y.X.; Chen, J.W.; Xia, W.S.; Liao, E.; Wang, H.B. Effects of superchilling on quality of crayfish (Procambarus clarkii): Water migration, biogenic amines accumulation, and nucleotides catabolism. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, D.; Li, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Qiao, G. Evaluation on the effects of phage cocktail in preventing Aeromonas veronii infection in Gibel carps (Carassius auratus gibelio). Aquaculture 2023, 563, 738998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Bravo, A.; Figueras, M.J. An Update on the Genus Aeromonas: Taxonomy, Epidemiology, and Pathogenicity. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.J.; Chen, P.L.; Tang, H.J.; Chen, H.M.; Tseng, F.C.; Shih, H.I.; Hung, Y.P.; Chung, C.H.; Ko, W.C. Incidence of Aeromonas bacteremia in southern Taiwan: Vibrio and Salmonella bacteremia as comparators. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2014, 47, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fu, X.Z.; Belwal, T.; Cravotto, G.; Luo, Z.S. Sono-physical and sono-chemical effects of ultrasound: Primary applications in extraction and freezing operations and influence on food components. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 60, 104726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piyasena, P.; Mohareb, E.; McKellar, R.C. Inactivation of microbes using ultrasound: A review. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2003, 87, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagong, H.G.; Lee, S.Y.; Chang, P.S.; Heu, S.; Ryu, S.; Choi, Y.J.; Kang, D.H. Combined effect of ultrasound and organic acids to reduce Escherichia coli O157:H7, Salmonella Typhimurium, and Listeria monocytogenes on organic fresh lettuce. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 145, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Ha, S.D. Reduction of Escherichia coli and Vibrio parahaemolyticus Counts on Freshly Sliced Shad (Konosirus punctatus) by Combined Treatment of Slightly Acidic Electrolyzed Water and Ultrasound Using Response Surface Methodology. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2015, 8, 1762–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.M.; Patange, A.; Sun, D.W.; Tiwari, B. Plasma-activated water: Physicochemical properties, microbial inactivation mechanisms, factors influencing antimicrobial effectiveness, and applications in the food industry. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 3951–3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.H.; Qiu, W.; Peng, J.L.; Xu, H.D.; Wang, D.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Ma, J. A Review on Additives-assisted Ultrasound for Organic Pollutants Degradation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.X.; Xu, W.C.; Xiong, L.M.; Jiang, N.; Xia, J.Y.; Zhu, Y.Z.; Wang, C.; Liu, Q.Y.; Ma, Y.H.; Luo, H.B. The combined effects of ultrasound and plasma-activated water on microbial inactivation and quality attributes of crayfish during refrigerated storage. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2023, 98, 106517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Cui, Y.C.; Zhang, M.W.; Wang, L.; Aihaiti, A.; Maimaitiyiming, R. Pulsed-control plasma-activated water: An emerging technology to assist ultrasound for fresh-cut produce washing. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2024, 102, 106739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royintarat, T.; Choi, E.H.; Boonyawan, D.; Seesuriyachan, P.; Wattanutchariya, W. Chemical-free and synergistic interaction of ultrasound combined with plasma-activated water (PAW) to enhance microbial inactivation in chicken meat and skin. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royintarat, T.; Choi, E.H.; Seesuriyachan, P.; Wattanutchariya, W. Ultrasound-assisted Plasma-activated Water for Bacterial Inactivation in Poultry Industry. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), Melbourne, Australia, 13–15 February 2019; pp. 1028–1032. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.C.; Sun, R.X.; Jiang, N.; Wang, Q.; Wang, C.; Liu, Q.Y.; Luo, H.B. Synergistic effects of ultrasound and plasma-activated water against Listeria innocua in crayfish disinfection by metabolomics analysis. Food Biosci. 2024, 61, 104597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.Y.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, B.; Sun, R.X.; Zhu, Y.Z.; Xu, W.C.; Wang, C.; Liu, Q.Y.; Ma, Y.H. Bacterial Changes in Boiled Crayfish between Different Storage Periods and Characterizations of the Specific Spoilage Bacteria. Foods 2023, 12, 3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.H.; Tian, E.Q.; Song, Y.; Sosnin, E.A.; Skakun, V.S.; Li, T.T.; Xia, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, X.S.; Liu, D.P. Inactivation of Shewanella putrefaciens by Plasma Activated Water. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2018, 38, 1035–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Tian, Y.; Li, Y.L.; Ma, R.A.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Fang, J. Bactericidal Effects against S-aureus and Physicochemical Properties of Plasma Activated Water stored at different temperatures. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 4789.2-2022; National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China, State Administration for Market Regulation. National Food Safety Standard: Microbiological Examination of Food—Enumeration of Aerobic Plate Count. China Standards Press: Beijing, China, 2022.
