Comparative Muscle Quality and Multiomic Analyses in Wild-Type and Yellow-Mutant Triplophysa siluroides: TGF-β/BMP-Mediated Covariation and Breeding for Muscle Quality
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish Preparation
2.2. Texture Determination
2.3. Histological Analysis
2.3.1. H&E Staining
2.3.2. Picrosirius Red Staining
2.3.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Analysis
2.4. Quantification of the Collagen Content in Muscle Tissue
2.5. Transcriptome Sequencing and Analysis
2.5.1. Total RNA Extraction and Transcriptome Sequencing
2.5.2. Transcriptome Data Analysis
2.5.3. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis of DEGs
2.6. Proteome Sequencing and Analysis
2.6.1. Total Protein Extraction and DIA (Data-Independent Acquisition) Data Collection
2.6.2. Spectrometric Data Analysis
2.6.3. Integrated Analysis of the Transcriptome and Proteome
2.7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR) Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Muscle Textural Characteristics of WT and YM T. siluroides
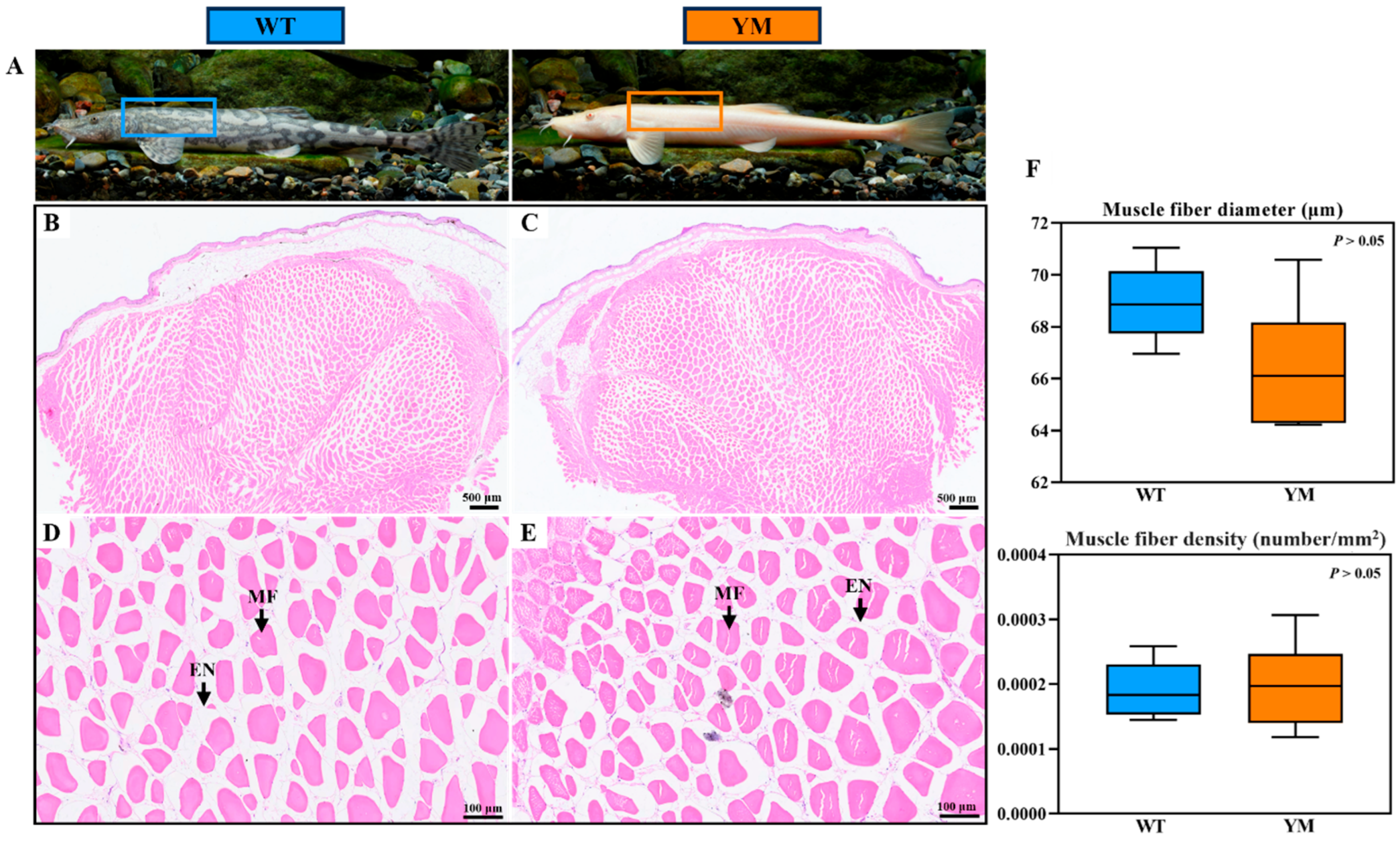
3.2. Muscle Fiber Structure of WT and YM T. siluroides
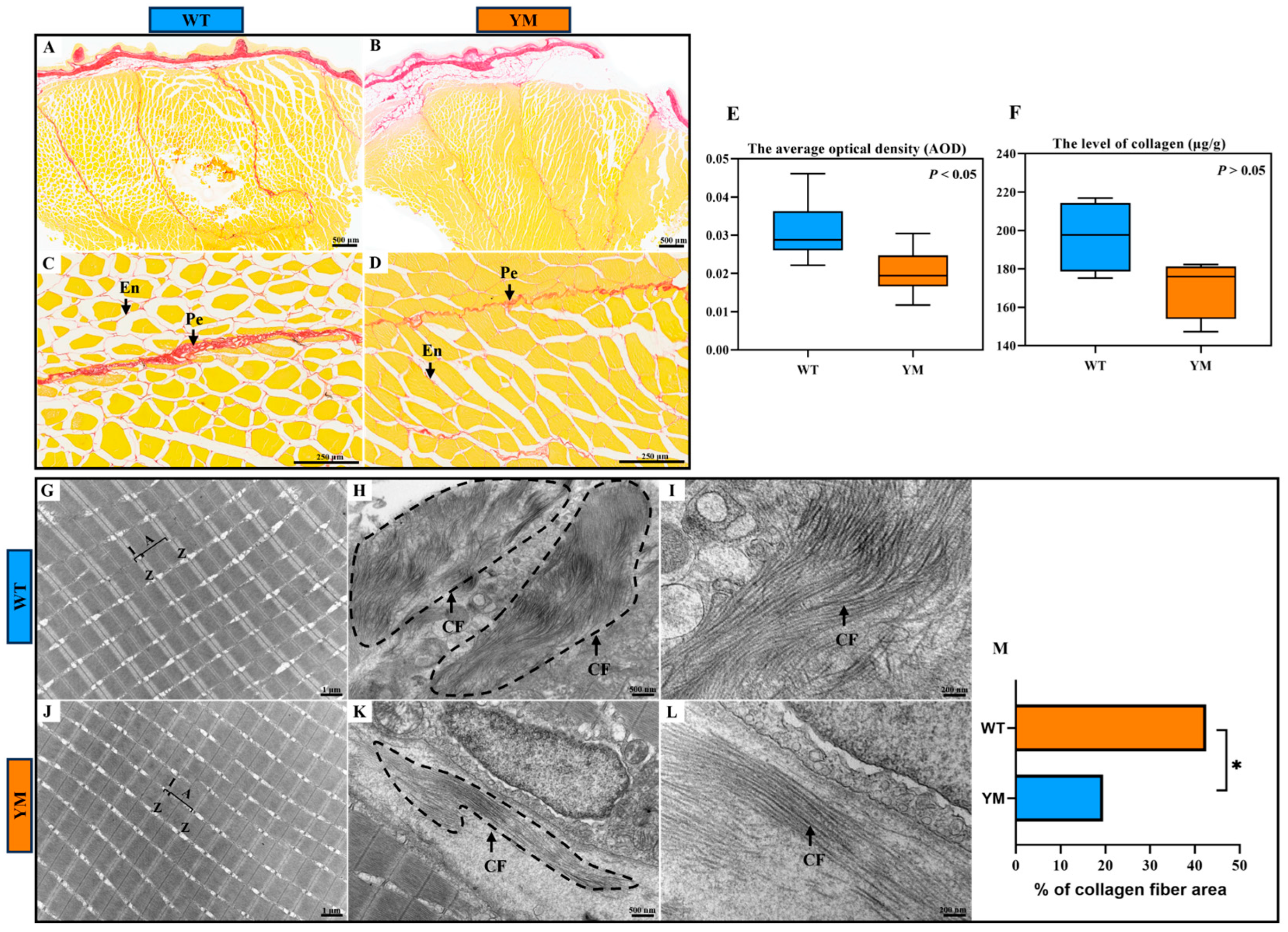
3.3. Muscle Collagen Content of WT and YM T. siluroides
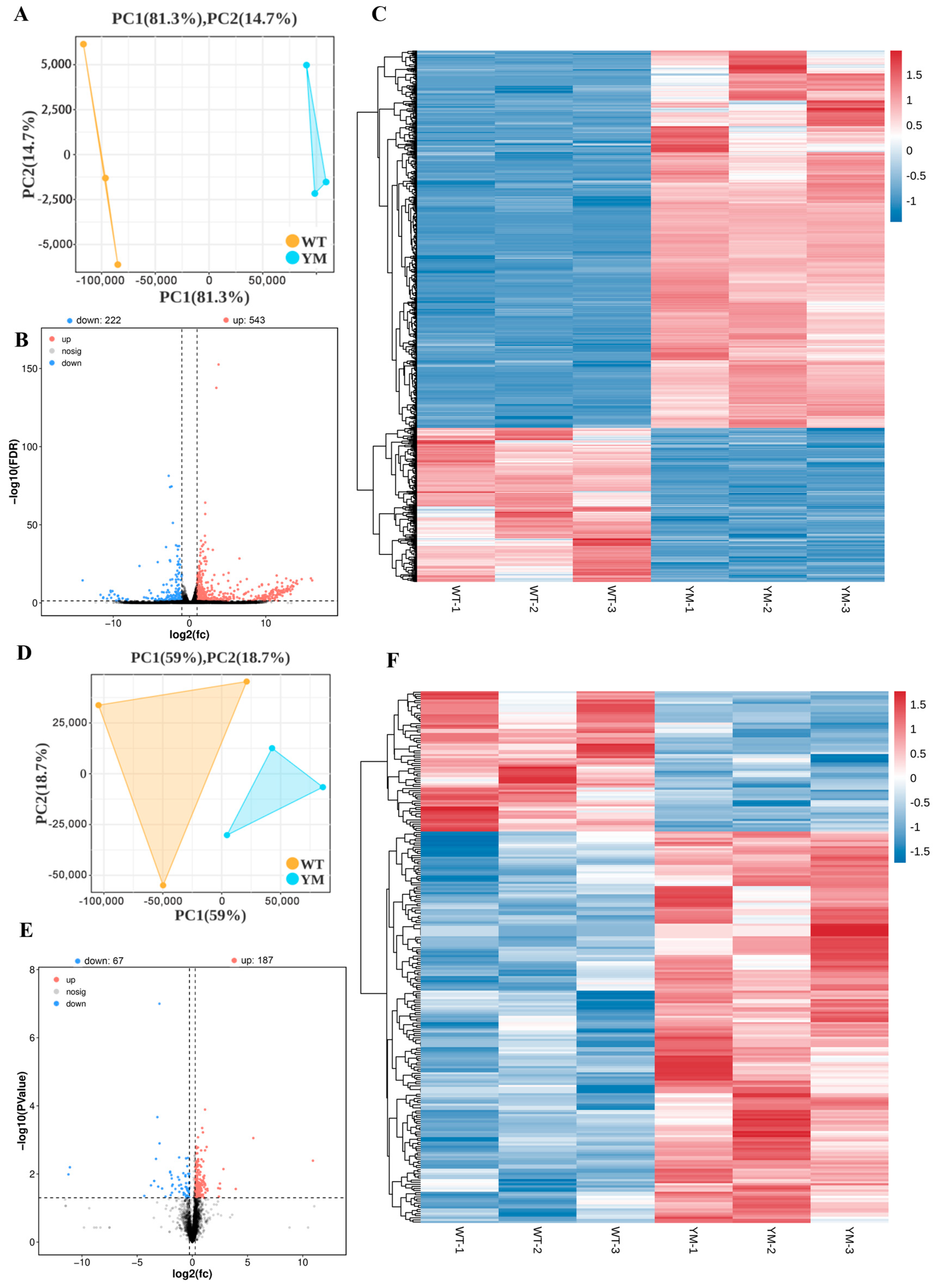
3.4. Differential Transcriptomic and Proteomic Analyses
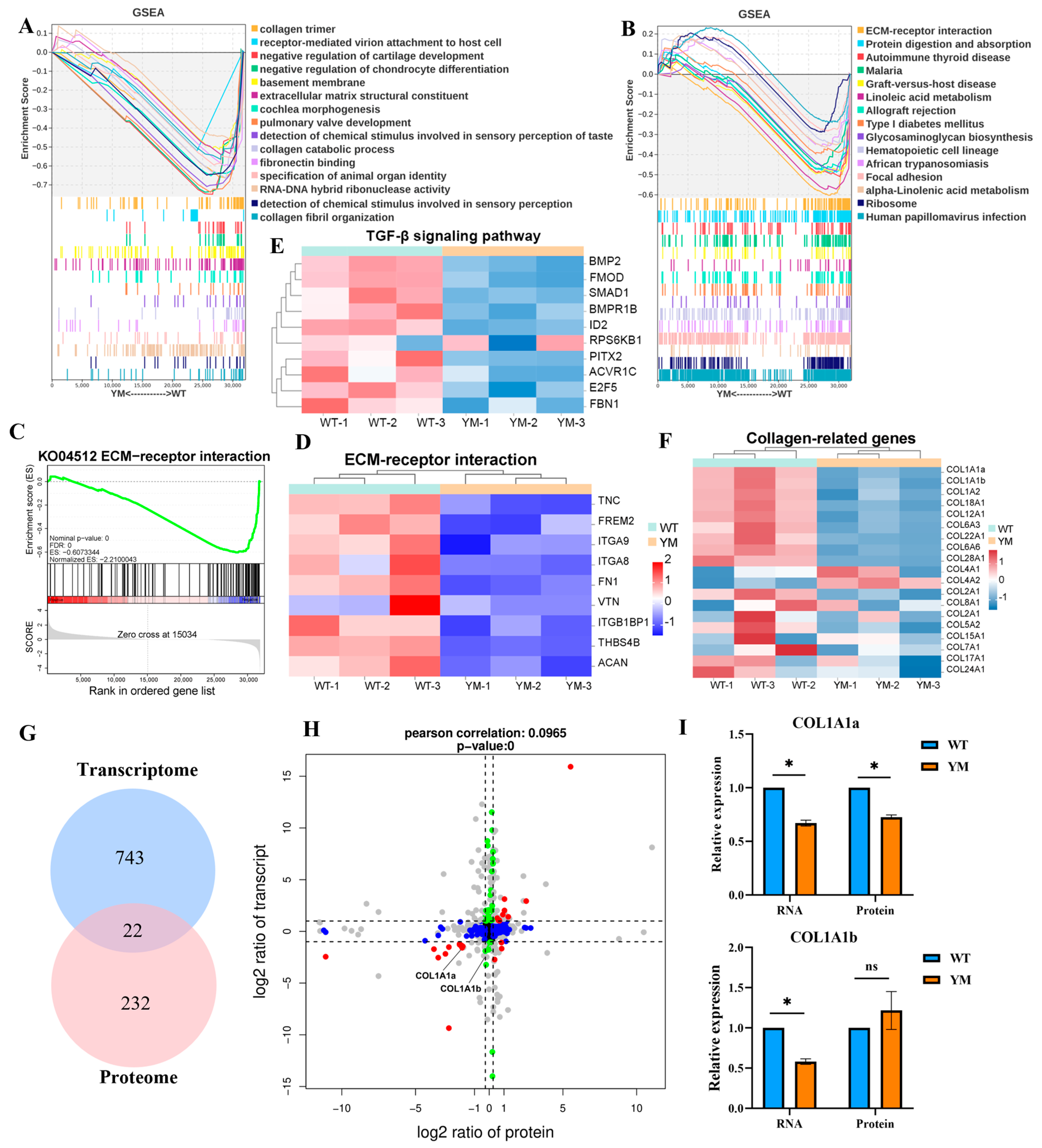
3.5. GSEA and Multiomic Co-Expression Analysis
3.6. Potential Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Differences in Muscle Hardness
3.7. qRT-PCR Verification
4. Discussion
4.1. Confirmation of Muscle Hardness Differences and Irrelevance of Myofiber Traits
4.2. Reduced Collagen Content Underlies Differences in Muscle Hardness
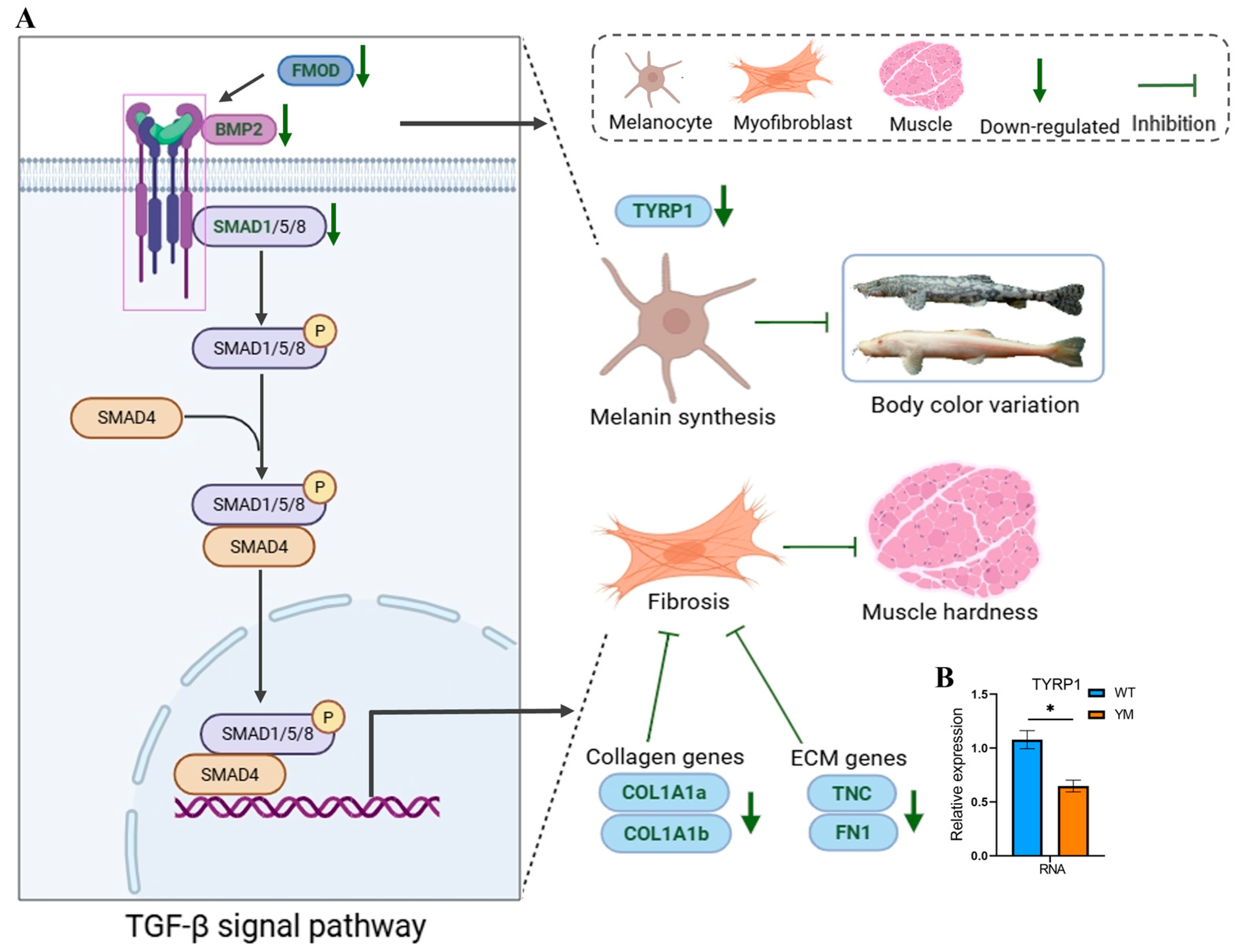
4.3. The TGF-β/BMP Pathway Mediates Collagen Regulation and Phenotypic Linkages
4.4. Limitations and Future Research Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Gene | Sequence (5′ to 3′) | Product (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| SMAD2-F | GTCCTCCATCTTGCCTTTCAC | 178 |
| SMAD2-R | GTCCAGTTGACCCGTTTTCTT | |
| DDIT4-F | CAAGCCTCGTGTCGGAAGA | 213 |
| DDIT4-R | TGGGGTCAAAGAACAGGTCA | |
| DCTN1-F | GAACCTAAAGGCAAGAACGATG | 145 |
| DCTN1-R | CGGCTTCAGGGGTTTCAG | |
| TGF-β1a-F | CATTGGAAATAAAACCCGCTAC | 126 |
