Anti-Vibrio parahaemolyticus Mechanism of Hexanal and Its Inhibitory Effect on Biofilm Formation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Bacterial Strains and Culture Conditions
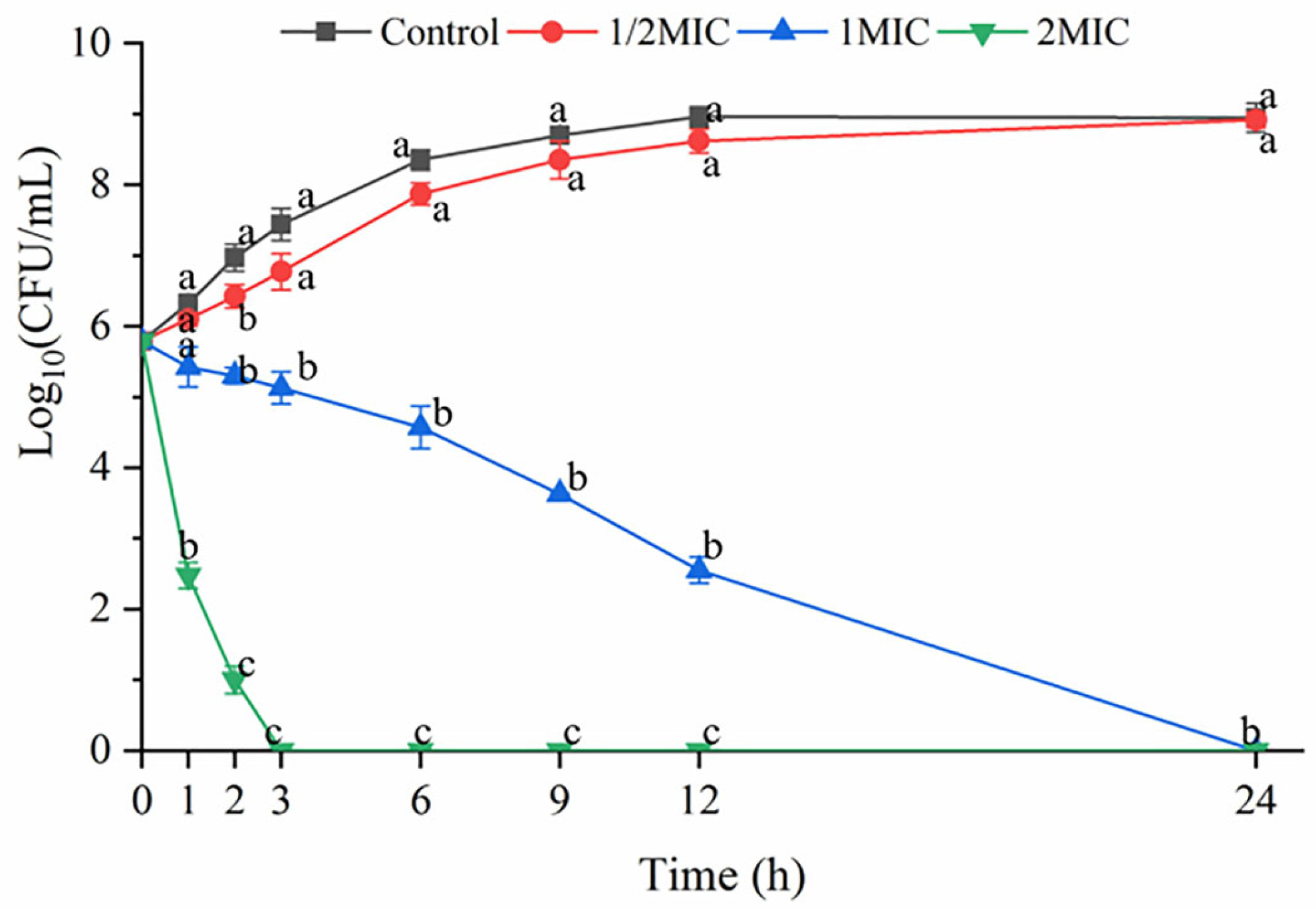
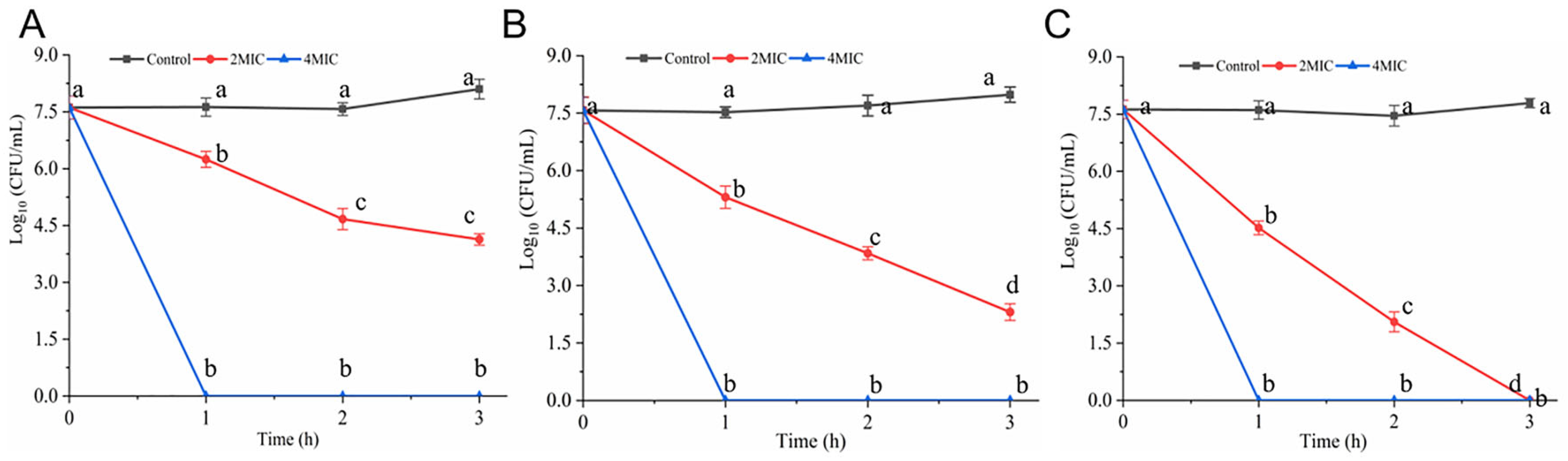
2.3. Time–Kill Curves Determination
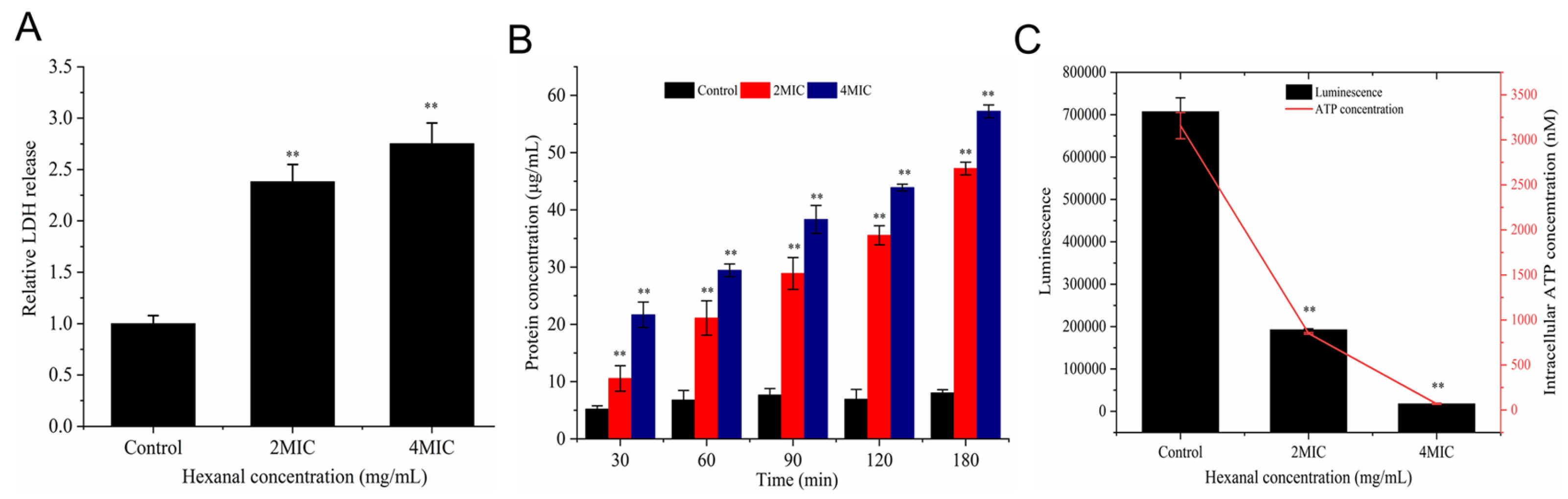
2.4. Lactic Dehydrogenase (LDH) Release Determination
2.5. Protein Leakage Determination
2.6. Intracellular ATP Concentration Determination
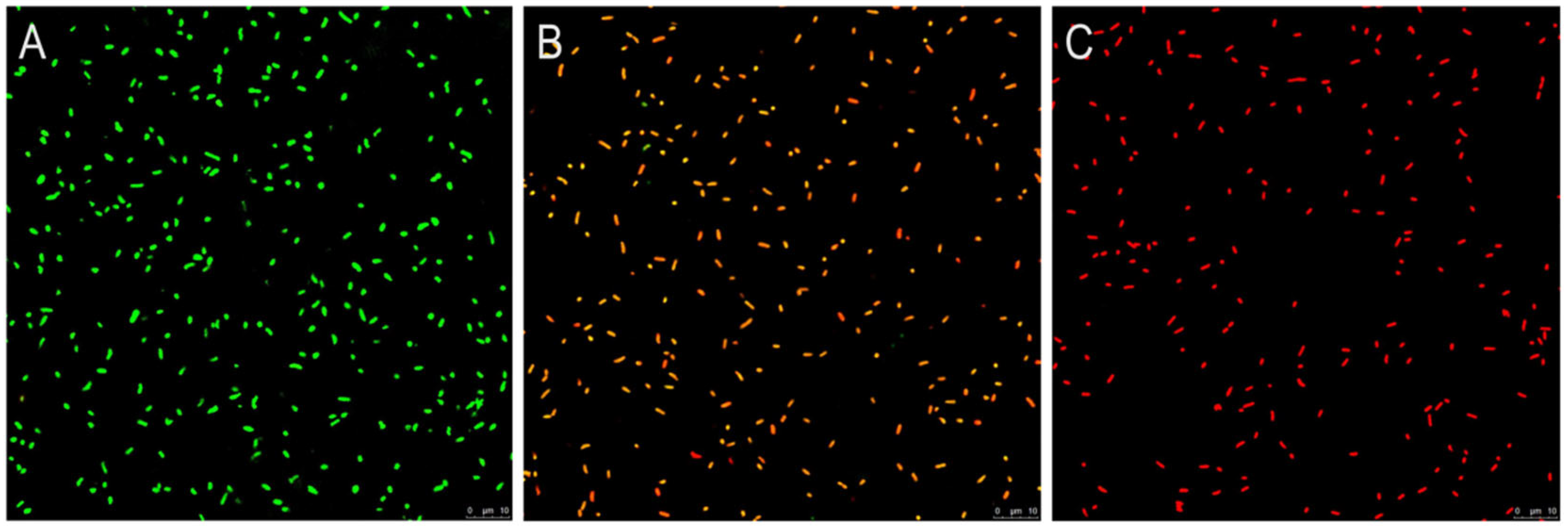
2.7. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope (CLSM) Observation
2.8. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) and Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) Observation
2.9. Determianation of Antibacterial Efficacy in Food System
2.10. Anti-Biofilm Activity Determinations
2.10.1. Crystal Violet (CV) Staining Assay
2.10.2. SEM Observation
2.10.3. Quantification of Extracellular Protein and Polysaccharide
2.10.4. Determination of Intracellular c-di-GMP Level
2.10.5. Isolation of RNA and RT-qPCR
2.11. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
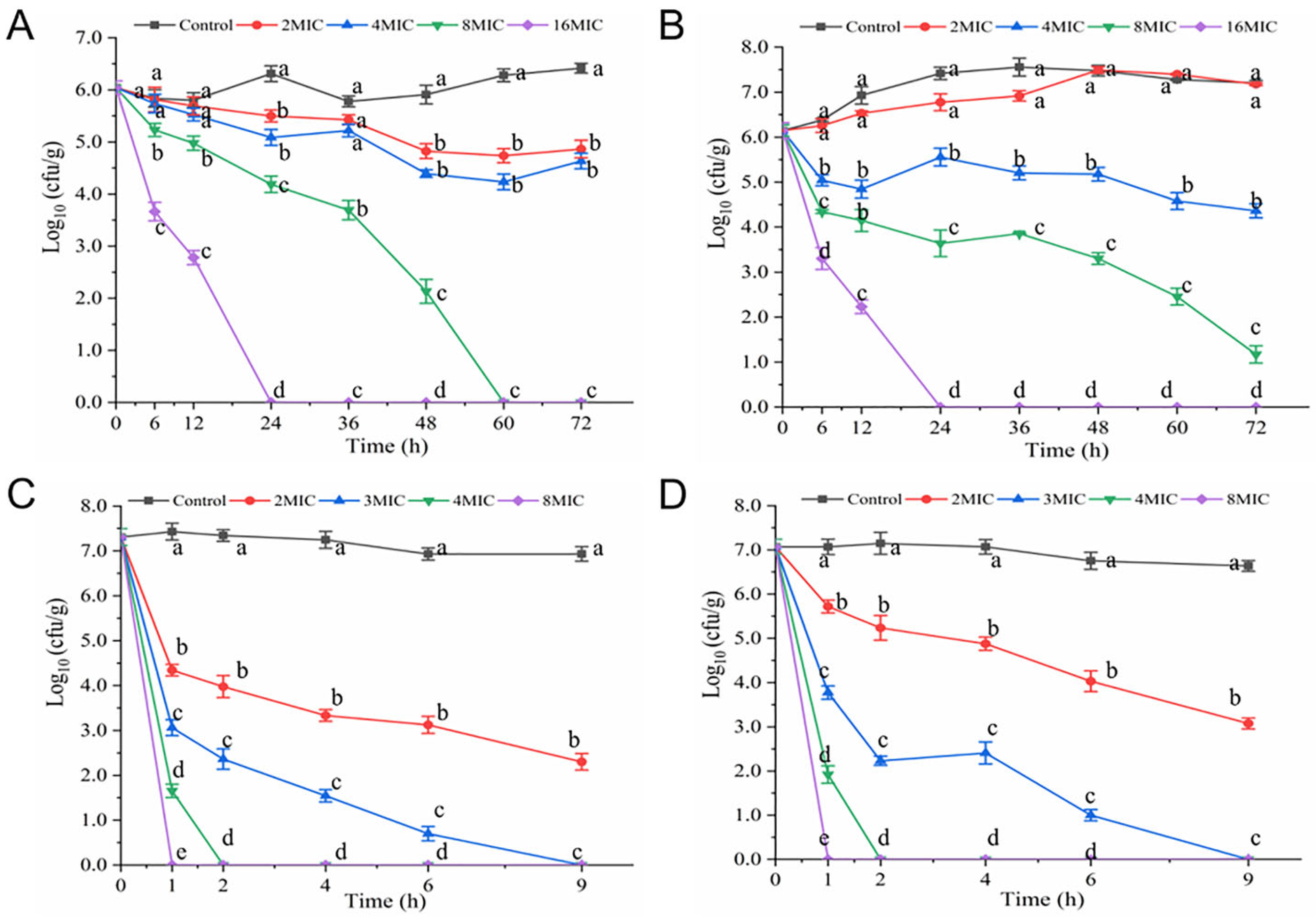
3.1. Time-Kill Curves
3.2. Lactic Dehydrogenase (LDH) Release
3.3. Protein Leakage
3.4. Intracellular ATP Concentration
3.5. CLSM Observation
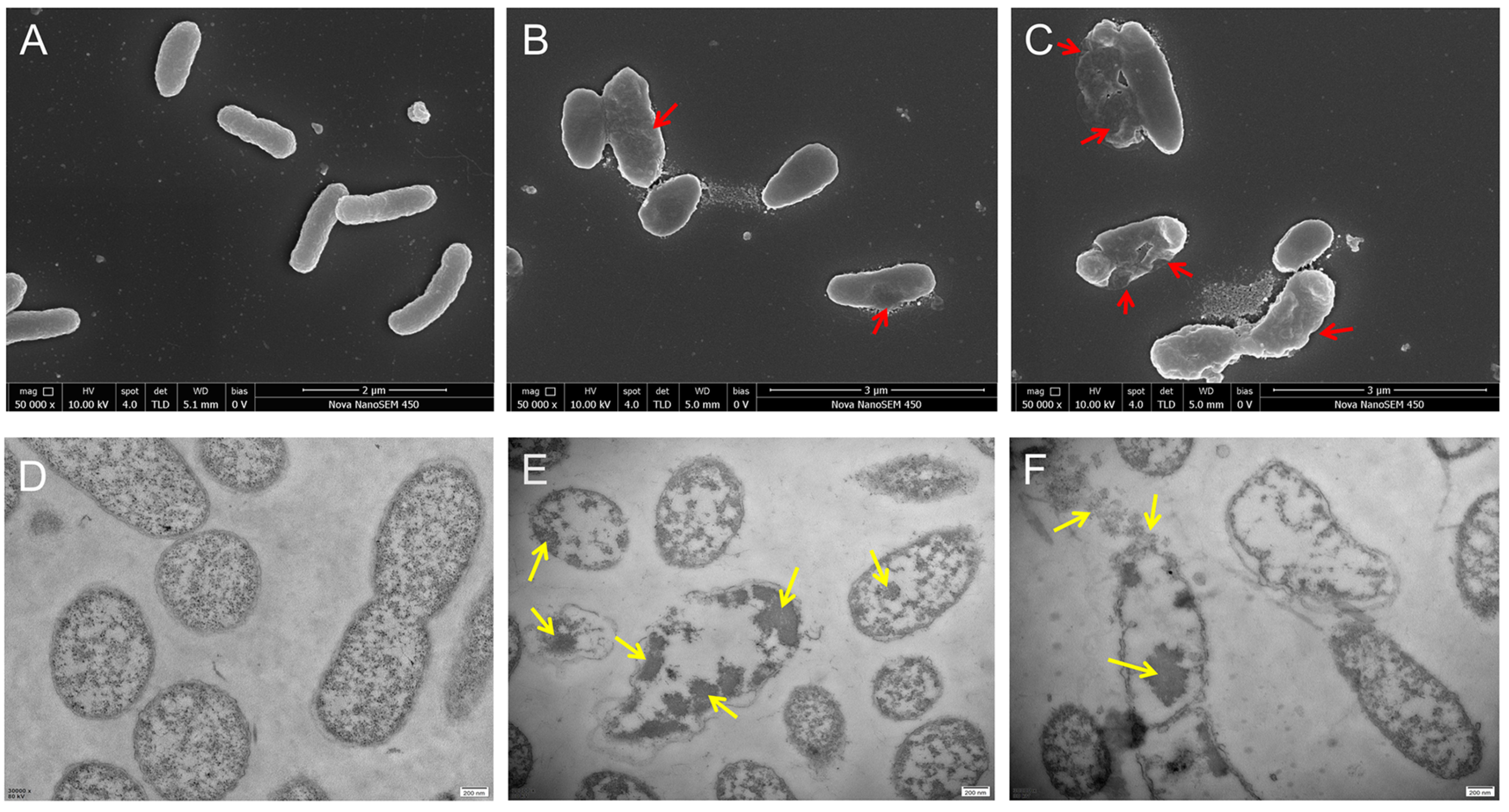
3.6. SEM and TEM Observation
3.7. Antibacterial Efficacy of Hexanal in Food System
3.8. Anti-Biofilm Effect of Hexanal on V. parahaemolyticus
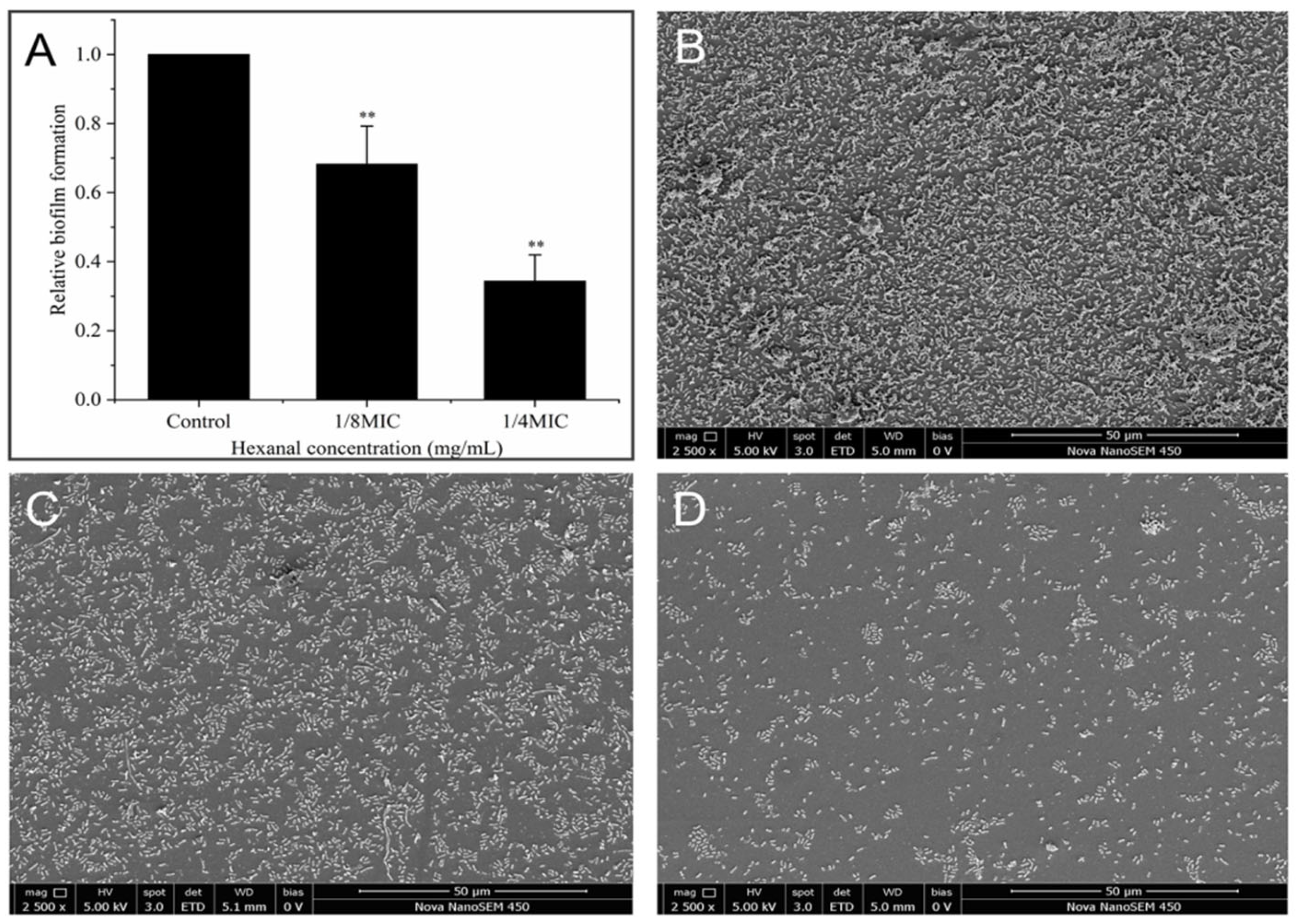
3.8.1. Crystal Violet (CV) Staining
3.8.2. SEM Observation for Biofilm Formation
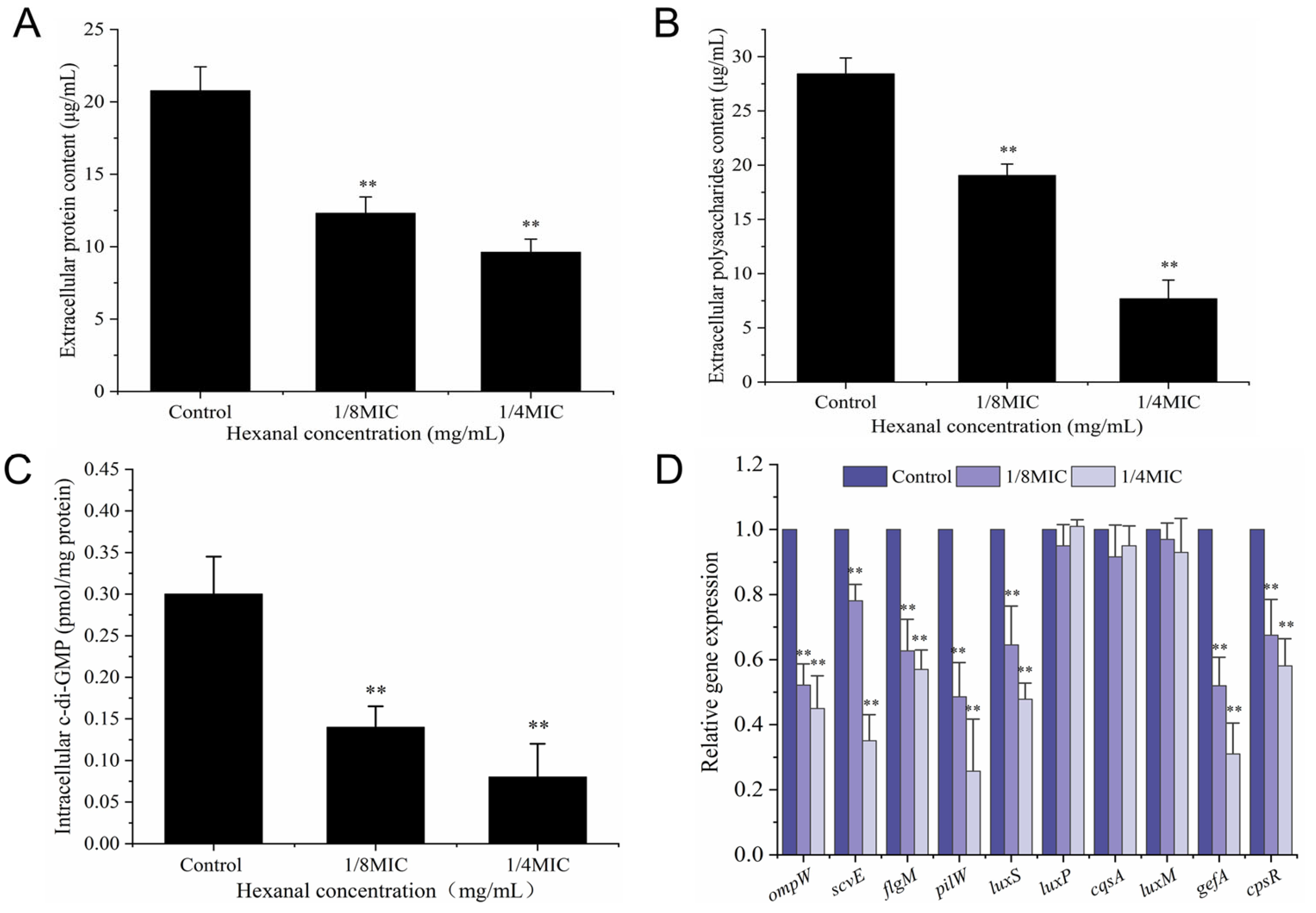
3.8.3. Extracellular Protein and Polysaccharide
3.8.4. Intracellular c-di-GMP Level
