Shaping Consumer Perceptions of Genetically Modified Foods: The Influence of Engineering, Science, and Design Signifiers in Packaging Disclosure Statements
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study 1: Comparison of US and International BDS Against the Proposed Design BDS
2.1.1. Study 1 Participants
2.1.2. Study 1 Bioengineered Disclosure Statement Selection
2.1.3. Study 1 Participant GMO Attitudes
2.1.4. Study 1 Effect of BDSs on Food-Related Attributes
2.1.5. Study 1 GMO Knowledge
2.1.6. Study 1 Importance of GMOs
2.2. Study 2: Comparison of Eight New BDSs Against Each Other and a Control Statement
2.2.1. Study 2 Participants
2.2.2. Study 2 Bioengineered Disclosure Statement Selection
2.2.3. Study 2 Participant GMO Attitudes
2.2.4. Study 2 Effect of BDSs on Food-Related Attributes
2.3. Reporting Results
3. Results
3.1. Study 1 Results
3.1.1. Study 1 GMO Attitudes
3.1.2. Study 1 Effect of BDSs on Food-Related Attributes
3.1.3. Study 1 Participant GMO Knowledge
3.1.4. Study 1 Participant GMO Importance
3.2. Study 2 Results
3.2.1. Study 2 Overall GMO Attitudes
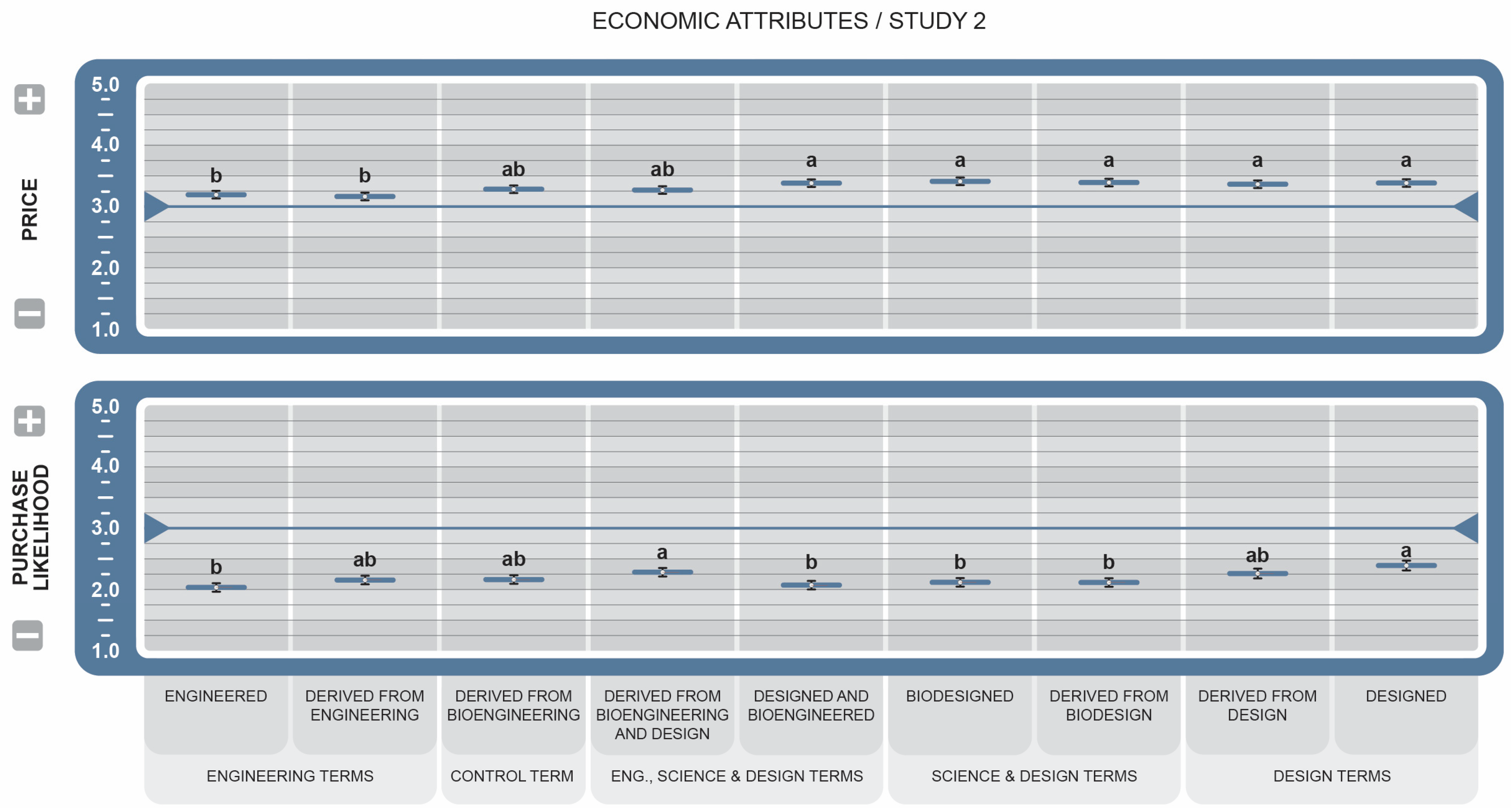
3.2.2. Effect of BDSs on Food-Related Attributes
4. Discussion
4.1. Study 1 Discussion
4.1.1. Study 1 Overall Attitudes
4.1.2. Assessing BDS Component Words
4.1.3. Effect of BDSs on Food-Related Attributes
4.1.4. GMO Knowledge and Importance
4.2. Study 2
4.2.1. Study 2 Overall Attitudes
4.2.2. Study 2 Effect of BDSs on Attributes
4.3. Future Studies
4.4. Limitations of the Current Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suldovsky, B.; Hallman, W. The National Bioengineered Food Disclosure Standard of 2016: Intersection of Technology and Public Understanding of Science in the United States. Societies 2022, 12, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebata, A.; Punt, M.; Wesseler, J. For the approval process of GMOs: The Japanese case. AgBioForum 2013, 16, 140–160. [Google Scholar]
- Regulation (EC) No 1830/2003 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 September 2003: Concerning the Traceability and Labeling of Genetically Modified Organisms and the Traceability of Food and Feed Products Produced from Genetically Modified Organisms and Amending Directive 2001/18/EC. Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/reg/2003/1830/oj (accessed on 28 February 2025).
