Homology Modeling of Sesame Allergenic Protein and Prediction of B-Cell Linear Antigenic Epitopes Using Immunoinformatic Tools
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Allergen Amino Acid Sequence Retrieval
2.2. Physicochemical Properties Analysis
2.3. Prediction of the Secondary Structure of Sesame Allergenic Proteins
2.4. Prediction of Antigenic Epitopes of Sesame Allergenic Proteins
2.4.1. BepiPred Prediction
2.4.2. Integrated Prediction
2.5. Prediction of the Tertiary Structure of Sesame Allergenic Proteins
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Prediction of Linear B-Cell Epitopes in Sesame Allergenic Proteins
3.1.1. Basic Physicochemical Properties of Sesame Allergenic Proteins
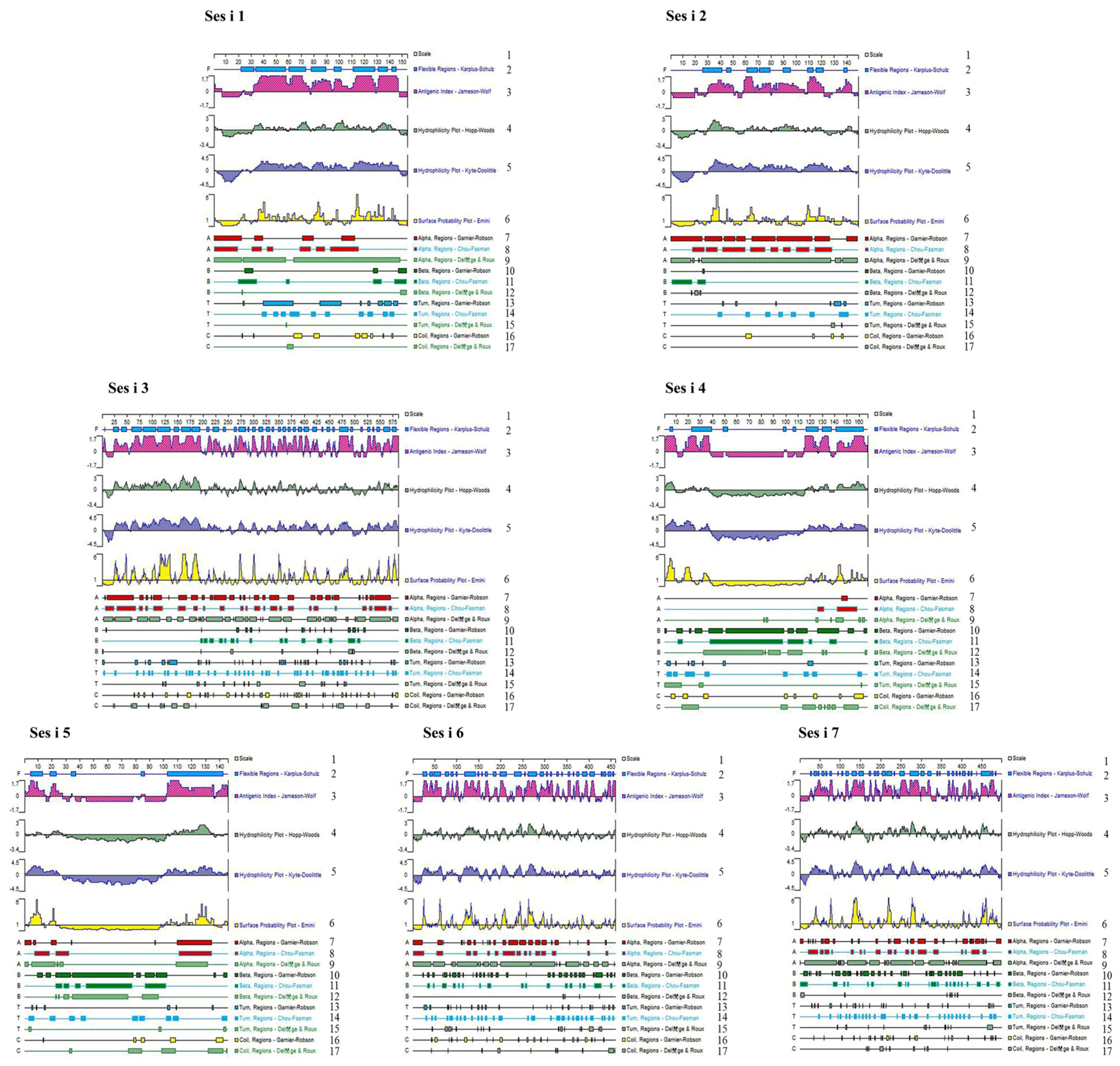
3.1.2. Prediction of Linear B-Cell Epitopes Using DNAStar
3.1.3. Prediction of B-Cell Linear Epitopes of Sesame Allergenic Proteins Using SOPMA
| Sesame Allergen | Source (Position) |
|---|---|
| Ses i 1 | 21~24, 33~34, 38~39, 50~52, 61~70, 78~85, 117~122, 134~149 |
| Ses i 2 | 22~24, 31, 62~67, 75~79, 94~97, 133~144 |
| Ses i 3 | 2~5, 24~29, 61~72, 82~85, 94~96, 99~102, 119~133, 142~151, 167~175, 179~181, 189~195, 199~201, 208~213, 240~244, 248~254, 261~264, 270~275, 280~283, 288~291, 297~302, 311~319, 325~330, 348~349, 359~363, 368~369, 381~394, 399~410, 414~420, 434~438, 441~449, 456~460, 465~483, 492~496, 501~505, 511~515, 524~530, 535~536, 553~555, 566~569, 574~584 |
| Ses i 4 | 2~37, 47~51, 57~58, 71~73, 78~84, 95, 98~103, 120~123, 157~160 |
| Ses i 5 | 5~15, 18~21, 33~37, 43~45, 47~49, 56~58, 63~70, 79~80, 85~88, 103~110, 135~145 |
| Ses i 6 | 22~32, 41~54, 59~62, 77~92, 98~101, 107~140, 147~151, 156~159, 165~170, 178~183, 187~191, 197~213, 220~221, 231~232, 242~247, 253~256, 260~264, 268~275, 291~298, 302~307, 312~317, 332~335, 338~346, 353~356, 363~366, 373~377, 382~384, 391~396, 403~407, 414~415, 421~423, 433~434, 444~448, 453~459 |
| Ses i 7 | 27~29, 36~47, 56~69, 74~78, 93~107, 113~117, 122~142, 145~146, 154~157, 162~165, 171~176, 184~190, 195~196, 203~225, 231~233, 243~244, 253~259, 265~268, 271~290, 303~310, 314~319, 324~329, 339~340, 344~347, 350~358, 365~368, 375~378, 385~389, 394~396, 403~409, 414~419, 427~428, 434~436, 446~447, 457~460, 466~485 |
3.1.4. Prediction of Sesame Allergenic Protein B-Cell Linear Epitopes Using BepiPred 1.0
| Sesame Allergen | Source (Position) |
|---|---|
| Ses i 1 | 22~45, 61~75, 78~87, 112~130, 134, 140~142 |
| Ses i 2 | 29~46, 63~65, 74~79, 112~118, 120, 138, 140 |
