Ultrasound-Assisted Determination of Selenium in Organic Rice Using Deep Eutectic Solvents Coupled with Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
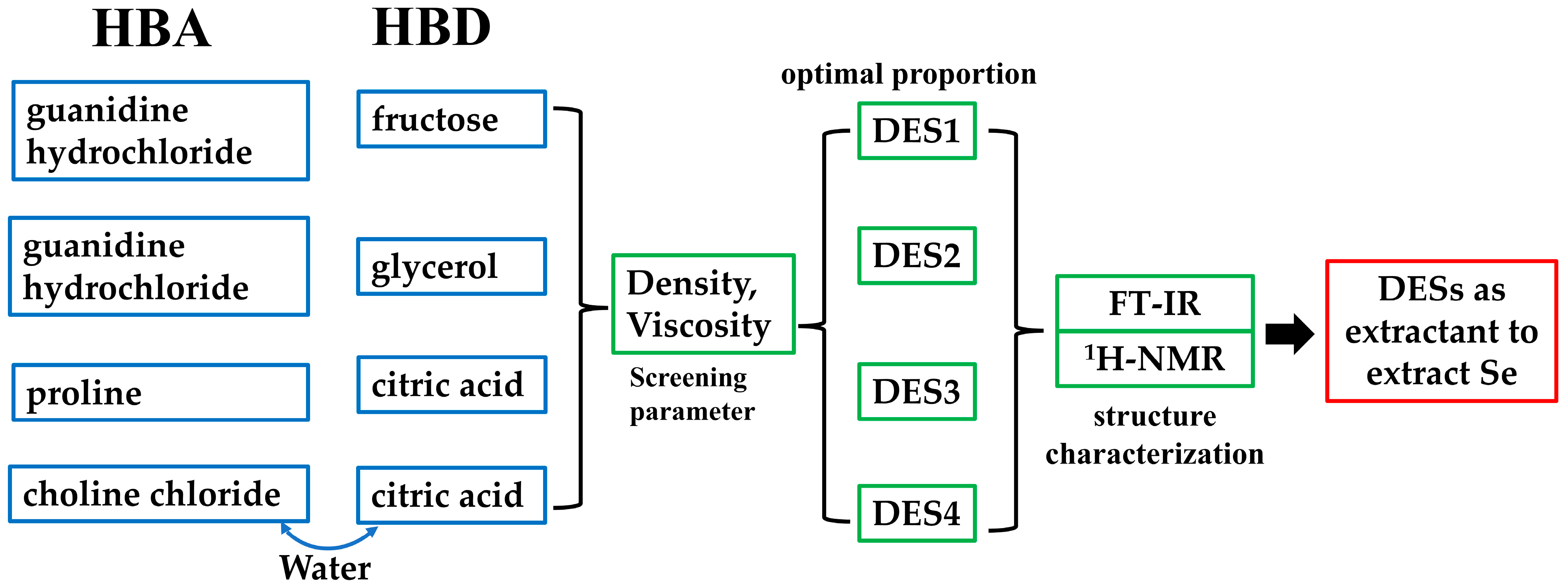
2.2. Synthesis of Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) by Mixture Design
2.3. Properties of DES
2.3.1. Density
2.3.2. Viscosity
2.3.3. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
2.3.4. Hydrogen Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (1H-NMR)
2.4. Sample Pretreatment and ICP-MS Analysis
2.4.1. Traditional Microwave-Assisted Acid Digestion (TM-AD)
2.4.2. Ultrasonic-Assisted Extraction (UAE)
2.4.3. ICP-MS Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
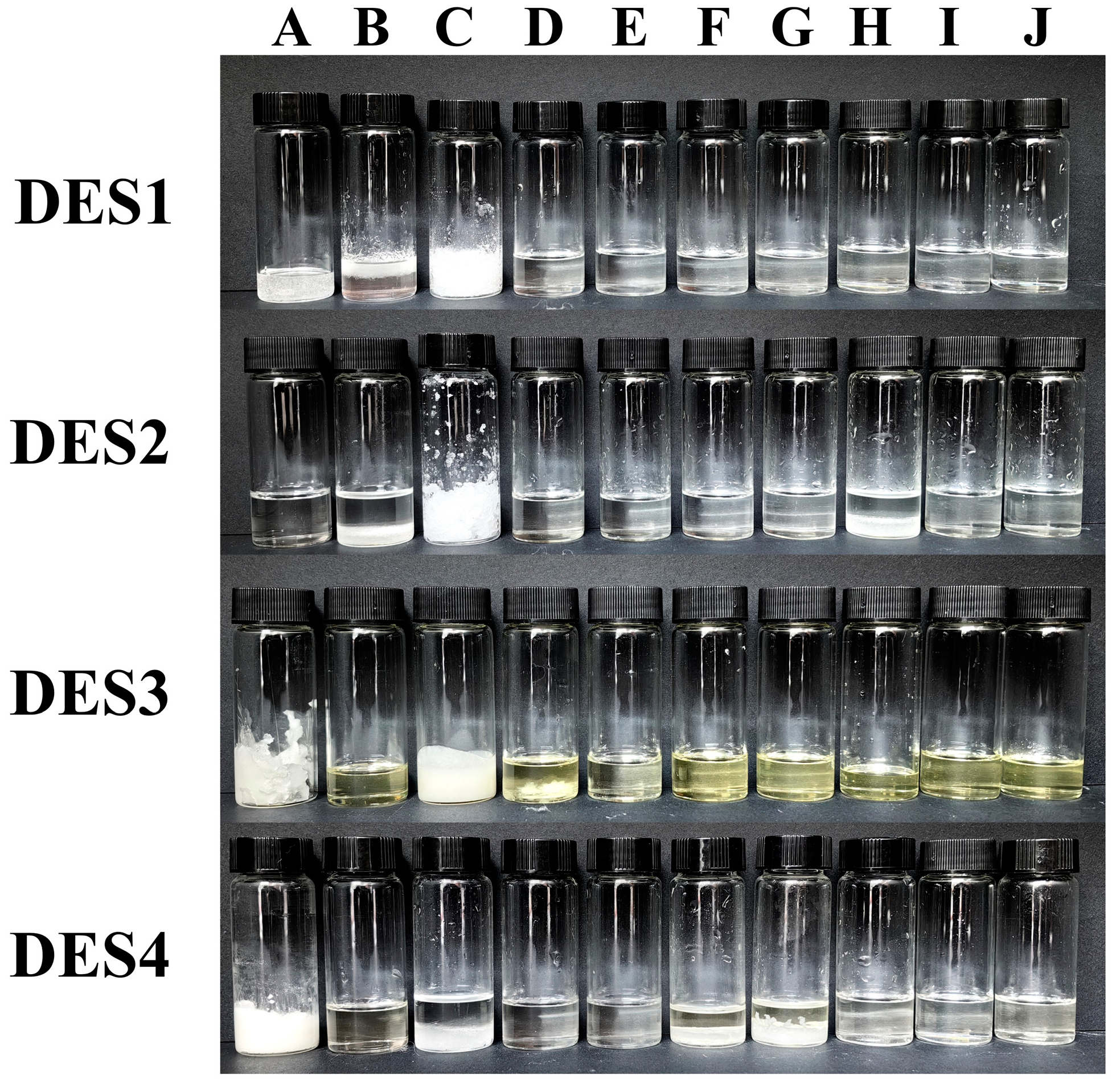
3.1. Liquid State of DES
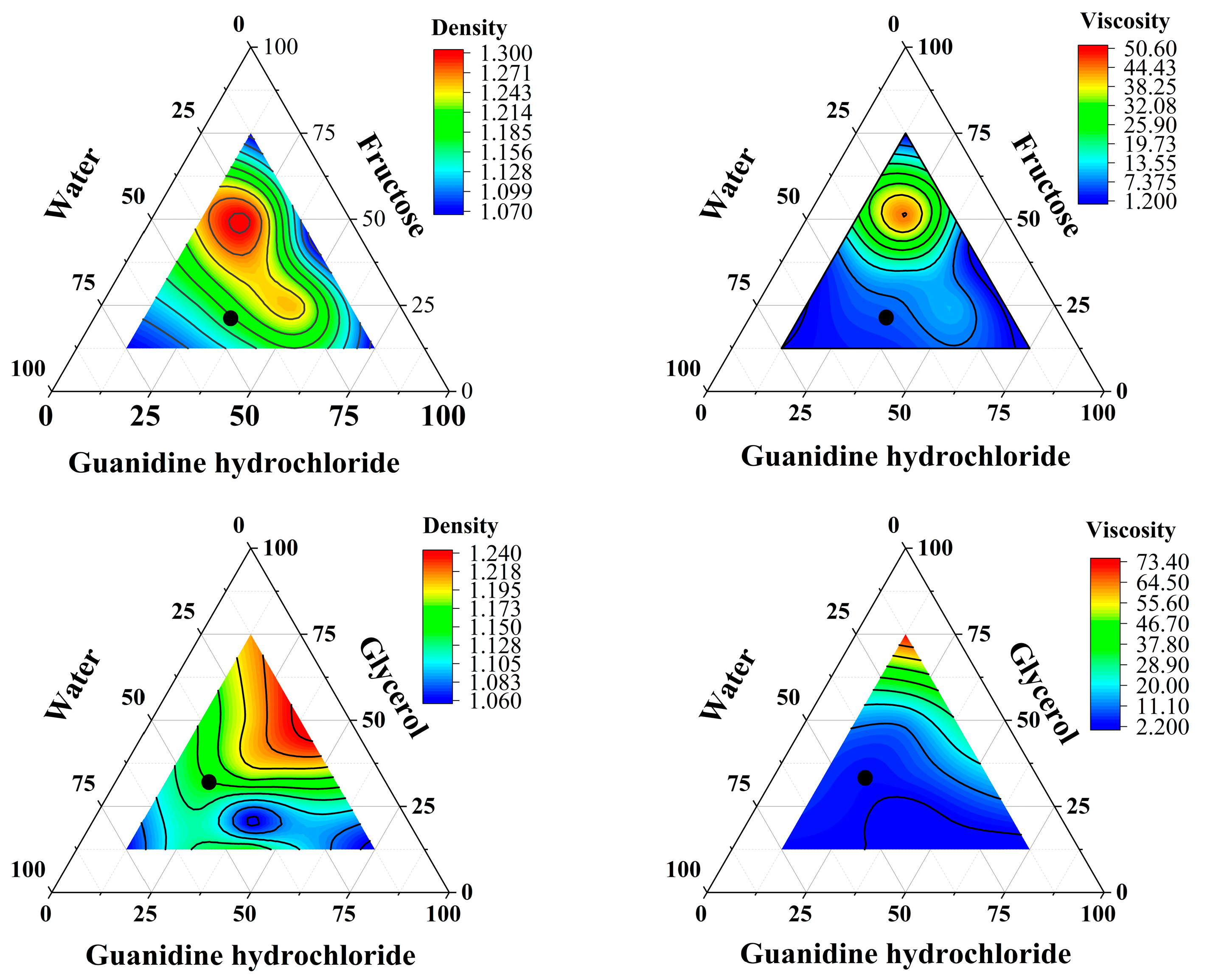
3.2. Density and Viscosity of DES
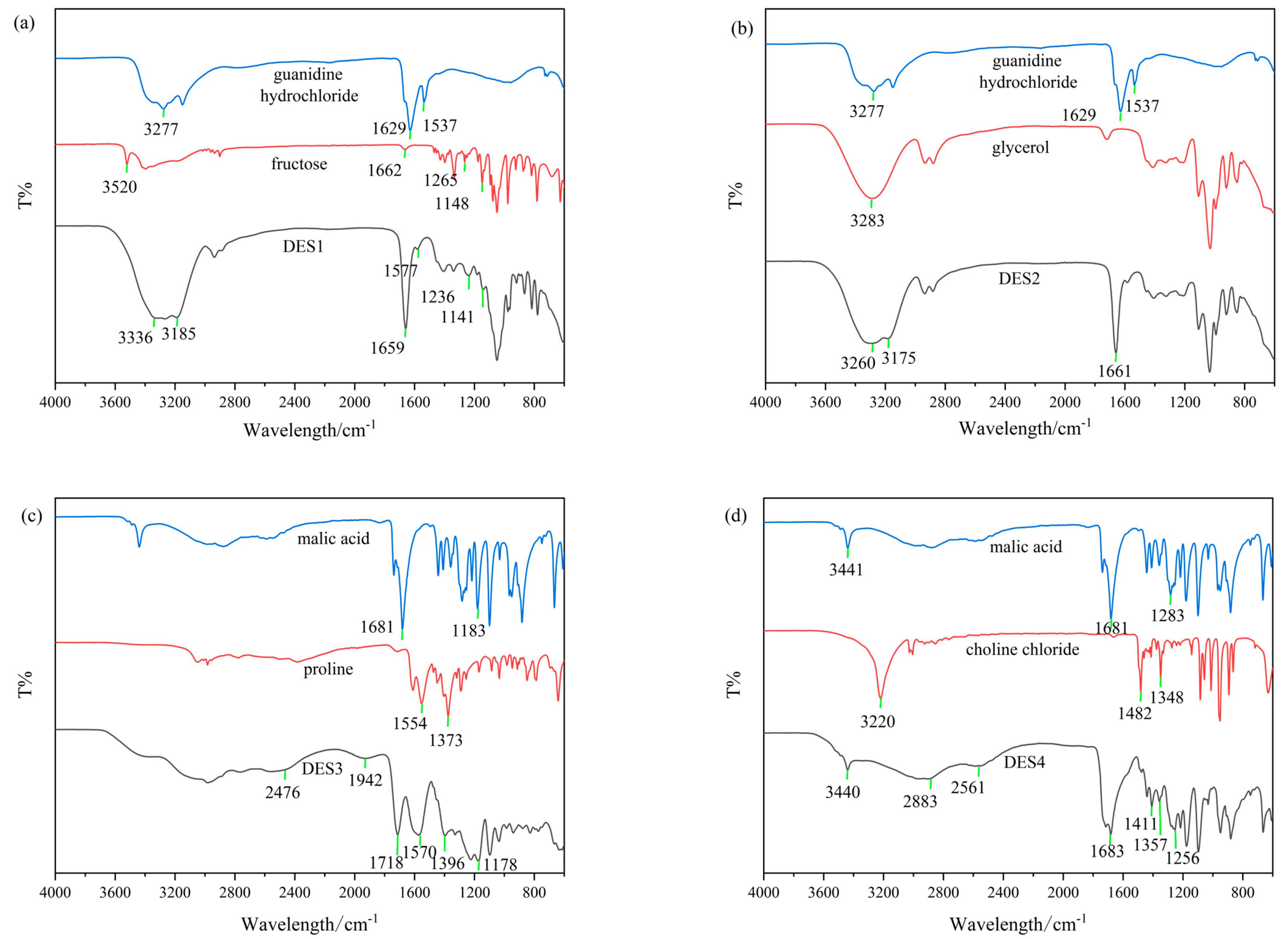
3.3. FT-IR Spectroscopy Analysis of DES
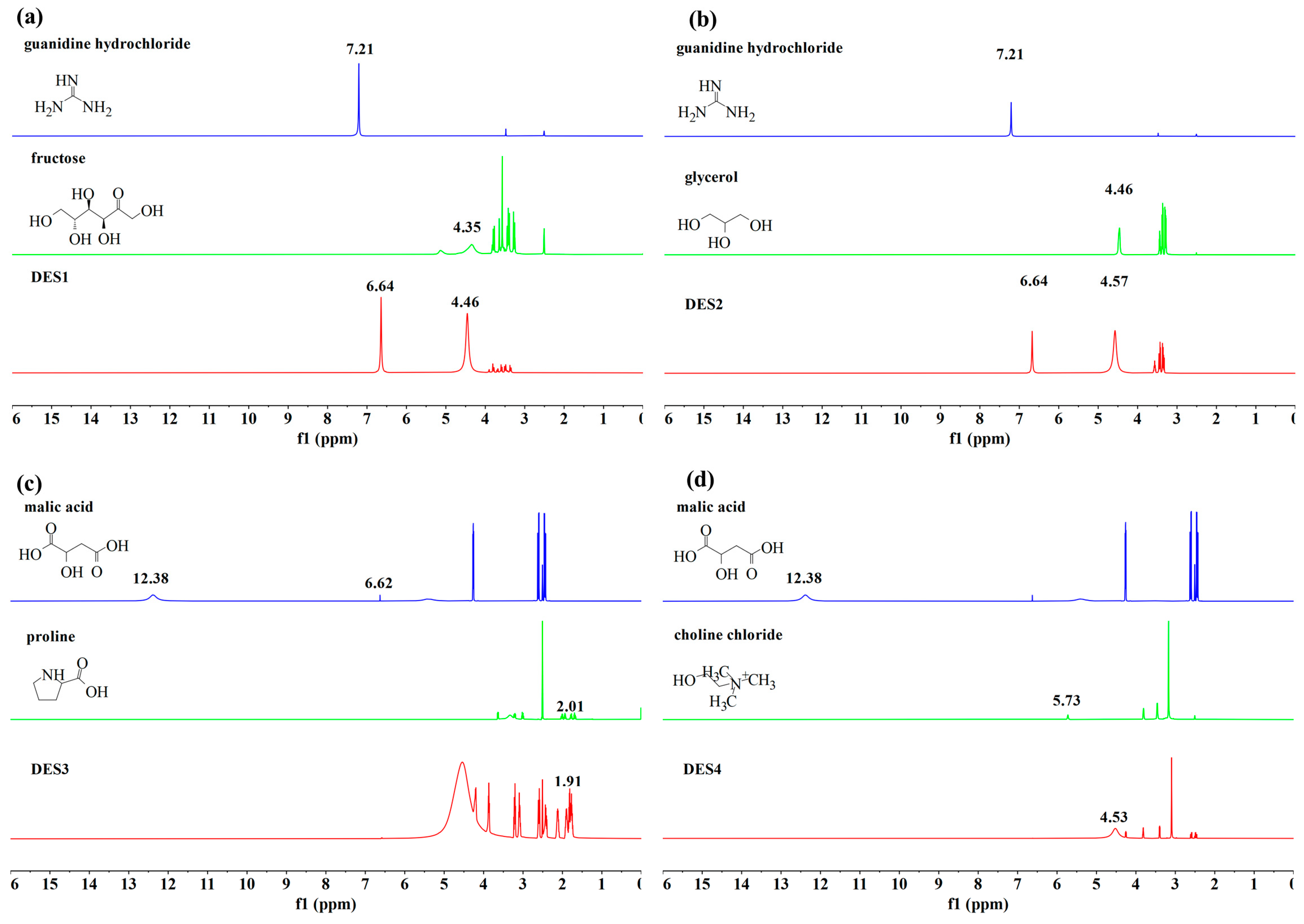
3.4. Analysis of DES by Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (1H NMR)
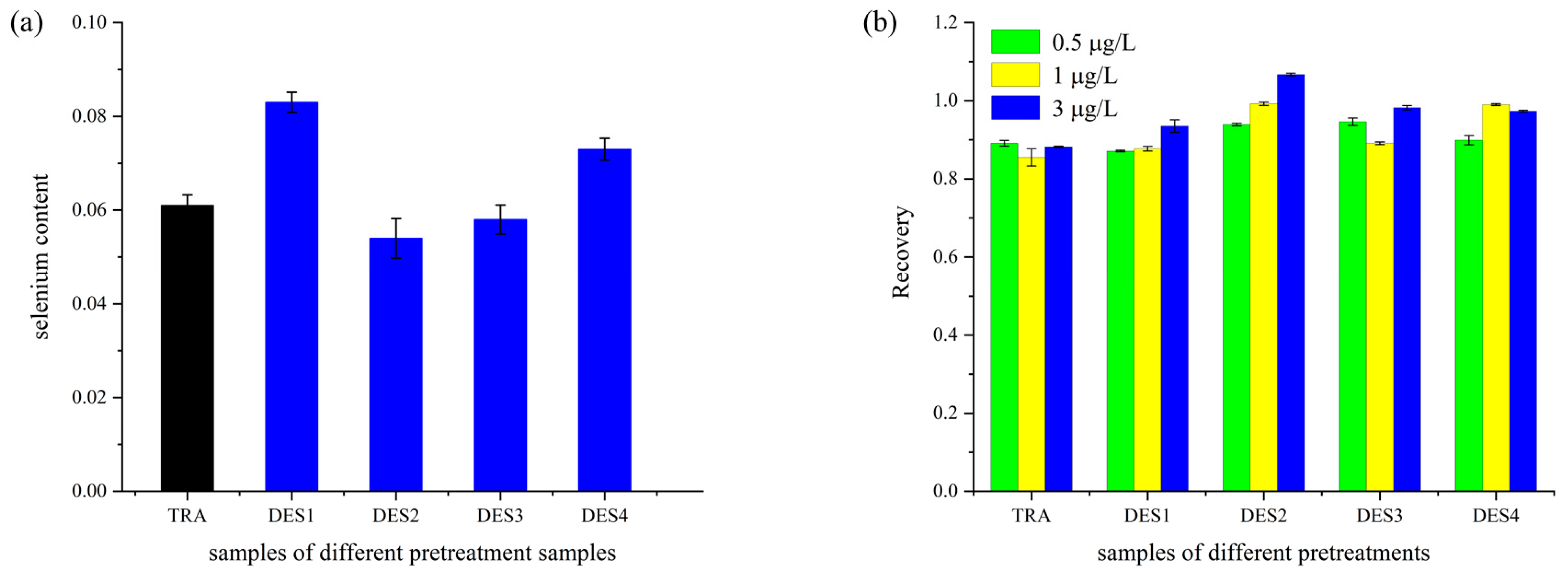
3.5. Analysis of Selenium-Enriched Rice Treated with DES Extraction
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, H.; Xie, X.; Wang, L. Selenium nutrition and human health. Food Ind. 2022, 43, 325–330. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, X.; Nong, K.; Lv, Q.; Qin, T.; Liang, X.; Gong, Z.; Huang, W. Research progress of the antioxidant effects of trace element selenium. China Food Addit. 2022, 33, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, K.; Guo, C.; Zhu, J.; Wei, Y.; Wu, M.; Huang, X.; Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; et al. The Whitening, Moisturizing, Anti-aging Activities, and Skincare Evaluation of Selenium-Enriched Mung Bean Fermentation Broth. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 837168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairweather-Tait, S.J.; Filippini, T.; Vinceti, M. Selenium status and immunity. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2023, 82, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, L.W.; Nardi, S.; Santoro, V.; Schiavon, M. The Relevance of Plant-Derived Se Compounds to Human Health in the SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) Pandemic Era. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, H.; Yu, Q.; Guo, D.; Wang, Y.; Duan, L.; Huang, W.; Zhou, J.; Wang, J.; Huang, P. The relationship between dietary selenium intake and telomere length among diabetes. Br. J. Nutr. 2023, 129, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Gao, J.; Fu, Z.; Chang, F. Research progress on the detection methods of total selenium in food. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2021, 12, 1653–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tie, M.; Li, B.; Sun, T.; Guan, W.; Liang, Y.; Li, H. HPLC-ICP-MS speciation of selenium in Se-cultivated Flammulina velutipes. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Zhu, W. Evaluation of uncertainty on determination of selenium contents in rice by hydride generation atomic fluorescence spectrometry. Storage Process 2015, 15, 62–67. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Huang, S.; Ju, H.; Chen, L.; Wu, H.; Zeng, T. Determination of organic selenium and inorganic selenium in food by hydride generation-atomic fluorescence spectrometry. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 41, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.L.C.; Bezerra, M.A.; Santos, A.S.; dos Santos, W.N.L.; Novaes, C.G.; de Oliveira, O.M.C.; Oliveira, M.L.; Garcia, R.L. Atomic absorption spectrometry—A multi element technique. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 100, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, A.A.S.C. From the first to the second twelve principles of green chemistry. Quim. Nova 2012, 35, 1250–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slootweg, J.C. Sustainable chemistry: Green, circular, and safe-by-design. One Earth 2024, 7, 754–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.R.; Chua, L.S.; Mustaffa, A.A. Ionic liquids as green solvent and their applications in bioactive compounds extraction from plants. Process Biochem. 2022, 122, 292–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, G.; Dhariwal, J.; Saha, M.; Trivedi, S.; Banjare, M.K.; Kanaoujiya, R.; Behera, K. Ionic liquids: Environmentally sustainable materials for energy conversion and storage applications. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 10296–10316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jesus, S.S.; Maciel Filho, R. Are ionic liquids eco-friendly? Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 157, 112039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelghany, T.M.; Hedya, S.A.; De Santis, C.; El-Rahman, S.S.A.; Gill, J.H.; Abdelkader, N.F.; Wright, M.C. Potential for cardiac toxicity with methylimidazolium ionic liquids. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 249, 114439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.A.; Muhammad, G.; Khan, M.N.; Mofijur, M.; Lv, Y.; Xiong, W.; Xu, J. Choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvents as green extractants for the isolation of phenolic compounds from biomass. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 309, 127445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Xie, Q.; Liu, Q.; Liu, J.; Wan, C.; Liang, D.; Zhang, H. Separation of phenolic compounds from oil mixtures by betaine-based deep eutectic solvents. Asia-Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 15, e2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Leron, R.B.; Caparanga, A.R.; Li, M. Henry’s constant of carbon dioxide-aqueous deep eutectic solvent (choline chloride/ethylene glycol, choline chloride/glycerol, choline chloride/malonic acid) systems. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2014, 68, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomba, L.; Werner, A.; Giner, B.; Lafuente, C. Deep Eutectic Solvents Formed by Glycerol and Xylitol, Fructose and Sorbitol: Effect of the Different Sugars in Their Physicochemical Properties. Molecules 2023, 28, 6023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents and Their Applications in Biotechnology. In Application of Ionic Liquids in Biotechnology; Itoh, T., Koo, Y.-M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 31–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levashov, A.S.; Buriy, D.S.; Konshin, V.V.; Andreev, A.A. Stille-type cross coupling reactions with tetraalkynyl stannanes. In Proceedings of the 20th International Electronic Conference on Synthetic Organic Chemistry, Online, 1–30 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, C.; Guo, Y.; Li, D.; Zong, J.; Ji, X.; Liu, C.; Lu, X. Molar Enthalpy of Mixing for Choline Chloride/Urea Deep Eutectic Solvent plus Water System. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2016, 61, 4172–4177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zounr, R.A.; Tuzen, M.; Khuhawar, M.Y. Determination of Selenium and Arsenic Ions in Edible Mushroom Samples by Novel Chloride-Oxalic Acid Deep Eutectic Solvent Extraction Using Graphite Furnace-Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. J. AOAC Int. 2018, 101, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, A.P.R.; Andrade, D.F.; Guimaraes, T.G.S.; Amaral, C.D.B.; Oliveira, A.; Gonzalez, M.H. Synthesis of