- Xu, Z.M.; Zhou, X.X.; Yang, W.S.; Zhang, Y.D.; Ye, Z.X.; Hu, S.H.; Ye, C.B.; Li, Y.X.; Lan, Y.; Shen, J.; et al. In vitro antimicrobial effects and mechanism of air plasma-activated water on Staphylococcus aureus biofilm. Plasma Process. Polym. 2020, 17, 1900270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.P.; Tang, Y.X.; Sun, L.; Xing, H.; Ma, H.L.; He, R.H. Ultrasonic irradiation of low intensity with a mode of sweeping frequency enhances the membrane permeability and cell growth rate of Candida tropicalis. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 37, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helander, I.M.; Mattila-Sandholm, T. Fluorometric assessment of Gram-negative bacterial permeabilisation. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 88, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.H.; Xu, H.B.; Zhuang, J.; Cui, D.J.; Ma, R.A.; Jiao, Z. Inhibition of Fungal Growth and Aflatoxin B1 Synthesis in Aspergillus flavus by Plasma-Activated Water. Foods. 2023, 12, 2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, R.R.; Chen, W.J.; Chen, H.M.; Zhong, Q.P.; Zhang, H.L.; Zhang, M.; Chen, W.X. Antibacterial mechanism of linalool against L. monocytogenes, a metabolomic study. Food Control. 2022, 132, 108533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Z.M.; Zhang, Z.L.; Cheng, C.; Ni, G.H.; Lan, Y.; Meng, Y.D.; Xia, W.D.; Chu, P.K. Preferential production of reactive species and bactericidal efficacy of gas-liquid plasma discharge. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 362, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.Y.; Tian, Y.; Ma, R.N.; Liu, Q.H.; Zhang, J. Effect of plasma activated water on the postharvest quality of button mushrooms, Agaricus bisporus. Food Chem. 2016, 197, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.W.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, S.G.; Kwon, J.; Lee, S.B.; Jung, W.J.; Lee, Y.M.; Jo, S.J.; Giri, S.S.; Yoon, S.H.; et al. Bactericidal efficacy of non-thermal plasma activation against Aeromonas hydrophila and immunological responses of koi (Cyprinus carpio haematopterus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 121, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongsopa, C.; Santalunai, S.; Thosdeekoraphat, T.; Kumkhong, S.; Nakharuthai, C.; Pasomboon, P.; Boonanuntanasarn, S. Optimisation of plasma-activated water: Plasma DBD technology and application in recirculating aquaculture system for Nile tilapia larval culture. Aquaculture. 2024, 591, 741049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Los, A.; Ziuzina, D.; Boehm, D.; Cullen, P.J.; Bourke, P. Inactivation Efficacies and Mechanisms of Gas Plasma and Plasma-Activated Water against Aspergillus flavus Spores and Biofilms: A Comparative Study. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e02619-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basiri, N.; Zarei, M.; Kargar, M.; Kafilzadeh, F. Effect of plasma-activated water on the biofilm-forming ability of Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis and expression of the related genes. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2023, 406, 110419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoux, C.M.G.; Patange, A.D.; Hinds, L.M.; Simpson, J.C.; O'Donnell, C.P.; Tiwari, B.K. Antimicrobial effects of airborne acoustic ultrasound and plasma activated water from cold and thermal plasma systems on biofilms. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.M.; Ojha, S.; Burgess, C.M.; Sun, D.W.; Tiwari, B.K. Inactivation efficacy and mechanisms of plasma activated water on bacteria in planktonic state. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 129, 1248–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, L.G.; Zou, W.