- Joint FAO/WHO Consultation on the Assessment of Biotechnology in Food Production and Processing as Related to Food Safety (1990: Geneva, Switzerland); World Health Organization; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Strategies for Assessing the Safety of Foods Produced by Biotechnology: Report of a Joint FAO/WHO Consultation [Held in Geneva from 5 to 10 November 1990]. World Health Organization, 1991. Available online: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/41465 (accessed on 28 February 2025).
- Rigaud, N. Biotechnology: Ethical and Social Debates. Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development (OECD), 2008. Available online: https://www.oecd.org/futures/long-termtechnologicalsocietalchallenges/40926844.pdf (accessed on 28 February 2025).
- Center for Food Safety (CFS). New Poll: Nearly Nine in 10 Americans Want Labels on GMO Food. [Press Release]. 2 December 2015. Available online: https://www.centerforfoodsafety.org/issues/976/ge-food-labeling/press-releases/4150/new-poll-nearly-nine-in-10-americans-want-labels-on-gmo-food (accessed on 28 February 2025).
- Halloran, J. Consumers Union Letter to US Senate in Support of GMO Labeling. Consumer Reports. Available online: https://advocacy.consumerreports.org/research/consumers-union-letter-to-us-senate-in-support-of-gmo-labeling/ (accessed on 3 March 2025).
- Kopicki, A. Strong Support for Labeling Modified Foods. The New York Times. 27 July 2013. Available online: https://www.nytimes.com/2013/07/28/science/strong-support-for-labeling-modified-foods.html?_r=0 (accessed on 28 February 2025).
- Lamb, S. Why We Need Mandatory Labeling of GMO Products. STAT News. 19 February 2020. Available online: https://www.statnews.com/2020/02/19/why-we-need-mandatory-labeling-of-gmo-products/ (accessed on 28 February 2025).
- HB. 112, Vermont General Assembly, Regular Session: An Act Relating to the Labeling of Food Produced with Genetic Engineering, § 4093. 2013. Available online: https://legislature.vermont.gov/statutes/fullchapter/09/082a (accessed on 28 February 2025).
- HB. 6527, Public Act No. 13-183, Connecticut General Assembly: An Act Concerning Genetically-Engineered Food, Sec. 3. 25 June 2013. Available online: https://www.pdx.edu/policy-consensus-center/sites/policyconsensuscenter.web.wdt.pdx.edu/files/2020-06/1-Governors-task-force-on-genetically-engineered-seeds-and-agric-prod.pdf (accessed on 28 February 2025).
- HP 0490, LD 718, Session—126th Maine Legislature an Act to Protect Maine Food Consumers’ Right to Know about Genetically Engineered Food and Seed Stock, Chapter 565, § 2592. 6 June 2013. Available online: https://www.mainelegislature.org/legis/bills/bills_126th/billtexts/HP049001.asp (accessed on 28 February 2025).
