Improving Foaming Properties and Quality of Pasteurized Milk Using Antimicrobial Agents from Wild Pediococcus acidilactici
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Evaluation of Free Fatty Acids in Raw Milk
2.3. Milk Treatment by CFS
2.4. Flavor Potential of Milk
2.5. Measuring the Foaming Capacity
2.6. Physicochemical Analysis of Milk
2.7. Aerobic Total Count Microorganisms
2.7.1. Counting of Psychrotrophic Microorganisms
2.7.2. Counting the Spore Forming Bacteria
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical, Microbiological, and Flavor Analysis of Raw Milk
3.2. Effect of the Physicochemical Properties and Free Fatty Acids of Raw Milk from Various Farms on the Foaming Properties
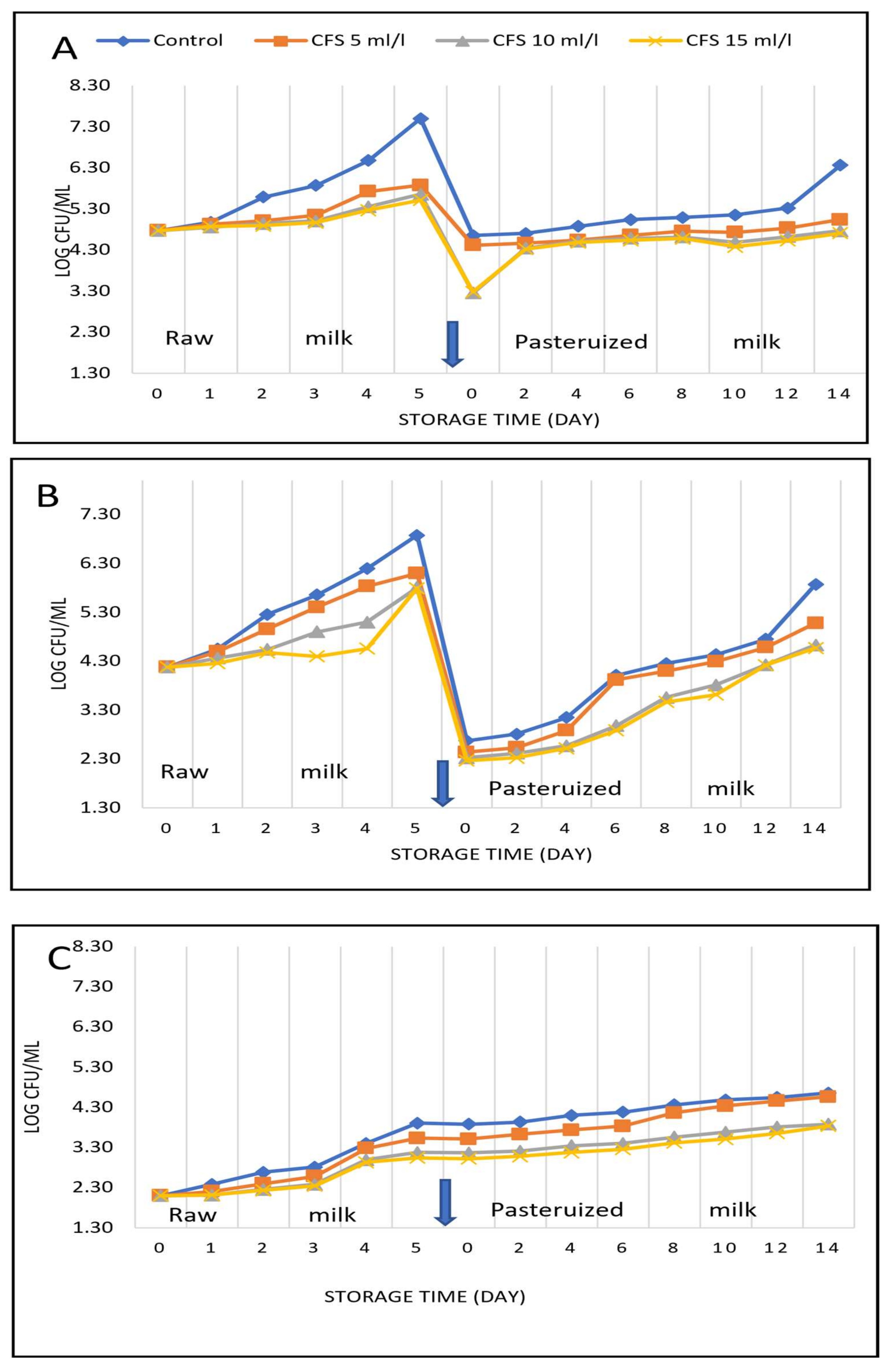
3.3. Effect of the Cell-Free Supernatant of Wild Pediococcus acidilactici on the Bacterial Count of Raw and Pasteurized Milk
3.4. Effect of the Cell-Free Supernatant of Wild Pediococcus acidilactici on the Foaming Capacity and Stability of Raw and Then Heat-Treated Milk
3.5. Effect of the Cell-Free Supernatant of Wild Pediococcus acidilactici and Nisin on the pH and Flavour of Raw and Then Heat-Treated Milk
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hettiarachchi, C.A.; Corzo-Martínez, M.; Mohan, M.S.; Harte, F.M. Enhanced Foaming and Emulsifying Properties of High-Pressure-Jet-Processed Skim Milk. Int. Dairy J. 2018, 87, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.M.; Bhandari, B.R.; Bansal, N. Foaming Properties of Milk Samples Collected at Various Processing Stages in a Dairy Processing Factory across Two Seasons. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 1470–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatakeyama, S.; Akiyama, M.; Yoneyama, R.; Watanabe, K.; Koizumi, R.; Miyaji, K.; Mizota, Y.; Ikeda, M.; Wakao, S. Effects of Manufacturing Conditions on the Foaming Properties of Milk and Sensory Characteris-Tics of Foamed Milk. LWT 2019, 99, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heck, J.M.L.; Van Valenberg, H.J.F.; Dijkstra, J.; Van Hooijdonk, A.C.M. Seasonal Variation in the Dutch Bovine Raw Milk Composition. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 4745–4755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Lewis, M.J.; Grandison, A.S. Effect of Seasonal Variation on the Composition and Properties of Raw Milk Destined for Processing in the UK. Food Chem. 2014, 158, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atasoy, A.F.; Türkoğlu, H. Changes of Composition and Free Fatty Acid Contents of Urfa Cheeses (a White-Brined Turkish Cheese) during Ripening: Effects of Heat Treatments and Starter Cultures. Food Chem. 2008, 110, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottar, J.F. Effect on the Quality of