Solvent-Free Catalytic Synthesis of Ethyl Butyrate Using Immobilized Lipase Based on Hydrophobically Functionalized Dendritic Fibrous Nano-Silica
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of DFNS-C8
2.3. Immobilization and Enzymatic Properties of Lipase CALB
2.4. Enzymatic Esterification of Ethyl Butyrate
2.5. Lipase Performance Evaluation
2.6. Molecular Docking Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
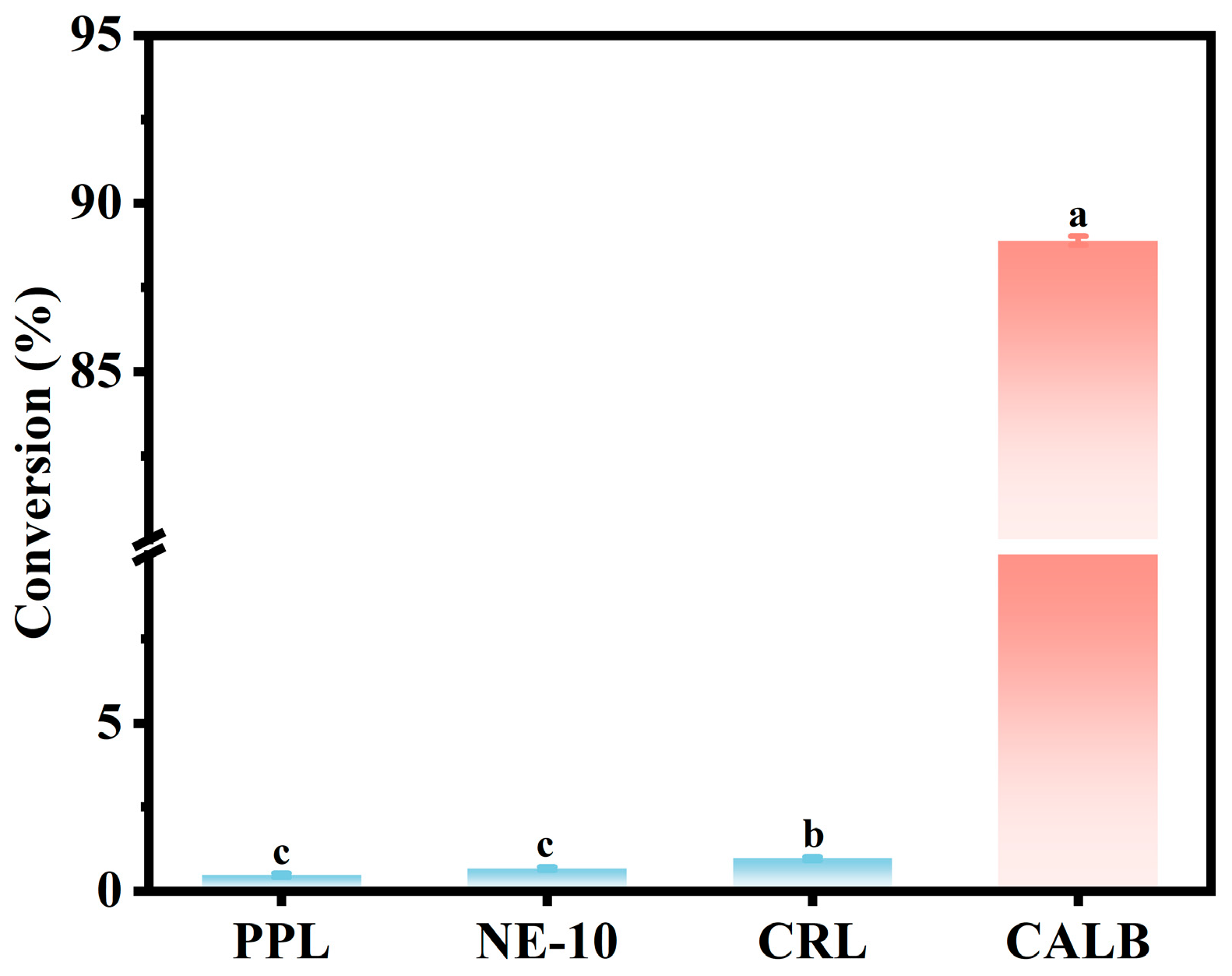
3.1. Lipase Screening
3.2. Characterization of DFNS, DFNS-C8 and CALB@DFNS-C8
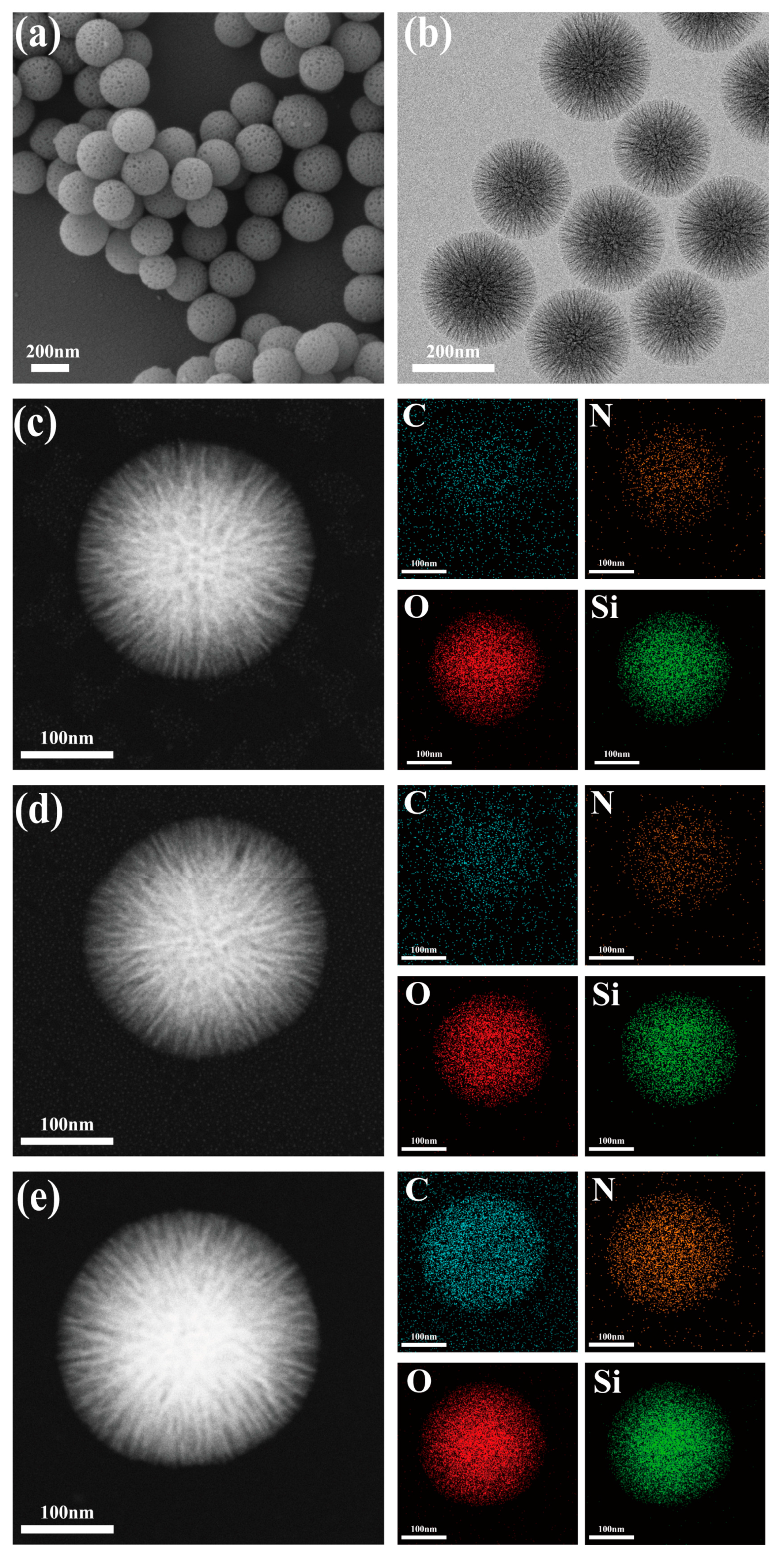
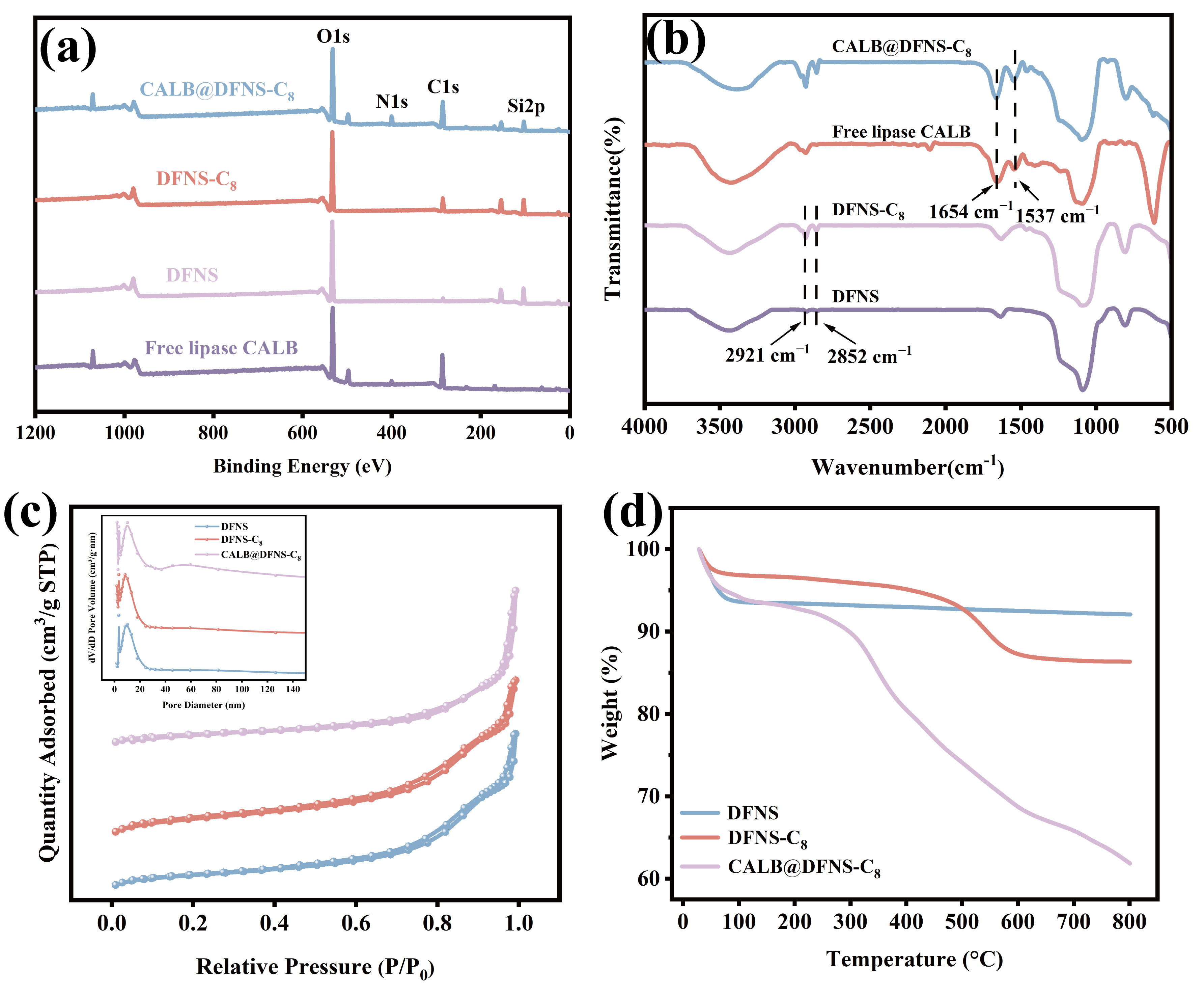
3.3. Lipase CALB Immobilization
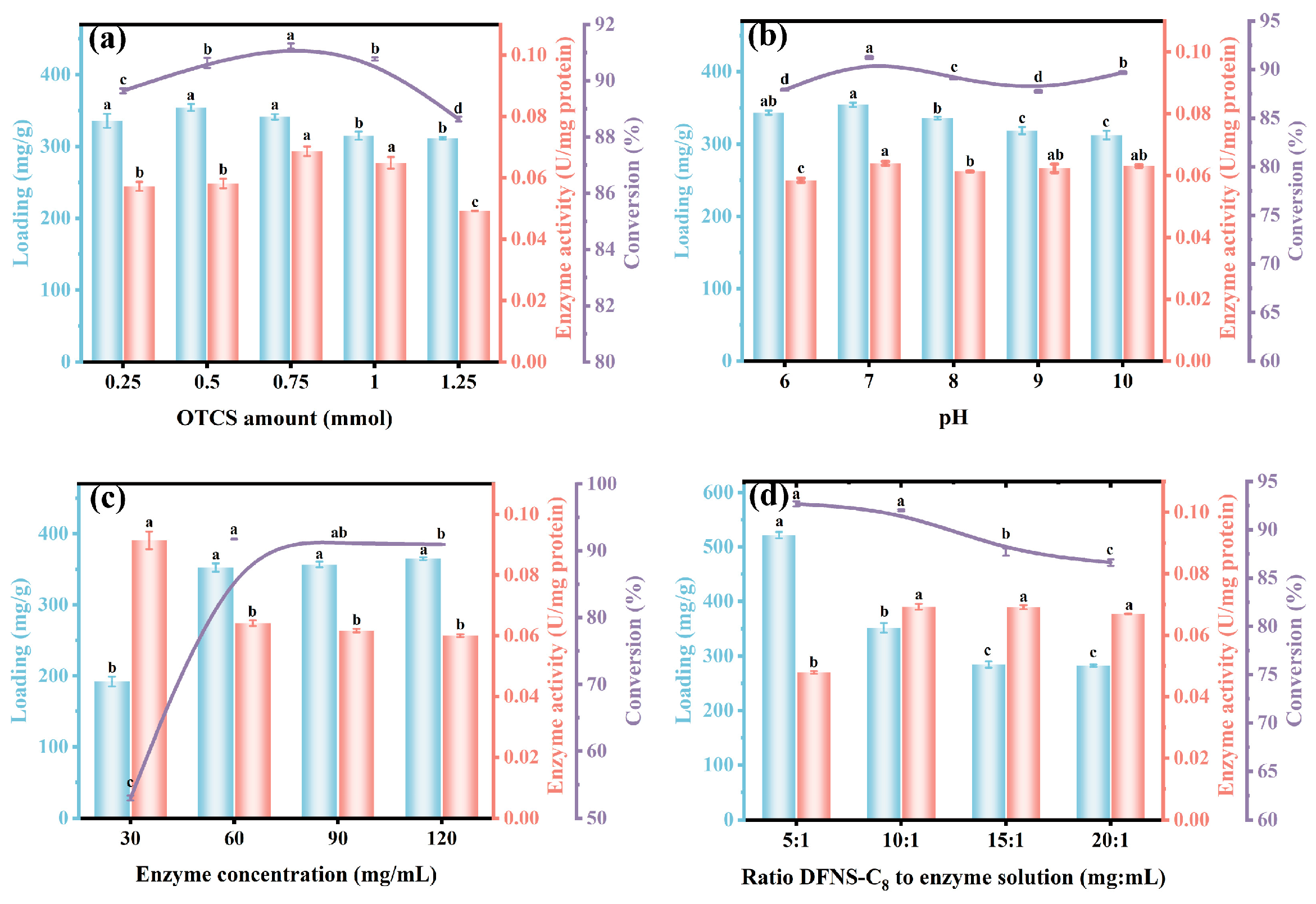
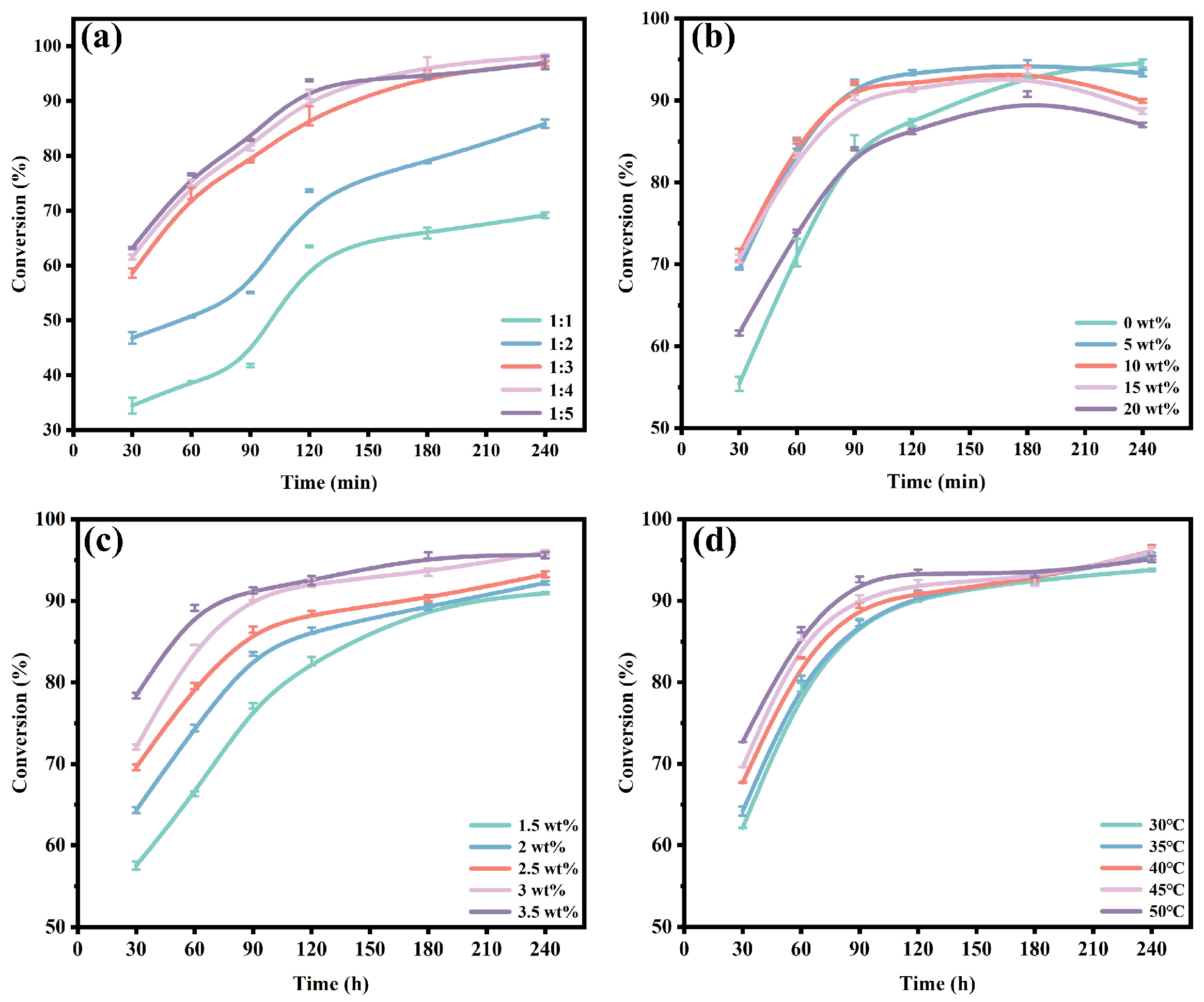
3.4. Optimization of Reaction Conditions
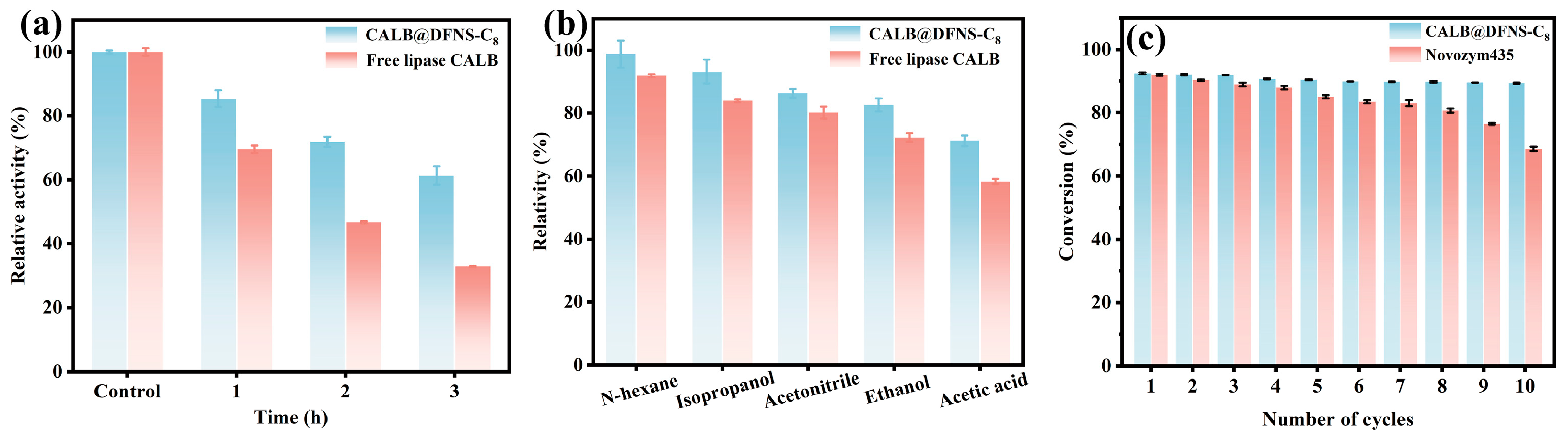
3.5. Catalytic Stability and Applicability Evaluation
| Flavor Esters | Acyl Acceptor | Main Flavor Characteristics | Conversion (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ethyl acetate | Ethanol | Sweet, Pear | 94. ± 0.4% |
| Propyl acetate | Propanol | Pear, Banana | 95.2 ± 0.1% |
| Butyl acetate | Butanol | Banana, Apple | 95.8 ± 0.4% |
| Pentyl acetate | Pentanol | Banana | 96.5 ± 0.3% |
| Hexyl acetate | Hexanol | Green apple, Pear | 97.9 ± 0.2% |
| Propyl butyrate | Propanol | Pineapple, Apple | 96.0 ± 0.3% |
| Butyl butyrate | Butanol | Pineapple, Mango | 96.1 ± 0.5% |
| Pentyl butyrate | Pentanol | Pineapple, Peach | 97.4 ± 0.2% |
| Hexyl butyrate | Hexanol | Pineapple, Banana | 98.1 ± 0.6% |
3.6. Molecular Docking Analysis
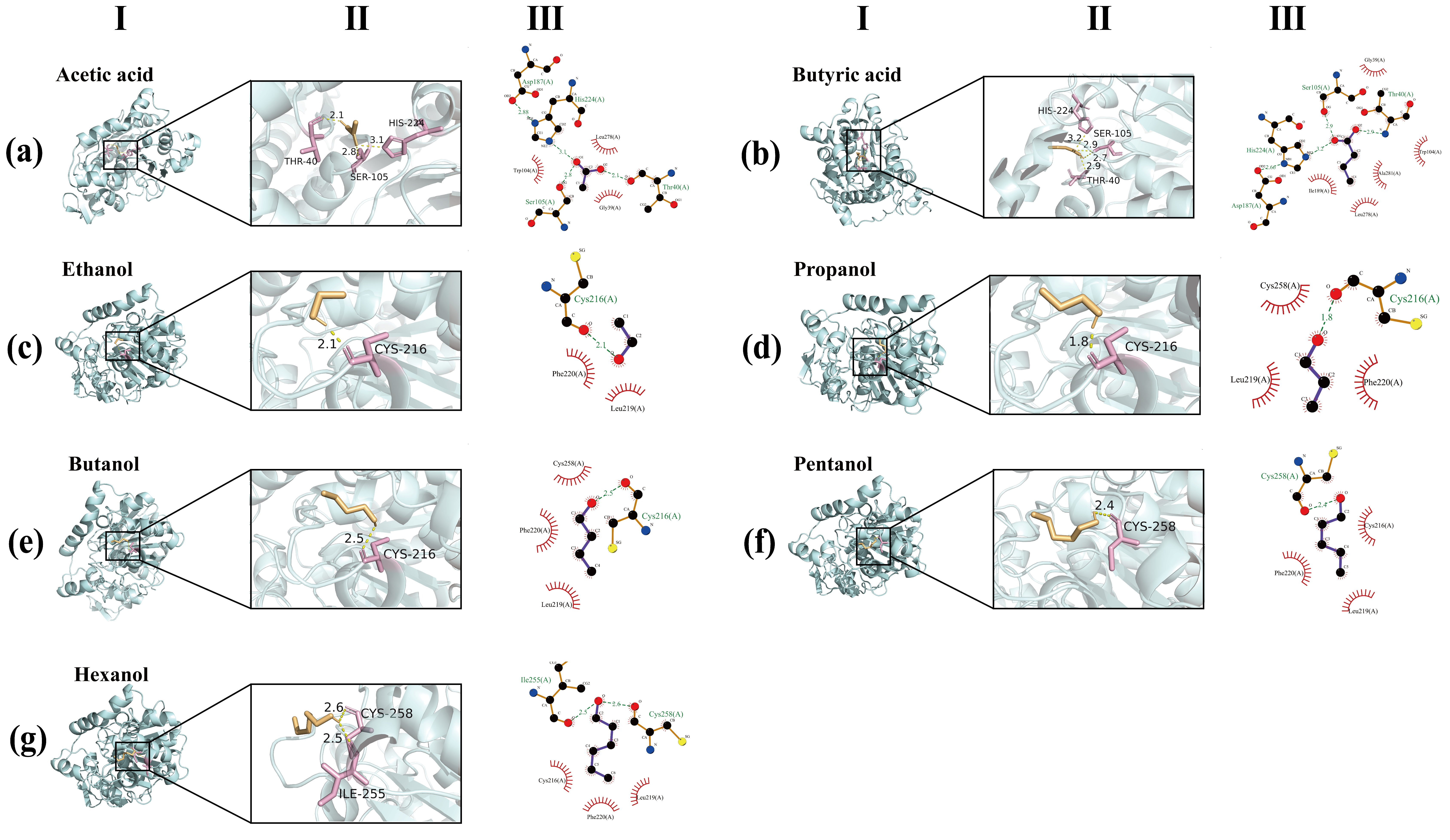
| Compounds | Binding Energy (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|
| Acetic acid | −3.1 |
| Butyric acid | −4.1 |
| Ethanol | −1.6 |
| Propanol | −1.9 |
| Butanol | −2.1 |
| Pentanol | −2.2 |
| Hexanol | −2.5 |
3.7. Comparison of Enzymatic Synthesis of Ethyl Butyrate
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- SÁ, A.G.A.; de Meneses, A.C.; de Araújo, P.H.H.; de Oliveira, D. A review on enzymatic synthesis of aromatic esters used as flavor ingredients for food, cosmetics and pharmaceuticals industries. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 69, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayramoglu, G.; Celikbicak, O.; Kilic, M.; Yakup Arica, M. Immobilization of Candida rugosa lipase on magnetic chitosan beads and application in flavor esters synthesis. Food Chem. 2022, 366, 130699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siva, S.; Meenatchi, V.; Bodkhe, G.A.; Kim, M. Exploring antibacterial ethyl cinnamate/cyclodextrin inclusion complex electrospun nanofibers. J. Mol. Liq. 2025, 426, 127311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Morais, M.C.; de Oliveira Lima, E.; Perez-Castillo, Y.; de Sousa, D.P. Synthetic Cinnamides and Cinnamates: Antimicrobial Activity, Mechanism of Action, and In Silico Study. Molecules 2023, 28, 1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosso, C.; Ferreira-Dias, S.; Pires-Cabral, P. Modelling and optimization of ethyl