Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometry (IRMS)-Based Authentication of the Geographic Origins of Volvariella volvacea (Bull.) Singer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
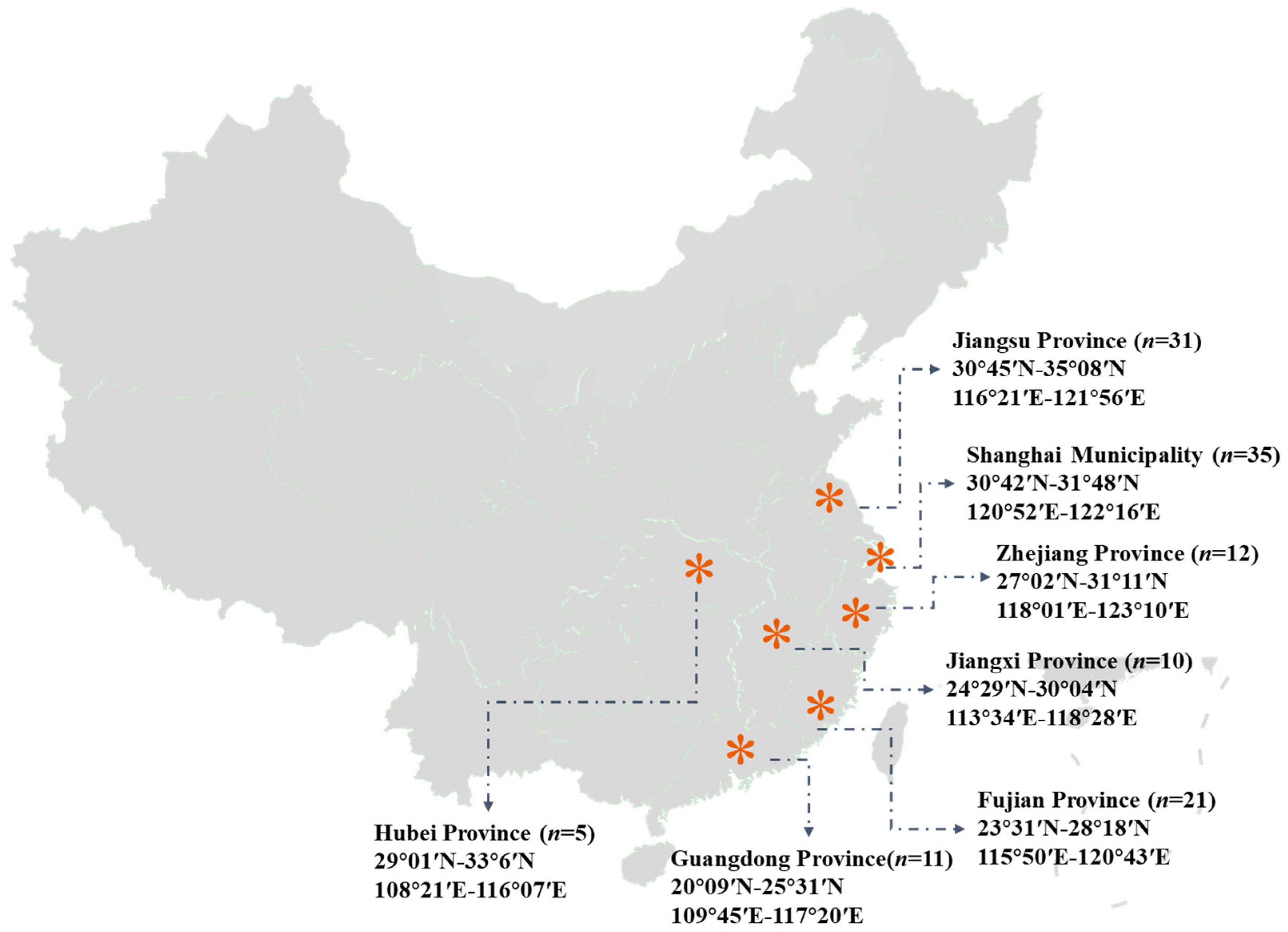
2.1. Sample Collection and Preparation
2.2. Protein, Amino Acids and Mineral Contents
2.3. Stable Isotope Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis and Chemometric Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Geographical Variation in Nutritional Composition of Volvariella volvacea