| Ses i 3 | 22~31, 38, 40~49, 62~75, 80~86, 94~104, 113~134, 143~152, 155~193, 240, 243~245, 250~253, 274, 312~318, 325~332, 370~373, 378~394, 400~409, 411, 413~414, 416~417, 436~447, 460, 468~487, 511, 513, 525~533, 545, 556~567, 575~585 |
| Ses i 4 | 1~25, 29~38, 119~135, 138~166 |
| Ses i 5 | 3~13, 23, 31~34, 104~116, 118~122, 125~145 |
| Ses i 6 | 21~31, 40~60, 62~64, 77~91, 111~113, 116, 121~137, 154~155, 157, 164~170, 198~211, 230~232, 234, 236~245, 259~278, 293~296, 326~327, 329~331, 336~338, 340~343, 354~358, 363, 373~374, 384~395, 403~413, 431~440, 455~459 |
| Ses i 7 | 24~27, 29~30, 35~43, 55~64, 67~68, 74~75, 77~80, 103~104, 116~118, 122~124, 127~139, 172~176, 186~191, 204~227, 250~257, 272~291, 303~320, 378~379, 402~408, 416~422, 446~451, 4576~459, 461~464, 467~484 |
| Sesame Allergen | Peptide | Source (Position) | Number of Peptides | Experimental Epitopes Position |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ses i 1 | NQQSQQCR, SQGRSPYGGE, STGNQQSEQS, QEGGYQEGQSQ, NMRPQ | 38~45, 61~70, 78~87, 116~126, 140~144 | 5 | |
| Ses i 2 | ANQGQ | 75~79 | 1 | 46–55, 48–57, 76–86 [19] |
| Ses i 3 | SESKDPE, QKHQGEHGRGGG, NRKSP, YQREKGRQDDDNPTDPEKQY, RRQGEGGGFS, KYREQQGREGGRGE, EQGRGR, RTQHG, AEPQT, RQDRR, PVSTPGE, AGGENP, RHEEGGIWPFGGESKGT, QQRPTHSNQYG, APHYNSKA, MSRSRGSYQGETRGRPSY, SSNQN, ANNNEK, SRSQQ, GPRQQQQGRAD | 23~29, 61~72, 81~85, 115~134, 142~151, 162~175, 188~193, 208~212, 240~244, 270~274, 312~318, 325~330, 378~394, 399~409, 441~448, 468~485, 511~515, 525~530, 563~567, 574~584 | 20 | |
| Ses i 4 | ADRDRP, QKGPST, RATGQGPLEYAKRGV, EKTKQAGEAI, STAKEGGREG | 2~7, 32~37, 119~133, 142~151, 153~162 | 5 | 35–40, 98–106, 130–139 [20] |
| Ses i 5 | YGQQQQTRA, TGKHPPGA, EQFSQQPVAGSQTS | 5~13, 103~110, 132~145 | 3 | 1–15, 11–25, 61–75, 71–85, 101–115, 111–125, 131–145 [45] |
| Ses i 6 | AIAQTREPRLTQGQ, GAQPSLRIQSEGGT, ELWDER, IRPNGLSLPNYHPSPR, ISIMVPG, HRSQRTMERTEASEQQDRGSVR, NDGSED, VPRSGEQEQQARQT, MQSEEEER, RPDEE, QEHRGRQL, AGNNGF, TGSPMR, GGRRS | 19~32, 41~54, 56~61, 77~92, 103~109, 117~138, 165~170, 199~212, 239~246, 260~264, 268~275, 391~396, 404~409, 455~459 | 14 | |
| Ses i 7 | LQSQQQHKL, AQEPTIRFE, DRNNQ, ETFERDTQPRQDRRR, NGGEP, GNAAN, NPQGGRQSYFGRPQTEKQQGET, KGQDDL, PGEEEEERWERDPYSGANG, NLDEPARA, NPHGGR, ASQDEG, VSRDE, STSRYSWPRSSRPMSYMPKP | 35~43, 56~64, 74~78, 127~141, 172~176, 186~190, 204~225, 252~257, 272~290, 303~310, 314~319, 403~408, 446~450, 466~485 | 14 |
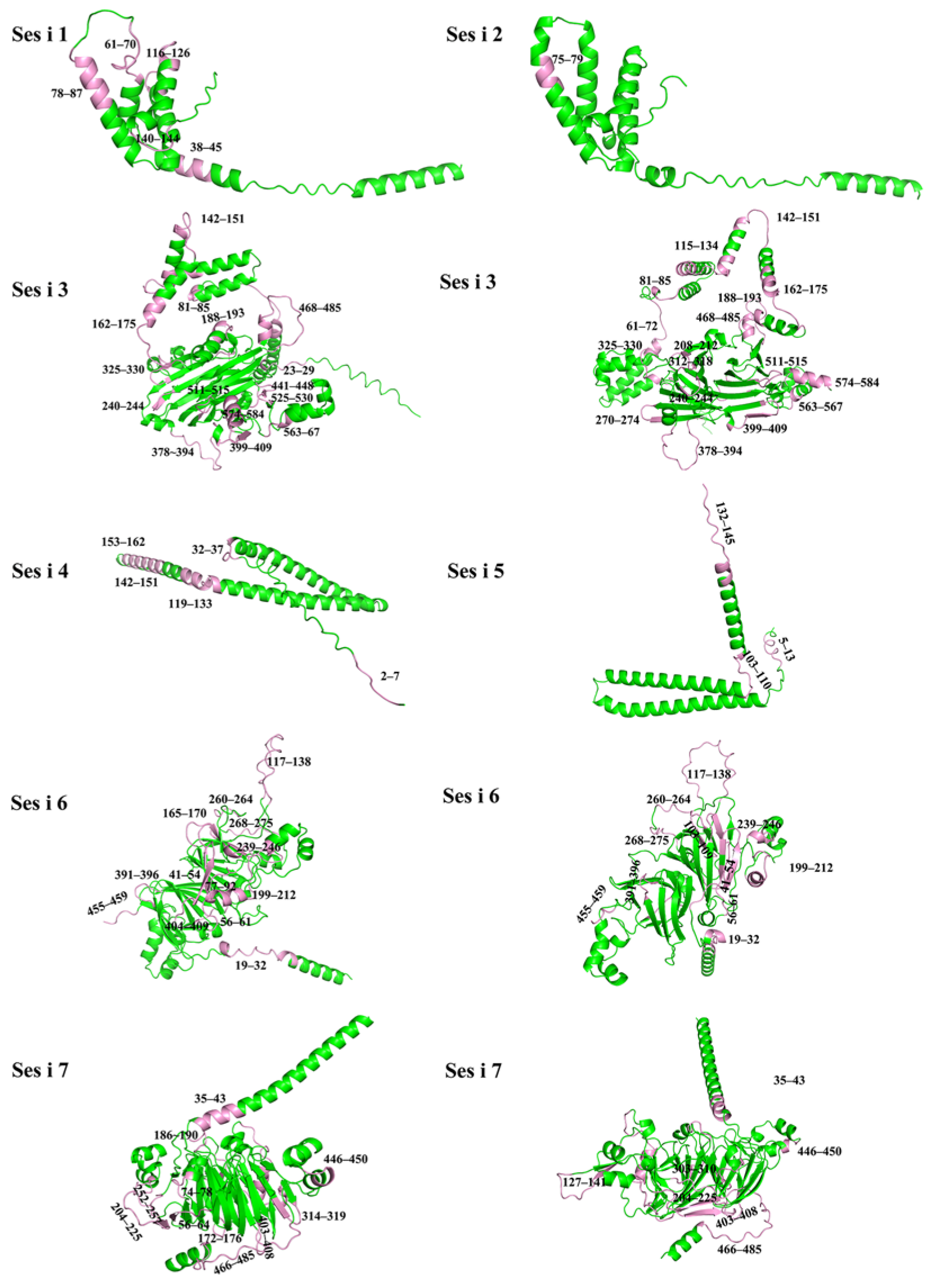
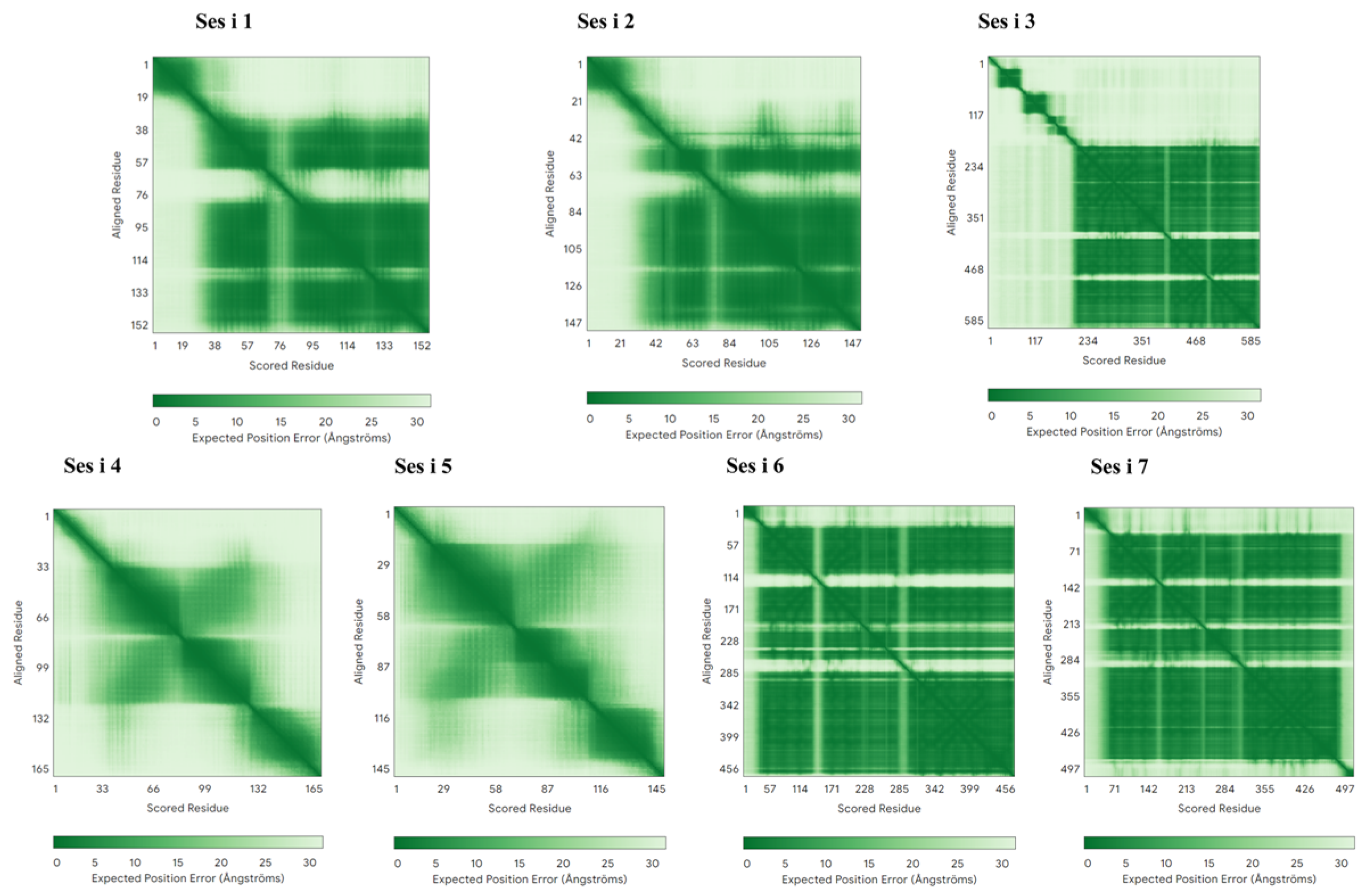
