Can the Contents of Biogenic Amines in Olomoucké Tvarůžky Cheeses Be Risky for Consumers?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cheese Sampling
2.2. Chemical Analysis
2.2.1. Chemicals and Standards
2.2.2. Determination of BA and PA
Sample Extraction for Amine Analysis
The Chromatographic Conditions
Calculation and Method Parameters
2.2.3. Determination of Physical–Chemical Properties
Surface and Specific Surface Area Calculation
Determination of pH Value in Cheeses
Determination of NaCl Content
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
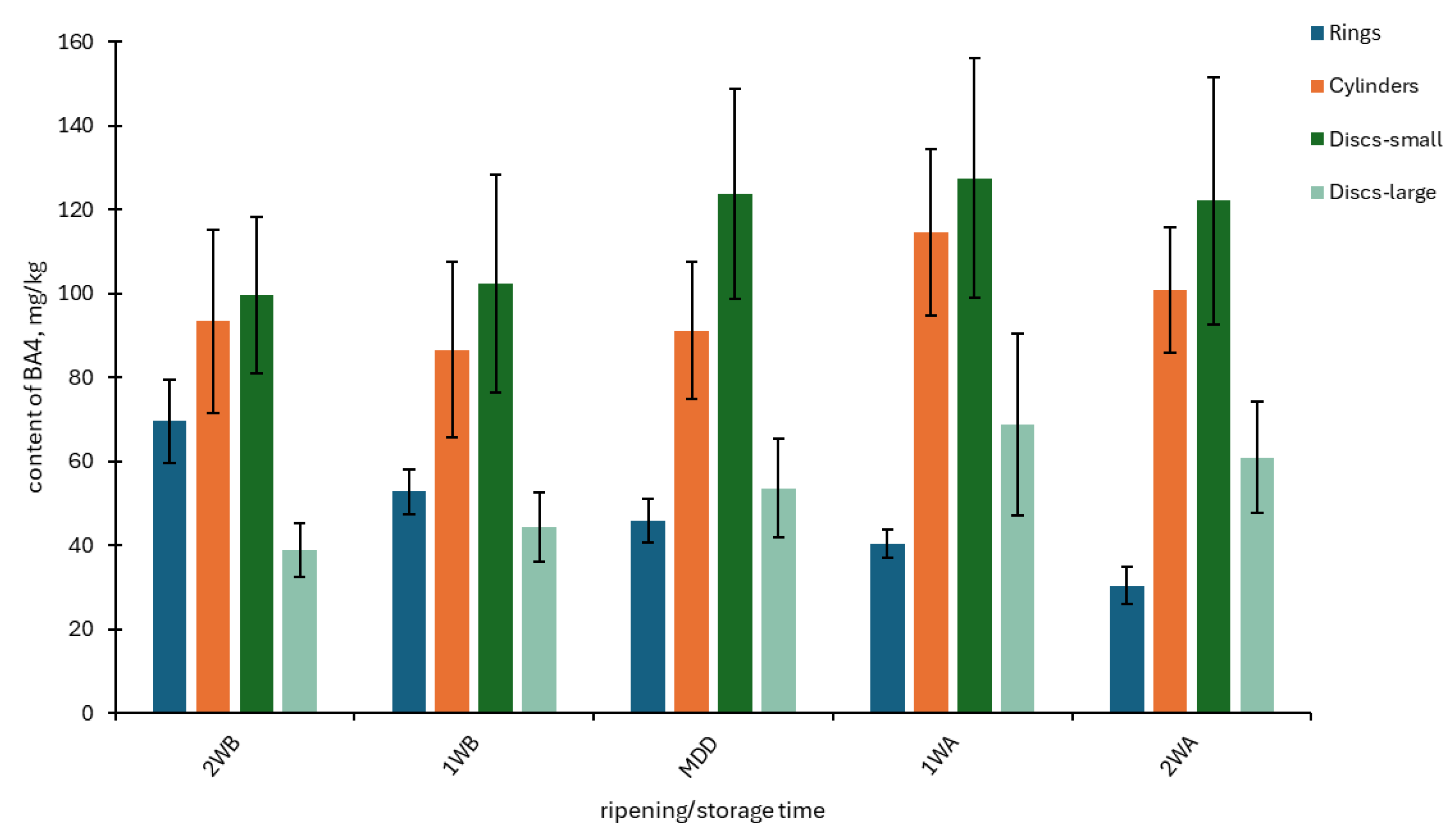
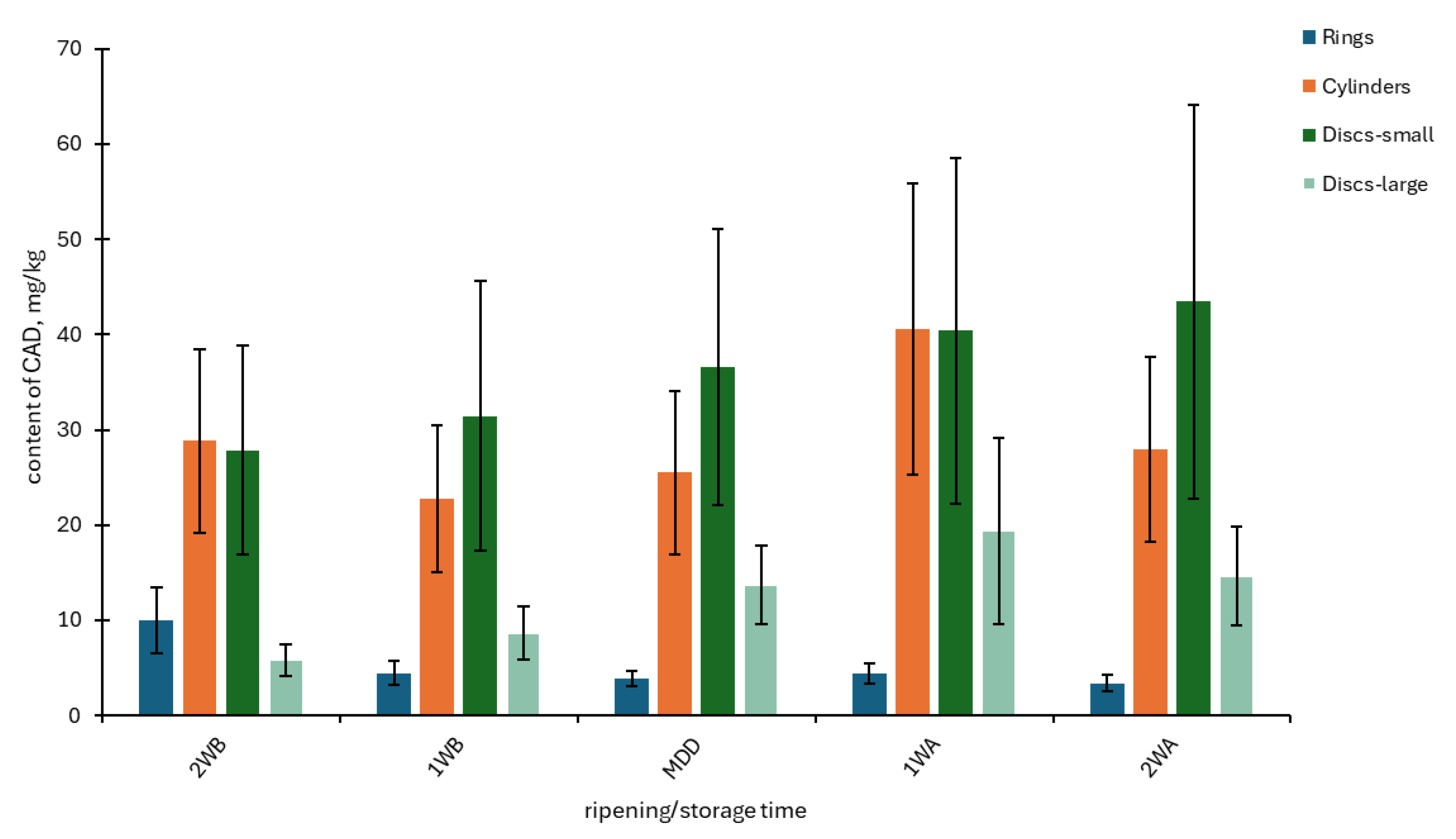
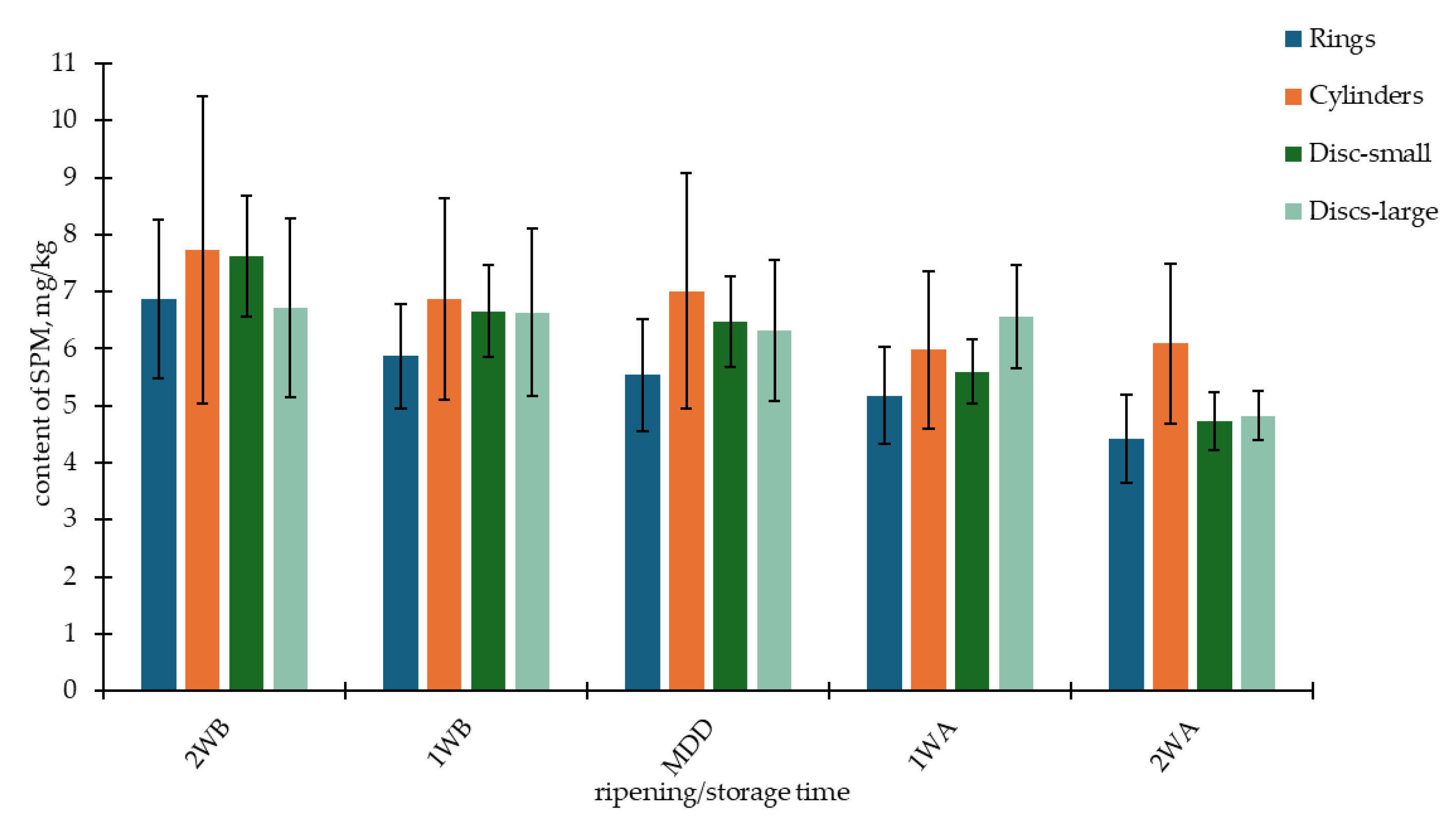
3.1. The Contents of BAs and PAs in OT Samples Depending on Batch, Year, and Storage Time
3.2. The Relationships Between BA Contents and Selected Chemical–Physical Properties of OT Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feddern, V.; Mazzuco, H.; Fonseca, F.N.; de Lima, G.J.M.M. A review on biogenic amines in food and feed: Toxicological aspects, impact on health and control measures. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2019, 59, 608–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalač, P. Health effects and occurrence of dietary polyamines: A review for the period 2005-mid 2013. Food Chem. 2014, 161, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Capillas, C.; Herrero, A.M. Impact of biogenic amines on food quality and safety. Foods 2019, 8, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moschou, P.N.; Wu, J.; Cona, A.; Tavladoraki, P.; Angelini, R.; Roubelakis-Angelakis, K.A. The