natural deep eutectic solvents using a mixture design for extraction of animal and plant samples prior to ICP-MS analysis. Talanta 2020, 216, 120956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, P.; He, X.; Ma, S.; Wang, S.; Niu, Q. Ultrasonic-Assisted Extraction of Antioxidants from Perilla frutescens Leaves Based on Tailor-Made Deep Eutectic Solvents: Optimization and Antioxidant Activity. Molecules 2023, 28, 7554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, D.; Shi, C.; Yuan, Q.; An, X.; Liu, Y. Mixture design of concrete using simplex centroid design method. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 89, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, M.A.; Lemos, V.A.; Novaes, C.G.; de Jesus, R.M.; Souza Filho, H.R.; Araujo, S.A.; Santos Alves, J.P. Application of mixture design in analytical chemistry. Microchem. J. 2020, 152, 104336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squeo, G.; De Angelis, D.; Leardi, R.; Summo, C.; Caponio, F. Background, Applications and Issues of the Experimental Designs for Mixture in the Food Sector. Foods 2021, 10, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravena, P.; Cea-Klapp, E.; Gajardo-Parra, N.F.; Held, C.; Garrido, J.M.; Canales, R.I. Effect of water and hydrogen bond acceptor on the density and viscosity of glycol-based eutectic solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 389, 122856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plastiras, O.-E.; Andreasidou, E.; Samanidou, V. Microextraction Techniques with Deep Eutectic Solvents. Molecules 2020, 25, 6026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Osch, D.J.G.P.; Dietz, C.H.J.T.; van Spronsen, J.; Kroon, M.C.; Gallucci, F.; Annaland, M.v.S.; Tuinier, R. A Search for Natural Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on Natural Components. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 2933–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Osch, D.J.G.P.; Zubeir, L.F.; van den Bruinhorst, A.; Rocha, M.A.A.; Kroon, M.C. Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents as water-immiscible extractants. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 4518–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Witkamp, G.-J.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Tailoring properties of natural deep eutectic solvents with water to facilitate their applications. Food Chem. 2015, 187, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.; Tang, S.; Tsona, N.T.; Du, L. The Influence of the Position of the Double Bond and Ring Size on the Stability of Hydrogen Bonded Complexes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabriele, F.; Chiarini, M.; Germani, R.; Tiecco, M.; Spreti, N. Effect of water addition on choline chloride/glycol deep eutectic solvents: Characterization of their structural and physicochemical properties. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 291, 111301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranska, H.; Kuduk-Jaworska, J.; Szostak, R.; Romaniewska, A. Vibrational spectra of racemic and enantiomeric malic acids. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2003, 34, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giubertoni, G.; Sofronov, O.O.; Bakker, H.J. Effect of intramolecular hydrogen-bond formation on the molecular conformation of amino acids. Commun. Chem. 2020, 3, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juric, T.; Uka, D.; Hollo, B.B.; Jovic, B.; Kordic, B.; Popovic, B.M. Comprehensive physicochemical evaluation of choline chloride-based natural deep eutectic solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 343, 116968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasdemir, H.U. Effects of intramolecular hydrogen bonding on nuclear magnetic resonance, electron paramagnetic resonance and molecular docking studies: Mexiletine molecule. J. Mol. Model. 