Integrated Biotechnological Strategies for the Sustainability and Quality of Mediterranean Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) and Sea Bream (Sparus aurata)
Abstract
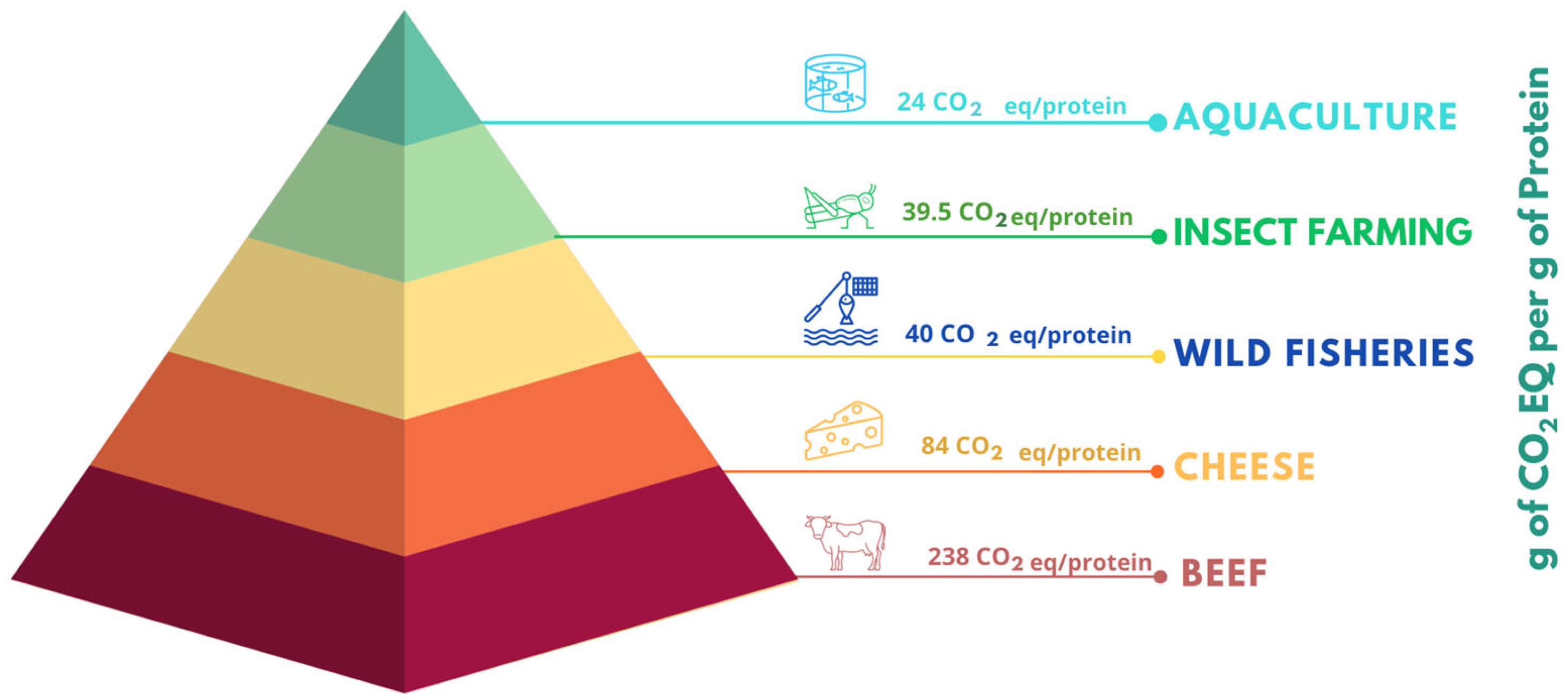
1. Introduction
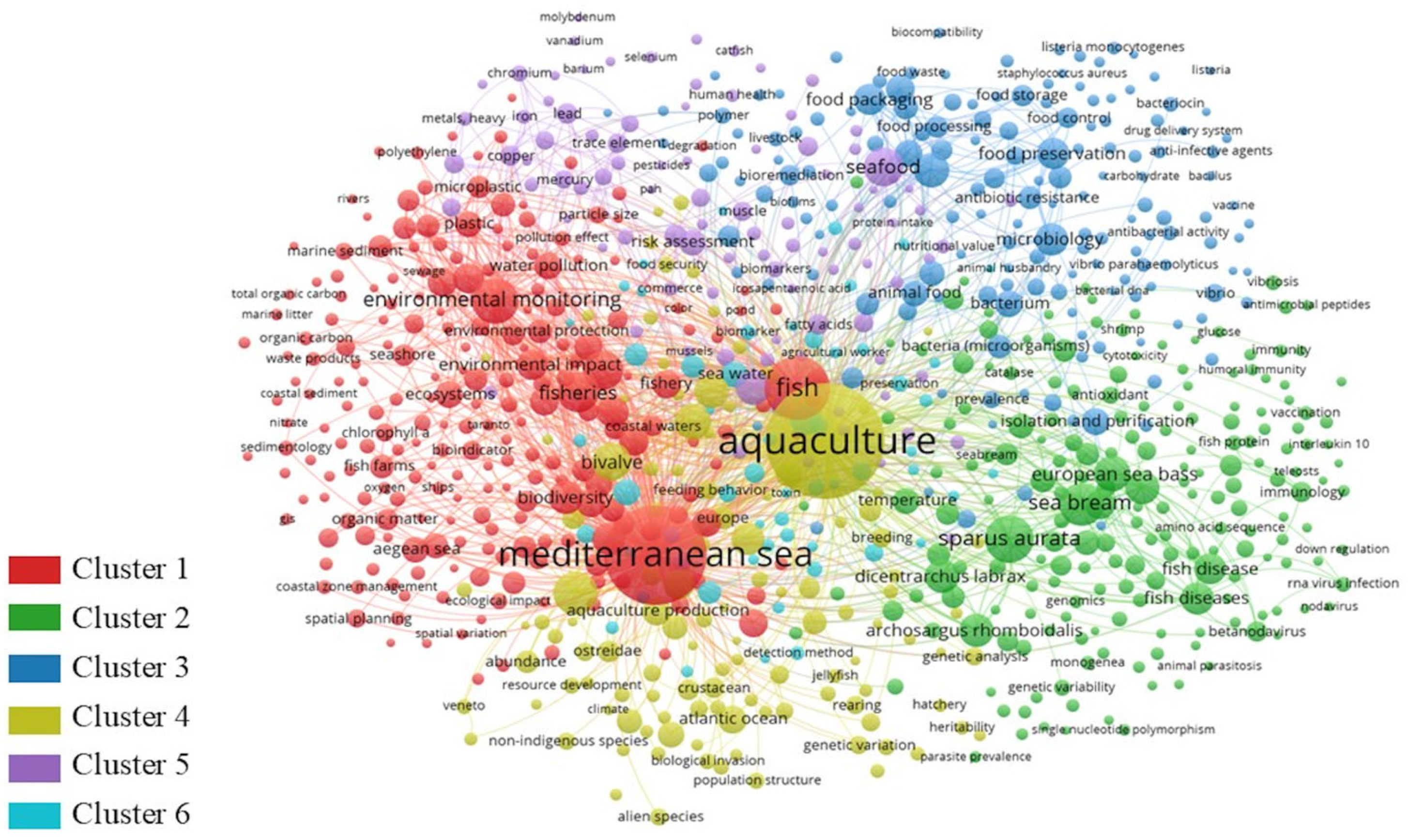
2. Quantitative Research Literature Analysis
3. Technological Systems for Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) and Sea Bream (Sparus aurata) Farming in the Mediterranean Area
3.1. Integrated Multi-Trophic Aquaculture (IMTA)
3.2. IMTA for Sea Bass and Sea Bream Farming
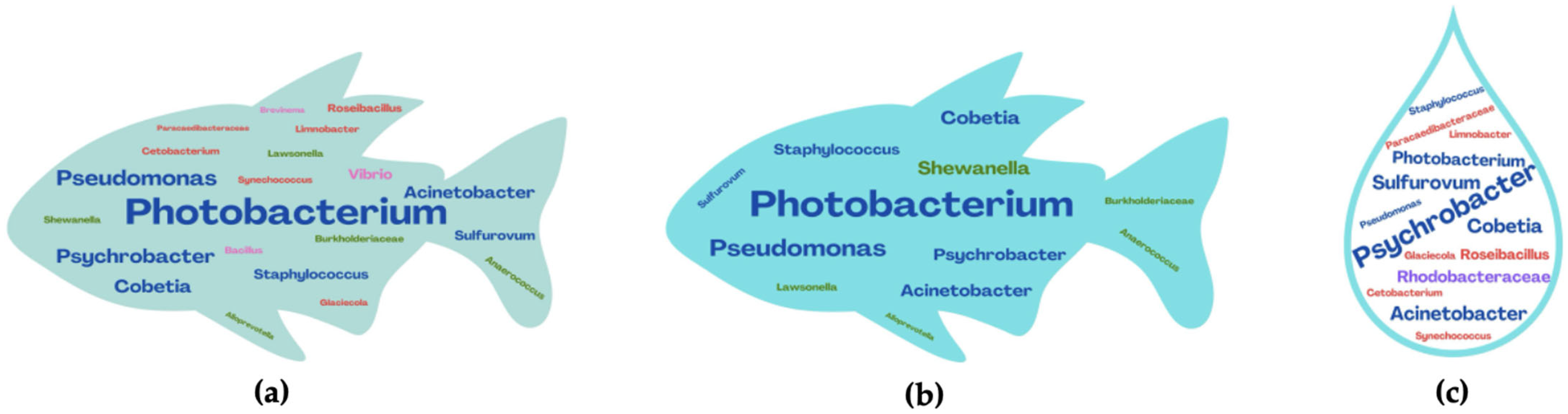
4. Sea Bream and Sea Bass Microbiota
4.1. Potential Pathogenic Microorganisms
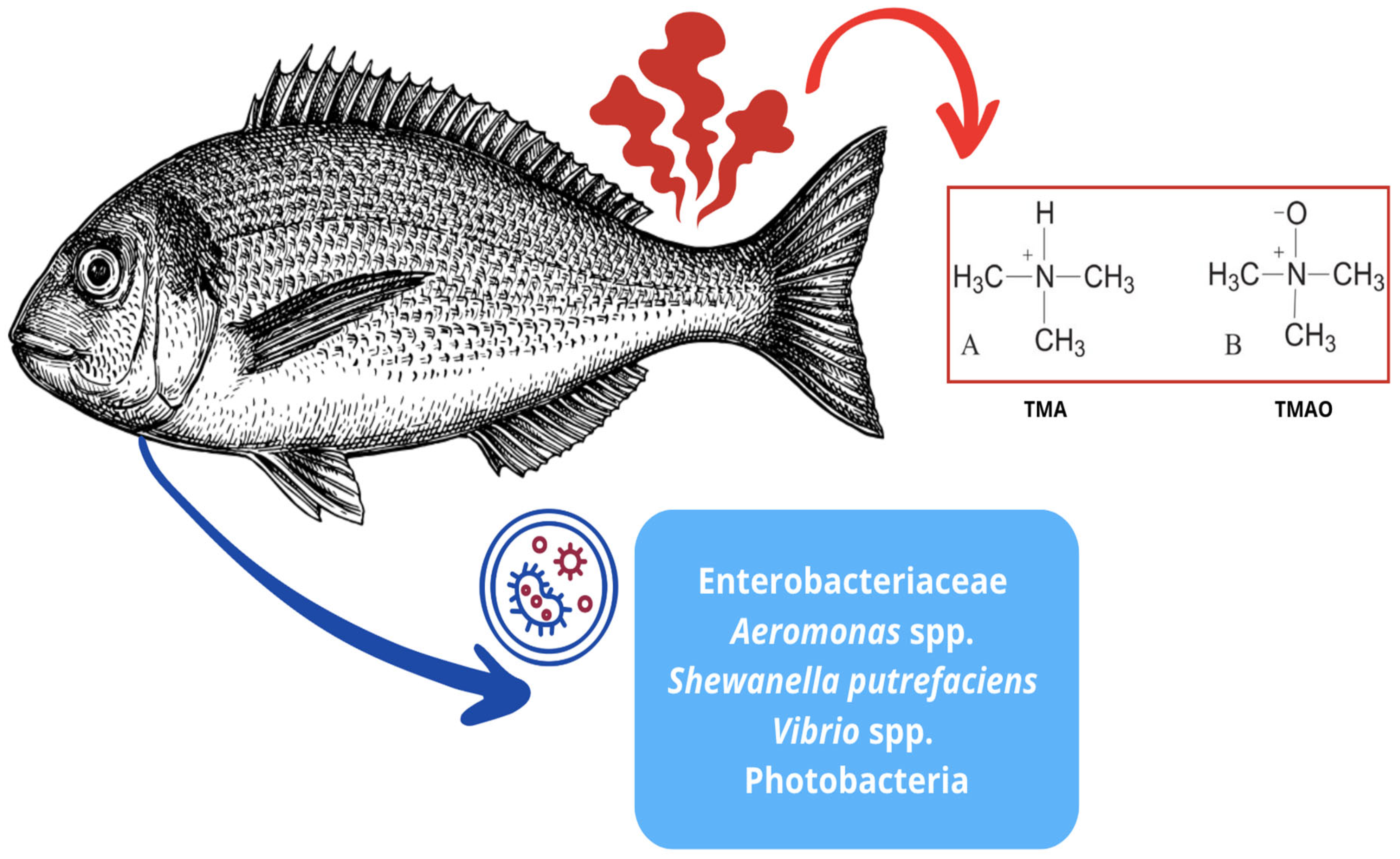
4.2. Spoilage Microorganisms
4.3. Useful Microorganisms and Biopreservation
5. Food Losses and Waste in the Fish Supply Chain
6. Packaging
6.1. Active and Intelligent Packaging
6.2. Edible Packaging
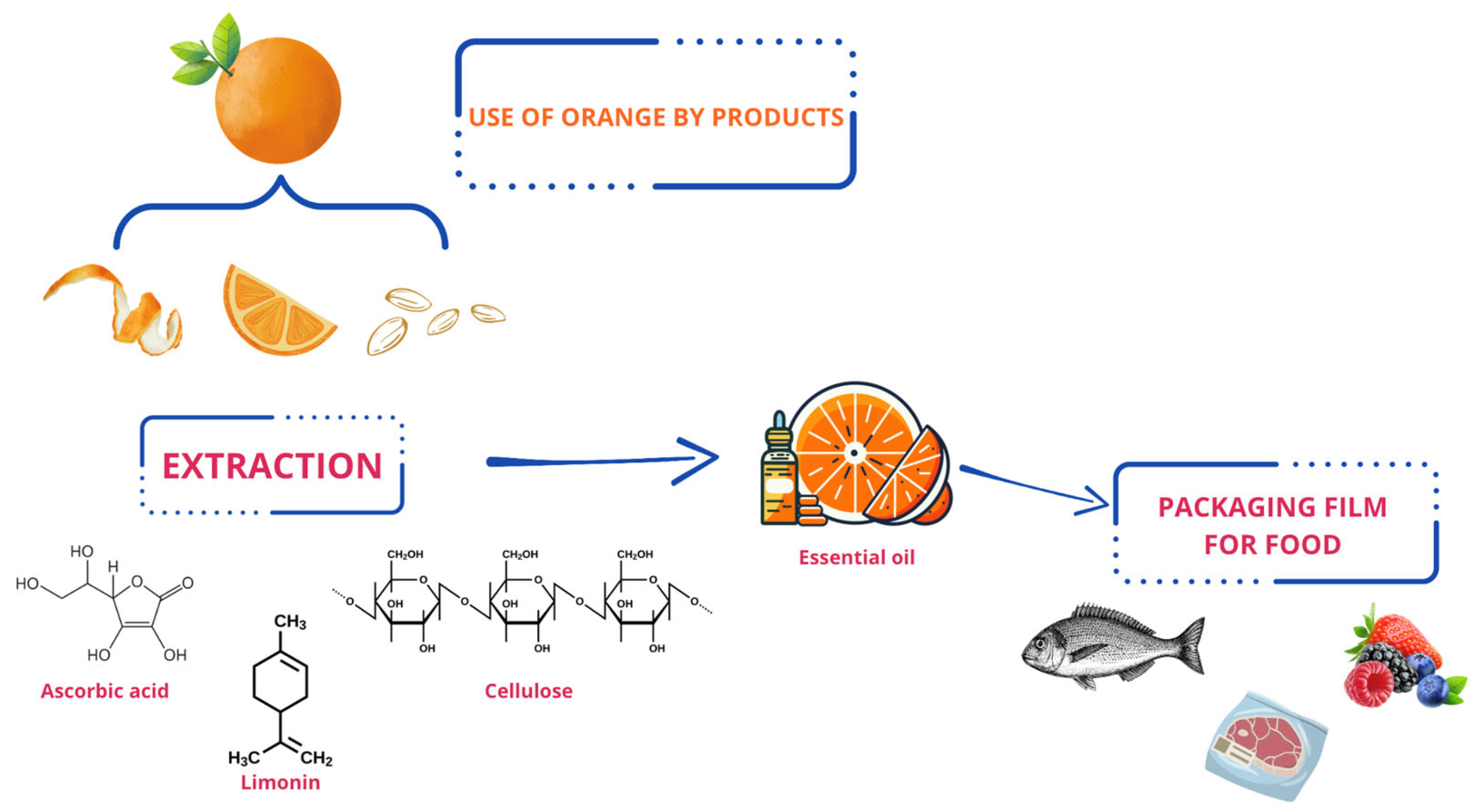
7. Use of Citrus By-Products for Safety and Shelf Life of Fish and Fish Products
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heilig, G.K. World population trends: How do they affect global food security? In Food Security at Different Scales: Demographic, Biophysical and Socio-Economic Considerations; AB-DLO: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2025; Volume 2050, p. 25. [Google Scholar]
- Hambrey, J. The 2030 agenda and the sustainable development goals: The challenge for aquaculture development and management. In FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Circular; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2017; Volume C1141. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.C.; Liu, W.H. Implementing the Slow Fish curriculum for SDGs: Strategies, challenges, and policy suggestions through a case study. Mar. Policy 2025, 173, 106538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, A.J.; Elliott, V.; Phang, S.C.; Claussen, J.E.; Harrison, J.; Murchie, K.J.; Steel, E.A.; Stokes, G.L. Inland fish and fisheries integral to achieving the Sustainable Development Goals. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansfield, E.J.; Micheli, F.; Fujita, R.; Fulton, E.A.; Gelcich, S.; Battista, W.; Bustamate, R.H.; Cao, L.; Daniels, B.N.; Finkbeiner, E.M.; et al. Anticipating trade-offs and promoting synergies between small-scale fisheries and aquaculture to improve social, economic, and ecological outcomes. NPJ Ocean Sustain. 2024, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicuro, B. The evolution of aquaculture in the Mediterranean region: An anthropo-genic climax stage? PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0290870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasik, Z.; Gunawan, S.; Handriana, T. Blue Economy and the Impact of Industrialisation on Sustainable Livelihoods: A Case Study of Fisheries in the North Coastal Region of Java. J. Ecohumanism 2024, 3, 2729–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teh, L.S.L.; Teh, L.C.L.; Giron-Nava, A.; Sumaila, U.R. Poverty line income and fisheries subsidies in developing country fishing communities. NPJ Ocean Sustain. 2024, 3, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gann-Perkal, H. Regional Collaboration for a Blue Economy in the Eastern Mediterranean. In Handbook of Sustainable Blue Economy; Leal Filho, W., Salvia, A.L., Eustachio, J.P.P., Dinis, M.A.P., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO; OECD. OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook 2024–2033; FAO: Rome, Italy; OECD: Paris, France, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés-Sánchez, A.D.J.; Diaz-Ramírez, M.; Torres-Ochoa, E.; Espinosa-Chaurand, L.D.; Rayas-Amor, A.A.; Cruz-Monterrosa, R.G.; Aguilar-Toalà, J.-E.; Salgado-Cruz, M.D.L.P. Processing, Quality and Elemental Safety of Fish. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, S.; Hong, H.; Zhang, L.; Luo, Y. Spoilage-related microbiota in fish and crustaceans during storage: Research progress and future trends. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 252–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagnostopoulos, D.A.; Parlapani, F.F.; Boziaris, I.S. The evolution of knowledge on seafood spoilage microbiota from the 20th to the 21st century: Have we finished or just begun? Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 120, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.A.; Singh, S.; Bahmid, N.A.; Ibrahim, S.A.; Sasidharan, A. Applying innovative technological interventions in the preservation and packaging of fresh seafood products to minimize spoilage—A systematic review and meta-analysis. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2024—Blue Transformation in Action; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schar, D.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Y.; Larsson, D.G.J.; Gilbert, M.; Van Boeckel, T.P. Twenty-year trends in antimicrobial resistance from aquaculture and fisheries in Asia. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2022. Towards Blue Transformation; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zoli, M.; Rossi, L.; Fronte, B.; Aubin, J.; Jaeger, J.; Wilfart, A.; Bibbiani, C.; Bacenetti, J. Environmental impact of different Mediterranean technological systems for European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) and Gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) farming. Aquac. Eng. 2024, 107, 102457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FishStatJ. FAO—FAO Fishery and Aquaculture Global Statistics. 2022. Available online: https://www.fao.org/fishery/en/statistics (accessed on 14 December 2024).