3.8.5. RT-qPCR Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, W.; Wang, J.; Qian, H.; Tan, L.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, H.; Pan, Y.; Zhao, Y. Insights into the role of extracellular DNA and extracellular proteins in biofilm formation of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, W.; Juang, F.; Chen, J. The immune response of Taiwan abalone Haliotis diversicolor supertexta and its susceptibility to Vibrio parahaemolyticus at different salinity levels. Fish Shellfish Immun. 2004, 16, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barberi, O.N.; Byron, C.J.; Burkholder, K.M.; Gelais, A.T.S.; Williams, A.K. Assessment of bacterial pathogens on edible macroalgae in coastal waters. J. Appl. Phycol. 2020, 32, 683–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Chen, L. Virulence, resistance, and genetic diversity of Vibrio parahaemolyticus recovered from commonly consumed aquatic products in Shanghai, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 160, 111554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.L.; Luedeke, C.H.M.; Bowers, J.C.; Garrett, N.; Fischer, M.; Parsons, M.B.; Bopp, C.A.; DePaola, A. Biochemical, serological, and virulence characterization of clinical and oyster Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 2343–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xie, J.; Li, H.; Tan, S.; Chen, Y.; Yu, H. Prevalence, antibiotic susceptibility and diversity of Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolates in seafood from South China. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Zang, J.; Yu, W.; Shi, X.; Wu, Y. Occurrence and identification of pathogenic Vibrio contaminants in common seafood available in a Chinese traditional market in Qingdao, Shandong province. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, N.; Mizan, M.F.R.; Jahid, I.K.; Ha, S.D. Biofilm formation by Vibrio parahaemolyticus on food and food contact surfaces increases with rise in temperature. Food Control 2016, 70, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas, S.T.A.; Rossi, B.F.; Bonsaglia, E.C.R.; Castilho, I.G.; Hernandes, R.T.; Fernandes, A.; Rall, V.L.M. Cross-contamination and biofilm formation by Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis on various cutting boards. Foodb. Pathog. Dis. 2018, 15, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kischkel, B.; Souza, G.K.; Chiavelli, L.U.R.; Pomini, A.M.; Svidzinski, T.I.E.; Negri, M. The ability of farnesol to prevent adhesion and disrupt Fusarium keratoplasticum biofilm. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2020, 104, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinbomi, J.; Wikandari, R.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Enhanced fermentative hydrogen and methane production from an inhibitory fruit-flavored medium with membrane-encapsulated cells. Membranes 2015, 5, 616–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, O.O.; da Cruz, J.N.; Franco, C.D.P.; Silva, S.G.; da Costa, W.A.; de Oliveira, M.S.; Andrade, E.H.D. First report on yield and chemical composition of essential oil extracted from Myrcia eximia DC (Myrtaceae) from the Brazilian amazon. Molecules 2020, 25, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horincar, V.B.; Parfene, G.; Tyagi, A.K.; Gottardi, D.; Dinica, R.; Guerzoni, M.E.; Bahrim, G. Extraction and characterization of volatile compounds and fatty acids from red and green macroalgae from the Romanian Black Sea in order to obtain valuable bioadditives and biopreservatives. J. Appl. Phycol. 2014, 26, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Shi, Y.; Mao, Y.; Yang, X.; Qin, K. Chemical composition and antibacterial activity of the essential oil isolated from Flos Lonicerae (Flower Buds of Lonicera macranthoides Hand.-Mazz.). Nat. Prod. Commun. 2021, 16, 1934578X2110083. [Google Scholar]
