Chemical Isotope Labeling Liquid Chromatograph-Mass Spectrometer: A Powerful Tool for Analyzing Non-Volatile Organic Acids in Baijiu
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Samples
2.2. Chemical Isotope Derivatization
2.3. LC-MS Analysis
2.4. Data Processing
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Profile of Non-Volatile Organic Acids in Baijiu
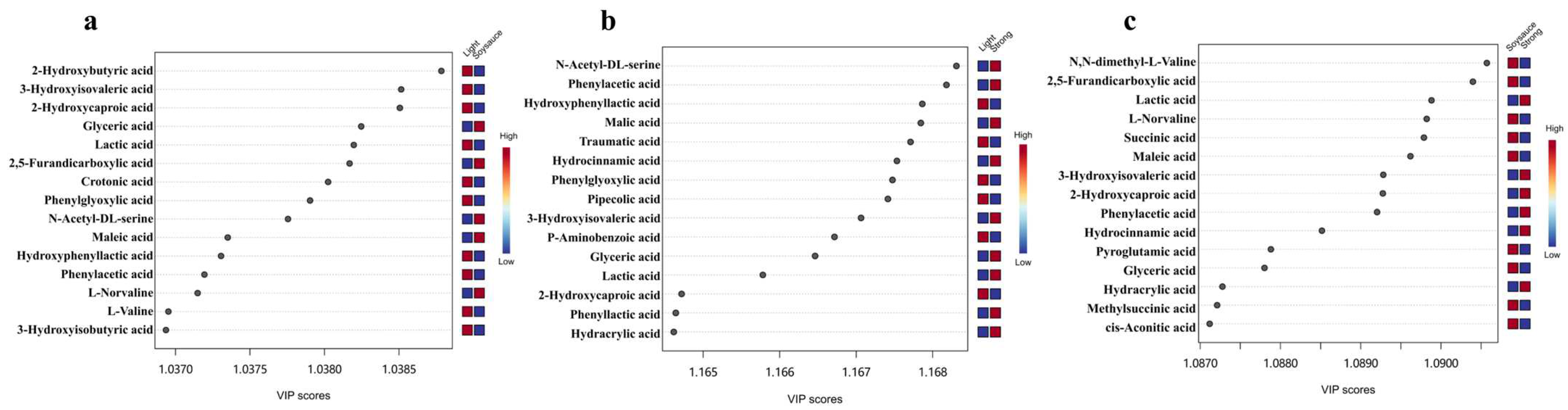
3.2. Comparison of Non-Volatile Organic Acids Among Three Flavor Types of Baijiu
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McGovern, P.E.; Zhang, J.; Tang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Hall, G.R.; Moreau, R.A.; Nunez, A.; Butrym, E.D.; Richards, M.P.; Wang, C.-S.; et al. Fermented beverages of pre- and proto-historic China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 17593–17598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Song, X.; Zhu, L.; Li, Q.; Zheng, F.; Geng, X.; Li, L.; Wu, J.; Li, H.; Sun, B. A flavoromics strategy for the differentiation of different types of Baijiu according to the non-volatile organic acids. Food Chem. 2022, 374, 131641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Li, X.; Song, X.; Jing, S.; Meng, S.; Zheng, F.; Li, H.; Li, Z.; Shen, C.; Shen, Y. Optimization and Validation of a Method for Analysis of Non-Volatile Organic Acids in Baijiu by Derivatization and its Application in Three Flavor-Types of Baijiu. Food Anal. Methods 2022, 15, 1606–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, Y. Mystery behind Chinese liquor fermentation. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 63, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Sun, B. Effect of Fermentation Processing on the Flavor of Baijiu. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 5425–5432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Z.; Li, X.; Sun, B. Flavor mystery of Chinese traditional fermented baijiu: The great contribution of ester compounds. Food Chem. 2022, 369, 130920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Ma, R. Cross-modal interactions caused by nonvolatile compounds derived from fermentation, distillation and aging to harmonize flavor. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 64, 6686–6713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, S.; Wollmann, N.; Schieberle, P.; Hofmann, T. Reconstitution of the flavor signature of Dornfelder red wine on the basis of the natural concentrations of its key aroma and taste compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 8866–8874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tian, Z.; Ma, Y.; Shao, F.; Huang, J.; Wu, H.; Tian, L. Origin Identification of the Sauce-Flavor Chinese Baijiu by Organic Acids, Trace Elements, and the Stable Carbon Isotope Ratio. J. Food Qual. 2019, 2019, 7525201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Fan, Z.; Du, A.; Shi, L. Untargeted foodomics reveals molecular mechanism of magnetic field effect on Feng-flavor Baijiu ageing. Food Res. Int. 2021, 149, 110681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Jing, S.; Song, X.; Zhu, L.; Zheng, F.; Sun, B. Reconstitution of the Flavor Signature of Laobaigan-Type Baijiu Based on the Natural Concentrations of Its Odor-Active Compounds and Nonvolatile Organic Acids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Lu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, F.; Yu, D.; Li, C.; Zheng, S.; Chen, B.; Liu, X.; Ma, M.; et al. In-depth profiling of carboxyl compounds in Chinese Baijiu based on chemical derivatization and ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography coupled to high-resolution mass spectrometry. Food Chem. X 2022, 15, 100440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Li, L. Chemical derivatization in LC-MS-based metabolomics study. Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 131, 115988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, F.; Ma, Y.; Song, C.; Penttinen, P.; Zhang, S.; Li, Z. Metabolic characterization of different-aged Monascus vinegars via HS-SPME-GC-MS and CIL LC-MS approach. LWT 2022, 172, 114169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Dong, L.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, S.; Zhan, J.; Li, J.; Li, L. Development of a High-Coverage Quantitative Metabolome Analysis Method Using Four-Channel Chemical Isotope Labeling LC-MS for Analyzing High-Salt Fermented Food. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 8827–8837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wang, X.; Chen, D.; Xu, E.G.; Luo, X.; Zeng, J.; Huan, T.; Li, L.; Wang, Y. Toxicity mechanisms of polystyrene microplastics in marine mussels revealed by high-coverage quantitative metabolomics using chemical isotope labeling liquid chromatography mass spectrometry. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 417, 126003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mung, D.; Li, L. Chemical isotope labeling liquid chromatography mass spectrometry for investigating acute dietary effects of cow milk consumption on human urine metabolome. J. Food Drug Anal. 2019, 27, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Li, H.; Han, W.; Chan, W.; Li, L. Metabolomic Coverage of Chemical-Group-Submetabolome Analysis: Group Classification and Four-Channel Chemical Isotope Labeling LC-MS. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 12108–12115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Li, R.; Zhou, J.; Zuniga, A.; Stanislaus, A.E.; Wu, Y.; Huan, T.; Zheng, J.; Shi, Y.; Wishart, D.S.; et al. MyCompoundID: Using an evidence-based metabolome library for metabolite identification. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 3401–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Chong, J.; Zhou, G.; de Lima Morais, D.A.; Chang, L.; Barrette, M.; Gauthier, C.; Jacques, P.-É.; Li, S.; Xia, J. MetaboAnalyst 5.0: Narrowing the gap between raw spectra and functional insights. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feunang, Y.D.; Eisner, R.; Knox, C.; Chepelev, L.; Hastings, J.; Owen, G.; Fahy, E.; Steinbeck, C.; Subramanian, S.; Bolton, E.; et al. ClassyFire: Automated chemical classification with a comprehensive, computable taxonomy. J. Cheminform. 2016, 8, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanase, R.; Senda, R.; Matsunaga, Y.; Narukawa, M. Taste Characteristics of Various Amino Acid Derivatives. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2022, 68, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samardzic, K.; Rodgers, K.J. Cytotoxicity and mitochondrial dysfunction caused by the dietary supplement l-norvaline. Toxicol. Vitr. 2019, 56, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, T.; Fujita, M.; Kodama, T.; Hada, T.; Higashino, K. Determination of D- and L-pipecolic acid in food samples including processed foods. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2003, 47, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Jing, S.; Wang, X.; Zheng, F.; Li, H.; Sun, B.; Li, Z. Evaluation of the Perceptual Interaction among Ester Odorants and Nonvolatile Organic Acids in Baijiu by GC-MS, GC-O, Odor Threshold, and Sensory Analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 13987–13995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulvik, A.; McCann, A.; Midttun, Ø.; Meyer, K.; Godfrey, K.M.; Ueland, P.M. Quantifying Precision Loss in Targeted Metabolomics Based on Mass Spectrometry and Nonmatching Internal Standards. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 7616–7624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, C.; Mao, Z.; Penttinen, P.; Zhang, F.; Dong, L.; Song, C.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, X.; Fu, X.; Zhang, S.; et al. Chemical Isotope Labeling Liquid Chromatograph-Mass Spectrometer: A Powerful Tool for Analyzing Non-Volatile Organic Acids in Baijiu. Foods 2025, 14, 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14061027
Zhao C, Mao Z, Penttinen P, Zhang F, Dong L, Song C, Xiong Y, Zhang X, Fu X, Zhang S, et al. Chemical Isotope Labeling Liquid Chromatograph-Mass Spectrometer: A Powerful Tool for Analyzing Non-Volatile Organic Acids in Baijiu. Foods. 2025; 14(6):1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14061027
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Chi, Zhenyu Mao, Petri Penttinen, Fengju Zhang, Ling Dong, Chuan Song, Yanfei Xiong, Xiaoping Zhang, Xin Fu, Suyi Zhang, and et al. 2025. "Chemical Isotope Labeling Liquid Chromatograph-Mass Spectrometer: A Powerful Tool for Analyzing Non-Volatile Organic Acids in Baijiu" Foods 14, no. 6: 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14061027
APA StyleZhao, C., Mao, Z., Penttinen, P., Zhang, F., Dong, L., Song, C., Xiong, Y., Zhang, X., Fu, X., Zhang, S., & Li, Z. (2025). Chemical Isotope Labeling Liquid Chromatograph-Mass Spectrometer: A Powerful Tool for Analyzing Non-Volatile Organic Acids in Baijiu. Foods, 14(6), 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14061027