- Vijayaram, S.; Tsigkou, K.; Zuorro, A.; Sun, Y.Z.; Rabetafika, H.; Razafindralambo, H. Inorganic nanoparticles for use in aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2023, 15, 1600–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho Pereira, J.; Lemoine, A.; Neubauer, P.; Junne, S. Perspectives for improving circular economy in brackish shrimp aquaculture. Aquac. Res. 2022, 53, 1169–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, J.P.; Backeljau, T.; Chapelle, G. Shells from aquaculture: A valuable biomaterial, not a nuisance waste product. Rev. Aquac. 2019, 11, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanati, C.; Willer, D.; Schubert, J.; Aldridge, D.C. Sustainable intensification of aquaculture through nutrient recycling and circular economies: More fish, less waste, blue growth. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2021, 30, 143–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K.; Mondal, B.; Sarkar, U.K.; Das, B.K.; Borah, S. Understanding and approaches towards circular bioeconomy of wastewater reuse in fisheries and aquaculture in India: An overview. Rev. Aquac. 2022, 15, 1100–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowler, D.; Chopin, T.; Martinez-Espiñeira, R.; Neori, A.; Nobre, A.; Noce, G.; Reid, G. The Economics of Integrated Multi-Trophic Aquaculture: Where Are We Now and Where DoWe Need to Go? Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 1579–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrington, K.; Ridler, N.; Chopin, D.; Robinson, S.; Robinson, B. Social Aspects of the Sustainability of Integrated Multi-Trophic Aquaculture. Aquac. Int. 2010, 18, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chary, K.; van Riel, A.J.; Muscat, A.; Wilfart, A.; Harchaoui, S.; Verdegem, M.; Filgueira, L.; Troell, M.; Henriksson, P.J.G.; de Boer, I.J.M.; et al. Transforming sustainable aquaculture by applying circularity principles. Rev. Aquac. 2024, 16, 656–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atieno, P.; Hendriks, S.L. Sustainable Development Goal 14: Life below water. In Handbook on Public Policy and Food Security; Edward Elgar Publishing: Cheltenham, UK, 2024; pp. 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Thakur, H.; Singh, A.; Ramasamy, V.; Mudgal, G. Poisoned Seas: Chemical Threats to Marine Life and Human Health. In Sustainable Development Goals Towards Environmental Toxicity and Green Chemistry World Sustainability Serie; Prakash, C., Kesari, K.K., Negi, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 167–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poore, J.; Nemecek, T. Reducing food’s environmental impacts through producers and consumers. Science 2018, 360, 987–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qaim, M.; Barrangou, R.; Ronald, P.C. Sustainability of animal-sourced foods and plant-based alternatives. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2400495121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oonincx, D.G.; De Boer, I.J. Environmental Impact of the Production of mealworms as a protein source for humans—A life cycle assessment. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, C.; Loubet, P.; da Costa, T.P.; Quintero, P.; Laso Cortabitarte, J.; Baptista de Desousa, D.; Cooney, R.; Mellet, S.; Sonnemann, G.; Rodrìguez, C.J.; et al. Packaging environmental impact on seafood supply chains: A review of life cycle assessment studies. J. Ind. Ecol. 2022, 26, 1961–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witter, A.; Murray, G.; Sumaila, U.R. Consumer seafood preferences related to alternative food networks and their value chains. Mar. Policy 2021, 131, 104694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista, R.C.; Horita, C.N.; Sant’Ana, A.S. Natural products with preservative properties for enhancing the microbiological safety and extending the shelf-life of seafood: A review. Food Res. Int. 2020, 127, 108762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoli, M.; Rossi, L.; Costantini, M.; Bibbiani, C.; Fronte, B.; Brambilla, F.; Bacenetti, J. Quantification and characterization of the environmental impact of sea bream and sea bass production in Italy. Clean. Environ. Syst. 2023, 9, 100118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leandro, M.G.; Zornu, J.; Le Breton, A.; Chérif, N.; Basurco, B.; Furones, D.; Muniesa, A.; Toffan, A.; Dalla Pozza, M.; Franzago, E.; et al. Quantification of biosecurity measures in Mediterranean European seabass and gilthead sea bream farms. Aquaculture 2025, 596, 741898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, J.; Gonçalves, R.; Branco, F.A. Bibliometric analysis and visualization of e-learning adoption using VOSviewer. Univers. Access Inf. Soc. 2024, 23, 1177–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitriyana, D.F.; Rusiyanto, R.; Maawa, W. Renewable Energy Application Research Using VOSviewer software: Bibliometric Analysis. Int. J. Sci. Adv.Technol. 2025, 1, 92–107. [Google Scholar]
- Trani, R.; Pierri, C.; Schiavo, A.; Lazic, T.; Mercurio, M.; Coccia, I.; Longo, C. Response of Hard-Bottom Macro-Zoobenthos to the Transition of a Mediterranean Mariculture Fish Plant (Mar Grande of Taranto, Ionian Sea) into an Integrated Multi-Trophic Aquaculture (IMTA) System. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Féon, S.; Dubois, T.; Jaeger, C.; Wilfart, A.; Akkal-Corfini, N.; Bacenetti, J.; Costantin, M.; Aubin, J. DEXiAqua, a model to assess the sustainability of aquaculture systems: Methodological development and application to a french salmon farm. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubin, J.; Papatryphon, E.; Van der Werf, H.M.G.; Chatzifotis, S. Assessment of the Environmental Impact of Carnivorous Finfish Production Systems Using Life Cycle Assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2008, 17, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmer, M.; Hansen, P.K.; Karakassis, I.; Borg, J.A.; Schembri, B.J. Monitoring of environmental impacts of marine aquaculture. In Aquaculture in the Ecosystem; Holmer, M., Black, K., Duarte, C.M., Marbà, N., Karakassis, I., Eds.; Springer: Torino, Italy, 2008; pp. 47–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biazi, V.; Marques, C. Industry 4.0-Based Smart Systems in Aquaculture: A Comprehensive Review. Aquacult. Eng. 2023, 103, 102360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’donncha, F.; Grant, J. Precision aquaculture. IEEE Internet Things Mag. 2019, 2, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troell, M.; Joyce, A.; Chopin, T.; Neori, A.; Buschmann, A.H.; Fang, J.G. Ecological Engineering in Aquaculture—Potential for Integrated Multi-Trophic Aquaculture (IMTA) in Marine Offshore Systems. Aquaculture 2009, 297, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, D.B.; Grutter, A.S.; Hutson, K.S. Cleaner shrimp are a sustainable option to treat parasitic disease in farmed fish. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, A.D.; Black, K.D. Going beyond the search for solutions: Understanding trade-offs in European integrated multi-trophic aquaculture development. Aquac. Environ. Interact. 2016, 8, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissar, S.; Bakhtiyar, Y.; Arafat, M.Y.; Andrabi, S.; Mir, Z.A.; Khan, N.A.; Langer, S. The evolution of integrated multi-trophic aquaculture in context of its design and components paving way to valorization via optimization and diversification. Aquaculture 2023, 565, 739074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giangrande, A.; Gravina, M.F.; Rossi, S.; Longo, C.; Pierri, C. Aquaculture and restoration: Perspectives from mediterranean sea experiences. Water 2021, 13, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleitou, P.; Kletou, D.; David, J. Is Europe Ready for Integrated Multi-Trophic Aquaculture? A Survey on the Perspectives of European Farmers and Scientists with IMTA Experience. Aquaculture 2018, 490, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, B.H.; Troell, M.F.; Krause, G.; Angel, D.L.; Grote, B.; Chopin, T. State of the Art and Challenges for Offshore Integrated Multi-Trophic Aquaculture (IMTA). Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, T.; Huang, D.; Liu, S. Integrated Multi-Trophic Aquaculture (IMTA) in Sanggou Bay, China. Aquac. Environ. Interact. 2016, 8, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carras, M.A.; Knowler, D.; Pearce, C.M.; Hamer, A.; Chopin, T.; Weaire, T. A Discounted Cash-Flow Analysis of Salmon Monoculture and Integrated Multi-Trophic Aquaculture in Eastern Canada. Aquac. Econ. Manag. 2020, 24, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanjani, M.H.; Zahedi, S.; Mohoammadi, A. Integrated Multitrophic Aquaculture (IMTA) as an Environmentally Friendly System for Sustainable Aquaculture: Functionality, Species, and Application of Biofloc Technology (BFT). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 67513–67531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, A.; Senff, P.; Glaser, M. Lessons for Coastal Applications of IMTA as a Way towards Sustainable Development: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 11920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.Q.; Yang, J.L.; Lai, X.X.; Li, W.; Zhan, M.J.; Zhang, C.P.; Jiang, J.Z.; Shu, H. Effects of integrated multi-trophic aquaculture on microbial communities, antibiotic resistance genes, and cultured species: A case study of four mariculture systems. Aquaculture 2022, 557, 738322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.L.; Zhou, F.; Ruan, Y.; Ma, B.; Ding, X.; Yue, X.; Ma, W.; Yin, X. Feed types driven differentiation of microbial community and functionality in marine integrated multitrophic aquaculture system. Water 2020, 12, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekirov, I.; Russell, S.L.; Antunes, C.M.; Finlay, B.B. Gut microbiota in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 859–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, L.M.P.; Cornet, J.; Donnay-Moreno, C.; Gouygou, J.P.; Berge, J.P.; Bacelar, M.; Escòrcio, C.; Rocha, E.; Malhão, F.; Cardinal, M. Quality Differences of Gilthead Sea Bream from Distinct Production Systems in Southern Europe: Intensive, Integrated, Semi-Intensive or Extensive Systems. Food Control 2011, 22, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotou, E.; Miliou, H.; Chatzoglou, E.; Schoina, E.; Politakis, N.; Kogiannou, D.; Fountoulaki, E.; Androni, A.; Konstantinopoulou, A.; Assimakopoulou, G.; et al. Growth Performance and Environmental Quality Indices and Biomarkers in a Co-Culture of the European Sea Bass with Filter and Deposit Feeders: A Case Study of an IMTA System. Fishes 2024, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlapani, F.F. Microbial diversity of seafood. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 37, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, L.M.P.; Linares, F.; Villanueva, J.L.R.; Silva, J.M.G.; Espe, M.; Escórcio, C.; Pires, M.A.; Saavedra, M.J.; Borges, P.; Medale, F. Dietary protein source or energy levels have no major impact on growth performance, nutrient utilisation or flesh fatty acids composition of market-sized Senegalese sole. Aquaculture 2011, 318, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarello, M.; Villeger, S.; Bouvier, C.; Bettarel, Y.; Bouvier, T. High diversity of skin-associated bacterial communities of marine fishes is promoted by their high variability among body parts, individuals and species. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2015, 91, fix061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quero, G.M.; Piredda, R.; Basili, M.; Maricchiolo, G.; Mirto, S.; Manini, E.; Seyfarth, A.M.; Candela, M.; Luna, G.M. Host-associated and environmental microbiomes in an open-sea Mediterranean gilthead sea bream fish farm. Microb. Ecol. 2023, 86, 1319–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milan, M.; Maroso, F.; Dalla Rovere, G.; Carraro, L.; Ferraresso, S.; Patarnello, T.l.; Bargelloni, L.; Cardazzo, B.; Fariselli, B. Tracing seafood at high spatial resolution using NGS-generated data and machine learning: Comparing microbiome versus SNPs. Food Chem. 2019, 286, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, A.; Cozzolino, D. How fishy is your fish? Authentication, provenance and traceability in fish and seafood by means of vibrational spectroscopy. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marimuthu, S.; Saikumar, A.; Badwaik, L.S. Food losses and wastage within food supply chain: A critical review of its generation, impact, and conversion techniques. Waste Dispos. Sustain. Energy 2024, 6, 661–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, M.; Kneifel, W.; Domig, K.J. A new view of the fish gut microbiome: Advances from next-generation sequencing. Aquaculture 2015, 448, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylvain, F.É.; Thomas, A. Symbionts: An Intricate Co-Dependence Relationship in a Changing Environment. In The Future of Amazonian Aquatic Biota; Springer: Cham, Germany, 2024; pp. 361–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Ju, C.; Mei, R.; Zhao, L.; Liu, J.; Yang, Y.; Guo, X.; Su, C.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, Q. Exploring the optimal integrated multi-trophic aquaculture (IMTA) patterns benefiting culture animals and natural water environment. Aquaculture 2024, 589, 741011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reale, A.; Tremonte, P.; Succi, M.; Di Renzo, T.; Capilongo, V.; Tipaldi, L.; Pannella, G.; Rosato, M.P.; Iaffaldano, N.; Coppola, R. Use of chitosan for the quality preservation of fresh sea bass fillets (Dicentrarchus labrax). Ind. Alim. 2011, 50, 13–20. [Google Scholar]
- Parlapani, F.F.; Michailidou, S.; Pasentsis, K.; Argiriou, A.; Krey, G.; Boziaris, I.S. A meta-barcoding approach to assess and compare the storage temperature-dependent bacterial diversity of gilt-head sea bream (Sparus aurata) originating from fish farms from two geographically distinct areas of Greece. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 278, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reale, A.; Sorrentino, E.; Iaffaldano, N.; Rosato, M.P.; Ragni, P.; Coppola, R.; Capitani, D.; Anatoli, P.S.; Tremonte, P.; Succi, M. Effects of ionizing radiation and modified atmosphere packaging on the shelf life of aqua-cultured sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 24, 2757–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Jia, Z.; An, J.; Ding, Y.; Chang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X. Insights into the fish protein degradation induced by the fish-borne spoiler Pseudomonas psychrophila and Shewanella putrefaciens: From whole genome sequencing to quality changes. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2024, 416, 110675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrentino, E.; Succi, M.; Tipaldi, L.; Pannella, G.; Maiuro, L.; Sturchio, M.; Coppola, R.; Tremonte, P. Antimicrobial activity of gallic acid against food-related Pseudomonas strains and its use as biocontrol tool to improve the shelf life of fresh black truffles. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 266, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacumin, L.; Jayasinghe, A.S.; Pellegrini, M.; Comi, G. Evaluation of Different Techniques, including Modified Atmosphere, under Vacuum Packaging, Washing, and Latilactobacillus sakei as a Bioprotective Agent, to Increase the Shelf-Life of Fresh Gutted Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) and Sea Bream (Sparus aurata) Stored at 6 ± 2 °C. Biology 2022, 11, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Lan, W.; Xie, J. Ultrasound assisted treatment improves the preservation performance of chitosan-grafted-chlorogenic acid on refrigerated sea bass (Lateolabrax japonicus) fillets. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 103, 900–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority; European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. The European Union One Health 2023 Zoonoses report. EFSA J. 2024, 22, e9106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrentino, E.; Tremonte, P.; Succi, M.; Iorizzo, M.; Pannella, G.; Lombardi, S.J.; Sturchio, M.; Coppola, R. Detection of Antilisterial Activity of 3-Phenyllactic Acid Using Listeria innocua as a Model. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, F.; Younes, A. Fish contamination: Analysis of the EU RASFF notifications over the last 23 years. Food Control 2024, 161, 110404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.C.C.P.; Floriano, B.; Villegas, I.M.B.; Rodríguez-Ruiz, J.P.; Posada-Izquierdo, G.D.; Zurera, G.; Pérez-Rodríguez, F. Study of the microbiological quality, prevalence of foodborne pathogens and product shelf-life of Gilthead Sea bream (Sparus aurata) and Sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) from aquaculture in estuarine ecosystems of Andalusia (Spain). Food Microb. 2020, 90, 103498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyautey, E.; Lapen, D.R.; Wilkes, G.; McCleary, K.; Pagotto, F.; Tyler, K.; Hartmann, A.; Piveteau, P.; Rieu, A.; Robertson, J. Distribution and characteristics of Listeria monocytogenes isolates from surface waters of the South Nation River watershed, Ontario, Canada. Appl. Envirom. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5401–5410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jami, M.; Ghanbari, M.; Zunabovic, M.; Domig, K.J.; Kneifel, W. Listeria monocytogenes in aquatic food products—A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 798–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, V.M.; Alves, V.F.; Destro, M.T.; De Martinis, E.C.P. Quantitative evaluation of Listeria monocytogenes in fresh and processed surubim fish (Pseudoplatystoma sp). Braz. J. Microbiol. 2008, 39, 527–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremonte, P.; Succi, M.; Coppola, R.; Sorrentino, E.; Tipaldi, L.; Ticariello, G.; Pannella, G.; Fraternali, F. Homology-based modeling of universal stress protein from Listeria innocua up-regulated under acid stress conditions. Front. Microb. 2016, 7, 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremonte, P.; Pannella, G.; Succi, M.; Tipaldi, L.; Sturchio, M.; Coppola, R.; Luongo, D.; Sorrentino, E. Antimicrobial activity of Lactobacillus plantarum strains isolated from different environments: A preliminary study. Int. Food Res. J. 2017, 24, 852–859. [Google Scholar]