- Caballero-Prado, C.J.; Merino-Mascorro, J.A.; Heredia, N.; Davila-Avina, J.; Garcia, S. Eugenol, citral, and hexanal, alone or in combination with heat, affect viability, biofilm formation, and swarming on Shiga-toxin-producing Escherichia coli. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 30, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakshinamoorthy, D.; Sundaresan, S.; Iyadurai, A.; Subramanian, K.S.; Janavi, G.J.; Paliyath, G.; Subramanian, J. Hexanal vapor induced resistance against major postharvest pathogens of banana (Musa acuminata L.). Plant Pathol. J. 2020, 36, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.F.; Zhang, S.B.; Lv, Y.Y.; Zhai, H.C.; Li, N.; Hu, Y.S.; Cai, J.P. Metabolomic analyses revealed multifaceted effects of hexanal on Aspergillus flavus growth. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2021, 105, 3745–3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kong, J.; Xie, Y.; Guo, Y.; Yu, H.; Cheng, Y.; Qian, H.; Shi, R.; Yao, W. Quorum-sensing inhibition by hexanal in biofilms formed by Erwinia carotovora and Pseudomonas fluorescens. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 109, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Dong, X.; Wang, Z.; Yue, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yue, T. TMT-based quantitative proteomics and non-targeted metabolomic analyses reveal the antibacterial mechanism of hexanal against Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 12105–12115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Li, X.; Luo, L.; Lu, Y.; Yan, H.; Qiao, Z.; Lu, X. A novel bacteriocin BMP11 and its antibacterial mechanism on cell envelope of Listeria monocytogenes and Cronobacter sakazakii. Food Control 2018, 91, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, T.; Song, W.; Sheng, Q.; Yue, T. Inhibitory effects of lactobionic acid on Vibrio parahaemolyticus planktonic cells and biofilms. Food Microbiol. 