butyrate production catalysed by Rhizopus oryzae lipase. J. Food Eng. 2013, 115, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Z.; Li, X.; Sun, B. Flavor mystery of Chinese traditional fermented baijiu: The great contribution of ester compounds. Food Chem. 2022, 369, 130920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, L.P.; Nogueira, I.B.R.; Ribeiro, A.M. Flavor Engineering: A comprehensive review of biological foundations, AI integration, industrial development, and socio-cultural dynamics. Food Res. Int. 2024, 196, 115100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-C.; Abrahamson, M.; Kapoor, Y.; Chauhan, A. Timolol transport from microemulsions trapped in HEMA gels. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 315, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, R.R.d.; dos Santos, M.M.; Medeiros, M.W.R.; Manoel, E.A.; Berenguer-Murcia, Á.; Freire, D.M.G.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; Ferreira-Leitão, V.S. Immobilized Lipases in the Synthesis of Short-Chain Esters: An Overview of Constraints and Perspectives. Catalysts 2025, 15, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Minhazul, K.A.H.M.; Li, X. The occurrence, enzymatic production, and application of ethyl butanoate, an important flavor constituent. Flavour Fragr. J. 2020, 35, 601–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, K.S.; Rathod, V.K. Process Intensification of Enzymatic Synthesis of Flavor Esters: A Review. Chem. Rec. 2022, 22, e202100213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilas Bôas, R.N.; de Castro, H.F. A review of synthesis of esters with aromatic, emulsifying, and lubricant properties by biotransformation using lipases. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2022, 119, 725–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Tian, T.; Bi, Y.; Cui, J. Immobilized lipase on MIL-53(Al)-AM11 with regulatable hydrophobic surface for flavor ester synthesis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 305, 141322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, E.S.; Machado, B.R.; Farias, B.S.d.; Han, L.H.; Santos, L.O.d.; Duarte, S.H.; Cadaval Junior, T.R.S.A.; Pinto, L.A.d.A.; Diaz, P.S. Bi-layer nanocapsules based on chitosan and xanthan gum for lipase immobilization. J. Mol. Liq. 2025, 434, 128031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangaraj, B.; Solomon, P.R. Immobilization of Lipases—A Review. Part I: Enzyme Immobilization. ChemBioEng Rev. 2019, 6, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, R.; Liu, Z.; Goh, K.-L.; Zivkovic, V.; Zheng, M. Solvent-free synthesis of diacylglycerols via enzymatic glycerolysis between edible oils and glycerol catalyzed by self-made immobilized lipase PS@LXTE-1000. Oil Crop Sci. 2024, 9, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.R.; Baek, K.-H. Lipase immobilization with support materials, preparation techniques, and applications: Present and future aspects. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 1624–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zieniuk, B.; Małajowicz, J.; Jasińska, K.; Wierzchowska, K.; Uğur, Ş.; Fabiszewska, A. Agri-Food and Food Waste Lignocellulosic Materials for Lipase Immobilization as a Sustainable Source of Enzyme Support—A Comparative Study. Foods 2024, 13, 3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.; Gong, N.; Chen, H.; Xie, B.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, D. Metal-organic framework-based tunable platform for the immobilization of lipase with enhanced activity in non-aqueous systems. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 300, 140272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xing, C.; Feng, M.; Su, Y.; Wang, Q.; Pang, D.; Feng, X.; Zhang, Y. Covalent Organic Framework Aerogels with Tailored Microenvironments for Optimizing Enzyme Immobilization and Catalytic Performance. Chin. J. Chem. 2025, 43, 3205–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Dai, L.; Liu, D.; Du, W. Rationally designing hydrophobic UiO-66 support for the enhanced enzymatic performance of immobilized lipase. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 4500–4506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.R.d.M.; Gonçalves, L.R.B.; da Silva, I.J. Innovations in packed-bed reactors utilizing immobilized lipase catalysts: A comprehensive technical and scientific review. Mol. Catal. 2025, 573, 114814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoel, E.A.; dos Santos, J.C.S.; Freire, D.M.G.; Rueda, N.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Immobilization of lipases on hydrophobic supports involves the open form of the enzyme. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2015, 71, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, Y.; Wang, L.; Xiao, F.-S. Catalysis Enhanced by Catalyst Wettability. ACS Nano 2025, 19, 7617–7633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Goh, K.-L.; Zivkovic, V.; Zheng, M. Novel Immobilized Enzyme System Using Hydrophobic Dendritic Mesoporous Silica Nanospheres for Efficient Flavor Ester Production. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 12403–12417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Goh, K.-L.; Zivkovic, V.; Zheng, M. Ultrasound-assisted enzymatic synthesis of cinnamyl acetate by immobilized lipase on ordered mesoporous silicon with CFD simulation and molecular docking analysis. Food Chem. 2025, 464, 141843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, M.C.M.d.; Santos, K.P.d.; Freire, R.M.; Barreto, A.C.H.; Fechine, P.B.A.; Gonçalves, L.R.B. Production of flavor esters catalyzed by lipase B from Candida antarctica immobilized on magnetic nanoparticles. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 34, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.-Y.; Yu, Z.-T.; Zhang, M.-T.; Li, A.-Q.; Liu, W.; Zhong, H.-X.; Wu, M.-Y.; Cheng, K.-K. Central Composite Design Optimization for the Synthesis of Butyl Acetate Catalyzed by Liquid Lipase. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, H.; Geng, H.; Zhang, L.; liu, G.; Yan, H.; Cao, R.; Zhu, J.; Hu, Y.; Xu, L. Covalent immobilization of lipase on an ionic liquid-functionalized magnetic Cu-based metal–organic framework with boosted catalytic performance in flavor ester synthesis. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 1302–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.-W.; Cai, X.; Dou, B.-J.; Qi, F.-Y.; Zhang, X.-J.; Liu, Z.-Q.; Zheng, Y.-G. Expression and characterization of a CALB-type lipase from Sporisorium reilianum SRZ2 and its potential in short-chain flavor ester synthesis. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2020, 14, 868–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.-W.; Lin, L.-G.; Ye, W.-C. Techniques for extraction and isolation of natural products: A comprehensive review. Chin. Med. 2018, 13, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aboagye, E.A.; Chea, J.D.; Yenkie, K.M. Systems level roadmap for solvent recovery and reuse in industries. iScience 2021, 24, 103114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, L.; Paula, A.V.; dos Santos, J.C.; Zanin, G.M.; de Castro, H.F. Enzymatic synthesis of monoglycerides by esterification reaction using Penicillium camembertii lipase immobilized on epoxy SiO2-PVA composite. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2010, 65, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, M.; Ge, X. Fabrication of fibrous amidoxime-functionalized mesoporous silica microsphere and its selectively adsorption property for Pb2+ in aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 297, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, T.; Liu, R.; Zhou, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, M. Enzymatic Deacidification and Aroma Characteristics Analysis of Rapeseed Oil Using Self-Made Immobilized Lipase CALB@MCM-41-C8. Foods 2024, 13, 2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.; Jin, J.; Wei, W.; Wu, G.; Wang, X.; Jin, Q. Hyperactivation of lipase by oil-water interface in interfacial immobilization on hierarchical porous hollow silica microsphere: Dynamics, mechanism and application. Food Biosci. 2024, 58, 103706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Chen, J.; Goh, K.L.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, M. Molecular docking simulation reveals the lipase-substrate binding mechanism in the enzymatic synthesis of diacylglycerol-enriched vegetable oils. Food Chem. 2025, 474, 143236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.; Yang, C.; Feng, Z.; Goh, K.-L.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, M. Insights into the enzymatic synthesis of alcoholic flavor esters with molecular docking analysis. LWT 2024, 200, 116206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, P.; Jana, A.K. Candida rugosa Lipase Immobilization on Fe3O4 Coated Carboxyl Functionalised Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes for Production of Food Flavour Esters. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2023, 28, 310–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Choi, Y.; Chang, P.