2024, 30, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Instrument Parameter | Parameter |
|---|---|
| Radiofrequency power | 1550 v |
| Plasma gas flow | 15 L/min |
| Auxiliary gas flow | 1 L/min |
| H2 flow rate | 3.5 mL/min |
| Sample uptake rate | 0.7 mL/min |
| Measurement mode | KED |
| Quadrupole bias | −16.0 V |
| Dwell time | 0.1 s |
| Washing time | 30 s |
| Monitored isotopes | 78Se |
| Replicates | 3 |
| Experiment | Component 1 (%mm−1) | Component 2 (%mm−1) | Water (%mm−1) | Density a (g/cm3) | Viscosity a (mPa·s) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DES1 | DES2 | DES3 | DES4 | DES1 | DES2 | DES3 | DES4 | ||||
| A | 12.5% | 75% | 12.5% | 1.43 ± 0.03 | 1.21 ± 0.03 | - c | - c | 9900.00 ± 1.28 | 73.28 ± 1.11 | - c | - c |
| B | 43.75% | 43.75% | 12.5% | 1.36 ± 0.01 b | 1.24 ± 0.02 b | 1.31 ± 0.03 | 1.30 ± 0.02 | 236.80 ± 1.56 b | 24.96 ± 0.31 b | 14,975.00 ± 1.67 | 353.50 ± 1.08 |
| C | 75% | 12.5% | 12.5% | - c | - c | - c | 1.09 ± 0.01 b | - c | - c | - c | 10.1 ± 0.11 b |
| D | 43.75% | 12.5% | 43.75% | 1.15 ± 0.02 | 1.15 ± 0.02 | 1.24 ± 0.01 | 1.09 ± 0.01 | 3.84 ± 0.03 | 2.24 ± 0.04 | 9.92 ± 0.11 | 9.50 ± 0.08 |
| E | 12.5% | 12.5% | 75% | 1.06 ± 0.01 | 1.07 ± 0.03 | 1.09 ± 0.01 | 1.05 ± 0.02 | 1.28 ± 0.02 | 2.88 ± 0.03 | 2.56 ± 0.04 | 7.50 ± 0.06 |
| F | 12.5% | 43.75% | 43.75% | 1.22 ± 0.02 | 1.14 ± 0.01 | 1.18 ± 0.02 | −1.14 ± 0.01 b | 8.96 ± 0.07 | 8.32 ± 0.08 | 26.88 ± 1.34 | 33.26 ± 0.15 b |
| G | 25% | 50% | 25% | 1.30 ± 0.02 | 1.20 ± 0.01 | 1.24 ± 0.01 | −1.16 ± 0.03 b | 50.56 ± 0.47 | 13.12 ± 0.11 | 224.32 ± 1.56 | 51.25 ± 0.33 b |
| H | 50% | 25% | 25% | 1.25 ± 0.03 | 1.17 ± 0.03 b | 1.30 ± 0.02 | 1.15 ± 0.01 | 12.16 ± 0.12 | 10.11 ± 0.13 b | 144.32 ± 1.42 | 32.96 ± 0.17 |