Dairy Products; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, T.M.; Bhandari, B.R.; Bansal, N. Functionality of Bovine Milk Proteins and Other Factors in Foaming Properties of Milk: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 4800–4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.M.; Bhandari, B.; Bansal, N. Influence of Milk Fat on Foam Formation, Foam Stability and Functionality of Aerated Dairy Products. In Dairy Fat Products and Functionality: Fundamental Science and Technology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 583–606. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, T.M.; Tanzil, A.; Bhandari, B.R.; Bansal, N. Effect of Surfactant Type on Foaming Properties of Milk. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2023, 16, 1781–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, A.I.; El-Sayed, I.M.; Awad, S. Bacteriocins: Nisin as an Alternative Source to Chemi-Cal Preservatives. In Natural Food Preservatives; Jenny Stanford Publishing: Singapore, 2023; pp. 51–85. ISBN 9781003367765. [Google Scholar]
- Setiarto, R.H.B.; Anshory, L. Bacteriocın, Plantaricin and Pediocin Bıosynthesis in Lactic Acid Bacteria, Antimicrobial Mechanism and Applications as Food Preservatives. Curr. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2024, 24, e0258161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, S.G.; Baglinière, F.; Marchand, S.; Van Coillie, E.; Vanetti, M.C.; De Block, J.; Heyndrickx, M. The biodiversity of the microbiota producing heat-resistant enzymes responsible for spoilage in processed bovine milk and dairy products. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchand, S.; Heylen, K.; Messens, W.; Coudijzer, K.; De Vos, P.; Dewettinck, K.; Herman, L.; De Block, J.; Heyndrickx, M. Seasonal influence on heat-resistant proteolytic capacity of Pseudomonas lundensis and Pseudomonas fragi, predominant milk spoilers isolated from Belgian raw milk samples. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 467–482. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.; Sadiq, F.A.; Burmølle, M.; Wang, N.I.; He, G. Insights into psychrotrophic bacteria in raw milk: A review. J. Food Prot. 2019, 82, 1148–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsaadany, K.; El-Sayed, A.I.; Awad, S. Identification, Safety Assessment, and Antimicrobial Characteristics of Cocci Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Traditional Egyptian Dairy Products. Foods 2024, 13, 3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 7932:2004; Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuffs—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Presumptive Bacillus Cereus—Olony-Count Technique. 3rd ed. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004.