polyamines and their catabolic products are significant players in the turnover of nitrogenous molecules in plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 5003–5015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardócz, S. Polyamines in food and their consequences for food quality and human health. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 1995, 6, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenis, Y.Y.; Elmetwally, M.A.; Maldonado-Estrada, J.G.; Bazer, F.W. Physiological importance of polyamines. Zygote 2017, 25, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkadi, L.S. Amino acids and biogenic amines as food quality factors. Pure Appl. Chem. 2019, 91, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirone, M.; Visciano, P.; Conte, F.; Paparella, A. Formation of biogenic amines in the cheese production chain: Favouring and hindering factors. Int. Dairy. J. 2022, 133, 105420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natrella, G.; Vacca, M.; Minervini, F.; Faccia, M.; De Angelis, M. A comprehensive review on the biogenic amines in cheeses: Their origin, chemical characteristics, hazard and reduction strategies. Foods 2024, 13, 2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, A.R. Significance of biogenic amines to food safety and human health. Food Res. Int. 1996, 29, 675–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Rio, B.; Fernandez, M.; Redruello, B.; Ladero, V.; Alvarez, M.A. New insights into the toxicological effects of dietary biogenic amines. Food Chem. 2024, 435, 137558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalač, P.; Glória, M.B.A. Biogenic amines in cheeses, wines, beers and sauerkraunt. In Biological Aspects of Biogenic Amines, Polyamines and Conjugates; Dandrifosse, G., Ed.; Transworld Research Network: Trivandrum, India, 2009; pp. 267–309. [Google Scholar]
- Samková, E.; Dadáková, E.; Pelikánová, T. Changes in biogenic amine and polyamine contents in smear-ripened cheeses during storage. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2013, 237, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standarová, E.; Borkovcová, I.; Dušková, M.; Přidalová, H.; Dračková, M.; Vorlová, L. Effect of some factors on the biogenic amines and polyamines content in blue-veined cheese Niva. Czech J. Food Sci. 2009, 27, S410–S413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standarová, E.; Vorlová, L.; Kordiovská, P.; Janštová, B.; Dračková, M.; Borkovcová, I. Biogenic amine production in Olomouc curd cheese (Olomoucke tvaruzky) at various storage conditions. Acta Vet. Brno 2010, 79, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferroukhi, I.; Chassard, C.; Mardon, J. A comprehensive overview of blue-veined cheeses. Int. Dairy. J. 2024, 154, 105926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, H.K.; Fiechter, G. UHPLC analysis of biogenic amines in different cheese varieties. Food Control 2018, 93, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleva, P.; Buňková, L.; Theimrová, E.; Bartošáková, V.; Buňka, F.; Purevdorj, K. Biogenic amines in smear and mould-ripened cheeses. Potravinarstvo Slovak J. Food Sci. 2014, 8, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdolec, N.; Bogdanović, T.; Severin, K.; Dobranić, V.; Kazazić, S.; Grbavac, J.; Pleadin, J.; Petričević, S.; Kiš, M. Biogenic amine content in retailed cheese varieties produced with commercial bacterial or mold cultures. Processes 2022, 10, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaguey-Hernández, Y.; Aguilar-Arteaga, K.; Ojeda-Ramirez, D.; Añorve-Morga, J.; González-Olivares, L.G.; Castañeda-Ovando, A. Biogenic amines levels in food processing: Efforts for their control in foodstuffs. Food Res. Int. 2021, 144, 110341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadighara, P.; Bekheir, S.A.; Shafaroodi, H.; Basaran, B.; Sadighara, M. Tyramine, a biogenic agent in cheese: Amount and factors affecting its formation, a systematic review. Food Prod. Process. Nutr. 2024, 6, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritschard, J.S.; Schuppler, M. The microbial diversity on the surface of smear-ripened cheeses and its impact on cheese quality and safety. Foods 2024, 13, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sablé, S.; Cottenceau, G. Current knowledge of soft cheeses flavor and related compounds. J. Agr. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 4825–4836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Commission Regulation (EU) No 702/2010 of 4 August 2010 Entering a Name in the Register of Protected Designations of Origin and Protected Geographical Indications (Olomoucké tvarůžky (PGI)). Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/ALL/?uri=CELEX%3A32010R0702 (accessed on 2 December 2024).