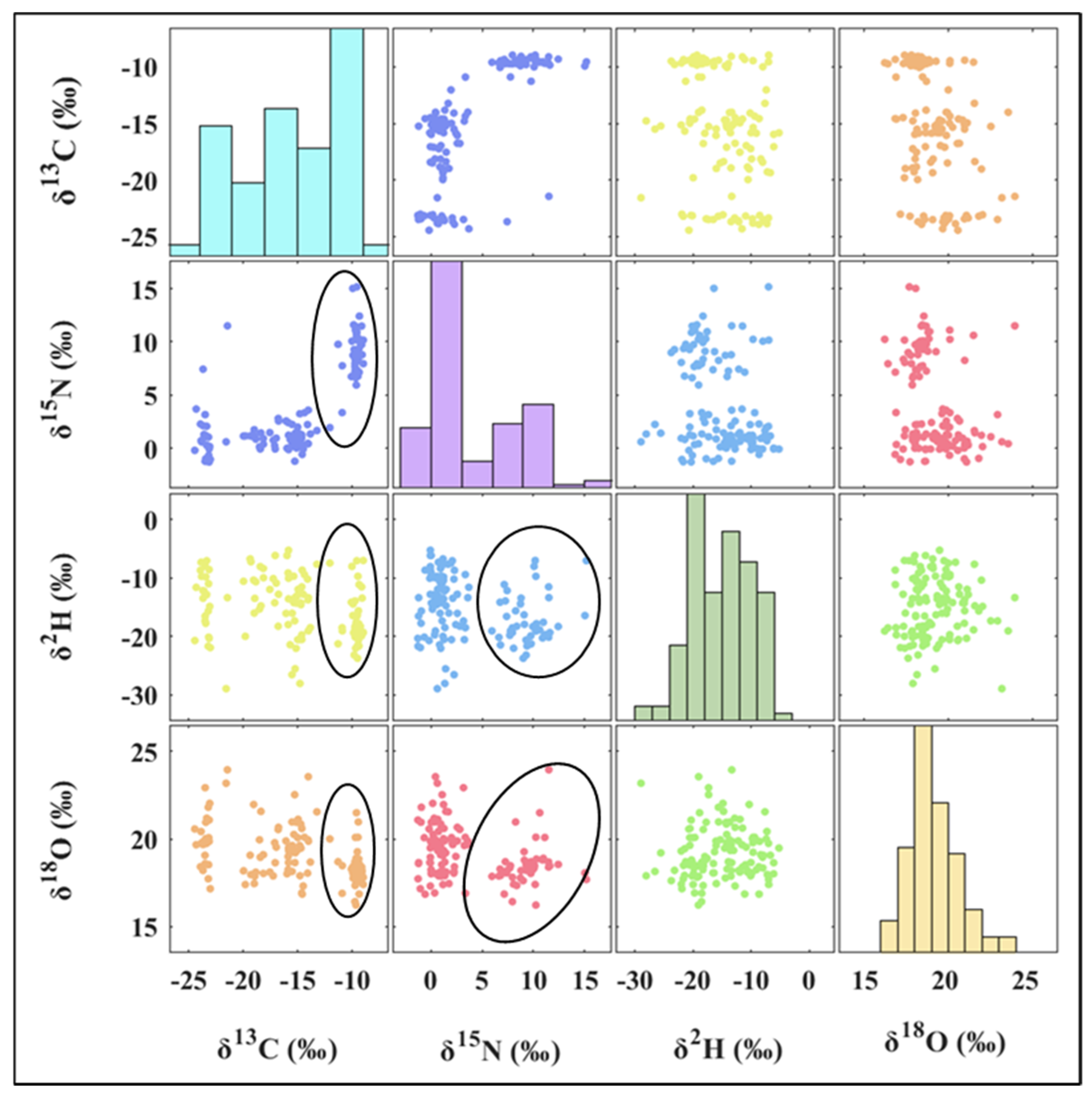
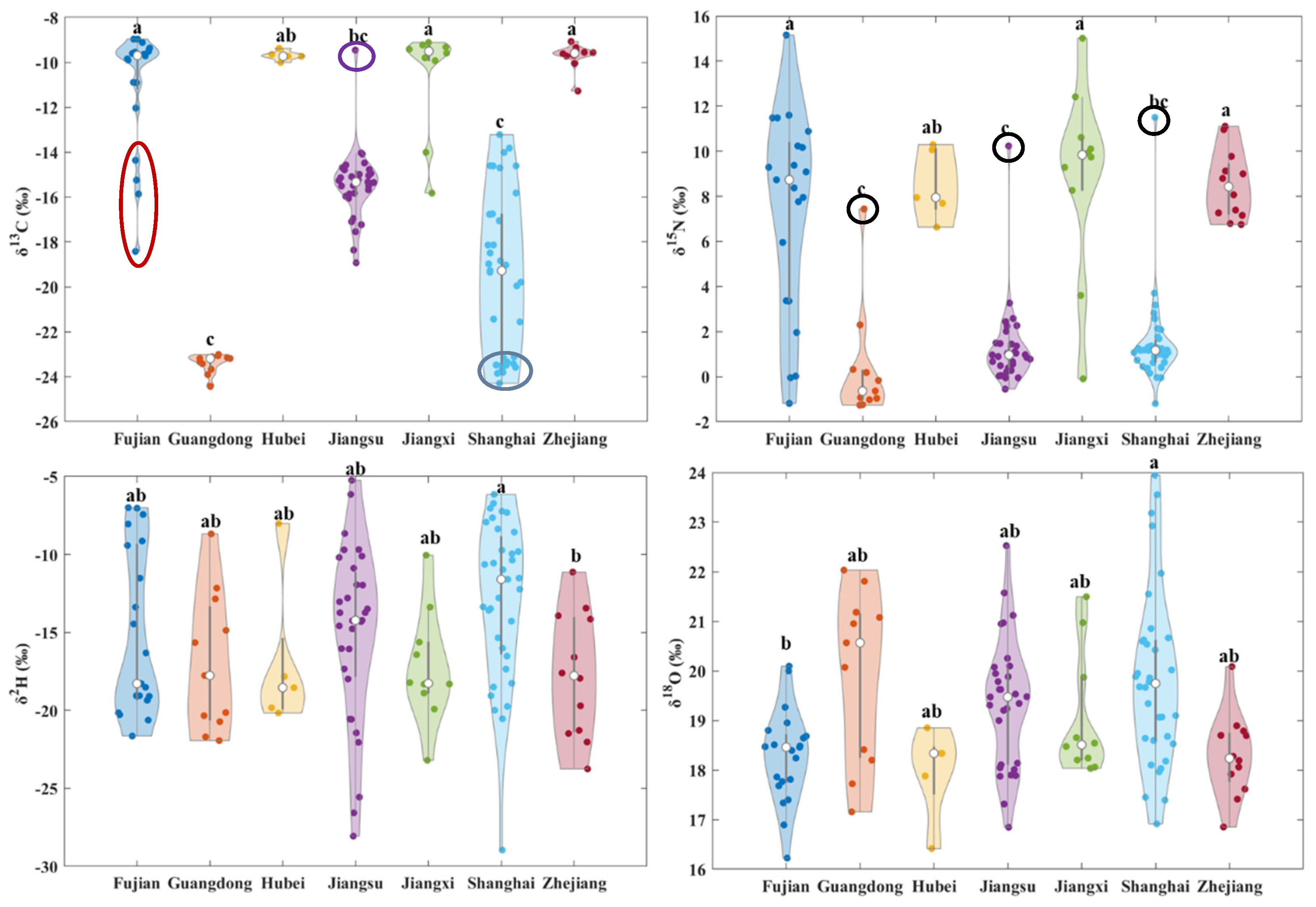
3.2. Stable Isotope Distribution of Volvariella volvacea from Different Origins
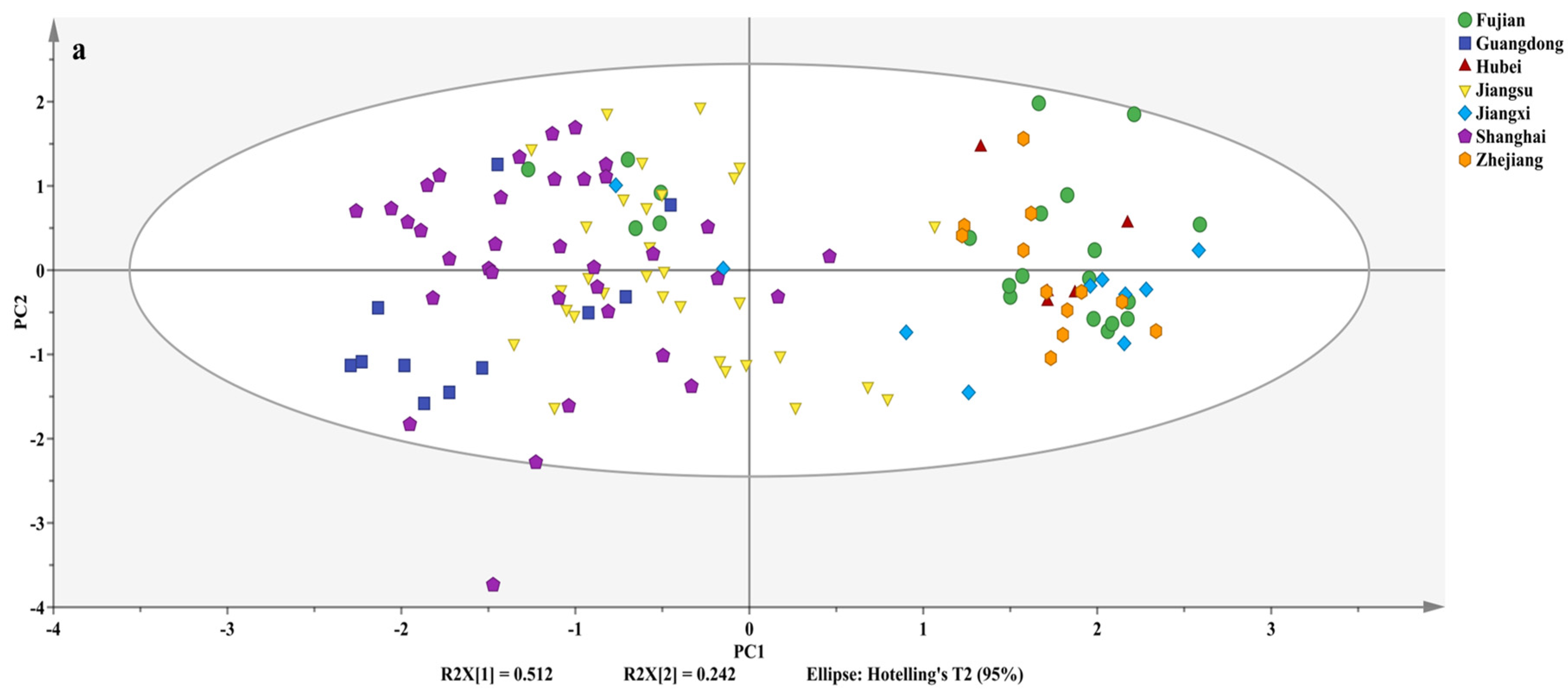
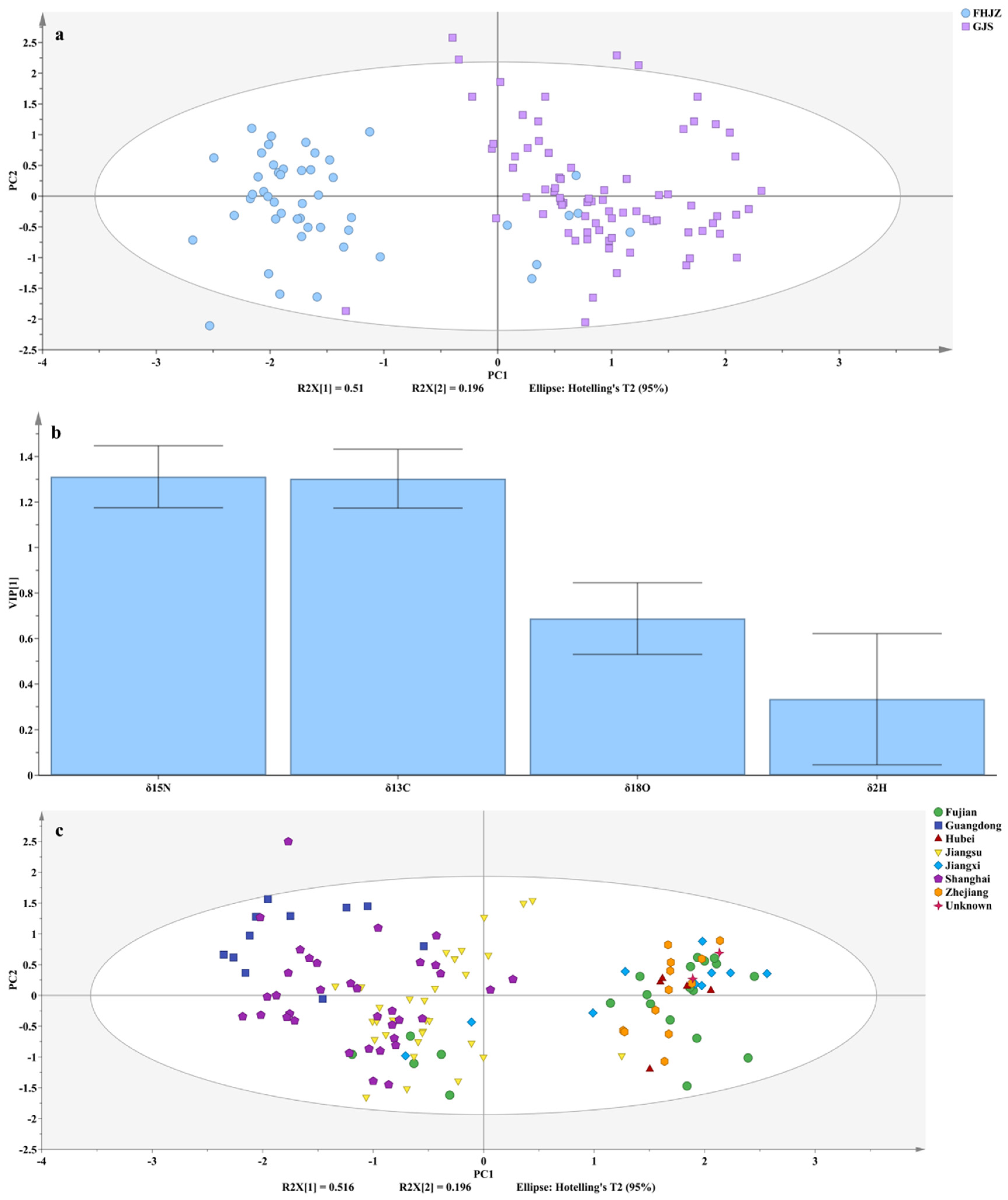
3.3. Origin Discrimination of Volvariella volvacea
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Ala | alanine |
| ANOVA | analysis of variance |
| Arg | arginine |
| Asp | aspartic acid |
| EAA | essential amino acids |
| FAO | the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization |
| FHJZ | Fujian, Hubei, Jiangxi, Zhejiang |
| GJS | Guangdong, Jiangsu, Shanghai |
| Glu | glutamic acid |
| Gly | glycine |
| His | histidine |
| Ile | isoleucine |
| Leu | leucine |
| Lys | lysine |
| Met | methionine |
| PCA | principal component analysis |
| Phe | phenylalanine |
| PLS-DA | partial least squares discriminant analysis |
| Pro | proline |
| Ser | serine |
| TAA | total amino acids |
| Thr | threonine |
| Tyr | tyrosine |
| Val | valine |
| VIP | Variable importance in projection |
References
- FAO; IFAD; UNICEF; WFP; WHO. The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World 2024—Financing to End Hunger, Food Insecurity and Malnutrition in All Its Forms; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Wang, Y. Application of identification and evaluation techniques for edible mushrooms: A review. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2023, 53, 634–654. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- FAOSTAT Data. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data (accessed on 23 December 2024).