| TGF-β1a-R | GCTTGATTCTCTTCTGACTTCTGC | |
| BMP2-F | TCAGAGACCCCTACTGGTTACTTAC | 190 |
| BMP2-R | GTTGCGTTTCACCCGTCTT | |
| SMAD3a-F | GCAGGTATCTCATAGGAAAGGACT | 106 |
| SMAD3a-R | CTCACAGTGTTCAATGGCTCTAAG | |
| SMAD4-F | GTTCTGCCAGTATGCCTTTGAC | 228 |
| SMAD4-R | GCCACAGGTCTGACAGGAGG | |
| COL1A1a-F | GTTCAGCTTTGTGGATATTCGGT | 226 |
| COL1A1a-R | GTTGGGGCAGTCGGTCGT | |
| COL1A1b-F | GCAGCGGTCCTTGTGGTG | 194 |
| COL1A1b-R | ATTTCTGGATTGGCACAGTCTG | |
| COL2A1-F | ACCAAGCGGCAGAAGGAA | 150 |
| COL2A1-R | CGGGGTGACAGAGTTTGAGAT | |
| HBB-F | AGGTGGCAGCTCATGGTAGAA | 202 |
| HBB-R | TCAGCATTGAAAACTGTGGGTC | |
| CTNNB1-F | GGCAACCCAGAGGAAGAGG | 161 |
| CTNNB1-R | TCCAAAGTCTCGGGGAACAT | |
| β-actin-F | GCTGAGAGAGAAATTGTCCGTG | 209 |
| β-actin-R | CCGCAAGACTCCATACCCA |
References
- Naylor, R.L.; Hardy, R.W.; Buschmann, A.H.; Bush, S.R.; Cao, L.; Klinger, D.H.; Little, D.C.; Lubchenco, J.; Shumway, S.E.; Troell, M. A 20-year retrospective review of global aquaculture. Nature 2021, 591, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, C.; Appelbaum, M.; Rao, Q. Aquatic food animals in the United States: Status quo and challenges. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 1336–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyldig, G.; Nielsen, D. A review of sensory and instrumental methods used to evaluate the texture of fish muscle. J. Texture Stud. 2001, 32, 219–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Chen, J.; He, H.; Duan, B.; You, C.; Hu, Z.; Cai, L.; Xiang, X.; Liang, R. EccDNA analysis provides novel insights into the molecular mechanism of firmness of fish fillet. Food Sci. Nutr. 2025, 13, e70268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Qiao, F.; Zhang, W.B.; Parisi, G.; Du, Z.Y.; Zhang, M.L. The flesh texture of teleost fish: Characteristics and interventional strategies. Rev. Aquac. 2024, 16, 508–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, E.M.; Liu, B.H.; Wang, G.J.; Yu, D.G.; Xie, J.; Xia, Y.; Gong, W.B.; Wang, H.H.; Li, Z.F.; Wei, N. Molecular cloning of type I collagen cDNA and nutritional regulation of type I collagen mRNA expression in grass carp. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2014, 98, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, M.; Kenney, P.B.; Rexroad, C.R.; Yao, J. Microarray gene expression analysis in atrophying rainbow trout muscle: A unique nonmammalian muscle degradation model. Physiol. Genom. 2006, 28, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, C.; Li, R.; Wen, Z.; Ge, W.; Shi, Q. Phylogenetic analysis of core melanin synthesis genes provides novel insights into the molecular basis of albinism in fish. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 707228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braasch, I.; Liedtke, D.; Volff, J.N.; Schartl, M. Pigmentary function and evolution of tyrp1 gene duplicates in fish. Pigment. Cell Melanoma Res. 2009, 22, 839–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyofuku, K.; Wada, I.; Valencia, J.C.; Kushimoto, T.; Ferrans, V.J.; Hearing, V.J. Oculocutaneous albinism types 1 and 3 are ER retention diseases: Mutation of tyrosinase or Tyrp1 can affect the processing of both mutant and wild-type proteins. Faseb J. 2001, 15, 2149–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieder, S.; Taourit, S.; Mariat, D.; Langlois, B.; Guérin, G. Mutations in the agouti (ASIP), the extension (MC1R), and the brown (TYRP1) loci and their association to coat color phenotypes in horses (Equus caballus). Mamm. Genome 2001, 12, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmutz, S.M.; Berryere, T.G.; Goldfinch, A.D. TYRP1 and MC1R genotypes and their effects on coat color in dogs. Mamm. Genome 2002, 13, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, T.; Duan, S.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; He, S. A chromosome-scale reference assembly of a Tibetan loach, Triplophysa siluroides. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Zhang, X.; Hou, F.; Zhang, X.; Song, Z. Threatened fishes of the world: Triplophysa siluroides (Herzenstein 1888) (Balitoridae). Environ. Biol. Fishes 2008, 83, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, L.; Wu, X.; Zou, Q.; Chen, Y.; Lai, J.; Song, M.; Li, F.; Liu, Y. Comparison of histological characteristics and nutrient composition in dorsum muscles of artificially cultured regular and yellow Triplophysa siluroides. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 140, 107194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Tao, Z.; Wen, H.; Qi, X.; Li, C.