- Komprda, T.; Rejchrtová, E.; Sládková, P.; Zemánek, L.; Vymlátilová, L. Effect of some external factors on the content of biogenic amines and polyamines in a smear-ripened cheese. Dairy. Sci. Technol. 2012, 92, 367–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olomoucké Tvarůžky. Traditionally Unique. Available online: https://www.tvaruzky.cz/?lang=en (accessed on 30 November 2024).
- Dadáková, E.; Křížek, M.; Pelikánová, T. Determination of biogenic amines in foods using ultra-performance liquid chromatography (UPLC). Food Chem. 2009, 116, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvak, Z.; Peterková, L.; Černá, E. Chemical and Physico-Chemical Methods in Quality Control of Milk and Dairy Products; Výskumný ústav potravinářský: Praha, Czech Republic, 1992; p. 221. [Google Scholar]
- Bockelmann, W. Cheese|Smear-Ripened Cheeses. In Encyclopedia of Dairy Sciences (Second Edition); Fuquay, J.W., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2011; pp. 753–766. [Google Scholar]
- Valdés-Stauber, N.; Scherer, S.; Seiler, H. Identification of yeasts and coryneform bacteria from the surface microflora of brick cheeses. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1997, 34, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA. Scientific Opinion on Risk Based Control of Biogenic Amine Formation in Fermented Foods. 2011. Available online: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/efsajournal/pub/2393 (accessed on 25 November 2024).
- Food Standard Agency: Comitee of Toxicity. Available online: https://cot.food.gov.uk/ (accessed on 25 November 2024).
