Environmental Stress and the Deterministic Assembly of Bacterial Communities in Daqu: The Role of Amino Acid Content Fluctuations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Determination of Physicochemical Indices
2.3. Quantitative Analysis of Carbohydrates and Amino Acids
2.4. Volatile Metabolites Analysis
2.5. DNA Extraction, Amplification, and Sequencing
2.6. Ecological Community Assembly Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sequence Quality Control
3.2. Temporal Changes in Fermentation Parameters and Metabolites
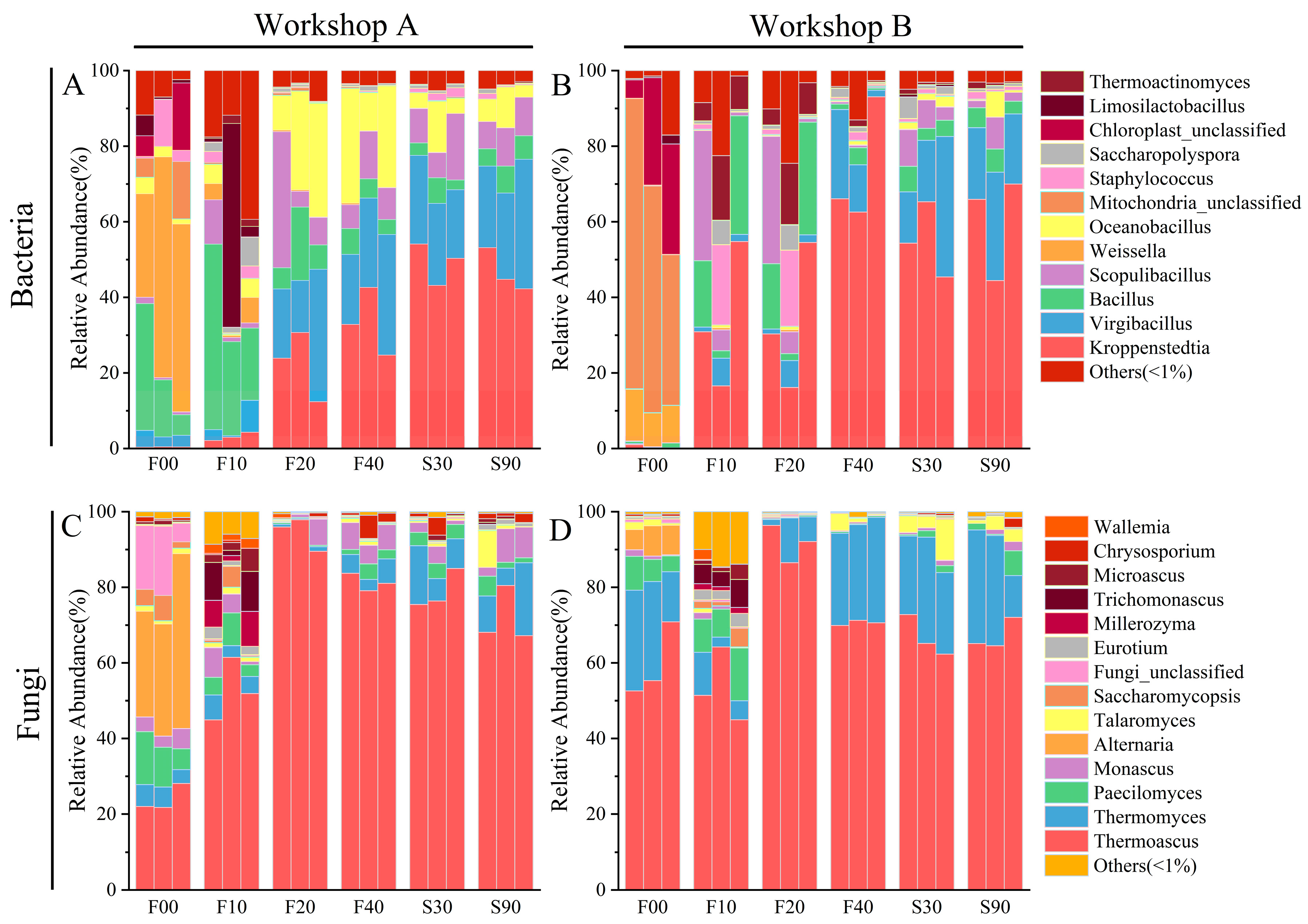
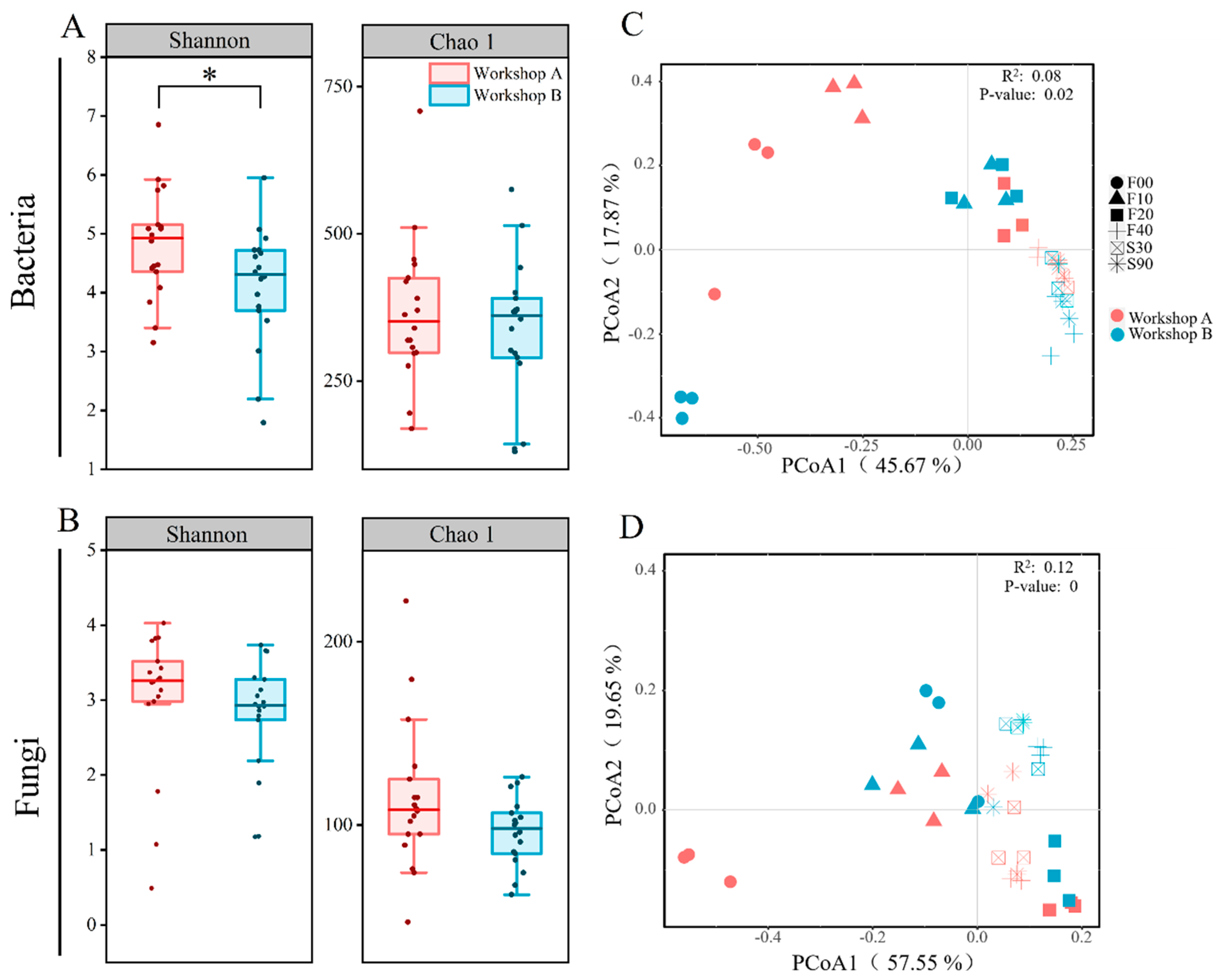
3.3. Microbial Diversity and Dynamics
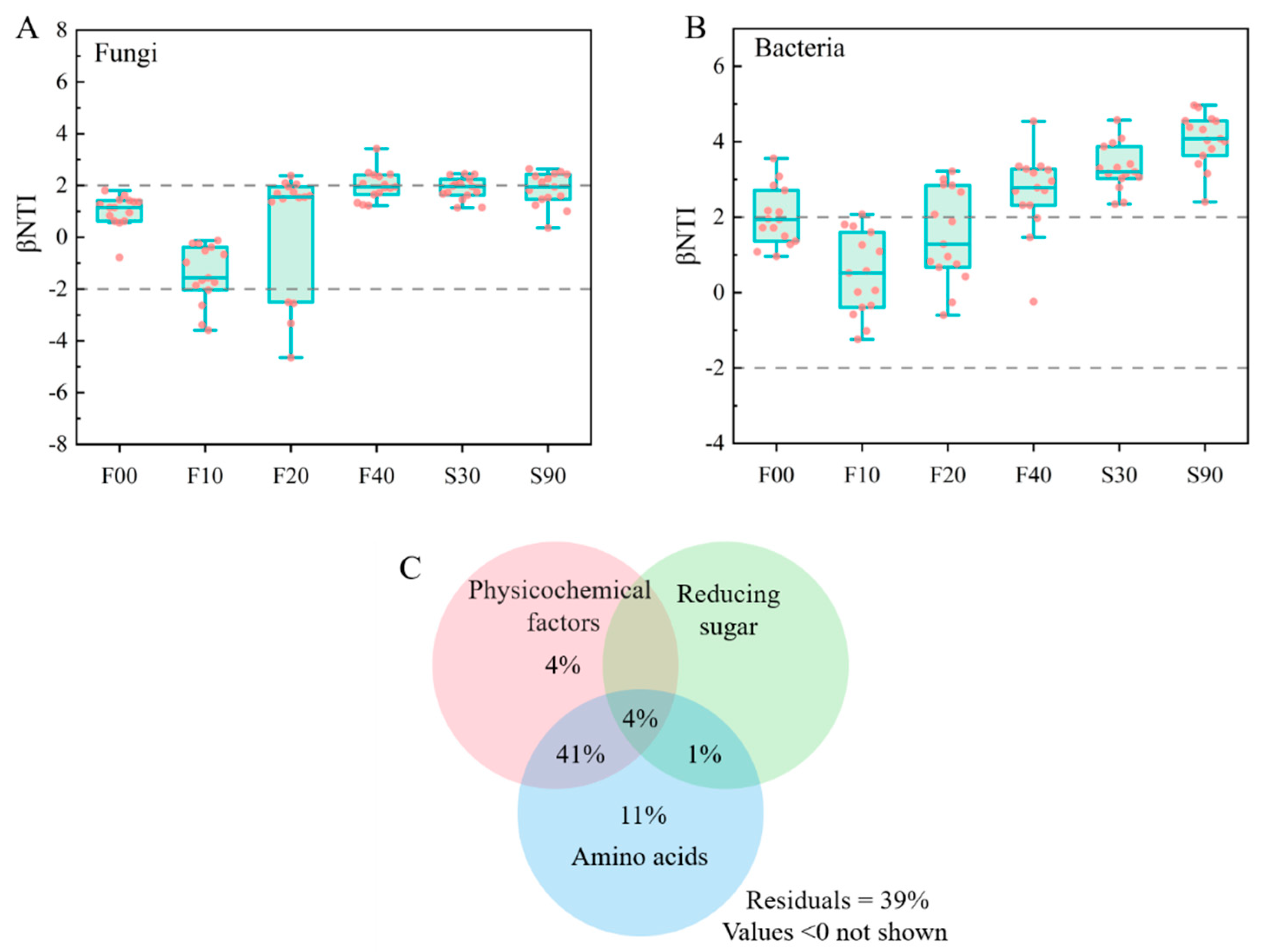
3.4. Community Assembly Patterns and Correlation Analysis
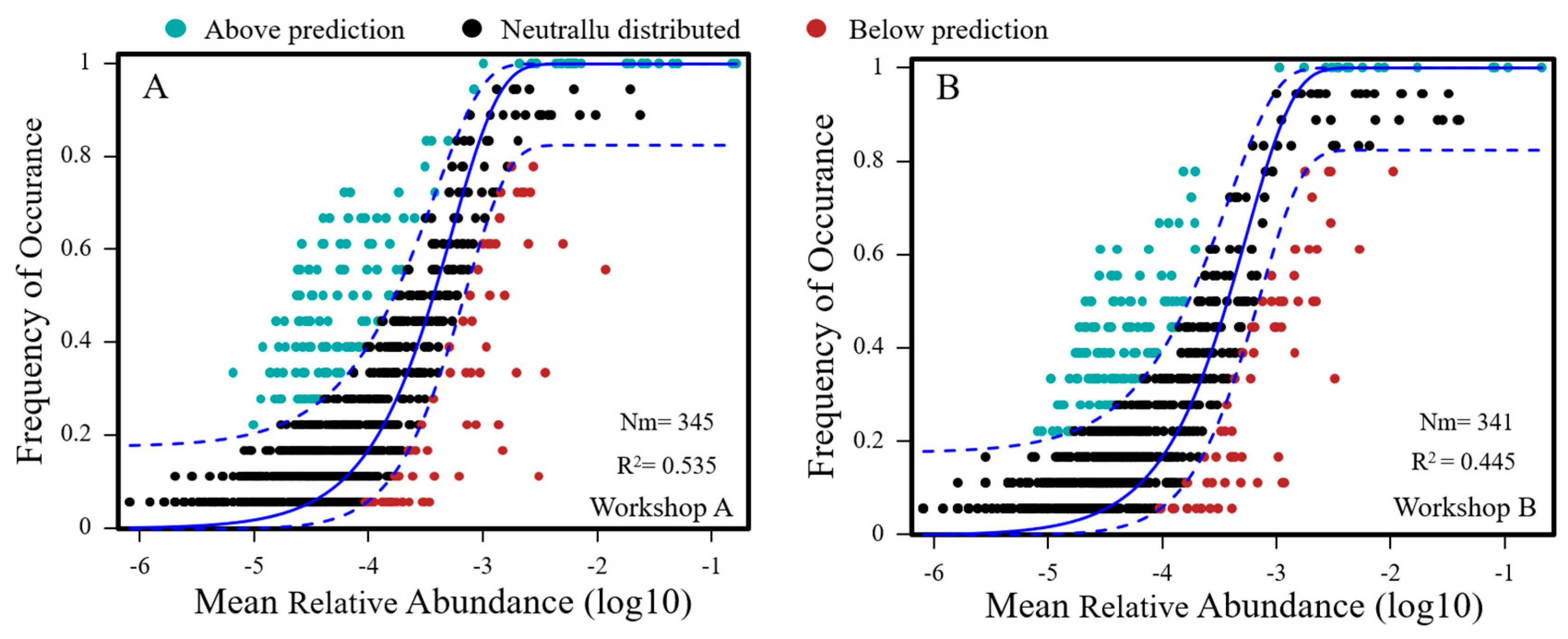
3.5. Fit to the Neutral Model of Community Assembly
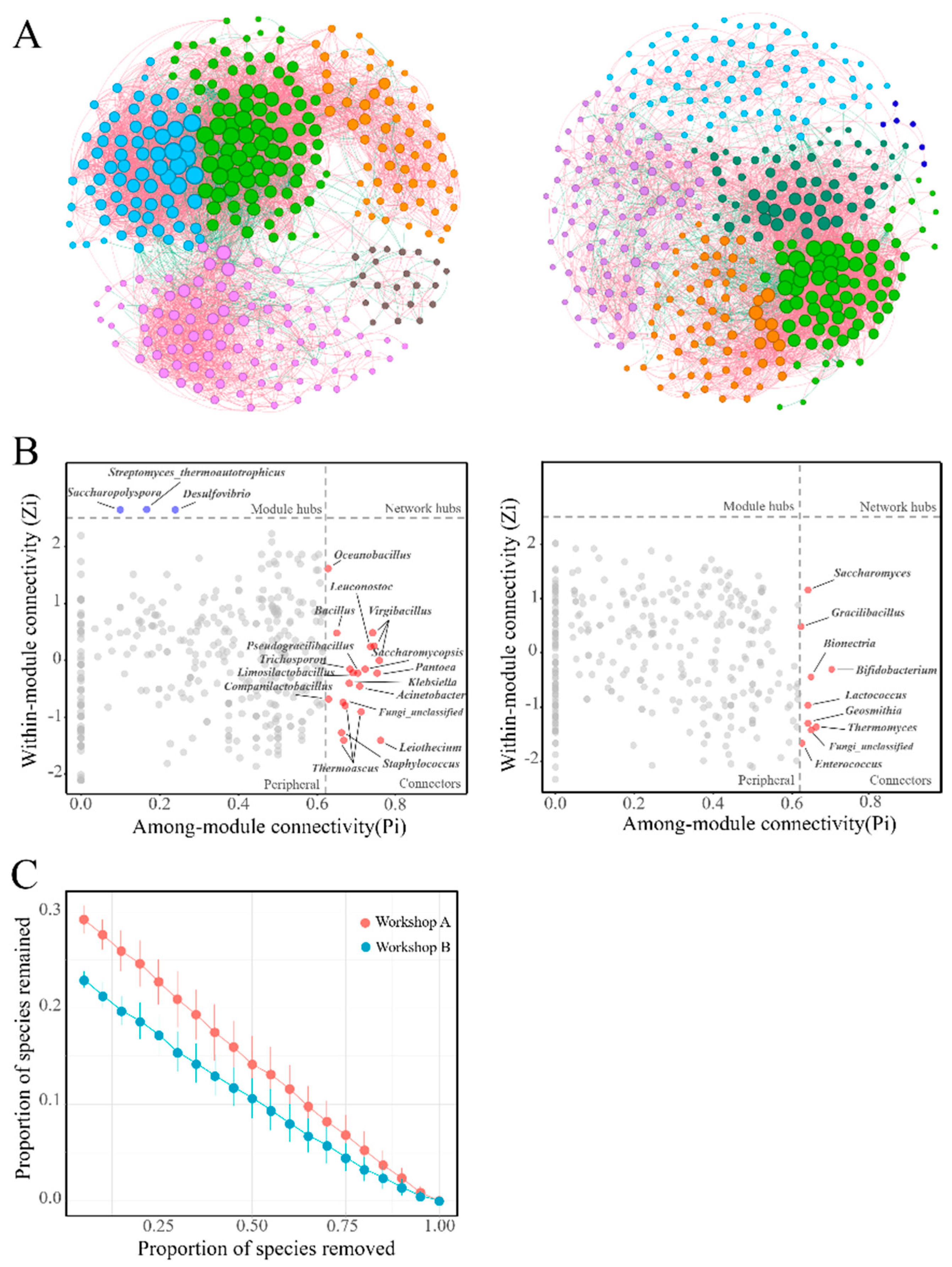
3.6. Complexity and Stability of Microbial Networks
3.7. Exploring for Abiotic Factors Driving the Keystone Node Metabolism
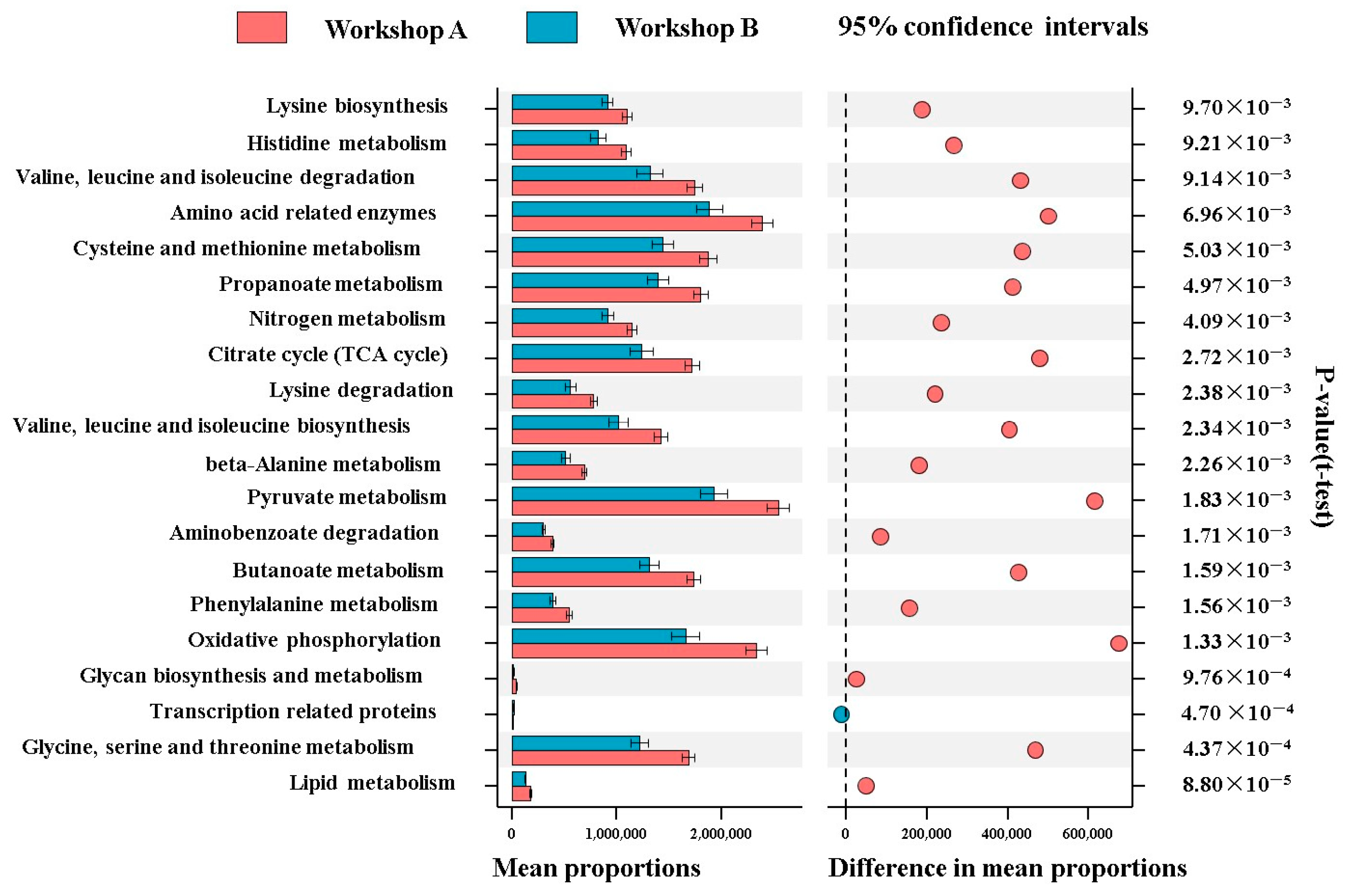
3.8. Prediction of Metabolic Pathways