3.2. Homology Modeling and Quality Assessment of Sesame Allergens
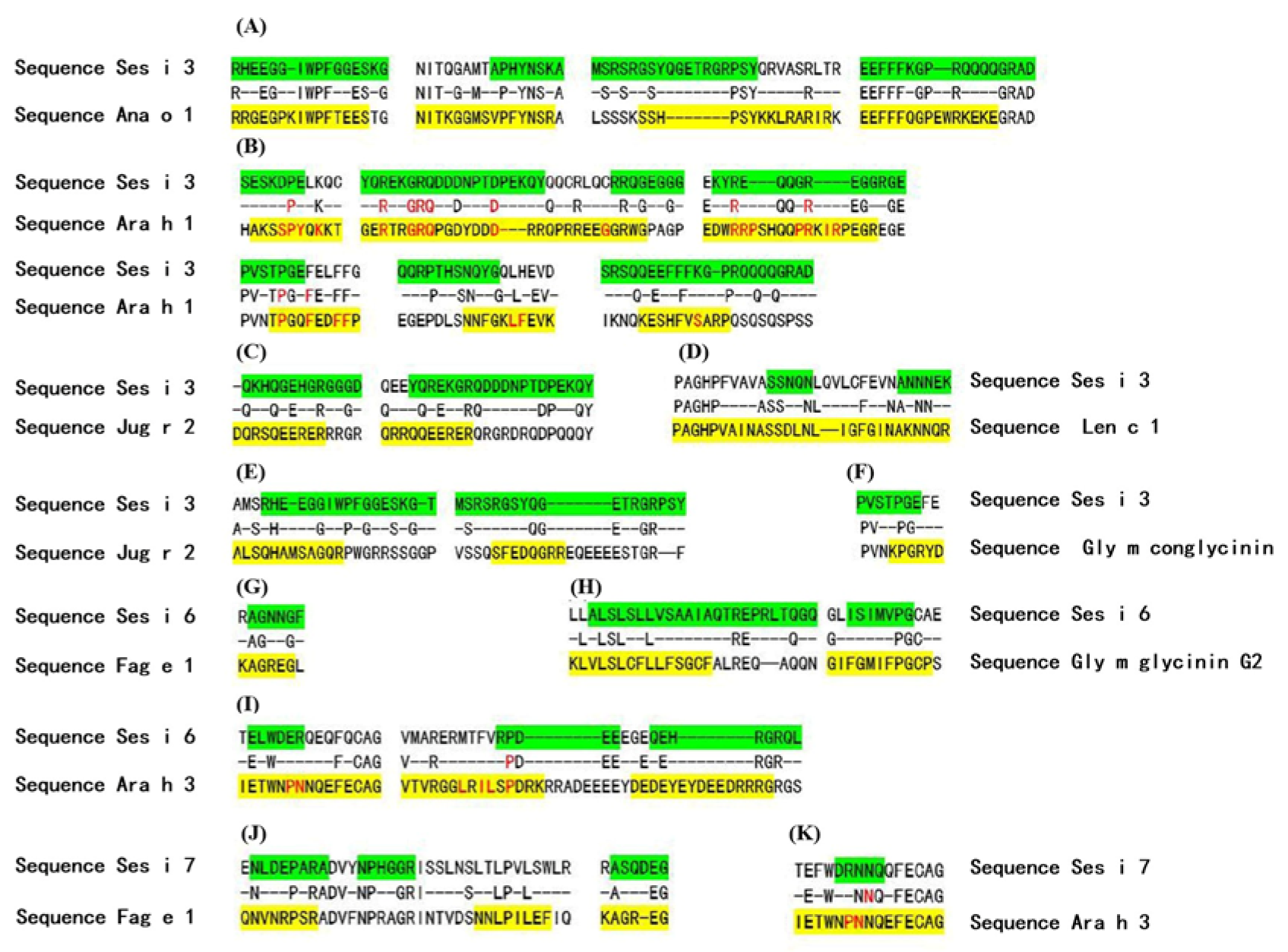
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chinthrajah, R.S.; Jones, S.M.; Kim, E.H.; Sicherer, S.H.; Shreffler, W.; Lanser, B.J.; Atri, N.; Babineau, D.C.; Adelman, D.C.; Iqbal, A.; et al. Updating the CoFAR Grading Scale for Systemic Allergic Reactions in Food Allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 149, 2166–2170.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florsheim, E.B.; Sullivan, Z.A.; Khoury-Hanold, W.; Medzhitov, R. Food allergy as a biological food quality control system. Cell 2021, 184, 1440–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayorga, C.; Palomares, F.; Cañas, J.A.; Pérez-Sanchez, N.; Núñez, R.; Torres, M.J.; Gómez, F. New Insights in Therapy for Food Allergy. Foods 2021, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adatia, A.; Clarke, A.E.; Yanishevsky, Y.; Ben-Shoshan, M. Sesame allergy: Current perspectives. J. Asthma Allergy 2017, 10, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güvenir, F.A.; Yörüsün, G.; Genis, C.; Yilmaz, D.; Selmanoglu, A.; Emeksiz, Z.S.; Misirlioglu, E.D. A Growing Cause of Food Allergies in Children: Sesame. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2025, 186, 984–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangur, V.; Acharya, H.G. The Global Rise and the Complexity of Sesame Allergy: Prime Time to Regulate Sesame in the United States of America? Allergies 2020, 1, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.; Greenthal, E.; Sorscher, S.; Lurie, P.; Spergel, J.M.; Kennedy, K. Adverse events and labeling issues related to suspected sesame allergy reported in an online survey. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2022, 128, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization; World Health Organization. Part 1—Review and validation of Codex Alimentarius priority allergen list through risk assessment. In Risk Assessment of Food Allergens; Meeting Report; Food Safety and Quality Series No, 14; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, N.A.; Lopata, A.L.; Colgrave, M.L. Analytical Methods for Allergen Control in Food Processing. Foods 2023, 12, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linacero, R.; Cuadrado, C. New Research in Food Allergen Detection. Foods 2022, 11, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenta, R.; Linhart, B.; Swoboda, I.; Niederberger, V. Recombinant allergens for allergen-specific immunotherapy: 10 years anniversary of immunotherapy with recombinant allergens. Allergy 2011, 66, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prickett, S.R.; Rolland, J.M.; O’Hehir, R.E. Immunoregulatory T cell epitope peptides: The new frontier in allergy therapy. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2015, 45, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyer, K.; Bardina, L.; Grishina, G.; Sampson, H.A. Identification of sesame seed allergens by 2-dimensional proteomics and Edman sequencing: Seed storage proteins as common food allergens. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2002, 110, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyer, K.; Grishina, G.; Bardina, L.; Sampson, H.A. Identification of 2 new sesame seed allergens: Ses i 6 and Ses i 7. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 119, 1554–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leduc, V.; Moneret-Vautrin, D.A.; Tzen, J.T.; Morisset, M.; Guerin, L.; Kanny, G. Identification of oleosins as major allergens in sesame seed allergic patients. Allergy 2006, 61, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastorello, E.A.; Varin, E.; Farioli, L.; Pravettoni, V.; Ortolani, C.; Ortolani, C.; Fortunato, D.; Giuffrida, M.G.; Rivolta, F.; Robino, A.; et al. The major allergen of sesame seeds (Sesamum indicum) is a 2S albumin. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Appl. 2001, 756, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, N.; Cogan, U.; Admon, A.; Dalal, I.; Katz, Y.; Hodos, N.; Karin, N.; Yannai, S. Allergy to sesame in humans is associated primarily with IgE antibody to a 14 kDa 2S albumin precursor. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2003, 41, 1165–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achouri, A.; Boye, J.I. Thermal processing, salt and high pressure treatment effects on molecular structure and antigenicity of sesame protein isolate. Food Res. Int. 2013, 53, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchand, C.; Astier, C.; Thouvenot, B.; Roitel, O.; Kanny, G.; Bihain, B.E.; Barre, A.; Rougé, P.; Jacquenet, S. IgE epitopes are within the hydrophobic domain of sesame oleosin Ses i 4. Rev. Fr. Allergol. 2022, 62, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, N.; Yannai, S.; Karin, N.; Levy, Y.; Reifen, R.; Dalal, I.; Cogan, U. Identification and characterization of linear B-cell epitopes of β-globulin, a major allergen of sesame seeds. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 114, 1151–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Ge, Y.; He, L.; Kang, W.; Huang, W.; Sun, J.-L.; Chen, Y. Effect of Roasting on the Conformational Structure and IgE Binding of Sesame Allergens. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 9442–9450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Sathe, S.K. Food Allergen Epitope Mapping. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 7238–7248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Nan, F.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Yu, Z.; Liu, F.; Li, J.; Zhou, X.; Niu, D.; et al. CRM197-conjugated multi antigen dominant epitope for effective human cytomegalovirus vaccine development. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 224, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, M.; Tang, X.; Xing, J.; Chi, H.; Zhan, W. Development and Evaluation of Recombinant B-Cell Multi-Epitopes of PDHA1 and GAPDH as Subunit Vaccines against Streptococcus iniae Infection in Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Vaccines 2023, 11, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, B.M.; Ascher, D.B.; Pires, D.E.V. epitope1D: Accurate taxonomy-aware B-cell linear epitope prediction. Brief Bioinform. 2023, 24, bbad114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, X.; Su, Z.; Li, W.; Chen, S.; Wang, L.; Sun, T.; Du, C.; Li, Z.; et al. A Newly Identified Spike Protein Targeted Linear B-Cell Epitope Based Dissolvable Microneedle Array Successfully Eliciting Neutralizing Activities against SARS-CoV-2 Wild-Type Strain in Mice. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2207474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, J.; Adler, J.; Dunger, J.; Evans, R.; Green, T.; Pritzel, A.; Ronneberger, O.; Willmore, L.; Ballard, A.J.; Bambrick, J.; et al. Accurate structure prediction of biomolecular interactions with AlphaFold 3. Nature 2024, 630, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Shan, X.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, L. Prediction and characterization of the linear IgE epitopes for the major soybean allergen beta-conglycinin using immunoinformatics tools. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 56, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, S.J.; Teuber, S.S.; Cheng, H.; Chen, D.; Comstock, S.S.; Ruan, S.; Schein, C.H. Computationally predicted IgE epitopes of walnut allergens contribute to cross-reactivity with peanuts. Allergy 2011, 66, 1522–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saivish, M.V.; Menezes, G.D.L.; Costa, V.G.D.; Silva, G.C.D.D.; Marques, R.E.; Nogueira, M.L.; Silva, R.A.D. Predicting Antigenic Peptides from Rocio Virus NS1 Protein for Immunodiagnostic Testing Using Immunoinformatics and Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Tripathi, S.; Sharma, N.; Patiyal, S.; Devi, N.L.; Raghava, G.P.S. A method for predicting linear and conformational B-cell epitopes in an antigen from its primary sequence. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 170, 108083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyte, J.; Doolittle, R.F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J. Mol. Biol. 1982, 157, 105–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopp, T.P.; Woods, K.R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 3824–3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jameson, B.A.; Wolf, H. The antigenic index: A novel algorithm for predicting antigenic determinants. Bioinformatics 1988, 4, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, P.Y.; Fasman, G.D. Empirical predictions of protein conformation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1978, 47, 251–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.M.; Penido, M.; dos Santos, M.S.; Doro, D.; de Freitas, E.; Michalick, M.S.; Grimaldi, G.; Gazzinelli, R.T.; Fernandes, A.P. Improved canine and human visceral leishmaniasis immunodiagnosis using combinations of synthetic peptides in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.H.; Wang, Y.; Mao, T.T.; Cao, Z.W.; Qiu, T.Y. Current Research and Development of Antigenic Epitope Prediction Tools. Prog. Biochem. Biophys. 2024, 51, 2532–2544. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld, L.; Shreffler, W.; Bardina, L.; Niggemann, B.; Wahn, U.; Sampson, H.A.; Beyer, K. Walnut Allergy in Peanut-Allergic Patients: Significance of Sequential Epitopes of Walnut Homologous to Linear Epitopes of Ara h 1, 2 and 3 in Relation to Clinical Reactivity. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2012, 157, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsaro, C.; Mallamace, D.; Neri, G.; Fazio, E. Hydrophilicity and hydrophobicity: Key aspects for biomedical and technological purposes. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2021, 580, 126189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchiba, Y.; Cortés, J.; Schiex, T.; Barbe, S. Molecular flexibility in computational protein design: An algorithmic perspective. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2021, 34, gzab011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Liu, Z.; Kan, B.; Gong, Y.; Ma, Z.; Wang, H. TMP-SSurface: A Deep Learning-Based Predictor for Surface Accessibility of Transmembrane Protein Residues. Crystals 2019, 9, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhou, X.; Cao, Y.; Cheng, X.; Li, N.; Hua, B.; Dang, H. Bioinformatics-based Analyses and B/Th Cell Epitope Prediction of Mugwort Pollen Allergen Art v 1 Protein. J. Vis. Exp. 2023, (202), e66517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, D.S.; Compadre, C.M.; Maleki, S.J.; Kopper, R.A.; Sampson, H.; Huang, S.K.; Burks, A.W.; Bannon, G.A. Biochemical and Structural Analysis of the IgE Binding Sites on Ara h1, an Abundant and Highly Allergenic Peanut Protein. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 13753–13759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vereda, A.; Andreae, D.A.; Lin, J.; Shreffler, W.G.; Ibanez, M.D.; Cuesta-Herranz, J.; Bardina, L.; Sampson, H.A. Identification of IgE sequential epitopes of lentil (Len c 1) by means of peptide microarray immunoassay. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 126, 596–601.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Robotham, J.M.; Teuber, S.S.; Tawde, P.; Sathe, S.K.; Roux, K.H. Ana o 1, a cashew (Anacardium occidental) allergen of the vicilin seed storage protein family. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2002, 110, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Tian, X.X.; Xiang, X.Y.; Qi, X.Y.; Zhou, H.R.; Xiao, P.Y.; An, T.Q.; Meng, F.D.; Wang, H.W. Epitope Mapping of Senecavirus A 3A Protein Using Monoclonal Antibodies. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2025, 2025, 3398924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, N.; Qin, Y.; Kang, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y. Molecular characterization, B-cell linear epitopes identification and key amino acids selection of the sesame allergen Ses i 5. Int. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 303, 140635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Gaur, S.N.; Arora, N. In silico identification of IgE-binding epitopes of osmotin protein. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Sesame Allergen | Source (Position) |
|---|---|
| Ses i 1 | 39~49, 5~52, 56, 60~70, 73, 78~81, 83, 85~87, 96~98, 100, 116~119, 123~126, 131~135, 138, 142~144 |
| Ses i 2 | 38~40, 61~64, 76, 78~79, 111~113, 139 |