- Arab, S.; Nalbone, L.; Giarratana, F.; Berbar, A. Occurrence of Vibrio spp. along the Algerian Mediterranean coast in wild and farmed Sparus aurata and Dicentrarchus labrax. Vet. World 2020, 13, 1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, P.V.; Brundha, A.R.; Kudre, T.G.; Sandesh, S.K. Valorization of Seafood Processing By-Products for Bioactive Compounds. In Nutraceutics from Agri-Food By-Products; Hoboken: New Jersey, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 319–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlapani, F.F.; Ferrocino, I.; Michailidou, S.; Argiriou, A.; Haroutounian, S.A.; Kokokiris, L.; Rantsiou, K.; Boziaris, I.S. Microbiota and volatilome profile of fresh and chill-stored deepwater rose shrimp (Parapenaeus longirostris). Food Res. Int. 2020, 132, 109057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaly, A.E.; Dave, D.; Budge, S.; Brooks, M.S. Fish Spoilage Mechanisms and Preservation Techniques: Review. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2010, 7, 859–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alasalvar, C.; Miyashita, K.; Shahidi, F.; Wanasundara, U. Handbook of Seafood Quality, Safety and Health Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Hou, Z.M.; Luo, Z.F.; Fang, Y.L.; Huang, L.C.; Wu, X.N.; Chen, Q.J.; Wang, Q.C. Impacts of microbial interactions on underground hydrogen storage in porous media: A comprehensive review of experimental, numerical, and field studies. Pet. Sci. 2024, 21, 4067–4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosado, D.; Pérez-Losada, M.; Severino, R.; Cable, J.; Xavier, R. Characterization of the skin and gill microbiomes of the farmed seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) and seabream (Sparus aurata). Aquaculture 2019, 500, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimat, V.; Barbieri, F.; Montanari, C.; Gardini, F.; Skroza, D.; Mekinić, I.G. Biopreservation of Fish. In Novel Approaches in Biopreservation for Food and Clinical Purposes; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; pp. 98–129. [Google Scholar]
- Fratianni, F.; Ombra, M.N.; Cozzolino, A.; Riccardi, R.; Spigno, P.; Tremonte, P.; Coppola, R.; Nazzaro, F. Phenolic constituents, antioxidant, antimicrobial and anti-proliferative activities of different endemic Italian varieties of garlic (Allium sativum L.). J. Funct. Foods 2016, 21, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, S.J.; Pannella, G.; Coppola, F.; Vergalito, F.; Maiuro, L.; Sicci, M.; Sorrentino, E.; Tremonte, P.; Coppola, R. Plant-Based Ingredients Utilized as Fat Replacers and Natural Antimicrobial Agents in Beef Burgers. Foods 2024, 13, 3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tremonte, P.; Pannella, G.; Lombardi, S.J.; Iorizzo, M.; Vergalito, F.; Cozzolino, A.; Maiuro, L.; Succi, M.; Sorrentino, E.; Coppola, R. Low-Fat and High-Quality Fermented Sausages. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrentino, E.; Reale, A.; Tremonte, P.; Maiuro, L.; Succi, M.; Tipaldi, L.; Di Renzo, T.; Pannella, G.; Coppola, R. Lactobacillus plantarum 29 inhibits Penicillium spp. involved in the spoilage of black truffles (Tuber aestivum). J. Food Sci. 2013, 78, M1188–M1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Succi, M.; Pannella, G.; Tremonte, P.; Tipaldi, L.; Coppola, R.; Iorizzo, M.; Lombardi, S.J.; Sorrentino, E. Sub-optimal pH preadaptation improves the survival of Lactobacillus plantarum strains and the malic acid consumption in wine-like medium. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathod, N.B.; Nirmal, N.P.; Pagarkar, A.; Özogul, F.; Rocha, J.M. Antimicrobial impacts of microbial metabolites on the preservation of fish and fishery products: A review with current knowledge. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto de Rezende, L.; Barbosa, J.; Teixeira, P. Analysis of Alternative Shelf Life-Extending Protocols and Their Effect on the Preservation of Seafood Products. Foods 2022, 11, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Kim, H.; Ryu, S. Bacteriophage and endolysin engineering for biocontrol of food pathogens/pathogens in the food: Recent advances and future trends. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 8919–8938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barache, N.; Belguesmia, Y.; Martinez, B.; Seal, B.S.; Drider, D.J.E. Bacteriocins and bacteriophages as dual biological players for food safety applications. Encyclopedia 2024, 4, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Guo, Z.; Xie, J. A critical analysis of the opportunities and challenges of phage application in seafood quality control. Foods 2024, 13, 3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.Q.; Tao, X.Y.; Zhang, H.; Rao, S.Q.; Gao, L.; Pan, Z.M.; Jiao, X.A. Isolation and characterization of virulent phages infecting Shewanella baltica and Shewanella putrefaciens, and their application for biopreservation of chilled channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 292, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, N.; Xia, H.; Hou, W.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Zhou, M. Biological characterization of Pseudomonas fluorescens Phage Pf17397_F_PD1 and its application in food preservation. J. Food Prot. 2023, 86, 100125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. 2021. Available online: http://www.fao.org/platform-food-loss-waste/en/ (accessed on 14 December 2024).