- McCabe-Sellers, B.J.; Staggs, C.G.; Bogle, M.L. Tyramine in foods and monoamine oxidase inhibitor drugs: A crossroad where medicine, nutrition, pharmacy, and food industry converge. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2006, 19, S58–S65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingemanse, J.; Kleinbloesem, C.H.; Crevoisier, C.; Lankhaar, G.; Gasser, U.E. Pharmacokinetic studies with a dual-release formulation of levodopa, a novel principle in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Eur. Neurol. 1998, 39, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sved, A.F.; Weeks, J.J.; Grace, A.A.; Smith, T.T.; Donny, E.C. Monoamine oxidase inhibition in cigarette smokers: From preclinical studies to tobacco product regulation. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 886496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wöhrl, S.; Hemmer, W.; Focke, M.; Rappersberger, K.; Jarisch, R. Histamine intolerance-like symptoms in healthy volunteers after oral provocation with liquid histamine. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2004, 25, 305–311. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrante, M.C.; Mercogliano, R. Focus on histamine production during cheese manufacture and processing: A review. Food Chem. 2023, 419, 136046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madejska, A.; Michalski, M.; Osek, J. Biogenic amines in rennet ripening cheeses as a health risk to consumers. Med. Weter. 2017, 73, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cwiková, O.; Franke, G. Biogenic amines in smear ripened cheeses. Potravinarstvo Slovak J. Food Sci. 2019, 13, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madejska, A.; Michalski, M.; Pawul-Gruba, M.; Osek, J. Histamine content in rennet ripening cheeses during storage at different temperatures and times. J. Vet. Res. 2018, 62, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macků, I.; Lazárková, Z.; Buňka, F.; Hrabě, J. Biogenic amine content in mould cheese during storage. Ecol. Chem. Eng. A 2009, 16, 1591–1597. [Google Scholar]
- Komprda, T.; Smělá, D.; Novická, K.; Kalhotka, L.; Šustová, K.; Pechová, P. Content and distribution of biogenic amines in Dutch-type hard cheese. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marijan, A.; Džaja, P.; Bogdanović, T.; Škoko, I.; Cvetnić, Z.; Dobranić, V.; Zdolec, N.; Šatrović, E.; Severin, K. Influence of ripening time on the amount of certain biogenic amines in rind and core of cow milk Livno cheese. Mljekarstvo 2014, 64, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gentès, M.C.; Caron, A.; St-Gelais, D. Biogenic amine reduction in low-sodium Cheddar cheese: Probiotic cultures as an additional solution. Int. Dairy. J. 2024, 148, 105809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, I.; Park, J.H.; Choi, H.-Y.; Jung, H.-K. Emerging innovations to reduce the salt content in cheese; effects of salt on flavor, texture, and shelf life of cheese; and current salt usage: A review. Korean J. Food Sci. An. 2017, 37, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferroukhi, I.; Bord, C.; Lavigne, R.; Chassard, C.; Mardon, J. Exploring alternative salting methods to reduce sodium content in blue-veined cheeses. Int. Dairy. J. 2023, 138, 105555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tidona, F.; Zago, M.; Carminati, D.; Giraffa, G. The reduction of salt in different cheese categories: Recent advances and future challenges. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 859694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mietz, J.L.; Karmas, E. Polyamine and histamine content of rockfish, salmon, lobster, and shrimp as an indicator of decomposition. J. Assoc. Off. Ana Chem. 1978, 61, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Shape | Physical Characteristics of One Piece | Number of Samplings | Number of Analysed Samples * | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight (g) | Surface Area (mm2) | Specific Surface Area (mm2/g) | 2011 | 2013 | 2019 | ||
| Rings | 29.9 ± 0.9 | 6645 ± 314 | 222 ± 9 | 6 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Cylinders | 30.6 ± 0.7 | 5334 ± 436 | 174 ± 12 | 4 | 10 | 5 | 5 |
| Discs–small | 18.9 ± 0.4 | 4599 ± 188 | 243 ± 11 | 4 | 5 | 10 | 5 |
| Discs–large | 27.2 ± 1.2 | 6082 ± 323 | 224 ± 12 | 3 | 5 | 10 | 0 |
| Total | - | - | - | 17 | 30 | 35 | 20 |
| PUT | CAD | HIM | TYM | SPD | SPM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOD (mg/kg) | 0.33 | 0.45 | 0.75 | 0.80 | 0.44 | 0.46 |
| LOQ (mg/kg) | 1.00 | 1.50 | 2.50 | 2.50 | 1.50 | 1.50 |
| RSD (%) | 3.48 | 3.21 | 3.44 | 4.39 | 4.57 | 4.08 |
| Recovery (%) | 88 | 90 | 87 | 91 | 88 | 85 |
| Batch Shape (Month/Year) | PUT | CAD | HIM | TYM | SPD | SPM | BA4 | PA2 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||
| Rings 1 (June/2011) | 6.02 ab | 2.68 | 8.79 a | 5.69 | 14.7 e | 2.75 | 18.6 ab | 2.50 | 2.15 bc | 0.54 | 3.79 abc | 0.87 | 48.1 ab | 12.0 | 5.94 bcd | 1.32 | |
| Rings 2 (November/2011) | 1.43 a | 0.54 | 5.63 a | 3.64 | 3.90 ab | 1.03 | 15.5 a | 2.87 | 1.69 ab | 0.20 | 1.81 a | 0.25 | 26.5 a | 6.66 | 3.50 ab | 0.39 | |
| Rings 3 (March/2013) | 2.64 a | 1.42 | 1.66 a | 0.36 | 36.2 f | 2.54 | 5.30 a | 2.08 | 5.20 g | 0.82 | 7.17 ef | 1.07 | 45.8 ab | 4.74 | 12.4 fg | 1.02 | |
| Rings 4 (May/2013) | 2.04 a | 0.38 | 1.89 a | 0.52 | 41.3 g | 4.83 | 13.3 a | 10.6 | 9.76 i | 1.39 | 5.32 cde | 0.70 | 58.6 abc | 14.4 | 15.1 hi | 1.84 | |
| Rings 5 (April/2019) | 1.31 a | 0.40 | 2.82 a | 1.10 | 1.51 a | 0.64 | 33.7 bc | 26.2 | 3.36 de | 0.48 | 3.99 abc | 1.40 | 39.3 ab | 27.9 | 7.35 cd | 1.41 | |
| Rings 6 (November/2019) | 4.19 a | 4.12 | 10.5 a | 12.2 | 15.3 e | 5.05 | 39.1 cd | 20.4 | 1.80 ab | 0.23 | 11.4 g | 3.47 | 69.1 bcd | 38.3 | 13.2 gh | 3.49 | |
| Cylinders 1 (October/2011) | 8.45 ab | 2.02 | 3.51 a | 1.17 | 8.75 bc | 1.82 | 50.8 def | 9.69 | 0.95 a | 0.17 | 2.43 ab | 0.53 | 71.5 bcde | 13.8 | 3.38 a | 0.67 | |
| Cylinders 2 (November/2011) | 21.6 c | 4.96 | 69.6 d | 21.3 | 4.44 abc | 0.79 | 8.85 a | 2.90 | 1.61 ab | 0.60 | 3.24 abc | 0.69 | 104 ef | 26.9 | 4.85 abc | 1.04 | |
| Cylinders 3 (May/2013) | 21.1 c | 4.36 | 35.7 c | 8.29 | 57.1 h | 3.29 | 57.6 ef | 4.76 | 4.23 efg | 0.45 | 6.77 def | 0.84 | 171 g | 15.7 | 11.0 fg | 1.06 | |
| Cylinders 4 (November/2019) | 3.45 a | 1.17 | 7.76 a | 1.94 | 13.9 de | 3.78 | 16.9 ab | 3.47 | 1.57 ab | 0.28 | 14.5 h | 3.76 | 42.1 ab | 10.1 | 16.1 i | 3.88 | |