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 21st ed.; AOAC: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 4833-1:2013; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Microor-Ganisms Part 1: Colony Count at 30 °C by the Pour Plate Technique. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013.
- ISO 17410:2019; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Psy-Chrotrophic Microorganisms. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- Kent, D.J.; Chauhan, K.; Boor, K.J.; Wiedmann, M.; Martin, N.H. Spore Test Parameters Matter: Mesophilic and Thermophilic Spore Counts Detected in Raw Milk and Dairy Powders Differ Significantly by Test Method. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 5180–5191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Xi, B.; Yang, X.; Wang, H.; He, X.; Li, W.; Gao, Y. Evaluation of Change in Quality Indices and Volatile Flavor Components in Raw Milk during Refrigerated Storage. LWT 2022, 165, 113674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasca, M.; Decimo, M.; Morandi, S.; Machado, S.G.; Bagliniére, F.; Vanetti, M.C.D. Psychrotrophic Bacteria. In Microbiology in Dairy Processing: Challenges and Opportunities; Poltronieri, P., Ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 37–61. ISBN 9781119114802. [Google Scholar]
- Lucassen-Reynders, E.H.; Benjamins, J.; Fainerman, V.B. Dilational Rheology of Protein Films Adsorbed at Fluid Interfaces. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 15, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Ho, M.T.; Bhandari, B.; Bansal, N. Foaming Properties of Milk Protein Dispersions at Different Protein Content and Casein to Whey Protein Ratios. Int. Dairy J. 2020, 109, 104758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, M.D.; Wiking, L.; Bjerring, M.; Larsen, H.C. Influence of Air Intake on the Concen-Tration of Free Fatty Acids and Vacuum Fluctuations during Automatic Milking. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 4596–4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiking, L.; Nielsen, J.H.; Båvius, A.K.; Edvardsson, A.; Svennersten-Sjaunja, K. Impact of Milking Frequencies on the Level of Free Fatty Acids in Milk, Fat Globule Size, and Fatty Acid Composi-Tion. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 1004–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiking, L.; Bjerring, M.; Løkke, M.M.; Løvendahl, P.; Kristensen, T. Herd Factors Influencing Free Fatty Acid Concentrations in Bulk Tank Milk. J. Dairy Res. 2019, 86, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Hadiatullah, H.; Guo, T.; Yao, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, X. Dairy Processing Affects the Gut Digestion and Microecology by Changing the Structure and Composition of Milk Fat Globules. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 10194–10205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiking, L. Milk Fat Globule Stability: Lipolysis with Special Reference to Automatic Milking Systems. Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences Uppsala. Acta Univ. Agric. Sueciae 2005, 49, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, L.; Sadiq, F.A.; Liu, T.; Flint, S.; Chen, J.; Yang, H.; Gu, J.; Zhang, G.; He, G. Psychrotrophic bacterial populations in Chinese raw dairy milk. LWT 2017, 84, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, S.C.; Martin, N.H.; Barbano, D.M.; Wiedmann, M. Influence of Raw Milk Quality on Processed Dairy Products: How Do Raw Milk Quality Test Results Relate to Product Quality and Yield? J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 10128–10149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yalew, K.; Pang, X.; Huang, S.; Zhang, S.; Yang, X.; Xie, N.; Wang, Y.; Lv, J.; Li, X. Recent Development in Detection and Control of Psychrotrophic Bacteria in Dairy Production: Ensuring Milk Quali-Ty. Foods 2024, 13, 2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusco, V.; Chieffi, D.; Fanelli, F.; Logrieco, A.F.; Cho, G.S.; Kabisch, J.; Böhnlein, C.; Franz, C.M.A.P. Microbial Quality and Safety of Milk and Milk Products in the 21st Century. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 2013–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauh, V.; Xiao, Y. The Shelf Life of Heat-Treated Dairy Products. Int. Dairy J. 2022, 125, 105235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.; Awad, S. Selection and Identification of Protective Culture for Controlling Staphylococcus Aureus in Fresh Domiati like Cheese. J. Food Saf. 2018, 38, e12418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.C.; Silva, S.P.; Ribeiro, S.C. Application of Bacteriocins and Protective Cultures in Dairy Food Preservation. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Farm | Fat % | Protein % | pH | FFA% | TC(log CFC/mL) | PS(log CFU/mL) | SF(log CFU/mL) | Flavor (9) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Farm 1 | 3.74 a | 3.35 a | 6.75 | 0.11 f | 4.34 c | 3.70 c | 2.18 c | 8.5 a |
| Farm 2 | 3.56 c | 3.21 b | 6.72 | 0.16 cd | 4.66 bc | 3.93 c | 2.40 b | 8.4 a |
| Farm 3 | 3.45 d | 3.14 c | 6.76 | 0.24 b | 4.55 c | 3.87 c | 2.41 b | 8.2 a |
| Farm 4 | 3.71 ab | 3.30 a | 6.72 | 0.12 f | 4.37 c | 3.72 c | 2.15 c | 8.1 a |
| Farm 5 | 3.65 c | 3.32 a | 6.73 | 0.11 f | 4.81 b | 4.01 c | 2.38 b | 8.3 a |
| Farm 6 | 3.56 c | 3.21 b | 6.76 | 0.25 b | 5.18 a | 4.38 a | 2.61 a | 7.2 b |
| Farm 7 | 3.48 d | 3.23 b | 6.74 | 0.35 a | 5.35 a | 4.67 a | 2.74 a | 7.4 b |
| Farm 8 | 3.39 d | 3.34 a | 6.77 | 0.24 b | 5.11 a | 4.26 a | 2.66 a | 7.1 c |
| Farm 9 | 3.62 c | 3.29 a | 6.75 | 0.19 c | 5.28 a | 4.42 a | 2.71 a | 7.2 c |
| Farm 10 | 3.59 c | 3.36 a | 6.76 | 0.19 c | 5.10 a | 4.26 a | 2.51 a | 7.8 b |
| Farm 11 | 3.75 a | 3.37 a | 6.75 | 0.11 f | 4.44 c | 3.79 c | 2.34 b | 8.5 a |
| Farm 12 | 3.58 c | 3.26 ab | 6.75 | 0.13 e | 4.88 b | 4.06 b | 2.45 a | 8.4 a |