- Kaza, S.; Yao, L.; Bhada-Tata, P.; Van Woerden, F. What a Waste 2.0: A Global Snapshot of Solid Waste Management to 2050; World Bank Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Love, D.C.; Asche, F.; Fry, J.; Nguyen, L.; Gephart, J.; Garlock, T.M.; Jenckins, L.D.; Anderson, J.L.; Brown, M.; Viglia, S.; et al. Aquatic food loss and waste rate in the United States is half of earlier estimates. Nat. Food 2023, 4, 1058–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racioppo, A.; Speranza, B.; Campaniello, D.; Sinigaglia, M.; Corbo, M.R.; Bevilacqua, A. Fish loss/waste and low-value fish challenges: State of art, advances, and perspectives. Foods 2021, 10, 2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tola, F.; Mosconi, E.M.; Branca, G.; Natali, F.; Gianvincenzi, M.; Nosova, B.; Colantoni, A. Analysis of wastage mechanisms in the supply chain of fish products in a circular economy perspective: Empirical research. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontominas, M.G.; Badeka, A.V.; Kosma, I.S.; Nathanailides, C.I. Innovative Seafood Preservation Technologies: Recent Developments. Animals 2021, 11, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, R.; Roy, K.; Pan, J.; Shah, B.R.; Mraz, J. Critical review on the use of essential oils against spoilage in chilled stored fish: A quantitative metaanalyses. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 111, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiepour, A.; Zahmatkesh, F.; Babakhani, A. Preservation Techniques to Increase the Shelf Life of Seafood Products: An Overview. J. Food Eng. Technol. 2024, 13, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, R.K.; Kakatkar, A.S.; Debbarma, A.; Mishra, P.K.; Kumar, V.; Shashidhar, R.; Chatterjee, S. Shelf-life extension of ready-to-cook Tilapia (Oreochromis spp.) fish balls using hurdle technology. Food Biosci. 2025, 163, 05739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.; Gine, G.R.; Lei, Y.; Shi, Z.; Jiang, B.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, H. Ready-to-Cook Foods: Technological Developments and Future Trends—A Systematic Review. Foods 2024, 13, 3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, M.R.; Hsieh, S.; Ricacho, N. Innovative food packaging, food quality and safety, and consumer perspectives. Processes 2022, 10, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Dewshmukh, R. Packaged Food Market Size, Share, Competitive Landscape and Trend Analysis Report, by Type, Sales Channel (Supermarket/Hypermarket, Specialty Stores, Grocery Stores, Online Stores, and Others: Global Opportunity Analysis and Industry Forecast, 2021–2030; Allied Market Research: Portland, OR, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, S.; Xu, X.W.; Ren, Y.; Bai, X.; Xia, X. Preparation of NH3- and H2S-sensitive intelligent pH indicator film from sodium alginate/black soybean seed coat anthocyanins and its use in monitoring meat freshness. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2023, 35, 100994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.B.; Huang, F.; Lu, Y.H.; Huang, J.M.; Ali, M.; Jia, X.Z.; Zeng, X.A.; Huang, Y.Y. Polysaccharide-based food packaging and intelligent packaging applications: A comprehensive review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 147, 104390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Wani, A.A.; Langowski, H.C. Food Packaging Materials: Testing & Quality Assurance; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wikstrom, F.; Verghese, K. Packaging strategies that save food: A research agenda for 2030. J. Ind. Ecol. 2018, 23, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnier, L.; Crié, D. Communicating packaging eco-friendliness: An exploration of consumers’ perceptions of eco-designed packaging. Int. J. Retail. Distrib. Manag. 2015, 43, 350–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominic, C.A.; Ostlund, S.; Buffington, J.; Masoud, M.M. Towards a conceptual sustainable packaging development model: A corrugated box case study. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2015, 28, 397.e413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cofelice, M.; Iftikhar, A.; Lopez, F.; De Leonardis, A. Effect of edible coatings on quality parameters and phenol composition of ready-to-eat Salanova lettuce. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2024, 250, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, A.R.; Boumans, H.; Slaghek, T.; Van Veen, J.; Rijk, R.; Van Zandvoort, M. Active and intelligent packaging for food: Is it the future? Food Addit. Contam. 2005, 22, 975–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Council Directive 89/107/EEC of 21 December 1988 on the Approximation of the Laws of the Member States Concerning Food Additives Authorized for Use in Foodstuffs Intended for Human Consumption. OJ L 40 11.02.1989, p. 27, ELI. Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/dir/1989/107/oj (accessed on 7 November 2024).
- Prasad, J.; Dixit, A.; Sharma, S.P.; Mwakosya, A.W.; Petkoska, A.T.; Upadhyay, A.; Kumar, N. Nanoemulsion based active packaging for food products. Foods Raw Mater. 2024, 12, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Chen, Y.; Liu, H.; Yu, L.; Baloch, Z.; Khalid, S.; Zu, J.; Chen, L. Starch-based antimicrobial films functionalized by pomegranate peel. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 129, 1120–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; Xiao, Q.; Ru, Y.; Hong, Q.; Weng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Xiao, A. Bio-based active packaging: Gallic acid modified agarose coatings in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) preservation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 255, 128196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Lan, W.; Xie, J. Phenolic acid-chitosan derivatives: An effective strategy to cope with food preservation problems. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 254, 127917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maleki, M.; Mohsenzadeh, M. Biodegradable Nanocomposite Film Based on Carboxymethyl Cellulose/Persian Gum Containing TiO2 and Fennel Essential Oil: Investigation of Chemical, Antimicrobial, and Sensory Properties on Rainbow Trout Fillet. J. Polym. Environ. 2022, 30, 3316–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshaghi, R.; Mohsenzadeh, M.; Ayala-Zavala, J.F. Bionanocomposite active packaging films based on carboxymethyl cellulose, myrrh gum, TiO2 nanoparticles and dill essential oil for preserving fresh-fish (Cyprinus carpio) meat quality. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 263, 129991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaani, M.; Cozzolino, C.A.; Castelli, G.; Farris, S. An overview of the intelligent packaging technologies in the food sector. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrucka, R.; Przekop, R. New perspectives in active and intelligent food packaging. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2019, 43, e14194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetinkaya, T.; Bildik, F.; Altay, F.; Ceylan, Z. Gelatin nanofibers with black elderberry, Au nanoparticles and SnO2 as intelligent packaging layer used for monitoring freshness of Hake fish. Food Chem. 2024, 437, 137843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 27 October 2004 on Materials and Articles Intended to Come into Contact with Food and Repealing Directives 80/590/EEC and 89/109/EEC. O J L 338, 13.11.2004. pp. 4–17. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX%3A02004R1935-20210327 (accessed on 14 December 2024).