2022, 103, 103963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, H.; Lin, H.; Wang, J. Synergistic effects of endolysin Lysqdvp001 and epsilon-poly-lysine in controlling Vibrio parahaemolyticus and its biofilms. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 343, 109112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Yu, H.H.; Song, Y.J.; Park, Y.J.; Lee, N.K.; Paik, H.D. Anti-biofilm effect of the cell-free supernatant of probiotic Saccharomyces cerevisiae against Listeria monocytogenes. Food Control 2021, 121, 107667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Zhong, K.; Wu, Y.; Elena, G.; Gao, H. Antibiofilm activity of shikimic acid against Staphylococcus aureus. Food Control 2019, 95, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, A.; Sugimoto, S.; Sato, F.; Hori, S.; Mizunoe, Y. A refined technique for extraction of extracellular matrices from bacterial biofilms and its applicability. Microb. Biotechnol. 2015, 8, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Cai, L.; Luo, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, T.; Wu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, R. Effect of sublethal dose of chloramphenicol on biofilm formation and virulence in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1275441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Lu, S.; Li, X.; Bai, F.; Wang, J.; Zhou, X.; Gao, R.; Zeng, M.; Zhao, Y. Effects of microbial diversity and phospholipids on flavor profile of caviar from hybrid sturgeon (Huso dauricus × Acipenser schrencki). Food Chem. 2022, 377, 131969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chang, T.; Yang, H.; Cui, M. Antibacterial mechanism of lactic acid on physiological and morphological properties of Salmonella Enteritidis, Escherichia coli and Listeria monocytogenes. Food Control 2015, 47, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, R.; Zhang, D.; Wang, X.; Sun, R.; Guo, W.; Yang, S.; Li, H.; Gong, G. Antibacterial