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Tu, Y.B.A.; Li, S.M.; Xin, T.X.; Zhou, T.Y.; Xu, S.; Zheng, P.W.; Pan, Q.S.; et al. Multifunctional MIL-101 nanoparticles with Fenton-like reactions to Co-deliver LL-37 peptide and Vancomycin for targeted NIR imaging and Drug-resistant bacteria treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 435, 135084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Shi, C.H.; Zhang, G.L.; Zhan, H.L.; Liu, B.N.; Li, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.H. Antimicrobial mechanism of 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid on Listeria monocytogenes membrane and virulence. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 572, 145–150. [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido, H. Molecular basis of bacterial outer membrane permeability revisited. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2003, 67, 593–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muheim, C.; Götzke, H.; Eriksson, A.U.; Lindberg, S.; Lauritsen, I.; Norholm, M.H.H.; Daley, D.O. Increasing the permeability of Escherichia coli using MAC13243. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Q.S.; Kang, C.D.; Niu, L.Y.; Zhao, D.B.; Li, K.; Bai, Y.H. Antibacterial activity and a membrane damage mechanism of plasma- activated water against Pseudomonas deceptionensis CM2. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 96, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.M.; Bai, M.; Li, C.Z.; Cui, H.Y.; Lin, L. Advances in the mechanism of different antibacterial strategies based on ultrasound technique for controlling bacterial contamination in food industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 105, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Hasan, M.S.; Islam, R.; Rana, R.; Sayem, A.; Sad, M.A.A.; Matin, A.; Raposo, A.; Zandonadi, R.P.; Han, H.; et al. Plasma-Activated Water for Food Safety and Quality: A Review of Recent Developments. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas, A.d.S.; Day, A.; Ikeh, M.; Kos, I.; Achan, B.; Quinn, J. Oxidative stress responses in the human fungal pathogen, Candida albicans. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 142–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Q.; Qin, J.R.; Wang, Z.; Chen, F.; Liao, X.J.; Hu, X.S.; Dong, L. Sodium copper chlorophyll mediated photodynamic treatment inactivates Escherichia coli via oxidative damage. Food Res. Int. 2022, 157, 111472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.Y.; Liu, D.H.; Ding, T. Nonthermal Plasma Induces the Viable-but-Nonculturable State in Staphylococcus aureus via Metabolic Suppression and the Oxidative Stress Response. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e02216-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorova, Y.; Yotinov, I.; Topalova, Y.; Benova, E.; Marinova, P.; Tsonev, I.; Bogdanov, T. Evaluation of the effect of cold atmospheric plasma on oxygenases? activities for application in water treatment technologies. Environ. Technol. 2019, 40, 3783–3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berndsen, C.E.; Bell, J.K. The structural biology and dynamics of malate dehydrogenases. Essays Biochem. 2024, 68, 57–72. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.Y.; Li, J.X.; Huang, W. Analysis of Main Spoilage Bacteria in Fresh Pork during Storage. Food Sci. 2015, 36, 173–176. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liao, X.; Su, Y.; Liu, D.; Chen, S.; Hu, Y.; Ye, X.; Wang, J.; Ding, T. Application of atmospheric cold plasma-activated water (PAW) ice for preservation of shrimps (Metapenaeus ensis). Food Control. 2018, 94, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.Z.; Chen, S.S. Identification of characteristic aroma-active compounds in steamed mangrove crab (Scylla serrata). Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 2081–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.X.; Chong, Y.Q.; Ding, Y.T.; Gu, S.Q.; Liu, L. Determination of the effects of different washing processes on aroma characteristics in silver carp mince by MMSE-GC-MS, e-nose and sensory evaluation. Food Chem. 2016, 207, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.W.; Sun, W.; Li, Z.H.; Shi, J.Y.