- Ahlawat, O.P.; Arora, B. Paddy straw mushroom (Volvariella volvacea) Cultivation. In Mushrooms in India Diversity, Improvement, Cultivation, Medicinal Uses and Value Addition for Rural Development; CRDT: New Delhi, India, 2016; pp. 165–182. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, S.; Yousaf, N.; Usman, M.; Javed, M.A.; Nawaz, M.; Ali, B.; Azam, M.; Ercisli, S.; Tirasci, S.; Ahmed, A.E. Volvariella volvacea (paddy straw mushroom): A mushroom with exceptional medicinal and nutritional properties. Heliyon 2024, 10, e39747. [Google Scholar]
- Ramkumar, L.; Ramanathan, T.; Johnprabagaran, J. Evaluation of nutrients, trace metals and antioxidant activity in Volvariella volvacea (Bull. Ex. Fr.) Sing. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2012, 24, 113–119. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, N.; Singha, S.M. Effects of composition, age and sterilization techniques of mother culture on the growth and yield of Volvariella volvacea (bull.) Singer. Bangladesh J. Bot. 2020, 49, 387–393. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, R.; Rava, M.; Boro, H.; Das, S. Fatty acid, amino acid, bioactive compounds and anti-microbial properties of wild Volvariella volvacea from Kokrajhar,(Assam), India. Mushroom Res. 2017, 26, 165–174. [Google Scholar]
- Sangthong, S.; Pintathong, P.; Pongsua, P.; Jirarat, A.; Chaiwut, P. Polysaccharides from Volvariella volvacea mushroom: Extraction, biological activities and cosmetic efficacy. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Qin, H.-J.; Li, Y.-W.; Ma, G.-X.; Yang, J.-S.; Wang, Q. Study on chemical constituents of an edible mushroom Volvariella volvacea and their antitumor activity in vitro. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 34, 1417–1422. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, M.; Wang, Y.; Su, E.; Zhang, J.; Tang, L.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zou, G.; Wan, J.; Bao, D. The promising application of a β-glucosidase inhibitor in the postharvest management of Volvariella volvacea. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2022, 185, 111784. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, M.; Zhang, Z.; Cai, H.; Wang, L.; Hu, C.; Li, D.; Chen, Y.; Kang, Y.; Li, L. Controlled moisture permeability of thermoplastic starch/polylactic acid/poly butylene adipate-co-terephthalate film for the autolysis of straw mushroom Volvariella volvacea. Food Chem. 2022, 373, 131409. [Google Scholar]
- Amir, N.F.; Mohd-Aris, A. Nutritional composition of volvariella volvacea grow using different cultivation techniques and substrate utilization. J. Acad. 2024, 12, 132–138. [Google Scholar]
- Diamantopoulou, P.; Papanikolaou, S.; Aggelis, G.; Philippoussis, A. Adaptation of Volvariella volvacea metabolism in high carbon to nitrogen ratio media. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Joha, N.S.M.; Misran, A.; Mahmud, T.M.M.; Abdullah, S.; Mohamad, A. Physical quality, amino acid contents, and health risk assessment of straw mushroom (Volvariella volvacea) at different maturity stages. Int. Food Res. J. 2021, 28, 181–188. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, D.; Melissari, F.; Le Feon, S.; Papadakis, A.; Zahariadis, T.; Chatzitheodorou, D.; Gellynck, X.; De Steur, H.; Schouteten, J.J. A holistic assessment of blockchain-based traceability systems: The case of protected designation of origin feta cheese production. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 230, 109863. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, D.; Ma, Y.; Yao, J.; Zhao, M.; Li, H.; Marchioni, E.; Zhou, L. Discriminate shiitake mushroom (Lentinus edodes) from different origins by lipidomics based on UHPLC-QE HR-AM/MS/MS. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 137, 106957. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, G.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Wang, Y. Rapid prediction of nucleosides content and origin traceability of Boletus bainiugan using Fourier transform near-infrared spectroscopy combined with chemometrics. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2025, 327, 125421. [Google Scholar]