| I | 25% | 25% | 50% | 1.16 ± 0.03 | 1.13 ± 0.02 | 1.17 ± 0.02 | 1.13 ± 0.01 | 6.08 ± 0.04 | 3.52 ± 0.04 | 13.44 ± 0.05 | 5.76 ± 0.07 |
| J | 33.33% | 33.33% | 33.33% | 1.25 ± 0.01 | 1.18 ± 0.02 | 1.24 ± 0.02 | 1.17 ± 0.02 | 8.96 ± 0.06 | 5.76 ± 0.02 | 49.28 ± 0.28 | 20.50 ± 0.17 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Chen, B.; Liu, Y.; Sun, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, N.; Qing, Y.; Elango, J.; Zhao, D.; Wu, W. Ultrasound-Assisted Determination of Selenium in Organic Rice Using Deep Eutectic Solvents Coupled with Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Foods 2025, 14, 384. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14030384
Zhang S, Chen B, Liu Y, Sun H, Zhang H, Li N, Qing Y, Elango J, Zhao D, Wu W. Ultrasound-Assisted Determination of Selenium in Organic Rice Using Deep Eutectic Solvents Coupled with Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Foods. 2025; 14(3):384. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14030384
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shanshan, Boyu Chen, Yu Liu, Haoyu Sun, Haixing Zhang, Na Li, Yang Qing, Jeevithan Elango, Dayun Zhao, and Wenhui Wu. 2025. "Ultrasound-Assisted Determination of Selenium in Organic Rice Using Deep Eutectic Solvents Coupled with Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry" Foods 14, no. 3: 384. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14030384
APA StyleZhang, S., Chen, B., Liu, Y., Sun, H., Zhang, H., Li, N., Qing, Y., Elango, J., Zhao, D., & Wu, W. (2025). Ultrasound-Assisted Determination of Selenium in Organic Rice Using Deep Eutectic Solvents Coupled with Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Foods, 14(3), 384. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14030384