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y. Comparative analysis of muscle quality, transcriptomic, and metabolomic profiles in yellow-mutant and wild-type northern snakehead (Channa argus): Implications for food quality and aquaculture breeding potential. Food Biosci. 2025, 68, 106496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Gong, Q.; Lai, J.; Song, M.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Ai, J.; Long, Z. Transcriptome analysis identifies candidate genes associated with skin color variation in Triplophysa siluroides. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. D 2020, 35, 100682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Yu, E.; Li, Z.; Zhang, K.; Tian, J.; Wang, G.; Xie, J.; Gong, W. Both TGF-β1 and Smad4 regulate type I collagen expression in the muscle of grass carp, Ctenopharyngodon idella. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 47, 907–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, E.; Ma, L.; Ji, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, G.; Xie, J.; Yu, D.; Kaneko, G.; Tian, J.; Zhang, K.; et al. Smad4-dependent regulation of type I collagen expression in the muscle of grass carp fed with faba bean. Gene 2019, 685, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botchkarev, V.A. Bone morphogenetic proteins and their antagonists in skin and hair follicle biology. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2003, 120, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katkat, E.; Demirci, Y.; Heger, G.; Karagulle, D.; Papatheodorou, I.; Brazma, A.; Ozhan, G. Canonical Wnt and TGF-β/BMP signaling enhance melanocyte regeneration but suppress invasiveness, migration, and proliferation of melanoma cells. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1297910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Jie, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, G.Q.; Sun, J.; Wu, L.P. Amphiphilic and fatigue-resistant organohydrogels for small-diameter vascular grafts. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, n5360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pertea, M.; Pertea, G.M.; Antonescu, C.M.; Chang, T.; Mendell, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. StringTie enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Hu, E.; Xu, S.; Chen, M.; Guo, P.; Dai, Z.; Feng, T.; Zhou, L.; Tang, W.; Zhan, L.I. clusterProfiler 4.0: A universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innovation 2021, 2, 100141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Chambers, A.G.; Cecchi, F.; Hembrough, T. Targeted data-independent acquisition for mass spectrometric detection of RAS mutations in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tumor biopsies. J. Proteom. 2018, 189, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Ishikawa, T.; Michiue, T.; Zhu, B.; Guan, D.; Maeda, H. Stability of endogenous reference genes in postmortem human brains for normalization of quantitative real-time PCR data: Comprehensive evaluation using geNorm, NormFinder, and BestKeeper. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2012, 126, 943–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, I.A.; Li, X.; Vieira, V.L.A.; Nickell, D.; Dingwall, A.; Alderson, R.; Campbell, P.; Bickerdike, R. Muscle and flesh quality traits in wild and farmed Atlantic salmon. Aquaculture 2006, 256, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincón, L.; Castro, P.L.; Álvarez, B.; Hernández, M.D.; Álvarez, A.; Claret, A.; Guerrero, L.; Ginés, R. Differences in proximal and fatty acid profiles, sensory characteristics, texture, colour and muscle cellularity between wild and farmed blackspot seabream (Pagellus bogaraveo). Aquaculture 2016, 451, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, M.V.; Shamasundar, B.A. Texture profile analysis and functional properties of gelatin from the skin of three species of fresh water fish. Int. J. Food Prop. 2015, 18, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczesniak, A.S. Texture is a sensory property. Food Qual. Prefer. 2002, 13, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.; Zhang, F.; Fu, F.; Ouyang, J.; Wei, Y.; Lin, S.; Jiang, C.; Yu, M.; Yang, H. Effects of quantitative marinating on meat quality, biogenic amines, and flavor compounds in crayfish meat. Front. Nutr. 2025, 12, 1573987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Listrat, A.; Lebret, B.; Louveau, I.; Astruc, T.; Bonnet, M.; Lefaucheur, L.; Picard, B.; Bugeon, J. How muscle structure and composition influence meat and flesh quality. Sci. World J. 