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, L. Research Trends in Jiang-Flavor Baijiu Fermentation: From Fermentation Microecology to Environmental Ecology. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 1362–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yi, Z.; Jin, Y.; Huang, M.; He, K.; Liu, D.; Luo, H.; Zhao, D.; He, H.; Fang, Y.; et al. Metatranscriptomics Reveals the Functions and Enzyme Profiles of the Microbial Community in Chinese Nong-Flavor Liquor Starter. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Wu, Q.; Xu, Y.; Sun, B. Synergistic Effect of Multiple Saccharifying Enzymes on Alcoholic Fermentation for Chinese Baijiu Production. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e00013-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Fang, C.; Wijffels, R.H.; Xu, Y. Can We Control Microbiota in Spontaneous Food Fermentation?—Chinese Liquor as a Case Example. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 110, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Niu, M.-S.; Yu, H.; Shi, W.; Chai, L.-J.; Lu, Z.-M.; Liu, X.-T.; Shen, C.-H.; Xu, Z.-H.; Wang, S.-T.; et al. Exploring the Contribution of Temperature-Adapted Microbiota to Enzyme Profile of Saccharification in Daqu Using Metagenomics and Metaproteomics. LWT 2024, 197, 115916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukami, T. Historical Contingency in Community Assembly: Integrating Niches, Species Pools, and Priority Effects. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2015, 46, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gralka, M.; Szabo, R.; Stocker, R.; Cordero, O.X. Trophic Interactions and the Drivers of Microbial Community Assembly. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, R1176–R1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoph, R.; Julien, B.; Gore, J. Strength of Species Interactions Determines Biodiversity and Stability in Microbial Communities. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 4, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Lu, J.; Nie, Y.; Li, C.; Du, H.; Xu, Y. Amino Acids Drive the Deterministic Assembly Process of Fungal Community and Affect the Flavor Metabolites in Baijiu Fermentation. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e02640-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-T.; Deng, Y.-K.; Zou, Y.-F.; Han, B.-L.; Pu, J.-Z.; Rao, J.-Q.; Huang, D.; Luo, H.-B. Linking Microbial Functional Gene Abundance and Daqu Extracellular Enzyme Activity: Implications for Carbon Metabolism during Fermentation. Foods 2022, 11, 3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Chen, L.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, W.; Yang, F.; Du, G.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L. The Differences in Carbohydrate Utilization Ability between Six Rounds of Sauce-Flavor Daqu. Food Res. Int. 2023, 163, 112184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Fan, W.; Xu, Y. Chameleon-like Microbes Promote Microecological Differentiation of Daqu. Food Microbiol. 2023, 109, 104144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Niu, J.; Ding, F.; Ren, Y.; Chen, X.; Han, B.-Z. Bacteria-Induced Amino Acid Metabolism Involved in Appearance Characteristics of High-Temperature Daqu. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Jin, Y.; Zhou, R.; Zhao, D.; Zheng, J.; Wu, C. Dynamic Succession of Microbial Community in Nongxiangxing Daqu and Microbial Roles Involved in Flavor Formation. Food Res. Int. 2022, 159, 111559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-H.; Chai, L.-J.; Wang, H.-M.; Lu, Z.-M.; Zhang, X.-J.; Xiao, C.; Wang, S.-T.; Shen, C.-H.; Shi, J.-S.; Xu, Z.