mechanism of thymol against Enterobacter sakazakii. Food Control 2021, 123, 107716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Tian, L.; Fu, J.; Liao, S.; Li, H.; Gai, Z.; Gong, G. Antibacterial mechanism of protocatechuic acid against Yersinia enterocolitica and its application in pork. Food Control 2022, 133, 108573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; Wang, R.; Agyekumwaa, A.K.; Yu, Y.; Xiao, X. Antibacterial effect of phenyllactic acid against Vibrio parahaemolyticus and its application on raw salmon fillets. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 154, 112586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Hao, L.; Xie, Q.; Lan, W.; Zhao, Y.; Pan, Y.; Wu, V.C.H. Antimicrobial effects and membrane damage mechanism of blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum L.) extract against Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Food Control 2020, 111, 107020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafudoulla, M.; Mizan, M.F.R.; Angela, J.H.; Park, S.H.; Ha, S.D. Antibacterial and antibiofilm mechanism of eugenol against antibiotic resistance Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Food Microbiol. 2020, 91, 103500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L. Antibiofilm effect and mechanism of protocatechuic aldehyde against Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1060506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Liu, J.; Zou, Y.; Li, S.; Zhao, D.; Wang, H.; Xia, X. Anti-Biofilm Activity of Laurel Essential Oil against Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Foods 2023, 12, 3658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmond, P.; Best, J.P.; Morgenroth, E.; Derlon, N. Linking composition of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) to the physical structure and