- Mahapatra, D.; Goswami, S.; Das, M. New-Age Packaging for Foods and Food Products. In Food Process Engineering and Technology: Safety, Packaging, Nanotechnologies and Human Health; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2024; pp. 165–187. [Google Scholar]
- Lalit, R.; Mayank, P.; Ankur, K. Natural Fibers and Biopolymers Characterization: A Future Potential Composite Material. Stroj. Cas. J. Mech. Eng. 2018, 68, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokoglu, N. Innovations in Seafood Packaging Technologies. Handbook of Seafood and Seafood Products Analysis; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; pp. 868–889. [Google Scholar]
- Zaragozá, P.; Fuentes, A.; Fernández-Segovia, I.; Vivancos, J.L.; Rizo, A.; Ros-Lis, J.V.; Barat, J.M.; Martínez-Máñez, R. Evaluation of sea bream (Sparus aurata) shelf life using an optoelectronic nose. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 1374–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacquit, A.; Frisby, J.; Diamond, D.; Lau, K.T.; Farrell, A.; Quilty, B.; Diamond, D. Development of a smart packaging for the monitoring of fish spoilage. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 466–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavassoli, M.; Khezerlou, A.; Bakhshizadeh, M.; Ebrahimi, A.; Abedi-Firoozjah, R.; Alizadeh-Sani, M.; Mohammadian, E.; Ehsani, A.; Hashemi, M. Smart packaging containing red poppy anthocyanins for fish freshness monitoring. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2024, 18, 3054–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, W.Y.; Le, G.T.; Tran, T.V.; Nguyen, N.H. Novel proximal fish freshness monitoring using batteryless smart sensor tag. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 248, 910–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cofelice, M.; Lopez, F.; Cuomo, F. Quality control of fresh-cut apples after coating application. Foods 2019, 8, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacovino, S.; Cofelice, M.; Sorrentino, E.; Cuomo, F.; Messia, M.C.; Lopez, F. Alginate-Based Emulsions and Hydrogels for Extending the Shelf Life of Banana Fruit. Gels 2024, 10, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sucharitha, K.V.; Beulah, A.M.; Ravikiran, K. Effect of chitosan coating on storage stability of tomatoes (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill). Int. Food Res. J. 2018, 25, 93–99. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Rhim, J.W. Titanium dioxide (TiO2) for the manufacture of multifunctional active food packaging films. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2022, 31, 100806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibowo, C.; Salsabila, S.; Muna, A.; Rusliman, D.; Wasisto, H.S. Advanced biopolymer-based edible coating technologies for food preservation and packaging. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2024, 23, e13275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhag, R.; Kumar, N.; Petkoska, A.T.; Upadhyay, A. Film formation and deposition methods of edible coating on food products: A review. Food Res. Int. 2020, 136, 109582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umaraw, P.; Munekata, P.E.S.; Verma, A.K.; Barba, F.J.; Singh, V.P.; Kumar, P.; Lorenzo, J.M. Edible films/coating with tailored properties for active packaging of meat, fish and derived products. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 98, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vettorazzi, A.; Lopez de Cerain, A.; Sanz-Serrano, J.; Gil, A.G.; Azqueta, A. European regulatory framework and safety assessment of food-related bioactive compounds. Nutrients 2020, 12, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcoléa, M.; Junior, M.B.S.; de Moura Oliveira, K.A.; Tussolini, L.; Leite, M.A.G.; Honorio-França, A.C.; França, E.L.; Pertuzatti, P.B. Bioactive compounds of honey from different regions of Brazil: The effect of simulated gastrointestinal digestion on antioxidant and antimicrobial properties. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 1310–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozdemirli, N.; Kamiloglu, S. Phytochemical Compounds of Citrus Fruits: Analytical Approach and Effect of Processing. In Citrus Fruits and Juice: Processing and Quality Profiling; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2024; pp. 89–107. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, A.; Sarkar, B. Polyphenols and terpenoids derived from Ocimum species as prospective hepatoprotective drug leads: A comprehensive mechanistic review. Phytochem. Rev. 2024, 15, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.A.H.; Rana, S.L.; Mohany, M.; Milošević, M.; Al-Rejaie, S.A.; Farooq, M.A.; Faisal, M.N.; Aleem, A. Fumaria indica (Hausskn.) Pugsley Hydromethanolic Extract: Bioactive Compounds Identification, Hypotensive Mechanism, and Cardioprotective Potential Exploration. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 3642–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morshdy, A.E.M.; El-Tahlawy, A.S.; Wageh, A.E.S.E.H.; Darwish, S.; Darwish, W.S. Coriander as a natural antimicrobial for meat products: A One Health perspective review. Theory Pract. Meat Process. 2024, 9, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Council Directive 2008/98/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 19 November 2008 on Waste and Repealing Certain Directives; OJ L 312, 22.11.2008. pp. 3–30. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/ALL/?uri=celex%3A32008L0098 (accessed on 10 January 2025).
- Haj Salem, M.; Aidi Wannes, W.; Mejri, H.; Belloumi, S.; Aouini, J.; Fares, N.; Selmi, S.; Msaada, K.; Sriti, J. Effect of regional disparities and solvent variations on the phenolic composition, antioxidant activity, and antibacterial efficacy of Cupressus sempervirens extracts. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2024, 34, 3810–3819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2008 on Food Additives; O. J. L. 354, 31.12. 2008. pp. 16–33. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?from=EN&uri=CELEX%3A02008R1333-20221031 (accessed on 14 December 2024).
- Weng, Z.; Zeng, F.; Wang, M.; Guo, S.; Tang, Z.; Itagaki, K.; Lin, Y.; Shen, X.; Cao, Y.; Duan, J.; et al. Antimicrobial activities of lavandulylated flavonoids in Sophora flavences against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus via membrane disruption. J. Adv. Res. 2024, 57, 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Liu, L.; Shen, H.; You, J.; Luo, Y. Effect of sodium alginate-based edible coating containing different antioxidants on quality and shelf life of refrigerated bream (Megalobrama amblycephala). Food Control. 2011, 22, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugihara, K.; Kamada, N. Metabolic network of the gut microbiota in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm. Regen. 2024, 44, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayeli, M.; Mehdizadeh, T.; Tajik, H.; Esmaeli, F.; Langroodi, A.M. Combined impacts of zein coating enriched with methanolic and ethanolic extracts of sour orange peel and vacuum packing on the shelf life of refrigerated rainbow trout. Flavour Fragr. J. 2019, 34, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisar, T.; Yang, X.; Alim, A.; Iqbal, M.; Wang, Z.C.; Guo, Y. Physicochemical responses and microbiological changes of bream (Megalobrama ambycephala) to pectin-based coatings enriched with clove essential oil during refrigeration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 124, 1156–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaeifar, M.; Mehdizadeh, T.; Mojaddar Langroodi, A.; Rezaei, F. Effect of chitosan edible coating enriched with lemon ver- bena extract and essential oil on the shelf life of vacuum rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). J. Food Saf. 2020, 40, e12781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanasopoulou, E.; Bigi, F.; Maurizzi, E.; Karellou, E.I.E.; Pappas, C.S.; Quartieri, A.; Tsironi, T. Synthesis and characterization of polysaccharide-and protein-based edible films and application as packaging materials for fresh fish fillets. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aşik, E.; Candoǧan, K. Effects of chitosan coatings incorporated with garlic oil on quality characteristics of shrimp. J. Food Qual. 2014, 37, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremenkamp, I.; Sousa Gallagher, M.J. Edible coatings for ready-to-eat products: Critical review of recent studies, sustainable packaging perspectives, challenges and emerging trends. Polymers 2025, 17, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choulitoudi, E.; Bravou, K.; Bimpilas, A.; Tsironi, T.; Tsimogiannis, D.; Taoukis, P.; Oreopoulou, V. Antimicrobial and antioxidant activity of Satureja thymbra in gilthead seabream fillets edible coating. Food Bioprod. Process. 2016, 100, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission Regulation (EC) No 1130/2011 of 11 November 2011 amending Annex III to Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council on food additives by establishing a Union list of food additives approved for use in food additives, food enzymes, food flavourings and nutrients. Off. J. Eur. Union 2011, 295, 178–204.
- Commission Regulation (EC) No 2023/2006 of 22 December 2006 on good manufacturing practice for materials and articles intended to come into contact with food. Off. J. Eur. Union 2006, 384, 75–78.