2016, 2016, 3182746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, I.A.; Alderson, R.; Sandham, C.; Dingwall, A.; Mitchell, D.; Selkirk, C.; Nickell, D.; Baker, R.; Robertson, B.; Whyte, D.; et al. Muscle fibre density in relation to the colour and texture of smoked Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Aquaculture 2000, 189, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigurgisladottir, S.; Sigurdardottir, M.S.; Torrissen, O.; Vallet, J.L.; Hafsteinsson, H. Effects of different salting and smoking processes on the microstructure, the texture and yield of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) fillets. Food Res. Int. 2000, 33, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, E.; Fu, B.; Wang, G.; Li, Z.; Ye, D.; Jiang, Y.; Ji, H.; Wang, X.; Yu, D.; Ehsan, H.; et al. Proteomic and metabolomic basis for improved textural quality in crisp grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus C.et V) fed with a natural dietary pro-oxidant. Food Chem. 2020, 325, 126906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, T. The role of intramuscular connective tissue in meat texture. Anim. Sci. J. 2010, 81, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Xia, J.; Zhang, X.; He, X.; Li, L.; Tang, R.; Chi, W.; Li, D. Diet affects muscle quality and growth traits of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus): A comparison between grass and artificial feed. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Ma, J.; Pan, X.; Mu, H.; Li, J.; Shentu, J.; Zhang, W.; Mai, K. Dietary hydroxyproline improves the growth and muscle quality of large yellow croaker Larimichthys crocea. Aquaculture 2016, 464, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periago, M.J.; Ayala, M.D.; López-Albors, O.; Abdel, I.; Martínez, C.; García-Alcázar, A.; Ros, G.; Gil, F. Muscle cellularity and flesh quality of wild and farmed sea bass, Dicentrarchus labrax L. Aquaculture 2005, 249, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zou, H.; Zhu, X.X.; Pang, J.; Xu, Q.; Jin, Q.Y.; Ding, Y.H.; Zhou, B.; Huang, D.S. Transforming growth factor β: A potential biomarker and therapeutic target of ventricular remodeling. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 53780–53790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrecchia, F.; Mauviel, A.; Farge, D. Transforming growth factor-β signaling through the Smad proteins: Role in systemic sclerosis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2006, 5, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismaeel, A.; Kim, J.S.; Kirk, J.S.; Smith, R.S.; Bohannon, W.T.; Koutakis, P. Role of transforming growth factor-β in skeletal muscle fibrosis: A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillege, M.; Galli, C.R.; Offringa, C.; de Wit, G.; Jaspers, R.T.; Hoogaars, W. TGF-β regulates collagen type I expression in myoblasts and myotubes via transient Ctgf and Fgf-2 expression. Cells 2020, 9, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, M.; Jiao, G.; Liu, H.; Wu, W.; Li, S.; Wang, Q.; Xu, D.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y. Biological silicon stimulates collagen type 1 and osteocalcin synthesis in human osteoblast-like cells through the BMP-2/Smad/RUNX2 signaling pathway. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2016, 173, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchida, K.; Zhu, Y.; Siva, S.; Dunn, S.R.; Sharma, K. Role of Smad4 on TGF-beta-induced extracellular matrix stimulation in mesangial cells. Kidney Int. 2003, 63, 2000–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimoto, M.; Sakamoto, R.; Mizuta, S.; Yoshinaka, R. Identification and characterization of molecular species of collagen in ordinary muscle and skin of the Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Food Chem. 2005, 90, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhan, F.; Hussain, Z.; Tauseef, I.; Shehzad, A.; Wahid, F. A review on recent advances and applications of fish collagen. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2021, 61, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasauer, S.M.; Neuhauss, S.C. Whole-genome duplication in teleost fishes and its evolutionary consequences. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2014, 289, 1045–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xie, R.; Luo, Y.; Shi, R.; Ling, Y.; Zhao, X.; Xu, X.; Chu, W.; Wang, X. Cooperation of TGF-β and FGF signalling pathways in skin development. Cell Prolif. 2023, 56, e13489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Group | Hardness/ (g) | Chewiness/ (g · sec) | Springiness/ (g · sec) | Cohesiveness/ (g · sec) | Gumminess/ (g · sec) | Resilience |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | 824.26 ± 156.35 * | 292.04 ± 85.67 | 0.92 ± 0.07 | 0.48 ± 0.05 | 346.48 ± 74.47 * | 0.34 ± 0.03 * |