- SB. 764, Public Law 114-216, 114th Congress, National Bioengineered Food Disclosure Standard. 29 July 2016. Available online: https://www.congress.gov/114/plaws/publ216/PLAW-114publ216.pdf (accessed on 28 February 2025).
- 7 CFR Part 66, National Bioengineered Food Disclosure Standard. 2018. Available online: https://www.ecfr.gov/current/title-7/subtitle-B/chapter-I/subchapter-C/part-66 (accessed on 28 February 2025).
- 7 CFR Part 66, Section V, National Bioengineered Food Disclosure Standard. 2018. Available online: https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2018/12/21/2018-27283/national-bioengineered-food-disclosure-standard#:~:text=Comment%3A%20Commenters,scope%20of%20disclosure (accessed on 28 February 2025).
- Hashemzadeh, H.; Karbasi, A.; Mohammadi, H.; Firoozzare, A.; Boccia, F. Investigating the Effect of Nudges on Consumers’ Willingness to Pay for Genetically Modified Corn Oil. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.C.; Ortega, D.L.; Caputo, V.; Lusk, J.L. Personality traits and consumer acceptance of controversial food technology: A cross-country investigation of genetically modified animal products. Food Qual. Prefer. 2019, 76, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusk, J.L.; Moore, M.; House, L.O.; Morrow, B. Influence of brand name and type of modification on consumer acceptance of genetically engineered corn chips: A preliminary analysis. Int. Food Agribus. Manag. Rev. 2001, 4, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukenya, J.O.; Wright, N.R. Determinants of consumer attitudes and purchase-intentions with regard to genetically modified tomatoes. Agribus. Int. J. 2007, 23, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chern, W.S.; Rickertsen, K.; Tsuboi, N.; Fu, T. Consumer acceptance and willingness to pay for genetically modified vegetable oil and salmon: A multiple-country assessment. AgBioForum 2002, 5, 105–112. [Google Scholar]
- Center for Food Safety (CFS). Lawsuit Challenges “Bioengineered” GMO Food Labeling. [Press Release]. 28 July 2020. Available online: https://www.centerforfoodsafety.org/press-releases/6100/lawsuit-challenges-bioengineered-gmo-food-labeling (accessed on 28 February 2025).
- Center for Food Safety (CFS). Lawsuit Challenges Restrictive and Unclear GMO Food Labeling Rules. [Press Release]. 16 November 2022. Available online: https://www.centerforfoodsafety.org/issues/976/ge-food-labeling/press-releases/6766/lawsuit-challenges-restrictive-and-unclear-gmo-food-labeling-rules (accessed on 28 February 2025).
- Center for Food Safety. Center for Food Safety Challenges Exemptions for Highly Refined Foods and Unfamiliar Terminology (Bioengineered) in GMO Food Labeling Regulations. 6 September 2023. Available online: https://www.centerforfoodsafety.org/press-releases/6850/legal-appeal-challenges-hidden-gmo-foods-in-marketplace (accessed on 28 February 2025).
- Hernandez, J. GMO Is Out, “bioengineered” Is in, as New US Food Labeling Rules Take Effect. NPR.org, 5 January 2022. Available online: https://www.npr.org/2022/01/05/1070212871/usda-bioengineered-food-label-gmo (accessed on 28 February 2025).
- Radelat, A. Senate Moves to Quash CTs GMO Food Labeling Law. The CT Mirror. 6 July 2016. Available online: https://ctmirror.org/2016/07/06/senate-poised-to-quash-connecticuts-gmo-food-labeling-law/ (accessed on 28 February 2025).
- Thaler, R.H.; Sunstein, C.R. Nudge: The Final Edition; Penguin Books, Yale University Press: New Haven, CT, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- de Araújo, P.D.; Araújo, W.M.C.; Patarata, L.; Fraqueza, M.J. Understanding the main factors that influence consumer quality perception and attitude towards meat and processed meat products. Meat Sci. 2022, 193, 108952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, W.; Aurisicchio, M.; Childs, P. Contaminated Interaction: Another Barrier to Circular Material Flows. J. Ind. Ecol. 2017, 21, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duschinsky, R. Ideal and unsullied: Purity, subjectivity, and social power. Crit. Psychol. 2011, 4, 147–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krippendorff, K. The Semantic Turn: A New Foundation for Design; CRC Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Baxter, W.L.; Aurisicchio, M.; Childs, P.R.N. Materials, use and contaminated interaction. Mater. Des. 2016, 90, 1218–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurisicchio, M.; Eng, N.L.; Ortíz Nicolás, J.C.; Childs, P.R.N.; Bracewell, R.H. On The Functions of Products. DS 68-10: Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Engineering Design (ICED 11), Impacting Society through Engineering Design, Vol. 10: Design Methods and Tools Pt. 2, Lyngby/Copenhagen, Denmark, 2011, August 15–19. Available online: https://www.designsociety.org/publication/30775/ON+THE+FUNCTIONS+OF+PRODUCTS (accessed on 28 February 2025).