- Giusti, A.; Tinacci, L.; Ricci, E.; Verdigi, F.; Narducci, R.; Vallone, L.; Gasperetti, L.; Armani, A. Next Generation Sequencing Technologies for the analysis of a poorly investigated foodstuff: Mushroom products authentication by metabarcoding. Food Control 2024, 165, 110675. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, J.F.; Chesson, L.A. Food Forensics: Stable Isotopes as a Guide to Authenticity and Origin; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, I.-M.; Kim, Y.-J.; Moon, H.-S.; Han, J.-G.; Kong, W.-S.; Yarnes, C.T.; Kim, S.-H. Improved accuracy of geographical origin identification of shiitake grown in sawdust medium: A compound-specific isotope model-based pilot study. Food Chem. 2022, 369, 130955. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, I.-M.; Kim, J.-T.; Moon, H.-S.; Kim, Y.-J.; Kim, S.-H. Geographical origin discrimination of Agaricus bisporus produced by the complete medium: A pilot study in South Korea. Food Chem. 2022, 386, 132820. [Google Scholar]
- Bateman, A.S.; Kelly, S.D. Fertilizer nitrogen isotope signatures. Isot. Environ. Health Stud. 2017, 43, 237–247. [Google Scholar]
- Dansgaard, W. Stable isotopes in precipitation. Tellus 1964, 16, 436–468. [Google Scholar]
- Craig, H. Isotopic variations in meteoric waters. Science 1961, 133, 1702–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, I.-M.; Kim, J.-K.; Han, J.-G.; Kong, W.-S.; Kim, S.-Y.; Yang, Y.-J.; An, Y.-J.; Kwon, C.; Chi, H.-Y.; Jung, M.Y.; et al. Potential geo-discriminative tools to trace the origins of the dried slices of shiitake (Lentinula edodes) using stable isotope ratios and OPLS-DA. Food Chem. 2019, 295, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB 5009.5-2016; National Food Safety Standard Determination of Protein in Foods. The Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB 5009.124-2016; National Food Safety Standard-Determination of Amino Acid in Foods. The Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB 5009.268-2016; National Food Safety Standard—Determination of Multi-Elements in Foods. The Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Liu, X.; Liu, Z.; Qian, Q.; Song, W.; Rogers, K.M.; Rao, Q.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Shao, S.; Tian, M.; et al. Isotope chemometrics determines farming methods and geographical origin of vegetables from Yangtze River Delta Region, China. Food Chem. 2021, 342, 128379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.-D.; Xu, Q.-S.; Liang, Y.-Z. libPLS: An integrated library for partial least squares regression and linear discriminant analysis. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2018, 176, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayik, G.A.; Tufail, T.; Anjum, F.M.; Ansari, M.J. Cereal Grains: Composition, Nutritional Attributes, and Potential Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zakhary, J.W.; El-Mahdy, A.R.; Abo-Bakr, T.M.; El Tabey-Shehata, A.M. Cultivation and chemical composition of the paddy-straw mushroom (Volvariella volvaceae). Food Chem. 1984, 13, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beluhan, S.; Ranogajec, A. Chemical composition and non-volatile components of Croatian wild edible mushrooms. Food Chem. 2011, 124, 1076–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assemie, A.; Abaya, G. The effect of edible mushroom on health and their biochemistry. Int. J. Microbiol. 2022, 2022, 8744788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguchi, F.; Kalaw, S.P.; Dulay, R.M.R.; Miyasawa, N.; Yoshimoto, H.; Seyama, T.; Reyes, R.G. Nutrient composition and functional activity of different stages in the fruiting body development of Philippine paddy straw mushroom, Volvariella volvacea (Bull.: Fr.) Sing. Adv. Environ. Biol. 2015, 9, 54–66. [Google Scholar]