- Food and Drug Administration. Code of Federal Regulations. Part 182: Substances Generally Recognized as Safe; Food and Drug Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; p. 3. [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi, A.D.; Sharma, R.; Agarwal, A.; Haleem, D.R. Nanoemulsions based edible coatings with potential food applications. Int. J. Biobased Plast. 2021, 3, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leporini, M.; Loizzo, M.R.; Sicari, V.; Pellicanò, T.M.; Reitano, A.; Dugay, A.; Deguin, B.; Tundis, R. Juice Enriched with Its By-Products (Peels and Leaves): Chemical Composition, In Vitro Bioactivity, and Impact of Processing. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, M.T.; Moreno, F.J.; Villamiel, M. Chemical and physicochemical characterization of orange by-products derived from industry. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 868–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavan, P.; Singh, A.K.; Kaur, G. Recent progress in the utilization of industrial waste and by-products of citrus fruits: A review. Food Process Eng. 2018, 41, e12895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Job, J.T.; Visakh, N.U.; Pathrose, B.; Alfarhan, A.; Rajagopal, R.; Thayyullathil, J.; Thejass, P.; Ramesh, V.; Narayanankutty, A. Composition and Biological Activities of the Essential Oil from Citrus reticulata Blanco Peels Collected from Agrowastes. Chem. Biodivers. 2024, 21, e202301223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayakumar, A.; Radoor, S.; Shin, G.H.; Kim, J.T. Lemon peel-based fluorescent carbon quantum dots as a functional filler in polyvinyl alcohol-based films for active packaging applications. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 209, 117968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremonte, P.; Succi, M.; Reale, A.; Di Renzo, T.; Sorrentino, E.; Coppola, R. Interactions between strains of Staphylococcus xylosus and Kocuria varians isolated from fermented meats. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 103, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belluco, C.Z.; Mendonça, F.J.; Zago, I.C.C.; Di Santis, G.W.; Marchi, D.F.; Soares, A.L. Application of orange albedo fat replacer in chicken mortadella. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 59, 3659–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdan, M.; Jaradat, N.; Al-Maharik, N.; Ismail, S.; Qadi, M. Chemical composition, cytotoxic effects, and antimicrobial activity of combined essential oils from Citrus meyeri, Citrus paradise, and Citrus sinensis leaves. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 210, 118096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M’hiri, N.; Ioannou, I.; Ghoul, M.; Boudhrioua, N.M. Proximate chemical composition of orange peel and variation of phenols and antioxidant activity during convective air drying. J. New Sci. 2015, 9, 881–890. [Google Scholar]
- Bandi, I.I.; Ibrahim, A.; Shehu, I.; Gobir, A.Z.S.; Bature, B.H.; Rara, S.S. Phytochemicals Screening, Proximate composition and Antioxidants Analysis of Italian Citrus paradisi Fruits. J. Trop. Pharm. Chem. 2024, 8, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, F.; Jin, R.; Sun, J.; Ma, B.; ì Bao, X. Evaluation of mechanical-pressed essential oil from Nanfeng mandarin (Citrus reticulata Blanco cv. Kinokuni) as a food preservative based on antimicrobial and antioxidant activities. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 95, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhikara, N.; Kour, R.; Jaglan, S.; Gupta, P.; Gat, Y.; Panghal, A. Citrus medica: Nutritional, phytochemical composition and health benefits—A review. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 1978–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Mejía, E.; Rosales-Conrado, N.; León-González, M.E.; Madrid, Y. Citrus peels waste as a source of value-added compounds: Extraction and quantification of bioactive polyphenols. Food Chem. 2019, 295, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos, F.K.F.; Barcellos-Silva, I.G.C.; Leite-Barbosa, O.; Ribeiro, R.; Cunha-Silva, Y.; Veiga-Junior, V.F. High Added-Value By-Products from Biomass: A Case Study Unveiling Opportunities for Strengthening the Agroindustry Value Chain. Biomass 2024, 4, 217–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calo, J.R.; Crandall, P.G.; O’Bryan, C.A.; Ricke, S.C. Essential oils as antimicrobials in food systems—A review. Food Control 2015, 54, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, S.; Aggarwal, P.; Kumar, A.; Kaur, S.; Yadav, R.; Babbar, N. Utilizing citrus peel waste: A review of essential oil extraction, characterization, and food-industry potential. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2024, 15, 5043–5064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froiio, F.; Mosaddik, A.; Morshed, M.T.; Paolino, D.; Fessi, H.; Elaissari, A. Edible polymers for essential oils encapsulation: Application in food preservation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 20932–20945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atares, L.; Chiralt, A. Essential oils as additives in biodegradable films and coatings for active food packaging. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 48, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozogul, Y.; Yuvka, İ.; Ucar, Y.; Durmus, M.; Kösker, A.R.; Öz, M.; Ozogul, F. Evaluation of effects of nanoemulsion based on herb essential oils (rosemary, laurel, thyme and sage) on sensory, chemical and microbiological quality of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) fillets during ice storage. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 75, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ucak, I.; Khalily, R.; Carrillo, C.; Tomasevic, I.; Barba, F.J. Potential of propolis extract as a natural antioxidant and antimicrobial in gelatin films applied to rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) fillets. Foods 2020, 9, 1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosio, C.M.S.; Ikeda, N.Y.; Miano, A.C.; Saldaña, E.; Moreno, A.M.; Stashenko, E.; Contreras-Castillo, C.J.; Da Gloria, E.M. Unraveling the selective antibacterial activity and chemical composition of citrus essential oils. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Filho, J.G.; de Deus, I.P.B.; Valadares, A.C.F.; Fernandes, C.C.; Estevam, E.B.B.; Egea, M.B. Chitosan film with citrus limonia essential oil: Physical and morphological properties and antibacterial activity. Colloids Interfaces 2020, 4, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisar, T.; Wang, Z.C.; Yang, X.; Tian, Y.; Iqbal, M.; Guo, Y. Characterization of citrus pectin films integrated with clove bud essential oil: Physical, thermal, barrier, antioxidant, and antibacterial properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 106, 670–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agdar GhareAghaji, M.; Zomordi, S.; Gharekhani, M.; Hanifian, S. Effect of edible coating based on salep containing orange (Citrus sinensis) peel essential oil on shelf life of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) fillets. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, e15737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabu, S.; Ashita, T.; Stephy, S. Chitosan and lemon peel extract coating on quality and shelf life of yellowfin tuna (Thunnus albacares) meat stored under refrigerated condition. Indian. J. Fish. 2020, 67, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilinç, B.; Sürengil, G.; Yalçın, T. The impact of edible film coatings with lemon and orange peel extracts on microbiological quality and shelf-life of squid (Loligo vulgaris) rings and rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) fillets. Kahramanmaraş Sütçü İmam Üniversitesi Tarım ve Doğa Dergisi 2023, 26, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahmandfar, R.; Tirgarian, B.; Dehghan, B.; Nemati, A. Changes in chemical composition and biological activity of essential oil from Thomson navel orange (Citrus sinensis L. Osbeck) peel under freezing, convective, vacuum, and microwave drying methods. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Film Composition | Sample | Storage (°C) | Results | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zein, orange peel extract | Fish fillets | 4 | Inhibition of the microbial population and lipid oxidation, resulting in shelf-life extension. | [165] |
| Pectin | Sea bream fillets | 4 | Inhibition of the microbial population | [166] |
| Chitosan and lemon extract | Rainbow trout fillets | 4 | Increase of the storage period | [167] |
| Pectin, gelatin, and HPMC | Chilled gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) fillets | 2 | Increase of the storage period | [168] |
| Chitosan and garlic essential oil | Shrimp meat | 4 | Antimicrobial activity | [169] |
| Chitosan | Smoked sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) | 4 | Increase of the storage period | [170] |
| Satureja thymbra essential oil | Sea bream fillets | 0 | Antimicrobial and antioxidant effects. Increase of the storage period | [171] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rosati, S.; Maiuro, L.; Lombardi, S.J.; Iaffaldano, N.; Di Iorio, M.; Cariglia, M.; Lopez, F.; Cofelice, M.; Tremonte, P.; Sorrentino, E. Integrated Biotechnological Strategies for the Sustainability and Quality of Mediterranean Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) and Sea Bream (Sparus aurata). Foods 2025, 14, 1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14061020
Rosati S, Maiuro L, Lombardi SJ, Iaffaldano N, Di Iorio M, Cariglia M, Lopez F, Cofelice M, Tremonte P, Sorrentino E. Integrated Biotechnological Strategies for the Sustainability and Quality of Mediterranean Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) and Sea Bream (Sparus aurata). Foods. 2025; 14(6):1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14061020
Chicago/Turabian StyleRosati, Sebastiano, Lucia Maiuro, Silvia Jane Lombardi, Nicolaia Iaffaldano, Michele Di Iorio, Michela Cariglia, Francesco Lopez, Martina Cofelice, Patrizio Tremonte, and Elena Sorrentino. 2025. "Integrated Biotechnological Strategies for the Sustainability and Quality of Mediterranean Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) and Sea Bream (Sparus aurata)" Foods 14, no. 6: 1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14061020
APA StyleRosati, S., Maiuro, L., Lombardi, S. J., Iaffaldano, N., Di Iorio, M., Cariglia, M., Lopez, F., Cofelice, M., Tremonte, P., & Sorrentino, E. (2025). Integrated Biotechnological Strategies for the Sustainability and Quality of Mediterranean Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) and Sea Bream (Sparus aurata). Foods, 14(6), 1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14061020