| Ses i 3 | 23, 25~28, 60~68, 81~85, 92, 96, 99~101, 115~135, 142~145, 151, 162~172, 174~175, 178~180, 186, 188~191, 193, 207~212, 220~225, 240~242, 262, 270~273, 280, 298~300, 316~317, 328~330, 332, 348~353, 359~361, 378~380, 390~392, 399~408, 416~418, 423, 445~448, 469~485, 492~493, 512~515, 525~529, 535~537, 563~566, 573~582 |
| Ses i 4 | 5~7, 29~30, 32~37, 117~121, 125, 132, 151, 153~162 |
| Ses i 5 | 5~7, 9, 19~22, 103~109, 132~135, 142 |
| Ses i 6 | 25~30, 32, 42, 44, 51~53, 56, 75~78, 87~90, 99, 118~123, 133~136, 148, 166~168, 185, 201~203, 239~241, 261~263, 268, 270~275, 278, 290, 292, 305, 312~315, 327~330, 352, 354, 364, 372, 374, 385, 391~392, 404, 406~409, 429, 433~434, 436~437, 444~447, 455~456 |
| Ses i 7 | 29, 34~38, 40, 45~47, 60, 74~78, 104~105, 115, 131~141, 146~149, 154, 172~173, 206~212, 214~219, 221~223, 232, 252~257, 273~274, 280~286, 307~308, 315~316, 366, 376, 404~407, 415~419, 447~450, 456~457, 461, 466~470, 473~478, 483~485 |
| Sesame Allergens | Ranking Score (pLDDT) | pTM |
|---|---|---|
| Ses i 1 | 0.79 | 0.63 |
| Ses i 2 | 0.74 | 0.61 |
| Ses i 3 | 0.78 | 0.66 |
| Ses i 4 | 0.58 | 0.3 |
| Ses i 5 | 0.67 | 0.31 |
| Ses i 6 | 0.92 | 0.84 |
| Ses i 7 | 0.87 | 0.82 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, X.; Wang, F.; Yu, N.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Xie, M.; Ge, Y.; Chen, Y. Homology Modeling of Sesame Allergenic Protein and Prediction of B-Cell Linear Antigenic Epitopes Using Immunoinformatic Tools. Foods 2025, 14, 4158. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234158
Ma X, Wang F, Yu N, Zhang J, Wang X, Xie M, Ge Y, Chen Y. Homology Modeling of Sesame Allergenic Protein and Prediction of B-Cell Linear Antigenic Epitopes Using Immunoinformatic Tools. Foods. 2025; 14(23):4158. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234158
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Xiuli, Fang Wang, Ning Yu, Jiukai Zhang, Xiaoxuan Wang, Meng Xie, Yiqiang Ge, and Ying Chen. 2025. "Homology Modeling of Sesame Allergenic Protein and Prediction of B-Cell Linear Antigenic Epitopes Using Immunoinformatic Tools" Foods 14, no. 23: 4158. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234158
APA StyleMa, X., Wang, F., Yu, N., Zhang, J., Wang, X., Xie, M., Ge, Y., & Chen, Y. (2025). Homology Modeling of Sesame Allergenic Protein and Prediction of B-Cell Linear Antigenic Epitopes Using Immunoinformatic Tools. Foods, 14(23), 4158. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234158