| Farm 13 | 3.67 b | 3.28 a | 6.74 | 0.14 d | 5.54 a | 4.16 b | 2.51 a | 8.2 a |
| Farm 14 | 3.81 a | 3.32 a | 6.78 | 0.16 cd | 4.72 b | 4.21 ab | 2.45 a | 8.2 a |
| Farm 15 | 3.66 b | 3.27 a | 6.77 | 0.17 cd | 4.83 b | 4.37 a | 2.54 a | 8.1 a |
| Farm | FFA/Fat % | Foam Capacity (mL/100 mL) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 3 min | 10 min | ||
| Farm 1 | 2.94 h | 39 a | 25 c | 15 b |
| Farm 2 | 4.49 d | 29.5 d | 22 d | 11 c |
| Farm 3 | 6.96 b | 28.5 d | 26 c | 13 c |
| Farm 4 | 3.23 g | 33.4 c | 30.2 b | 15 b |
| Farm 5 | 3.01 gh | 36.6 b | 34.9 a | 23 a |
| Farm 6 | 7.02 b | 18 f | 8.5 f | 4.1 e |
| Farm 7 | 10.06 a | 16 f | 5.7 g | 3.2 e |
| Farm 8 | 7.08 b | 23 e | 18 e | 6.7 d |
| Farm 9 | 5.25 c | 32 d | 20 d | 15.8 b |
| Farm 10 | 5.29 c | 38 a | 34 a | 24 a |
| Farm 11 | 2.93 h | 38 a | 36 a | 25 a |
| Farm 12 | 3.63 f | 31.5 d | 28.7 b | 14.6 b |
| Farm 13 | 3.81 f | 32.6 d | 29.8 b | 14.8 b |
| Farm 14 | 4.20 e | 3 c | 31 b | 15.7 b |
| Farm 15 | 4.64 d | 30 d | 24 c | 12.8 c |
| Storage Time (Days) | Raw Milk | Heat-Treated Milk | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 | |
| Control | 0.09 a | 0.14 a | 0.19 a | 0.27 a | 0.39 a | 0.47 a | 0.48 a | 0.52 a | 0.54 a | 0.55 a | 0.56 a | 0.57 a | 0.57 a | 0.58 a |
| CFS 5 mL/L | 0.10 a | 0.13 b | 0.15 b | 0.23 b | 0.25 b | 0.29 b | 0.38 b | 0.39 b | 0.39 b | 0.44 b | 0.45 b | 0.46 b | 0.45 b | 0.51 b |
| CFS 10 mL/L | 0.11 a | 0.12 b | 0.15 c | 0.20 c | 0.28 c | 0.30 c | 0.34 c | 0.31 c | 0.34 c | 0.35 c | 0.38 c | 0.37 c | 0.39 c | 0.44 c |
| CFS 15 mL/L | 0.11 a | 0.12 b | 0.15 c | 0.18 c | 0.21 d | 0.27 d | 0.26 d | 0.26 d | 0.32 c | 0.34 c | 0.31 d | 0.33 d | 0.33 d | 0.38 d |
| a. Raw Milk | ||||||||||||||||
| Storage Time (Days) | Received Milk | 1st day | 2nd day | 3rd day | 4th day | 5th day | ||||||||||
| Foaming Capacity at | ||||||||||||||||
| 0 | 10 min | 0 | 10 min | 0 | 10 min | 0 | 10 min | 0 | 10 min | 0 | 10 min | |||||
| Control | 35 a | 18 a | 34 a | 16 b | 31 b | 16 b | 26 b | 7 d | 26 b | 6 d | 23 b | 6 d | ||||
| CFS 5 mL/L | 35 a | 18 a | 35 a | 17 a | 32 a | 16 a | 29 a | 12 c | 26 a | 11 c | 25 a | 10 c | ||||
| CFS 10 mL/L | 35 a | 18 a | 35 a | 18 a | 33 a | 17 a | 31 a | 14 b | 30 a | 13 b | 29 a | 12 b | ||||
| CFS 15 mL/L | 35 a | 18 a | 35 a | 18 a | 33 a | 17 a | 32 a | 15 a | 31 a | 14 a | 30 a | 14 a | ||||
| b. After Pasteurization | ||||||||||||||||
| Storage Time (Days) | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 | ||||||||
| Foaming Capacity at | ||||||||||||||||
| 0 | 10 min | 0 | 10 min | 0 | 10 min | 0 | 10 min | 0 | 10 min | 0 | 10 min | 0 | 10 min | 0 | 10 min | |
| Control | 23 d | 9 c | 21 c | 7 c | 18 c | 7 c | 17 c | 6 d | 17 c | 5 c | 15 c | 5 d | 14 c | 4 c | 10 c | 3 d |
| CFS 5 mL/L | 26 c | 14 b | 26 b | 12 b | 24 b | 12 b | 23 b | 11 c | 22 b | 10 b | 21 b | 9 c | 18 b | 8 b | 16 b | 7 c |
| CFS 10 mL/L | 29 b | 16 a | 29 a | 15 a | 29 a | 14 a | 27 b | 13 b | 26 a | 13 a | 26 b | 11 b | 24 a | 11 a | 22 b | 10 b |