-H. Community-Level Bioaugmentation Results in Enzymatic Activity- and Aroma-Enhanced Daqu through Altering Microbial Community Structure and Metabolic Function. Food Biosci. 2024, 57, 103630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Liu, X.; Gao, T.; Gu, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Ma, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, J. Unraveling the Correlations between Bacterial Diversity, Physicochemical Properties and Bacterial Community Succession during the Fermentation of Traditional Chinese Strong-Flavor Daqu. LWT 2022, 154, 112764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, W.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Wang, S.; Huang, D.; Luo, H.; Zhao, L. Dynamic Analysis Caffeic Acid Production Driven by the Key Physicochemical Factor and Microbial Community Succession in Baijiu Daqu: A Multi-Microorganism Fermentation of Solid-State Fermentation System. LWT 2023, 190, 115542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Cheng, Y.; Zuo, Q.; Huang, Y.; Wang, L. Exploring the Impacts of Traditional Crafts on Microbial Community Succession in Jiang-Flavored Daqu. Food Res. Int. 2022, 158, 111568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louw, N.L.; Lele, K.; Ye, R.; Edwards, C.B.; Wolfe, B.E. Microbiome Assembly in Fermented Foods. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 77, 381–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, D.; Mu, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Qi, Q.; Mu, Y.; Su, W. Exploring the Heterogeneity of Community and Function and Correspondence of “Species-Enzymes” among Three Types of Daqu with Different Fermentation Peak-Temperature via High-Throughput Sequencing and Metagenomics. Food Res. Int. 2024, 176, 113805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Chai, L.-J.; Fang, G.-Y.; Mei, J.-L.; Lu, Z.-M.; Zhang, X.-J.; Xiao, C.; Wang, S.-T.; Shen, C.-H.; Shi, J.-S.; et al. Spatial Heterogeneity of the Microbiome and Metabolome Profiles of High-Temperature Daqu in the Same Workshop. Food Res. Int. 2022, 156, 111298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Rao, J.; Zou, Y.; Liao, L.; Huang, D.; Luo, H. The Community Assembly Patterns Determined Differences between the Surface and the Core Microbial Communities of Nongxiangxing Daqu. LWT 2023, 183, 114936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- QB/T 4257-2011; General Methods of Analysis for Daqu. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2011.