| Discs–small 1 (October/2011) | 36.8 d | 5.03 | 128 e | 27.7 | 41.2 g | 5.22 | 36.1 cd | 4.12 | 1.16 ab | 0.23 | 3.18 abc | 0.50 | 242 h | 33.8 | 4.35 ab | 0.67 | |
| Discs–small 2 (March/2013) | 21.1 c | 3.53 | 28.5 bc | 5.89 | 4.63 abc | 0.59 | 64.6 f | 11.7 | 3.87 def | 0.61 | 4.49 bcd | 0.85 | 119 f | 21.2 | 8.36 de | 1.01 | |
| Discs–small 3 (April/2013) | 2.39 a | 0.38 | 3.46 a | 0.99 | 54.1 h | 5.36 | 37.0 cd | 6.42 | 4.48 fg | 0.55 | 7.95 f | 1.67 | 97.0 def | 9.92 | 12.4 fg | 1.61 | |
| Discs–small 4 (November/2019) | 21.0 c | 15.7 | 16.5 ab | 5.76 | 17.5 e | 3.78 | 53.0 def | 18.3 | 2.04 bc | 0.30 | 8.43 f | 1.20 | 108 f | 41.7 | 10.5 ef | 1.44 | |
| Discs–large 1 (November/2011) | 11.9 b | 6.48 | 26.3 bc | 14.6 | 9.35 cd | 1.84 | 41.3 cde | 9.19 | 1.30 ab | 0.58 | 2.95 ab | 0.86 | 88.8 cdef | 31.1 | 4.26 ab | 1.42 | |
| Discs–large 2 (March/2013) | 4.16 a | 0.79 | 8.88 a | 4.21 | 3.05 a | 0.97 | 8.64 a | 5.04 | 3.00 cd | 0.68 | 7.87 f | 2.32 | 24.7 a | 6.71 | 10.9 efg | 1.86 | |
| Discs–large 3 (May/2013) | 2.13 a | 0.41 | 2.16 a | 0.42 | 38.9 fg | 2.26 | 3.17 a | 0.57 | 8.13 h | 1.66 | 7.81 f | 1.32 | 46.4 ab | 2.37 | 15.9 i | 2.16 | |
| The effect of (%; p-value) | Year | 8 *** | 18 *** | 30 *** | 2 *** | 56 *** | 50 *** | 4 *** | 63 *** | ||||||||
| Batch | 75 *** | 73 *** | 68 *** | 75 *** | 37 *** | 32 *** | 83 *** | 24 *** | |||||||||
| Storage | 1 ** | 1 ** | 0 ns | 0 ns | 0 * | 3 *** | 1 ns | 3 *** | |||||||||
| R2 (%) | 84.2 | 92.2 | 97.4 | 78.0 | 93.5 | 85.6 | 87.7 | 89.2 | |||||||||
| Weight (g) (n = 82) | Specific Surface Area (mm2/g) (n = 82) | pH (n = 40) | Salt Content (%) (n = 40) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 26.98 ± 4.79 (17.9–32.1) | 218 ± 26 (154–272) | 7.27 ± 0.68 (6.14–8.31) | 4.95 ± 0.22 (4.42–5.46) | |
| PUT | −0.7375 *** | 0.3626 *** | 0.2130 | −0.1152 |
| CAD | −0.5010 *** | 0.3204 ** | 0.0190 | −0.0947 |
| HIM | −0.2162 | 0.1921 | −0.1560 | −0.2609 |
| TYM | −0.4418 *** | 0.3775 *** | 0.1778 | −0.0692 |
| BA4 | −0.6374 *** | 0.4349 *** | 0.1303 | −0.1328 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Samková, E.; Dadáková, E.; Matějková, K.; Hasoňová, L.; Janoušek Honesová, S. Can the Contents of Biogenic Amines in Olomoucké Tvarůžky Cheeses Be Risky for Consumers? Foods 2025, 14, 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14030456
Samková E, Dadáková E, Matějková K, Hasoňová L, Janoušek Honesová S. Can the Contents of Biogenic Amines in Olomoucké Tvarůžky Cheeses Be Risky for Consumers? Foods. 2025; 14(3):456. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14030456
Chicago/Turabian StyleSamková, Eva, Eva Dadáková, Kateřina Matějková, Lucie Hasoňová, and Simona Janoušek Honesová. 2025. "Can the Contents of Biogenic Amines in Olomoucké Tvarůžky Cheeses Be Risky for Consumers?" Foods 14, no. 3: 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14030456
APA StyleSamková, E., Dadáková, E., Matějková, K., Hasoňová, L., & Janoušek Honesová, S. (2025). Can the Contents of Biogenic Amines in Olomoucké Tvarůžky Cheeses Be Risky for Consumers? Foods, 14(3), 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14030456