| CFS 15 mL/L | 31 a | 17 a | 30 a | 15 a | 29 a | 15 a | 28 a | 14 a | 28 a | 14 a | 27 a | 14 a | 27 a | 13 a | 26 a | 12 a |
| Sample | pH | Flavor Score (Hedonic Scale 9) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | CFS 5 mL/L | CFS 10 mL/L | CFS 15 mL/L | Nisin 6 mg/L | Control | CFS 5 mL/L | CFS 10 mL/L | CFS 15 mL/L | Nisin 6 mg/L | |
| Day 0-R | 6.71 | 6.68 | 6.66 | 6.64 | 6.71 | 8.31 a | 7.37 b | 7.12 c | 6.78 d | 8.38 a |
| Day 1-R | 6.68 | 6.68 | 6.66 | 6.64 | 6.70 | 8.05 b | 7.35 c | 7.11 d | 6.57 e | 8.24 a |
| Day 2-R | 6.66 | 6.67 | 6.65 | 6.63 | 6.70 | 7.57 b | 7.31 b | 6.94 c | 6.46 d | 8.17 a |
| Day 3-R | 6.65 | 6.66 | 6.65 | 6.63 | 6.69 | 7.27 b | 6.64 c | 6.64 c | 6.41 c | 8.09 a |
| Day 4-R | 6.63 | 6.64 | 6.64 | 6.62 | 6.68 | 7.02 b | 6.54 c | 6.54 c | 6.38 c | 7.98 a |
| Day 5-R | 6.60 | 6.63 | 6.64 | 6.62 | 6.67 | 6.95 b | 6.45 c | 6.48 c | 6.29 d | 7.81 a |
| Day 0-P | 6.6 | 6.63 | 6.64 | 6.62 | 6.67 | 6.92 b | 6.41 c | 6.42 c | 6.28 c | 7.80 a |
| Day 2-P | 6.6 | 6.63 | 6.64 | 6.61 | 6.67 | 6.18 c | 6.40 b | 6.36 b | 6.19 c | 7.78 a |
| Day 4-P | 6.58 | 6.62 | 6.64 | 6.60 | 6.66 | 5.59 d | 6.36 b | 6.34 b | 6.14 c | 7.62 a |
| Day 6-P | 6.58 | 6.61 | 6.64 | 6.60 | 6.66 | 5.06 c | 6.29 b | 6.17 b | 6.08 b | 7.54 a |
| Day 8-P | 6.54 | 6.60 | 6.61 | 6.60 | 6.66 | ND | 6.07 b | 6.02 b | 6.06 b | 7.45 a |
| Day 10-P | 5.85 | 6.43 | 6.54 | 6.59 | 6.66 | ND | 5.89 c | 6.47 b | 6.34 b | 7.36 a |
| Day 12-P | 5.42 | 6.15 | 6.45 | 6.54 | 6.66 | ND | ND | 5.35 c | 6.22 b | 7.25 a |
| Day 14-P | 5.14 | 5.87 | 6.35 | 6.45 | 6.65 | ND | ND | ND | 6.14 b | 7.08 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Awad, S.; EL-Sayed, A.I.M.; Amer, D.; Atef, D.; Ashraf, M.; Kan, J.; Du, M.; Elsaadany, K. Improving Foaming Properties and Quality of Pasteurized Milk Using Antimicrobial Agents from Wild Pediococcus acidilactici. Foods 2025, 14, 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14040641
Awad S, EL-Sayed AIM, Amer D, Atef D, Ashraf M, Kan J, Du M, Elsaadany K. Improving Foaming Properties and Quality of Pasteurized Milk Using Antimicrobial Agents from Wild Pediococcus acidilactici. Foods. 2025; 14(4):641. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14040641
Chicago/Turabian StyleAwad, Sameh, Abeer I. M. EL-Sayed, Dina Amer, Dalia Atef, Mona Ashraf, Jianquan Kan, Muying Du, and Khaled Elsaadany. 2025. "Improving Foaming Properties and Quality of Pasteurized Milk Using Antimicrobial Agents from Wild Pediococcus acidilactici" Foods 14, no. 4: 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14040641
APA StyleAwad, S., EL-Sayed, A. I. M., Amer, D., Atef, D., Ashraf, M., Kan, J., Du, M., & Elsaadany, K. (2025). Improving Foaming Properties and Quality of Pasteurized Milk Using Antimicrobial Agents from Wild Pediococcus acidilactici. Foods, 14(4), 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14040641