- Feibleman, J.K. Pure Science, Applied Science, Technology, Engineering: An Attempt at Definitions. Technol. Cult. 1961, 2, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koen, B.V. Definition of the Engineering Method; American Society for Engineering Education: Washington, DC, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Norman, D.A. Signifiers, Not Affordances. Interactions 2008, 15, 18–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melles, M.; Albayarak, A.; Goossesn, R. Innovating health care: Key Characteristics of human-centered design. Int. J. Qual. Health Care 2021, 33, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, D.A. The Design of Everyday Things: Revised and Expanded Edition; Basic Books: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Q&A: Genetically Modified Food. 14 February 2017. Available online: http://www.who.int/foodsafety/areas_work/food-technology/faq-genetically-modified-food/en/ (accessed on 28 February 2025).
- Lefebvre, S.; Cook, L.A.; Griffiths, M.A. Consumer perceptions of genetically modified foods: A mixed-method approach. J. Consum. Mark. 2019, 36, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcar, M.; Latorre-Pérez, A.; Molina-Menor, E.; Domínguez, M. Words, images, and gender: Lessons from a survey on the public perception of synthetic biology and related disciplines. EMBO Rep. 2019, 20, e48401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adalja, A.; Liaukonytė, J.; Wang, E.; Zhu, X. GMO and non-GMO labeling effects: Evidence from a quasi-natural experiment. Mark. Sci. 2023, 42, 233–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Wang, H.H. Do Consumers View the Genetically Modified Food Labeling Systems Differently? “Contains GMO” Versus “Non-GMO” Labels. Chin. Econ. 2021, 54, 376–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuralt, K.M. The importance of labeling products with a GMO or non-GMO label. Med. Law Soc. 2021, 14, 43–76. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, S.; Arora, N. GMO Labeling Policy and Consumer Choice. J. Mark. 2022, 86, 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Veeman, M.M.; Adamowicz, W.L. Labelling genetically modified food: Heterogeneous consumer preferences and the value of information. Can. J. Agric. Econ. 2005, 53, 83–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heslop, L.A. If we label it, will they care? The effect of GM-ingredient labelling on consumer responses. J. Consum. Policy 2006, 29, 203–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Henneberry, S. Changing attitudes toward genetically modified foods in urban China. China Agric. Econ. Rev. 2017, 9, 397–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.H.; Harrison, R.W. Factors influencing urban consumers’ acceptance of genetically modified foods. Rev. Agric. Econ. 2007, 29, 700–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozin, P.; Royzman, E.B. Negativity Bias, Negativity Dominance, and Contagion. Personal. Soc. Psychol. Rev. 2001, 5, 296–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Dong, H.; Choi, J.; Chang, S.R. Sentiment change and negative herding: Evidence from microblogging and news. J. Bus. Res. 2022, 142, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roe, B.; Teisl, M.F. Genetically modified food labeling: The impacts of message and messenger on consumer perceptions of labels and products. Food Policy 2007, 32, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Non-GMO Project. The Butterfly Helps Your Business Grow. Available online: https://www.nongmoproject.org/get-non-gmo-verified/ (accessed on 18 November 2024).
- USDA Agriculture Marketing Service, About Organic Labeling. Available online: https://www.ams.usda.gov/rules-regulations/organic/labeling (accessed on 18 November 2024).
- Harrison, R.W.; Boccaletti, S.; House, L. Risk perceptions of urban Italian and United States consumers for genetically modified foods. AgBioForum 2005, 7, 195–201. [Google Scholar]
- Puduri, V.S.; Govindasamy, R.; Nettimi, N. Consumers’ Perceptions Toward Usefulness of Genetically Modified Foods A Study of Select Consumers in USA. IUP J. Agric. Econ. 2010, 7, 7–17. [Google Scholar]
- Wunderlich, S.; Gatto, K.A. Consumer perception of genetically modified organisms and sources of information. Adv. Nutr. 2015, 6, 842–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielby, H.; Sandøe, P.; Lassen, J. The role of scientific knowledge in shaping public attitudes to GM technologies. Public Underst. Sci. 2013, 22, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, G.A.; Burnham, T.A. Consumer response to genetically modified foods: Market segment analysis and implications for producers and policy makers. J. Agric. Resour. Econ. 2001, 26, 387–403. [Google Scholar]
- Lenzner, T.; Höhne, J.K.; Gavras, K. Innovating Web Probing: Comparing Written and Oral Answers to Open-Ended Probing Questions in a Smartphone Survey. J. Surv. Stat. Methodol. 2024, 12, 1295–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFadden, B.; Van Eenennaam, A.; Goddard, E.; Lusk, J.; McCluskey, J.; Smyth, S.J.; Taheripour, F.; Tyner, W.E. Gains Foregone by Going GMO Free: Potential Impacts on Consumers, the Environment, and Agricultural Producers. CAST Commentary, QTA2021-2, 2021. Available online: https://cast-science.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/QTA2021-2-GMO-Free-1.pdf (accessed on 28 February 2025).