- GB/T 18246-2019; Determination of Amino Acids in Feeds. China Standards Press: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Fan, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, F.; Li, H.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, F. Characterization of Key Aroma Com-pounds in Laobaigan Chinese Baijiu by GC×GC-TOF/MS and Means of Molecular Sensory Science. Flavour Fragr. J. 2019, 34, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegen, J.C.; Lin, X.; Konopka, A.E.; Fredrickson, J.K. Stochastic and Deterministic Assembly Processes in Subsurface Microbial Communities. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1653–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xun, W.; Li, W.; Xiong, W.; Ren, Y.; Liu, Y.; Miao, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, N.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, R. Diversity-Triggered Deterministic Bacterial Assembly Constrains Community Functions. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloan, W.T.; Lunn, M.; Woodcock, S.; Head, I.M.; Nee, S.; Curtis, T.P. Quantifying the Roles of Immigration and Chance in Shaping Prokaryote Community Structure. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Ren, K.; Isabwe, A.; Chen, H.; Liu, M.; Yang, J. Stochastic Processes Shape Microeukaryotic Community Assembly in a Subtropical River across Wet and Dry Seasons. Microbiome 2019, 7, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xiong, S.; Du, T.; Xiao, M.; Peng, Z.; Xie, M.; Guan, Q.; Xiong, T. Effects of Microbial Succession on the Dynamics of Flavor Metabolites and Physicochemical Properties during Soy Sauce Koji Making. Food Biosci. 2023, 53, 102636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Chen, P.; Tian, J.; Huang, D.; Luo, H.; Huang, D. Predicting the Moisture Content of Daqu with Hyperspectral Imaging. Int. J. Food Eng. 2021, 17, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Liu, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Du, G. Genome Sequencing and Flavor Compound Biosynthesis Pathway Analyses of Bacillus Licheniformis Isolated from Chinese Maotai-Flavor Liquor-Brewing Microbiome. Food Biotechnol. 2020, 34, 193–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Ma, K.; Song, Y.; Wang, Z.; Fu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Cui, M.; Tang, N.; Xing, X. Exploring the Diversity of the Fungal Community in Chinese Traditional Baijiu Daqu Starters Made at Low-, Medium- and High-Temperatures. LWT 2022, 162, 113408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Q.; Lu, J.; Qiao, M.; Li, C.; Xiao, D.; Guo, X. Characterization of Key Aroma Compounds and Relationship between Aroma Compounds and Sensory Attributes in Different Quality of High Temperature Daqu. LWT 2024, 194, 115801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Gao, R.; Zhao, Y.; Miu, L.; Wang, M.; Liu, P.; Chen, J.; Fan, P. Relationship between sensory indexes, physicochemical indexes, microbial community and volatile compounds in high-temperature Daqu. Food Ferment. Ind. 2022, 48, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Fang, C.; Xing, S.; Guo, Y.; Li, X.; Han, X.; Lin, L.; Zhang, C. Heterogenetic Mechanism in High-Temperature Daqu Fermentation by Traditional Craft and Mechanical Craft: From Microbial Assembly Patterns to Metabolism Phenotypes. Food Res. Int. 2024, 187, 114327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Cheng, W.; Wang, X.; Xue, Y.; Chen, X.; Han, B.-Z. Understanding the Shifts of Microbial Community and Metabolite Profile From Wheat to Mature Daqu. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 714726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Sun, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, H.; Ma, D.; Zhang, Z. Unraveling the Correlations between Microbial Communities and Metabolic Profiles of Strong-Flavor Jinhui Daqu with Different Storage Periods. Food Microbiol. 2024, 121, 104497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Cheng, Y.; Shi, Q.; Ge, X.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Y. Metagenomic Analyses Reveal Microbial Communities and Functional Differences between Daqu from Seven Provinces. Food Res. Int. 2023, 172, 113076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Dong, S.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, R.; Han, S.; Hou, J.; Pan, C. Dynamic Changes and Correlations of Microbial Communities, Physicochemical Properties, and Volatile Metabolites during Daqu Fermentation of Taorong-Type Baijiu. LWT 2023, 173, 114290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Zheng, J.; Xie, J.; Zhao, D.; Qiao, Z.-W.; Huang, D.; Luo, H.-B. Effects of Environmental Factors on the Microbial Community Changes during Medium-High Temperature Daqu Manufacturing. Food Res. Int. 2022, 153, 110955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Luo, Y.; Yao, Y.; Ji, W.; Xia, X. Multidimensional Analysis of Wheat Original Crucial Endogenous Enzymes Driving Microbial Communities Metabolism during High-Temperature Daqu Fermentation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2024, 413, 110589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegen, J.C.; Lin, X.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Chen, X.; Kennedy, D.W.; Murray, C.J.; Rockhold, M.L.; Konopka, A. Quantifying Community Assembly Processes and Identifying Features That Impose Them. ISME J. 2013, 7, 2069–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, S.; Martiny, J.B.H.; Allison, S.D. Effects of Dispersal and Selection on Stochastic Assembly in Microbial Communities. ISME J. 2017, 11, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Ning, D.; Yang, Y.; He, N.; Li, X.; Cornell, C.R.; Bates, C.T.; Filimonenko, E.