- Okoro, I.O.; Achuba, F.I. Proximate and mineral analysis of some wild edible mushrooms. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 7720–7724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banik, S.; Nandi, R. Effect of supplementation of rice straw with biogas residual slurry manure on the yield, protein and mineral contents of oyster mushroom. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2004, 20, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Nakashita, R.; Ishikawa, N.K.; Tabuchi, A.; Sakuno, E.; Tokimoto, K. A comparison of dried shiitake mushroom in log cultivation and mycelial cultivation from different geographical origins using stable carbon and nitrogen isotope analysis. Bunseki Kagaku 2015, 64, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, I.-M.; Han, J.-G.; Kong, W.-S.; Kim, J.-K.; An, M.-J.; Lee, J.-H.; An, Y.-J.; Jung, M.Y.; Kim, S.-H. Regional discrimination of Agaricus bisporus mushroom using the natural stable isotope ratios. Food Chem. 2018, 264, 92–100. [Google Scholar]



| Nutrients | Fujian | Guangdong | Hubei | Jiangsu | Jiangxi | Shanghai | Zhejiang |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein | 29.77 ± 1.59 b | 33.46 ± 3.12 a | 29.56 ± 1.11 b | 32.42 ± 1.06 ab | 31.78 ± 3.92 ab | 32.32 ± 1.80 ab | 29.49 ± 1.40 b |
| Ala | 1.47 ± 0.14 b | 2.50 ± 0.50 a | 1.54 ± 0.13 ab | 1.83 ± 0.12 ab | 1.61 ± 0.13 ab | 1.90 ± 0.17 a | 1.51 ± 0.08 ab |
| Arg | 1.25 ± 0.10 b | 1.23 ± 0.17 b | 1.29 ± 0.10 ab | 1.31 ± 0.50 ab | 1.33 ± 0.10 ab | 1.48 ± 0.24 a | 1.15 ± 0.09 b |
| Asp | 2.18 ± 0.17 a | 2.21 ± 0.20 a | 2.24 ± 0.13 a | 2.34 ± 0.39 a | 2.43 ± 0.22 a | 2.47 ± 0.31 a | 2.20 ± 0.14 a |
| Glu | 3.69 ± 0.31 b | 3.71 ± 0.38 b | 3.77 ± 0.18 b | 4.61 ± 0.28 a | 4.04 ± 0.54 ab | 3.62 ± 0.61 b | 3.96 ± 0.43 ab |
| Gly | 1.01 ± 0.07 b | 1.19 ± 0.15 a | 0.98 ± 0.05 b | 1.11 ± 0.11 ab | 1.08 ± 0.06 ab | 1.19 ± 0.08 a | 0.99 ± 0.06 b |
| His | 0.53 ± 0.04 b | 0.67 ± 0.09 a | 0.59 ± 0.05 ab | 0.62 ± 0.07 ab | 0.57 ± 0.04 ab | 0.65 ± 0.08 a | 0.52 ± 0.03 b |
| Ile | 1.14 ± 0.08 b | 1.40 ± 0.19 a | 1.19 ± 0.10 ab | 1.27 ± 0.15 ab | 1.22 ± 0.09 ab | 1.32 ± 0.13 a | 1.12 ± 0.06 b |
| Leu | 1.77 ± 0.14 a | 1.71 ± 0.26 a | 1.83 ± 0.12 a | 1.89 ± 0.26 a | 1.95 ± 0.17 a | 1.99 ± 0.41 a | 1.74 ± 0.09 a |
| Lys | 1.46 ± 0.11 b | 1.59 ± 0.16 b | 1.55 ± 0.10 b | 1.53 ± 0.20 ab | 1.70 ± 0.20 ab | 1.82 ± 0.18 a | 1.45 ± 0.06 b |
| Met | 0.78 ± 0.07 ab | 0.83 ± 0.10 ab | 0.88 ± 0.03 a | 0.85 ± 0.05 a | 0.79 ± 0.06 ab | 0.74 ± 0.10 b | 0.87 ± 0.10 ab |
| Phe | 1.15 ± 0.09 a | 0.81 ± 0.09 c | 1.09 ± 0.08 ab | 0.86 ± 0.09 bc | 1.27 ± 0.13 a | 1.08 ± 0.18 ab | 1.13 ± 0.06 ab |
| Pro | 1.21 ± 0.07 bc | 1.35 ± 0.13 ab | 1.19 ± 0.06 bc | 1.35 ± 0.08 ab | 1.28 ± 0.15 abc | 1.37 ± 0.07 a | 1.17 ± 0.03 c |
| Ser | 1.18 ± 0.08 b | 1.26 ± 0.11 ab | 1.17 ± 0.05 b | 1.28 ± 0.12 ab | 1.30 ± 0.10 ab | 1.34 ± 0.19 a | 1.19 ± 0.06 ab |
| Thr | 1.23 ± 0.08 b | 1.46 ± 0.17 ab | 1.20 ± 0.09 b | 1.36 ± 0.10 ab | 1.33 ± 0.11 ab | 1.42 ± 0.09 a | 1.23 ± 0.06 b |
| Tyr | 0.80 ± 0.09 a | 0.54 ± 0.07 b | 0.74 ± 0.08 a | 0.65 ± 0.07 ab | 0.91 ± 0.07 a | 0.78 ± 0.13 a | 0.79 ± 0.09 a |
| Val | 1.29 ± 0.11 b | 1.60 ± 0.22 a | 1.30 ± 0.06 b | 1.43 ± 0.16 ab | 1.39 ± 0.11 ab | 1.52 ± 0.09 a | 1.26 ± 0.07 b |
| EAA | 8.81 ± 0.63 a | 9.40 ± 0.98 a | 9.04 ± 0.31 a | 9.19 ± 0.79 a | 9.65 ± 0.84 a | 9.89 ± 1.05 a | 8.80 ± 0.48 a |
| TAA | 22.14 ± 1.55 a | 24.07 ± 2.56 a | 22.55 ± 1.23 a | 24.19 ± 1.57 a | 24.21 ± 2.26 a | 24.72 ± 2.42 a | 22.29 ± 1.37 a |
| Ca | 985.01 ± 465.73 a | 421.69 ± 341.62 ab | 1203.11 ± 466.56 a | 706.93 ± 517.23 ab | 723.17 ± 587.96 ab | 221.07 ± 121.26 b | 1110.72 ± 239.681 a |
| Cu | 46.55 ± 9.06 a | 36.29 ± 16.53 a | 38.42 ± 10.61 a | 42.96 ± 14.41 a | 42.11 ± 11.33 a | 44.77 ± 22.39 a | 47.72 ± 5.24 a |
| Fe | 484.42 ± 184.85 ab | 127.87 ± 102.97 cd | 770.71 ± 159.32 a | 281.90 ± 145.59 bc | 361.62 ± 106.75 b | 58.85 ± 16.84 d | 652.45 ± 134.24 a |
| K | 42.72 ± 3.06 a | 43.64 ± 2.15 a | 42.87 ± 1.04 a | 45.77 ± 5.04 a | 40.30 ± 0.80 a | 41.20 ± 3.13 a | 41.48 ± 2.01 a |
| Mn | 24.95 ± 9.33 ab | 15.85 ± 6.02 b | 25.48 ± 2.37 a | 17.99 ± 4.74 ab | 22.34 ± 10.88 ab | 12.26 ± 1.89 b | 26.86 ± 3.32 a |