-S. Interface-based kinetic model considering the integral stereoselectivity of lipases on tricapryloylglycerol in a reverse micelle system. Food Chem. 2025, 465, 141403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Zhang, X.; Wang, T.; Geng, H.; Wang, L.; Jiang, L.; Elfalleh, W. Immobilized Candida antarctica lipase B (CALB) on functionalized MCM-41: Stability and catalysis of transesterification of soybean oil and phytosterol. Food Biosci. 2021, 40, 100906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, C.; Zhong, H.; Gu, T.; Goh, K.-L.; Han, Z.; Zheng, M.; Zhou, Y. Green and efficient synthesis of highly liposoluble and antioxidant L-ascorbyl esters by immobilized lipases. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 379, 134772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saberi, S.; Zhiani, R.; Mehrzad, J.; Motavalizadehkakhky, A. Synthesis and characterization of a novel TEMPO@FeNi3/DFNS–laccase magnetic nanocomposite for the reduction of nitro compounds. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 27297–27304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlumberger, C.; Thommes, M. Characterization of Hierarchically Ordered Porous Materials by Physisorption and Mercury Porosimetry—A Tutorial Review. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 8, 2002181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, T.; Singha, D.; Pal, A.; Nandi, M. Mesoporous silica based recyclable probe for colorimetric detection and separation of ppb level Hg2+ from aqueous medium. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayne, L.; Ulijn, R.V.; Halling, P.J. Effect of pore size on the performance of immobilised enzymes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 9000–9010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghazi, I.; De Segura, A.G.; Fernández-Arrojo, L.; Alcalde, M.; Yates, M.; Rojas-Cervantes, M.L.; Plou, F.J.; Ballesteros, A. Immobilisation of fructosyltransferase from Aspergillus aculeatus on epoxy-activated Sepabeads EC for the synthesis of fructo-oligosaccharides. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2005, 35, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, S.; Zheng, M. Broadly adapted and efficient enzymatic transesterification production of medium and long-chain triglycerides via coconut oil and long-chain triacylglycerols. Food Chem. 2025, 469, 142499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pota, G.; Bifulco, A.; Parida, D.; Zhao, S.; Rentsch, D.; Amendola, E.; Califano, V.; Costantini, A. Tailoring the hydrophobicity of wrinkled silica nanoparticles and of the adsorption medium as a strategy for immobilizing lipase: An efficient catalyst for biofuel production. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 328, 111504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, R.C.; Ortiz, C.; Berenguer-Murcia, Á.; Torres, R.; Fernández-Lafuente, R. Modifying enzyme activity and selectivity by immobilization. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6290–6307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabi, G.J.; de Souza, L.; Abellanas-Perez, P.; Tardioli, P.W.; Mendes, A.A.; Rocha-Martin, J.