| YM | 558.52 ± 90.66 | 225.54 ± 68.17 | 0.91 ± 0.03 | 0.48 ± 0.06 | 266.64 ± 57.97 | 0.29 ± 0.06 |
| Sample | Raw Data (bp) | Clean Data (bp) | Q20 Rate (%) | Q30 Rate (%) | GC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT1 | 5,437,641,300 | 5,422,137,909 | 99.28 | 97.83 | 49.00 |
| WT2 | 6,819,118,500 | 6,801,906,889 | 99.35 | 98.00 | 48.72 |
| WT3 | 6,110,957,100 | 6,090,850,604 | 99.37 | 98.08 | 49.35 |
| YM1 | 5,910,464,400 | 5,890,548,425 | 99.36 | 98.06 | 48.24 |
| YM2 | 6,096,620,700 | 6,071,460,680 | 99.34 | 98.01 | 48.68 |
| YM3 | 5,579,437,200 | 5,565,578,952 | 99.31 | 97.84 | 48.31 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ni, L.; Li, F.; Li, P.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Du, J.; Lai, J.; Liu, Y. Comparative Muscle Quality and Multiomic Analyses in Wild-Type and Yellow-Mutant Triplophysa siluroides: TGF-β/BMP-Mediated Covariation and Breeding for Muscle Quality. Foods 2025, 14, 4196. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14244196
Ni L, Li F, Li P, Chen Y, Liu Y, Du J, Lai J, Liu Y. Comparative Muscle Quality and Multiomic Analyses in Wild-Type and Yellow-Mutant Triplophysa siluroides: TGF-β/BMP-Mediated Covariation and Breeding for Muscle Quality. Foods. 2025; 14(24):4196. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14244196
Chicago/Turabian StyleNi, Luyun, Feiyang Li, Pengcheng Li, Yeyu Chen, Yan Liu, Jun Du, Jiansheng Lai, and Ya Liu. 2025. "Comparative Muscle Quality and Multiomic Analyses in Wild-Type and Yellow-Mutant Triplophysa siluroides: TGF-β/BMP-Mediated Covariation and Breeding for Muscle Quality" Foods 14, no. 24: 4196. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14244196
APA StyleNi, L., Li, F., Li, P., Chen, Y., Liu, Y., Du, J., Lai, J., & Liu, Y. (2025). Comparative Muscle Quality and Multiomic Analyses in Wild-Type and Yellow-Mutant Triplophysa siluroides: TGF-β/BMP-Mediated Covariation and Breeding for Muscle Quality. Foods, 14(24), 4196. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14244196