hydraulic resistance of membrane biofilms. Water Res. 2018, 132, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Gao, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, J.; Jin, T.; Qin, N.; Ren, X.; Xia, X. Antibiofilm effect of sodium butyrate against Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Food Control 2022, 131, 108422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenal, U.; Reinders, A.; Lori, C. Cyclic di-GMP: Second messenger extraordinaire. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengge, R. High-specificity local and global c-di-GMP signaling. Trends Microbiol. 2021, 29, 993–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, D.; Liu, X.; Li, J. Targeted phytogenic compounds against Vibrio parahaemolyticus biofilms. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2024, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shang, W.; Wang, J.; Liao, Z.; Fang, X.; Zhong, Q. Transcriptomic analysis reveals the antibiofilm mechanism of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus MS1 against Vibrio parahaemolyticus. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 176, 114529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, F.; Yuan, Y.; Li, X.; Zhong, X.; Yang, M. Quorum sensing signal synthases enhance Vibrio parahaemolyticus swarming motility. Mol. Microbiol. 2023, 120, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, X.; Yang, W.; Liu, S.; Liu, X.; Yuan, S.; An, L.; Ren, A.; Bai, F.; Li, J.; Li, X.; et al. Inhibition effect of marine active peptides SF on dual-species biofilms of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Aeromonas sobria. Food Biosci. 2024, 61, 104697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Genes | Primer | Sequences (5′–3′) |
|---|---|---|
| puvA | Forward | CAAACTCACTCAGACTC |
| Reverse | CGAACCGATTCAACAC | |
| ompW | Forward | TCGTGTCACCAAGTGTTTTCG |