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Zhou, J.; et al. Precipitation Balances Deterministic and Stochastic Processes of Bacterial Community Assembly in Grassland Soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 168, 108635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramoneda, J.; Jensen, T.B.N.; Price, M.N.; Casamayor, E.O.; Fierer, N. Taxonomic and Environmental Distribution of Bacterial Amino Acid Auxotrophies. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devendran, S.; Shrestha, R.; Alves, J.M.P.; Wolf, P.G.; Ly, L.; Hernandez, A.G.; Méndez-García, C.; Inboden, A.; Wiley, J.; Paul, O.; et al. Clostridium Scindens ATCC 35704: Integration of Nutritional Requirements, the Complete Genome Sequence, and Global Transcriptional Responses to Bile Acids. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e00052-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veith, N.; Solheim, M.; van Grinsven, K.W.A.; Olivier, B.G.; Levering, J.; Grosseholz, R.; Hugenholtz, J.; Holo, H.; Nes, I.; Teusink, B.; et al. Using a Genome-Scale Metabolic Model of Enterococcus Faecalis V583 To Assess Amino Acid Uptake and Its Impact on Central Metabolism. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 1622–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walzem, R.L.; Dillard, C.J.; German, J.B. Whey Components: Millennia of Evolution Create Functionalities for Mammalian Nutrition: What We Know and What We May Be Overlooking. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2002, 42, 353–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mee, M.T.; Collins, J.J.; Church, G.M.; Wang, H.H. Syntrophic Exchange in Synthetic Microbial Communities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E2149–E2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Du, H.; Zhao, D.; Qiao, Z.; Zheng, J.; Yu, X.; Xu, Y. Stochastic Processes Drive the Assembly and Metabolite Profiles of Keystone Taxa during Chinese Strong-Flavor Baijiu Fermentation. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e05103-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Jiang, Y.-H.; Yang, Y.; He, Z.; Luo, F.; Zhou, J. Molecular Ecological Network Analyses. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.M.; Guo, X.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, N.; Ning, D.; Shi, Z.; Zhou, X.; Wu, L.; Yang, Y.; et al. Climate Warming Enhances Microbial Network Complexity and Stability. Nat. Clim. Change 2021, 11, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Nuccio, E.E.; Shi, Z.J.; He, Z.; Zhou, J.; Firestone, M.K. The Interconnected Rhizosphere: High Network Complexity Dominates Rhizosphere Assemblages. Ecol. Lett. 2016, 19, 926–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xun, W.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Ren, Y.; Xiong, W.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, N.; Miao, Y.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, R. Specialized Metabolic Functions of Keystone Taxa Sustain Soil Microbiome Stability. Microbiome 2021, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coyte, K.Z.; Schluter, J.; Foster, K.R. The Ecology of the Microbiome: Networks, Competition, and Stability. Science 2015, 35, 663–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontaine, C.; Guimarães Jr, P.R.; Kéfi, S.; Loeuille, N.; Memmott, J.; van der Putten, W.H.; van Veen, F.J.F.; Thébault, E. The Ecological and Evolutionary Implications of Merging Different Types of Networks. Ecol. Lett. 2011, 14, 1170–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Fan, W.; Xu, Y. GC × GC-TOF/MS and UPLC-Q-TOF/MS Based Untargeted Metabolomics Coupled with Physicochemical Properties to Reveal the Characteristics of Different Type Daqus for Making Soy Sauce Aroma and Flavor Type Baijiu. LWT 2021, 146, 111416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, A.; Li, P.; Liu, J. Dynamics and Functionalities of Bacterial Community during Foxtail Millet Dough Fermentation by Metagenomic Analysis. J. Future Foods 2024, 4, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, M.; Leung, P.M.; Shelley, G.; Jirapanjawat, T.; Nauer, P.A.; Van Goethem, M.W.; Bay, S.K.; Islam, Z.F.; Jordaan, K.; Vikram, S.; et al. Multiple Energy Sources and Metabolic Strategies Sustain Microbial Diversity in Antarctic Desert Soils. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2025322118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Z.; Tang, S.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, G.; Luo, X.; Wang, X. Environmental Stress and the Deterministic Assembly of Bacterial Communities in Daqu: The Role of Amino Acid Content Fluctuations. Foods 2025, 14, 725. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14050725
Chen Z, Tang S, Zhu X, Zhu G, Luo X, Wang X. Environmental Stress and the Deterministic Assembly of Bacterial Communities in Daqu: The Role of Amino Acid Content Fluctuations. Foods. 2025; 14(5):725. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14050725
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Zhihao, Shaopei Tang, Xia Zhu, Guojun Zhu, Xiaoye Luo, and Xiaodan Wang. 2025. "Environmental Stress and the Deterministic Assembly of Bacterial Communities in Daqu: The Role of Amino Acid Content Fluctuations" Foods 14, no. 5: 725. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14050725
APA StyleChen, Z., Tang, S., Zhu, X., Zhu, G., Luo, X., & Wang, X. (2025). Environmental Stress and the Deterministic Assembly of Bacterial Communities in Daqu: The Role of Amino Acid Content Fluctuations. Foods, 14(5), 725. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14050725