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhai, X.D.; Hu, X.T.; Zou, X.B. Hydrogen sulfide gas sensing toward on-site monitoring of chilled meat spoilage based on ratio-type fluorescent probe. Food Chem. 2022, 396, 133654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, B.; Durance, T. Headspace volatiles of sockeye and pink salmon as affected by retort process. J. Food Sci. 2000, 65, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yuan, L.; Liu, H.J.; Liu, H.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, M.A.; Gao, R.C. Analysis of the changes of volatile flavor compounds in a traditional Chinese shrimp paste during fermentation based on electronic nose, SPME-GC-MS and HS-GC-IMS. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2023, 12, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pongsetkul, J.; Benjakul, S.; Vongkamjan, K.; Sumpavapol, P.; Osako, K.; Faithong, N. Changes in volatile compounds, ATP-related compounds and antioxidative properties of Kapi, produced from Acetes vulgaris, during processing and fermentation. Food Biosci. 2017, 19, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.J.; Xu, S.Y.; Wang, Z. Kinetics of lipid oxidation and off-odor formation in silver carp mince: The effect of lipoxygenase and hemoglobin. Food Res. Int. 2009, 42, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, A.; Osako, K.; Ohshima, T. Identification and characterisation of headspace volatiles of fish miso, a Japanese fish meat based fermented paste, with special emphasis on effect of fish species and meat washing. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.W.; Zhang, M. Analysis of volatile compounds in Chinese Mitten Crab (Eriocheir sinensis). J. Food Drug Anal. 2006, 14, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Baker, S.M.; Goodrich-Schneider, R.M.; Montazeri, N.; Sarnoski, P.J. Aroma Profile Characterization of Mahi-Mahi and Tuna for Determining Spoilage Using Purge and Trap Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| ID. | Volatile Compounds | Relative Amount (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | US-PAW | ||
| 1 | Sulphur-containing compounds | 72.16 | 47.82 |
| 2 | Ketones | 1.61 | 17.08 |
| 3 | N, O-containing compounds | 1.11 | 8.49 |
| 4 | Acids | 0.1 | 3.43 |
| 5 | Hydrocarbons | 4.11 | 5.99 |
| 6 | Alcohols | 0 | 4.03 |
| 7 | Esters | 8.48 | 8.74 |
| 8 | Phenolic | 0.11 | 0.86 |
| 9 | Others | 12.32 | 3.56 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, W.; Sun, R.; Qin, Z.; Deng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Luo, H.; Jiang, N.; Cheng, H.; Ren, M. Antibacterial Mechanism and Flavour Impact of Ultrasound and Plasma-Activated Water Combination on Aeromonas veronii in Crayfish. Foods 2025, 14, 926. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14060926
Xu W, Sun R, Qin Z, Deng Z, Liu Y, Zhang H, Luo H, Jiang N, Cheng H, Ren M. Antibacterial Mechanism and Flavour Impact of Ultrasound and Plasma-Activated Water Combination on Aeromonas veronii in Crayfish. Foods. 2025; 14(6):926. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14060926
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Weicheng, Rongxue Sun, Zhanke Qin, Ziai Deng, Yi Liu, Haojie Zhang, Haibo Luo, Ning Jiang, Hao Cheng, and Maozhi Ren. 2025. "Antibacterial Mechanism and Flavour Impact of Ultrasound and Plasma-Activated Water Combination on Aeromonas veronii in Crayfish" Foods 14, no. 6: 926. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14060926
APA StyleXu, W., Sun, R., Qin, Z., Deng, Z., Liu, Y., Zhang, H., Luo, H., Jiang, N., Cheng, H., & Ren, M. (2025). Antibacterial Mechanism and Flavour Impact of Ultrasound and Plasma-Activated Water Combination on Aeromonas veronii in Crayfish. Foods, 14(6), 926. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14060926