| Reverse | CGTGGCTGAATGGTGTTGC | |
| scvE | Forward | GACAGGTCGTGATGCCATTC |
| Reverse | GGCGATGATGACCGAAGTG | |
| flgM | Forward | TTGATCGTGCCCAAGCAGAA |
| Reverse | TCTAGGCTCAATTCGCCGC | |
| pilW | Forward | AGCTCCTATCGTGAAAGCCG |
| Reverse | AAGCTGTGCGCGGTAGTATT | |
| luxS | Forward | GCAGGGTTTGACTCCACACT |
| Reverse | TGATGGCTGCTGCAATGAGT | |
| luxP | Forward | GTTCTGCTGAGCTAGACGCTATC |
| Reverse | AGTACACCGTTGGTACAGGTTTG | |
| cqsA | Forward | ACTTCCACACTCAAGAGCAATA |
| Reverse | GTTCAAGCGAGCCAAAGAAC | |
| luxM | Forward | TGCCCTTGTTGTCACTTTCT |
| Reverse | CGTTGGTTCCAGTCTTGGATTA | |
| gefA | Forward | GCTTTACAACAACTACGTGG |
| Reverse | GGTATCTGACAAAGTATCAC | |
| cpsR | Forward | TGTCTAGCAACCGCACTAACC |
| Reverse | GCTCTTACAACTCGGCTTCAC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, Q.; Ning, M.; Zeng, X.; He, X.; Bai, Z.; Gu, S.; Yuan, Y.; Yue, T. Anti-Vibrio parahaemolyticus Mechanism of Hexanal and Its Inhibitory Effect on Biofilm Formation. Foods 2025, 14, 703. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14040703
Fan Q, Ning M, Zeng X, He X, Bai Z, Gu S, Yuan Y, Yue T. Anti-Vibrio parahaemolyticus Mechanism of Hexanal and Its Inhibitory Effect on Biofilm Formation. Foods. 2025; 14(4):703. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14040703
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Qiuxia, Mengge Ning, Xuejun Zeng, Xiangxiang He, Zhouya Bai, Shaobin Gu, Yahong Yuan, and Tianli Yue. 2025. "Anti-Vibrio parahaemolyticus Mechanism of Hexanal and Its Inhibitory Effect on Biofilm Formation" Foods 14, no. 4: 703. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14040703
APA StyleFan, Q., Ning, M., Zeng, X., He, X., Bai, Z., Gu, S., Yuan, Y., & Yue, T. (2025). Anti-Vibrio parahaemolyticus Mechanism of Hexanal and Its Inhibitory Effect on Biofilm Formation. Foods, 14(4), 703. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14040703