| Mg | 1242.25 ± 124.71 ab | 1121.81 ± 73.92 bc | 1338.93 ± 61.17 a | 1120.69 ± 165.87 abc | 1076.11 ± 150.06 bc | 1062.41 ± 51.03 c | 1250.78 ± 55.99 a |
| Na | 513.43 ± 190.50 a | 304.48 ± 337.47 b | 453.17 ± 103.80 ab | 319.04 ± 53.19 ab | 254.08 ± 208.22 ab | 227.21 ± 71.97 b | 405.53 ± 162.88 ab |
| Se | 0.29 ± 0.17 a | 0.09 ± 0.09 b | 0.30 ± 0.06 a | 0.15 ± 0.09 ab | 0.17 ± 0.09 ab | 0.11 ± 0.05 ab | 0.28 ± 0.04 a |
| Sr | 4.02 ± 1.90 a | 1.81 ± 1.17 ab | 4.31 ± 1.13a | 1.46 ± 1.07 ab | 2.55 ± 2.88 ab | 0.97 ± 0.38 b | 4.57 ± 1.03 a |
| Zn | 58.90 ± 3.88 b | 64.50 ± 7.74 b | 61.35 ± 3.63 b | 80.34 ± 4.03 a | 65.03 ± 10.42 ab | 64.44 ± 7.14 b | 57.26 ± 2.68 b |
| Origins | δ13C/‰ | δ15N/‰ | δ2H/‰ | δ18O/‰ | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Median | Mean ± SD | Median | Mean ± SD | Median | Mean ± SD | Median | |
| Fujian | −10.98 ± 2.67 a | −9.70 | 7.38 ± 4.47 a | 8.74 | −15.20 ± 5.27 ab | −18.29 | 18.28 ± 0.93 b | 18.46 |
| Guangdong | −23.41 ± 0.43 c | −23.20 | 0.36 ± 2.56 c | −0.64 | −16.98 ± 4.45 ab | −17.76 | 19.92 ± 1.74 ab | 20.57 |
| Hubei | −9.70 ± 0.22 ab | −9.74 | 8.53 ± 1.59 ab | 7.95 | −16.88 ± 5.04 ab | −18.54 | 17.96 ± 0.93 ab | 18.34 |
| Jiangsu | −15.46 ± 1.61 bc | −15.34 | 1.32 ± 1.87 c | 0.96 | −15.02 ± 5.64 ab | −14.22 | 19.37 ± 1.29 ab | 19.47 |
| Jiangxi | −10.57 ± 2.35 a | −9.51 | 8.89 ± 4.29 a | 9.84 | −17.23 ± 3.63 ab | −18.26 | 19.05 ± 1.27 ab | 18.51 |
| Shanghai | −19.48 ± 3.61 c | −19.28 | 1.48 ± 1.98 bc | 1.17 | −12.92 ± 5.11 a | −11.60 | 19.84 ± 1.74 a | 19.74 |
| Zhejiang | −9.72 ± 0.55 a | −9.60 | 8.51 ± 1.54 a | 8.43 | −17.75 ± 4.00 b | −17.77 | 18.29 ± 0.83 ab | 18.23 |
| Geographic Origin | Accuracy/% | Total Accuracy/% | The VIP Order |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong–Jiangsu–Shanghai | 98.70 | 93.60 | δ15N > δ13C > 1 > δ18O > δ2H |
| Fujian–Hubei–Jiangxi–Zhejiang | 85.42 | ||
| Guangdong | 100 | 100.00 | δ13C > 1 > δ15N > δ18O > δ2H |
| Jiangsu | 100 | ||
| Guangdong | 63.64 | 86.96 | δ13C > δ2H > 1 > δ15N > δ18O |
| Shanghai | 94.29 | ||
| Jiangsu | 93.55 | 81.82 | δ13C > 1 > δ2H > δ18O > δ15N |
| Shanghai | 71.43 | ||
| Fujian | 100 | 80.77 | δ13C > 1 > δ18O > δ2H > δ15N |
| Hubei | 0 | ||
| Fujian | 100.00 | 74.19 | δ18O > 1 > δ2H > δ15N > δ13C |
| Jiangxi | 20.00 | ||
| Fujian | 85.71 | 63.64 | δ13C > δ2H > 1 > δ15N > δ18O |
| Zhejiang | 25.00 | ||
| Hubei | 60.00 | 86.67 | δ18O> 1 > δ13C > δ15N > δ2H |
| Jiangxi | 100.00 | ||
| Hubei | 40.00 | 76.47 | δ18O > 1 > δ2H > δ13C > δ15N |
| Zhejiang | 91.67 | ||
| Jiangxi | 60.00 | 68.18 | δ18O > 1 > δ13C > δ2H > δ15N |
| Zhejiang | 75.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Rao, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Geng, H.; Lu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Chen, S.; Li, P.; Song, W. Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometry (IRMS)-Based Authentication of the Geographic Origins of Volvariella volvacea (Bull.) Singer. Foods 2025, 14, 1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14061074
Liu X, Rao Q, Zhang Q, Geng H, Lu Y, Liu Z, Chen S, Li P, Song W. Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometry (IRMS)-Based Authentication of the Geographic Origins of Volvariella volvacea (Bull.) Singer. Foods. 2025; 14(6):1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14061074
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xing, Qinxiong Rao, Qicai Zhang, Hao Geng, Yangyang Lu, Zhu Liu, Shanshan Chen, Peijun Li, and Weiguo Song. 2025. "Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometry (IRMS)-Based Authentication of the Geographic Origins of Volvariella volvacea (Bull.) Singer" Foods 14, no. 6: 1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14061074
APA StyleLiu, X., Rao, Q., Zhang, Q., Geng, H., Lu, Y., Liu, Z., Chen, S., Li, P., & Song, W. (2025). Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometry (IRMS)-Based Authentication of the Geographic Origins of Volvariella volvacea (Bull.) Singer. Foods, 14(6), 1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14061074