- Bovay, J.; Alston, J.M. GMO food labels in the United States: Economic implications of the new law. Food Policy 2018, 78, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, C.A.; Gruere, G.P. International approaches to the labeling of genetically modified foods. Choices 2003, 18, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Mather, D.W.; Knight, J.G.; Insch, A.; Holdsworth, D.K.; Ermen, D.F.; Breitbarth, T. Social stigma and consumer benefits: Trade-offs in adoption of genetically modified foods. Sci. Commun. 2012, 34, 487–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teisl, M.F.; Garner, L.; Roe, B.; Vayda, M.E. Labeling genetically modified foods: How do US consumers want to see it done? AgBioForum 2003, 6, 48–54. [Google Scholar]
- Vecchione, M.; Feldman, C.; Wunderlich, S. Consumer knowledge and attitudes about genetically modified food products and labelling policy. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 66, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bower, G.H. Affect and cognition. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 1983, 302, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig-Lewis, N.; Palmer, A.; Dermody, J.; Urbye, A. Consumers’ evaluations of ecological packaging—Rational and emotional approaches. J. Environ. Psychol. 2014, 37, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesque, F.; Coutrot, A.; Cox, S.; de Souza, L.C.; Baez, S.; Cardona, J.F.; Mulet-Perreault, H.; Flanagan, E.; Neely-Prado, A.; Clarens, M.F.; et al. Does culture shape our understanding of others’ thoughts and emotions? An investigation across 12 countries. Neuropsychology 2022, 36, 664–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallman, W.K. Consumer Perception of Food Attributes; Routledge, CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 44–61. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, V.; Negi, S.; Kumar, P.; Srivastava, D.K. Global Status of Genetically Modified Crops. In Agricultural Biotechnology: Latest Research and Trends; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; pp. 305–322. Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-981-16-2339-4_13 (accessed on 28 February 2025).
- Dizon, F.; Costa, S.; Rock, C.; Harris, A.; Husk, C.; Mei, J. Genetically Modified (GM) Foods and Ethical Eating. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, R287–R291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]












| Importance | Total Participants | Percentage of Participants |
|---|---|---|
| Extremely important | 150 | 11.32% |
| Very important | 212 | 16.00% |
| Moderately important | 219 | 16.53% |
| Somewhat important | 291 | 21.96% |
| Slightly important | 267 | 20.15% |
| Not at all important | 186 | 14.04% |
| Total | 1325 | 100% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Howell, B.F.; Newcomb, E.M.; Loh, D.W.; Jackson, A.R.; Dunn, M.L.; Jefferies, L.K. Shaping Consumer Perceptions of Genetically Modified Foods: The Influence of Engineering, Science, and Design Signifiers in Packaging Disclosure Statements. Foods 2025, 14, 909. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14060909
Howell BF, Newcomb EM, Loh DW, Jackson AR, Dunn ML, Jefferies LK. Shaping Consumer Perceptions of Genetically Modified Foods: The Influence of Engineering, Science, and Design Signifiers in Packaging Disclosure Statements. Foods. 2025; 14(6):909. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14060909
Chicago/Turabian StyleHowell, Bryan F., Ellyn M. Newcomb, D. Wendell Loh, Asa R. Jackson, Michael L. Dunn, and Laura K. Jefferies. 2025. "Shaping Consumer Perceptions of Genetically Modified Foods: The Influence of Engineering, Science, and Design Signifiers in Packaging Disclosure Statements" Foods 14, no. 6: 909. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14060909
APA StyleHowell, B. F., Newcomb, E. M., Loh, D. W., Jackson, A. R., Dunn, M. L., & Jefferies, L. K. (2025). Shaping Consumer Perceptions of Genetically Modified Foods: The Influence of Engineering, Science, and Design Signifiers in Packaging Disclosure Statements. Foods, 14(6), 909. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14060909