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Enzyme loading in the support and medium composition during immobilization alter activity, specificity and stability of octyl agarose-immobilized Eversa Transform. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 295, 139667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Andrade Silva, T.; Keijok, W.J.; Guimarães, M.C.C.; Cassini, S.T.A.; de Oliveira, J.P. Impact of immobilization strategies on the activity and recyclability of lipases in nanomagnetic supports. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Feng, N.; Li, Y.; Fei, X.; Tian, J.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y. Hydrogen-bonded lipase-hydrogel microspheres for esterification application. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 606, 1229–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudu, A.I.; Lăcătuş, M.A.; Bencze, L.C.; Paizs, C.; Toşa, M.I. Green Process for the Enzymatic Synthesis of Aroma Compounds Mediated by Lipases Entrapped in Tailored Sol–Gel Matrices. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 5461–5469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ACS Appl Mater InterfacesZhao, J.; Ma, M.; Yan, X.; Wan, D.; Zeng, Z.; Yu, P.; Gong, D. Immobilization of lipase on β-cyclodextrin grafted and aminopropyl-functionalized chitosan/Fe3O4 magnetic nanocomposites: An innovative approach to fruity flavor esters esterification. Food Chem. 2022, 366, 130616. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.; Rivera, J.G.; He, L.; Kulkarni, H.; Lee, D.-K.; Messersmith, P.B. Facile, high efficiency immobilization of lipase enzyme on magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles via a biomimetic coating. BMC Biotech. 2011, 11, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpena, M.; Fraga-Corral, M.; Otero, P.; Nogueira, R.A.; Garcia-Oliveira, P.; Prieto, M.A.; Simal-Gandara, J. Secondary Aroma: Influence of Wine Microorganisms in Their Aroma Profile. Foods 2021, 10, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Kumar, S.; Sahney, R.; Dahiya, P. Green synthesis of iron-alginate nanoparticle for Taguchi-assisted immobilization of Candida rugosa lipase and its application in the synthesis of butyl butyrate ester. Process Biochem. 2024, 139, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Zhu, J.; Wang, H.; Qian, M.C.; Xiao, Z. Comparative Investigation of Aroma-Active Volatiles in (“Ruixue”, “Liangzhi”, “Crystal Fuji,” and “Guifei”) Apples by Application of Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry–Olfactometry (GC–MS–O) and Two-Dimensional Gas Chromatography-Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry (GC × GC-qMS) Coupled with Sensory Molecular Science. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 25229–25250. [Google Scholar]
- Nazarian, Z.; Arab, S.S. Solvent-dependent activity of Candida antarctica lipase B and its correlation with a regioselective mono aza-Michael addition—experimental and molecular dynamics simulation studies. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uppenberg, J.; Oehrner, N.; Norin, M.; Hult, K.; Kleywegt, G.J.; Patkar, S.; Waagen, V.; Anthonsen, T.; Jones, T.A. Crystallographic and molecular-modeling studies of lipase B from Candida antarctica reveal a stereospecificity pocket for secondary alcohols. Biochemistry 1995, 34, 16838–16851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Yu, X.; Chen, R.; Chen, X.; Liu, L. Green synthesis of (R)-3-TBDMSO glutaric acid methyl monoester using Novozym 435 in non-aqueous media. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 75160–75166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjørnelund, H.D.; Vind, J.; Brask, J.; Woodley, J.M.; Peters, G.H.J. Candida antarctica lipase B performance in organic solvent at varying water activities studied by molecular dynamics simulations. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2023, 21, 5451–5462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zisis, T.; Freddolino, L.; Turunen, P.; van Teeseling, M.C.F.; Rowan, A.E.; Blank, K.G. Interfacial Activation of Candida antarctica Lipase B: Combined Evidence from Experiment and Simulation. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 5969–5979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Błaszczyk, J.; Kiełbasiński, P. Quarter of a Century after: A Glimpse at the Conformation and Mechanism of Candida antarctica Lipase B. Crystals 2020, 10, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, R.R.C.; Neto, D.M.A.; Fechine, P.B.A.; Lopes, A.A.S.; Gonçalves, L.R.B.; dos Santos, J.C.S.; de Souza, M.C.M.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Ethyl Butyrate Synthesis Catalyzed by Lipases A and B from Candida antarctica Immobilized onto Magnetic Nanoparticles. Improvement of Biocatalysts’ Performance under Ultrasonic Irradiation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paludo, N.; Alves, J.S.; Altmann, C.; Ayub, M.A.Z.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; Rodrigues, R.C. The combined use of ultrasound and molecular sieves improves the synthesis of ethyl butyrate catalyzed by immobilized Thermomyces lanuginosus lipase. Ultrason. Sonochem 2015, 22, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, C.; Cai, J.; Huang, L.; Zhu, X.; Xu, Z. Biocatalytic production of ethyl butyrate from butyric acid with immobilized Candida rugosa lipase on cotton cloth. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2011, 72, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmat, S.; Anwer, A.H.; Husain, Q. Immobilization of lipase onto novel constructed polydopamine grafted multiwalled carbon nanotube impregnated with magnetic cobalt and its application in synthesis of fruit flavours. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 140, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, U.M.F.; Lima de Matos, L.J.B.; de Souza, M.C.M.; Pinheiro, B.B.; dos Santos, J.C.S.; Gonçalves, L.R.B. Efficient biotechnological synthesis of flavor esters using a low-cost biocatalyst with immobilized Rhizomucor miehei lipase. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2019, 46, 597–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrutika, P.; Datta, M. Lipase from Solvent-Tolerant Pseudomonas sp. DMVR46 Strain Adsorb on Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes: Application for Enzymatic Biotransformation in Organic Solvents. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 177, 1313–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Samples | Atomic (%) | BET Analysis | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | N | O | Si | Surface Area (m2/g) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Pore Size (nm) | |
| DFNS | 29.6 | / | 52.2 | 18.2 | 449.6 | 1.5 | 8.8 |
| DFNS-C8 | 38.3 | / | 45.0 | 16.7 | 309.1 | 1.0 | 8.8 |
| CALB@DFNS-C8 | 46.6 | 1.3 | 37.7 | 14.4 | 48.1 | 0.4 | 11.8 |
| Lipases | Solvents | Reaction Parameters | Conversion (%) | Reusability Cycles (Conversion %) | Catalytic Efficiency (mmol·g−1·h−1) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRL@Cottoncloth | cyclohexane | 1:2.4 a, 25 b, 8 c | 91.2 | 12 (83.0) | 1.3 | [68] |
| CRL@PDA-Co-MWCNT | n-heptane | 1:3 a, 40 b, 24 c | 78.02 | 6 (49.0) | / | [69] |
| CRL@MMWCNTs | n-heptane | 1:2 a, 35 b, 6 c | 89.7 | 11 (57.0) | / | [39] |
| RML@CS | n-heptane | 1:1 a, 25 b, 6 c | 92.0 | 10 (50.0) | 6.1 | [70] |
| Lipozyme TLIM | / | 1:1 a, 30 b, 6 c | 90.0 | 10 (90.0) | / | [67] |
| DMVR46@MWCNTs | n-heptane | 0.2:0.15 a, 40 b, 48 c | 81.0 | 15 | 1.35 | [71] |
| CALB@MNP | n-heptane | 1:1 a, 45 b, 6 c | 97.5 | 10 (80) | 13.0 | [66] |
| CALA@MNP | n-heptane | 1:1 a, 45 b, 6 c | 99.2 | 10 (80) | 16.5 | [66] |
| CALB@MNP | n-heptane | 1:1 a, 25 b, 8 c | 97.8 | 10 (74) | 4.8 | [27] |
| CALB@DFNS-C8 | / | 1:3 a, 40 b, 4 c | 96.0 | 10 (89) | 35.1 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zheng, H.; Zheng, M. Solvent-Free Catalytic Synthesis of Ethyl Butyrate Using Immobilized Lipase Based on Hydrophobically Functionalized Dendritic Fibrous Nano-Silica. Foods 2025, 14, 4272. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14244272
Wang M, Zhang Y, Gao Y, Zheng H, Zheng M. Solvent-Free Catalytic Synthesis of Ethyl Butyrate Using Immobilized Lipase Based on Hydrophobically Functionalized Dendritic Fibrous Nano-Silica. Foods. 2025; 14(24):4272. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14244272
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Mengqi, Yi Zhang, Yunqi Gao, Huanyu Zheng, and Mingming Zheng. 2025. "Solvent-Free Catalytic Synthesis of Ethyl Butyrate Using Immobilized Lipase Based on Hydrophobically Functionalized Dendritic Fibrous Nano-Silica" Foods 14, no. 24: 4272. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14244272
APA StyleWang, M., Zhang, Y., Gao, Y., Zheng, H., & Zheng, M. (2025). Solvent-Free Catalytic Synthesis of Ethyl Butyrate Using Immobilized Lipase Based on Hydrophobically Functionalized Dendritic Fibrous Nano-Silica. Foods, 14(24), 4272. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14244272





